Worcester, Worcestershire on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Worcester ( ) is a
"The Late Roman and Post-Roman Settlement, 4th century ‚Äď 680". Worcester City Council (Worcester), 2005.
/ref>
 Worcester became a centre of monastic learning and church power.
Worcester became a centre of monastic learning and church power.
 The city council was organised by a system of co-option, with 24 members of the high chamber and 48 of the lower. Committees appointed two bailiffs and made financial decisions; the two chambers agreed the city's rules or ordinances.
By late medieval times the population had reached 1,025 families, excluding the cathedral quarter, so that it probably stood under 10,000. Worcester's suburbs extended beyond the limits of its walls
Manufacture of cloth and allied trades was significant for the city.
The city council was organised by a system of co-option, with 24 members of the high chamber and 48 of the lower. Committees appointed two bailiffs and made financial decisions; the two chambers agreed the city's rules or ordinances.
By late medieval times the population had reached 1,025 families, excluding the cathedral quarter, so that it probably stood under 10,000. Worcester's suburbs extended beyond the limits of its walls
Manufacture of cloth and allied trades was significant for the city.
 Worcester equivocated, then sided with Parliament before the outbreak of the
Worcester equivocated, then sided with Parliament before the outbreak of the
 Worcester in the late 18th and early 19th centuries was a major centre for glove-making, employing nearly half the glovers in England at its peak (over 30,000 people). employed by 150 firms. At this time nearly half the glove makers in Britain could be found in Worcestershire. In the 19th century, the industry declined as import taxes on foreign competitors, mainly French, were much reduced.
Riots took place in 1831, in response to the defeat of the
Worcester in the late 18th and early 19th centuries was a major centre for glove-making, employing nearly half the glovers in England at its peak (over 30,000 people). employed by 150 firms. At this time nearly half the glove makers in Britain could be found in Worcestershire. In the 19th century, the industry declined as import taxes on foreign competitors, mainly French, were much reduced.
Riots took place in 1831, in response to the defeat of the
/ref> In 1882 Worcester hosted the Worcestershire Exhibition with sections for fine arts, historical manuscripts and industrial items, receiving over 222,000 visitors.
File:Castle shield on Foregate railway bridge, Worcester - geograph.org.uk - 1629621.jpg, The "ancient" arms of the city on the railway bridge near Foregate Street station
File:Black Pear shield on Foregate railway bridge - geograph.org.uk - 1628858.jpg, The "modern" arms of the city on the railway bridge near Foregate Street station
File:Gate, Cripplegate Park, Worcester - geograph.org.uk - 1329819.jpg, The coat of arms as shown on the entrance gate to Cripplegate Park
File:Guildhall Coat of Arms - geograph.org.uk - 1066268.jpg, The coat of arms as shown in the Guildhall, with the "modern" placed over the "ancient"

 A statue of Sir Edward Elgar, commissioned from Kenneth Potts and unveiled in 1981, stands at the end of Worcester High Street facing the cathedral, yards from the original location of his father's music shop, which was demolished in the 1960s. Elgar's birthplace was the nearby village of Broadheath. Plaques installed in the city include a dedication to the medieval Jewish community at Copenhagen Street.
There are two large wooded areas in the city, Perry Wood and Nunnery Wood, covering 12 and 21 hectares. Perry Wood is often said to be where
A statue of Sir Edward Elgar, commissioned from Kenneth Potts and unveiled in 1981, stands at the end of Worcester High Street facing the cathedral, yards from the original location of his father's music shop, which was demolished in the 1960s. Elgar's birthplace was the nearby village of Broadheath. Plaques installed in the city include a dedication to the medieval Jewish community at Copenhagen Street.
There are two large wooded areas in the city, Perry Wood and Nunnery Wood, covering 12 and 21 hectares. Perry Wood is often said to be where
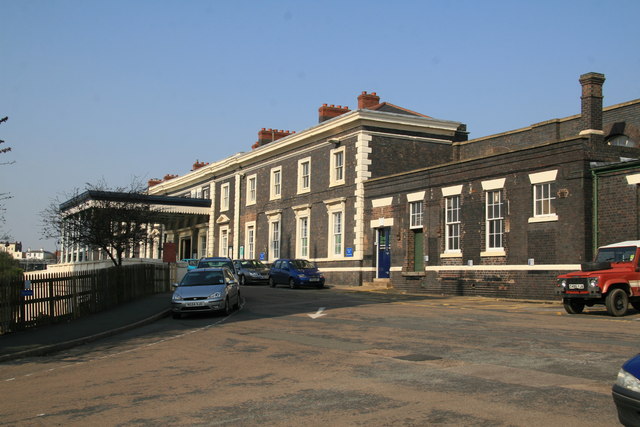

 Worcester has three railway stations. and are in the city centre. A third station on the edge of the city, , opened in 2020.
The
Worcester has three railway stations. and are in the city centre. A third station on the edge of the city, , opened in 2020.
The
 The city had two park and ride sites: off the A38 in Perdiswell and at
The city had two park and ride sites: off the A38 in Perdiswell and at
 The famous 18th-century actress
The famous 18th-century actress
 In birth order:
* Hannah Snell (1723‚Äď1792), famous for impersonating a man and enlisting in the
In birth order:
* Hannah Snell (1723‚Äď1792), famous for impersonating a man and enlisting in the
Worcester City CouncilHistory of the City of Worcester
{{Authority control Populated places on the River Severn County towns in England Local government in Worcestershire Cities in the West Midlands (region) Towns in Worcestershire Boroughs in England Former civil parishes in Worcestershire
cathedral city
City status in the United Kingdom is granted by the the Crown, monarch of the United Kingdom to specific centres of population, which might or might not meet the generally accepted definition of city, cities. , there are List of cities in the Un ...
in Worcestershire
Worcestershire ( , ; written abbreviation: Worcs) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England. It is bordered by Shropshire, Staffordshire, and the West Midlands (county), West ...
, England, of which it is the county town
In Great Britain and Ireland, a county town is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county, and the place where public representatives are elected to parliament. Following the establishment of county councils in ...
. It is south-west of Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
, north of Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city, non-metropolitan district and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West England, South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean ...
and north-east of Hereford
Hereford ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of the ceremonial county of Herefordshire, England. It is on the banks of the River Wye and lies east of the border with Wales, north-west of Gloucester and south-west of Worcester. With ...
. The population was 103,872 in the 2021 census.
The River Severn
The River Severn (, ), at long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in t ...
flanks the western side of the city centre, overlooked by Worcester Cathedral
Worcester Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of Christ and Blessed Mary the Virgin, is a Church of England cathedral in Worcester, England, Worcester, England. The cathedral is the seat of the bishop of Worcester and is the Mother Church# ...
. Worcester is the home of Royal Worcester Porcelain, Lea & Perrins
Lea & Perrins (L&P) is a United Kingdom-based subsidiary of Kraft Heinz, originating in Worcester, England where it continues to operate. It is the manufacturer of Lea & Perrins Worcestershire sauce, a condiment first invented and sold in 1837 ...
(makers of traditional Worcestershire sauce
Worcestershire sauce or Worcester sauce (UK: ) is a fermented liquid condiment invented by pharmacists John Wheeley Lea and William Henry Perrins in the city of Worcester in Worcestershire, England, during the first half of the 19th century ...
), the University of Worcester
The University of Worcester is a public research university, based in Worcester, England. With a history dating back to 1946, the university began awarding degrees in 1997 and was granted full university status in 2005.
History
In 1946 an Emerg ...
, and ''Berrow's Worcester Journal
''Berrow's Worcester Journal'' is a weekly freesheet tabloid newspaper, based in Worcester, England. Owned by Newsquest, the newspaper is delivered across central and southern Worcestershire.
History
16th century printing press
Worcester was ...
'', claimed as the world's oldest newspaper. The composer Edward Elgar
Sir Edward William Elgar, 1st Baronet, (; 2 June 1857 ‚Äď 23 February 1934) was an English composer, many of whose works have entered the British and international classical concert repertoire. Among his best-known compositions are orchestr ...
(1857‚Äď1934) grew up in the city.
The Battle of Worcester
The Battle of Worcester took place on 3 September 1651 in and around the city of Worcester, England and was the last major battle of the 1642 to 1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms. A Parliamentarian army of around 28,000 under Oliver Cromwell def ...
in 1651 was the final battle of the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
, during which Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in British history. He came to prominence during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially ...
's New Model Army
The New Model Army or New Modelled Army was a standing army formed in 1645 by the Parliamentarians during the First English Civil War, then disbanded after the Stuart Restoration in 1660. It differed from other armies employed in the 1639 t ...
defeated King Charles II's Royalists
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of gover ...
.
History
Early history
The trade route past Worcester, later part of theRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
Ryknild Street
Icknield Street or Ryknild Street is a Roman road in England, with a route roughly south-west to north-east. It runs from the Fosse Way at Bourton on the Water in Gloucestershire () to Templeborough in South Yorkshire (). It passes through A ...
, dates from Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
times. It commanded a ford crossing over the River Severn
The River Severn (, ), at long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in t ...
, which was tidal below Worcester, and fortified
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Lat ...
by the Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs modern British citizenship and nationality, w ...
about 400 BC.
Charcoal from the Forest of Dean
The Forest of Dean is a geographical, historical and cultural region in the western part of the Counties of England, county of Gloucestershire, England. It forms a roughly triangle, triangular plateau bounded by the River Wye to the west and no ...
enabled Romans to operate pottery kilns and ironworks. They may also have built a small fort. While there is some evidence that the late Iron Age defensive ditches on the east bank may have been dug out during the first century AD, there is no other evidence to suggest that this was used as a fort by the Romans. Scatters of military equipment and coins found in the city centre from this early period may instead have been lost during the course of road building, or won by the local inhabitants in battle, rather than being left by a Roman military garrison. There is no sign of municipal buildings to indicate an administrative role.
In the 3rd century AD, Roman Worcester occupied a larger area than the subsequent medieval city, but silting caused the abandonment of Sidbury. Industrial production ceased and the settlement contracted to a defended position along the lines of the old British fort at the river terrace's southern end.City of Worcester"The Late Roman and Post-Roman Settlement, 4th century ‚Äď 680". Worcester City Council (Worcester), 2005.
/ref>
Anglo-Saxon town
The form of the place name varied over time. At its settlement in the 7th century, by the Angles of Mercia, it was ''Weogorna''. After centuries of warfare against the Vikings and Danelaw it had become a centre for the Anglo-Saxon army or ''here'' known as ''Weogorna ceastre'' (Worcester Camp). TheWeorgoran
The Weogoran (Old English: "people of the winding river") were a people of Saxon England, a precursor of the minor kingdom of Hwicce. The Weogoran were centred on Worcester ('). They were probably (though not certainly) West Saxons and occup ...
were probably a sub-tribe of the larger kingdom of the Hwicce
Hwicce () was a kingdom in Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon England. According to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', the kingdom was established in 577, after the Battle of Deorham. After 628, the kingdom became a client or sub-kingdom of Mercia as a result ...
, which occupied present-day Worcestershire, Gloucestershire and western Wiltshire. In 680, Worcester was chosen as their fort over the larger Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city, non-metropolitan district and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West England, South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean ...
, and the royal court at Winchcombe
Winchcombe () is a market town and civil parish in the Borough of Tewkesbury in the county of Gloucestershire, England, situated northeast of Cheltenham. The population was recorded as 4,538 in the 2011 United Kingdom census, 2011 census and ...
as the episcopal see
An episcopal see is the area of a bishop's ecclesiastical jurisdiction.
Phrases concerning actions occurring within or outside an episcopal see are indicative of the geographical significance of the term, making it synonymous with ''diocese'' ...
of a new bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
, suggesting there was already an established and powerful Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
community.
 Worcester became a centre of monastic learning and church power.
Worcester became a centre of monastic learning and church power. Oswald of Worcester
Oswald of Worcester (died 29 February 992) was Archbishop of York from 972 to his death in 992. He was of Danish ancestry, but brought up by his uncle, Oda of Canterbury, who sent him to France to the abbey of Fleury to become a monk. After a ...
, appointed Bishop in 961, was an important reformer alongside the Archbishop of York. The last Anglo-Saxon Bishop of Worcester, St Wulfstan or Wulstan, was a reformer, who remained in office until he died in 1095.
The city became a focus of violent tax resistance against the monarch Harthacnut
Harthacnut (; "Tough-knot"; ‚Äď 8 June 1042), traditionally Hardicanute, sometimes referred to as Canute III, was King of Denmark from 1035 to 1042 and King of England from 1040 to 1042.
Harthacnut was the son of King Cnut the Great (wh ...
(also King of Denmark) in 1041. The townspeople tried to defend themselves by occupying the Severn island of Bevere, two miles up river. After Harthacnut's men had sacked the city and set it alight, agreement was reached and the populace returned to rebuild.
