Worms, Germany on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
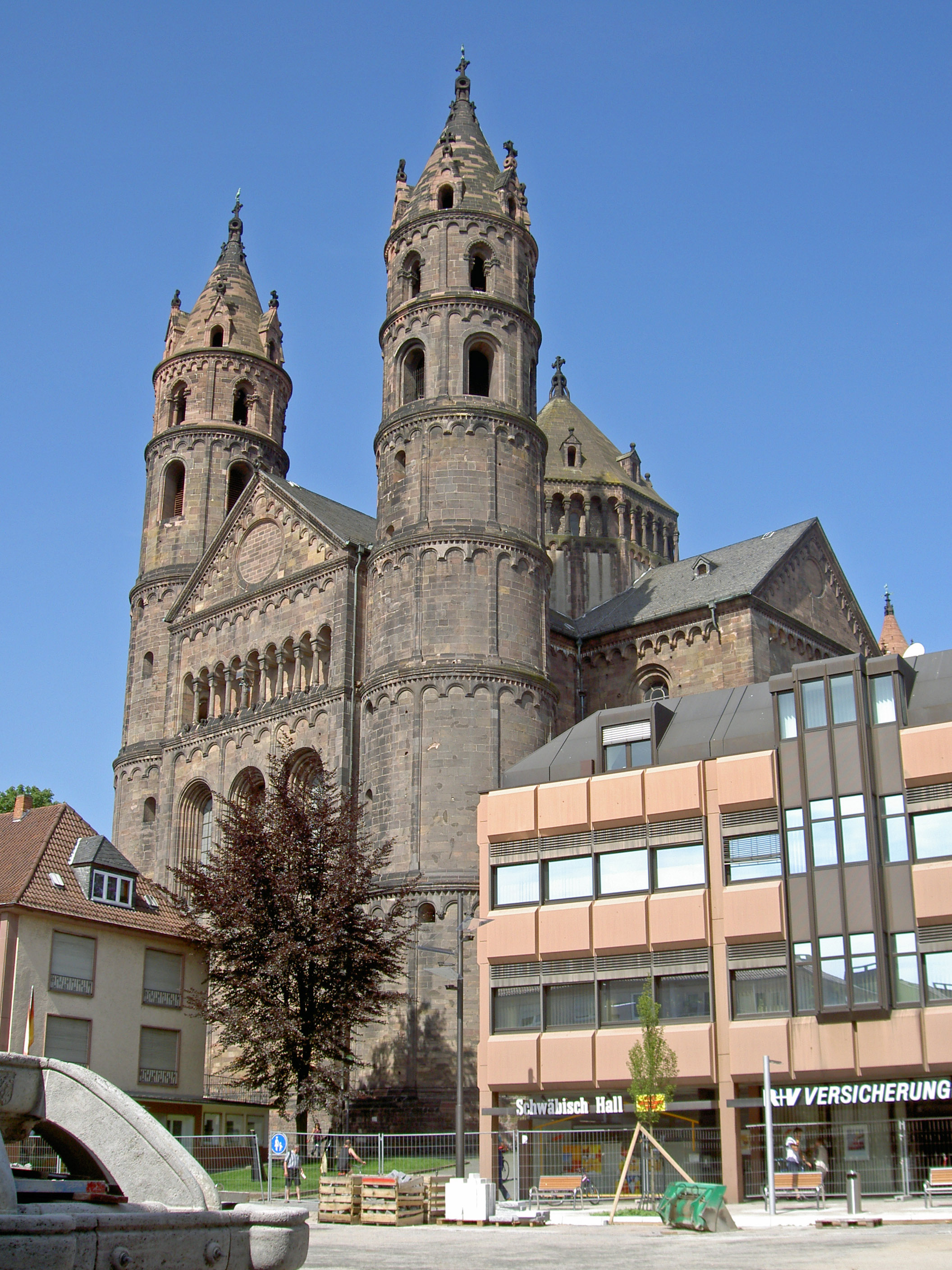

 Worms (; ) is a city in
Worms (; ) is a city in
 Worms' name is of Celtic origin: ''Borbetomagus'' meant "settlement in a watery area". This was eventually transformed into the
Worms' name is of Celtic origin: ''Borbetomagus'' meant "settlement in a watery area". This was eventually transformed into the
 Roman inscriptions, altars, and
Roman inscriptions, altars, and
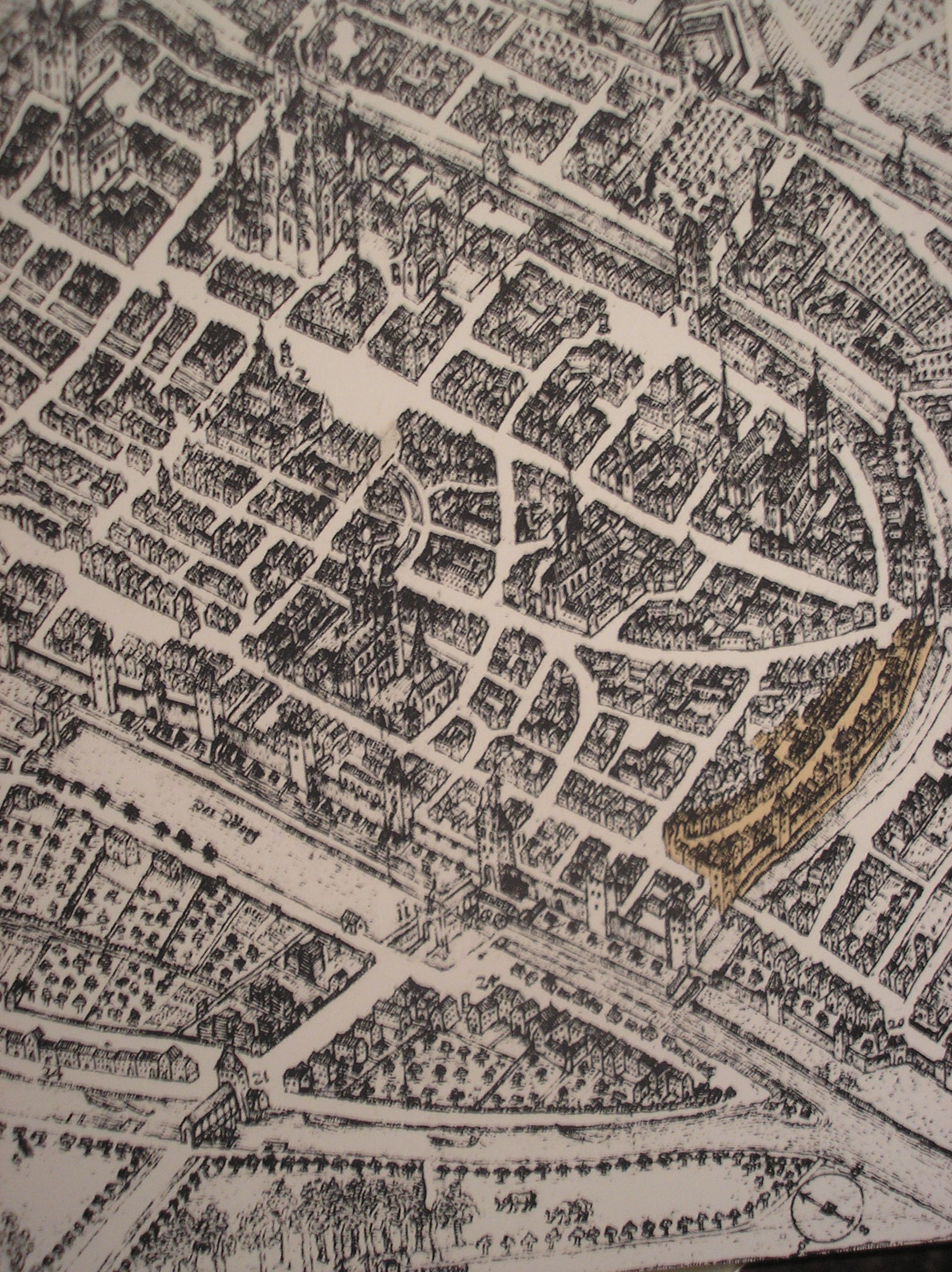 The bishopric of Worms existed by at least 614. In the Frankish Empire, the city was the location of an important palace of Charlemagne. The bishops administered the city and its territory. The most famous of the early medieval bishops was Burchard of Worms. In 868, an important synod was held in Worms. Around 900, the circuit wall was rebuilt according to the wall-building ordinance of Bishop Thietlach.
Worms prospered in the High Middle Ages. Having received far-reaching privileges from King Henry IV as early as 1074, the city became an imperial free city. The bishops resided at Ladenburg and only had jurisdiction over Worms Cathedral itself. In 1122, the Concordat of Worms was signed; the 1495 imperial diet met here and made an attempt at reforming the disintegrating Imperial Circle Estates by the Imperial Reform. Most important, among more than 100 imperial diets held at Worms, that of 1521 (commonly known as ''the'' Diet of Worms) ended with the Edict of Worms, in which Martin Luther was declared a heretic after refusing to recant his religious beliefs. Worms was also the birthplace of the first Bibles of the Reformation, both Martin Luther's German Bible and
The bishopric of Worms existed by at least 614. In the Frankish Empire, the city was the location of an important palace of Charlemagne. The bishops administered the city and its territory. The most famous of the early medieval bishops was Burchard of Worms. In 868, an important synod was held in Worms. Around 900, the circuit wall was rebuilt according to the wall-building ordinance of Bishop Thietlach.
