Yeovil Town L on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Yeovil ( ) is a town and
 In the 1800s Yeovil was a glove-making centre, whose the population expanded fast. In the mid-19th century it became linked to the rest of Britain by a complex of railway lines, with competition between the broad gauge lines of the
In the 1800s Yeovil was a glove-making centre, whose the population expanded fast. In the mid-19th century it became linked to the rest of Britain by a complex of railway lines, with competition between the broad gauge lines of the
 Officially designated as Yeovil Municipal Borough in 1854, the town continued to lend its name to the area with the creation of the
Officially designated as Yeovil Municipal Borough in 1854, the town continued to lend its name to the area with the creation of the
 Yeovil is in the south of Somerset, close to the border with
Yeovil is in the south of Somerset, close to the border with

 One symbol of Yeovil is "Jack the Treacle Eater", a
One symbol of Yeovil is "Jack the Treacle Eater", a
 Bus services linking the centre to Yeovil Junction are run by
Bus services linking the centre to Yeovil Junction are run by
 The
The
 The town's
The town's
School for Scoundrels
/ref> Later they were adapted by
Yeovil Town CouncilEconomy of Yeovil
{{Authority control Towns in South Somerset Civil parishes in Somerset Market towns in Somerset
civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties, or their combined form, the unitary authority ...
in the district of South Somerset
South Somerset is a local government district in Somerset, England.
The South Somerset district covers an area of ranging from the borders with Devon, Wiltshire and Dorset to the edge of the Somerset Levels. It has a population of approxim ...
, England. The population of Yeovil at the last census (2011) was 45,784. More recent estimates show a population of 48,564. It is close to Somerset's southern border with Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset (unitary authority), Dors ...
, from London, south of Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
, from Sherborne
Sherborne is a market town and civil parish in north west Dorset, in South West England. It is sited on the River Yeo, on the edge of the Blackmore Vale, east of Yeovil. The parish includes the hamlets of Nether Coombe and Lower Clatcombe. ...
and from Taunton
Taunton () is the county town of Somerset, England, with a 2011 population of 69,570. Its thousand-year history includes a 10th-century monastic foundation, Taunton Castle, which later became a priory. The Normans built a castle owned by the ...
. The aircraft and defence industries which developed in the 20th century made it a target for bombing in the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
; they are still major employers. Yeovil Country Park, which includes Ninesprings
Ninesprings is a country park situated in the South East of Yeovil, Somerset, the United Kingdom. It is the largest country park in South Somerset, spanning over .
The site lies on Yeovil Sands (a yellow micaceous sand) of the Upper Lias, in ...
, is one of several open spaces with educational, cultural and sporting facilities. Religious sites include the 14th-century Church of St John the Baptist. The town is on the A30 and A37 roads and has two railway stations.
History
Archaeological surveys have yieldedPalaeolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος '' lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone to ...
burial and settlement sites mainly to the south of the modern town, particularly in Hendford, where a Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
golden torc
A torc, also spelled torq or torque, is a large rigid or stiff neck ring in metal, made either as a single piece or from strands twisted together. The great majority are open at the front, although some had hook and ring closures and a few had ...
(twisted collar) was found.
Yeovil is on the main Roman road from Dorchester to the Fosse Way at Ilchester
Ilchester is a village and civil parish, situated on the River Yeo or Ivel, five miles north of Yeovil, in the English county of Somerset. Originally a Roman town, and later a market town, Ilchester has a rich medieval history and was a nota ...
. The route of the old road is aligned with the A37 from Dorchester, Hendford Hill, Rustywell, across the Westland site, to Larkhill Road and Vagg Lane, rejoining the A37 at the ''Halfway House'' pub in the Ilchester Road. The Westland site has evidence of a small Roman town. There were several Roman villa
A Roman villa was typically a farmhouse or country house built in the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, sometimes reaching extravagant proportions.
Typology and distribution
Pliny the Elder (23–79 AD) distinguished two kinds of villas n ...
s (estates) in the area. Finds have been made at East Coker
East Coker is a village and civil parish in the South Somerset district of Somerset, England. Its nearest town is Yeovil, to the north. The village has a population of 1,667. The parish includes the hamlets and areas of North Coker, Burton, ...
, West Coker
West Coker is a large village and civil parish in Somerset, England, situated south west of Yeovil in the South Somerset district.
History
The name Coker comes from Coker Water ("crooked stream" from the Celtic ''Kukro'').
Artifacts from early ...
and Lufton.
Medieval times
Yeovil was first named in a Saxon charter dated 880 as Gifle. It derives from theCeltic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
river-name ''gifl'' "forked river", an earlier name of the River Yeo.
The estate was bequeathed in the will of King Alfred the Great to his youngest son Aethelweard. It was recorded in the Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
as ''Givele'', a thriving market community. The parish of Yeovil was part of the Stone
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks ...
Hundred
100 or one hundred (Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 and preceding 101.
In medieval contexts, it may be described as the short hundred or five score in order to differentiate the English and Germanic use of "hundred" to de ...
. After the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conque ...
, the manor, later known as Hendford, was granted to the Count of Eu
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
and his tenant Hugh Maltravers, whose descendants became Earls of Arundel
Earl of Arundel is a title of nobility in England, and one of the oldest extant in the English peerage. It is currently held by the Duke of Norfolk, and is used (along with the Earl of Surrey) by his heir apparent as a courtesy title. The ...
and held the lordship
A lordship is a territory held by a lord. It was a landed estate that served as the lowest administrative and judicial unit in rural areas. It originated as a unit under the feudal system during the Middle Ages. In a lordship, the functions of econ ...
until 1561. In 1205 it was granted a charter by King John. By the 14th century, the town had gained the right to elect a portreeve
A portreeve ( ang, hæfenrēfa, sometimes spelled Port-reeve) or port warden is the title of a historical official in England and Wales possessing authority (political, administrative, or fiscal) over a town. The details of the office have fluctu ...
.
The Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
exacted a heavy toll, killing about half the population.
In 1499 a major fire destroyed many wooden, thatch-roofed buildings in the town. Yeovil suffered further fires in 1620 and 1643.