Medieval
Norman Conquest
The first Norman Sheriff of Worcestershire,Urse d'Abetot
Urse d'Abetot (‚Äď1108) was a Norman who followed King William I to England, and became Sheriff of Worcestershire and a royal official under him and Kings William II and Henry I. He was a native of Normandy and moved to England shortly after t ...
oversaw the construction of a new castle at Worcester,Barlow ''William Rufus'' p. 152 although nothing now remains of the castle.Pettifer ''English Castles'' p. 280 Worcester Castle
Worcester Castle was a Norman people, Norman fortification built between 1068 and 1069 in Worcester, England, Worcester, England by Urse d'Abetot on behalf of William the Conqueror. The castle had a motte-and-bailey design and was located on the ...
was in place by 1069. Its outer bailey was built on land that had previously been the cemetery for the monks of the Worcester cathedral chapter.Williams "Introduction" ''Digital Domesday'' "Norman Settlement" section The motte
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or Bailey (castle), bailey, surrounded by a protective Rampart (fortificati ...
of the castle overlooked the river, just south of the cathedral.Holt "Worcester in the Time of Wulfstan" ''St Wulfstan and His World'' pp. 132‚Äď133.
Early medieval
Worcester's growth and position as a market town for goods and produce rested on its river crossing and bridge and its position on the road network. The nearest Severn bridges in the 14th century were atGloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city, non-metropolitan district and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West England, South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean ...
and Bridgnorth
Bridgnorth is a market town and civil parish in Shropshire, England. The River Severn splits it into High Town and Low Town, the upper town on the right bank and the lower on the left bank of the River Severn. The population at the United Kingd ...
. The main road from London to mid-Wales ran through Worcester, then north-west to Kidderminster
Kidderminster is a market town and civil parish in Worcestershire, England, south-west of Birmingham and north of Worcester, England, Worcester. Located north of the River Stour, Worcestershire, River Stour and east of the River Severn, in th ...
, Bridgnorth and Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury ( , ) is a market town and civil parish in Shropshire (district), Shropshire, England. It is sited on the River Severn, northwest of Wolverhampton, west of Telford, southeast of Wrexham and north of Hereford. At the 2021 United ...
, and via Bromsgrove
Bromsgrove is a town in Worcestershire, England, about north-east of Worcester and south-west of Birmingham city centre. It had a population of 34,755 in at the 2021 census. It gives its name to the wider Bromsgrove District, of which it is ...
to Coventry
Coventry ( or rarely ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands county, in England, on the River Sherbourne. Coventry had been a large settlement for centurie ...
and on to Derby
Derby ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area on the River Derwent, Derbyshire, River Derwent in Derbyshire, England. Derbyshire is named after Derby, which was its original co ...
. Southward it connected with Tewkesbury
Tewkesbury ( ) is a market town and civil parish in the north of Gloucestershire, England. The town grew following the construction of Tewkesbury Abbey in the twelfth century and played a significant role in the Wars of the Roses. It stands at ...
and Gloucester.
Worcester was a centre of religious life. The several monasteries up to the dissolution included Greyfriars, Blackfriars, the Penitent Sisters, and the Benedictine Priory, now Worcester Cathedral. Monastic houses provided hospital and educational services, including Worcester School.
The 12th-century town (then better defended) was attacked in 1139, 1150 and 1151 during the civil war between King Stephen and Empress Matilda
Empress Matilda (10 September 1167), also known as Empress Maud, was one of the claimants to the English throne during the civil war known as the Anarchy. The daughter and heir of Henry I, king of England and ruler of Normandy, she went to ...
, daughter of Henry I Henry I or Henri I may refer to:
:''In chronological order''
* Henry I the Fowler, King of Germany (876‚Äď936)
* Henry I, Duke of Bavaria (died 955)
* Henry I of Austria, Margrave of Austria (died 1018)
* Henry I of France (1008‚Äď1060)
* Henry ...
. The 1139 attack again resulted in a fire that destroyed part of the city, with citizens being held for ransom. Another fire in 1189 destroyed much of the city for the fourth time that century.
Worcester received its first royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but ...
in 1189. In 1227 under a new charter allowed a guild of merchants was created, with a trading monopoly for those admitted. Worcester's institutions grew more slowly than those of most county towns.
Jewish persecution and expulsions
Worcester had a smallJewish population
the world's core Jewish population (those identifying as Jews above all else) was estimated at 15.8 million, which is approximately 0.2% of the 8 billion worldwide population. Israel hosts the largest core Jewish population in the world with ...
by the late 12th century. Jewish life probably centred round what is now Copenhagen Street. The Diocese was hostile to the Jewish community. Peter of Blois
Peter of Blois (; French: ''Pierre de Blois''; ) was a French cleric, theologian, poet and diplomat. He is particularly noted for his corpus of Latin letters.
Early life and education
Peter of Blois was born about 1130. Earlier opinion tended t ...
was commissioned by a Bishop of Worcester, probably John of Coutances
John of Coutances was a medieval Bishop of Worcester.
John was a nephew of Walter of Coutances, Bishop of Lincoln and was treasurer of the diocese of Lisieux before his uncle appointed him Archdeacon of Oxford sometime before December 1184. He a ...
, to write an anti-Judaic treatise around 1190. William de Blois as Bishop of Worcester imposed strict rules on Jews within the diocese in 1219. As elsewhere in England, Jews had to wear square white badges, supposedly representing ''tabulae''. Blois wrote to Pope Gregory IX
Pope Gregory IX (; born Ugolino di Conti; 1145 ‚Äď 22 August 1241) was head of the Catholic Church and the ruler of the Papal States from 19 March 1227 until his death in 1241. He is known for issuing the '' Decretales'' and instituting the Pa ...
in 1229 to request further powers of enforcement. In 1263 Worcester's Jewish residents were attacked by a baronial force under Robert Earl Ferrers and Henry de Montfort
Sir Henry de Montfort (November 1238 – 4 August 1265) was the son of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, and with his father played an important role in the struggle of the barons against Henry III of England, King Henry III. Henry's ...
. Most were killed. The Worcester massacre was part of a wider campaign by allies of Simon de Montfort
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, 1st Earl of Chester ( ‚Äď 4 August 1265), also known as Simon V de Montfort, was an English nobleman of French origin and a member of the English peerage, who led the baronial opposition to the rule of ...
at the start of the Second Barons' War
The Second Barons' War (1264‚Äď1267) was a civil war in Kingdom of England, England between the forces of barons led by Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, Simon de Montfort against the royalist forces of Henry III of England, King Hen ...
. In January 1275, Jews still in Worcester were expelled to Hereford
Hereford ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of the ceremonial county of Herefordshire, England. It is on the banks of the River Wye and lies east of the border with Wales, north-west of Gloucester and south-west of Worcester. With ...
.
Late medieval
Worcester elected its Member of Parliament at the Guildhall, by the loudest shout rather than the raising of hands. Members of Parliament had to own freehold property worth 40 shillings a year. Their wages were levied by the Constable.Craft guilds
Medieval and early modern Worcester developed a system of craftguild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular territory. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradespeople belonging to a professional association. They so ...
s to regulate who could work in a trade, lay down trade practices and training, and provide social support for members. The city's late medieval ordinances banned tilers from forming a guild and encouraged tilers to settle in Worcester to trade freely. Roofs of thatch and wooden chimneys were banned to reduce risks of fire.
Early modern period
The Dissolution saw the Priory's status change, as it lost its Benedictine monks. As elsewhere, Worcester had to set up "public" schools to replace monastic education. This led to the establishment of King's School. Worcester School continued to teach. St Oswald's Hospital survived the dissolution, later providingalmshouses
An almshouse (also known as a bede-house, poorhouse, or hospital) is charitable organization, charitable public housing, housing provided to people in a particular community, especially during the Middle Ages. They were often built for the povert ...
; the charity and its housing survives to the present day.
The city gained the right to elect a mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a Municipal corporation, municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilitie ...
, and was designated a county corporate
A county corporate or corporate county was a type of subnational division used for the administration of justice in certain towns and cities in England, Wales, and Ireland. They arose when the monarch gave a borough corporation the right to appoi ...
in 1621, giving it autonomy from local government. Thereafter Worcester was governed by a mayor, recorder and six aldermen. Councillors were selected by co-option.
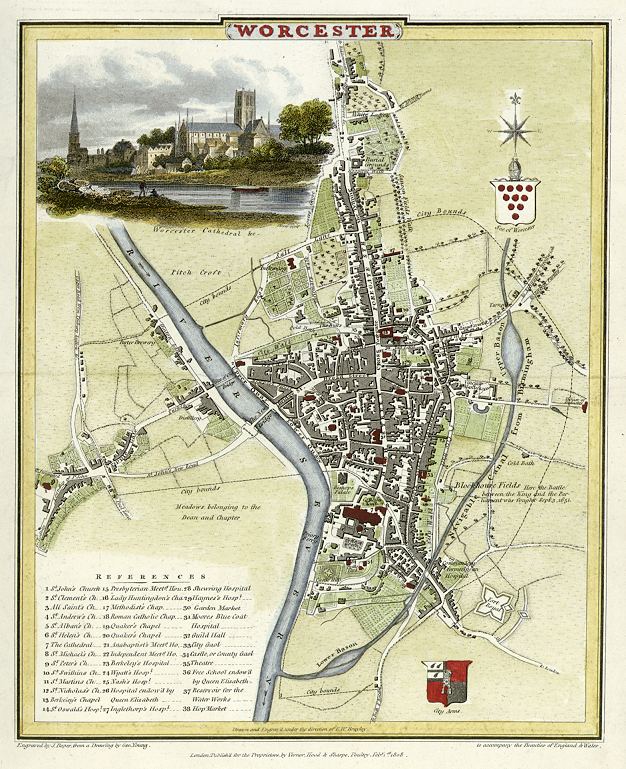
Worcester contained green spaces such as orchards and fields between its main streets, within the city wall, as appears on Speed
In kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a non-negative scalar quantity. Intro ...
's map of 1610. The walls were still more or less complete at the time, but suburbs had been established beyond them.
Civil war
 Worcester equivocated, then sided with Parliament before the outbreak of the
Worcester equivocated, then sided with Parliament before the outbreak of the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
in 1642 but was swiftly occupied by the Royalists. Parliament briefly retook the city after the Battle of Powick Bridge
The battle of Powick Bridge was a skirmish fought on 23 September 1642 south of Worcester, England, during the First English Civil War. It was the first engagement between elements of the principal field armies of the Royalists and Parliament ...
of September 1642, and ransacked the cathedral, where stained glass was smashed and the organ destroyed, along with library books and monuments.
The Parliamentary commander, the Earl of Essex
Earl of Essex is a title in the Peerage of England which was first created in the 12th century by King Stephen of England. The title has been recreated eight times from its original inception, beginning with a new first Earl upon each new cre ...
was soon forced to withdraw, and the city spent the rest of the war under Royalist occupation. Worcester was a garrison town and had to sustain and billet a large number of Royalist troops. During the Royalist occupation, the suburbs were destroyed to make defence easier. High taxation was imposed, and many male residents pressed into the army.
As Royalist power collapsed in May 1646, Worcester was placed under siege. Worcester had some 5,000 civilians and a Royalist garrison of about 1,500 men facing a New Model Army
The New Model Army or New Modelled Army was a standing army formed in 1645 by the Parliamentarians during the First English Civil War, then disbanded after the Stuart Restoration in 1660. It differed from other armies employed in the 1639 t ...
force of 2,500‚Äď5,000. The city surrendered on 23 July.
In 1651 a Scottish army, 16,000 strong, marched south along the west coast in support of Charles II's attempt to regain the Crown. As the army approached, Worcester Council voted to surrender, fearing further violence and destruction. The Parliamentary garrison withdrew to Evesham
Evesham () is a market town and Civil parishes in England, parish in the Wychavon district of Worcestershire, in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands region of England. It is located roughly equidistant between Worcester, England, Worceste ...
in the face of the overwhelming numbers against them. The Scots were billeted in and around the city, joined by very limited local forces.
The Battle of Worcester
The Battle of Worcester took place on 3 September 1651 in and around the city of Worcester, England and was the last major battle of the 1642 to 1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms. A Parliamentarian army of around 28,000 under Oliver Cromwell def ...
took place on 3 September 1651. Charles II was easily defeated by Cromwell's forces of 30,000 men. Charles II returned to his headquarters in what is now known as King Charles House in the Cornmarket, before fleeing in disguise with help of one of his officers, Francis Talbot to Boscobel House
Boscobel House () is a Grade II* listed building in the parish of Boscobel in Shropshire. It has been, at various times, a farmhouse, a hunting lodge, and a holiday home; but it is most famous for its role in the escape of Charles II after the ...
in Shropshire
Shropshire (; abbreviated SalopAlso used officially as the name of the county from 1974‚Äď1980. The demonym for inhabitants of the county "Salopian" derives from this name.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the West M ...
, from where he eventually escaped to France. Worcester was then heavily looted by the Parliamentarian army. The city council estimated £80,000 of damage was done and subsequent debts were still not recovered in the 1670s.