Worms prospered in the High Middle Ages. Having received far-reaching privileges from King Henry IV as early as 1074, the city became an imperial free city. The bishops resided at Ladenburg and only had jurisdiction over Worms Cathedral itself. In 1122, the Concordat of Worms was signed; the 1495 imperial diet met here and made an attempt at reforming the disintegrating Imperial Circle Estates by the Imperial Reform. Most important, among more than 100 imperial diets held at Worms, that of 1521 (commonly known as ''the'' Diet of Worms) ended with the Edict of Worms, in which Martin Luther was declared a heretic after refusing to recant his religious beliefs. Worms was also the birthplace of the first Bibles of the Reformation, both Martin Luther's German Bible and
 In 1689 during the
In 1689 during the
 Prominent students, rabbis, and scholars of Worms include Shlomo Yitzhaki (Rashi) who studied with R. Yizhak Halevi, Meir of Rothenburg (Maharam), Elazar Rokeach, Yaakov ben Moshe Levi Moelin (Maharil), and Yair Bacharach. At the rabbinical synod held at Worms at the turn of the 11th century, Rabbi Gershom ben Judah (Rabbeinu Gershom) explicitly prohibited
Prominent students, rabbis, and scholars of Worms include Shlomo Yitzhaki (Rashi) who studied with R. Yizhak Halevi, Meir of Rothenburg (Maharam), Elazar Rokeach, Yaakov ben Moshe Levi Moelin (Maharil), and Yair Bacharach. At the rabbinical synod held at Worms at the turn of the 11th century, Rabbi Gershom ben Judah (Rabbeinu Gershom) explicitly prohibited
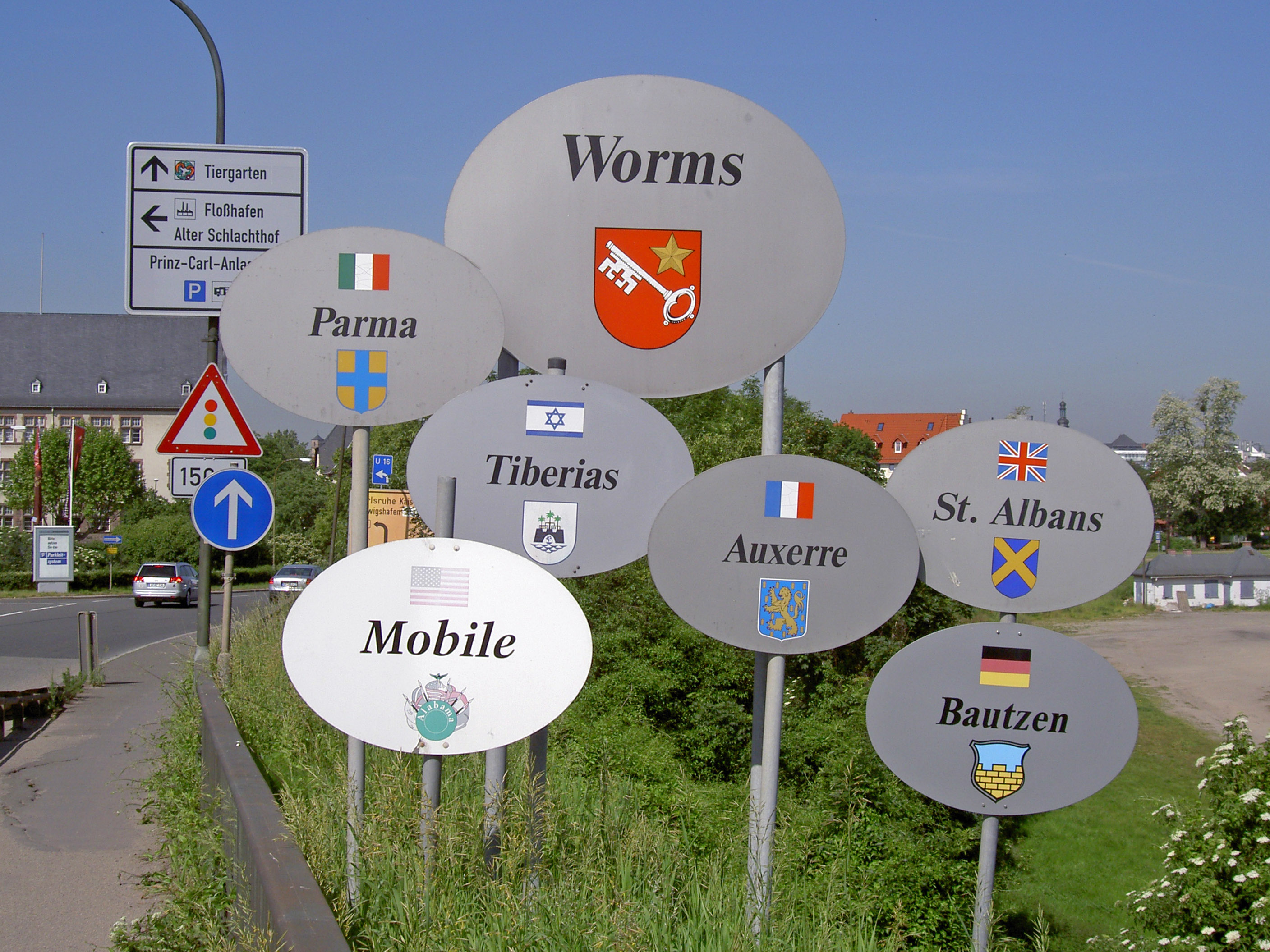 Worms is twinned with:
*
Worms is twinned with:
*
online review
*
Official website
of the city of Worms
Explore the ShUM Sites of Speyer, Worms and Mainz in the UNESCO collection on Google Arts and Culture''Nibelungenmuseum''
website
wormser-dom.de
website of the Worms Cathedral with pictures (click on the "Bilder" link in the left panel)
Wormatia
Worms football club *The website of th
Jewish Museum of Worms
{{Authority control 1789 disestablishments Historic Jewish communities States and territories established in the 11th century Former states and territories of Rhineland-Palatinate Rhenish Hesse Holocaust locations in Germany Urban districts of Rhineland-Palatinate Free imperial cities

 Worms (; ) is a city in
Worms (; ) is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; ; ; ) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the sixteen states. Mainz is the capital and largest city. Other cities are ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, situated on the Upper Rhine
Upper Rhine ( ; ; kilometres 167 to 529 of the Rhine) is the section of the Rhine between the Middle Bridge, Basel, Middle Bridge in Basel, Switzerland, and the Rhine knee in Bingen am Rhein, Bingen, Germany. It is surrounded by the Upper Rhine P ...
about south-southwest of Frankfurt am Main
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
. It had about 84,646 inhabitants .