Ownership
After the dissolution of the monasteries the lord of the manor was the family of John Horsey ofClifton Maybank
Clifton Maybank is a hamlet and civil parish in the English county of Dorset. It is located about a mile southwest of the village of Bradford Abbas. It is known for Clifton Maybank House, a country house with surviving Tudor fabric. Dorset Coun ...
from 1538 to 1610 followed by the Phelips family until 1846 when it passed to the Harbins of Newton Surmaville. Babylon Hill
Babylon Hill () in Dorset is a 2.2 hectare geological Site of Special Scientific Interest designated in 1977.Battle of Babylon Hill
The Battle of Babylon Hill was an indecisive skirmish that took place between Cavaliers, Royalist and Roundheads, Parliamentarian forces near Yeovil, in South West England, on 7 September 1642, during the early stages of the First English Civil ...
, during the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
, which resulted in the Earl of Bedford
Earl of Bedford is a title that has been created three times in the Peerage of England and is currently a subsidiary title of the Dukes of Bedford. The first creation came in 1138 in favour of Hugh de Beaumont. He appears to have been degraded fr ...
's Roundheads
Roundheads were the supporters of the Parliament of England during the English Civil War (1642–1651). Also known as Parliamentarians, they fought against King Charles I of England and his supporters, known as the Cavaliers or Royalists, who ...
forcing back Sir Ralph Hopton
Ralph Hopton, 1st Baron Hopton, (159628 September 1652), was an English politician, soldier and landowner. During the 1642 to 1646 First English Civil War, he served as Royalist commander in the West Country, and was made Baron Hopton of Stra ...
's Cavalier
The term Cavalier () was first used by Roundheads as a term of abuse for the wealthier royalist supporters of King Charles I and his son Charles II of England during the English Civil War, the Interregnum, and the Restoration (1642 – ) ...
s to Sherborne
Sherborne is a market town and civil parish in north west Dorset, in South West England. It is sited on the River Yeo, on the edge of the Blackmore Vale, east of Yeovil. The parish includes the hamlets of Nether Coombe and Lower Clatcombe. ...
.
Development
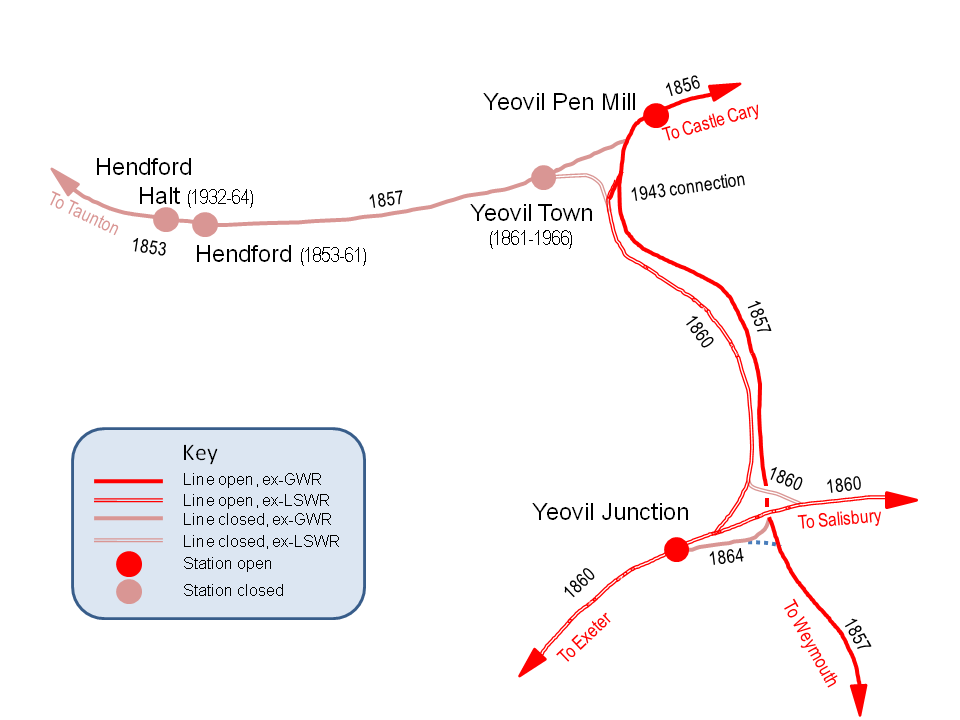
 In the 1800s Yeovil was a glove-making centre, whose the population expanded fast. In the mid-19th century it became linked to the rest of Britain by a complex of railway lines, with competition between the broad gauge lines of the
In the 1800s Yeovil was a glove-making centre, whose the population expanded fast. In the mid-19th century it became linked to the rest of Britain by a complex of railway lines, with competition between the broad gauge lines of the Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
(GWR) and the standard gauge lines of the London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exeter ...
(LSWR). In 1853 the Great Western Railway line was opened between Taunton and Yeovil.
The town's first railway was a branch line from the Bristol and Exeter Railway near Taunton
Taunton () is the county town of Somerset, England, with a 2011 population of 69,570. Its thousand-year history includes a 10th-century monastic foundation, Taunton Castle, which later became a priory. The Normans built a castle owned by the ...
to a terminus at on the western side of the town, which opened on 1 October 1853. As an associate of the GWR, this was a broad-gauge line. The GWR itself opened Yeovil Pen Mill railway station
Yeovil Pen Mill railway station is one of two stations serving the town of Yeovil, Somerset, England. The station is situated just under a mile to the east of the town centre. The station is located south of , on the Heart of Wessex Line. The ...
on the east side of the town as part of its route from London on 1 September 1856, extended to Weymouth on 1 January 1857), and the original line from Taunton connected with this. The LSWR route from London reached Hendford on 1 June 1860, but a month later the town was by-passed by an extension of the LSWR to Exeter. A new station at was provided south of the town from where passengers could catch a connecting service to Hendford. On 1 June 1861 passenger trains were withdrawn from Hendford and transferred to a new, more central, Yeovil Town railway station
Yeovil Town railway station was a railway station serving the town of Yeovil in Somerset, England. The station was on the Yeovil to Taunton Line and also had shuttle services to Pen Mill and Yeovil Junction stations. The station opened on 1 J ...
.
In 1854, the town gained borough status and had its first mayor. In the early 20th century Yeovil had around 11,000 inhabitants and was dominated by the defence industry, making it a target of German raids during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. The worst bombing was in 1940 and continued until 1942. During that time 107 high-explosive bombs fell on the town, 49 people died, 68 houses were totally destroyed and 2,377 damaged.