After the Restoration
After therestoration of the monarchy
Restoration is the act of restoring something to its original state. This may refer to:
*Conservation and restoration of cultural property
**Audio restoration
**Conservation and restoration of immovable cultural property
**Film restoration
** Image ...
in 1660, Worcester cleverly used its location as the site of the final battles of the First Civil War (1646) and Third Civil War (1651) to mount an appeal for compensation from Charles II. Though not based on historical fact, it invented the epithet ''Fidelis Civitas'' (The Faithful City), since included in the city's coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon f ...
.
During the 18th century Worcester experienced significant economic growth, and in 1748 Daniel Defoe
Daniel Defoe (; born Daniel Foe; 1660 ‚Äď 24 April 1731) was an English writer, merchant and spy. He is most famous for his novel ''Robinson Crusoe'', published in 1719, which is claimed to be second only to the Bible in its number of translati ...
could note that 'the inhabitants are generally esteemed rich, being full of business, occasioned chiefly by the clothing-trade'. The Royal Worcester Porcelain Company was established at Warmstry Slip in 1751, and from the later 18th century the city became a major centre for the glove
A glove is a garment covering the hand, with separate sheaths or openings for each finger including the thumb. Gloves protect and comfort hands against cold or heat, damage by friction, abrasion or chemicals, and disease; or in turn to provide a ...
making industry.
The wealth of 18th- and 19th-century Worcester is reflected in the city's architecture, which has been described as 'one of the most impressive Georgian streetscapes in the Midlands'. Many public buildings were built or rebuilt in this period, including the Grade I listed Worcester Guildhall
The Worcester Guildhall is a municipal building in the High Street, Worcester, England. It is a Grade I listed building.
History and architecture
The first guildhall on the site was a timber-framed structure constructed as a meeting place for l ...
, the city bridge, and the Royal Infirmary. Large stretches of the city walls were removed by 1796, allowing for continued expansion along Foregate Street, The Tything, and Upper Tything, and many townhouses were built or remodelled in brick.
Worcester was a popular destination for wealthy visitors, who came to the annual Three Choirs Festival
200px, Worcester cathedral
200px, Gloucester cathedral
The Three Choirs Festival is a music festival held annually at the end of July, rotating among the cathedrals of the Three Counties (Hereford, Gloucester, and Worcester) and originally fe ...
and horse races on Pitchcroft
Worcester Racecourse is a thoroughbred horse racing venue located in the city of Worcester, Worcestershire, England.'' British Racing and Racecourses'' () by Marion Rose Halpenny - Page 247 Horse racing has taken place here since at least 1718. ...
. However, parts of the city suffered from significant poverty, and in 1794 a large workhouse
In Britain and Ireland, a workhouse (, lit. "poor-house") was a total institution where those unable to support themselves financially were offered accommodation and employment. In Scotland, they were usually known as Scottish poorhouse, poorh ...
was built on the edge of the city at Tallow Hill.
Industrial revolution and Victorian era
 Worcester in the late 18th and early 19th centuries was a major centre for glove-making, employing nearly half the glovers in England at its peak (over 30,000 people). employed by 150 firms. At this time nearly half the glove makers in Britain could be found in Worcestershire. In the 19th century, the industry declined as import taxes on foreign competitors, mainly French, were much reduced.
Riots took place in 1831, in response to the defeat of the
Worcester in the late 18th and early 19th centuries was a major centre for glove-making, employing nearly half the glovers in England at its peak (over 30,000 people). employed by 150 firms. At this time nearly half the glove makers in Britain could be found in Worcestershire. In the 19th century, the industry declined as import taxes on foreign competitors, mainly French, were much reduced.
Riots took place in 1831, in response to the defeat of the Reform Bill
The Reform Acts (or Reform Bills, before they were passed) are legislation enacted in the United Kingdom in the 19th and 20th century to enfranchise new groups of voters and to redistribute seats in the House of Commons of the Parliament of the U ...
, reflecting discontent with the city administration and the lack of democratic representation. Citizens petitioned the House of Lords for permission to build a County Hall. Local government reform took place in 1835, which for the first time created election procedures for councillors, but also restricted the ability of the city to buy and sell property. Political corruption, particularly bribing of voters, was endemic in Parliamentary elections, contributing to a string of Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civiliza ...
victories even against a wider swing to the Liberals, and was investigated in the 1890s and by a Royal Commission
A royal commission is a major ad-hoc formal public inquiry into a defined issue in some monarchies. They have been held in the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Norway, Malaysia, Mauritius and Saudi Arabia. In republics an equi ...
in 1906.
The British Medical Association
The British Medical Association (BMA) is a registered trade union and professional body for physician, doctors in the United Kingdom. It does not regulate or certify doctors, a responsibility which lies with the General Medical Council. The BMA ...
(BMA) was founded in the Board Room of the old Worcester Royal Infirmary building in Castle Street in 1832. Corn trading which had taken place in the Corn Market on the east side of the city moved to the new Corn Exchange
A corn exchange is a building where merchants trade grains. The word "corn" in British English denotes all cereal grains, such as wheat and barley; in the United States these buildings were called grain exchanges. Such trade was common in towns ...
in Angel Street in the mid-19th century.
The Kays Kays or KAYS may refer to:
* KAYS (AM), a radio station
* Waycross-Ware County Airport, by ICAO code
* Kays Catalogues, a former UK mail order catalogue
* Kays Ruiz-Atil, French footballer
* Kays of Scotland, a manufacturer and supplier of curling ...
mail-order business was founded in Worcester in 1889 and operated from various premises in the city until 2007. It was then bought out by Reality, owner of the Grattan catalogue. The Kays warehouse was demolished in 2008 and replaced by housing.
In 1815 the Worcester and Birmingham Canal
The Worcester and Birmingham Canal is a canal linking Birmingham and Worcester in England. It starts in Worcester, as an 'offshoot' of the River Severn (just after the river lock) and ends in Gas Street Basin in Birmingham. It is long.
There ...
opened. Railways reached Worcester in 1850, with Shrub Hill, initially only running to Birmingham. Foregate Street was opened in 1860. The WMR lines became part of the Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, ...
after 1 August 1863. The railways gave Worcester jobs building passenger coaches and signalling. Alongside Worcester Shrub Hill station in Shrub Hill Road were the Worcester Engine Works. Their polychrome
Polychrome is the "practice of decorating architectural elements, sculpture, etc., in a variety of colors." The term is used to refer to certain styles of architecture, pottery, or sculpture in multiple colors.
When looking at artworks and ...
brick building was erected about 1864 and probably designed by Thomas Dickson. However, only 84 locomotives were built there and the works closed in 1871. The chairman was Alexander Clunes Sheriff
Alexander Clunes Sheriff (1816 ‚Äď 17 March 1878) was an English businessman and Liberal Party politician who was active in local government and sat in the House of Commons from 1865 to his death in 1878.
Sheriff was the son of A. Sherriff. He w ...
.Debretts House of Commons and the Judicial Bench 1870/ref> In 1882 Worcester hosted the Worcestershire Exhibition with sections for fine arts, historical manuscripts and industrial items, receiving over 222,000 visitors.
20th century to present
The Foregate Street cast-iron railway bridge was remodelled by theGreat Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, ...
in 1908 with a decorative cast-iron exterior serving no structural purpose. Rail reorganisation in 1922 saw the Midland Railway's routes from Shrub Hill absorbed into the London, Midland and Scottish Railway
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMSIt has been argued that the initials LMSR should be used to be consistent with London and North Eastern Railway, LNER, Great Western Railway, GWR and Southern Railway (UK), SR. The London, Midland an ...
.
By the mid-20th century, only a few Worcester glove firms survived, as gloves became less fashionable and free trade enabled cheaper imports from the Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
. Nevertheless, at least three glove manufacturers survived into the late 20th century: Dent Allcroft, Fownes and Milore. In the 1940s, some Jewish refugees from Europe settled in Worcester. Emil Rich, a refugee from Germany, founded one of Worcester's last remaining glovemakers, Milore Glove Factory. Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 19268 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. ...
's coronation gloves were designed by Emil Rich and manufactured in the Worcester factory.
Worcester was a centre for recruitment of soldiers to fight in the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 ‚Äď 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, into the Worcestershire Regiment
The Worcestershire Regiment was a line infantry regiment in the British Army, formed in 1881 under the Childers Reforms by the amalgamation of the 29th (Worcestershire) Regiment of Foot and the 36th (Herefordshire) Regiment of Foot. The regiment ...
, based at Norton Barracks
Norton Barracks is a former military installation in Norton, Worcestershire. The keep is a Grade II listed building.
History
The barracks were built in the Fortress Gothic Revival Style between 1874 and 1877. Their creation took place as part o ...
. The regiment took part in early battles in the war, most notably at the Battle of Gheluvelt in October 1914. The Vicar of St Paul's, Geoffrey Studdert Kennedy, became an army chaplain, later known as 'Woodbine Willy', as he brought cigarettes to soldiers during fighting and exposed himself to physical danger.
The inter-war years saw rapid growth in engineering and machine-tool manufacturing firms such as James Archdale and H. W. Ward, castings for the motor industry from Worcester Windshields and Casements, valve design and manufacture from Alley & MacLellan, Sentinel Valve Works, mining machinery from Mining Engineering Company (MECO) ‚Äď later part of Joy Mining Machinery ‚Äď and open-top cans from Williamsons, although G. H. Williamson and Sons had become part of the Metal Box Co in 1930. Later the company became Carnaud Metal Box PLC.
During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 ‚Äď 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the city was chosen to be the seat of an evacuated government in case of mass German invasion. The War Cabinet, along with Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 ‚Äď 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
and some 16,000 state workers, would have moved to Hindlip Hall
Hindlip Hall is a stately home in Hindlip, Worcestershire, England. The first major hall was built before 1575, and it played a significant role in both the Babington and the Gunpowder plots, where it hid four people in priest holes. It was H ...
(now part of the complex forming the Headquarters of West Mercia Police
West Mercia Police (), formerly the West Mercia Constabulary, is the territorial police force responsible for policing the counties of Herefordshire, Shropshire (including Telford and Wrekin) and Worcestershire in England. The force area cover ...
), north of Worcester. The former RAF station RAF Worcester
Royal Air Force Worcester, or more simply RAF Worcester, is a former Royal Air Force relief landing ground (RLG) which was located north east of Worcester city centre, Worcestershire, England and south west of Droitwich Spa, Worcestershire.
...
was located north-east of Worcester.
A fuel-storage depot was built for the government in 1941‚Äď42 by Shell-Mex and BP
Shell-Mex and BP Limited was a British joint venture between petroleum companies Shell and BP. It was formed in 1932 when both companies decided to merge their United Kingdom marketing operations,Reference and contact details: GB 1566 SMBP Title: ...
(later operated by Texaco
Texaco, Inc. ("The Texas Company") is an American Petroleum, oil brand owned and operated by Chevron Corporation. Its flagship product is its Gasoline, fuel "Texaco with Techron". It also owned the Havoline motor oil brand. Texaco was an Independ ...
) on the eastern bank of the River Severn, about a mile south of Worcester. It was at one time used as a civil reserve storing gas oil and then aviation kerosene for USAFE. It closed in the early 1990s. Worcester Porcelain operated in Worcester until 2009, when the factory closed due to the recession.
In the 1950s and 1960s large areas of the medieval centre of Worcester were demolished and rebuilt. This was condemned by many such as Nikolaus Pevsner
Sir Nikolaus Bernhard Leon Pevsner (30 January 1902 ‚Äď 18 August 1983) was a German-British art historian and architectural historian best known for his monumental 46-volume series of county-by-county guides, ''The Buildings of England'' (195 ...
who described it as a "totally incomprehensible... act of self-mutilation". There is however still a significant area of medieval Worcester remaining, examples of which can be seen along City Walls Road, Friar Street and New Street.
Governance
There are two tiers of local government covering Worcester, atdistrict
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municip ...
(city) and county
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
level: Worcester City Council
Worcester City Council is the local authority for Worcester, a non-metropolitan district with city status in Worcestershire, England. The council consists of 35 councillors, elected from 15 wards.
History
Worcester was an ancient borough whi ...
and Worcestershire County Council
Worcestershire County Council is the county council for the non-metropolitan county of Worcestershire in England. Its headquarters are at County Hall in Worcester, the county town. The council consists of 57 councillors and there is no over ...
. There are two civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government. Civil parishes can trace their origin to the ancient system of parishes, w ...
es within the city at Warndon
Warndon is a northeastern suburb of Worcester in Worcestershire, England. It is also a civil parish which is named after the suburb.
The parish, which includes the villages of Trotshill and Warndon was part of Droitwich Rural District until 1 ...
and St Peter the Great County, which form a third tier of local government in those areas; the rest of the city is an unparished area
In England, an unparished area is an area that is not covered by a civil parish (the lowest level of local government, not to be confused with an ecclesiastical parish). Most urbanised districts of England are either entirely or partly unparis ...
