Wimbledon, England on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wimbledon () is a suburb of southwest London, England, southwest of

 The first decades of the 19th century were relatively quiet for Wimbledon, with a stable rural population coexisting alongside nobility and wealthy merchants from the city. Renewed upheaval came in 1838, when the opening of the
The first decades of the 19th century were relatively quiet for Wimbledon, with a stable rural population coexisting alongside nobility and wealthy merchants from the city. Renewed upheaval came in 1838, when the opening of the
 Wimbledon's population continued to grow in the early 20th century, as was recognised in 1905, when the urban district was incorporated as the
Wimbledon's population continued to grow in the early 20th century, as was recognised in 1905, when the urban district was incorporated as the
 In 2012 the businesses in Wimbledon voted to introduce a Business Improvement District. "Love Wimbledon" was formed in April 2012, funded and managed by the business community to promote and enhance the town centre. Those who work within Wimbledon can apply for a 'Privilege Card' which provides discounts and benefits within the town centre.
The UK's leading car-sharing company
In 2012 the businesses in Wimbledon voted to introduce a Business Improvement District. "Love Wimbledon" was formed in April 2012, funded and managed by the business community to promote and enhance the town centre. Those who work within Wimbledon can apply for a 'Privilege Card' which provides discounts and benefits within the town centre.
The UK's leading car-sharing company
 In the 1870s, at the bottom of the hill on land between the railway line and Worple Road, the All-England Croquet Club had begun to hold its annual championships. But the popularity of
In the 1870s, at the bottom of the hill on land between the railway line and Worple Road, the All-England Croquet Club had begun to hold its annual championships. But the popularity of
 For many years
For many years
 The New Wimbledon Theatre is a
The New Wimbledon Theatre is a
 The ''Polka Theatre'' is a children's theatre in Wimbledon,
The ''Polka Theatre'' is a children's theatre in Wimbledon,
 * Bob Astles (1924–2012), former associate of Ugandan presidents
* Bob Astles (1924–2012), former associate of Ugandan presidents
this map
*Kemi Badenoch (1980), Leader of the Opposition (United Kingdom), Leader of the Opposition and Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party since 2024 *Dame June Whitfield (1925–2018), actress *William Wilberforce (1759–1833), anti-slavery campaigner
 *Cannizaro Park
*Richmond Park
*
*Cannizaro Park
*Richmond Park
*
Southside House
*Wimbledon Lawn Tennis Museum
Wimbledon Museum
*Wimbledon Windmill
History of Antiquities of the Parish of Wimbledon
', Simpkin, Marshall, & co., 1865 *Brown, John W., ''Lysons's History of Wimbledon'', Local History Reprints, 1991, *Milward, Richard, ''Historic Wimbledon, Caesar's Camp to Centre Court'', The Windrush Press and Fielders of Wimbledon, 1989, *Milward, Richard, ''New Short History of Wimbledon'', Wimbledon Society, 1989
merton.gov.uk
Community
lovewimbledon.orgwimbledon-village.com
History
british-history.ac.uk
The Environs of London: Volume 1: County of Surrey, 1792, "Wimbledon", pp. 519–540, Daniel Lysons
british-history.ac.uk
A History of the County of Surrey: Volume 4, 1912, "Parishes: Wimbledon", pp. 120–125, H. E. Malden (editor) {{Authority control Wimbledon, London, Areas of London Districts of the London Borough of Merton Major centres of London
Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Since the early 19th century, Charing Cross has been the notional "centre of London" and became the point from which distances from London are measured. ...
; it is the main commercial centre of the London Borough of Merton
The London Borough of Merton () is a London borough in London, England. The borough was formed under the London Government Act 1963 in 1965 by the merger of the Municipal Borough of Mitcham, the Municipal Borough of Wimbledon and the Merton ...
. Wimbledon had a population of 68,189 in 2011 which includes the electoral wards of Abbey, Wimbledon Town and Dundonald, Hillside, Wandle, Village, Raynes Park and Wimbledon Park.
It is home to the Wimbledon Championships
The Wimbledon Championships, commonly called Wimbledon, is a tennis tournament organised by the All England Lawn Tennis and Croquet Club in collaboration with the Lawn Tennis Association annually in Wimbledon, London. It is chronologically the ...
and New Wimbledon Theatre
The New Wimbledon Theatre is situated on the Broadway, Wimbledon, London, in the London Borough of Merton. It is a Listed building, Grade II listed Edwardian era, Edwardian theatre built by the theatre lover and entrepreneur, J. B. Mulholland, w ...
, and contains Wimbledon Common
Wimbledon Common is a large open space in Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon, southwest London. There are three named areas: Wimbledon Common, Putney Heath, and Putney Lower Common, which together are managed under the name Wimbledon and Putney Co ...
, one of the largest areas of common land
Common land is collective land (sometimes only open to those whose nation governs the land) in which all persons have certain common rights, such as to allow their livestock to graze upon it, to collect wood, or to cut turf for fuel.
A person ...
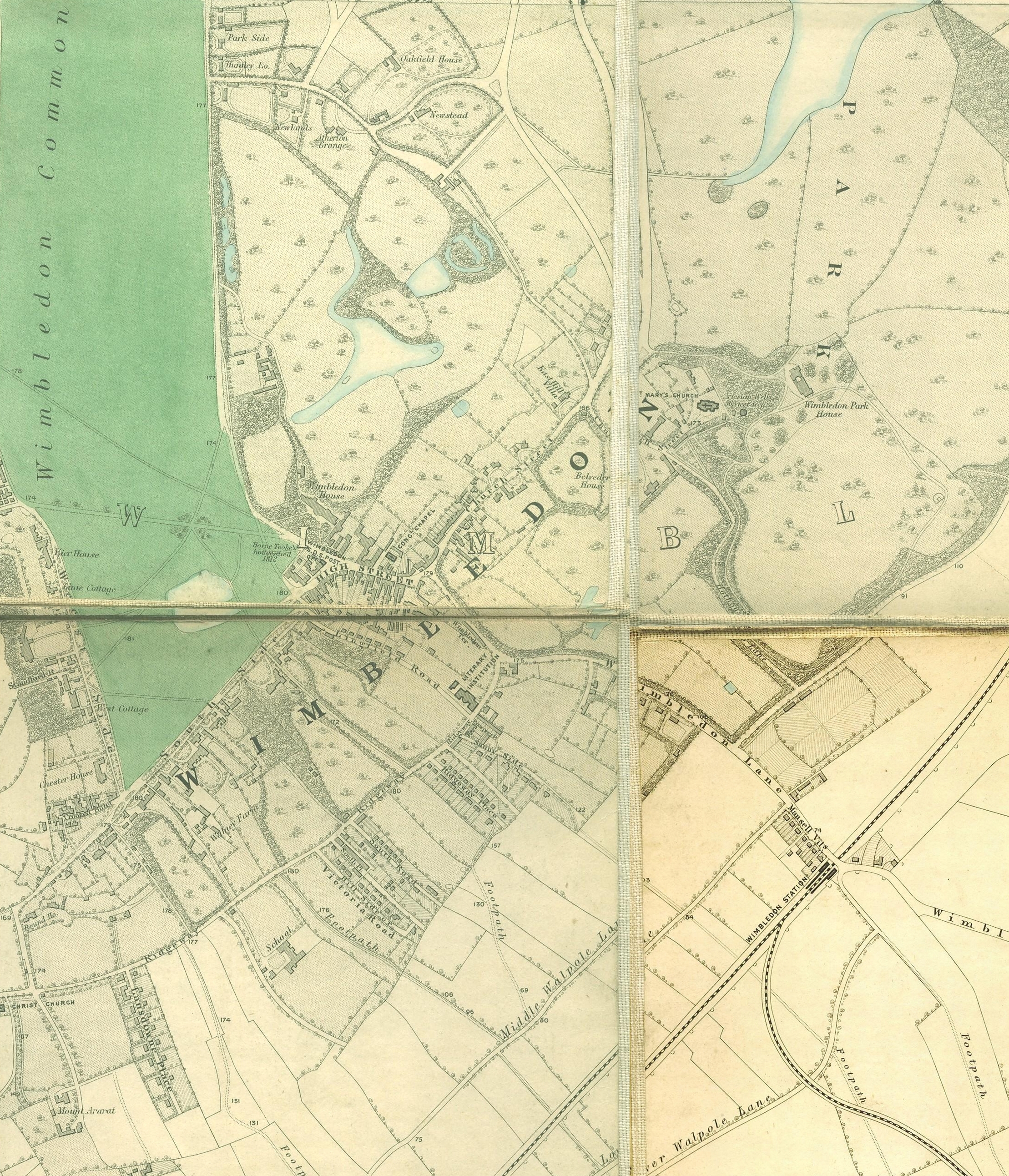
in London. The residential and retail area is split into two sections known as the "village" and the "town", with the High Street being the rebuilding of the original medieval village, and the "town" having first developed gradually after the building of the railway station in 1838.
Wimbledon has been inhabited since at least the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
when the hill fort
A hillfort is a type of fortification, fortified refuge or defended settlement located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late Bronze Age Europe, European Bronze Age and Iron Age Europe, Iron Age. So ...
on Wimbledon Common is thought to have been constructed. In 1086 when the Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
was compiled, Wimbledon was part of the manor of Mortlake
Mortlake is a suburban district of the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames on the south bank of the River Thames between Kew and Barnes, London, Barnes. Historically it was part of Surrey and until 1965 was in the Municipal Borough of Barnes ...
. The ownership of the manor of Wimbledon changed between various wealthy families many times during its history, and the area also attracted other wealthy families who built large houses such as Eagle House, Wimbledon Manor House and Warren House.
The village developed with a stable rural population coexisting with nobility and wealthy merchants from the city. In the 18th century the ''Dog and Fox'' public house became a stop on the stagecoach
A stagecoach (also: stage coach, stage, road coach, ) is a four-wheeled public transport coach used to carry paying passengers and light packages on journeys long enough to need a change of horses. It is strongly sprung and generally drawn by ...
run from London to Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Hampshire, England. Most of Portsmouth is located on Portsea Island, off the south coast of England in the Solent, making Portsmouth the only city in En ...
, then in 1838 the London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exete ...
(L&SWR) opened a station to the southeast of the village at the bottom of Wimbledon Hill. The location of the station shifted the focus of the town's subsequent growth away from the original village centre.
Wimbledon was a municipal borough
A municipal borough was a type of local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state.
Local governments typically constitute a subdivision of ...
in the county of Surrey from 1905 to 1965, when it became part of the London Borough of Merton as part of the creation of Greater London
Greater London is an administrative area in England, coterminous with the London region, containing most of the continuous urban area of London. It contains 33 local government districts: the 32 London boroughs, which form a Ceremonial count ...
.
Wimbledon has established minority groups
The term "minority group" has different meanings, depending on the context. According to common usage, it can be defined simply as a group in society with the least number of individuals, or less than half of a population. Usually a minority g ...
; among the prominent ones being British Asian
British Asians (also referred to as Asian Britons) are British people of Asian people, Asian descent. They constitute a significant and growing minority of the people living in the United Kingdom, with a population of 5.76 million people or 8.6 ...
s (mainly British Pakistanis
British Pakistanis (; also known as Pakistani British people or Pakistani Britons) are British people, Britons or residents of the United Kingdom whose ancestral roots lie in Pakistan. This includes people born in the UK who are of Pakistani ...
and British Sri Lankans
British Sri Lankans are an ethnic group referring to British people who can trace their ancestry to Sri Lanka. It can refer to a variety of ethnicities and races, including Sinhalese, Tamils, Moors/Muslims and Burghers. They may identify wit ...