Industrial businesses developed round the Hendford railway goods station to such a degree that a small was opened on 2 May 1932 for passengers, but the growth of road transport and a desire to rationalise the rail network led to half of the railway stations
A train station, railway station, railroad station or depot is a railway facility where trains stop to load or unload passengers, freight or both. It generally consists of at least one platform, one track and a station building providing such ...
in Yeovil being closed in 1964. First to go was Hendford Halt, closed on 15 June along with the line to Taunton, then closed on 2 October. Long-distance trains from Pen Mill were withdrawn on 11 September 1961, leaving only with a service to London, but the service between there and Pen Mill, the two remaining stations, was also withdrawn from 5 May 1968.
As a former centre of Britain's leather industry, the town is post-industrial in character. Journalist John Harris, for instance, described the towns Taunton, Yeovil and Bridgwater as a "post-industrial, hardscrabble place that contain 19 of the council wards in the 20% of English areas classed as the most deprived."
Governance

 Officially designated as Yeovil Municipal Borough in 1854, the town continued to lend its name to the area with the creation of the
Officially designated as Yeovil Municipal Borough in 1854, the town continued to lend its name to the area with the creation of the local government district
The districts of England (also known as local authority districts or local government districts to distinguish from unofficial city districts) are a level of subnational division of England used for the purposes of local government. As the st ...
of Yeovil on 1 April 1974, with the merging several neighbouring rural and urban districts, which is today known as South Somerset
South Somerset is a local government district in Somerset, England.
The South Somerset district covers an area of ranging from the borders with Devon, Wiltshire and Dorset to the edge of the Somerset Levels. It has a population of approxim ...
. Some suburbs fall within the civil parishes
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties, or their combined form, the unitary authority. ...
of Yeovil Without
Yeovil Without is a civil parish in the South Somerset district of Somerset, England.
It lies on the northern edge of Yeovil. It includes both suburbs of Yeovil, including the Bucklers Mead development, and rural areas including the hamlets of ...
and Brympton.
Yeovil still has a town council, which took over the functions of the Charter Trustees in 1982. It has responsibility for the management of recreational and leisure facilities, open spaces and play areas. In 2005, Yeovil Town Council became the first large council in Somerset to be awarded Quality Town Council status. Yeovil Town Council is based at the Town House
A townhouse, townhome, town house, or town home, is a type of terraced housing. A modern townhouse is often one with a small footprint on multiple floors. In a different British usage, the term originally referred to any type of city residence ...
.
There are five electoral wards
The wards and electoral divisions in the United Kingdom are electoral districts at sub-national level, represented by one or more councillors. The ward is the primary unit of English electoral geography for civil parishes and borough and dist ...
covering Yeovil.
Yeovil
Yeovil ( ) is a town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in the district of South Somerset, England. The population of Yeovil at the last census (2011) was 45,784. More recent estimates show a population of 48,564. It is close to Somer ...
is a county constituency
In the United Kingdom (UK), each of the electoral areas or divisions called constituencies elects one member to the House of Commons.
Within the United Kingdom there are five bodies with members elected by electoral districts called " constitue ...
represented in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
of the Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative suprema ...
. It elects one Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
(MP). It covers the Somerset towns of Yeovil, Chard, Crewkerne
Crewkerne ( ) is a town and electoral ward in Somerset, England, southwest of Yeovil and east of Chard all in the South Somerset district. The civil parish of West Crewkerne includes the hamlets of Coombe, Woolminstone and Henley – and b ...
and Ilminster
Ilminster is a minster town and civil parish in the South Somerset district of Somerset, England, with a population of 5,808. Bypassed in 1988, the town now lies just east of the junction of the A303 (London to Exeter) and the A358 (Taunton to ...
. Until 1983 Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
was split into four constituencies and Yeovil constituency also covered Ilchester
Ilchester is a village and civil parish, situated on the River Yeo or Ivel, five miles north of Yeovil, in the English county of Somerset. Originally a Roman town, and later a market town, Ilchester has a rich medieval history and was a nota ...
, Martock
Martock is a large village and civil parish in Somerset, England, situated on the edge of the Somerset Levels north west of Yeovil in the South Somerset district. The parish includes Hurst, approximately one mile south of the village, and Bow ...
and Somerton Somerton may refer to:
Places Australia
* Somerton, New South Wales
* Somerton Park, South Australia, a seaside Adelaide suburb
** Somerton Man, unsolved case of an unidentified man found dead in 1948 on the Somerton Park beach
* Somerton, Victoria ...
, but these were moved into the new constituency of Somerton and Frome. From the 2010 general election, Yeovil constituency regained Ilchester, to equalise the constituency populations. The Boundary Commission for England
The boundary commissions in the United Kingdom are non-departmental public bodies responsible for determining the boundaries of constituencies for elections to the House of Commons. There are four boundary commissions:
* Boundary Commission for ...
estimate that the electorate
Electorate may refer to:
* The people who are eligible to vote in an election, especially their number e.g. the term ''size of (the) electorate''
* The dominion of a Prince-elector
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, ...
of Yeovil constituency after the boundary changes to be 77,049. The current MP is Marcus Fysh
Marcus John Hudson Fysh (born 8 November 1970) is a British politician and former investment manager who has served as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Yeovil since 2015. A member of the Conservative Party, he served as Parliamentary Under-S ...
of the Conservative Party
The Conservative Party is a name used by many political parties around the world. These political parties are generally right-wing though their exact ideologies can range from center-right to far-right.
Political parties called The Conservative P ...
.
Geography
 Yeovil is in the south of Somerset, close to the border with
Yeovil is in the south of Somerset, close to the border with Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset (unitary authority), Dors ...
, from London, south of Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
and from Taunton
Taunton () is the county town of Somerset, England, with a 2011 population of 69,570. Its thousand-year history includes a 10th-century monastic foundation, Taunton Castle, which later became a priory. The Normans built a castle owned by the ...
. It lies in the centre of the Yeovil Scarplands
The Yeovil Scarplands are a natural region in southern England in the counties of Somerset and Dorset.
The region is listed as National Character Area 140 by Natural England, the UK Government's advisor on the natural environment. It covers an ...
, a natural region
A natural region (landscape unit) is a basic geographic unit. Usually, it is a region which is distinguished by its common natural features of geography, geology, and climate.
From the ecology, ecological point of view, the naturally occurring fl ...
of England. The suburbs include Summerlands, Hollands, Houndstone, Preston Plucknett
Preston Plucknett is a suburb of Yeovil in Somerset, England. It was once a small village, and a separate civil parish until 1930, when it was absorbed into the neighbouring parishes of Yeovil, Brympton and West Coker. It was listed in the Dome ...