A pre-Roman foundation, Worms is one of the oldest cities in northern Europe. It was the capital of the Kingdom of the Burgundians in the early fifth century, hence is the scene of the medieval legends referring to this period, notably the first part of the '' Nibelungenlied''.
Worms has been a Roman Catholic bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
since at least 614, and was an important palatinate of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
. Worms Cathedral is one of the imperial cathedrals and among the finest examples of Romanesque architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe that was predominant in the 11th and 12th centuries. The style eventually developed into the Gothic style with the shape of the arches providing a simple distinction: the Ro ...
in Germany. Worms prospered in the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention ...
as an imperial free city. Among more than a hundred imperial diets held at Worms, the Diet of 1521 (commonly known as ''the'' Diet of Worms) ended with the Edict of Worms, in which Martin Luther
Martin Luther ( ; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, Theology, theologian, author, hymnwriter, professor, and former Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. Luther was the seminal figure of the Reformation, Pr ...
was declared a heretic. Worms is also one of the historical ShUM-cities as a cultural center of Jewish life in Europe during the Middle Ages. Its Jewish sites (along with those in Speyer and Mainz) were inscribed on the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage List
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritag ...
in 2021.
Today, the city is an industrial centre and is famed as the origin of '' Liebfraumilch'' wine. Its other industries include chemicals, metal goods, and fodder.
Name
 Worms' name is of Celtic origin: ''Borbetomagus'' meant "settlement in a watery area". This was eventually transformed into the
Worms' name is of Celtic origin: ''Borbetomagus'' meant "settlement in a watery area". This was eventually transformed into the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
name ''Vormatia'', in use since the 6th century, which was preserved in the Medieval Hebrew form ''Vermayza'' (ורמייזא) and the contemporary Polish form ''Wormacja''.
According to a legend printed in the 17th century in the book ''Ma'aseh Nisim'' by Juspa Schammes, the origin of the city's name is attributed to the mythical creature lint-wurm. This creature, resembling a snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have s ...
and a worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateria, bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limb (anatomy), limbs, and usually no eyes.
Worms vary in size from microscopic to over in length for marine ...
, arrived in the city of Germisa and terrorized its inhabitants. Every day, the people held a lottery to determine which of them would be sacrificed to the lint-wurm in order to spare the city from destruction. Eventually, the lot fell on the queen. One of the city's heroes refused to allow her to sacrifice herself and offered to replace her on the condition that if he survived, she would marry him. The queen agreed, and he donned iron armor. After the lint-wurm swallowed him, he cut his way out from the inside and killed it. He married the queen, became king, and renamed the city to Worms to commemorate this tale.
Geography
Worms is located on the west bank of the River Rhine between the cities ofLudwigshafen
Ludwigshafen, officially Ludwigshafen am Rhein (; meaning "Ludwig I of Bavaria, Ludwig's Port upon the Rhine"; Palatine German dialects, Palatine German: ''Ludwichshafe''), is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in the German state of Rh ...
and Mainz
Mainz (; #Names and etymology, see below) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, and with around 223,000 inhabitants, it is List of cities in Germany by population, Germany's 35th-largest city. It lies in ...
. On the northern edge of the city, the Pfrimm flows into the Rhine, and on the southern edge, the Eisbach flows into the Rhine.
Boroughs
Worms has 13 boroughs (or "quarters") around the city centre. They are:Climate
The climate in the Rhine Valley is cool in winter and very warm in summer. Rainfall is below average for the surrounding areas. Winter snow accumulation is low and often melts quickly.History
Antiquity
Worms was in ancient times a Celtic city named ''Borbetomagus'', perhaps meaning "water meadow". Later it was conquered by the GermanicVangiones
The Vangiones appear first in history as an ancient Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe of unknown provenance. They threw in their lot with Ariovistus in his bid of 58 BC to invade Gaul through the Doubs river valley and lost to Julius Caesar in a ba ...
tribe. In 14 BC, Romans under the command of Drusus captured and fortified the city, and from that time onwards, a small troop of infantry and cavalry was garrisoned there. The Romans renamed the city as ''Augusta Vangionum'', after the then-emperor and the local tribe. The name does not seem to have taken hold, however, and from ''Borbetomagus'' developed the German ''Worms'' and Latin ''Wormatia''; as late as the modern period, the city name was written as ''Wormbs''. The garrison grew into a small town with a regular Roman street plan, a forum, and temples for the main gods Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
, Juno, Minerva
Minerva (; ; ) is the Roman goddess of wisdom, justice, law, victory, and the sponsor of arts, trade, and strategy. She is also a goddess of warfare, though with a focus on strategic warfare, rather than the violence of gods such as Mars. Be ...
(whose temple was the site of the later cathedral), and Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
.
 Roman inscriptions, altars, and
Roman inscriptions, altars, and votive offering
A votive offering or votive deposit is one or more objects displayed or deposited, without the intention of recovery or use, in a sacred place for religious purposes. Such items are a feature of modern and ancient societies and are generally ...
s can be seen in the archaeological museum, along with one of Europe's largest collections of Roman glass
Roman glass objects have been recovered across the Roman Empire in domestic, industrial and funerary contexts. Glass was used primarily for the production of vessels, although mosaic tiles and window glass were also produced. Roman glass producti ...