. Worcester forms one of the six local government districts
The districts of England (officially, local authority districts, abbreviated LADs) are a level of subnational division of England used for the purposes of local government. As the structure of local government in England is not uniform, there ...
within the county.
Worcester City Council is based at Worcester Guildhall
The Worcester Guildhall is a municipal building in the High Street, Worcester, England. It is a Grade I listed building.
History and architecture
The first guildhall on the site was a timber-framed structure constructed as a meeting place for l ...
on the High Street in the city centre. Worcestershire County Council also has its headquarters in Worcester, being based at County Hall in Spetchley Road, on the eastern outskirts of the city.
Worcester was an ancient borough
An ancient borough was a historic unit of lower-tier local government in England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the Law of the United Kingdom#Legal jurisdictions, three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the co ...
which had held city status
City status is a symbolic and legal designation given by a monarch, national or subnational government. A municipality may receive city status because it already has the qualities of a city, or because it has some special purpose.
Historically, ci ...
from time immemorial
Time immemorial () is a phrase meaning time extending beyond the reach of memory, record, or tradition, indefinitely ancient, "ancient beyond memory or record". The phrase is used in legally significant contexts as well as in common parlance.
...
. When elected county councils were established in 1889, the city was considered large enough to run its own county-level services and so it became a county borough, independent from the surrounding Worcestershire County Council.
Worcester was reformed to become a non-metropolitan district
Non-metropolitan districts, or colloquially "shire districts", are a type of Districts of England, local government district in England. As created, they are sub-divisions of non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties (colloquially ''s ...
in 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
. The city had its territory enlarged, gaining the parishes of Warndon
Warndon is a northeastern suburb of Worcester in Worcestershire, England. It is also a civil parish which is named after the suburb.
The parish, which includes the villages of Trotshill and Warndon was part of Droitwich Rural District until 1 ...
and St Peter the Great County, and it was transferred to the short-lived county of Hereford and Worcester
Hereford and Worcester ( ) was an English non-metropolitan county created on 1 April 1974 by the Local Government Act 1972 from the areas of the former administrative county of Herefordshire, most of Worcestershire (except Halesowen, Stourbridg ...
. Hereford and Worcester was abolished in 1998, since when a re-established Worcestershire County Council has been the upper-tier authority for Worcester.
Worcester's one Member of Parliament (MP) is Tom Collins
The Tom Collins is a Collins cocktail made from gin, lemon juice, sugar, and carbonated water. This "gin and sparkling lemonade" drink is typically served in a Collins glass over ice with a cherry garnish. A non-alcoholic "Collins mix" drink mi ...
of the Labour Party, who has represented the Worcester constituency since the July 2024 general election.
Coat of arms
The city of Worcester is unusual among English cities in having an arms of alliance as the main part of its coat of arms. The shield on thedexter
Dexter may refer to:
People
* Dexter (given name)
* Dexter (surname)
* Dexter (singer), Brazilian rapper Marcos Fernandes de Omena (born 1973)
* Famous Dex, also known as Dexter, American rapper Dexter Tiewon Gore Jr. (born 1993)
Places United ...
side is the "ancient" arms: ''Quarterly sable
The sable (''Martes zibellina'') is a species of marten, a small omnivorous mammal primarily inhabiting the forest environments of Russia, from the Ural Mountains throughout Siberia, and northern Mongolia. Its habitat also borders eastern Kaz ...
and gules
In heraldry, gules () is the tincture with the colour red. It is one of the class of five dark tinctures called "colours", the others being azure (blue), sable (black), vert (green) and purpure (purple).
Gules is portrayed in heraldic hatch ...
, a castle triple-towered argent
In heraldry, argent () is the tincture of silver, and belongs to the class of light tinctures called "metals". It is very frequently depicted as white and usually considered interchangeable with it. In engravings and line drawings, regions to b ...
''. First recorded in 1569 but probably older, there is little doubt that it refers to Worcester Castle, now vanished. The shield on the sinister
Sinister commonly refers to:
* Evil
* Ominous
Sinister may also refer to:
Left side
* Sinister, Latin for the direction "left"
* Sinister, in heraldry, is the bearer's true left side (viewers' right side) of an escutcheon or coat of arms; see dex ...
side is the "modern" arms: ''Argent, a fess between three pears sable''. Despite its name, the modern arms goes back to 1634. It is said to represent a visit of Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
to the city in 1575, when according to folklore, she saw a tree with black pears on Foregate and was so impressed with it that she allowed Worcester to have pears on its coat of arms. The city has used several mottos: one is ''Floreat semper fidelis civitas'', Latin for "Let the faithful city ever flourish", while the one currently used is ''Civitas in bello et pace fidelis'' (A city faithful in peace and war). Both refer to Worcester's support for Royalists in the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
.
Geography
The district is bounded by the districts ofMalvern Hills
The Malvern Hills are in the English counties of Worcestershire, Herefordshire and a small area of northern Gloucestershire, dominating the surrounding countryside and the towns and villages of the district of Malvern. The highest summit af ...
to the west, and Wychavon
Wychavon () is a local government district in Worcestershire, England. The largest towns therein are Evesham and Droitwich Spa; the council is based in the town of Pershore. The district also includes numerous villages and surrounding rural ...
to the east. The population of the local government district in 2021 was 103,837. The built up area extends slightly beyond the city boundaries in places and had a population in 2021 of 105,465.
Notable suburbs include Barbourne, Blackpole, Cherry Orchard, Claines
Claines is a village to the north of Worcester in the county of Worcestershire, England. It is located on the east bank of the River Severn. Claines is situated in the heart of Worcestershire on the A449 between Worcester and Kidderminster. It ...
, Diglis
Diglis is an inner-city area and suburb of Worcester in Worcestershire, England. It is located around half a mile south of the city centre on the banks of River Severn. The Worcester and Birmingham Canal starts in Diglis, connected to the Seve ...
, Dines Green, Henwick, Northwick, Red Hill, Ronkswood, St Peter the Great (also known as St Peter's), Tolladine, Warndon
Warndon is a northeastern suburb of Worcester in Worcestershire, England. It is also a civil parish which is named after the suburb.
The parish, which includes the villages of Trotshill and Warndon was part of Droitwich Rural District until 1 ...
and Warndon Villages. Most of Worcester is on the eastern side of the River Severn
The River Severn (, ), at long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in t ...
. However, Henwick, Lower Wick
Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is situated about five miles south west of Dursley, eighteen miles southwest of Gloucester and fifteen miles northeast of Bristol. Lower Wick is within the civil ...
, St John's and Dines Green are on the western side.
Climate
Worcester enjoys a temperate climate with generally warm summers and mild winters. However, it can experience more extreme weather and flooding is often a problem. In 1670, theRiver Severn
The River Severn (, ), at long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in t ...
burst its banks in the worst flood ever seen by the city. The closest flood height to the Flood of 1670 was when torrential rains caused the Severn to flood in July 2007, which is recorded in the Diglis Basin
Diglis Basin is a canal basin on the Worcester and Birmingham Canal. It is situated in Diglis in the centre of Worcester, England, near The Commandery (a command post during the English Civil War).
To the north is Tibberton (8.41 miles an ...
. This recurred in 2014.
During the winters of 2009‚Äď2010 and 2010‚Äď2011, the city underwent long periods of sub-freezing temperatures and heavy snowfalls. In December 2010 the temperature dropped to in nearby Pershore. The Severn and the River Teme partly froze over in Worcester during this cold period. By contrast, Worcester recorded a temperature on 2 August 1990. Between 1990 and 2003, weather data for the area was collected at Barbourne, Worcester. Since the closure of this weather station, the nearest is located at Pershore.

Green belt
Worcester is in a regionalgreen belt
A green belt or greenbelt is a policy, and land-use zone designation used in land-use planning to retain areas of largely undeveloped, wilderness, wild, or agricultural landscape, land surrounding or neighboring urban areas. Similar concepts ...
that extends into the surrounding counties. It is set to reduce urban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city". Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted ...
between the cities and towns in the nearby West Midlands conurbations centred round Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
and Coventry
Coventry ( or rarely ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands county, in England, on the River Sherbourne. Coventry had been a large settlement for centurie ...
, to discourage further convergence, protect the identity of outlying communities, encourage brownfield
Brownfield is previously-developed land that has been abandoned or underused, and which may carry pollution, or a risk of pollution, from industrial use. The specific definition of brownfield land varies and is decided by policy makers and l ...
reuse, and preserve nearby countryside
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry are typically describ ...
. This is done by restricting inappropriate development within the designated areas and imposing strict conditions on permitted building.
Within the city boundary, there is a small area of green belt north of the Worcester and Birmingham canal and of the Perdiswell and Northwick suburbs. This is part of a larger isolated tract south of the main green belt that extends into the adjacent Wychavon district, minimising urban sprawl between Fernhill Heath and Droitwich Spa, and keeping them separate. The green belt was first drawn up under Worcestershire County Council
Worcestershire County Council is the county council for the non-metropolitan county of Worcestershire in England. Its headquarters are at County Hall in Worcester, the county town. The council consists of 57 councillors and there is no over ...
in 1975; the size within the borough in 2017 amounted to some .
Demography and religion
The 2011 census put Worcester's population at 98,768. About 93.4 per cent were classed as white, of whom 89.1 percentage points wereWhite British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the White population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population was 49 ...
‚Äď higher than the national average. The largest religious group consists of Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
, with 63.7 per cent of the city's population. Those reporting no religion or declining to state an allegiance make up 32.3 per cent. The next largest religious group, Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
, makes up 2.9 per cent. The ethnic minorities include people of Pakistani
Pakistanis (, ) are the citizens and nationals of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. Pakistan is the fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the second-largest Muslim population as of 2023. As much as ...
, Bangladeshi
Bangladeshis ( ) are the citizens and nationals of Bangladesh, a South Asian country centred on the transnational historical region of Bengal along the Bay of Bengal, eponymous bay.
Bangladeshi nationality law, Bangladeshi citizenship was fo ...
, Chinese
Chinese may refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China.
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic ...
, Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Associated with India
* of or related to India
** Indian people
** Indian diaspora
** Languages of India
** Indian English, a dialect of the English language
** Indian cuisine
Associated with indigenous peoples o ...
, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
and Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Polish people, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
* Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin ...
origin, the largest single group being British Pakistanis
British Pakistanis (; also known as Pakistani British people or Pakistani Britons) are British people, Britons or residents of the United Kingdom whose ancestral roots lie in Pakistan. This includes people born in the UK who are of Pakistani ...
, numbering around 1,900: 1.95 per cent of the population. This has led to Worcester containing a small but diverse range of religious groups; as well as the prominent Anglican Worcester Cathedral
Worcester Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of Christ and Blessed Mary the Virgin, is a Church of England cathedral in Worcester, England, Worcester, England. The cathedral is the seat of the bishop of Worcester and is the Mother Church# ...
, there are also Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, United Reformed
The United Reformed Church (URC) is a Protestant Christian church in the United Kingdom. As of 2024 it had approximately 44,000 members in around 1,250 congregations with 334 stipendiary ministers.
The URC is a Trinitarian church whose theolog ...
and Baptist
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches ge ...
churches, a large centre for the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, denomination and the ...
, a small number of Islamic
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
mosques and a number of smaller groups for oriental religions such as Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
and the International Society for Krishna Consciousness
The International Society for Krishna Consciousness (ISKCON), commonly known as the Hare Krishna movement, is a religious organization that follows the Gaudiya Vaishnava tradition of Hinduism. It was founded on 13 July 1966 in New York City by ...
.
Worcester is the seat of a Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
bishop, whose official signature is the personal Christian name followed by ''Wigorn''. (abbreviating the Latin ''Wigorniensis'', meaning ''of Worcester''). This is also used occasionally to abbreviate the name of the county. The previous Archdeacon of Worcester
An archdeacon is a senior clergy position in the Church of the East, Chaldean Catholic Church, Syriac Orthodox Church, Anglican Communion, St Thomas Christians, Eastern Orthodox churches and some other Christian denominations, above that of most ...
, Robert Jones, inducted in November 2014, had been Rector of St Barnabas with Christ Church in Worcester for eight years. He retired on 30 November 2023
Economy
Manufacturing
One of Worcester's famous products,Lea & Perrins
Lea & Perrins (L&P) is a United Kingdom-based subsidiary of Kraft Heinz, originating in Worcester, England where it continues to operate. It is the manufacturer of Lea & Perrins Worcestershire sauce, a condiment first invented and sold in 1837 ...
Worcestershire sauce
Worcestershire sauce or Worcester sauce (UK: ) is a fermented liquid condiment invented by pharmacists John Wheeley Lea and William Henry Perrins in the city of Worcester in Worcestershire, England, during the first half of the 19th century ...
, is made and bottled at a Midland Road factory, its home since 16 October 1897. Messrs Lea and Perrins originally partnered a chemist's shop on the site of the Debenhams's store in Crowngate Shopping Centre.