, Penn Mill, New Town, Hendford, Old Town, Forest Hill, Abbey Manor, Great Lyde. Outlying villages include East Coker
East Coker is a village and civil parish in the South Somerset district of Somerset, England. Its nearest town is Yeovil, to the north. The village has a population of 1,667. The parish includes the hamlets and areas of North Coker, Burton, ...
, West Coker
West Coker is a large village and civil parish in Somerset, England, situated south west of Yeovil in the South Somerset district.
History
The name Coker comes from Coker Water ("crooked stream" from the Celtic ''Kukro'').
Artifacts from early ...
, Hardington Mandeville
Hardington Mandeville is a village and civil parish in Somerset, England, situated south west of Yeovil in the South Somerset district. The village has a population of 585.
History
The Hardington part of the name of the village means ''settle ...
, Evershot
Evershot is a village and civil parish in the county of Dorset in southwest England, situated approximately south of Yeovil in Somerset. It is the second highest village in the county at above sea-level. Evershot parish encompasses part of th ...
, Halstock
__NOTOC__
Halstock is a village and civil parish in the county of Dorset in southern England, situated approximately south of Yeovil in Somerset. It lies on the route of the ancient Harrow Way. In the 2011 census the parish had a populatio ...
, Stoford, Barwick, Sutton Bingham, Mudford
Mudford is a village and parish in Somerset, England, situated from Yeovil in the South Somerset district on the River Yeo. The village has a population of 696. The parish includes the hamlets of Mudford Sock, West Mudford and Up Mudford.
Th ...
and Yetminster. Other nearby villages include Bradford Abbas
Bradford Abbas is a village and civil parish in north west Dorset, England, southeast of Yeovil and southwest of Sherborne. The parish includes the small settlement of Saxon Maybank to the north. In the 2011 census the population of the parish ...
, Thornford
Thornford is a village and civil parish in north west Dorset, England, situated in the Yeo valley southwest of Sherborne. Dorset County Council's 2013 mid-year estimate of the population of the parish is 830.
Thornford is in Thornhackett Parish ...
Corscombe
Corscombe is a village and civil parish in the English county of Dorset, in the Dorset Council administrative area. The parish includes the small settlements of Benville and Toller Whelme to the south and in the 2011 census had a population of ...
, Montacute (with Montacute House
Montacute House is a late Elizabethan era, Elizabethan mansion with a garden in Montacute, South Somerset.
An example of English architecture during a period that was moving from the medieval Gothic to the Renaissance Classical, and one of fe ...
) and Pendomer. The village of Brympton, now almost a suburb of Yeovil, contains the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
manor of Brympton d'Evercy
Brympton d'Evercy (alternatively Brympton House), a grade I listed manor house near Yeovil in the county of Somerset, England, has been called the most beautiful in England. In 1927 the British magazine '' Country Life'' devoted three articles ...
. Tintinhull
Tintinhull is a village and civil parish near Yeovil, south west of Ilchester, in Somerset, England. The village is close to the A303. It is on the Fosse Way.
In addition to a school of around 100 pupils, Tintinhull has a church, park, swimmin ...
, also close to Yeovil, features the National Trust-owned Tintinhull House and Gardens.
Ninesprings Country Park is in the south-east near Penn Hill, linked by a cycle way along the route of the old railway to Riverside Walk, Wyndham Hill and Summerhouse Hill, forming the Yeovil Country Park.
Climate
Like the rest ofSouth West England
South West England, or the South West of England, is one of nine official regions of England. It consists of the counties of Bristol, Cornwall (including the Isles of Scilly), Dorset, Devon, Gloucestershire, Somerset and Wiltshire. Cities and ...
, Yeovil has a temperate climate generally wetter and milder than the rest of the country. The annual mean temperature is about and shows seasonal and diurnal variation, but the sea has a modifying effect. January is the coldest month, with mean minimum temperatures between and . July and August are the warmest months, with mean daily maxima around .
The south-west of England is in a favoured location for the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
high pressure zone, when it extends north-eastwards towards the UK, particularly in summer. However, convective
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convec ...
cloud often forms inland, especially near hills, reducing the number of hours of sunshine, whose annual average annual is about 1,700 hours.
Rainfall tends to be associated with Atlantic depressions or with convection. The Atlantic depressions are more vigorous in autumn and winter, when most of the rain that falls in the south-west is from that source. Average rainfall is about . November to March have the highest mean wind speeds, with June to August having the lightest winds. The predominant wind direction is from the south-west.
Demography
At the 2011 census, the population of the built-up area (which extends beyond Yeovil civil parish to include the urban parts ofYeovil Without
Yeovil Without is a civil parish in the South Somerset district of Somerset, England.
It lies on the northern edge of Yeovil. It includes both suburbs of Yeovil, including the Bucklers Mead development, and rural areas including the hamlets of ...
and Brympton parishes) was 45,784, forming 28% of the population of South Somerset
South Somerset is a local government district in Somerset, England.
The South Somerset district covers an area of ranging from the borders with Devon, Wiltshire and Dorset to the edge of the Somerset Levels. It has a population of approxim ...
district.
Economy

AgustaWestland
AgustaWestland was an Anglo-Italian helicopter design and manufacturing company, which was a wholly owned subsidiary of Finmeccanica (now known as Leonardo). It was formed in July 2000 as an Anglo-Italian multinational company, when Finmeccani ...
manufactures helicopters in Yeovil, and Normalair Garratt, (Honeywell) builder of aircraft oxygen systems, is also based there.
Yeovil's role as a centre of the aircraft and defence industries continued into the 21st century, despite attempts to diversify and the creation of industrial estates. In January 1986 a proposed sale of Westland Helicopters
Westland Helicopters was a British aircraft manufacturer. Originally Westland Aircraft, the company focused on helicopters after the Second World War. It was amalgamated with several other British firms in 1960 and 1961.
In 2000, it merged ...
to the US Sikorsky Aircraft group led to the Westland affair
The Westland affair in 1985–86 was an episode in which Margaret Thatcher, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, and her Secretary of State for Defence, Michael Heseltine, went public over a cabinet dispute with questions raised about whether ...
, a crisis in the Thatcher government, resignation of Michael Heseltine
Michael Ray Dibdin Heseltine, Baron Heseltine, (; born 21 March 1933) is a British politician and businessman. Having begun his career as a property developer, he became one of the founders of the publishing house Haymarket. Heseltine served ...
as Secretary of State for Defence
The secretary of state for defence, also referred to as the defence secretary, is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, with overall responsibility for the business of the Ministry of Defence. The incumbent is a membe ...