. Local potters worked in the town's south quarter. Fragments of '' amphorae'' contain traces of olive oil from Hispania Baetica
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces created in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula) in 27 BC. Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of ...
, doubtless transported by sea and then up the Rhine by ship.
During the disorders of 411–413 AD, Roman usurper Jovinus established himself in Borbetomagus as a puppet-emperor with the help of King Gunther of the Burgundians
The Burgundians were an early Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared east in the middle Rhine region in the third century AD, and were later moved west into the Roman Empire, in Roman Gaul, Gaul. In the first and seco ...
, who had settled in the area between the Rhine and Moselle
The Moselle ( , ; ; ) is a river that rises in the Vosges mountains and flows through north-eastern France and Luxembourg to western Germany. It is a bank (geography), left bank tributary of the Rhine, which it joins at Koblenz. A sm ...
some years before. The city became the capital of the Burgundian kingdom under Gunther (also known as Gundicar). Few remains of this early Burgundian kingdom survive, because in 436, it was all but destroyed by a combined army of Romans (led by Aëtius) and Huns (led by Attila
Attila ( or ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in early 453. He was also the leader of an empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Gepids, among others, in Central Europe, C ...
); a belt clasp found at Worms-Abenheim is a museum treasure. Provoked by Burgundian raids against Roman settlements, the combined Romano-Hunnic army destroyed the Burgundian army at the Battle of Worms (436), killing King Gunther. About 20,000 are said to have been killed. The Romans led the survivors southwards to the Roman district of Sapaudia (modern-day Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
). The story of this war later inspired the ''Nibelungenlied''. The city appears on the Peutinger Map, dated to the fourth century.
Middle Ages
William Tyndale
William Tyndale (; sometimes spelled ''Tynsdale'', ''Tindall'', ''Tindill'', ''Tyndall''; – October 1536) was an English Biblical scholar and linguist who became a leading figure in the Protestantism, Protestant Reformation in the year ...
's first complete English New Testament by 1526.
Modern era
 In 1689 during the
In 1689 during the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between Kingdom of France, France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial poss ...
, Worms (like the nearby towns and cities of Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; ; ) is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, fifth-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg, and with a population of about 163,000, of which roughly a quarter consists of studen ...
, Mannheim
Mannheim (; Palatine German language, Palatine German: or ), officially the University City of Mannheim (), is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, second-largest city in Baden-Württemberg after Stuttgart, the States of Ger ...
, Oppenheim
Oppenheim ( or ) is a town in the Mainz-Bingen district of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Geography
Location
The town lies on the Upper Rhine in Rhenish Hesse between Mainz and Worms. It is the seat of the Verbandsgemeinde (special ad ...
, Speyer
Speyer (, older spelling ; ; ), historically known in English as Spires, is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate in the western part of the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany with approximately 50,000 inhabitants. Located on the left bank of the r ...
, and Bingen) was sacked by troops of Louis XIV of France
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
, though the French only held the city for a few weeks. In 1743, the Treaty of Worms was signed, forming a political alliance between Great Britain, Austria, and the Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica among other names, was a State (polity), country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century, and from 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of ...
. In 1792, the city was occupied by troops of the First French Republic
In the history of France, the First Republic (), sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic (), was founded on 21 September 1792 during the French Revolution. The First Republic lasted u ...
during the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars () were a series of sweeping military conflicts resulting from the French Revolution that lasted from 1792 until 1802. They pitted French First Republic, France against Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Habsb ...
. The Bishopric of Worms was secularized
In sociology, secularization () is a multilayered concept that generally denotes "a transition from a religious to a more worldly level." There are many types of secularization and most do not lead to atheism or irreligion, nor are they automatica ...
in 1801, with the city being annexed into the First French Empire
The First French Empire or French Empire (; ), also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from ...
. In 1815, Worms passed to the Grand Duchy of Hesse
The Grand Duchy of Hesse and by Rhine () was a grand duchy in western Germany that existed from 1806 to 1918. The grand duchy originally formed from the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt in 1806 as the Grand Duchy of Hesse (). It assumed the name ...
in accordance with the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
, and the city was subsequently administered within Rhenish Hesse.
After the Battle of the Bulge
The Battle of the Bulge, also known as the Ardennes Offensive or Unternehmen Die Wacht am Rhein, Wacht am Rhein, was the last major German Offensive (military), offensive Military campaign, campaign on the Western Front (World War II), Western ...
in early 1945, Allied armies advanced into the Rhineland in preparation for a massive assault into the heart of the Reich. Worms was a German strongpoint on the west bank of the Rhine, and the forces there resisted the Allied advance tenaciously. Worms was, thus, heavily bombed by the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
and the U.S. Army Air Forces in two attacks on February 21 and March 18, 1945, respectively. A postwar survey estimated that 39% of the town's developed area was destroyed. The RAF attack on Feb. 21 was aimed at the main railway station on the edge of the inner city, and at chemical plants southwest of the inner city, but also destroyed large areas of the city centre. Carried out by 334 bombers, the attack in a few minutes rained 1,100 tons of bombs on the inner city, and Worms Cathedral was among the buildings set on fire. The Americans did not enter the city until the Rhine crossings began after the seizure of the Remagen Bridge.