), British Ghanaians, Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
and Irish people
The Irish ( or ''Na hÉireannaigh'') are an ethnic group and nation native to the island of Ireland, who share a common ancestry, history and Culture of Ireland, culture. There have been humans in Ireland for about 33,000 years, and it has be ...
.
Nearby major settlements include Morden
Morden is a district and town in South London, England, now within the London Borough of Merton, in the ceremonial county of Greater London. It adjoins Merton Park and Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon to the north, Mitcham to the east, Sutton, Londo ...
, Mitcham
Mitcham is an area within the London Borough of Merton in South London, England. It is centred southwest of Charing Cross. Originally a village in the county of Surrey, today it is mainly a residential suburb, and includes Mitcham Common. It ...
, Colliers Wood
Colliers Wood is an area in south west London, England, in the London Borough of Merton. It is a mostly residential area, but has a busy high street around Colliers Wood tube station on London Underground's Northern line. The high street is pa ...
, Raynes Park
Raynes Park is a residential suburb, railway station and local centre near Wimbledon, London, and is within the London Borough of Merton. It is situated southwest of Wimbledon Common, to the northwest of Wimbledon Chase and to the east of Ne ...
, Roehampton
Roehampton is an area in southwest London, sharing its SW15 postcode with neighbouring Putney and Kingston Vale, and takes up a far western strip, running north to south, in the London Borough of Wandsworth. It contains a number of large counc ...
, Southfields
Southfields is a district of inner London located within the London Borough of Wandsworth, England, 5.6 miles (9 km) south-west of Charing Cross, with a small portion of the area extending into the neighbouring London Borough of Merton. So ...
, Putney
Putney () is an affluent district in southwest London, England, in the London Borough of Wandsworth, southwest of Charing Cross. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.
History
Putney is an ...
, Wimbledon Chase, Merton Park
Merton Park is an area in London Borough of Merton. Bordering areas are Colliers Wood, Morden, South Wimbledon and Raynes Park. It is southwest of Charing Cross. It lies east of Kingston upon Thames, west of Mitcham and north of Sutton.
...
, New Malden
New Malden is a suburban area in southwest London, England. It is within the Royal Borough of Kingston upon Thames and the London Borough of Merton, and is from Charing Cross. Neighbouring localities include Kingston upon Thames, Kingston, Norb ...
and South Wimbledon.
History
Early history
Wimbledon has been inhabited since at least theIron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
when the hill fort
A hillfort is a type of fortification, fortified refuge or defended settlement located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late Bronze Age Europe, European Bronze Age and Iron Age Europe, Iron Age. So ...
on Wimbledon Common
Wimbledon Common is a large open space in Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon, southwest London. There are three named areas: Wimbledon Common, Putney Heath, and Putney Lower Common, which together are managed under the name Wimbledon and Putney Co ...
, the second-largest in London, is thought to have been constructed. The original nucleus
Nucleus (: nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucleu ...
of Wimbledon was at the top of the hill close to the common – the area now known locally as "the village".
The village is referred to as "Wimbedounyng" in a charter signed by King Edgar the Peaceful in 967. The name Wimbledon means "Wynnman's hill", with the final element of the name being the Celtic "dun" (hill). The name is shown on J. Cary's 1786 map of the London area as "Wimbleton", and the current spelling appears to have been settled on relatively recently in the early 19th century, the last in a long line of variations.
At the time the Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
was compiled (around 1086), Wimbledon was part of the manor of Mortlake
Mortlake is a suburban district of the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames on the south bank of the River Thames between Kew and Barnes, London, Barnes. Historically it was part of Surrey and until 1965 was in the Municipal Borough of Barnes ...
, and so was not recorded. The ownership of the manor of Wimbledon changed hands many times during its history. The manor was held by the church until 1398 when Thomas Arundel
Thomas Arundel (1353 – 19 February 1414) was an English clergyman who served as Lord Chancellor and Archbishop of York during the reign of Richard II, as well as Archbishop of Canterbury in 1397 and from 1399 until his death, an outspoken o ...
, Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the Primus inter pares, ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the bishop of the diocese of Canterbury. The first archbishop ...
fell out of favour with Richard II
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward, Prince of Wales (later known as the Black Prince), and Joan, Countess of Kent. R ...
and was exiled. The manor was confiscated and became crown property.
The manor remained crown property until the reign of Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
when it was granted briefly to Thomas Cromwell
Thomas Cromwell (; – 28 July 1540) was an English statesman and lawyer who served as List of English chief ministers, chief minister to King Henry VIII from 1534 to 1540, when he was beheaded on orders of the king, who later blamed false cha ...
, Earl of Essex
Earl of Essex is a title in the Peerage of England which was first created in the 12th century by King Stephen of England. The title has been recreated eight times from its original inception, beginning with a new first Earl upon each new cre ...
, until Cromwell was executed in 1540 and the land was again confiscated. The manor was next held by Henry VIII's last wife and widow Catherine Parr
Catherine Parr ( – 5 September 1548) was Queen of England and Ireland as the last of the six wives of King Henry VIII from their marriage on 12 July 1543 until Henry's death on 28 January 1547. Catherine was the final queen consort o ...
until her death in 1548 when it again reverted to the monarch.
In the 1550s, Henry's daughter, Mary I
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain as the wife of King Philip II from January 1556 until her death in 1558. She made vigorous a ...
, granted the manor to Cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal most commonly refers to
* Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of three species in the family Cardinalidae
***Northern cardinal, ''Cardinalis cardinalis'', the common cardinal of ...
Reginald Pole
Reginald Pole (12 March 1500 – 17 November 1558) was an English cardinal and the last Catholic Archbishop of Canterbury, holding the office from 1556 to 1558 during the Marian Restoration of Catholicism.
Early life
Pole was born at Stourt ...
who held it until his death in 1558 when it once again become royal property. Mary's sister, Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
held the property until 1574 when she gave the manor house (but not the manor) to Christopher Hatton
Sir Christopher Hatton (12 December 1540 – 20 November 1591) was an English politician, Lord Chancellor of England and a favourite of Elizabeth I of England. He was one of the judges who found Mary, Queen of Scots guilty of treason.
Early ...
, who sold it in the same year to Sir Thomas Cecil, Earl of Exeter. The lands of the manor were given to the Cecil family in 1588 and a new manor house, Wimbledon Palace, was constructed and gardens laid out in the formal Elizabethan
The Elizabethan era is the epoch in the Tudor period of the history of England during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I (1558–1603). Historians often depict it as the golden age in English history. The Roman symbol of Britannia (a female per ...
style.
17th century
Wimbledon's proximity to the capital was beginning to attract other wealthy families. In 1613 Robert Bell, Master of the Worshipful Company of Girdlers and a director of theBritish East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
built Eagle House as a home at an easy distance from London. The Cecil family retained the manor for fifty years, before it was bought by Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
in 1638 for his Queen, Henrietta Maria
Henrietta Maria of France (French language, French: ''Henriette Marie''; 25 November 1609 – 10 September 1669) was List of English royal consorts, Queen of England, List of Scottish royal consorts, Scotland and Ireland from her marriage to K ...
.
Following the King's execution in 1649, the manor passed rapidly among various parliamentarian owners, including the Leeds
Leeds is a city in West Yorkshire, England. It is the largest settlement in Yorkshire and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds Metropolitan Borough, which is the second most populous district in the United Kingdom. It is built aro ...
Member of Parliament (MP) Adam Baynes and the civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
general John Lambert; Lambert drafted the Instrument of Government
The Instrument of Government was the first constitution of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland and was also the first codified and written constitution in England. It was drafted by Major-General John Lambert in 1653.
Anteced ...
, the founding document of the Protectorate
The Protectorate, officially the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland, was the English form of government lasting from 16 December 1653 to 25 May 1659, under which the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotl ...
, at Wimbledon. After the restoration of the monarchy in 1660, it was returned to Henrietta Maria (now as mother of the new King, Charles II).
The Dowager Queen
A queen dowager or dowager queen (compare: princess dowager or dowager princess) is a title or status generally held by the widow of a king. In the case of the widow of an emperor, the title of empress dowager is used. Its full meaning is clear ...
sold the manor in 1661 to George Digby, 2nd Earl of Bristol
George Digby, 2nd Earl of Bristol (5 November 161220 March 1677) was an English politician and peer who sat in the House of Commons from 1640 until 1641, when he was raised to the House of Lords by a writ of acceleration. He supported the Ro ...
, who employed John Evelyn
John Evelyn (31 October 162027 February 1706) was an English writer, landowner, gardener, courtier and minor government official, who is now best known as a diary, diarist. He was a founding Fellow of the Royal Society.
John Evelyn's Diary, ...
to improve and update the landscape in accordance with the latest fashions, including grotto
A grotto or grot is a natural or artificial cave or covered recess.
Naturally occurring grottoes are often small caves near water that are usually flooded or often flooded at high tide.
Sometimes, artificial grottoes are used as garden fea ...
s and fountains. After his death in 1677, the manor was sold again to the Lord High Treasurer
The Lord High Treasurer was an English government position and has been a British government position since the Acts of Union of 1707. A holder of the post would be the third-highest-ranked Great Officer of State in England, below the Lord H ...
, Thomas Osborne, Earl of Danby.

18th century
The Osborne family sold the manor to Sir Theodore Janssen in 1712. Janssen, a director of theSouth Sea Company
The South Sea Company (officially: The Governor and Company of the merchants of Great Britain, trading to the South Seas and other parts of America and for the encouragement of the Fishery) was a British joint-stock company founded in Ja ...
, began a new house to replace the one built by the Cecils, but the spectacular collapse of the company meant it was never finished.
The next owner was Sarah Churchill, Duchess of Marlborough
Sarah Churchill, Duchess of Marlborough, Princess of Mindelheim, Countess of Nellenburg (née Jenyns, spelt Jennings in most modern references; 5 June 1660 (Old Style) – 18 October 1744), was an English courtier who rose to be one of th ...
, who increased the land belonging to the manor and completed the construction of a house to replace Jansen's unfinished effort in 1736. On her death in 1744, the property passed to her grandson, John Spencer, and subsequently to the first Earl Spencer.
The village continued to grow and the 18th-century introduction of stagecoach
A stagecoach (also: stage coach, stage, road coach, ) is a four-wheeled public transport coach used to carry paying passengers and light packages on journeys long enough to need a change of horses. It is strongly sprung and generally drawn by ...
services from the ''Dog and Fox'' made the journey to London routine, although not without the risk of being held-up by highwaymen
A highwayman was a robber who stole from travellers. This type of thief usually travelled and robbed by horse as compared to a footpad who travelled and robbed on foot; mounted highwaymen were widely considered to be socially superior to foo ...
, such as Jerry Abershawe
Louis Jeremiah Abershawe (c. 1773 – 3 August 1795), better known as Jerry Abershawe, or Abershaw, was an English highwayman who terrorised travellers, mostly along the road between Kingston upon Thames and London, in the late eighteenth centur ...
on the Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Hampshire, England. Most of Portsmouth is located on Portsea Island, off the south coast of England in the Solent, making Portsmouth the only city in En ...