, and two weeks later of Secretary of State for Trade and Industry
The secretary of state for business, energy and industrial strategy, is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, with responsibility for the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy. The incumbent is a memb ...
Leon Brittan
Leon Brittan, Baron Brittan of Spennithorne, (25 September 193921 January 2015) was a British Conservative politician and barrister who served as a European Commissioner from 1989 to 1999. As a member of Parliament from 1974 to 1988, he serv ...
, who admitted leaking a governmental law officer's letter harshly critical of Heseltine. AgustaWestland, created through the acquisition of Westland by Finmeccanica in 2000, remains the main employer in Yeovil.
Yeovil Aerodrome , (sometimes known as Yeovil/Westland "Judwin" to avoid confusion with nearby RNAS Yeovilton
Royal Naval Air Station Yeovilton, or RNAS Yeovilton, (HMS ''Heron'') is an airfield of the Royal Navy and British Army, sited a few miles north of Yeovil, Somerset. It is one of two active Fleet Air Arm bases (the other being RNAS Culdrose) ...
), is west of the town centre. British defence giant BAE Systems
BAE Systems plc (BAE) is a British multinational arms, security, and aerospace company based in London, England. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe, and ranked the seventh-largest in the world based on applicable 2021 revenues. ...
also runs a site producing high-integrity networked software, mainly for the armed forces.
Screwfix Direct based in Houndstone started life as Woodscrew Supply Company in 1979. It is now a subsidiary of Kingfisher plc
Kingfisher plc is a British Multinational corporation, multinational retailing company headquartered in London, England.
It has over 1,300 stores in nine countries, and its brands include B&Q, Castorama, Brico Dépôt and Screwfix. Kingfisher i ...
. The company warehouse relocated to Stoke-on-Trent
Stoke-on-Trent (often abbreviated to Stoke) is a city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Staffordshire, England, with an area of . In 2019, the city had an estimated population of 256,375. It is the largest settlement ...
after failing to gain planning permission for expansion.
Quedam Shopping Centre has some 45 shops: the usual high-street chains, several independents, and a multi-storey car park
A multistorey car park ( British and Singapore English) or parking garage (American English), also called a multistory, parking building, parking structure, parkade (mainly Canadian), parking ramp, parking deck or indoor parking, is a bui ...
with about 650 spaces.
In 2015, leather manufacturer Pittards bought back its 1964 purpose-built tannery in Sherborne Road, Yeovil.
Landmarks
 One symbol of Yeovil is "Jack the Treacle Eater", a
One symbol of Yeovil is "Jack the Treacle Eater", a folly
In architecture, a folly is a building constructed primarily for decoration, but suggesting through its appearance some other purpose, or of such extravagant appearance that it transcends the range of usual garden buildings.
Eighteenth-cent ...
consisting of a small archway topped by a turret with a statue on top. This stands in the village of Barwick, just to the south of the town. The hamstone
Hamstone is the name given to a honey-coloured building stone from Ham Hill, Somerset, England. It is a well-cemented medium to coarse grained limestone characterised by marked bedding planes of clay inclusions and less well-cemented material ...
Abbey Farm House was built about 1420 by John Stourton II, known as Jenkyn, as was Abbey Barn.
Hendford Manor in the town centre was built about 1720 and has since been converted into offices. It is a Grade II* listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
. Newton Surmaville is a small park and house also known as Newton House, built in 1608–1612 for Robert Harbin, a Yeovil merchant. It is a Grade I listed building.
Yeovil's two theatres are the Octagon, and the Swan, now a ten-screen cinema and 18-lane tenpin bowling alley.
Yeovil District Hospital
Yeovil District Hospital is a healthcare facility in Yeovil, Somerset, England. It is managed by Yeovil District Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
History
The hospital has its origins in a general dispensary established at the suggestion of Dr El ...
NHS Foundation Trust
A foundation trust is a semi-autonomous organisational unit within the National Health Service in England. They have a degree of independence from the Department of Health and Social Care (and, until the abolition of SHAs in 2013, their local st ...
provides local health services.
Yeovil Railway Centre
The Yeovil Railway Centre is a small railway museum at Yeovil Junction railway station, Yeovil Junction on the London and South Western Railway, L&SWR West of England Main Line between Salisbury railway station, Salisbury and Exeter Central railw ...
is a small museum created in 1993 in response to British Rail's decision to remove the turntable
A phonograph, in its later forms also called a gramophone (as a trademark since 1887, as a generic name in the UK since 1910) or since the 1940s called a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogu ...
from Yeovil Junction. About of track along the Clifton Maybank spur is used for demonstration trains.
Transport
The two railway stations serve separate lines.Yeovil Pen Mill
Yeovil Pen Mill railway station is one of two stations serving the town of Yeovil, Somerset, England. The station is situated just under a mile to the east of the town centre. The station is located south of , on the Heart of Wessex Line. The ...
is on the Bristol to Weymouth line, served by Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
services, and Yeovil Junction is on the London Waterloo to Exeter line served by South Western Railway. Both are some distance from the centre of Yeovil: Pen Mill just under to the east and Junction just over to the south.
 Bus services linking the centre to Yeovil Junction are run by
Bus services linking the centre to Yeovil Junction are run by South West Coaches
South West Coaches is a privately owned bus company that operates services around Dorset, Somerset, and Wiltshire, in South West England.
History
Reggie Wake started bus services from South Barrow in February 1930. Business expanded during Wor ...
except on Sundays and bank holidays, when a service is operated by . The latter firm also operates a service to Pen Mill,
Yeovil has bus services from , First Hampshire & Dorset
First Hampshire & Dorset is a bus operator providing services in the counties of Hampshire and Dorset. It is a subsidiary of FirstGroup.
History
First Hampshire & Dorset was created out of various different smaller companies which were merged o ...
, South West Coaches
South West Coaches is a privately owned bus company that operates services around Dorset, Somerset, and Wiltshire, in South West England.
History
Reggie Wake started bus services from South Barrow in February 1930. Business expanded during Wor ...
, Stagecoach South West and Damory Coaches, and coach services from National Express
National Express Group is a British multinational public transport company headquartered in Birmingham, England. It operates bus, coach, train and tram services in the United Kingdom, Ireland (National Express operates Eurolines in conjunction ...
, Berrys Coaches and South West Tours. Many of the listed services serve Yeovil College
Yeovil College is a tertiary college for further education and higher education based in Yeovil, Somerset. It maintains a main campus in the town and, at a second site, a Construction Skills Centre. In conjunction with the universities of Bourn ...