Worcester has what is claimed to be the oldest newspaper in the world still in publication: ''Berrow's Worcester Journal
''Berrow's Worcester Journal'' is a weekly freesheet tabloid newspaper, based in Worcester, England. Owned by Newsquest, the newspaper is delivered across central and southern Worcestershire.
History
16th century printing press
Worcester was ...
''. It traces its descent from a news-sheet started in 1690.
The foundry heritage of the city is represented by Morganite Crucible at Norton which produces graphitic shaped products and cements for use in the modern industry. The city is home to the European manufacturing plant of Yamazaki Mazak Corporation
is a Japanese machine tool builder based in Oguchi, Japan. In most of the world they are referred to as Mazak.
History
The company was founded in 1919 in Nagoya by Sadakichi Yamazaki as a small company making pots and pans. During the 1920s i ...
, a global Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
ese machine tool builder A machine tool builder is a corporation or person that builds machine tools, usually for sale to manufacturing, manufacturers, who use them to manufacture products. A machine tool builder runs a machine factory, which is part of the machine industry ...
established here in 1980.
Worcester Heating Systems was started in the city in 1962 by Cecil Duckworth. The company was bought by Bosch and renamed Worcester Bosch in 1996.
Retail trade
The city is a major retail centre, with several covered shopping centres to accommodate the major chains and many independent shops and restaurants, particularly in Friar Street and New Street. Worcester's main shopping centre is the High Street, with several major retail chains. The High Street was controversially part-modernised in 2005, and further modernised in 2015; with current redevelopment of Cathedral Plaza and Lychgate Shopping Centre. Much of the protest came at the felling of old trees, the duration of the work (caused by weather and an archaeological find) and removal of flagstones outside the city's 18th-century Guildhall. The other main thoroughfares are the Shambles and Broad Street. The Cross and its immediate surrounding area are the city's financial centre for most of Worcester's main bank branches. There are three main covered shopping centres in the city centre: CrownGate Shopping Centre, Cathedral Plaza and Reindeer Court. There is also an unenclosed shopping area immediately east of the city centre called St Martin's Quarter. There are three retail parks, the Elgar and Blackpole retail parks located in theinner suburb
An inner suburb is a suburban community central to a large city, or at the inner city and central business district. The urban density is usually lower than the inner city or central business district, but higher than that of the city's rural‚ ...
of Blackpole, and the Shrub Hill Retail Park in neighbouring St Martin's Quarter. Retailers such as Asda
Asda Stores Limited (), trading as Asda and often styled as ASDA, is a British supermarket and petrol station chain. Its headquarters is in Leeds, England. The company was incorporated as Associated Dairies and Farm Stores in 1949. It expanded ...
, B&M and Aldi
Aldi (German pronunciation: ), stylised as ALDI, is the common company brand name of two German multinational family-owned discount supermarket chains operating over 12,000 stores in 18 countries. The chain was founded by brothers Karl and ...
are all located close to St Martin's Quarter.
Attractions
The most famous landmark in Worcester is the AnglicanWorcester Cathedral
Worcester Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of Christ and Blessed Mary the Virgin, is a Church of England cathedral in Worcester, England, Worcester, England. The cathedral is the seat of the bishop of Worcester and is the Mother Church# ...
. Officially the Cathedral Church of Christ and the Blessed Virgin Mary, it was known as Worcester Priory before the English Reformation
The English Reformation began in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away first from the authority of the pope and bishops Oath_of_Supremacy, over the King and then from some doctrines and practices of the Catholic Church ...
. Construction began in 1084. Its crypt dates from the 11th century. It includes the only circular chapter house in the country. It houses the tombs of King John and Prince Arthur.
Near the cathedral is the spire of St Andrew's Church, known as Glover's Needle. The rest of the church was demolished in 1949.
The Parish Church of St Helen, on the north side of the High Street, is mainly medieval, with a west tower rebuilt in 1813. The east end, re-fenestration and porch were completed by Frederick Preedy
Frederick Preedy (2 June 1820 – 28 March 1898) was an architect and glass painter in England.
Life
Preedy was born in Offenham near Evesham in Worcestershire and died at his son's home in Croydon. During his early life, his family moved f ...
in 1857‚Äď1863. There was further restoration, by Aston Webb
Sir Aston Webb, (22 May 1849 ‚Äď 21 August 1930) was a British architect who designed the principal facade of Buckingham Palace and the main building of the Victoria and Albert Museum, among other major works around England, many of them in par ...
in 1879‚Äď1880. It is a Grade II*listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Hi ...
.
The high-water marks from the flood of 1670 and more recent flood levels are shown on a brass plate on a wall adjacent to the path along the river that leads to the cathedral.
Museums include Worcester City Art Gallery and Museum, Greyfriars' House, the Infirmary Museum, Tudor House Museum, George Marshall Medical Museum, RAF Defford Museum, Museum of Royal Worcester, Mercian Regiment Museum, the Commandery, and Worcestershire Yeomanry Museum. The Battle of Worcester site is just south of the city. Limited parts of Worcester's city wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or Earthworks (military), earthworks to extensive military fortifications such as ...
remain.
The Hive, on the north side of the River Severn
The River Severn (, ), at long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in t ...
at the former cattle market site, is Worcester's joint public and university library and archive centre, heralded as "the first of its kind in Europe", and a prominent feature on the skyline. With seven towers and a golden rooftop, it has gained recognition, winning two international awards
An award, sometimes called a distinction, is given to a recipient as a token of recognition of excellence in a certain field. When the token is a medal, ribbon or other item designed for wearing, it is known as a decoration.
An award may be d ...
for building design and sustainability.
The city's three main open spaces Cripplegate Park, Gheluvelt Park and Fort Royal Park, the last on the site of an English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
battle. In addition, there is an open area known as Pitchcroft to the north of the city centre on the east bank of the River Severn
The River Severn (, ), at long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in t ...
, which is a public space except on days when it is used for horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance activity, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its bas ...
. Gheluvelt Park commemorates the part played by Worcestershire Regiment
The Worcestershire Regiment was a line infantry regiment in the British Army, formed in 1881 under the Childers Reforms by the amalgamation of the 29th (Worcestershire) Regiment of Foot and the 36th (Herefordshire) Regiment of Foot. The regiment ...
's 2nd Battalion in the Battle of Gheluvelt in the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 ‚Äď 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
.
 A statue of Sir Edward Elgar, commissioned from Kenneth Potts and unveiled in 1981, stands at the end of Worcester High Street facing the cathedral, yards from the original location of his father's music shop, which was demolished in the 1960s. Elgar's birthplace was the nearby village of Broadheath. Plaques installed in the city include a dedication to the medieval Jewish community at Copenhagen Street.
There are two large wooded areas in the city, Perry Wood and Nunnery Wood, covering 12 and 21 hectares. Perry Wood is often said to be where
A statue of Sir Edward Elgar, commissioned from Kenneth Potts and unveiled in 1981, stands at the end of Worcester High Street facing the cathedral, yards from the original location of his father's music shop, which was demolished in the 1960s. Elgar's birthplace was the nearby village of Broadheath. Plaques installed in the city include a dedication to the medieval Jewish community at Copenhagen Street.
There are two large wooded areas in the city, Perry Wood and Nunnery Wood, covering 12 and 21 hectares. Perry Wood is often said to be where Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in British history. He came to prominence during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially ...
met and made a pact with the Devil. Nunnery Wood is integral to the adjacent Worcester Woods Country Park, itself next door to County Hall on the east side of the city.
Transport

Road
TheM5 Motorway
The M5 is a motorway in England linking the Midlands with the South West England, South West. It runs from junction 8 of the M6 motorway, M6 at West Bromwich near Birmingham to Exeter in Devon. Heading south-west, the M5 runs east of West Brom ...
runs north‚Äďsouth immediately to the east of the city. It is accessed by junction 6 (Worcester North) and junction 7 (Worcester South). It connects Worcester to most parts of the country, including London, which is only using the A44 via the Cotswolds
The Cotswolds ( ) is a region of central South West England, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper River Thames to an escarpment above the Severn Valley and the Vale of Evesham. The area is defined by the bedroc ...
and M40. A faster journey to London is possible via the M5, M42 and M40, but with an increased distance of .
The main roads through the city include the A449 road
The A449 is a major road in the United Kingdom. It runs north from junction 24 of the A48 road at Newport in South Wales to Stafford in Staffordshire.
The southern section of the road, between Ross on Wye and Newport forms part of the trun ...
south-west to Malvern and north to Kidderminster
Kidderminster is a market town and civil parish in Worcestershire, England, south-west of Birmingham and north of Worcester, England, Worcester. Located north of the River Stour, Worcestershire, River Stour and east of the River Severn, in th ...
. The A44 runs south-east to Evesham
Evesham () is a market town and Civil parishes in England, parish in the Wychavon district of Worcestershire, in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands region of England. It is located roughly equidistant between Worcester, England, Worceste ...
and west to Leominster
Leominster ( ) is a market town in Herefordshire, England; it is located at the confluence of the River Lugg and its tributary the River Kenwater. The town is north of Hereford and south of Ludlow in Shropshire. With a population of almos ...
and Aberystwyth
Aberystwyth (; ) is a University town, university and seaside town and a community (Wales), community in Ceredigion, Wales. It is the largest town in Ceredigion and from Aberaeron, the county's other administrative centre. In 2021, the popula ...
and crosses Worcester Bridge. The A38 trunk road runs south to Tewkesbury
Tewkesbury ( ) is a market town and civil parish in the north of Gloucestershire, England. The town grew following the construction of Tewkesbury Abbey in the twelfth century and played a significant role in the Wars of the Roses. It stands at ...
and Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city, non-metropolitan district and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West England, South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean ...
and north-north-east to Droitwich
Droitwich Spa (often abbreviated to Droitwich ) is an historic spa town in the Wychavon district in northern Worcestershire, England, on the River Salwarpe. It is located approximately south-west of Birmingham and north-east of Worcester.
...
and Bromsgrove
Bromsgrove is a town in Worcestershire, England, about north-east of Worcester and south-west of Birmingham city centre. It had a population of 34,755 in at the 2021 census. It gives its name to the wider Bromsgrove District, of which it is ...
and Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
. The A4103
The A4103 is an A-road which runs from Worcester to the A480 in Stretton Sugwas, a village west of Hereford. The road is a primary route as far as the junction with the A465 east of Hereford, and is liable to flooding at Bransford, where it ...
goes west-south-west to Hereford
Hereford ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of the ceremonial county of Herefordshire, England. It is on the banks of the River Wye and lies east of the border with Wales, north-west of Gloucester and south-west of Worcester. With ...
. The A422
The A422 is an "A" road for east‚Äďwest journeys in south central England, connecting the county towns of Bedford and Worcester by way of Milton Keynes, Buckingham, Brackley, Banbury and Stratford-upon-Avon. For most of its length, it is a nar ...
heads east to Alcester
Alcester ( ) is a market town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in the Stratford-on-Avon District in Warwickshire, England. It is west of Stratford-upon-Avon, and 7 miles south of Redditch. The town dates back to the times of Roman ...
, branching from the A44 a mile east of the M5. The city is partly ringed by A4440.
Carrington Bridge on the A4440 is the second road bridge across the Severn, linking the A38 from Worcester towards Gloucester with the A449 to Malvern. It is one of Worcestershire's busiest roads. The single-carriageway bridge was doubled with work being completed on 5 August 2022, making the Southern Link Road dual between junction 7 of the M5 and Powick Roundabout.
Rail
 Worcester has three railway stations. and are in the city centre. A third station on the edge of the city, , opened in 2020.
The
Worcester has three railway stations. and are in the city centre. A third station on the edge of the city, , opened in 2020.
The Cotswold line
The Cotswold Line is an railway line between and in England.
History Early years
The line between Oxford and Worcester was built under an 1845 Act of Parliament and opened in 1851 as part of the Oxford, Worcester and Wolverhampton Railway ...
towards Great Malvern
Great Malvern is an area of the civil parish of Malvern, Worcestershire, Malvern, in the Malvern Hills District, Malvern Hills district, in the county of Worcestershire, England. It lies at the foot of the Malvern Hills, a designated Area of O ...
and Hereford
Hereford ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of the ceremonial county of Herefordshire, England. It is on the banks of the River Wye and lies east of the border with Wales, north-west of Gloucester and south-west of Worcester. With ...
crosses Foregate Street on an arched cast-iron bridge. Between Foregate Street and the St John's area of the city, heading towards Malvern and Hereford, the line crosses the Worcester viaduct over the River Severn.
Worcester Shrub Hill lies about a mile east of the city centre on Shrub Hill Road. It is on part of today's Cross Country Route
The Cross Country Route is a long-distance railway route in England, which runs from to via , , and or . Inter-city services on the route, which include some of the longest passenger journeys in the UK such as to , are operated by CrossC ...
, looping off the Birmingham to Gloucester railway.
