Y′CbCr on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 YCbCr, Y′CbCr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of
YCbCr, Y′CbCr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of
 Y′CbCr signals (prior to scaling and offsets to place the signals into digital form) are called
Y′CbCr signals (prior to scaling and offsets to place the signals into digital form) are called
 A different form of Y′CbCr is specified in the ITU-R BT.709 standard, primarily for
A different form of Y′CbCr is specified in the ITU-R BT.709 standard, primarily for
/ref>msdn.microsoft.com, Recommended 8-Bit YUV Formats for Video Rendering
/ref> The notation of "YUV" followed by three numbers is vague: the three numbers could refer to the subsampling (as is done in "YUV420"), or it could refer to bit depth in each channel (as is done in "YUV565"). The unambiguous way to refer to these formats is via the
 * UYVY: the byte-swapped reverse of YUY2, runs in the format
* UYVY: the byte-swapped reverse of YUY2, runs in the format
 * YV12 follows the same general design as I420, only the order between the U and V images is flipped.
* NV12 is possibly the most commonly-used 8-bit 4:2:0 format. It is the default for Android camera preview.
* YV12 follows the same general design as I420, only the order between the U and V images is flipped.
* NV12 is possibly the most commonly-used 8-bit 4:2:0 format. It is the default for Android camera preview.fourcc.com YUV pixel formas
/ref> The entire image in Y is written out, followed by interleaved lines that go U0, V0, U1, V1, etc. There are also "tiled" variants of planar formats.
Y′CbCr calculator
including BT.1886
Color Space Visualization
YCbCr Definition
Software resources for packed pixels: * Kohn, Mike
Y′UV422 to RGB using SSE/Assembly
libyuv
pixfc-sse
– C library of SSE-optimized color format conversions
– Sample / Demo YUV/RGB video files in many YUV formats, help you for the testing. {{Color space Color space
 YCbCr, Y′CbCr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of
YCbCr, Y′CbCr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital represe ...
s used as a part of the color image pipeline
An image pipeline or video pipeline is the set of components commonly used between an image source (such as a camera, a scanner, or the rendering engine in a computer game), and an image renderer (such as a television set, a computer screen, a comp ...
in digital video
Digital video is an electronic representation of moving visual images (video) in the form of encoded digital data. This is in contrast to analog video, which represents moving visual images in the form of analog signals. Digital video comprises ...
and photography
Photography is the visual arts, art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is empl ...
systems. Like YPBPR, it is based on RGB
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green, and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three ...