In the attacks, 239 inhabitants were killed in the first and 141 in the second; 35,000 (60% of the population of 58,000) were made homeless. In all, 6,490 buildings were severely damaged or destroyed. After the war, the inner city was rebuilt, mostly in modern style. Around a third of Worms's buildings is from before 1950. Postwar Worms became part of the new state of Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; ; ; ) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the sixteen states. Mainz is the capital and largest city. Other cities are ...
; the borough Rosengarten, on the east bank of the Rhine, was lost to Hesse.
Worms today fiercely vies with the cities Trier
Trier ( , ; ), formerly and traditionally known in English as Trèves ( , ) and Triers (see also Names of Trier in different languages, names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle (river), Moselle in Germany. It lies in a v ...
and Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
for the title of "Oldest City in Germany". A multimedia '' Nibelungenmuseum'' was opened in 2001, and a yearly festival in front of the ''Dom'', the Worms Cathedral, attempts to recapture the atmosphere of the pre-Christian period.
In 2010, the Worms synagogue was firebombed. Eight corners of the building were set ablaze, and a Molotov cocktail
A Molotov cocktail (among several other names – ''see '') is a hand-thrown incendiary weapon consisting of a frangible container filled with flammable substances and equipped with a Fuse (explosives), fuse (typically a glass bottle filled wit ...
was thrown at a window, but with no injuries. Kurt Beck, Minister-President of Rhineland-Palatinate, condemned the attack and vowed to mobilize all necessary resources to find the perpetrators, saying, "We will not tolerate such an attack on a synagogue".
The Jewish community of ''Varmayza''
The Free Imperial City of Worms, known in medieval Hebrew by the name ''Varmayza'' or ''Vermaysa'' (Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
: וורמיזא, וורמישא), was a centre of medieval Ashkenazic Jewry. The Jewish community was established there in the late 10th century, and Worms's first synagogue
A synagogue, also called a shul or a temple, is a place of worship for Jews and Samaritans. It is a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels) where Jews attend religious services or special ceremonies such as wed ...
was erected in 1034. The Jewish community settled in a separate neighborhood in the city called the Judengasse. In 1096, 800 to 1000 Jews were murdered by crusaders and the local mob, what later became known as Rhineland massacres
The Rhineland massacres, also known as the German Crusade of 1096 or ''Gzerot Tatnó'' (, "Edicts of 4856"), were a series of mass murders of Jews perpetrated by mobs of French and German Christians of the People's Crusade in the year 1096 ( ...
or ''Gzerot Tatnó'' (Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
: גזרות תתנ"ו, "Edicts of 4856"). The Jewish Cemetery in Worms, dating from the 11th century, is believed to be the oldest surviving ''in situ'' cemetery in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
. The Rashi Synagogue, which dates from 1175 and was carefully reconstructed after its desecration on ''Kristallnacht
( ) or the Night of Broken Glass, also called the November pogrom(s) (, ), was a pogrom against Jews carried out by the Nazi Party's (SA) and (SS) paramilitary forces along with some participation from the Hitler Youth and German civilia ...
'', is the oldest in Germany.
 Prominent students, rabbis, and scholars of Worms include Shlomo Yitzhaki (Rashi) who studied with R. Yizhak Halevi, Meir of Rothenburg (Maharam), Elazar Rokeach, Yaakov ben Moshe Levi Moelin (Maharil), and Yair Bacharach. At the rabbinical synod held at Worms at the turn of the 11th century, Rabbi Gershom ben Judah (Rabbeinu Gershom) explicitly prohibited
Prominent students, rabbis, and scholars of Worms include Shlomo Yitzhaki (Rashi) who studied with R. Yizhak Halevi, Meir of Rothenburg (Maharam), Elazar Rokeach, Yaakov ben Moshe Levi Moelin (Maharil), and Yair Bacharach. At the rabbinical synod held at Worms at the turn of the 11th century, Rabbi Gershom ben Judah (Rabbeinu Gershom) explicitly prohibited polygamy
Polygamy (from Late Greek , "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marriage, marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, it is called polygyny. When a woman is married to more tha ...
for the first time. The community's customs were collected and written by Juspa Schammes in a ''Minhagbuch (book of customs)'' and preserve ancient traditions unique to the community.
The Jewish community was destroyed and expelled from the city several times. The main expulsions were both in 1615 after the city's residents committed a pogrom
A pogrom is a violent riot incited with the aim of Massacre, massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe late 19th- and early 20th-century Anti-Jewis ...
against the Jewish community and in 1689 during the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between Kingdom of France, France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial poss ...
by troops of Louis XIV of France
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
(with all the city's citizens), After a few years, the Jews were allowed to return to live in the city. Despite this, until ''Kristallnacht
( ) or the Night of Broken Glass, also called the November pogrom(s) (, ), was a pogrom against Jews carried out by the Nazi Party's (SA) and (SS) paramilitary forces along with some participation from the Hitler Youth and German civilia ...
'' in 1938, the Jewish Quarter of Worms was a centre of Jewish life. It was among the oldest Jewish communities that maintained continuity over time, and a beautiful example of this is the 900th anniversary celebrations of the synagogue held in 1934.