Both stations have frequent trains to Birmingham via Droitwich Spa
Droitwich Spa (often abbreviated to Droitwich ) is an historic spa town in the Wychavon district in northern Worcestershire, England, on the River Salwarpe. It is located approximately south-west of Birmingham and north-east of Worcester.
T ...
, through Kidderminster
Kidderminster is a market town and civil parish in Worcestershire, England, south-west of Birmingham and north of Worcester, England, Worcester. Located north of the River Stour, Worcestershire, River Stour and east of the River Severn, in th ...
and Stourbridge
Stourbridge () is a market town in the Metropolitan Borough of Dudley in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. Situated on the River Stour, Worcestershire, River Stour, the town lies around west of Birmingham,
at the southwester ...
into Birmingham Snow Hill and Birmingham Moor Street
Birmingham Moor Street, also known as Moor Street station, is one of three main railway stations in the city centre of Birmingham, England, along with Birmingham New Street and Birmingham Snow Hill.
Today's Moor Street station is a combinati ...
then onwards usually to Dorridge
Dorridge is a large village in the Metropolitan Borough of Solihull in the West Midlands (county), England. Historically part of the historic county of Warwickshire, the village is encompassed within the electoral ward of Dorridge and Hockley He ...
or Whitlocks End, or via Bromsgrove
Bromsgrove is a town in Worcestershire, England, about north-east of Worcester and south-west of Birmingham city centre. It had a population of 34,755 in at the 2021 census. It gives its name to the wider Bromsgrove District, of which it is ...
and University
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
and Birmingham New Street
Birmingham New Street, also known as New Street station, is the largest and busiest of the three main railway stations in Birmingham city centre, England, and a central hub of the British railway system. It is a major destination for Avanti ...
. These services are run by West Midlands Trains
West Midlands Trains (WMT) is a British train operating company. It operates passenger trains on the West Midlands franchise between London and the English Midlands under two trading names: within the West Midlands region as West Midlands Rai ...
. From both stations, trains run to Pershore
Pershore () is a market town and civil parish in the Wychavon district in Worcestershire, England, on the banks of the River Avon, Warwickshire, River Avon. At the 2011 UK census, census, the population was 7,125. The town is best known for Per ...
, Evesham
Evesham () is a market town and Civil parishes in England, parish in the Wychavon district of Worcestershire, in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands region of England. It is located roughly equidistant between Worcester, England, Worceste ...
and onto the Cotswolds, Oxford
Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town.
The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuou ...
and London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
.
Buses
The main operator in and around the city is . A few smaller operators provide services in Worcester, including Astons, DRM and LMS Travel. Diamond Bus operates a service fromKidderminster
Kidderminster is a market town and civil parish in Worcestershire, England, south-west of Birmingham and north of Worcester, England, Worcester. Located north of the River Stour, Worcestershire, River Stour and east of the River Severn, in th ...
to communities along the A449. The terminus and interchange for many bus services is Crowngate bus station in the city centre.
 The city had two park and ride sites: off the A38 in Perdiswell and at
The city had two park and ride sites: off the A38 in Perdiswell and at Sixways Stadium
Sixways Stadium is a stadium in Worcester, England. It is currently used for rugby union and association football matches and is the home stadium of Premier 15s side Worcester Warriors Women, football side Worcester Raiders F.C., Worcester Ra ...
next to the M5. Worcestershire County Council
Worcestershire County Council is the county council for the non-metropolitan county of Worcestershire in England. Its headquarters are at County Hall in Worcester, the county town. The council consists of 57 councillors and there is no over ...
voted to close both in 2014 as part of a package of cutbacks. The service at Sixways Stadium has since been reinstated, with LMS Travel operating the W3 route to Worcestershire Royal Hospital
The Worcestershire Royal Hospital is an acute general hospital located in Charles Hastings Way in Worcester, England. It is managed by the Worcestershire Acute Hospitals NHS Trust. The hospital replaced the Worcester Royal Infirmary in 2002 as the ...
, but avoiding the city centre bus station.
Air
Worcester's nearest major airport isBirmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
, which is accessible by road and rail. Gloucestershire Airport
Gloucestershire Airport , formerly Staverton Airport, is a small airport located in Churchdown, England. It lies west of Cheltenham, near the city of Gloucester and close to the M5 motorway. Its operator claims it to be Gloucestershire's larg ...
is about 25 miles away and provided general aviation connections and scheduled services with Citywing
Citywing (a trading name of Citywing Aviation Services Limited) was an Isle of Man-based company that sold seats on scheduled air flights operated under charter. Flights linked several airports in the British Isles, with the company having a ba ...
to Jersey
Jersey ( ; ), officially the Bailiwick of Jersey, is an autonomous and self-governing island territory of the British Islands. Although as a British Crown Dependency it is not a sovereign state, it has its own distinguishing civil and gov ...
, the Isle of Man
The Isle of Man ( , also ), or Mann ( ), is a self-governing British Crown Dependency in the Irish Sea, between Great Britain and Ireland. As head of state, Charles III holds the title Lord of Mann and is represented by a Lieutenant Govern ...
and Belfast
Belfast (, , , ; from ) is the capital city and principal port of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan and connected to the open sea through Belfast Lough and the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel ...
. Citywing ceased trading in 2017 after entering administration.
Cycling
Worcester is on routes 45 and 46 of the National Cycle Network. There are various routes around the city.Diglis
Diglis is an inner-city area and suburb of Worcester in Worcestershire, England. It is located around half a mile south of the city centre on the banks of River Severn. The Worcester and Birmingham Canal starts in Diglis, connected to the Seve ...
Bridge, a pedestrian and Cycle bridge across the Severn, opened in 2010 to St Peter's with Lower Wick
Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is situated about five miles south west of Dursley, eighteen miles southwest of Gloucester and fifteen miles northeast of Bristol. Lower Wick is within the civil ...
. Beryl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium Silicate minerals#Cyclosilicates, silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and Aquamarine (gem), aquamarine. Naturally occurring Hex ...
bikes were introduced in 2024 to hire across Worcester, providing 175 e-bikes and 50 pedal bikes, from a network of 53 bays.
Waterways
TheRiver Severn
The River Severn (, ), at long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in t ...
is navigable through Worcester, and here it links to the Worcester and Birmingham Canal
The Worcester and Birmingham Canal is a canal linking Birmingham and Worcester in England. It starts in Worcester, as an 'offshoot' of the River Severn (just after the river lock) and ends in Gas Street Basin in Birmingham. It is long.
There ...
, which connects Worcester with Birmingham and the rest of the national canal network. Historically used for the transport of goods, the canal network is now mostly used for leisure boating.
Education
TheUniversity of Worcester
The University of Worcester is a public research university, based in Worcester, England. With a history dating back to 1946, the university began awarding degrees in 1997 and was granted full university status in 2005.
History
In 1946 an Emerg ...
was awarded university status in 2005 by the Privy Council, having been known since 1997 as University College Worcester (UCW) and before that as Worcester College of Higher Education. From 2005 to 2010 it was the fastest growing university in the UK, more than doubling its student population. The university has an independent Worcester Students Union institution. The city is also home to two colleges, Worcester Sixth Form College
Worcester Sixth Form College is a 16-19 Academy in Worcester, England. It is located in the south-east of the city and was founded on the site of the former Worcester Grammar School for Girls following reorganisation in 1983. The College joine ...
and Heart of Worcestershire College
Heart of Worcestershire College is an academic institution with campuses at Worcester, Malvern, Redditch and Bromsgrove. It was established in August 2014 on the merging of Worcester College of Technology and North East Worcestershire College ...
.
High schools
The high schools located in the city are Bishop Perowne CofE College,Blessed Edward Oldcorne Catholic College
Blessed Edward Oldcorne Catholic College is a coeducational Roman Catholic secondary school located in Worcester, England, locally referred to as "Blesseds". It is a co-educational school, in which there are just over 1,000 students, aged bet ...
, Christopher Whitehead Language College, Tudor Grange Academy Worcester, Nunnery Wood High School
Nunnery Wood High School is a coeducational secondary school which is located in Worcester, Worcestershire, England. The school campus is located on the edge of Worcester, surrounded by some of gardens and playing fields, which it shares with th ...
and New College Worcester
New College Worcester (or NCW; formerly RNIB New College) is an independent boarding and day school for students, aged 11‚Äď19, who are blind or partially sighted. It caters for around 80 students. It is located in the city of Worcester, Engl ...
, which caters for blind and partially sighted pupils aged 11‚Äď18.
Independent schools
Worcester is the seat of numerousindependent schools
A private school or independent school is a school not administered or funded by the government, unlike a public school. Private schools are schools that are not dependent upon national or local government to finance their financial endowme ...
. The Royal Grammar School (founded in 1291) and Alice Ottley School
The Alice Ottley School was an independent all-girls' school in Worcester that existed under this name ‚Äď referencing its first headmistress ‚Äď between 1883 and 2007 before it merged with the Worcester Royal Grammar School. She had already r ...
merged in 2007. The King's School was re-founded in 1541 under King Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
, and is a co-educational day school standing next to Worcester Cathedral
Worcester Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of Christ and Blessed Mary the Virgin, is a Church of England cathedral in Worcester, England, Worcester, England. The cathedral is the seat of the bishop of Worcester and is the Mother Church# ...
. St Mary's School, a girls' Catholic school, was the one remaining single-sex independent school, but closed in July 2014. Other independent schools include the Independent Christian School, the River School in Fernhill Heath
Fernhill Heath is a village in Worcestershire, England. It is in the civil parish of North Claines in Wychavon
Wychavon () is a local government district in Worcestershire, England. The largest towns therein are Evesham and Droitwich Spa ...
and New College Worcester
New College Worcester (or NCW; formerly RNIB New College) is an independent boarding and day school for students, aged 11‚Äď19, who are blind or partially sighted. It caters for around 80 students. It is located in the city of Worcester, Engl ...
.
Hospitals
TheWorcestershire Royal Hospital
The Worcestershire Royal Hospital is an acute general hospital located in Charles Hastings Way in Worcester, England. It is managed by the Worcestershire Acute Hospitals NHS Trust. The hospital replaced the Worcester Royal Infirmary in 2002 as the ...
is the principal NHS
The National Health Service (NHS) is the term for the publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom: the National Health Service (England), NHS Scotland, NHS Wales, and Health and Social Care (Northern ...
hospital serving the city and county of Worcester. It opened in 2002, replacing the Worcester Royal Infirmary.
The former Worcester Eye Hospital was based in the Grade II listed Thornloe House, Barbourne Road, from 1940 to 1995.
St Oswald's Hospital on the Tything was founded as alsmhouses and is now a care home.
Sport
*Worcestershire County Cricket Club
Worcestershire County Cricket Club is one of eighteen first-class county clubs within the domestic cricket structure of England and Wales. It represents the historic county of Worcestershire. Its Vitality Blast T20 team has been rebranded ...
, whose home ground is New Road
* Worcester City Football Club
*Worcester Sorcerers Baseball Club, whose home ground is Norton Parish Hall
*Worcester Hockey Club has teams entered in the West Hockey Leagues.
*Worcester St Johns Cycling Club
*Worcester Wolves
The Worcester Wolves are a basketball club in Worcester, England, Worcester, England. The team plays in the National Basketball League (England), NBL Division 2, the third tier of British basketball. The club was formed in 2000, and from 2006 u ...
, a professional basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
team in the British Basketball League
The British Basketball League (BBL) was a men's professional basketball sports league, league in Great Britain. Since its establishment in 1987 the BBL represented the highest level of basketball competition within the United Kingdom. The orga ...
, plays at the Worcester Arena.
*Worcester Racecourse
Worcester Racecourse is a thoroughbred horse racing venue located in the city of Worcester, Worcestershire, England.'' British Racing and Racecourses'' () by Marion Rose Halpenny - Page 247 Horse racing has taken place here since at least 1718 ...
is on an open area known as "Pitchcroft" on the east bank of the River Severn
The River Severn (, ), at long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in t ...
.
*Worcester Rugby Football Club is an amateur rugby union club, founded in 1871.
* Worcester Raiders F.C., is a professional football club.
*Worcester Warriors
Worcester Warriors are a professional rugby union club based in Worcester, England. They most recently played in Premiership Rugby, the top division of English rugby union, before being suspended by the Rugby Football Union, RFU in September 2 ...
, is a professional rugby union club.
Culture
Festivals and shows
Every three years Worcester becomes home to theThree Choirs Festival
200px, Worcester cathedral
200px, Gloucester cathedral
The Three Choirs Festival is a music festival held annually at the end of July, rotating among the cathedrals of the Three Counties (Hereford, Gloucester, and Worcester) and originally fe ...
, which dates from the 18th century and is credited with being the oldest music festival in the British Isles. The location rotates between the cathedral cities of Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city, non-metropolitan district and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West England, South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean ...