primaries; the two are generally equivalent, but YCBCR is intended for digital video
Digital video is an electronic representation of moving visual images (video) in the form of encoded digital data. This is in contrast to analog video, which represents moving visual images in the form of analog signals. Digital video comprises ...
, while YPBPR is designed for use in analog systems.
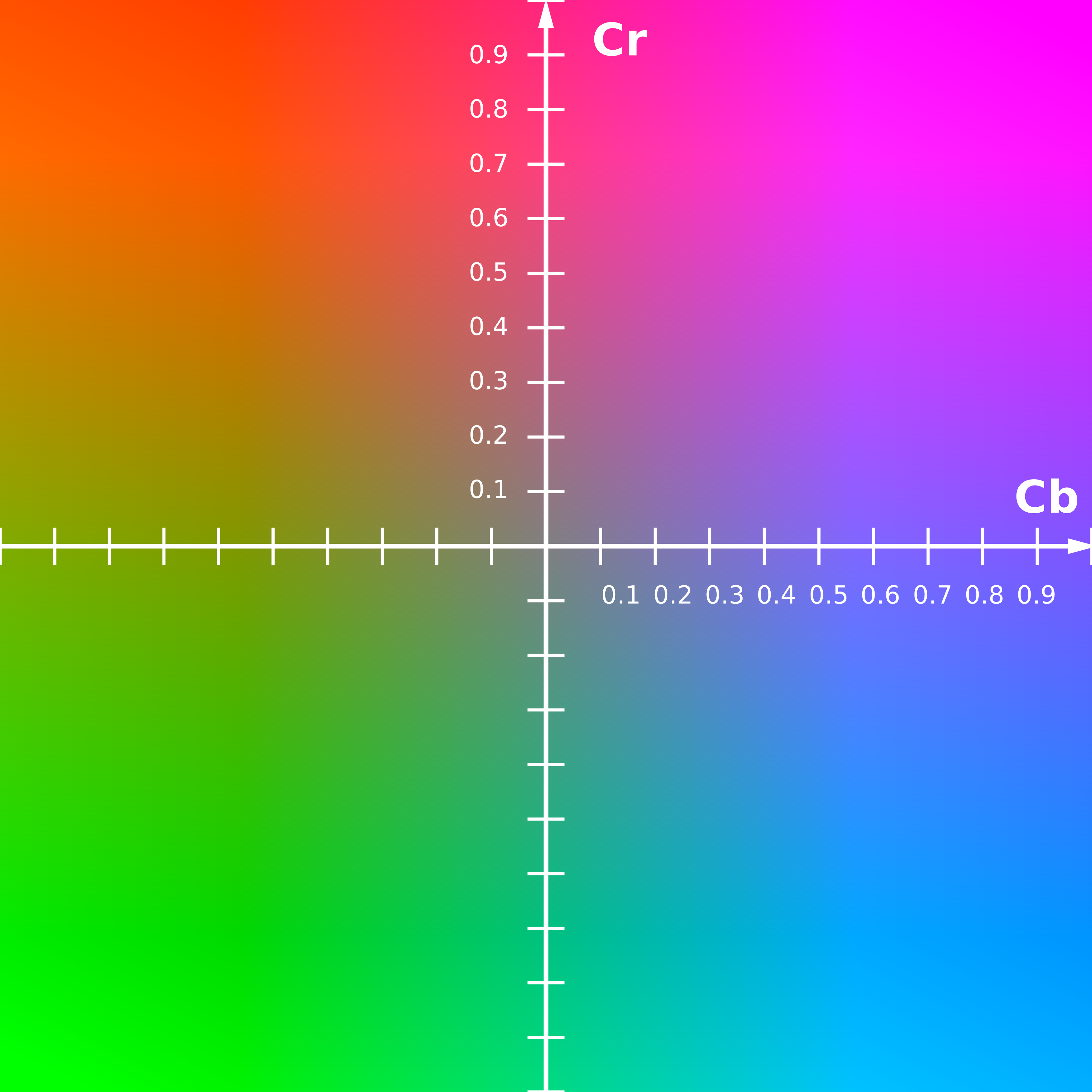
Y′ is the luma component, and CB and CR are the blue-difference and red-difference chroma components. Luma Y′ (with prime
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways ...
) is distinguished from luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls wit ...
Y, meaning that light intensity is nonlinearly encoded based on gamma corrected RGB
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green, and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three ...
primaries.
Y′CbCr color spaces are defined by a mathematical coordinate transformation
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine and standardize the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The coordinates are ...
from an associated RGB primaries and white point
A white point (often referred to as reference white or target white in technical documents) is a set of tristimulus values or chromaticity coordinates that serve to define the color "white" in image capture, encoding, or reproduction. Depending o ...
. If the underlying RGB color space
RGB color spaces are a category of additive colorimetric color spaces specifying part of its absolute color space definition using the RGB color model.
RGB color spaces are commonly found describing the mapping of the RGB color model to human p ...
is absolute, the Y′CbCr color space is an absolute color space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog signal, analog or a Di ...
as well; conversely, if the RGB space is ill-defined, so is Y′CbCr. The transformation is defined in equations 32, 33 in ITU-T
The International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is one of the three Sectors (branches) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). It is responsible for coordinating Standardization, standards fo ...
H.273.
Rationale
Black and white television was in wide use before color television. Due to the number of existing TV sets and cameras, some form ofbackward compatibility
In telecommunications and computing, backward compatibility (or backwards compatibility) is a property of an operating system, software, real-world product, or technology that allows for interoperability with an older legacy system, or with Input ...
was desired for the new color broadcasts. French engineer Georges Valensi M. Georges Valensi (1889–1980) was a French telecommunications engineer who, in 1938, invented and patented a method of transmitting color images via luma and chrominance so that they could be received on both color and black & white television s ...
