Wilhelmine Of Prussia, Margravine Of Brandenburg-Bayreuth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Princess Wilhelmine of Prussia (Friederike Sophie Wilhelmine; 3 July 170914 October 1758) was a Prussian princess and composer. She was the eldest daughter of
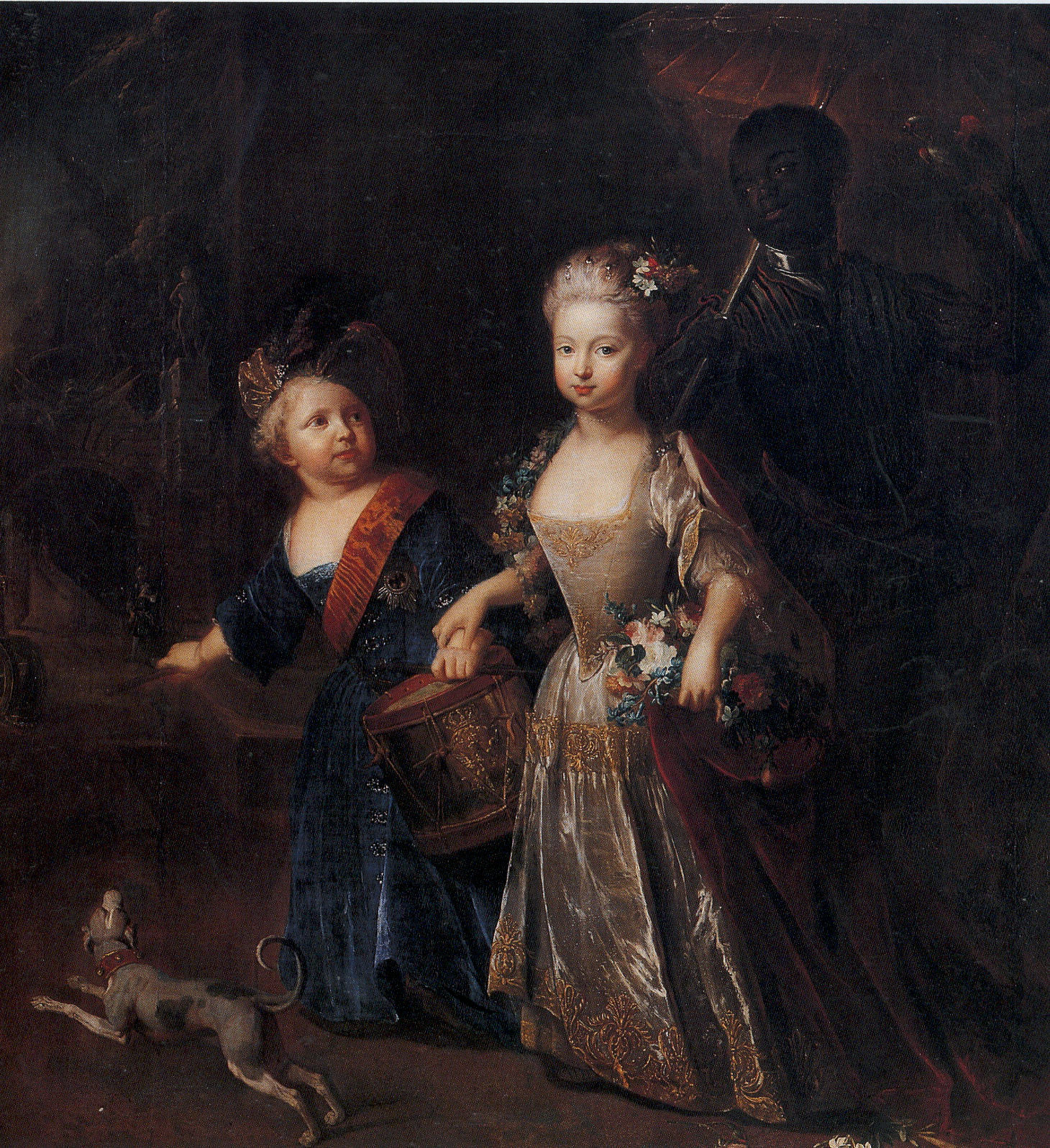 Born in Berlin, Wilhelmine shared the unhappy childhood of her brother,
Born in Berlin, Wilhelmine shared the unhappy childhood of her brother,
 When Wilhelmine's spouse came into his inheritance in 1735, the pair set about making Bayreuth a miniature
When Wilhelmine's spouse came into his inheritance in 1735, the pair set about making Bayreuth a miniature
 The margravine's memoirs, ''Memoires de ma vie'', written or revised in French between 1748 and her death, are preserved in the Royal Library of Berlin. They were first printed in two forms in 1810: a German translation down to the year 1733 from the firm of Cotta of Tübingen; and a version in French published by Vieweg of Brunswick, and coming down to 1742. There were several subsequent editions, including a German one published at
The margravine's memoirs, ''Memoires de ma vie'', written or revised in French between 1748 and her death, are preserved in the Royal Library of Berlin. They were first printed in two forms in 1810: a German translation down to the year 1733 from the firm of Cotta of Tübingen; and a version in French published by Vieweg of Brunswick, and coming down to 1742. There were several subsequent editions, including a German one published at
"Memoirs of Wilhelmine, Margravine of Bayreuth"
''worldcat.org'' Retrieved August 4, 2019
''Argenore'' (opera)
from the Hamburg Opera House * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Wilhelmine Of Prussia, Princess 1709 births 1758 deaths German classical composers 18th-century classical composers 18th-century German women writers 18th-century German composers 18th-century German women musicians 18th-century German writers Margravines of Brandenburg-Bayreuth Musicians from Berlin People from the Margraviate of Brandenburg People from Bayreuth House of Hohenzollern German Baroque composers German women classical composers German memoirists Prussian princesses Lutenists from the Holy Roman Empire German women memoirists Daughters of kings Children of Frederick William I of Prussia Daughters of princes regnant Daughters of prince-electors
Frederick William I of Prussia
Frederick William I (; 14 August 1688 – 31 May 1740), known as the Soldier King (), was King in Prussia and Elector of Brandenburg from 1713 until his death in 1740, as well as Prince of Neuchâtel.
Born in Berlin, he was raised by the Hugu ...
and Sophia Dorothea of Hanover
Sophia Dorothea of Hanover ( – 28 June 1757; ) was Queen in Prussia and Electress of Brandenburg during the reign of her husband, King Frederick William I, from 1713 to 1740. She was the mother of Frederick the Great (King Frederick II of ...
, and a granddaughter of George I of Great Britain
George I (George Louis; ; 28 May 1660 – 11 June 1727) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland from 1 August 1714 and ruler of the Electorate of Hanover within the Holy Roman Empire from 23 January 1698 until his death in 1727. ...
. She was the older sister of Frederick the Great