, Hereford
Hereford ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of the ceremonial county of Herefordshire, England. It is on the banks of the River Wye and lies east of the border with Wales, north-west of Gloucester and south-west of Worcester. With ...
and Worcester. Famous for championing English music, especially that of Elgar
Sir Edward William Elgar, 1st Baronet, (; 2 June 1857 ‚Äď 23 February 1934) was an English composer, many of whose works have entered the British and international classical concert repertoire. Among his best-known compositions are orchestr ...
, Vaughan Williams
Ralph Vaughan Williams ( ; 12 October 1872‚Äď 26 August 1958) was an English composer. His works include operas, ballets, chamber music, secular and religious vocal pieces and orchestral compositions including nine symphonies, written over ...
and Gustav Holst
Gustav Theodore Holst (born Gustavus Theodore von Holst; 21 September 1874 ‚Äď 25 May 1934) was an English composer, arranger and teacher. Best known for his orchestral suite ''The Planets'', he composed many other works across a range ...
, Worcester hosted the festival in July 2017, but had to postpone its 2020 festival until 2021.
The Worcester Festival (established in 2003 by Chris Jaeger MBE) occurs in August and consists of music, theatre, cinema
Cinema may refer to:
Film
* Film or movie, a series of still images that create the illusion of moving image
** Film industry, the technological and commercial institutions of filmmaking
** Filmmaking, the process of making a film
* Movie theate ...
and workshop events, along with a beer festival.
For one weekend a year the city plays host to the Worcester Music Festival ‚Äď a weekend of original music performed predominantly by local bands and musicians. All performances are free and take place around the city centre in bars, clubs, community buildings, churches and the central library.
Founded in 2012, the Worcester Film Festival, places Worcestershire on the film-making map and encourages local people to get involved in making film. The first festival took place at the Hive and included screenings, workshops and talks.
The Victorian-themed Christmas Fayre is a busy event in late November/early December, with over 200 stalls lining the streets, and over 100,000 visitors.
The CAMRA
The Campaign for Real Ale (CAMRA) is an independent voluntary consumer organisation headquartered in St Albans, which promotes real ale, real cider, cider and perry and traditional British pubs and clubs.
History
The organisation was founde ...
Worcester Beer, Cider and Perry Festival takes place for three days each August on Pitchcroft Race Course. It is the largest beer festival in the West Midlands and in the UK top ten with attendances of around 14,000.
The Worcester Vegan Market began in 2021 and takes place in late spring and fall. The Vegan Market fills High Street and Cathedral Square with vegan vendors, vegan food sellers, and vegan food trucks.
Arts and cinema
 The famous 18th-century actress
The famous 18th-century actress Sarah Siddons
Sarah Siddons (''n√©e'' Kemble; 5 July 1755 ‚Äď 8 June 1831) was a Welsh actress, the best-known Tragedy, tragedienne of the 18th century. Contemporaneous critic William Hazlitt dubbed Siddons as "tragedy personified".
She was the elder siste ...
made her acting début at the Theatre Royal in Angel Street. Her sister, the novelist Ann Julia Kemble Hatton, otherwise Ann of Swansea, was born in the city. Also born in Worcester was Matilda Alice Powles, better known as Vesta Tilley
Matilda Alice Powles, Lady de Frece (13May 186416September 1952) was an English music hall performer. She adopted the stage name Vesta Tilley and became one of the best-known male impersonators of her era. Her career lasted from 1869 until 19 ...
, a leading male impersonator and music hall artiste.
In present-day Worcester, the Swan Theatre Swan Theatre may refer to:
* The Swan (theatre), an Elizabethan playhouse
* Swan Theatre, Stratford-upon-Avon, a theatre belonging to the Royal Shakespeare Company in Stratford-upon-Avon, England
* Swan Theatre, Worcester
The Swan Theatre is a t ...
stages professional touring and local amateur productions and is the base for the Worcester Repertory Company. Past heads have included John Doyle and David Wood OBE. The current artistic director of the company and the theatre is Chris Jaeger MBE.
Stars who started their careers in the Worcester Repertory Company and the Swan Theatre Swan Theatre may refer to:
* The Swan (theatre), an Elizabethan playhouse
* Swan Theatre, Stratford-upon-Avon, a theatre belonging to the Royal Shakespeare Company in Stratford-upon-Avon, England
* Swan Theatre, Worcester
The Swan Theatre is a t ...
include Imelda Staunton
Dame Imelda Mary Philomena Bernadette Staunton (born 9 January 1956) is an English actress and singer. After training at the Royal Academy of Dramatic Art, Staunton began her career in repertory theatre in 1976 and appeared in various theatre pr ...
, Sean Pertwee
Sean Carl Roland Pertwee (born 4 June 1964) is an English actor, narrator and producer. His credits include ''Chancer'' (1990), '' Leon the Pig Farmer'' (1992), '' Cadfael'' (1994), ''Bodyguards'' (1997), ''Event Horizon'' (1997), '' Stiff Upp ...
, Celia Imrie
Celia Diana Savile Imrie (born 15 July 1952) is a British actress and author. She is best known for her film roles, including the '' Bridget Jones'' film series, '' Calendar Girls'' (2003), '' Nanny McPhee'' (2005), '' The Best Exotic Marigold ...
, Rufus Norris
Sir Rufus John Norris (born 16 January 1965) is a British theatre and film director, who was the artistic director and chief executive of the National Theatre from 2015 to 2025. He received the Society of London Theatre Special Award in 2025 f ...
, Kevin Whately
Kevin Whately OBE (born 6 February 1951) is an English actor. He is best known for his roles as Neville "Nev" Hope in the comedy drama ''Auf Wiedersehen, Pet''; Robert "Robbie" Lewis in the British crime drama ''Inspector Morse'' (1987‚Äď2000) ...
and Bonnie Langford
Bonita Melody Lysette Langford (born 22 July 1964) is an English actress, dancer and singer. She came to prominence as a child star in the 1970s, when she had a notable role in the TV series '' Just William''.
In the 1980s, she played companio ...
. Directors too have made a name for themselves: Phyllida Lloyd
Phyllida Christian Lloyd, (born 17 June 1957) is an English film and theatre director and producer.
Her theatre work includes directing productions at the Royal Court Theatre and Royal National Theatre, and opera director for Opera North and ...
starting her career as an associate under John Doyle.
Huntingdon Hall is a historic church now used as venue for an eclectic range of musical and comedy performances. Recent acts have included Van Morrison
Sir George Ivan "Van" Morrison (born 31 August 1945) is a Northern Irish singer-songwriter and musician whose recording career started in the 1960s. Morrison's albums have performed well in the UK and Ireland, with more than 40 reaching the UK ...
, Eddie Izzard
Suzy Eddie Izzard ( ; born Edward John Izzard, 7 February 1962) is a British stand-up comedian, actor and activist. Her comedic style takes the form of what appears to the audience as rambling whimsical monologues and self-referential pantomi ...
, Jack Dee
James Andrew Innes "Jack" Dee (born 24 September 1961) is an English stand-up comedian, actor, presenter, and writer known for his sarcasm, irony, and deadpan humour. He wrote and starred in the sitcom '' Lead Balloon'' and hosts the panel show ...
, Omid Djalili
Omid Djalili (; born 30 September 1965) is a British comedian, actor, and writer.
Early life and education
Djalili was born on 30 September 1965 in St Mary Abbots Hospital in Kensington, London, to Iranian Bah√° ľ√≠ parents Ahmad and Parvane ...
and Jason Manford
Jason John Manford (born 26 May 1981) is an English comedian, presenter, actor and singer.
Manford was a team captain on the Channel 4 panel show ''8 Out of 10 Cats'' from 2007 until 2010 and has presented numerous television shows for the BBC an ...
.
The Marrs Bar (in Pierpoint Street) is a venue for gigs and stand-up comedy.
Worcester has two multi-screen cinemas; the Vue Cinema complex is located in Friar Street and the Odeon in Foregate Street ‚Äď both were 3D-equipped by March 2010.
Six local cultural organisations are working with Worcester City Council on plans to bring The Scala and Corn Exchange in Angel Place back into use as an arts centre, with investment from the government's Future High Streets Fund. As well as three performance and creative spaces, the Council intends that the two historic buildings will be a hub providing music, film, and other performance facilities.
The northern suburb of Northwick has the Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French (), is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design that first Art Deco in Paris, appeared in Paris in the 1910s just before World War I and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920 ...
Northwick Cinema. Built in 1938, it contains one of only two remaining interiors in Britain designed by John Alexander. The original perspective drawings are held by RIBA
''Riba'' (, or , ) is an Arabic word used in Islamic law and roughly translated as " usury": unjust, exploitative gains made in trade or business. ''Riba'' is mentioned and condemned in several different verses in the Qur'an3:130
. It was a bingo
Bingo or B-I-N-G-O may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Gaming
* Bingo, a game using a printed card of numbers
** Bingo (British version), a game using a printed card of 15 numbers on three lines; most commonly played in the UK and Ireland
** B ...
hall from 1966 to 1982, then empty until 1991, a music venue until 1996, and empty again until autumn 2006, when it became an antiques and lifestyle centre, owned by Grey's Interiors, which was previously located in the Tything.
Worcester was home to the electronic music
Electronic music broadly is a group of music genres that employ electronic musical instruments, circuitry-based music technology and software, or general-purpose electronics (such as personal computers) in its creation. It includes both music ...
producer and collaborator Mike Paradinas
Michael Robert Paradinas (born 26 September 1971), better known by his stage name őľ-Ziq (pronounced "music" or mu-zik), is an English electronic musician from Wimbledon, London. He was associated with the electronic style intelligent dance mus ...
and his record label
"Big Three" music labels
A record label or record company is a brand or trademark of Sound recording and reproduction, music recordings and music videos, or the company that owns it. Sometimes, a record label is also a Music publisher, ...
Planet Mu
Planet Mu is an English electronic music record label created and run by Mike Paradinas. The label started out as a subsidiary of Virgin Records then Paradinas set up the label independent of Virgin. After releasing intelligent dance music, the ...
, until the label moved to London in 2007.
Media
Newspapers
Radio stations
Television
Local news and television programmes are provided byBBC West Midlands
BBC Midlands is the BBC English Regions, BBC English Region producing local radio and World Wide Web, web content for the City of Birmingham, West Midlands (county), West Midlands, Herefordshire, Shropshire, Staffordshire, Warwickshire, Worcest ...
and ITV Central
ITV Central, previously known as Central Independent Television, Carlton Central, ITV1 for Central England and commonly referred to as simply Central, is the Independent Television franchisee in the English Midlands. It was created following ...
from the Ridge Hill TV transmitter.
In popular culture
''Mildred Arkell''
The depression that hit the Worcester glove industry in the 1820s and 1830s is the background to a three-volume novel, ''Mildred Arkell'', by the Victorian novelist Ellen Wood (then Mrs Henry Wood).''Cadfael Chronicles''
The well-researched historical novel ''The Virgin in the Ice
''The Virgin in the Ice'' is a medieval mystery novel by Ellis Peters, set in late 1139. It is the sixth novel in The Cadfael Chronicles, first published in 1982 ( 1982 in literature).
It was adapted for radio by BBC Radio 4 in 1992 and for ...
'', part of Ellis Peters
Edith Mary Pargeter (28 September 1913 ‚Äď 14 October 1995), also known by her pen name Ellis Peters, was an English author of works in many categories, especially history and historical fiction, and was also honoured for her translations of ...
' ''The Cadfael Chronicles
''The Cadfael Chronicles'' is a series of historical murder mysteries written by the English author Edith Pargeter (1913‚Äď1995) under the name Ellis Peters. Set in the 12th century in England during the Anarchy, the novels focus on a Welsh B ...
'' series, depicts Worcester at the time of the Anarchy. It begins with the words:
"It was early in November of 1139 that the tide of civil war, lately so sluggish and inactive, rose suddenly to wash over the city of Worcester, wash away half of its livestock, property and women and send all those of its inhabitants who could get away in time scurrying for their lives northwards away from the marauders." (These are mentioned as arriving fromGloucester Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city, non-metropolitan district and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West England, South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean ..., leaving a long lasting legacy of bitterness between the two cities.)
Twinning
Worcester is twinned with: *Kleve
Kleve (; traditional ; ; ; ; ; Low Rhenish: ''Kleff'') is a town in the Lower Rhine region of northwestern Germany near the Netherlands, Dutch border and the River Rhine. From the 11th century onwards, Cleves was capital of a county and lat ...
, Germany
*Le Vésinet
Le Vésinet () is a suburban Communes of France, commune in the Yvelines Departments of France, department in the Île-de-France Regions of France, region in north-central France. It is a part of the affluent outer suburbs of western Paris, from ...
, France
*Worcester
Worcester may refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Worcester, England, a city and the county town of Worcestershire in England
** Worcester (UK Parliament constituency), an area represented by a Member of Parliament
* Worcester Park, London, Engl ...
, Massachusetts, US
*Ukmergńó
Ukmergńó (; previously ''Vilkmergńó''; ) is a city in Vilnius County, Lithuania, located northwest of Vilnius. It is the administrative center of the Ukmergńó District Municipality.