Road. The stagecoach horses would be stabled at the rear of the pub in what are now named Wimbledon Village Stables.
The 1735 manor house burnt down in the 1780s and was replaced in 1801 by Wimbledon Park House, built by the second Earl. At the time the manor estate included Wimbledon Common (as a heath
A heath () is a shrubland habitat found mainly on free-draining infertile, acidic soils and is characterised by open, low-growing woody vegetation. Moorland is generally related to high-ground heaths with—especially in Great Britain—a coole ...
) and the enclosed parkland around the manor house. Its area corresponded to the modern Wimbledon Park. The house stood east of St Mary's church.
Wimbledon House, a separate residence close to the village at the south end of Parkside (near Peek Crescent), was home in the 1790s to the exiled French statesman Vicomte de Calonne, and later to the mother of the writer Frederick Marryat
Captain Frederick Marryat (10 July 1792 – 9 August 1848) was a Royal Navy officer and novelist. He is noted today as an early pioneer of nautical fiction, particularly for his semi-autobiographical novel '' Mr Midshipman Easy'' (1836). He is ...
. Their association with the area is recorded in the names of nearby Calonne and Marryat roads. Directly south of the common, the early 18th-century Warren House ( Cannizaro House from 1841) was home to a series of grand residents.
19th-century development
 The first decades of the 19th century were relatively quiet for Wimbledon, with a stable rural population coexisting alongside nobility and wealthy merchants from the city. Renewed upheaval came in 1838, when the opening of the
The first decades of the 19th century were relatively quiet for Wimbledon, with a stable rural population coexisting alongside nobility and wealthy merchants from the city. Renewed upheaval came in 1838, when the opening of the London and South Western Railway
The London and South Western Railway (LSWR, sometimes written L&SWR) was a railway company in England from 1838 to 1922. Originating as the London and Southampton Railway, its network extended to Dorchester and Weymouth, to Salisbury, Exete ...
(L&SWR) brought a station to the south-east of the village, at the bottom of Wimbledon Hill. The location of the station shifted the focus of the town's subsequent growth away from the original village centre.
For several years Wimbledon Park was leased to the Duke of Somerset
Duke of Somerset, from the county of Somerset, is a title that has been created five times in the peerage of England. It is particularly associated with two families: the Beauforts, who held the title from the creation of 1448, and the Seymours ...
, who briefly in the 1820s employed a young Joseph Paxton
Sir Joseph Paxton (3 August 1803 – 8 June 1865) was an English gardener, architect, engineer and Liberal Party (UK), Liberal Member of Parliament. He is best known for designing the Crystal Palace, which was built in Hyde Park, London, Hyde ...
as one of his gardeners, but in the 1840s the Spencer family sold the park off as building land. A period of residential development began with large detached houses in the north of the park. In 1864, the Spencers attempted to get parliamentary permission to enclose the common as a new park with a house and gardens and to sell part for building. Following an enquiry, permission was refused and a board of conservators was established in 1871 to take ownership of the common and preserve it in its natural condition.
In the second half of the century, Wimbledon experienced a very rapid expansion of its population. From under 2,700 residents recorded in the 1851 census, the population grew by a minimum of 60 per cent each decade up to 1901, to increase fifteen-fold in fifty years. Large numbers of villas and terraced houses were built along the roads from the centre towards neighbouring Putney, Merton Park
Merton Park is an area in London Borough of Merton. Bordering areas are Colliers Wood, Morden, South Wimbledon and Raynes Park. It is southwest of Charing Cross. It lies east of Kingston upon Thames, west of Mitcham and north of Sutton.
...
and Raynes Park
Raynes Park is a residential suburb, railway station and local centre near Wimbledon, London, and is within the London Borough of Merton. It is situated southwest of Wimbledon Common, to the northwest of Wimbledon Chase and to the east of Ne ...
.
Transport links improved further with railway lines to Croydon (Wimbledon and Croydon Railway, opened in 1855) and Tooting (Tooting, Merton and Wimbledon Railway, opened in 1868). The District Railway
The Metropolitan District Railway, also known as the District Railway, was a passenger railway that served London, England, from 1868 to 1933. Established in 1864 to complete an " inner circle" of lines connecting railway termini in London, the ...
(now the London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or as the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent home counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England.
The Undergro ...
District line
The District line is a London Underground line running from in the east and Edgware Road tube station (Circle, District and Hammersmith & City lines), Edgware Road in the west to in west London, where it splits into multiple branches. One br ...
) extended its service over new tracks from Putney in 1889.
The commercial and civic development of the town also accelerated. Ely's department store
A department store is a retail establishment offering a wide range of consumer goods in different areas of the store under one roof, each area ("department") specializing in a product category. In modern major cities, the department store mad ...
opened in 1876 and shops began to stretch along Broadway towards Merton. Wimbledon built its first police station in 1870. Cultural developments included a Literary Institute by the early 1860s and the opening of Wimbledon Library in 1887. The religious needs of the growing population led to an Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
church-building programme, starting with the rebuilding of St Mary's Church in 1849 and the construction of Christ Church (1859) and Trinity Church (1862).
Street names reflect events: Denmark Road, Denmark Avenue and the ''Alexandra'' pub on Wimbledon Hill mark the marriage of Edward, Prince of Wales, to Princess Alexandra of Denmark
Alexandra of Denmark (Alexandra Caroline Marie Charlotte Louise Julia; 1 December 1844 – 20 November 1925) was List of British royal consorts, queen-consort of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Empress of India, from 22 Januar ...
.
The change of character of Wimbledon from village to small town was recognised under the Local Government Act 1894
The Local Government Act 1894 ( 56 & 57 Vict. c. 73) was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales outside the County of London. The act followed the reforms carried out at county leve ...
, which formed Wimbledon Urban District with an elected council
A council is a group of people who come together to consult, deliberate, or make decisions. A council may function as a legislature, especially at a town, city or county/shire level, but most legislative bodies at the state/provincial or natio ...
.
Modern history
 Wimbledon's population continued to grow in the early 20th century, as was recognised in 1905, when the urban district was incorporated as the
Wimbledon's population continued to grow in the early 20th century, as was recognised in 1905, when the urban district was incorporated as the Municipal Borough of Wimbledon
Wimbledon was a local government district in north-east Surrey from 1866 to 1965 covering the town of Wimbledon and its surrounding area. It was part of the London postal district and Metropolitan Police District.
History
Wimbledon Local Gover ...
, with the power to select a mayor.
By 1910, Wimbledon had established the beginnings of the Wimbledon School of Art
Wimbledon College of Arts, formerly Wimbledon School of Art, is a constituent college of the University of the Arts London, a public art university in London, England. The college specialises in theatre, screen and performance arts and design ...
at the Gladstone Road Technical Institute and acquired its first cinema and the theatre. Unusually, the facilities at its opening included Victorian-style Turkish baths.
By the 1930s, residential expansion had peaked in Wimbledon and the new focus for local growth had moved to neighbouring Morden
Morden is a district and town in South London, England, now within the London Borough of Merton, in the ceremonial county of Greater London. It adjoins Merton Park and Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon to the north, Mitcham to the east, Sutton, Londo ...
, which had remained rural until the arrival of the Underground at Morden station in 1926. Wimbledon station
Wimbledon is an interchange station in the centre of Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon for London Underground, Tramlink, London Trams and National Rail services, and is the only station in London that provides an interchange between the London Underg ...
was rebuilt by the Southern Railway with a simple Portland stone facade for the opening of a new railway branch line from Wimbledon to Sutton
Sutton (''south settlement'' or ''south town'' in Old English) may refer to:
Places
United Kingdom
England
In alphabetical order by county:
* Sutton, Bedfordshire
* Sutton, Berkshire, a List of United Kingdom locations: Stu-Sz#Su, location
* S ...
in 1930.
In 1931, the council built a new red brick and Portland stone
Portland stone is a limestone geological formation (formally named the Portland Stone Formation) dating to the Tithonian age of the Late Jurassic that is quarried on the Isle of Portland in Dorset, England. The quarries are cut in beds of whi ...
Town Hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or municipal hall (in the Philippines) is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses the city o ...
next to the station, on the corner of Queen's Road and Wimbledon Bridge. The architects were Bradshaw Gass & Hope
Bradshaw Gass & Hope is an English architect, architectural practice founded in 1862 by Jonas James Bradshaw (–1912). It is Bolton's oldest architectural practice and has exhibited archive drawings in London and Manchester. The style "Bradshaw ...
.
Damage to housing stock in Wimbledon and other parts of London during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
led to a final major building phase when many earlier Victorian houses with large grounds in Wimbledon Park were sub-divided into flats or demolished and replaced with apartment blocks. Other parts of Wimbledon Park, which had previously escaped being built upon, saw local authority estates constructed by the borough council, to house some of those who had lost their homes.
During the 1970s and 1980s, Wimbledon town centre struggled to compete commercially with more developed centres at Kingston
Kingston may refer to:
Places
* List of places called Kingston, including the six most populated:
** Kingston, Jamaica
** Kingston upon Hull, England
** City of Kingston, Victoria, Australia
** Kingston, Ontario, Canada
** Kingston upon Thames, ...
and Sutton
Sutton (''south settlement'' or ''south town'' in Old English) may refer to:
Places
United Kingdom
England
In alphabetical order by county:
* Sutton, Bedfordshire
* Sutton, Berkshire, a List of United Kingdom locations: Stu-Sz#Su, location
* S ...
. Part of the problem was the shortage of locations for large anchor stores to attract customers. After some years in which the council seemed unable to find a solution, The Centre Court shopping centre was developed on land next to the station, providing a much-needed focus, and opened in 1990. The shopping centre incorporated the old town hall building. A new portico, in keeping with the old work, was designed by Sir George Grenfell-Baines, who had worked on the original designs over fifty years before.
Geography
Wimbledon lies in the south-west area of London, south ofWandsworth
Wandsworth Town () is a district of south London, within the London Borough of Wandsworth southwest of Charing Cross. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.
Toponymy
Wandsworth takes its name ...
, south-west of Tooting
Tooting is a district in South London, forming part of the London Borough of Wandsworth. It is located south south-west of Charing Cross.
History
Tooting has been settled since pre-Anglo-Saxons, Saxon times. The name is of Anglo-Saxon ori ...
, three miles northwest of Mitcham
Mitcham is an area within the London Borough of Merton in South London, England. It is centred southwest of Charing Cross. Originally a village in the county of Surrey, today it is mainly a residential suburb, and includes Mitcham Common. It ...
, north of Sutton
Sutton (''south settlement'' or ''south town'' in Old English) may refer to:
Places
United Kingdom
England
In alphabetical order by county:
* Sutton, Bedfordshire
* Sutton, Berkshire, a List of United Kingdom locations: Stu-Sz#Su, location
* S ...
and east of Kingston upon Thames
Kingston upon Thames, colloquially known as Kingston, is a town in the Royal Borough of Kingston upon Thames, south-west London, England. It is situated on the River Thames, south-west of Charing Cross. It is an ancient market town, notable as ...
, in Greater London
Greater London is an administrative area in England, coterminous with the London region, containing most of the continuous urban area of London. It contains 33 local government districts: the 32 London boroughs, which form a Ceremonial count ...
. It is south-west of Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Since the early 19th century, Charing Cross has been the notional "centre of London" and became the point from which distances from London are measured. ...