. All bus routes except First West of England local routes towards the Western side of the town serve Yeovil bus station. North Dorset Community Accessible Transport (NORDCAT) provides a bookable service to places without other forms of public transport.
The town is on the A30 – the main route between London and the South West until it was supplanted by the A303
The A303 is a trunk road in southern England, running between Basingstoke in Hampshire and Honiton in Devon via Stonehenge. Connecting the M3 and the A30, it is part of one of the main routes from London to Devon and Cornwall. It is a pri ...
to its north. Junction 25 of the M5 motorway
The M5 is a motorway in England linking the Midlands with the South West England, South West. It runs from junction 8 of the M6 motorway, M6 at West Bromwich near Birmingham to Exeter in Devon. Heading south-west, the M5 runs east of West Brom ...
, giving access to Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
and the Midlands, is about to the west, near Taunton
Taunton () is the county town of Somerset, England, with a 2011 population of 69,570. Its thousand-year history includes a 10th-century monastic foundation, Taunton Castle, which later became a priory. The Normans built a castle owned by the ...
. Yeovil is also on the mainly single-carriageway A37 north–south road between Bristol and Weymouth.
Education
Further education
Further education (often abbreviated FE) in the United Kingdom and Ireland is education in addition to that received at secondary school, that is distinct from the higher education (HE) offered in universities and other academic institutions. I ...
in Yeovil is mainly offered by Yeovil College
Yeovil College is a tertiary college for further education and higher education based in Yeovil, Somerset. It maintains a main campus in the town and, at a second site, a Construction Skills Centre. In conjunction with the universities of Bourn ...
, with land-based studies available at a Yeovil centre of Bridgwater College
Bridgwater and Taunton College is a further education college based in the heart of Somerset, England, with main centres in Bridgwater, Taunton and Cannington. It educates approximately 3000 students between the ages of 16–18 in academic and ...
, and some provision through private providers. The town also has a higher education centre, University Centre Yeovil, whose main degree-awarding body is Bournemouth University
Bournemouth University is a public university in Bournemouth, England, with its main campus situated in neighbouring Poole. The university was founded in 1992; however, the origins of its predecessor date back to the early 1900s.
The univer ...
, with University of the West of England
The University of the West of England (also known as UWE Bristol) is a public research university, located in and around Bristol, England.
The institution was know as the Bristol Polytechnic in 1970; it received university status in 1992 and ...
offering some courses.
Secondary education in Yeovil is provided by four schools: Westfield Academy
Westfield Academy (formerly Westfield Community Technology College) is a coeducational secondary school and sixth form with academy status, located in the Holywell Estate in Watford, Hertfordshire, England.
Previously a community school ...
on Stiby Road; Preston School
Preston School is a secondary school with specialist Business and Enterprise College status in Yeovil, Somerset, England. In 2017, enrolment was 975 students aged 11 to 18 years. In July 2011, the school became an Academy (English school), Acade ...
, with actress Sarah Parish
Sarah Parish (born 7 June 1968) is an English actress. She is known for her work on television series including: ''The Pillars of the Earth'', ''Peak Practice'', '' Hearts and Bones'', ''Cutting It'', ''Doctor Who'', '' Mistresses'', ''Merlin'', ...
among its past pupils; and Bucklers Mead Academy
Buckler's Mead Academy is a secondary school and specialist Technology College in Yeovil, Somerset, England. As of 2014, it has 907 students between the ages of 11 and 16. The school offers a range of subjects including art, beliefs and values, ...
with past pupils including Sir Ian Botham
Ian Terence Botham, Baron Botham, (born 24 November 1955) is an English cricket commentator, member of the House of Lords, a former cricketer who has been chairman of Durham County Cricket Club since 2017 and charity fundraiser.
Hailed as one ...
.
Places of worship
 The
The Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
Church of St John The Baptist dates from the late 14th century. Its -high tower is in four stages, with set-back offset corner buttresses. It is capped by openwork balustrading matching the 19th-century parapets. There are two-light late 14th-century windows on all sides at bell-ringing and bell-chamber levels, the latter having fine pierced stonework grilles. There is a stair turret to the north-west corner, with a weather vane
A wind vane, weather vane, or weathercock is an instrument used for showing the direction of the wind. It is typically used as an architectural ornament to the highest point of a building. The word ''vane'' comes from the Old English word , m ...
termination. The church is a Grade I listed building.
Yeovil has a Roman Catholic Holy Ghost Church, three Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's b ...
churches (Preston Road, St Marks, Chelston Avenue, and Vicarage Street), a Baptist
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only ( believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul compe ...
church in South Street, the Salvation Army
Salvation (from Latin: ''salvatio'', from ''salva'', 'safe, saved') is the state of being saved or protected from harm or a dire situation. In religion and theology, ''salvation'' generally refers to the deliverance of the soul from sin and its c ...
, Elim Pentecostal Church
The Elim Pentecostal Church is a UK-based Pentecostal Christian denomination.
History
George Jeffreys (1889–1962), a Welshman, founded the ''Elim Pentecostal Church'' in Monaghan, Ireland in 1915. Jeffreys was an evangelist with a Welsh Co ...
, Yeovil Community Church (Evangelical, based at The GateWay), Yeovil Family Church (New Frontiers), and several other Anglican churches.
There is a mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
on Sherborne Road which was opened to worshippers in May 2017.
Sport
 The town's
The town's football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
team, Yeovil Town F.C.
Yeovil Town Football Club is a professional association football club based in the town of Yeovil, Somerset, England. The team competes in the , the fifth tier of the English football league system. The club's home ground is Huish Park, built i ...
, plays in green and white livery at Huish Park
Huish Park is a football stadium located in Yeovil, Somerset, England. The stadium has been home to Yeovil Town F.C. since its completion in 1990, following their relocation from Huish. Huish Park has a capacity of 9,565 (of which two stands ...
, and currently competes in the National League
The National League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the National League (NL), is the older of two leagues constituting Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, and the world's oldest extant professional team s ...