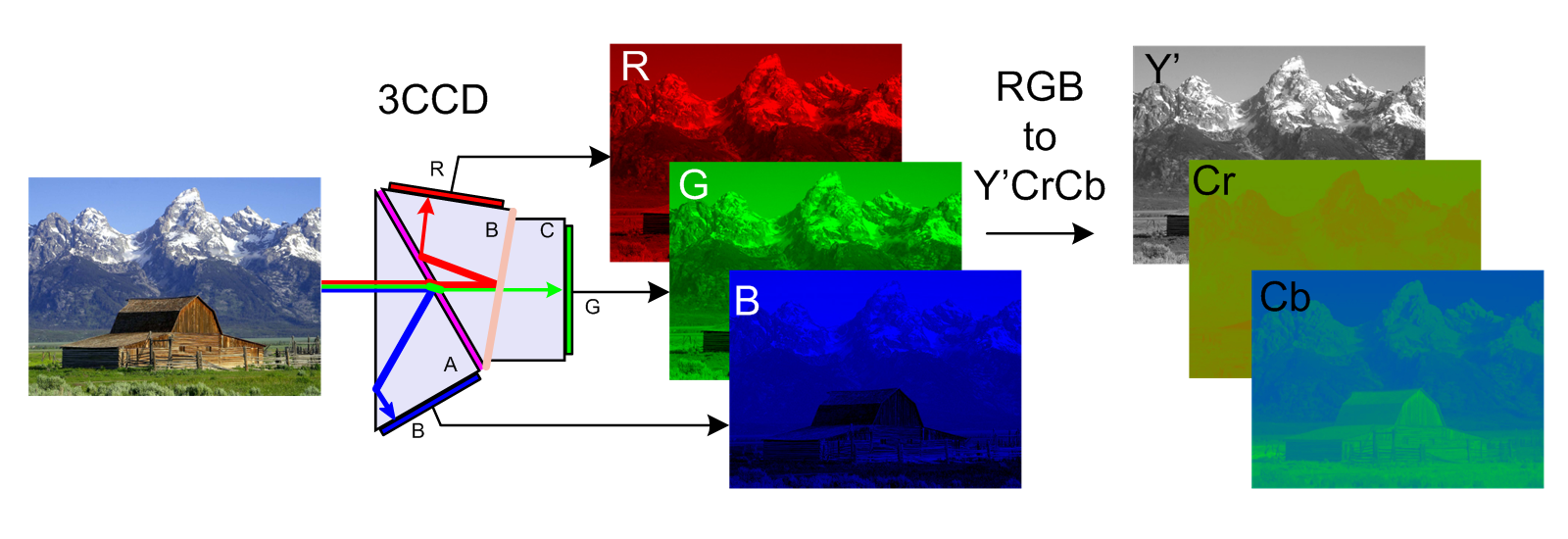
developed and patented a system for transmitting RGB color as luma and chroma signals in 1938. This would allow existing black and white televisions to process only the luma information and ignore the chroma, essentially packaging a black and white video within the color video. Because of this backward compatibility, the system based on Valensi's idea was called compatible color. In the same way, a black and white broadcast could be received by a color television without any additional processing circuitry. To preserve existing broadcast frequency allocations, the new chroma information was given lower bandwidth than the luma information. This is possible because humans are more sensitive to the black-and-white information (see image example to the right). This is called chroma subsampling
Chroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for Chrominance, chroma information than for luma (video), luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences t ...
.
YCbCr and Y′CbCr are a practical approximation to color processing and perceptual uniformity, where the primary color
Primary colors are colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a broad range of colors in, e.g., electronic displays, color prin ...
s corresponding roughly to red, green, and blue are processed into perceptually meaningful information. By doing this, subsequent image/video processing, transmission and storage can do operations and introduce errors in perceptually meaningful ways. Y′CbCr is used to separate out a luma signal (Y′) that can be stored with high resolution or transmitted at high bandwidth and two chroma components (CB and CR) that can be bandwidth-reduced, subsampled, compressed, or otherwise treated separately for improved system efficiency.
Conversions
YCbCr is sometimes abbreviated to YCC. Typically the terms Y′CbCr, YCbCr,YPbPr
YPbPr or Y'P'bP'r, also written as , is a color space used in video electronics, in particular in reference to component video cables. Like YCBCR, it is based on gamma corrected RGB primaries; the two are numerically equivalent but YPBPR is de ...
, and YUV are used interchangeably, leading to some confusion. The main difference is that YPbPr is used with analog images and YCbCr with digital images, leading to different scaling values for Umax and Vmax (in YCbCr both are ) when converting to/from YUV. Y′CbCr and YCbCr differ due to the values being gamma corrected or not.
The equations below give a better picture of the common principles and general differences between these formats.