. The area is identified in the London Plan
The London Plan is the statutory spatial development strategy for the Greater London area in the United Kingdom that is written by the Mayor of London and published by the Greater London Authority. It is updated from time to time.
The regio ...
as one of 35 major centres in Greater London.
It is considered an affluent suburb with its grand Victorian houses, modern housing and low-rise apartments. The residential area splits into two sections: the village and the town, with the village near the common centred on the High Street, being part of the original medieval village, and now a prime residential area of London commanding high prices, and the "town" being part of the modern development, centred on The Broadway, since the building of the railway station in 1838.
The majority of the adult population of around 68,200 adults belong to the ABC1
ABC TV, formerly known as ABC1, is an Australian national public television network. It is owned and operated by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation, and is the flagship (broadcasting), flagship ABC Television (Australian TV network), A ...
social group. The population grew from around 1,000 at the start of the 19th century to around 55,000 in 1911, a figure which has remained reasonably stable since.
Demography
Wimbledon is covered by several wards in the London Borough of Merton, making it difficult to produce statistics for the town as a whole. The largest ethnic groups (up to 10%) in the wards according to the 2011 census are: *Village (northern areas and the village): 65% White British, 16% Other White *Wimbledon Park (north-east): 60% White British, 18% Other White *Hillside (west of centre): 56% White British, 20% Other White *Dundonald (south of centre): 61% White British, 18% Other White *Raynes Park (west of centre): 61% White British, 16% Other White *Trinity (east from centre): 56% White British, 18% Other WhiteGovernance and representation
At the time theDomesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
was compiled (around 1086), Wimbledon was part of the manor of Mortlake. From 1328 to 1536, a manor of Wimbledon was recorded as belonging to the Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the Primus inter pares, ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the bishop of the diocese of Canterbury. The first archbishop ...
.
The manor of Wimbledon changed hands many times during its history. Wimbledon was an Ancient Parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government. Civil parishes can trace their origin to the ancient system of parishes, w ...
from the medieval period, later being re-organised as the Municipal Borough of Wimbledon within the county of Surrey
Surrey () is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Greater London to the northeast, Kent to the east, East Sussex, East and West Sussex to the south, and Hampshire and Berkshire to the wes ...
.
In 1965, the London Government Act 1963
The London Government Act 1963 (c. 33) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which created Greater London and a new local government structure within it. The Act significantly reduced the number of local government districts in the ...
abolished the Municipal Borough of Wimbledon, Merton and Morden Urban District
Merton Urban District (1907–1913) and Merton and Morden Urban District (1913–1965) was an urban district in Surrey, England. It was formed in 1907 from the parish of Merton and was expanded in 1913 to take in Morden. The district was abolishe ...
and the Municipal Borough of Mitcham
Mitcham was a local government district in north east Surrey from 1915 to 1965 around the town of Mitcham.
History
Mitcham local government district was created in 1915 as an urban district from part of the abolished Croydon Rural District. It ...
, creating instead the London Borough of Merton. Initially, the new administrative centre was at Wimbledon Town Hall, but it moved to the 14-storey Crown House in Morden in the early 1990s.
It is now the Parliamentary constituency of Wimbledon
Wimbledon most often refers to:
* Wimbledon, London, a district of southwest London
* Wimbledon Championships, the oldest tennis tournament in the world and one of the four Grand Slam championships
Wimbledon may also refer to:
Places London
* W ...
, and since 2024
The year saw the list of ongoing armed conflicts, continuation of major armed conflicts, including the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the Myanmar civil war (2021–present), Myanmar civil war, the Sudanese civil war (2023–present), Sudane ...
has been represented by Paul Kohler, a Liberal Democrat
Several political parties from around the world have been called the Liberal Democratic Party, Democratic Liberal Party or Liberal Democrats. These parties have usually followed liberalism as ideology, although they can vary widely from very progr ...
MP.
Economy
 In 2012 the businesses in Wimbledon voted to introduce a Business Improvement District. "Love Wimbledon" was formed in April 2012, funded and managed by the business community to promote and enhance the town centre. Those who work within Wimbledon can apply for a 'Privilege Card' which provides discounts and benefits within the town centre.
The UK's leading car-sharing company
In 2012 the businesses in Wimbledon voted to introduce a Business Improvement District. "Love Wimbledon" was formed in April 2012, funded and managed by the business community to promote and enhance the town centre. Those who work within Wimbledon can apply for a 'Privilege Card' which provides discounts and benefits within the town centre.
The UK's leading car-sharing company Zipcar
Zipcar is an American car sharing, car-sharing company and a subsidiary of Avis Budget Group. Zipcar provides vehicle reservations to its members, billable by the minute, hour or day; members may have to pay a monthly or annual membership fee i ...
has its UK headquarters in Wimbledon. Other notable organisations with head offices in Wimbledon include CIPD, Ipsotek, United Response
United Response is a charity operating in England and Wales, providing a range of support and services for around 2,000 people with learning disabilities, mental health needs, or physical disabilities.
History
United Response was founded in ...
, the Communication Workers Union (United Kingdom)
The Communication Workers Union (CWU) is the main trade union in the United Kingdom for people working for telephone, cable, digital subscriber line (DSL), postal delivery, and tech companies. It has 110,000 members in Royal Mail as well as mor ...
and, until 2022, Lidl
Lidl ( ) is a trademark, used by two Germany, German international discount supermarket, discount retailer chain store, chains that operates over 12,600 stores. The ''LD Stiftung'' operates the stores in Germany and the ''Lidl Stiftung & Co. K ...
.
Media
The '' Wimbledon Times'' (formerly ''Wimbledon Guardian'') provides local news in print and online.The Tennis Championships
 In the 1870s, at the bottom of the hill on land between the railway line and Worple Road, the All-England Croquet Club had begun to hold its annual championships. But the popularity of
In the 1870s, at the bottom of the hill on land between the railway line and Worple Road, the All-England Croquet Club had begun to hold its annual championships. But the popularity of croquet
Croquet ( or ) is a sport which involves hitting wooden, plastic, or composite balls with a mallet through hoops (often called Wicket, "wickets" in the United States) embedded in a grass playing court.
Variations
In all forms of croquet, in ...
was waning as the new sport of lawn tennis
Tennis is a List of racket sports, racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent (singles (tennis), singles) or between two teams of two players each (doubles (tennis), doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket st ...
began to spread, and after initially setting aside just one of its lawns for tennis, the club decided to hold its first Lawn Tennis Championship in July 1877. By 1922, the popularity of tennis had grown to the extent that the club's small ground could no longer cope with the numbers of spectators and the renamed All England Lawn Tennis and Croquet Club
The All England Lawn Tennis and Croquet Club (AELTC), also known as the All England Club, based at Church Road, Wimbledon, London, England, is a Gentlemen's club, private members' club. It is best known as the venue for the Wimbledon Championsh ...
moved to new grounds close to Wimbledon Park.
Wimbledon historian Richard Milward recounts how King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until Death and state funeral of George V, his death in 1936.
George w ...
opened the new courts. "He (the king) gave three blows on a gong, the tarpaulins were removed, the first match started – and the rain came down." The club's old grounds continue to be used as the sports ground for Wimbledon High School
Wimbledon High School is a Private schools in the United Kingdom, private girls' day school in Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon, South West (London sub region), South West London. It is a Girls' Day School Trust school and is a member of the Girls' ...
.
Sport
Horse riding
Wimbledon Village Stables is the oldest recorded riding stables in England. The late Richard Milward MA, a local historian, researched the background of horses in Wimbledon over the years and found that the first recorded stables belonged to the Lord of the Manor, and are detailed in the Estate's accounts of 1236–37. Stables on the current site, behind the ''Dog & Fox'' pub in the High Street, were founded in 1915 by William Kirkpatrick and named Hilcote Stables; William's daughter Jean took over on his retirement and continued to visit the stables until her death in 2005. From 1969 Hilcote Stables were leased to Colin Crawford, and when they came up for sale in 1980 renamed Wimbledon Village Stables. It is now approved by the British Horse Society and the Association of British Riding Schools. It offers horse-riding lessons and hacks on Wimbledon Common and in Richmond Park.Horse racing
In 1792 the Rev. Daniel Lysons published ''The Environs of London: being a historical account of the towns, villages, and hamlets, within twelve miles of that capital'' in which he wrote: "In the early part of the present century there were annual races upon this common, which had then a King's plate." However, he gives no further details and does not say how successful horse racing was or how long it lasted.Rifle shooting
In the 1860s, the newly formedNational Rifle Association
The National Rifle Association of America (NRA) is a gun rights advocacy group based in the United States. Founded in 1871 to advance rifle marksmanship, the modern NRA has become a prominent Gun politics in the United States, gun rights ...
held its first competition - the " Imperial Meeting" - on Wimbledon Common. The association and the annual competition grew rapidly and by the early 1870s, rifle ranges were established on the common. In 1878 the competitions were lasting two weeks and attracting nearly 2,500 competitors, housed in temporary camps set up across the common. By the 1880s, however, the power and range of rifles had advanced to the extent that shooting in an increasingly populated area was no longer considered safe. The last meeting was held in 1889 before the NRA moved to Bisley in Surrey.
Wimbledon
Wimbledon most often refers to:
* Wimbledon, London, a district of southwest London
* Wimbledon Championships, the oldest tennis tournament in the world and one of the four Grand Slam championships
Wimbledon may also refer to:
Places London
* W ...
, a small farming locality in New Zealand, was named after this district in the 1880s after a local resident shot a bullock from a considerable distance away. The shot was considered by onlookers to be worthy of the rifle-shooting championships held in Wimbledon at the time.
The Wimbledon Cup
The Wimbledon Cup is a marksmanship trophy that was established in the 1870s.
It is awarded annually during the National Rifle & Pistol Matches which are held at Camp Perry, Ohio and has become the most prestigious prize in US long-range rifl ...
trophy, first awarded in Wimbledon for high-power rifles in 1866, was presented to the American rifle team in 1875 and a century and a half later continued to be awarded by the National Rifle Association of America
The National Rifle Association of America (NRA) is a gun rights advocacy group based in the United States. Founded in 1871 to advance rifle marksmanship, the modern NRA has become a prominent Gun politics in the United States, gun rights ...
.
Football
From a small, long-establishednon-League
Non-League football describes association football, football leagues played outside the top leagues of a country. Usually, it describes leagues which are not fully professional. The term is primarily used for football in England, where it is ...
team, Wimbledon Football Club had from 1977 climbed quickly through the ranks of the Football League
The English Football League (EFL) is a league of professional association football, football clubs from England and Wales. Founded in 1888 as the Football League, it is the oldest football league in Association football around the world, the w ...
structure, reaching the highest national professional league in 1986 and winning the FA Cup
The Football Association Challenge Cup, more commonly known as the FA Cup, is an annual Single-elimination tournament, knockout association football, football competition in domestic Football in England, English football. First played during ...
against Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
in 1988.
Wimbledon moved into a stadium at Plough Lane in 1912 and played there for 79 years until beginning a ground share with Crystal Palace
Crystal Palace may refer to:
Places Canada
* Crystal Palace Complex (Dieppe), a former amusement park now a shopping complex in Dieppe, New Brunswick
* Crystal Palace Barracks, London, Ontario
* Crystal Palace (Montreal), an exhibition buildin ...
at Selhurst Park
Selhurst Park is a football stadium in Selhurst, in the London Borough of Croydon, England, which is the home ground of Premier League club Crystal Palace. The stadium was designed by Archibald Leitch and opened in 1924. It has hosted interna ...
near Croydon
Croydon is a large town in South London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a Districts of England, local government district of Greater London; it is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater Lond ...