Frederick II (; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was the monarch of Prussia from 1740 until his death in 1786. He was the last Hohenzollern monarch titled ''King in Prussia'', declaring himself ''King of Prussia'' after annexing Royal Prussia ...
. In 1731, she married Frederick Frederick may refer to:
People
* Frederick (given name), the name
Given name
Nobility
= Anhalt-Harzgerode =
* Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670)
= Austria =
* Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria fro ...
, Margrave
Margrave was originally the Middle Ages, medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or a monarchy, kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain Feudal ...
of Brandenburg-Bayreuth
The Principality of Bayreuth () or Margraviate of Brandenburg-Bayreuth (''Markgraftum Brandenburg-Bayreuth'') was an immediate territory of the Holy Roman Empire, ruled by a Franconian branch of the Hohenzollern dynasty. Since Burgrave Frederi ...
. The baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
buildings and parks built during her tenure shape much of the present appearance of the town of Bayreuth
Bayreuth ( or ; High Franconian German, Upper Franconian: Bareid, ) is a Town#Germany, town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtel Mountains. The town's roots date back to 11 ...
, Germany.
Early life
 Born in Berlin, Wilhelmine shared the unhappy childhood of her brother,
Born in Berlin, Wilhelmine shared the unhappy childhood of her brother, Frederick the Great
Frederick II (; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was the monarch of Prussia from 1740 until his death in 1786. He was the last Hohenzollern monarch titled ''King in Prussia'', declaring himself ''King of Prussia'' after annexing Royal Prussia ...
, whose friend and confidante she remained all her life, with the exception of one short interval. She was fiercely beaten and abused by her governess during her childhood. Wilhelmine later wrote: "Not a day passed that she he governessdid not prove upon me the fearful power of her fists." The mistreatment continued until the prince's governess finally said to their mother, who had been oblivious to the abuse, that she would not be surprised if Wilhelmine was eventually beaten until she was crippled. After this, the governess was promptly replaced.
Being the eldest daughter in her family, she was early the target of discussions about political marriages. Her mother, Queen Sophia Dorothea, wished her to marry her nephew Frederick, Prince of Wales
Frederick, Prince of Wales (Frederick Louis, German: ''Friedrich Ludwig''; 31 January 1707 – 31 March 1751) was the eldest son and heir apparent of King George II of Great Britain. He grew estranged from his parents, King George and Queen C ...
, but on the British side there was no inclination to make an offer of marriage except in exchange for substantial concessions that Wilhelmine's father would not accept. The fruitless intrigues carried on by Sophia Dorothea to bring about this match played a large part in Wilhelmine's early life. Her father, on the other hand, preferred a match with the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful Dynasty, dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout ...