Worms today has only a very small Jewish population, and a recognizable Jewish community as such no longer exists. After renovations in the 1970s and 1980s, though, many of the buildings of the quarter can be seen in a close-to-original state, preserved as an outdoor museum. The Jewish sites (along with those in Speyer and Mainz) were inscribed on the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage List
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritag ...
in 2021.
Main sights
*The renovated (1886–1935) RomanesqueCathedral
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually s ...
, dedicated to St Peter (12th–13th century)
* Reformation Memorial church of the Holy Trinity, the city's largest Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
church (17th century)
* St Paul's Church (''Pauluskirche'') (13th century)
* St Andrew's Collegiate Church (''Andreaskirche'') (13th century)
*St Martin's Church (''Martinskirche'') (13th century)
*''Liebfrauenkirche'' (15th century)
* Luther Monument (''Lutherdenkmal'') (1868) (designed by Ernst Rietschel)
* ShUM city of Worms, UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
** Rashi Synagogue and Mikvah
A mikveh or mikvah (, ''mikva'ot'', ''mikvot'', or ( Ashkenazic) ''mikves'', lit., "a collection") is a bath used for ritual immersion in Judaism to achieve ritual purity.
In Orthodox Judaism, these regulations are steadfastly adhered t ...
**Jewish Museum
A Jewish museum is a museum which focuses upon Jews and may refer seek to explore and share the Jewish experience in a given area.
Notable Jewish museums include:
Albania
* Solomon Museum, Berat
Australia
* Jewish Museum of Australia, Melbourn ...
in the Rashi-House
**Jewish Cemetery
A Jewish cemetery ( ''beit almin'' or ''beit kvarot'') is a cemetery where Jews are buried in keeping with Halakha, Jewish tradition. Cemeteries are referred to in several different ways in Hebrew, including ''beit kevarot'' (house of s ...
* Nibelungen Museum, celebrating the Middle High German
Middle High German (MHG; or ; , shortened as ''Mhdt.'' or ''Mhd.'') is the term for the form of High German, High German language, German spoken in the High Middle Ages. It is conventionally dated between 1050 and 1350, developing from Old High ...
epic poem '' Das Nibelungenlied'' (''The Song of the Nibelungs'')
* Magnuskirche, the city's smallest church, which possibly originates from the eighth century
Twin towns – sister cities
 Worms is twinned with:
*
Worms is twinned with:
* Auxerre
Auxerre ( , , Burgundian language (Oïl), Burgundian: ''Auchoirre'') is the capital (Prefectures in France, prefecture) of the Yonne Departments of France, department and the fourth-largest city in the Burgundy historical region southeast of Par ...
, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
* Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin (), until 1868 ''Budissin'' in German, is a town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the Bautzen (district), district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree (river), Spree river, is the eighth most ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
* Mobile, United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
* Ningde
Ningde,; Foochow Romanized: Nìng-dáik; also known as ''Mindong''; zh, s=闽东, p=Mǐndōng, links=no; Foochow Romanized: Mìng-dĕ̤ng; lit. East of Fujian previously Chinese postal romanization, romanized as Ningteh and Ning-Taik, is a prefe ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
* Parma
Parma (; ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, Giuseppe Verdi, music, art, prosciutto (ham), Parmesan, cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,986 inhabitants as of 2025, ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
* St Albans
St Albans () is a cathedral city in Hertfordshire, England, east of Hemel Hempstead and west of Hatfield, Hertfordshire, Hatfield, north-west of London, south-west of Welwyn Garden City and south-east of Luton. St Albans was the first major ...
, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
* Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; , ; ) is a city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee in northern Israel. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's Four Holy Cities, along with Jerusalem, Heb ...
, Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
People
* Saint Erentrude, or Erentraud ( 650–710), virgin saint of the Roman Catholic Church * Heribert of Cologne ( 970–1021, archbishop-elector ofCologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
and Chancellor of the Holy Roman Empıre
* Isaac ben Eliezer Halevi (died 1070), French rabbi
* Minna of Worms (died 1096), influential Jewish citizen, victim of the Worms massacre (1096)
*Rashi
Shlomo Yitzchaki (; ; ; 13 July 1105) was a French rabbi who authored comprehensive commentaries on the Talmud and Hebrew Bible. He is commonly known by the List of rabbis known by acronyms, Rabbinic acronym Rashi ().
Born in Troyes, Rashi stud ...
(Shlomo Yitzhaki; 1040–1105), rabbi, studied in the Worms Yeshiva in 1065–1070
* Meir of Rothenburg (1215–1293), rabbi and poet
* Yaakov ben Moshe Levi Moelin (1365-1427), Rabbi
A rabbi (; ) is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi—known as ''semikha''—following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of t ...
of Mainz
Mainz (; #Names and etymology, see below) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, and with around 223,000 inhabitants, it is List of cities in Germany by population, Germany's 35th-largest city. It lies in ...
.
* Hans Folz (1435/1440–1513), notable medieval author
* Conrad Meit (or Conrat Meit) (1480s–1550/1551), Renaissance sculptor, mostly in the Low Countries
* Isaac ben Eliezer, 15th-century rabbi
* Juspa Schammes (1604–1678), caretaker of the Worms Synagogue and writer
* Yair Bacharach (1638–1702), rabbi, was the chief rabbi of worms in 1699–1702
*Johann Nikolaus Götz
Johann Nikolaus Götz (July 9, 1721 – November 4, 1781) was a German poet from Worms, Germany, Worms.
