|
VLC Media Player
VLC media player (previously the VideoLAN Client and commonly known as simply VLC) is a free and open-source, portable, cross-platform media player software and streaming media server developed by the VideoLAN project. VLC is available for desktop operating systems and mobile platforms, such as Android, iOS and iPadOS. VLC is also available on digital distribution platforms such as Apple's App Store, Google Play, and Microsoft Store. VLC supports many audio and video compression methods and file formats, including DVD-Video, Video CD and streaming protocols. It is able to stream media over computer networks and can transcode multimedia files. The default distribution of VLC includes many free decoding and encoding libraries, avoiding the need for finding/calibrating proprietary plugins. The libavcodec library from the FFmpeg project provides many of VLC's codecs, but the player mainly uses its own muxers and demuxers. It also has its own protocol implementations. It also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TvOS
tvOS (formerly known as Apple TV Software) is an operating system developed by Apple Inc. for the Apple TV, a digital media player. In the first-generation Apple TV, Apple TV Software was based on Mac OS X. Starting with the second-generation, it is based on the iOS operating system and has many similar frameworks, technologies, and concepts. The second and third generation Apple TV have several built-in applications, but do not support third-party applications. On September 9, 2015 at a media event, Apple announced the fourth generation Apple TV, with support for third-party applications. Apple changed the name of the Apple TV operating system to tvOS, adopting the camel case nomenclature that they were using for their other operating systems, iOS and watchOS. History On October 30, 2015, the fourth generation Apple TV became available, and shipped with tvOS 9.0. On November 9, 2015, tvOS 9.0.1 was released, primarily an update to address minor issues. tvOS 9.1 was relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Portability
A computer program is said to be portable if there is very low effort required to make it run on different platforms. The pre-requirement for portability is the generalized abstraction between the application logic and system interfaces. When software with the same functionality is produced for several computing platforms, portability is the key issue for development cost reduction. Strategies for portability Software portability may involve: * Transferring installed program files to another computer of basically the same architecture. * Reinstalling a program from distribution files on another computer of basically the same architecture. * Building executable programs for different platforms from source code; this is what is usually understood by "porting". Similar systems When operating systems of the same family are installed on two computers with processors with similar instruction sets it is often possible to transfer the files implementing program files between them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free And Open-source Software
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is a term used to refer to groups of software consisting of both free software and open-source software where anyone is freely licensed to use, copy, study, and change the software in any way, and the source code is openly shared so that people are encouraged to voluntarily improve the design of the software. This is in contrast to proprietary software, where the software is under restrictive copyright licensing and the source code is usually hidden from the users. FOSS maintains the software user's civil liberty rights (see the Four Essential Freedoms, below). Other benefits of using FOSS can include decreased software costs, increased security and stability (especially in regard to malware), protecting privacy, education, and giving users more control over their own hardware. Free and open-source operating systems such as Linux and descendants of BSD are widely utilized today, powering millions of servers, desktops, smartphones (e.g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Lesser General Public License
The GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) is a free-software license published by the Free Software Foundation (FSF). The license allows developers and companies to use and integrate a software component released under the LGPL into their own (even proprietary) software without being required by the terms of a strong copyleft license to release the source code of their own components. However, any developer who modifies an LGPL-covered component is required to make their modified version available under the same LGPL license. For proprietary software, code under the LGPL is usually used in the form of a shared library, so that there is a clear separation between the proprietary and LGPL components. The LGPL is primarily used for software libraries, although it is also used by some stand-alone applications. The LGPL was developed as a compromise between the strong copyleft of the GNU General Public License (GPL) and more permissive licenses such as the BSD licenses and the MI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the four freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The license was the first copyleft for general use and was originally written by the founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), Richard Stallman, for the GNU Project. The license grants the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. These GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. It is more restrictive than the Lesser General Public License and even further distinct from the more widely used permissive software licenses BSD, MIT, and Apache. Historically, the GPL license family has been one of the most popular software licenses in the free and open-source software domain. Prominent free software programs licensed under the GPL include the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