RGB conversion
R'G'B' to Y′PbPr
 Y′CbCr signals (prior to scaling and offsets to place the signals into digital form) are called
Y′CbCr signals (prior to scaling and offsets to place the signals into digital form) are called YPbPr
YPbPr or Y'P'bP'r, also written as , is a color space used in video electronics, in particular in reference to component video cables. Like YCBCR, it is based on gamma corrected RGB primaries; the two are numerically equivalent but YPBPR is de ...
and are created from the corresponding gamma-adjusted RGB
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green, and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three ...
(red, green, and blue) source using three defined constants KR, KG, and KB as follows:
:
where KR, KG, and KB are ordinarily derived from the definition of the corresponding RGB space and required to satisfy .
The equivalent matrix
Matrix (: matrices or matrixes) or MATRIX may refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Matrix (mathematics), a rectangular array of numbers, symbols or expressions
* Matrix (logic), part of a formula in prenex normal form
* Matrix (biology), the m ...
manipulation is often referred to as the "color matrix":
:
And its inverse:
:
Here, the prime (′) symbols mean gamma correction
Gamma correction or gamma is a Nonlinearity, nonlinear operation used to encode and decode Relative luminance, luminance or CIE 1931 color space#Tristimulus values, tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the s ...
is being used; thus R′, G′, and B′ nominally range from 0 to 1, with 0 representing the minimum intensity (e.g., for display of the color black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
) and 1 the maximum (e.g., for display of the color white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
). The resulting luma (Y) value will then have a nominal range from 0 to 1, and the chroma (PB and PR) values will have a nominal range from -0.5 to +0.5. The reverse conversion process can be readily derived by inverting the above equations.
Y′PbPr to Y′CbCr
When representing the signals in digital form, the results are scaled and rounded and offsets are typically added. For example, the scaling and offset applied to the Y′ component per specification (e.g.MPEG-2
MPEG-2 (a.k.a. H.222/H.262 as was defined by the ITU) is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods ...
) results in the value of 16 for black and the value of 235 for white when using an 8-bit representation. The standard has 8-bit digitized versions of CB and CR scaled to a different range of 16 to 240. Consequently, rescaling by the fraction (235-16)/(240-16) = 219/224 is sometimes required when doing color matrixing or processing in YCbCr space, resulting in quantization distortions when the subsequent processing is not performed using higher bit depths.
The scaling that results in the use of a smaller range of digital values than what might appear to be desirable for representation of the nominal range of the input data allows for some "overshoot" and "undershoot" during processing without necessitating undesirable clipping. This " headroom" and "toeroom" can also be used for extension of the nominal color gamut
In color reproduction and colorimetry, a gamut, or color gamut , is a convex set containing the colors that can be accurately represented, i.e. reproduced by an output device (e.g. printer or display) or measured by an input device (e.g. cam ...
as specified by xvYCC
xvYCC or extended-gamut YCbCr is a color space that can be used in the video electronics of television sets to support a gamut 1.8 times as large as that of the sRGB color space. xvYCC was proposed by Sony, specified by the IEC in October 2005 ...
.
The value 235 accommodates a maximum overshoot of (255 - 235) / (235 - 16) = 9.1%, which is slightly larger than the theoretical maximum overshoot ( Gibbs' Phenomenon) of about 8.9% of the maximum (black-to-white) step. The toeroom is smaller, allowing only 16 / 219 = 7.3% overshoot, which is less than the theoretical maximum overshoot of 8.9%. In addition, because values 0 and 255 are reserved in HDMI, the room is actually slightly less.
Y′CbCr to xvYCC
Since the equations defining Y′CbCr are formed in a way that rotates the entire nominal RGB color cube and scales it to fit within a (larger) YCbCr color cube, there are some points within the Y′CbCr color cube that ''cannot'' be represented in the corresponding RGB domain (at least not within the nominal RGB range). This causes some difficulty in determining how to correctly interpret and display some Y′CbCr signals. These out-of-range Y′CbCr values are used byxvYCC
xvYCC or extended-gamut YCbCr is a color space that can be used in the video electronics of television sets to support a gamut 1.8 times as large as that of the sRGB color space. xvYCC was proposed by Sony, specified by the IEC in October 2005 ...
to encode colors outside the BT.709 gamut.ITU-R BT.601 conversion
The form of Y′CbCr that was defined forstandard-definition television
Standard-definition television (SDTV; also standard definition or SD) is a television system that uses a resolution that is not considered to be either high or enhanced definition. ''Standard'' refers to offering a similar resolution to the ...
use in the ITU-R
The ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) is one of the three sectors (divisions or units) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and is responsible for radio communications.