, as their progress through the Football League
The English Football League (EFL) is a league of professional association football, football clubs from England and Wales. Founded in 1888 as the Football League, it is the oldest football league in Association football around the world, the w ...
meant that redeveloping Plough Lane to the required modern standards was impractical. The stadium stood dormant for 10 years until it was finally demolished in 2001. A housing development now occupies the site.
AFC Wimbledon
AFC Wimbledon is an English professional association football club based in Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon, London Borough of Merton, London. The team competes in , the third tier of the English football league system.
The club was founded in ...
, the phoenix club founded to replace the departed team (see Milton Keynes Dons
Milton Keynes Dons Football Club, usually abbreviated to MK Dons, is a professional association football club based in Milton Keynes, Buckinghamshire, England. The team competes in EFL League Two, the fourth level of the English football leag ...
), played for a number of years in Kingston upon Thames; in 2020, however, they moved into a new stadium, again named Plough Lane
Plough Lane, currently known as the Cherry Red Records Stadium for sponsorship reasons, is a multi-purpose football stadium in Wimbledon, south-west London, which has been the home of AFC Wimbledon since 3 November 2020. A groundshare with rug ...
, on the site of the former greyhound track and a short distance from its namesake.
Cricket
Wimbledon Cricket Club is based at The Wimbledon Club and also plays matches at Raynes Park Sports Ground.Field hockey
There are a number offield hockey
Field hockey (or simply referred to as hockey in some countries where ice hockey is not popular) is a team sport structured in standard hockey format, in which each team plays with 11 players in total, made up of 10 field players and a goalk ...
clubs in the area. Wimbledon Hockey Club
Wimbledon Hockey Club is a professional field hockey club based in Wimbledon, London, England. It was established in 1883 and fields nine men's sides, seven ladies' sides as well as a comprehensive junior section. The men's 1st XI play in the Me ...
competes in the Men's England Hockey League
The Men's England Hockey League is a field hockey league organised by England Hockey that features men's teams from England and Wales.
Format Regular season
There are 62 teams in the league, the top tier consists of a Premier Division of ...
, the Women's England Hockey League
The Women's England Hockey League is a field hockey league organised by England Hockey that features women's teams from England. From 2011–2020 it was sponsored by Investec and was referred to as the Investec Women's Hockey League.
Format
...
and the South East Hockey League. Berrylands Hockey Club, Merton Hockey Club and Mitcham Ladies Hockey Club are also nearby and compete in the South East Hockey League.
Motorcycle speedway
 For many years
For many years Wimbledon Stadium
Wimbledon Stadium, also known as Wimbledon Greyhound Stadium, was a greyhound racing track located in Wimbledon in southwest London, England.
It also hosted stock car and other small circuit motor racing events, and until 2005 hosted motorc ...
hosted to Greyhound racing
Greyhound racing is an organized, competitive sport in which greyhounds are raced around an oval track. The sport originates from Hare coursing, coursing. Track racing uses an artificial lure (usually a form of windsock) that travels ahead of th ...
, as well as Stock car racing
Stock car racing is a form of Auto racing, automobile racing run on oval track racing, oval tracks and road courses. It originally used Production vehicle, production-model cars, hence the name "stock car", but is now run using cars specifical ...
and motorcycle speedway
Motorcycle speedway, usually referred to simply as speedway, is a motorcycle sport involving four and sometimes up to six riders competing over four clockwise, anti-clockwise laps of an oval circuit. The motorcycles are specialist machines that ...
. Speedway began at Wimbledon Stadium
Wimbledon Stadium, also known as Wimbledon Greyhound Stadium, was a greyhound racing track located in Wimbledon in southwest London, England.
It also hosted stock car and other small circuit motor racing events, and until 2005 hosted motorc ...
in 1928. The local team, the ''"Dons"'', was successful over the decades. It started out in 1929 as a member of the Southern League and operated until the Second World War. The track re-opened in 1946 and the Dons operated in the top flight for many years. In the 1950s the track was home to two World Champions: Ronnie Moore and Barry Briggs. In the Dons' last season, 2005, the team finished second in The National Conference League, but after the collapse of lease-renewal talks with the Greyhound Racing Association (owners of the stadium), the high increase in rent required meant the team was wound up. The stadium was demolished in 2017.
Running
There are two active running clubs in Wimbledon Park called Hercules Wimbledon and the Wimbledon Windmilers. Both clubs includes some top athletes as well as beginners. AParkrun
Parkrun (stylised as parkrun) is a collection of 5K run, events for runners, walkers and volunteers that take place every Saturday morning at more than 2,000 locations in 23 countries across five continents.
Parkrun was founded by Paul Sinto ...
is held every Saturday morning. Prior to Parkrun, a similar event had been held as the Wimbledon Common Time Trial.
Theatres
New Wimbledon Theatre
 The New Wimbledon Theatre is a
The New Wimbledon Theatre is a Grade II listed
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, H ...
Edwardian
In the United Kingdom, the Edwardian era was a period in the early 20th century that spanned the reign of King Edward VII from 1901 to 1910. It is commonly extended to the start of the First World War in 1914, during the early reign of King Ge ...
theatre built by J. B. Mullholland as the Wimbledon Theatre, on the site of a large house with spacious grounds. The theatre was designed by Cecil Aubrey Masey and Roy Young (possibly after a 1908 design by Frank H Jones). It opened on 26 December 1910 with the pantomime
Pantomime (; informally panto) is a type of musical comedy stage production designed for family entertainment, generally combining gender-crossing actors and topical humour with a story more or less based on a well-known fairy tale, fable or ...
''Jack and Jill''. The theatre was very popular between the wars, with appearances by Gracie Fields
Dame Gracie Fields (born Grace Stansfield; 9 January 189827 September 1979) was a British actress, singer and comedian. A star of cinema and music hall, she was one of the top ten film stars in Britain during the 1930s and was considered the h ...
, Sybil Thorndike
Dame Agnes Sybil Thorndike, Lady Casson (24 October 18829 June 1976) was an English actress whose stage career lasted from 1904 to 1969.
Trained in her youth as a concert pianist, Thorndike turned to the stage when a medical problem with her h ...
, Ivor Novello
Ivor Novello (born David Ivor Davies; 15 January 1893 – 6 March 1951) was a Welsh actor, dramatist, singer and composer who became one of the most popular British entertainers of the first half of the 20th century.
He was born into a musical ...
, Markova and Noël Coward
Sir Noël Peirce Coward (16 December 189926 March 1973) was an English playwright, composer, director, actor, and singer, known for his wit, flamboyance, and what ''Time (magazine), Time'' called "a sense of personal style, a combination of c ...
. Lionel Bart's Oliver!
''Oliver!'' is a stage musical, with book, music and lyrics by Lionel Bart. The musical is based upon the 1838 novel ''Oliver Twist'' by Charles Dickens.
It premiered at the Wimbledon Theatre, southwest London in 1960 before opening in the W ...
and Half A Sixpence, starring Tommy Steele
Sir Thomas Hicks (born 17 December 1936), known professionally as Tommy Steele, is an English entertainer, regarded as Britain's first teen idol and rock and roll star.
After being discovered at the 2i's Coffee Bar in Soho, London, Steele recor ...
, received their world premières at the theatre in the 1960s, before transferring to the West End.
The theatre was saved from redevelopment by the Ambassador Theatre Group
ATG Entertainment, formerly The Ambassador Theatre Group (ATG), is a major international live entertainment organisation headquartered in the United Kingdom, with offices in Woking (head office), London, New York, Sydney, Mannheim and Cologne. ...
in 2004. With several refurbishments, notably in 1991 and 1998, it retains its baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
and Adamesque internal features. The golden statue on the dome depicts Laetitia, the Roman Goddess of Gaiety, and was an original fixture back in 1910. Laetitia is holding a laurel crown as a symbol of celebration. The statue was removed during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, as it was thought to be a direction finder for German bombers. It was eventually replaced in 1991.
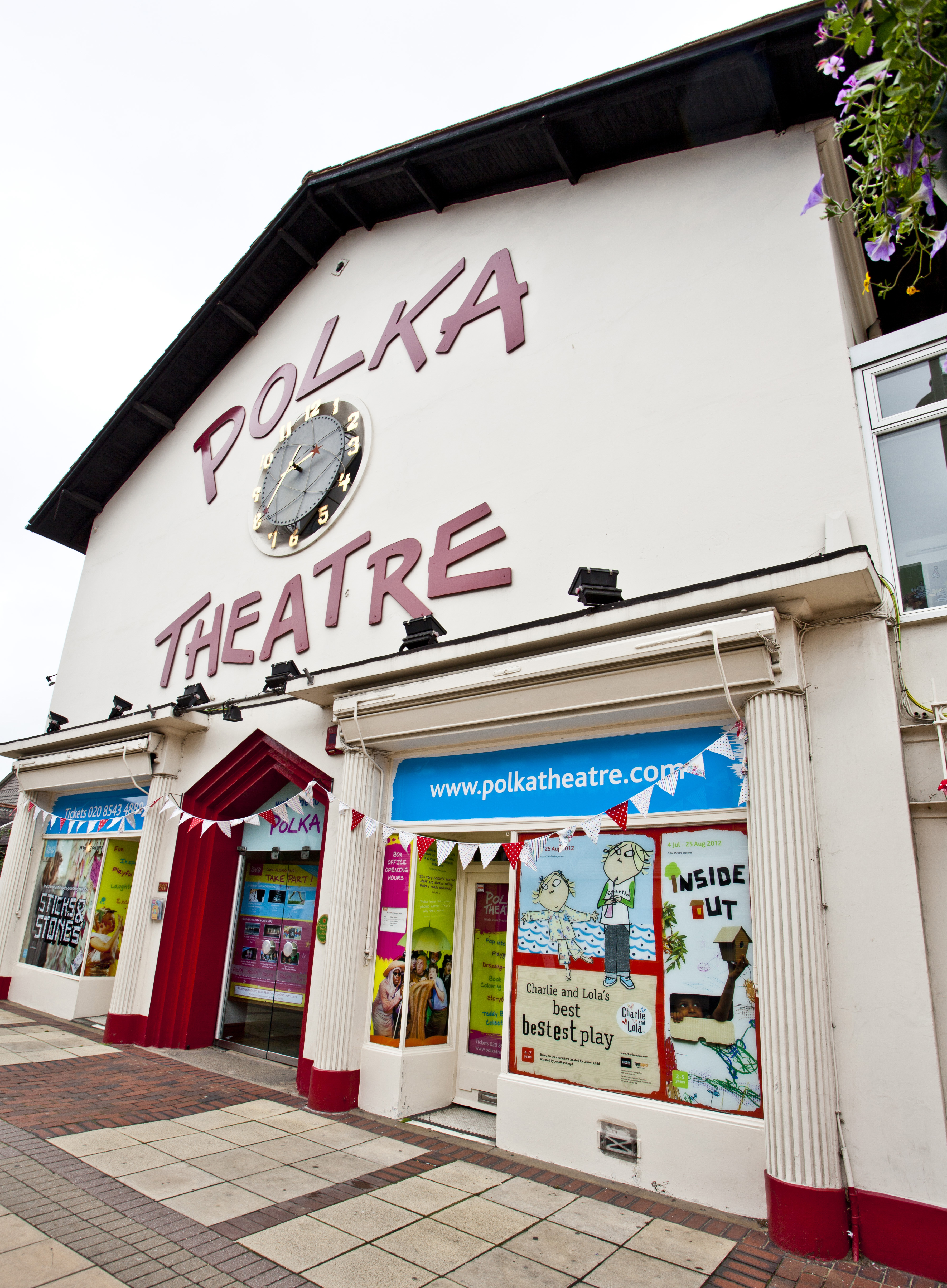
Polka Children's Theatre
 The ''Polka Theatre'' is a children's theatre in Wimbledon,
The ''Polka Theatre'' is a children's theatre in Wimbledon, London Borough of Merton
The London Borough of Merton () is a London borough in London, England. The borough was formed under the London Government Act 1963 in 1965 by the merger of the Municipal Borough of Mitcham, the Municipal Borough of Wimbledon and the Merton ...
