XF9C 1 Aircraft Hooking Onto USS Akron, May 1932 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Curtiss F9C Sparrowhawk is a light 1930s
"Composite History"
''Flight'' 1 November 1937 The increasing use of airships in the armed forces of various countries led to variations on the idea of using aircraft with them, with major uses being for reconnaissance, extending the reach of the airship beyond the horizon, and to provide the airship with a degree of self-defence. In the late 1920s, the US Navy began experimenting with its airships, initially using as a platform for testing the concept of the so-called Although designed as a pursuit plane or fighter, the Sparrowhawk's primary duty in service was
Although designed as a pursuit plane or fighter, the Sparrowhawk's primary duty in service was 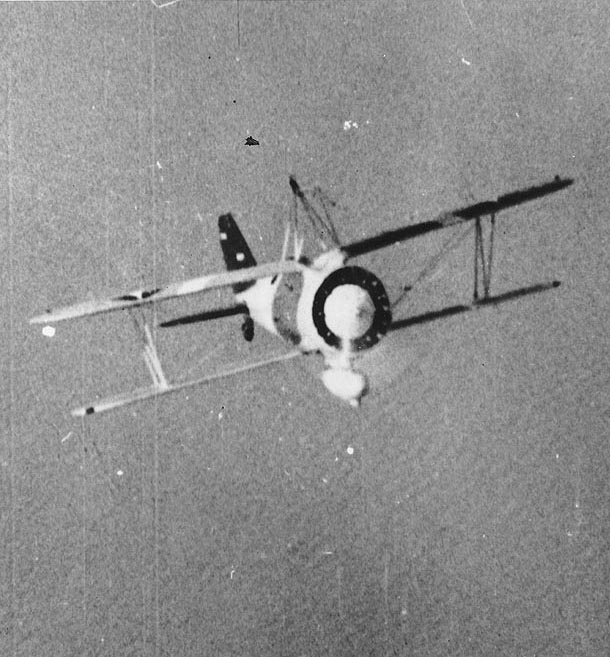 To achieve launching and recovery from the airship in flight, a 'skyhook' system was developed. The Sparrowhawk had a hook mounted above its top wing that attached to the cross-bar of a trapeze mounted on the carrier airship. For launching, the biplane's hook was engaged on the trapeze inside the airship's (internal) hangar, the trapeze was lowered clear of the hull into the (moving) airship's slipstream and, engine running, the Sparrowhawk would then disengage its hook and fall away from the airship. For recovery, the biplane would fly underneath its mother ship, until beneath the trapeze, climb up from below, and hook onto the cross-bar. The width of the trapeze cross-bar allowed a certain lateral lee-way in approach, the biplane's hook mounting had a guide rail to provide protection for the turning propeller (see photo), and engagement of the hook was automatic on positive contact between hook and trapeze. More than one attempt might have to be made before a successful engagement was achieved, for example in gusty conditions. Once the Sparrowhawk was securely caught, it could then be hoisted by the trapeze back within the airship's hull, the engine being cut as it passed the hangar door. Although seemingly a tricky maneuver, pilots soon learned the technique and it was described as being much easier than landing on a moving, pitching and rolling aircraft carrier. Almost inevitably, the pilots soon acquired the epithet " The men on the Flying Trapeze" and their aircraft were decorated with appropriate unit emblems.
Once the system was fully developed, in order to increase their scouting endurance while the airship was on over-water operations, the Sparrowhawks would have their landing gear removed and replaced by a fuel tank. When the airship was returning to base, the biplanes' landing gear would be replaced so that they could land independently again.
For much of their service with the airships, the Sparrowhawks' effectiveness was greatly hampered by their poor radio equipment, and they were effectively limited to remaining within sight of the airship. However, in 1934 new direction-finding sets and new voice radios were fitted which allowed operations beyond visual range, exploiting the extended range offered by the belly fuel tanks and allowing the more vulnerable mother ship to stay clear of trouble.
One interesting use of the Sparrowhawks was to act as 'flying ballast'. The airship could take off with additional ballast or fuel aboard instead of its airplanes. Once the airship was cruising, the aircraft would be flown aboard, the additional weight being supported by dynamic lift until the airship lightened.