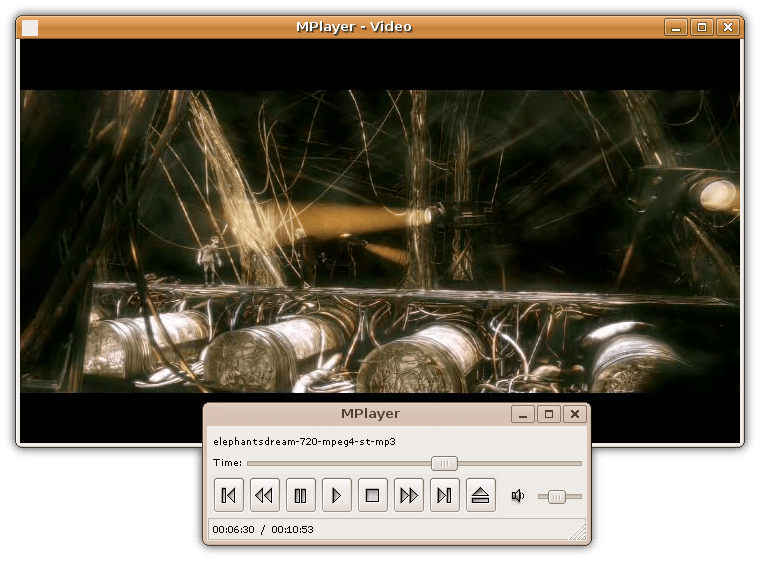
Media Player (software)
Media player software is a type of application software for playing multimedia computer files like audio and video files. Media players commonly display standard media control icons known from physical devices such as tape recorders and CD players, such as play ( ), pause ( ), fastforward (⏩️), backforward (⏪), and stop ( ) buttons. In addition, they generally have progress bars (or "playback bars"), which are sliders to locate the current position in the duration of the media file. Mainstream operating systems have at least one default media player. For example, Windows comes with Windows Media Player, Microsoft Movies & TV and Groove Music, while macOS comes with QuickTime Player and Music. Linux distributions come with different media players, such as SMPlayer, Amarok, Audacious, Banshee, MPlayer, mpv, Rhythmbox, Totem, VLC media player, and xine. Android comes with Google Play Music for audio and Google Phot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerPC
PowerPC (with the backronym Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC – Performance Computing, sometimes abbreviated as PPC) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple– IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM. PowerPC, as an evolving instruction set, has been named Power ISA since 2006, while the old name lives on as a trademark for some implementations of Power Architecture–based processors. PowerPC was the cornerstone of AIM's PReP and Common Hardware Reference Platform (CHRP) initiatives in the 1990s. Originally intended for personal computers, the architecture is well known for being used by Apple's Power Macintosh, PowerBook, iMac, iBook, eMac, Mac Mini, and Xserve lines from 1994 until 2005, when Apple migrated to Intel's x86. It has since become a niche in personal computers, but remains popular for embedded and high-performance processors. Its use in 7th generation of video game consoles and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIPS Architecture
MIPS (Microprocessor without Interlocked Pipelined Stages) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures (ISA)Price, Charles (September 1995). ''MIPS IV Instruction Set'' (Revision 3.2), MIPS Technologies, Inc. developed by MIPS Computer Systems, now MIPS Technologies, based in the United States. There are multiple versions of MIPS: including MIPS I, II, III, IV, and V; as well as five releases of MIPS32/64 (for 32- and 64-bit implementations, respectively). The early MIPS architectures were 32-bit; 64-bit versions were developed later. As of April 2017, the current version of MIPS is MIPS32/64 Release 6. MIPS32/64 primarily differs from MIPS I–V by defining the privileged kernel mode System Control Coprocessor in addition to the user mode architecture. The MIPS architecture has several optional extensions. MIPS-3D which is a simple set of floating-point SIMD instructions dedicated to common 3D tasks, MDMX (MaDMaX) which is a more extens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM64
AArch64 or ARM64 is the 64-bit extension of the ARM architecture family. It was first introduced with the Armv8-A architecture. Arm releases a new extension every year. ARMv8.x and ARMv9.x extensions and features Announced in October 2011, ARMv8-A represents a fundamental change to the ARM architecture. It adds an optional 64-bit architecture, named "AArch64", and the associated new "A64" instruction set. AArch64 provides user-space compatibility with the existing 32-bit architecture ("AArch32" / ARMv7-A), and instruction set ("A32"). The 16-32bit Thumb instruction set is referred to as "T32" and has no 64-bit counterpart. ARMv8-A allows 32-bit applications to be executed in a 64-bit OS, and a 32-bit OS to be under the control of a 64-bit hypervisor. ARM announced their Cortex-A53 and Cortex-A57 cores on 30 October 2012. Apple was the first to release an ARMv8-A compatible core (Cyclone) in a consumer product (iPhone 5S). AppliedMicro, using an FPGA, was the first to demo ARMv8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Architecture
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configured for various environments. Arm Ltd. develops the architectures and licenses them to other companies, who design their own products that implement one or more of those architectures, including system on a chip (SoC) and system on module (SOM) designs, that incorporate different components such as memory, interfaces, and radios. It also designs cores that implement these instruction set architectures and licenses these designs to many companies that incorporate those core designs into their own products. There have been several generations of the ARM design. The original ARM1 used a 32-bit internal structure but had a 26-bit address space that limited it to 64 MB of main memory. This limitation was removed in the ARMv3 series, which h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X86-64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit version of the x86 instruction set, first released in 1999. It introduced two new modes of operation, 64-bit mode and compatibility mode, along with a new 4-level paging mode. With 64-bit mode and the new paging mode, it supports vastly larger amounts of virtual memory and physical memory than was possible on its 32-bit predecessors, allowing programs to store larger amounts of data in memory. x86-64 also expands general-purpose registers to 64-bit, and expands the number of them from 8 (some of which had limited or fixed functionality, e.g. for stack management) to 16 (fully general), and provides numerous other enhancements. Floating-point arithmetic is supported via mandatory SSE2-like instructions, and x87/MMX style registers are generally not used (but still available even in 64-bit mode); instead, a set of 16 vector registers, 128 bits each, is used. (Each register can store one or two double-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)