, for children up to 13. The theatre contains two performance spaces – a 300-seat main auditorium and a 70-seat studio dedicated to early-year performances. Polka also has a creative learning studio, a garden, an outdoor playground, an indoor play area, exhibition spaces, and a cafe. It is a producing theatre, which also tours shows nationally and internationally, and provides a range of education and community engagement programmes for children as a registered charity and an Arts Council England
Arts Council England is an arm's length non-departmental public body of the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport, Department for Culture, Media and Sport. It is also a registered charity. It was formed in 1994 when the Arts Council o ...
National Portfolio Organisation. It is also funded by the London Borough of Merton
The London Borough of Merton () is a London borough in London, England. The borough was formed under the London Government Act 1963 in 1965 by the merger of the Municipal Borough of Mitcham, the Municipal Borough of Wimbledon and the Merton ...
and a number of private charitable trusts and foundations, individuals and firms. The theatre (formerly the Holy Trinity Halls in Wimbledon) opened in November 1979.
Transport
*Wimbledon station
Wimbledon is an interchange station in the centre of Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon for London Underground, Tramlink, London Trams and National Rail services, and is the only station in London that provides an interchange between the London Underg ...
*Wimbledon Chase railway station
Wimbledon most often refers to:
* Wimbledon, London, a district of southwest London
* Wimbledon Championships, the oldest tennis tournament in the world and one of the four Grand Slam championships
Wimbledon may also refer to:
Places London
* ...
*Raynes Park railway station
Raynes Park railway station serves the district of Raynes Park in the London Borough of Merton. It is south-west of and is situated between and on the South West Main Line. The next station along on the Sutton and Mole Valley lines, Mole ...
*Wimbledon Park tube station
Wimbledon Park is a London Underground station in Wimbledon. It is on the Wimbledon branch of the District line, between Wimbledon and Southfields stations. The station is located on Arthur Road close to the junction with Melrose Avenue close ...
*South Wimbledon tube station
South Wimbledon is a London Underground station in South Wimbledon, a suburb of Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon in south-west London. It is on the Northern line, between Colliers Wood tube station, Colliers Wood and Morden tube station, Morden sta ...
* Dundonald Road Tram Stop
National Rail
Wimbledon is part of Oyster Fare Zone 3.Bus
Wimbledon is served byLondon Buses
London Buses is the subsidiary of Transport for London (TfL) that manages most bus services in London, England. It was formed following the Greater London Authority Act 1999 that transferred control of London Regional Transport (LRT) bus s ...
routes 57, 93, 131 131 may refer to:
*131 (number)
*AD 131
*131 BC
*131 (album), the album by Emarosa
*131 (MBTA bus), the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority bus. For the MBTA bus, see 131 (MBTA bus).
*131 (New Jersey bus), the New Jersey Transit bus
*131 Val ...
, 156
Year 156 ( CLVI) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Silvanus and Augurinus (or, less frequently, year 909 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 156 for thi ...
, 163
Year 163 ( CLXIII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Laelianus and Pastor (or, less frequently, year 916 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 163 for this y ...
, 164, 200
Year 200 ( CC) was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Severus and Victorinus (or, less frequently, year 953 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 200 for this y ...
, 219 and 493
Year 493 ( CDXCIII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Albinus and Eusebius (or, less frequently, year 1246 ''ab urbe condita''). The denomination 493 for th ...
and night bus N87. It is also served by Tramlink route 3.
Literature
In literature, Wimbledon provides the principal setting for several comic novels by author Nigel Williams (including the best-selling '' The Wimbledon Poisoner'' and '' They Came from SW19''), as well as for Elisabeth Beresford's series of children's stories about theWombles
''The Wombles'' are fictional pointy-nosed, furry creatures created by Elisabeth Beresford and originally appearing in a series of children's novels from 1968. They live in burrows, where they aim to help the environment by collecting and recyc ...
.
Wimbledon was given as the site where the sixth Martian
Mars, the fourth planet from the Sun, has appeared as a setting in works of fiction since at least the mid-1600s. Trends in the planet's portrayal have largely been influenced by advances in planetary science. It became the most popular celes ...
invasion cylinder landed in H. G. Wells
Herbert George Wells (21 September 1866 – 13 August 1946) was an English writer, prolific in many genres. He wrote more than fifty novels and dozens of short stories. His non-fiction output included works of social commentary, politics, hist ...
' book ''The War of the Worlds
''The War of the Worlds'' is a science fiction novel by English author H. G. Wells. It was written between 1895 and 1897, and serialised in '' Pearson's Magazine'' in the UK and ''Cosmopolitan'' magazine in the US in 1897. The full novel was ...
'' and is mentioned briefly in the same author's ''The Time Machine
''The Time Machine'' is an 1895 dystopian post-apocalyptic science fiction novella by H. G. Wells about a Victorian scientist known as the Time Traveller who travels to the year 802,701. The work is generally credited with the popularizati ...
'' and '' When the Sleeper Wakes''.
Each October thousands attend the Wimbledon BookFest, which has been running since 2006. Over 60 events are held around Wimbledon, including at the Big Tent on the Common.
Notable residents
 * Bob Astles (1924–2012), former associate of Ugandan presidents
* Bob Astles (1924–2012), former associate of Ugandan presidents Milton Obote
Apollo Milton Obote (28 December 1925 – 10 October 2005) was a Ugandan politician who served as the second prime minister of Uganda from 1962 to 1966 and the second president of Uganda from 1966 to 1971 and later from 1980 to 1985.
A Lango, ...
and Idi Amin
Idi Amin Dada Oumee (, ; 30 May 192816 August 2003) was a Ugandan military officer and politician who served as the third president of Uganda from 1971 until Uganda–Tanzania War, his overthrow in 1979. He ruled as a Military dictatorship, ...
* Ben Barnes (born 1981), actor
*Joseph Bazalgette
Sir Joseph William Bazalgette (; 28 March 1819 – 15 March 1891) was an English civil engineering, civil engineer. As Chief Engineer of London's Metropolitan Board of Works, his major achievement was the creation of the London Main Drainage, t ...
(1819–1891), civil engineer; his creation in the mid 19th century of the sewer network for central London eliminated the incidence of cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
epidemics
*Raymond Briggs
Raymond Redvers Briggs (18 January 1934 – 9 August 2022) was an English illustrator, cartoonist, graphic novelist and author. Achieving critical and popular success among adults and children, he is best known in Britain for his 1978 story ...
(1934–2022), cartoonist
* John Lyde-Brown (died 1787), director of the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
; resident of Cannizaro House; his collection of classical sculpture was acquired by Catherine II
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter III ...
of Russia in 1787 and is held by the Hermitage Museum
The State Hermitage Museum ( rus, Государственный Эрмитаж, r=Gosudarstvennyj Ermitaž, p=ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)ɨj ɪrmʲɪˈtaʂ, links=no) is a museum of art and culture in Saint Petersburg, Russia, and holds the large ...
*James Brunlees
Sir James Brunlees FRSE MICE (1816 – 1892) was a Scottish civil engineer. He was President of the Institution of Civil Engineers for 1882-3.
He was born in Kelso in the Scottish Borders in 1816.
Early life
Brunlees was the son of John Brun ...
(1816–1892), engineer, lived at Argyle Lodge, Parkside
*Josephine Butler
Josephine Elizabeth Butler (; 13 April 1828 – 30 December 1906) was an English feminist and social reformer in the Victorian era. She campaigned for women's suffrage, the right of women to better education, the end of coverture in B ...
(1828–1906), feminist campaigner of the Victorian era, Blue Plaque
A blue plaque is a permanent sign installed in a public place in the United Kingdom, and certain other countries and territories, to commemorate a link between that location and a famous person, event, or former building on the site, serving a ...
at 8 North View, Wimbledon Common
* George Edward Cates (1892–1917), World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious decoration of the Orders, decorations, and medals of the United Kingdom, British decorations system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British ...
recipient
*Duke (1784–1841) and Duchess of Cannizzaro
*Ernst Boris Chain
Sir Ernst Boris Chain (19 June 1906 – 12 August 1979) was a German-born British biochemist and co-recipient of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his work on penicillin.
Life and career
Chain was born in Berlin, the son of Marg ...
(1906–1979), joint winner of the 1945 Nobel Prize in Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine () is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute, Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single ...
for the discovery of penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
. Blue Plaque at 9 North View, Wimbledon Common
*Mavis Cheek
Mavis Mary Cheek (née Wilson, 25 February 1948 – 14 June 2023) was an English novelist. She was the author of fifteen novels, several of which have been translated into other languages. Cheeks' debut novel ''Pause Between Acts'' won the 1988 S ...
(1948-2023), novelist born and brought up in Wimbledon.
*Sarah Churchill, Duchess of Marlborough
Sarah Churchill, Duchess of Marlborough, Princess of Mindelheim, Countess of Nellenburg (née Jenyns, spelt Jennings in most modern references; 5 June 1660 (Old Style) – 18 October 1744), was an English courtier who rose to be one of th ...
(1660–1744), close friend of Queen Anne, resident of Wimbledon Manor House
*Norman Coburn
Norman Coburn (born 6 March 1937) is an Australian former actor, playwright and writer best known for his television serial and soap opera roles. He started his early career in theatre, film and television in the United Kingdom in the mid-1950s. ...
(born 1937), Australian actor played Donald Fisher
Donald George Fisher (September 3, 1928 – September 27, 2009) was an American billionaire businessman and philanthropist. He co-founded the Gap Inc. clothing stores with his wife Doris F. Fisher.
Early life and education
Fisher was born i ...
in Australian soap opera ''Home and Away
''Home and Away'' (''H&A'') is an Australian television soap opera. It was created by Alan Bateman and commenced broadcast on the Seven Network on 17 January 1988. Bateman came up with the concept of the show during a trip to Kangaroo Point, N ...
''
*Annette Crosbie
Annette Crosbie (born 12 February 1934) is a Scottish actress.Annette Crosbie fi ...
(born 1934), actress, screen wife of ''One Foot in the Grave
''One Foot in the Grave'' is a British television British sitcom, sitcom written by David Renwick. There were six series (each consisting of six half-hour episodes) and seven Christmas specials over a period of ten years from early 1990 to late ...
''s Victor Meldrew
*Jack Davenport
Jack Arthur Davenport (born 1 March 1973) is an English actor. He is best known for his roles in the television series '' This Life'' and ''Coupling'', and as James Norrington in the ''Pirates of the Caribbean'' series. He has also appeared i ...