Ukmergńó (Vilkmergńó) was mentioned for the first time as a ...
, Lithuania
In February 2009 Worcester City Council's Twinning Association began discussing an application to twin Worcester with the Palestinian city of Gaza
Gaza may refer to:
Places Palestine
* Gaza Strip, a Palestinian territory on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea
** Gaza City, a city in the Gaza Strip
** Gaza Governorate, a governorate in the Gaza Strip
Mandatory Palestine
* Gaza Sub ...
. Councillor Alan Amos
Alan Thomas Amos (born 10 November 1952) is a British politician who sat as Conservative Member of Parliament for Hexham from 1987 to 1992. After a spell in the Labour Party, he was elected as a Conservative member of Worcester City Council a ...
introduced the application, which was passed at its first stage by a majority of 35‚Äď6, but later rejected by the executive committee of the City of Worcester Twinning Association for lack of funding.
Notable people
 In birth order:
* Hannah Snell (1723‚Äď1792), famous for impersonating a man and enlisting in the
In birth order:
* Hannah Snell (1723‚Äď1792), famous for impersonating a man and enlisting in the Royal Marines
The Royal Marines provide the United Kingdom's amphibious warfare, amphibious special operations capable commando force, one of the :Fighting Arms of the Royal Navy, five fighting arms of the Royal Navy, a Company (military unit), company str ...
, was born and brought up in Worcester.
* Elizabeth Blower (c. 1757/63 ‚Äď post-1816), novelist, poet and actress, was born and raised in Worcester.
*Ann Hatton
Ann Julia Hatton (Birth name, n√©e Kemble, published as Ann of Swansea; 29 April 1764 ‚Äď 26 December 1838), was a popular novelist in Britain in the early 19th century and author of ''Tammany'', the first known libretto by a woman.
Biography
...
(1764‚Äď1838), writer of the Kemble family, was born in Worcester.
* James White (1775‚Äď1820), founder of first advertising agency in 1800 in London, was born in Worcester.
*John Mathew Gutch
John Mathew Gutch (1776-1861) was an English journalist and historian.
Life
John Mathew, eldest son of John Gutch, was born in 1776, probably at Oxford, and was educated at Christ's Hospital, where he was the schoolfellow of Samuel Taylor Coler ...
(1776‚Äď1861), journalist, lived with his second wife at Barbourne, a suburb north of Worcester, from 1823 until his death.
* Jabez Allies (1787‚Äď1856), a Worcestershire folklorist and antiquarian lived at Lower Wick, now part of Worcester.
*Sir Charles Hastings
Sir Charles Hastings (11 January 1794 ‚Äď 30 July 1866) was a medical surgeon and a founder of the British Medical Association, the BMA, (then known as the Provincial Medical and Surgical Association) on 19 July 1832.
He was also a notable life ...
(1794‚Äď1866), British Medical Association founder, lived in Worcester for most of his life.
* Revd Thomas Davis (1804‚Äď1887), a hymn-writer born in Worcester.
*Philip Henry Gosse
Philip Henry Gosse (; 6 April 1810 ‚Äď 23 August 1888), known to his friends as Henry, was an English natural history, naturalist and populariser of natural science, prolific author, "Father of the Aquarium", scientific illustrator, lecturer, e ...
(1810‚Äď1888), naturalist, was born in Worcester.
* Mrs. Henry Wood (1814‚Äď1887), writer, was born in Worcester.
*Alexander Clunes Sheriff
Alexander Clunes Sheriff (1816 ‚Äď 17 March 1878) was an English businessman and Liberal Party politician who was active in local government and sat in the House of Commons from 1865 to his death in 1878.
Sheriff was the son of A. Sherriff. He w ...
(1816‚Äď1878), City Alderman, businessman and Liberal MP, grew up in Worcester.
*Edward Leader Williams
Sir Edward Leader Williams (28 April 1828 – 1 January 1910) was an English civil engineer, chiefly remembered as the designer of the Manchester Ship Canal, but also heavily involved in other canal projects in north Cheshire.
Early life
W ...
(1828‚Äď1910), designer of the Manchester Ship Canal
The Manchester Ship Canal is a inland waterway in the North West England, North West of England linking Manchester to the Irish Sea. Starting at the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary at Eastham, Merseyside, Eastham, near Ellesmere Port, Cheshire, it ...
, was born and brought up at Diglis House in Worcester.
*Benjamin Williams Leader
Benjamin Williams Leader (12 March 1831 ‚Äď 22 March 1923) was a British landscape painter.
Life and work
Early years and training
Leader was born in Worcester, England, Worcester as Benjamin Leader Williams, the son, and third child of e ...
(1831‚Äď1923), brother of previous, landscape artist
*Sir Thomas Brock
Sir Thomas Brock (1 March 184722 August 1922) was an English sculptor and medallist, notable for the creation of several large public sculptures and monuments in Britain and abroad in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries.
His mo ...
(1847‚Äď1922), sculptor
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sc ...
, best known for the London Victoria Memorial, was born in Worcester in 1847. Worcestershire Royal Hospital is in a road named after him.
*Vesta Tilley
Matilda Alice Powles, Lady de Frece (13May 186416September 1952) was an English music hall performer. She adopted the stage name Vesta Tilley and became one of the best-known male impersonators of her era. Her career lasted from 1869 until 19 ...
(1864‚Äď1952), music hall performer who adopted this stage name aged 11, was born in Worcester. She became a noted male impersonator.
*Sir Edward Elgar
Sir Edward William Elgar, 1st Baronet, (; 2 June 1857 ‚Äď 23 February 1934) was an English composer, many of whose works have entered the British and international classical concert repertoire. Among his best-known compositions are orchestr ...
(1857‚Äď1934), composer, was born in Lower Broadheath, just outside Worcester, and he lived in the city from the age of two. His father ran a music shop in High Street; a statue of Elgar stands near the original site. His early musical career was based around the city, and his first major work was commissioned for the Three Choirs Festival there.
*William Morris, 1st Viscount Nuffield
William Richard Morris, 1st Viscount Nuffield (10 October 1877 ‚Äď 22 August 1963), was an English motor manufacturer and philanthropist. He was the founder of Morris Motors Limited and is remembered for establishing the Nuffield Foundation, th ...
(1877‚Äď1963), founder of Morris Motors and philanthropist, spent the first three years in Worcester.
* Geoffrey Studdert Kennedy (1883‚Äď1929, "Woodbine Willy"), poet and author, was Vicar of St Paul's Church. As an army chaplain in the First World War he would hand out Woodbine cigarettes to men in the trenches.
* Ernest Payne (1884‚Äď1961) was born in Worcester and rode for St Johns Cycling Club, winning a gold medal in team pursuit at the 1908 Summer Olympics
The 1908 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the IV Olympiad and also known as London 1908) were an international multi-sport event held in London, England, from 27 April to 31 October 1908. The 1908 Games were originally schedu ...
in London.
*Sheila Scott
Sheila Christine Scott OBE (n√©e Hopkins; 27 April 1922 ‚Äď 20 October 1988) was an English aviator who broke over 100 aviation records through her long-distance flight endeavours, which included a "world and a half" flight in 1971. On this fl ...
(1922‚Äď1988), aviator, was born in Worcester.
* Louise Johnson (1940‚Äď2012), biochemist and protein crystallographer, was born in Worcester.
*Timothy Garden, Baron Garden
Timothy Garden, Baron Garden (23 April 1944 ‚Äď 9 August 2007) was a senior commander in the Royal Air Force (RAF) who later became a university professor and a Liberal Democrat politician.
Garden gained degrees from both Oxford and Cambridge u ...
(1944‚Äď2007), Air Marshal and Liberal Democrat politician, was born and educated in Worcester.
*Dave Mason
David Thomas Mason (born 10 May 1946) is an English singer-songwriter and guitarist from Worcester, who came to prominence in 1967 as a founding member of the rock band Traffic. While with Traffic, he wrote and sang lead vocals on two of the b ...
(born 1946), musician, singer, songwriter and guitarist, was born in Worcester.
* Martin Gale (born 1949), painter, based in Ireland.
*Lee Cornes
Lee Cornes is an English television actor and writer born in Worcester.
A stand up comedian since 1980, he was a regular compere at London's Comedy Store throughout the 1980s and won best Stand Up Comedian at the Charrington London Fringe Awa ...
(born 1951), comedian and actor known for television roles in ''Blackadder'', ''The Young Ones'' and ''Bottom'' series, was born in Worcester.
* David McGreavy (born 1951, the "Monster of Worcester"), lived and committed child murders in Worcester.
*Imran Khan
Imran Ahmed Khan Niazi (born 5 October 1952) is a Pakistani politician, philanthropist, and former cricketer who served as the 19th prime minister of Pakistan from August 2018 until April 2022. He was the founder of the political party Pak ...
(born 1952), cricketer and Prime Minister of Pakistan, attended the Royal Grammar School Worcester
The Royal Grammar School Worcester (also known as RGS Worcester and RGSW) is an 11-18 co-educational, private day school and sixth form in Worcester, Worcestershire, England. Founded before 1291, it is one of the oldest British independent day ...
and played cricket for Worcestershire County Cricket Club
Worcestershire County Cricket Club is one of eighteen first-class county clubs within the domestic cricket structure of England and Wales. It represents the historic county of Worcestershire. Its Vitality Blast T20 team has been rebranded ...
(1971‚Äď1976).
*Stephen Dorrell
Stephen James Dorrell (born 25 March 1952) is a British Liberal Democrat politician. He served as the Conservative Member of Parliament (MP) for Loughborough between 1979 and 1997 and then for Charnwood from 1997 to 2015.
Dorrell most recen ...
(born 1952), English Conservative politician and former government minister, was born in Worcester.
*Karl Hyde
Karl Hyde (born 10 May 1957) is an English musician, composer and artist. He is a founding member of British electronic group Underworld. Hyde has also released a solo album, made albums with Brian Eno and Matthew Herbert, and contributed towar ...
(born 1957), English musician, frontman of trance music group Underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underworld.
...
was born in Worcester.
*Vincenzo Nicoli
Vincenzo Nicoli (born 27 July 1958) is a British actor who appears in film, television and theatre. He is best known for roles in blockbuster films, such as Alan Jude in the 1992 science fiction film '' Alien³'' (1992), Enrico Biscaglia in the ...
(born 1958), British actor.
*Isabelle Jane Foulkes
Isabelle "Issi" Jane Foulkes (, 12 July 1970 ‚Äď 31 October 2001) was an Anglo-Welsh artist, textile designer and disability campaigner. She designed the Welsh fingerspelling alphabet and worked with charities including Hearing Dogs for Deaf Peo ...
(1970‚Äď2001), Anglo-Welsh artist, textile designer and disability campaigner
*Donncha O'Callaghan
Donncha O'Callaghan (born 24 March 1979) is an Irish retired rugby union player. He spent most of his career with his home province Munster, spending 17 seasons with the province and winning five major trophies, before finishing his career with ...
(born 1979), Irish Rugby Union player. Joined Worcester Warriors in 2015 from Munster Rugby Irish and British and Irish Lions International.
*Ben Humphrey
Ben Humphrey (born 28 May 1986 in Worcester, U.K.) is an English actor, director, writer, lecturer and criminal court Magistrate. He graduated from Bristol Old Vic Theatre School in 2007 and is also an associate of LAMDA.
He was the Artistic ...
(born 1986), British actor, director and writer, associate director of the Worcester Repertory Company.
*Kit Harington
Christopher Catesby Harington (born 26 December 1986), known professionally as Kit Harington, is an English actor. He is best known for his role as Jon Snow (character), Jon Snow in the HBO fantasy television series ''Game of Thrones'' (2011‚Ä ...
(born 1986), actor, lived in Worcester and attended the Chantry School and Worcester Sixth Form College. He plays the character Jon Snow in ''Game of Thrones
''Game of Thrones'' is an American Fantasy television, fantasy Drama (film and television), drama television series created by David Benioff and for HBO. It is an adaptation of ''A Song of Ice and Fire'', a series of high fantasy novels by ...
''.
*Kai Alexander
Kai Alexander (born 7 June 1997) is a British actor. Alexander began his career with roles in the award winning series ''Catastrophe'' and later went on to appear in ''Pistol'', notably playing Richard Branson. He is best known for his role as ...
(born 1997), British actor, born in Worcester.
* Matt Richards (born 2002), British Swimmer, born and raised in Worcester. Double Olympic champion.
Notes
See also
* Jewish community of Worcester *Bishop of Worcester
The Bishop of Worcester is the Ordinary (officer), head of the Church of England Anglican Diocese of Worcester, Diocese of Worcester in the Province of Canterbury, England. The title can be traced back to the foundation of the diocese in the ...
* List of mayors of Worcester
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * *External links
Worcester City Council
{{Authority control Populated places on the River Severn County towns in England Local government in Worcestershire Cities in the West Midlands (region) Towns in Worcestershire Boroughs in England Former civil parishes in Worcestershire