Its role is to manage the international radio-frequenc ...
BT.601 (formerly CCIR 601
ITU-R Recommendation BT.601, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 601 or BT.601 (or its former name CCIR 601), is a standard originally issued in 1982 by the Comité consultatif international pour la radio, CCIR (an organizati ...
) standard for use with digital component video is derived from the corresponding RGB space (ITU-R BT.470-6 System M primaries) as follows:
:
From the above constants and formulas, the following can be derived for ITU-R BT.601.
Analog YPbPr from analog R'G'B' is derived as follows:
:
Digital Y′CbCr (8 bits per sample) is derived from analog R'G'B' as follows:
:
or simply componentwise
:
The resultant signals range from 16 to 235 for Y′ (Cb and Cr range from 16 to 240); the values from 0 to 15 are called ''footroom'', while the values from 236 to 255 are called ''headroom''. The same quantisation ranges, different for Y and Cb, Cr also apply to BT.2020 and BT.709.
Alternatively, digital Y′CbCr can derived from digital R'dG'dB'd (8 bits per sample, each using the full range with zero representing black and 255 representing white) according to the following equations:
:
In the formula below, the scaling factors are multiplied by . This allows for the value 256 in the denominator, which can be calculated by a single bitshift.
:
If the R'd G'd B'd digital source includes footroom and headroom, the footroom offset 16 needs to be subtracted first from each signal, and a scale factor of needs to be included in the equations.
The inverse transform is:
:
The inverse transform without any roundings (using values coming directly from ITU-R BT.601 recommendation) is:
:
This form of Y′CbCr is used primarily for older standard-definition television
Standard-definition television (SDTV; also standard definition or SD) is a television system that uses a resolution that is not considered to be either high or enhanced definition. ''Standard'' refers to offering a similar resolution to the ...
systems, as it uses an RGB model that fits the phosphor emission characteristics of older CRTs.
ITU-R BT.709 conversion
HDTV
High-definition television (HDTV) describes a television or video system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since at least 1933; in more recent times, it ref ...
use. The newer form is also used in some computer-display oriented applications, as sRGB
sRGB (standard RGB) is a colorspace, for use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was initially proposed by HP and Microsoft in 1996 and became an official standard of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 6 ...
(though the matrix used for sRGB form of YCbCr, sYCC, is still BT.601). In this case, the values of Kb and Kr differ, but the formulas for using them are the same. For ITU-R BT.709, the constants are:
:
This form of Y′CbCr is based on an RGB model that more closely fits the phosphor emission characteristics of newer CRTs and other modern display equipment.
The conversion matrices for BT.709 are these:
:
The definitions of the R', G', and B' signals also differ between BT.709 and BT.601, differ within BT.601 depending on the type of TV system in use (625-line as in PAL
Phase Alternating Line (PAL) is a color encoding system for analog television. It was one of three major analogue colour television standards, the others being NTSC and SECAM. In most countries it was broadcast at 625 lines, 50 fields (25 ...
and SECAM
SECAM, also written SÉCAM (, ''Séquentiel de couleur à mémoire'', French for ''sequential colour memory''), is an analog color television system that was used in France, Russia and some other countries or territories of Europe and Africa. ...
or 525-line as in NTSC
NTSC (from National Television System Committee) is the first American standard for analog television, published and adopted in 1941. In 1961, it was assigned the designation System M. It is also known as EIA standard 170.
In 1953, a second ...
), and differ further in other specifications. In different designs, there are differences in the definitions of the R, G, and B chromaticity coordinates, the reference white point, the supported gamut range, the exact gamma pre-compensation functions for deriving R', G', and B' from R, G, and B, and in the scaling and offsets to be applied during conversion from R'G'B' to Y′CbCr. So proper conversion of Y′CbCr from one form to the other is not just a matter of inverting one matrix and applying the other. In fact, when Y′CbCr is designed ideally, the values of KB and KR are derived from the precise specification of the RGB color primary signals, so that the luma (Y′) signal corresponds as closely as possible to a gamma-adjusted measurement of luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls wit ...
(typically based on the CIE 1931 measurements of the response of the human visual system to color stimuli).
ITU-R BT.2020 conversion
The ITU-R BT.2020 standard uses the same gamma function as BT.709. It defines: * Non-constant luminance Y'CbCr, similar to the previous entries, except with different and . * Constant luminance Y'cCbcCrc, a formulation where Y' is the gamma-codec version of the trueluminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls wit ...