(born 1973), actor
*Sandy Denny
Alexandra Elene MacLean Denny (6 January 1947 – 21 April 1978) was an English singer-songwriter who was lead singer of the British folk rock band Fairport Convention. She has been described as " guably the pre-eminent British folk-rock sin ...
(1947–1978), singer, born at the Nelson Hospital
*Laurence Doherty
Hugh Laurence Doherty (8 October 1875 – 21 August 1919) was a British tennis player and the younger brother of tennis player Reginald Doherty. He was a six-time Grand Slam champion and a double Olympic Gold medalist at the Tennis at the 1900 ...
(1875–1919), winner of thirteen Wimbledon tennis championships and two Olympic gold medals
*Reginald Doherty
Reginald "Reggie" or "R. F." Frank Doherty (14 October 1872 – 29 December 1910) was a British tennis player and the older brother of tennis player Laurence Doherty. He was known in the tennis world as "R.F." rather than "Reggie".
(1872–1910), winner of twelve Wimbledon tennis championships and three Olympic gold medals
*Hugh Dowding
Air Chief Marshal Hugh Caswall Tremenheere Dowding, 1st Baron Dowding, (24 April 1882 – 15 February 1970) was a senior officer in the Royal Air Force. He was Air Officer Commanding RAF Fighter Command during the Battle of Britain and is gene ...
(1882–1970), commander of RAF Fighter Command
RAF Fighter Command was one of the commands of the Royal Air Force. It was formed in 1936 to allow more specialised control of fighter aircraft. It operated throughout the Second World War, winning fame during the Battle of Britain in 1940. The ...
during the Battle of Britain
The Battle of Britain () was a military campaign of the Second World War, in which the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) of the Royal Navy defended the United Kingdom (UK) against large-scale attacks by Nazi Germany's air force ...
in 1940, Blue Plaque at 3 St Mary's Road
*Henry Dundas
Henry Dundas, 1st Viscount Melville, Privy Council (United Kingdom), PC, FRSE (28 April 1742 – 28 May 1811), styled as Lord Melville from 1802, was a British politician who served as Home Secretary from 1791 to 1794 and First Lord of the Ad ...
, Viscount Melville
Viscount Melville, of Melville in the County of Edinburgh, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom.
Origins
The title was created on 24 December 1802 for the notable lawyer and politician Henry Dundas. He was created Baron Dunira, ...
(1742–1811), Home Secretary
The secretary of state for the Home Department, more commonly known as the home secretary, is a senior minister of the Crown in the Government of the United Kingdom and the head of the Home Office. The position is a Great Office of State, maki ...
and Secretary of State for War
The secretary of state for war, commonly called the war secretary, was a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, which existed from 1794 to 1801 and from 1854 to 1964. The secretary of state for war headed the War Offic ...
to William Pitt the Younger
William Pitt (28 May 1759 – 23 January 1806) was a British statesman who served as the last prime minister of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain from 1783 until the Acts of Union 1800, and then first Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, p ...
, resident of Cannizaro House
* Maria Fetherstonhaugh (1847–1918), novelist, bought a house by Wimbledon Windmill in 1905, where Robert Baden-Powell
Lieutenant-General Robert Stephenson Smyth Baden-Powell, 1st Baron Baden-Powell, ( ; 22 February 1857 – 8 January 1941) was a British Army officer, writer, founder of The Boy Scouts Association and its first Chief Scout, and founder, with ...
as her guest wrote ''Scouting for Boys
''Scouting for Boys: A handbook for instruction in good citizenship'' is a book on Boy Scout training, published in various editions since 1908. Early editions were written and illustrated by Robert Baden-Powell with later editions being exten ...
''.
* Sid Field (1904–1950), English comedy actor, lived at 44 Parkside.
*Charles James Fox
Charles James Fox (24 January 1749 – 13 September 1806), styled ''The Honourable'' from 1762, was a British British Whig Party, Whig politician and statesman whose parliamentary career spanned 38 years of the late 18th and early 19th centurie ...
(1749–1806), Britain's first Foreign Secretary under prime minister Marquess of Rockingham
Marquess of Rockingham, in the County of Northampton, was a title in the Peerage of Great Britain. It was created in 1746 for Thomas Watson-Wentworth, 1st Marquess of Rockingham, Thomas Watson-Wentworth, 1st Earl of Malton. The Watson family ...
; took over Rockingham's Church Road house after the latter's death in 1782
*Ford Madox Ford
Ford Madox Ford (né Joseph Leopold Ford Hermann Madox Hueffer ( ); 17 December 1873 – 26 June 1939) was an English novelist, poet, critic and editor whose journals ''The English Review'' and ''The Transatlantic Review (1924), The Transatlant ...
(1873–1939), author; works include ''The Good Soldier
''The Good Soldier: A Tale of Passion'' is a 1915 novel by the British writer Ford Madox Ford. It is set just before World War I, and chronicles the tragedy of Edward Ashburnham and his seemingly perfect marriage, along with that of his two A ...
'' and ''Parade's End
''Parade's End'' is a tetralogy of novels by the British novelist and poet Ford Madox Ford, first published from 1924 to 1928. The novels chronicle the life of a member of the English gentry before, during and after World War I. The setting is ...
''
* John William Godward (1861–1922), painter
*Charles Gore
Charles Gore (22 January 1853 – 17 January 1932) was a Church of England bishop, first of Worcester, then Birmingham, and finally of Oxford. He was one of the most influential Anglican theologians of the 19th century, helping reconcile the ...
born 1853, Wimbledon, theologian.
*Charles Patrick Graves
Charles Patrick Ranke Graves (1 December 1899 – 20 February 1971) was a British journalist, travel writer and novelist. He came from a large literary family. Among his nine siblings were the writers Robert Graves and Philip Graves.
Early li ...
(1899–1971), journalist
*Robert Graves
Captain Robert von Ranke Graves (24 July 1895 – 7 December 1985) was an English poet, soldier, historical novelist and critic. His father was Alfred Perceval Graves, a celebrated Irish poet and figure in the Gaelic revival; they were b ...
(1895–1985), poet
* Victoria Hamilton (born 1971), actress
*George Hamilton-Gordon, 4th Earl of Aberdeen
George Hamilton-Gordon, 4th Earl of Aberdeen (28 January 178414 December 1860), styled Lord Haddo from 1791 to 1801, was a British statesman, diplomat and landowner, successively a Tory, Conservative and Peelite politician and specialist in f ...
(1784–1860), prime minister 1852–55; resident of Cannizaro House
* Imogen Hassal (1942–1980), actress
*Ted Heath
Sir Edward Richard George Heath (9 July 1916 – 17 July 2005) was a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1970 to 1974 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 1965 to 1975. Heath also served for 51 year ...
(1902–1969), bandleader
*Georgette Heyer
Georgette Heyer (; 16 August 1902 – 4 July 1974) was an English novelist and short-story writer, in both the Regency romance and detective fiction genres. Her writing career began in 1921, when she turned a story conceived for her ail ...
(1902–1974), novelist born and raised in Wimbledon. She wrote her first five novels there. Two later novels, ''Pastel'' and ''Behold, Here's Poison'', are set in a suburb very like Wimbledon.
*Mark Hollis
Mark David Hollis (4 January 1955 – February 2019) was an English musician and singer-songwriter. He achieved commercial success and critical acclaim in the 1980s and 1990s as the co-founder, lead singer and principal songwriter of the band ...
(1955–2019), musician
* Leslie Hore-Belisha, 1st Baron Hore-Belisha (1893–1957), Minister of Transport, 1934–7 who introduced the driving test and the Belisha Beacon
A Belisha beacon () is a yellow-coloured globe lamp atop a tall black and white striped pole, marking pedestrian crossings of roads in the United Kingdom, Ireland, and other places that were historically influenced by Britain, such as Hong Kong, ...
; then Secretary of State for War
The secretary of state for war, commonly called the war secretary, was a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, which existed from 1794 to 1801 and from 1854 to 1964. The secretary of state for war headed the War Offic ...
, 1937–40
*Thomas Hughes
Thomas Hughes (20 October 1822 – 22 March 1896) was an English lawyer, judge, politician and author. He is most famous for his novel ''Tom Brown's School Days'' (1857), a semi-autobiographical work set at Rugby School, which Hughes had atte ...
(1822–1896), author of the 1857 novel ''Tom Brown's Schooldays
''Tom Brown's School Days'' (sometimes written ''Tom Brown's Schooldays'', also published under the titles ''Tom Brown at Rugby'', ''School Days at Rugby'', and ''Tom Brown's School Days at Rugby'') is a novel by Thomas Hughes, published in 18 ...
'' which was written in Wimbledon
*James Hunt
James Simon Wallis Hunt (29 August 1947 – 15 June 1993) was a British racing driver and broadcaster, who competed in Formula One from to . Nicknamed "the Shunt", Hunt won the Formula One World Drivers' Championship in with McLaren, and wo ...
(1947–1993), racing driver and commentator. Formula 1 World Champion 1976
* John Innes (1829–1904), property developer and philanthropist
* Sir Theodore Janssen of Wimbledon (c.1658–1748), director of the South Sea Company
The South Sea Company (officially: The Governor and Company of the merchants of Great Britain, trading to the South Seas and other parts of America and for the encouragement of the Fishery) was a British joint-stock company founded in Ja ...
and founder-member of the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
. Resident of Wimbledon Manor House. The grounds of his later house bordered the east side of the High Street.
*Paul Jerricho
Paul Jerricho (born 18 November 1948) is a British actor.
Early life
Brought up in the Caribbean, Jerricho got into the acting bug after playing Joseph in a Nativity play. He received his training at the Drama Centre London.
Personal life ...
, actor
*Hetty King
Winifred Emms (4 April 1883 – 28 September 1972), best known by her stage name Hetty King, was an English entertainer who performed in the music halls as a male impersonator over some 70 years.
Early life
She was born in New Brighton, Ches ...
(1883–1972), music hall artiste and male impersonator. A blue commemorative plaque was erected on her home in Palmerston Road, Wimbledon by The Music Hall Guild of Great Britain and America
The Music Hall Guild of Great Britain and America and the Theatre and Film Guild of Great Britain and America is a registered theatre charity and non-profit making theatre organisation based in London. The Guild's patrons include Brian Crouche ...
in November 2010.
*Vanessa Kirby
Vanessa Nuala Kirby (born 18 April 1987 or 1988) is an English actress and producer. She rose to international prominence with her portrayal of Princess Margaret in the Netflix drama series ''The Crown'' (2016–2017), for which she won the Bri ...
(born 1988), actress
* Don Lang (1925–1992), with his band, a mainstay of Britain's first television rock and roll programme ''Six-Five Special
''Six-Five Special'' is a British television programme launched in February 1957 when both television and rock and roll were in their infancy in Britain.
Description
''Six-Five Special'' was the BBC's first attempt at a rock-and-roll programme. ...
''
* Alvar Lidell (1908–1981), BBC radio announcer; his voice was well known during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
*Jenny Lind
Johanna Maria Lind (Madame Goldschmidt) (6 October 18202 November 1887) was a Swedish opera singer, often called the "Swedish Nightingale". One of the most highly regarded singers of the 19th century, she performed in soprano roles in opera in ...
(1820–1887), the Swedish Nightingale, at Argyle Lodge, Parkside.