To achieve launching and recovery from the airship in flight, a 'skyhook' system was developed. The Sparrowhawk had a hook mounted above its top wing that attached to the cross-bar of a trapeze mounted on the carrier airship. For launching, the biplane's hook was engaged on the trapeze inside the airship's (internal) hangar, the trapeze was lowered clear of the hull into the (moving) airship's slipstream and, engine running, the Sparrowhawk would then disengage its hook and fall away from the airship. For recovery, the biplane would fly underneath its mother ship, until beneath the trapeze, climb up from below, and hook onto the cross-bar. The width of the trapeze cross-bar allowed a certain lateral lee-way in approach, the biplane's hook mounting had a guide rail to provide protection for the turning propeller (see photo), and engagement of the hook was automatic on positive contact between hook and trapeze. More than one attempt might have to be made before a successful engagement was achieved, for example in gusty conditions. Once the Sparrowhawk was securely caught, it could then be hoisted by the trapeze back within the airship's hull, the engine being cut as it passed the hangar door. Although seemingly a tricky maneuver, pilots soon learned the technique and it was described as being much easier than landing on a moving, pitching and rolling aircraft carrier. Almost inevitably, the pilots soon acquired the epithet " The men on the Flying Trapeze" and their aircraft were decorated with appropriate unit emblems.
Once the system was fully developed, in order to increase their scouting endurance while the airship was on over-water operations, the Sparrowhawks would have their landing gear removed and replaced by a fuel tank. When the airship was returning to base, the biplanes' landing gear would be replaced so that they could land independently again.
For much of their service with the airships, the Sparrowhawks' effectiveness was greatly hampered by their poor radio equipment, and they were effectively limited to remaining within sight of the airship. However, in 1934 new direction-finding sets and new voice radios were fitted which allowed operations beyond visual range, exploiting the extended range offered by the belly fuel tanks and allowing the more vulnerable mother ship to stay clear of trouble.
One interesting use of the Sparrowhawks was to act as 'flying ballast'. The airship could take off with additional ballast or fuel aboard instead of its airplanes. Once the airship was cruising, the aircraft would be flown aboard, the additional weight being supported by dynamic lift until the airship lightened.
 ;XF9C-1
:First prototype. One built. BuAer
;XF9C-1
:First prototype. One built. BuAer
 Only one intact Sparrowhawk survives today.
Only one intact Sparrowhawk survives today.  The remains of a further four aircraft lie at the underwater wreck-site of the ''Macon''; the aircraft were found in their
The remains of a further four aircraft lie at the underwater wreck-site of the ''Macon''; the aircraft were found in their This Day in Aviation February 1935 F9c-2 Sparrowhawk
/ref>
biplane
A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two main wings stacked one above the other. The first powered, controlled aeroplane to fly, the Wright Flyer, used a biplane wing arrangement, as did many aircraft in the early years of aviation. While ...
fighter aircraft
Fighter aircraft (early on also ''pursuit aircraft'') are military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air supremacy, air superiority of the battlespace. Domina ...
that was carried by the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
airship
An airship, dirigible balloon or dirigible is a type of aerostat (lighter-than-air) aircraft that can navigate through the air flying powered aircraft, under its own power. Aerostats use buoyancy from a lifting gas that is less dense than the ...
s and . It is an example of a parasite fighter
A parasite aircraft is a component of a composite aircraft which is carried aloft and air launched by a larger carrier aircraft or mother ship to support the primary mission of the carrier. The carrier craft may or may not be able to later recove ...
, a small airplane designed to be deployed from a larger aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, i ...
such as an airship or bomber.
Design and development
The concept of fixed-wing aircraft being carried and launched fromairship
An airship, dirigible balloon or dirigible is a type of aerostat (lighter-than-air) aircraft that can navigate through the air flying powered aircraft, under its own power. Aerostats use buoyancy from a lifting gas that is less dense than the ...
s was initially developed during the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
- initially, this proposal originated in the United Kingdom, to allow British interceptors to conserve fuel by being carried to an altitude whereby they could then engage German zeppelins.H. J. C Harpe"Composite History"
''Flight'' 1 November 1937 The increasing use of airships in the armed forces of various countries led to variations on the idea of using aircraft with them, with major uses being for reconnaissance, extending the reach of the airship beyond the horizon, and to provide the airship with a degree of self-defence. In the late 1920s, the US Navy began experimenting with its airships, initially using as a platform for testing the concept of the so-called
parasite aircraft
A parasite aircraft is a component of a composite aircraft which is carried aloft and air launched by a larger carrier aircraft or mother ship to support the primary mission of the carrier. The carrier craft may or may not be able to later recove ...