. Known as the "Glovers" (referring to the town's glove-making past), it was founded in 1895 and won, as Football Conference (the then name of National League) champions in 2003, promotion to the English Football League
The English Football League (EFL) is a league of professional football clubs from England and Wales. Founded in 1888 as the Football League, the league is the oldest such competition in the world. It was the top-level football league in Engl ...
for the first time in its history. It had achieved numerous FA Cup
The Football Association Challenge Cup, more commonly known as the FA Cup, is an annual knockout football competition in men's domestic English football. First played during the 1871–72 season, it is the oldest national football competi ...
victories over Football League sides in the past 50 years, and since joining the League has won promotion again – as League Two
The English Football League Two (often referred to as League Two for short or Sky Bet League Two for sponsorship purposes, and known as the Football League Two from 2004 until 2016) is the third and lowest division of the English Football Lea ...
champions in 2005 and League One play-off winners in 2013. However, the stay in tier 2 of English football only lasted for a season. In women's football, Yeovil Town L.F.C.
Bridgwater United Women's Football Club are an English women's association football club based in Bridgwater, Somerset who were previously known as Yetminster Ladies, Sherborne Ladies, Yeovil Town Ladies and Yeovil United. Founded in 1990, they ...
was founded in 1990 and won promotion to England's highest tier, the FA Women's Super League
The Women's Super League (WSL), currently known as the Barclays Women's Super League (BWSL) for sponsorship reasons, is the highest league of women's football in England. Established in 2010, it is run by the Football Association and features ...
, in 2016.
Other football teams in the town include Westland's Sports Football Club, which plays at Alvington Lane, and Pen Mill Football Club.
Yeovil Olympiads Athletics Club
Yeovil Olympiads Athletics Club was the first track and field athletics club in Yeovil, Somerset, England. The club is based at the Bill Whistlecroft Athletics Arena, formerly Yeovil Arena before it was renamed on 14 September 2014.
This club wa ...
, founded in 1969, has produced many international athletes. The first was Eric Berry, who came 6th in the 1973 European Juniors in the hammer event. Olympians who started with the club include Max Robertson
William Maxwell Robertson (28 August 1915 – 20 November 2009) was a sports commentator, radio and television presenter and author. He is best remembered for his forty years of tennis coverage on BBC Radio.
Life and career
Robertson was ...
and Gary Jennings, both 400-metre hurdlers.
Yeovil is home to Ivel Barbarians Rugby Club, formed in 1995 by a merger of the Yeovil and Westlands clubs. South Somerset Warriors
South Somerset Warriors were a rugby league team based in Yeovil, Somerset. They played in the South West Division of the Rugby League Conference.
History
''South Somerset Warriors'' were formed in 2010 and joined the South West Division of ...
formed in 2010 and played in the South West Division of the Rugby League Conference
The Rugby League Conference (RLC) (also known as the Co-operative Rugby League Conference as a result of sponsorship from The Co-operative Group), was a series of regionally based divisions of amateur rugby league teams spread throughout England, ...
until it folded in 2011.
The Goldenstones Pool and Leisure Centre provides a swimming pool, a teaching pool, a gym, sauna, steam room, spectator area and workout studio. Preston Sports Centre has undergone an £800,000 refurbishment, which included adding a gym and dance studio.
In late July 2007, South Somerset District Council plans were made public by the ''Western Gazette
The ''Western Gazette'' is a regional newspaper, published every Thursday in Yeovil, Somerset, England.
In 2012, Local World acquired owners Northcliffe Media from Daily Mail and General Trust. Trinity Mirror took control of Local Worl ...
'' to build a £21-million Yeovil Sports Zone on Yeovil Recreation Ground, which has been a popular open green space with the local community for over 70 years. Residents fought to protect it, leading to rejection of the proposals in 2009, and further consultations in 2010.
The recreation space known as Mudford Rec was frequented by England cricket star Ian Botham during a childhood stay in Yeovil. Another regeneration project would have meant demolishing Foundry House, a former glove factory, but a local campaign led to this becoming a listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
. It will now be converted into a restaurant and offices and new shop and houses built on the surrounding site.
Popular culture
Yeovil is known inThomas Hardy
Thomas Hardy (2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, including the poetry of William Word ...
's Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
as "Ivell". It is also one of three main locations in John Cowper Powys
John Cowper Powys (; 8 October 187217 June 1963) was an English philosopher, lecturer, novelist, critic and poet born in Shirley, Derbyshire, where his father was vicar of the parish church in 1871–1879. Powys appeared with a volume of verse ...
's 1929 novel, ''Wolf Solent
''Wolf Solent'' is a novel by John Cowper Powys (1872–1963) that was written while he was based in Patchin Place, New York City, and travelling around the US as a lecturer. It was published by Simon and Schuster in May 1929 in New York. The Br ...
''.
Yeovil is the location for the fictional ''School of Lifemanship'' in a series of novels by Stephen Potter: ''Gamesmanship'' (1947), ''Lifemanship'' (1950), ''One-Upmanship'' (1952), ''Supermanship'' (1958), ''Anti-Woo'' (1965) and ''The Complete Golf Gamesmanship'' (1968). These were adapted for the 1960 film ''School for Scoundrels School for Scoundrels may refer to:
* ''School for Scoundrels'' (1960 film), a British comedy film starring Ian Carmichael, Terry-Thomas and Alistair Sim
* ''School for Scoundrels'' (2006 film), an American film based on the above, featuring Bil ...
'', starring Alastair Sim
Alastair George Bell Sim, CBE (9 October 1900 – 19 August 1976) was a Scottish character actor who began his theatrical career at the age of thirty and quickly became established as a popular West End performer, remaining so until his ...
, Terry-Thomas
Terry-Thomas (born Thomas Terry Hoar Stevens; 10 July 19118 January 1990) was an English character actor and comedian who became internationally known through his films during the 1950s and 1960s. He often portrayed disreputable members of th ...
, Ian Carmichael
Ian Gillett Carmichael, OBE (18 June 1920 – 5 February 2010) was an English actor who worked prolifically on stage, screen and radio in a career spanning 70 years. He found prominence in the films of the Boulting brothers, including ...
and Irene Handl
Irene Handl (27 December 1901 – 29 November 1987) was a British author and character actress who appeared in more than 100 British films.
Life
Irene Handl was born in Maida Vale, London, the younger of two daughters of an Austria-born father ...
.Internet Movie DatabaseSchool for Scoundrels
/ref> Later they were adapted by
Barry Took
Barry Took (19 June 192831 March 2002) was an English writer, television presenter and comedian. His decade-and-a-half writing partnership with Marty Feldman led to the television series ''Bootsie and Snudge'', the radio comedy ''Round the Hor ...
for a BBC TV comedy series, ''One-Upmanship'' (1974–1978), starring Richard Briers
Richard David Briers (14 January 1934 – 17 February 2013) was an English actor whose five-decade career encompassed film, radio, stage and television.