.
For both, the coefficients derived from the primaries are:
:
For NCL, the definition is classical: ; ; . The encoding conversion can, as usual, be written as a matrix. The decoding matrix for BT.2020-NCL is this with 14 decimal places:
:
The smaller values in the matrix are not rounded; they are precise values. For systems with limited precision (8 or 10 bit, for example) a lower precision of the above matrix could be used, for example, retaining only 6 digits after the decimal point.
The CL version, YcCbcCrc, codes:
* . This is the gamma function applied to the true luminance calculated from linear RGB.
* if otherwise . and are the theoretical minimum and maximum of corresponding to the gamut. The rounded "practical" values are , . The full derivation can be found in the recommendation.
* if otherwise . Again, and are theoretical limits. The rounded values are , .
The CL function can be used when preservation of luminance is of primary importance (see: ), or when "there is an expectation of improved coding efficiency for delivery." The specification refers to Report ITU-R BT.2246 on this matter. BT.2246 states that CL has improved compression efficiency and luminance preservation, but NCL will be more familiar to a staff that has previously handled color mixing and other production practices in HDTV YCbCr.
BT.2020 does not define PQ and thus HDR; it is further defined in SMPTE ST 2084 and BT.2100. BT.2100 will introduce the use of ICTCP, a semi-perceptual colorspace derived from linear RGB with good hue linearity. It is "near-constant luminance".
SMPTE 240M conversion
The SMPTE 240M standard (used on theMUSE
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, the Muses (, ) were the Artistic inspiration, inspirational goddesses of literature, science, and the arts. They were considered the source of the knowledge embodied in the poetry, lyric p ...
analog HD television system) defines YCC with these coefficients:
:
The coefficients are derived from SMPTE 170M primaries and white point, as used in 240M standard.
JPEG conversion
JFIF
The JPEG File Interchange Format (JFIF) is an image file format standard published as ITU-T Recommendation T.871 and ISO/IEC 10918-5. It defines supplementary specifications for the Digital container format, container format that contains the image ...
usage of JPEG
JPEG ( , short for Joint Photographic Experts Group and sometimes retroactively referred to as JPEG 1) is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by digital photography. The degr ...
supports a modified Rec. 601 Y′CbCr, where Y′, CB, and CR have the full 8-bit range of ...255 Below are the conversion equations expressed to six decimal digits of precision. (For ideal equations, see ITU-T T.871.)
Note that for the following formula, the range of each input (R,G,B) is also the full 8-bit range of ...255
:
And back:
:
The above conversion is identical to sYCC when the input is given as sRGB, except that IEC 61966-2-1:1999/Amd1:2003 only gives four decimal digits.
JPEG also defines a "YCCK" format from Adobe for CMYK
The CMYK color model (also known as process color, or four color) is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation ''CMYK'' refers ...
input. In this format, the "K" value is passed as-is, while CMY are used to derive YCbCr with the above matrix by assuming , , and . As a result, a similar set of subsampling techniques can be used.
Coefficients for BT.470-6 System B, G primaries
: These coefficients are not in use and were never in use.Chromaticity-derived luminance systems
H.273 also describes constant and non-constant luminance systems which are derived strictly from primaries and white point, so that situations like sRGB/BT.709 default primaries of JPEG that use BT.601 matrix (that is derived from BT.470-6 System M) do not happen.Numerical approximations
Prior to the development of fastSIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel computer, parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneousl ...
floating-point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic on subsets of real numbers formed by a ''significand'' (a Sign (mathematics), signed sequence of a fixed number of digits in some Radix, base) multiplied by an integer power of that ba ...
processors, most digital implementations of RGB → Y′UV used integer math, in particular fixed-point approximations. Approximation means that the precision of the used numbers (input data, output data and constant values) is limited, and thus a precision loss of typically about the last binary digit is accepted by whoever makes use of that option in typically a trade-off to improved computation speeds.
Y′ values are conventionally shifted and scaled to the range 6, 235(referred to as studio swing or "TV levels") rather than using the full range of , 255(referred to as full swing or "PC levels"). This practice was standardized in SMPTE-125M in order to accommodate signal overshoots ("ringing") due to filtering. U and V values, which may be positive or negative, are summed with 128 to make them always positive, giving a studio range of 16–240 for U and V. (These ranges are important in video editing and production, since using the wrong range will result either in an image with "clipped" blacks and whites or a low-contrast image.)