. The success of these tests led to the decision to build two new airships capable of accommodating an on-board air group of specially designed aircraft. This was ultimately developed into the Curtiss Sparrowhawk.
 Although designed as a pursuit plane or fighter, the Sparrowhawk's primary duty in service was
Although designed as a pursuit plane or fighter, the Sparrowhawk's primary duty in service was reconnaissance
In military operations, military reconnaissance () or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, the terrain, and civil activities in the area of operations. In military jargon, reconnai ...
, enabling the airships it served to search a much wider area of ocean. The Sparrowhawk was primarily chosen for service aboard the large rigid-framed airships ''Akron'' and ''Macon'' because of its small size ( long and with only a wingspan), though its weight, handling and range characteristics, and also downward visibility from the cockpit, were not ideal for its reconnaissance role. The theoretical maximum capacity of the airships' hangar was five aircraft, one in each hangar bay and one stored on the trapeze but, in the ''Akron'', two structural girders obstructed the aft two hangar bays, limiting her to a maximum complement of three Sparrowhawks. A modification to remove this limitation was pending at the time of the airship's loss. ''Macon'' had no such limitation and she routinely carried four airplanes.
 To achieve launching and recovery from the airship in flight, a 'skyhook' system was developed. The Sparrowhawk had a hook mounted above its top wing that attached to the cross-bar of a trapeze mounted on the carrier airship. For launching, the biplane's hook was engaged on the trapeze inside the airship's (internal) hangar, the trapeze was lowered clear of the hull into the (moving) airship's slipstream and, engine running, the Sparrowhawk would then disengage its hook and fall away from the airship. For recovery, the biplane would fly underneath its mother ship, until beneath the trapeze, climb up from below, and hook onto the cross-bar. The width of the trapeze cross-bar allowed a certain lateral lee-way in approach, the biplane's hook mounting had a guide rail to provide protection for the turning propeller (see photo), and engagement of the hook was automatic on positive contact between hook and trapeze. More than one attempt might have to be made before a successful engagement was achieved, for example in gusty conditions. Once the Sparrowhawk was securely caught, it could then be hoisted by the trapeze back within the airship's hull, the engine being cut as it passed the hangar door. Although seemingly a tricky maneuver, pilots soon learned the technique and it was described as being much easier than landing on a moving, pitching and rolling aircraft carrier. Almost inevitably, the pilots soon acquired the epithet " The men on the Flying Trapeze" and their aircraft were decorated with appropriate unit emblems.
Once the system was fully developed, in order to increase their scouting endurance while the airship was on over-water operations, the Sparrowhawks would have their landing gear removed and replaced by a fuel tank. When the airship was returning to base, the biplanes' landing gear would be replaced so that they could land independently again.
For much of their service with the airships, the Sparrowhawks' effectiveness was greatly hampered by their poor radio equipment, and they were effectively limited to remaining within sight of the airship. However, in 1934 new direction-finding sets and new voice radios were fitted which allowed operations beyond visual range, exploiting the extended range offered by the belly fuel tanks and allowing the more vulnerable mother ship to stay clear of trouble.
One interesting use of the Sparrowhawks was to act as 'flying ballast'. The airship could take off with additional ballast or fuel aboard instead of its airplanes. Once the airship was cruising, the aircraft would be flown aboard, the additional weight being supported by dynamic lift until the airship lightened.