Briers first came to prominence as George Starling in ''Marriage Lines'' (1961–66), but ...
and Peter Jones.
Local band The Chesterfields
The Chesterfields are an English indie pop band from Yeovil, Somerset, England. Hardcore fans tended to refer to them as "The Chesterf!elds", with an exclamation mark replacing the "i", following the example of the band's logo.
The band was form ...
released a single called "Last train to Yeovil" and pop band Bubblegum Splash a song called "18:10 to Yeovil Junction". The folk band Show of Hands
Show of Hands is an English acoustic roots/ folk duo formed in 1986 by singer-songwriter Steve Knightley (guitars, mandolin, mandocello, cuatro) and composer and multi-instrumentalist Phil Beer (vocals, guitars, violin, viola, mandolin, mando ...
wrote a song called "Yeovil Town" about violence and crime they experienced after playing a small gig in Yeovil.
Yeovil is the home town of Gary Strang (played by Martin Clunes
Alexander Martin Clunes OBE DL (born 28 November 1961) is an English actor, comedian, director and television presenter. He is best known for portraying Martin Ellingham in the ITV comedy-drama series ''Doc Martin'' and Gary Strang in ''Men Be ...
) in the TV comedy ''Men Behaving Badly
''Men Behaving Badly'' is a British sitcom that was created and written by Simon Nye. It follows the lives of Gary Strang (Martin Clunes) and his flatmates Dermot Povey (Harry Enfield; series 1 only) and Tony Smart (Neil Morrissey; series 2 on ...
''.
International tie
Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu and xh, eGoli ), colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, or "The City of Gold", is the largest city in South Africa, classified as a megacity, and is one of the 100 largest urban areas in the world. According to Demo ...
, South Africa, has a suburb called Yeoville
Yeoville is an inner city neighbourhood of Johannesburg, in the province of Gauteng, South Africa. It is located in Region F (previously Region 8). It is widely known and celebrated for its diverse, pan-African population but notorious for it ...
, so named in 1890 by Thomas Yeo Sherwell, a native of Yeovil in England. He named the streets after his sons, friends and business associates.
Notable people
Among several notable Yeovil people, Robert Harbin, born in 1526, was amercer
Mercer may refer to:
Business
* Mercer (car), a defunct American automobile manufacturer (1909–1925)
* Mercer (consulting firm), a large human resources consulting firm headquartered in New York City
* Mercer (occupation), a merchant or trader, ...
by profession, who lived and died in Yeovil and is buried in St John the Baptist Church. His house, Newton Surmaville, was completed on the edge of the town in 1612. He was granted a coat of arms in May 1612 and given the title "Gentleman", but not knighted. Stukeley Westcott was an early American settler (17th century) and co-founder with Roger Williams
Roger Williams (21 September 1603between 27 January and 15 March 1683) was an English-born New England Puritan minister, theologian, and author who founded Providence Plantations, which became the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantation ...
and 11 others, of Providence, Rhode Island
Providence is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Rhode Island. One of the oldest cities in New England, it was founded in 1636 by Roger Williams, a Reformed Baptist theologian and religious exile from the Massachusetts Bay ...
(1636), an early American asylum of religious freedom.
Alison Adburgham (1912–1997), social historian and fashion journalist, was born in Yeovil, as were film historian William K. Everson
Keith William Everson (8 April 1929 – 14 April 1996) was an English- American archivist, author, critic, educator, collector, and film historian. He also discovered several lost films. Everson's given first names were Keith William, but he r ...
in 1929, and traditionalist Catholic writer and public figure Michael T. Davies in 1936.
Sportspeople from Yeovil include Luton Town
Luton Town Football Club () is a professional association football club based in the town of Luton, Bedfordshire, England, that competes in the Championship, the second tier of the English football league system. Founded in 1885, it is nicknam ...
defender Martin Cranie, Olympic pentathlete Sam Weale, and his twin brother Chris Weale, who is a former professional goalkeeper. Heather Stanning
Heather Mary Stanning OBE (born 26 January 1985) is a retired British professional rower, a member of the Great Britain Rowing Team, and Royal Artillery officer. Ranked number 1 female rower in the world in 2016, she is a double Olympic champi ...
, a gold-medallist rower in the 2012 Olympic Games, was born in Yeovil.
England Women's Rugby World Cup winner 2014 and freedom of the town holder Marlie Packer
Marlie Packer (born 2 October 1989) is an English rugby union player (back row / flanker) for Saracens and women. She was part of the winning 2014 Women's Rugby World Cup squad.
International career
Packer began her international career play ...
is from Yeovil.
The arts are represented by Jim Cregan
James Cregan (born 9 March 1946) is an English rock guitarist and bassist, best known for his associations with Family, Steve Harley & Cockney Rebel and Rod Stewart. Cregan is a former husband of the singer Linda Lewis and worked with her as a ...
, a guitarist with Steve Harley & Cockney Rebel
Steve Harley & Cockney Rebel are a British glam rock band from the early 1970s from London. Their music covers a range of styles from pop to progressive rock. Over the years they have had five albums in the UK Albums Chart and twelve singles in ...
, musician John Parish
John Parish (born 11 April 1959) is an English musician, songwriter, composer and record producer.
Parish is best known for his work with singer-songwriter PJ Harvey. He has also worked with such artists as Eels, Aldous Harding, Tracy Chapm ...
, and his younger sister, actress Sarah Parish
Sarah Parish (born 7 June 1968) is an English actress. She is known for her work on television series including: ''The Pillars of the Earth'', ''Peak Practice'', '' Hearts and Bones'', ''Cutting It'', ''Doctor Who'', '' Mistresses'', ''Merlin'', ...
. Artist Flora Twort
Flora Caroline Twort (24 June 1893 – 1985) was an English painter who specialised in watercolours and pastels of the scenes and people of Petersfield, Hampshire.
Twort was born in Yeovil, Somerset; her parents were Albert Samuel Twort a ...
was born in Yeovil in 1893.
See also
*RNAS Yeovilton (HMS Heron)
Royal Naval Air Station Yeovilton, or RNAS Yeovilton, (HMS ''Heron'') is an airfield of the Royal Navy and British Army, sited a few miles north of Yeovil, Somerset. It is one of two active Fleet Air Arm bases (the other being RNAS Culdrose) ...
References
External links
*Yeovil Town Council
{{Authority control Towns in South Somerset Civil parishes in Somerset Market towns in Somerset