Approximate 8-bit matrices for BT.601
These matrices round all factors to the closest 1/256 unit. As a result, only one 16-bit intermediate value is formed for each component, and a simple right-shift with rounding can take care of the division. For studio-swing: : For full-swing: : Google's Skia used to use the above 8-bit full-range matrix, resulting in a slight greening effect on JPEG images encoded by Android devices, more noticeable on repeated saving. The issue was fixed in 2016, when the more accurate version was used instead. Due to SIMD optimizations in libjpeg-turbo, the accurate version is actually faster.Packed pixel formats and conversion
RGB files are typically encoded in 8, 12, 16 or 24 bits per pixel. In these examples, we will assume 24 bits per pixel, which is written as RGB888. The standard byte format is simplyr0, g0, b0, r1, g1, b1, ....
YCbCr Packed pixel
In packed pixel or chunky framebuffer organization, the bits defining each pixel are clustered and stored consecutively. For example, if there are 16 bits per pixel, each pixel is represented in two consecutive (contiguous) 8-bit bytes in the fra ...
formats are often referred to as "YUV". Such files can be encoded in 12, 16 or 24 bits per pixel. Depending on subsampling, the formats can largely be described as 4:4:4, 4:2:2, and 4:2:0p. The apostrophe after the Y is often omitted, as is the "p" (for planar) after YUV420p. In terms of actual file formats, 4:2:0 is the most common, as the data is more reduced, and the file extension is usually ".YUV". The relation between data rate and sampling (A:B:C) is defined by the ratio between Y to U and V channel.msdn.microsoft.com, YUV Video Subtypes/ref>msdn.microsoft.com, Recommended 8-Bit YUV Formats for Video Rendering
/ref> The notation of "YUV" followed by three numbers is vague: the three numbers could refer to the subsampling (as is done in "YUV420"), or it could refer to bit depth in each channel (as is done in "YUV565"). The unambiguous way to refer to these formats is via the
FourCC
A FourCC ("four-character code") is a sequence of four bytes (typically ASCII) used to uniquely identify data formats. It originated from the OSType or ResType metadata system used in classic Mac OS and was adopted for the Amiga/Electronic Arts ...
code.
To convert from RGB to YUV or back, it is simplest to use RGB888 and 4:4:4. For 4:1:1, 4:2:2, and 4:2:0, the bytes need to be converted to 4:4:4 first.
4:4:4
4:4:4 is straightforward, as no pixel-grouping is done: the difference lies solely in how many bits each channel is given and their arrangement. The basic scheme uses 3 bytes per pixel, with the ordery0, u0, v0, y1, u1, v1 (using "u" for Cb and "v" for Cr; the same applies to content below). In computers, it is more common to see a format, which adds an alpha channel and goes a0, y0, u0, v0, a1, y1, u1, v1, because groups of 32-bits are easier to deal with.
4:2:2
4:2:2 groups 2 pixels together horizontally in each conceptual "container". Two main arrangements are: * YUY2: also called YUYV, runs in the formaty0, u, y1, v.u, y0, v, y1.
4:1:1
4:1:1 is rarely used. Pixels are in horizontal groups of 4.4:2:0
4:2:0 is very commonly used. The main formats are IMC2, IMC4, YV12, and NV12. All of these four formats are "planar", meaning that the Y, U, and V values are grouped together instead of interspersed. They all occupy 12 bits per pixel, assuming an 8-bit channel. * IMC2 first lays the full images out in Y. It then arranges each line of chroma in the order of V0 ... Vn, U0 ... Un, where ''n'' is the number of chroma samples per line, equal to half the width of Y. * IMC4 is similar to IMC2, except it runs in U0 ... Un, V0 ... Vn. * I420 is a simpler design and is more commonly used. The entire image in Y is written out, followed by the image in U, then by the whole image in V./ref> The entire image in Y is written out, followed by interleaved lines that go U0, V0, U1, V1, etc. There are also "tiled" variants of planar formats.
References
External links
Y′CbCr calculator
including BT.1886
Color Space Visualization
YCbCr Definition
Software resources for packed pixels: * Kohn, Mike
Y′UV422 to RGB using SSE/Assembly
libyuv
pixfc-sse
– C library of SSE-optimized color format conversions
– Sample / Demo YUV/RGB video files in many YUV formats, help you for the testing. {{Color space Color space