To achieve launching and recovery from the airship in flight, a 'skyhook' system was developed. The Sparrowhawk had a hook mounted above its top wing that attached to the cross-bar of a trapeze mounted on the carrier airship. For launching, the biplane's hook was engaged on the trapeze inside the airship's (internal) hangar, the trapeze was lowered clear of the hull into the (moving) airship's slipstream and, engine running, the Sparrowhawk would then disengage its hook and fall away from the airship. For recovery, the biplane would fly underneath its mother ship, until beneath the trapeze, climb up from below, and hook onto the cross-bar. The width of the trapeze cross-bar allowed a certain lateral lee-way in approach, the biplane's hook mounting had a guide rail to provide protection for the turning propeller (see photo), and engagement of the hook was automatic on positive contact between hook and trapeze. More than one attempt might have to be made before a successful engagement was achieved, for example in gusty conditions. Once the Sparrowhawk was securely caught, it could then be hoisted by the trapeze back within the airship's hull, the engine being cut as it passed the hangar door. Although seemingly a tricky maneuver, pilots soon learned the technique and it was described as being much easier than landing on a moving, pitching and rolling aircraft carrier. Almost inevitably, the pilots soon acquired the epithet " The men on the Flying Trapeze" and their aircraft were decorated with appropriate unit emblems.
Once the system was fully developed, in order to increase their scouting endurance while the airship was on over-water operations, the Sparrowhawks would have their landing gear removed and replaced by a fuel tank. When the airship was returning to base, the biplanes' landing gear would be replaced so that they could land independently again.
For much of their service with the airships, the Sparrowhawks' effectiveness was greatly hampered by their poor radio equipment, and they were effectively limited to remaining within sight of the airship. However, in 1934 new direction-finding sets and new voice radios were fitted which allowed operations beyond visual range, exploiting the extended range offered by the belly fuel tanks and allowing the more vulnerable mother ship to stay clear of trouble.
One interesting use of the Sparrowhawks was to act as 'flying ballast'. The airship could take off with additional ballast or fuel aboard instead of its airplanes. Once the airship was cruising, the aircraft would be flown aboard, the additional weight being supported by dynamic lift until the airship lightened.
Variants
 ;XF9C-1
:First prototype. One built. BuAer
;XF9C-1
:First prototype. One built. BuAer number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
8731. Scrapped in 1936.
;XF9C-2
:Second prototype. One built. BuAer number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
9264.
;F9C-2 Sparrowhawk
:Single-seat fighter biplane. 6 built. BuAer numbers
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
9056 - 9061
Operators
; *United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
Surviving aircraft
 Only one intact Sparrowhawk survives today.
Only one intact Sparrowhawk survives today. Bureau of Aeronautics
The Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer) was the U.S. Navy's material-support organization for naval aviation from 1921 to 1959. The bureau had "cognizance" (''i.e.'', responsibility) for the design, procurement, and support of naval aircraft and rela ...
(BuAer) number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
9056 was pending write-off at NAS Hampton Roads in 1939 when it was transferred to the Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase a ...
. In later years it had been rebuilt, using parts from the surviving F9C-2 (BuAer number 9057) and the XF9C-2 (9264). It was previously at the National Museum of Naval Aviation
The National Naval Aviation Museum, formerly known as the National Museum of Naval Aviation and the Naval Aviation Museum, is a military and aerospace museum located at Naval Air Station Pensacola, Florida.
Founded in 1962 and moved to its curr ...
, at NAS Pensacola, and is currently displayed at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center
The Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, also called the Udvar-Hazy Center, is the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum (NASM)'s annex at Dulles International Airport in the Chantilly area of Fairfax County, Virginia. It holds numerous exhibits, ...
of the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum collection, wearing the markings of F9C-2 A9056 of USS ''Macon''.
 The remains of a further four aircraft lie at the underwater wreck-site of the ''Macon''; the aircraft were found in their
The remains of a further four aircraft lie at the underwater wreck-site of the ''Macon''; the aircraft were found in their hangar
A hangar is a building or structure designed to hold aircraft or spacecraft. Hangars are built of metal, wood, or concrete. The word ''hangar'' comes from Middle French ''hanghart'' ("enclosure near a house"), of Germanic origin, from Frankish ...
when the wreck was discovered and documented in 1990 and 1991. These are known to have been BuAer numbers 9058 to 9061./ref>
Specifications (F9C-2)
See also
References
Further reading
* * {{USN fightersF9C Sparrowhawk
The Curtiss F9C Sparrowhawk is a light 1930s biplane fighter aircraft that was carried by the United States Navy airships and . It is an example of a parasite fighter, a small airplane designed to be deployed from a larger aircraft such as an ...
Curtiss F9C
Single-engined tractor aircraft
Biplanes
Parasite aircraft
Aircraft first flown in 1931
Aircraft with fixed conventional landing gear