Biography
Götz was born in Worms, Germany, Worms. He studied theology at university of Halle, Halle (1739–1742), where he became intimate ...
(1721–1781), poet
* Ferdinand Eberstadt (1808–1888), textile merchant and mayor of Worms
* Samuel Adler (1809–1891), German-American Reform
Reform refers to the improvement or amendment of what is wrong, corrupt, unsatisfactory, etc. The modern usage of the word emerged in the late 18th century and is believed to have originated from Christopher Wyvill's Association movement, which ...
rabbi
* Solomon Loeb (1828–1903), American banker and philanthropist
Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives for the public good, focusing on quality of life". Philanthropy contrasts with business initiatives, which are private initiatives for private good, focusing on material ...
* John Derst (1838–1928), baker
* Friedrich Gernsheim (1839–1916), composer, conductor and pianist
* Ida Straus (1849–1912), wife of Isidor Straus, voluntarily remained with husband on board the RMS ''Titanic''
* Ludwig Edinger (1855–1918), anatomist and neurologist
* Siegfried Guggenheim (1873–1961), lawyer, notary and art collector
* Hugo Sinzheimer (1875–1945), legal scholar, member of the Constitutional Convention of 1919
*Hermann Staudinger
Hermann Staudinger (; 23 March 1881 – 8 September 1965) was a German organic chemist who demonstrated the existence of macromolecules, which he characterized as polymers. For this work he received the 1953 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
He is also ...
(1881–1965), organic chemist, Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outst ...
1953
* Emil Stumpp (1886–1941), cartoonist, died in jail after doing an unflattering portrait of Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
* Rudi Stephan (1887–1915), composer
* Hanya Holm (1893–1992), choreographer, dancer, educator and one of the founders of American Modern Dance
* Richard Hildebrandt (1897–1951), politician in Nazi Germany and member of the Reichstag executed for war crimes
*Curtis Bernhardt
Curtis Bernhardt (15 April 1899 – 22 February 1981) was a German film director born in Worms, Germany, under the name Kurt Bernhardt.
Career
He trained as an actor in Germany, and performed on the stage, before starting as a film director in ...
(1899–1981), film director
* Hans Hinkel (1901–1960), journalist and Nazi cultural functionary
* Hans Diller (1905–1977), classical scholar specializing in Ancient Greek medicine
* Vladimir Kagan (1927–2016), furniture designer
* Rolf Wilhelm Brednich (born 1935), folklorist
* Florian Gerster (born 1949), politician (SPD), former chairman of the Federal Employment Agency
*Rod Temperton
Rodney Lynn Temperton (9 October 1949 – 25 September 2016) was an English musician, songwriter, and record producer.
Temperton was the keyboardist and principal songwriter for the 1970s funk band Heatwave, writing songs including "Star of a ...
(1949–2016), English songwriter, record producer and musician
* Monika Stolz (born 1951), politician (CDU), Member of Landtag Baden-Württemberg since 2001
*Petra Gerster
Petra Gerster (; born 25 January 1955) is a German journalist and news presenter.
Early life and education
Starting in 1973, Gerster studied German studies, Slavic studies, and literature with a grant of the German Academic Scholarship Foundat ...
(born 1955), television journalist (ZDF)
* Markus Weinmann (born 1974), agricultural scientist in the area of plant physiology
Plant physiology is a subdiscipline of botany concerned with the functioning, or physiology, of plants.
Plant physiologists study fundamental processes of plants, such as photosynthesis, respiration, plant nutrition, plant hormone functions, tr ...
*Timo Hildebrand
Timo Hildebrand (born 5 April 1979) is a German former professional footballer who played as a goalkeeper.
Hildebrand holds a Bundesliga record for keeping a clean sheet for the most consecutive minutes (884 minutes), which he set during the 2 ...
(born 1979), footballer
* Marvin Dienst (born 1997), German racing driver
*Alica Schmidt
Alica Megan Schmidt (; born 8 November 1998) is a German runner. She was part of the national team that came second in the 4 × 400 metres relay event at the 2017 European Athletics U20 Championships, and third in the same discipline at the 2019 ...
(born 1998), track and field athlete, fitness coach
See also
* WormserReferences
Further reading
* Bönnen, Gerold (ed.). ''Geschichte der Stadt Worms'' 'History of the City of Worms''(in German) (Second edition, supdated and expanded edition). Darmstadt: Theiss. . * Reuter, Fritz (2009). ''Warmaisa: 1000 Jahre Juden in Worms'' 'Warmaisa: 1000 Years of Jews in Worms''(in German) (3. Aufl ed.). Norderstedt: Books on Demand. . * Roemer, Nils H. ''German City, Jewish Memory: The Story of Worms'' (Brandeis University Press, 2010)online review
*
External links
*ThOfficial website
of the city of Worms
Explore the ShUM Sites of Speyer, Worms and Mainz in the UNESCO collection on Google Arts and Culture
website
wormser-dom.de
website of the Worms Cathedral with pictures (click on the "Bilder" link in the left panel)
Wormatia
Worms football club *The website of th
Jewish Museum of Worms
{{Authority control 1789 disestablishments Historic Jewish communities States and territories established in the 11th century Former states and territories of Rhineland-Palatinate Rhenish Hesse Holocaust locations in Germany Urban districts of Rhineland-Palatinate Free imperial cities