*Sir Joseph Norman Lockyer
Sir Joseph Norman Lockyer (17 May 1836 – 16 August 1920) was an English scientist and astronomer. Along with the French scientist Pierre Janssen, he is credited with discovering the gas helium. Lockyer also is remembered for being the fo ...
(1836–1920), scientist and astronomer; joint discoverer of helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
*James Murdoch
James Rupert Jacob Murdoch (born 13 December 1972) is an American - British businessman. He is the younger son of media mogul Rupert Murdoch and the former chief executive officer (CEO) of 21st Century Fox from 2015 to 2019.
He was the chairma ...
(born 1972), younger son of media mogul Rupert Murdoch
Keith Rupert Murdoch ( ; born 11 March 1931) is an Australian - American retired business magnate, investor, and media mogul. Through his company News Corp, he is the owner of hundreds of List of assets owned by News Corp, local, national, a ...
and former chief executive officer (CEO) of 21st Century Fox
Twenty-First Century Fox, Inc., which did business as 21st Century Fox, was an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate based in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It was formed on June 28, 2013, as the legal successor ...
*Frederick Marryat
Captain Frederick Marryat (10 July 1792 – 9 August 1848) was a Royal Navy officer and novelist. He is noted today as an early pioneer of nautical fiction, particularly for his semi-autobiographical novel '' Mr Midshipman Easy'' (1836). He is ...
(1792–1848), author, Blue Plaque at Gothic Lodge, 6 Woodhayes Road
* Tony McGuinness (born 1959), guitarist and songwriter, Above and Beyond
*Michael McIntyre
Michael Hazen James McIntyre (born 21 February 1976) is a British comedian, writer, and television presenter. In 2012, he was the highest-grossing stand-up comedian in the world. He currently presents the variety and stand-up comedy show '' Mic ...
(born 1976), comedian born in the area
* Thomas Ralph Merton (1888–1969), physicist
* Marcus Mumford (born 1987), lead singer and songwriter, Mumford & Sons
Mumford & Sons are a British folk rock band formed in London in 2007. The band consists of Marcus Mumford (lead vocals, acoustic guitar, electric guitar, drums), Ted Dwane (vocals, double bass, bass guitar), and Ben Lovett (British musician), B ...
* John Murray III (1808–1892), publisher; significant publications include Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
's ''The Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life'')The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by M ...
''; Murray built a house called "Newstead" on four acres at Somerset Road.
* Horatio, Viscount Nelson (1758–1805), admiral; Nelson's estate, Merton Place, included part of Wimbledon at the eastern end of the Broadway, though, strictly he was a resident of Merton the neighbouring parish
* Margaret Noble or Sister Nivedita (1867-1911), campaigner for Indian Independence
*Alan Pardew
Alan Scott Pardew (born 18 July 1961) is an English football manager and former professional footballer, who most recently managed Greek Super League club Aris Thessaloniki.
Pardew's highest achievements in the sport include reaching the FA Cup ...
(born 1961), football manager
*Michelle Paver
Michelle Paver (born 7 September 1960) is a British novelist. She is best known for her children's historical fantasy series '' Chronicles of Ancient Darkness'', set in prehistoric Europe, which started with '' Wolf Brother'', in 2004. It has s ...
(born 1960), author, '' Chronicles of Ancient Darkness''
*Charles Pepys, 1st Earl of Cottenham
Charles Christopher Pepys, 1st Earl of Cottenham, (; 29 April 178129 April 1851) was an English lawyer, judge and politician. He was twice Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain.
Background and education
Cottenham was born in London, the second ...
(1781–1851), Lord Chancellor; judge in the landmark 1841 court case Saunders v Vautier
, (1841) 4 Beav 115 is a leading English trusts law case. It laid down the rule of Equity (law), equity which provides that, if all of the beneficiary (trust), beneficiaries in the trust law, trust are of Age of majority, adult age and under ...
* Sir William Henry Preece (1834–1913), developed English telephone system; Blue Plaque at Gothic Lodge, 6 Woodhayes Road.
*Oliver Reed
Robert Oliver Reed (13 February 1938 – 2 May 1999) was an English actor, known for his upper-middle class, macho image and his heavy-drinking, "hellraiser" lifestyle. His screen career spanned over 40 years, between 1955 and 1999. At the ...
(1938–1999), actor
*Margaret Rutherford
Dame Margaret Taylor Rutherford (11 May 1892 – 22 May 1972) was an English actress of stage, film and television.
Rutherford came to national attention following World War II in the film adaptations of Noël Coward's ''Blithe Spirit (1945 f ...
(1892–1972), actress, Blue Plaque at 4 Berkeley Place
*Arthur Schopenhauer
Arthur Schopenhauer ( ; ; 22 February 1788 – 21 September 1860) was a German philosopher. He is known for his 1818 work ''The World as Will and Representation'' (expanded in 1844), which characterizes the Phenomenon, phenomenal world as ...
(1788–1860), philosopher, Blue Plaque at Eagle House where he lived in 1803
*Ridley Scott
Sir Ridley Scott (born 30 November 1937) is an English film director and producer. He directs films in the Science fiction film, science fiction, Crime film, crime, and historical drama, historical epic genres, with an atmospheric and highly co ...
(born 1937), film director; films include ''Blade Runner
''Blade Runner'' is a 1982 science fiction film directed by Ridley Scott from a screenplay by Hampton Fancher and David Peoples. Starring Harrison Ford, Rutger Hauer, Sean Young, and Edward James Olmos, it is an adaptation of Philip K. Di ...
'' and ''Gladiator''.
*Haile Selassie I of Ethiopia
Haile Selassie I (born Tafari Makonnen or '' Lij'' Tafari; 23 July 189227 August 1975) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1930 to 1974. He rose to power as the Regent Plenipotentiary of Ethiopia (') under Empress Zewditu between 1916 and 1930. Wid ...
(1892–1975), guest at a house in Parkside while in exile from Ethiopia owing to the Italian invasion; his statue stands in Cannizaro Park.
* Renu Setna, actor
*Brian Sewell
Brian Alfred Christopher Bushell Sewell (; 15 July 1931 – 19 September 2015) was an English art critic. He wrote for the ''Evening Standard'' and had an acerbic view of conceptual art and the Turner Prize. ''The Guardian'' described him as ...
(1931–2015), art critic and media personality
* Mark Edgley Smith (1955–2008), composer
*Steve-O
Stephen Gilchrist Glover (born June 13, 1974), known professionally as Steve-O, is an American stunt performer, comedian, media personality, and podcast host. His career is mostly centered on his shocking and pain-inducing stunts in the realit ...
(born 1974), entertainer, born in Wimbledon
*Jamie T (born 1986), musician
*David Tipper (born 1976), producer, composer, DJ
*John Horne Tooke (1736–1812), politician, lived at Chester House, Wimbledon, Chester House on Wimbledon Common
Wimbledon Common is a large open space in Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon, southwest London. There are three named areas: Wimbledon Common, Putney Heath, and Putney Lower Common, which together are managed under the name Wimbledon and Putney Co ...
*Arnold Toynbee (historian, born 1852), Arnold Toynbee (1852–1883), economic historian, Blue Plaque at 49 Wimbledon Parkside
*Joseph Toynbee (1815–1866), surgeon, Blue Plaque at 49 Wimbledon Parkside
*Ralph Tubbs (1912–1996), architect; his buildings include the Dome of Discovery and Charing Cross Hospital
*Keith Walker (cricketer), Keith Walker (1922–1989), cricketer
*Charles Watson-Wentworth, 2nd Marquess of Rockingham (1730–1782), twice Prime Minister. His Church Road house adjoined the grounds of Sir Theodore Janssen's and was previously occupied by a Mr Rush as shown othis map
*Kemi Badenoch (1980), Leader of the Opposition (United Kingdom), Leader of the Opposition and Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party since 2024 *Dame June Whitfield (1925–2018), actress *William Wilberforce (1759–1833), anti-slavery campaigner
Amenities
Major public open spaces
 *Cannizaro Park
*Richmond Park
*
*Cannizaro Park
*Richmond Park
*Wimbledon Common
Wimbledon Common is a large open space in Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon, southwest London. There are three named areas: Wimbledon Common, Putney Heath, and Putney Lower Common, which together are managed under the name Wimbledon and Putney Co ...
* Wimbledon Park
Museums
Southside House
*Wimbledon Lawn Tennis Museum
Wimbledon Museum
*Wimbledon Windmill
Schools
Secondary
*Ricards Lodge High School, Lake Road, Wimbledon (girls) *Rutlish School, Rutlish School, Watery Lane, Merton Park (boys) *Ursuline High School (Wimbledon), Ursuline High School, Crescent Road, Wimbledon (Catholic Church, RC, girls) *Wimbledon College, Wimbledon College, Edge Hill, Wimbledon (RC, boys) *Wimbledon High School
Wimbledon High School is a Private schools in the United Kingdom, private girls' day school in Wimbledon, London, Wimbledon, South West (London sub region), South West London. It is a Girls' Day School Trust school and is a member of the Girls' ...
, Mansel Road, Wimbledon (girls)Primary
*Dundonald Primary School (Wimbledon), Dundonald Primary School *Garfield Primary school (Mixed) Garfield road, Wimbledon *Hollymount Primary School (Mixed), Cambridge Road, West Wimbledon *Holy Trinity Primary School, Church of England, Effra Road, Wimbledon *St. Mary's Catholic Primary School, Russell Road, Wimbledon *Wimbledon Chase Primary School, Wimbledon Chase Primary School, Merton Hall Road, Wimbledon *Wimbledon Park Primary School, Havana Road, Wimbledon Park *Bishop Gilpin, Lake Road, Wimbledon ParkIndependent
*Allenswood Boarding Academy (Girls' School), Albert Road, Wimbledon – founded 1870, closed 1950s *Donhead, Donhead Lodge (Boys' School), Edge Hill, Wimbledon *Ursuline Preparatory School, Wimbledon (closed 2024) *Hall School Wimbledon (Mixed School), The Downs, Wimbledon *King's College School, King's College School, Southside, Wimbledon *The Norwegian School in London (Norwegian School), Arteberry Road, Wimbledon *Wimbledon High School, Wimbledon High School (Girls' School), Mansel Road, Wimbledon *Old Central School, Church of England, Camp Road, Wimbledon – founded 1758, closed 1960s *The Rowans School (Mixed, Primary School), Drax Avenue, WimbledonPlaces of worship
See also
* Crooked BilletReferences
Bibliography *Bartlett, William A.,History of Antiquities of the Parish of Wimbledon
', Simpkin, Marshall, & co., 1865 *Brown, John W., ''Lysons's History of Wimbledon'', Local History Reprints, 1991, *Milward, Richard, ''Historic Wimbledon, Caesar's Camp to Centre Court'', The Windrush Press and Fielders of Wimbledon, 1989, *Milward, Richard, ''New Short History of Wimbledon'', Wimbledon Society, 1989
External links
Local authoritiesmerton.gov.uk
Community
lovewimbledon.org
History
british-history.ac.uk
The Environs of London: Volume 1: County of Surrey, 1792, "Wimbledon", pp. 519–540, Daniel Lysons
british-history.ac.uk
A History of the County of Surrey: Volume 4, 1912, "Parishes: Wimbledon", pp. 120–125, H. E. Malden (editor) {{Authority control Wimbledon, London, Areas of London Districts of the London Borough of Merton Major centres of London