.
Marriage
After much talk of other matches came to nothing, Wilhelmine was eventually married in 1731 to herHohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, ; , ; ) is a formerly royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) German dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenburg, Prussia, the German Empire, and Romania. ...
kinsman, Frederick, Margrave of Brandenburg-Bayreuth. Frederick had been engaged to Wilhelmine's younger sister, Sophie
Sophie is a feminine given name, another version of Sophia, from the Greek word for "wisdom".
People with the name Born in the Middle Ages
* Sophie, Countess of Bar (c. 1004 or 1018–1093), sovereign Countess of Bar and lady of Mousson
* Soph ...
, but at the last moment King Frederick William I decided to replace her with Wilhelmine. The groom was not consulted in this decision.
This marriage was only accepted by Wilhelmine under threats from her father and with a view to lightening her brother's disgrace. It was initially a happy marriage, but was eventually clouded first by limited financial resources and then by a love affair of the future Margrave
Margrave was originally the Middle Ages, medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or a monarchy, kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain Feudal ...
with Dorothea von Marwitz, whose rise as an official mistress at the court of Bayreuth was bitterly resented by her brother Frederick the Great and caused an estrangement of some three years between him and Wilhelmine.
Margravine
 When Wilhelmine's spouse came into his inheritance in 1735, the pair set about making Bayreuth a miniature
When Wilhelmine's spouse came into his inheritance in 1735, the pair set about making Bayreuth a miniature Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; ) is a former royal residence commissioned by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, in the Yvelines, Yvelines Department of Île-de-France, Île-de-France region in Franc ...
. Their building projects included the rebuilding of their summer residence (now part of the Hermitage Museum
The State Hermitage Museum ( rus, Государственный Эрмитаж, r=Gosudarstvennyj Ermitaž, p=ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)ɨj ɪrmʲɪˈtaʂ, links=no) is a museum of art and culture in Saint Petersburg, Russia, and holds the large ...
); the rebuilding of the great Bayreuth opera house; the building of a second, new opera house; the building of a theater; and the reconstruction of the Bayreuth palace. The so-called ''Bayreuth Rococo
Rococo, less commonly Roccoco ( , ; or ), also known as Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and dramatic style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpte ...
'' style of architecture is renowned even today. The pair also founded the University of Erlangen
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Univ ...
. All of these ambitious undertakings pushed the court to the verge of bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the deb ...
.
The margravine made Bayreuth one of the chief intellectual centers of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, surrounding herself with a court of wits and artists that accrued added prestige from the occasional visits of Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778), known by his ''Pen name, nom de plume'' Voltaire (, ; ), was a French Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment writer, philosopher (''philosophe''), satirist, and historian. Famous for his wit ...
and Frederick the Great.
Wilhelmine's brother Frederick granted her an allowance in exchange for troops, following the same procedure with her sisters. With the outbreak of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
, Wilhelmine's interests shifted from dilettantism to diplomacy. Austrian diplomats were trying to influence the court of Bayreuth to take their side against Prussia. In September 1745, during the Silesian war, Wilhelmine met with Maria Theresa of Austria. This almost destroyed her intimate relationship with her brother. In 1750 Wilhelmine visited the Prussian court for several weeks and met famous contemporaries such as Voltaire, Maupertuis and La Mettrie. In June 1754, the siblings met for the last time, after which Frederick swore her his eternal loyalty. She acted as eyes and ears for her brother in southern Germany until her death at Bayreuth
Bayreuth ( or ; High Franconian German, Upper Franconian: Bareid, ) is a Town#Germany, town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtel Mountains. The town's roots date back to 11 ...
on 14 October 1758, the day of Frederick's defeat by the Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
n forces of Leopold Josef Graf Daun at the Battle of Hochkirch
The Battle of Hochkirch took place on 14 October 1758, during the Third Silesian War (part of the Seven Years' War). After several weeks of maneuvering for position, an Austrian army of 80,000 commanded by Lieutenant Field Marshal Leopold Jos ...
. Although Frederick had lost many friends and family to death throughout his life, Wilhelmine's hit him the hardest. He suffered from severe illness for a week following news of Wilhelmine's death and fell into a depression from which he never fully recovered.
On the tenth anniversary of her death, her devastated brother had the Temple of Friendship built at Sanssouci
Sanssouci () is a historical building in Potsdam, near Berlin. Built by Prussian King Frederick the Great as his summer palace, it is often counted among the German rivals of Versailles. While Sanssouci is in the more intimate Rococo style and ...
in her memory.
Works
 The margravine's memoirs, ''Memoires de ma vie'', written or revised in French between 1748 and her death, are preserved in the Royal Library of Berlin. They were first printed in two forms in 1810: a German translation down to the year 1733 from the firm of Cotta of Tübingen; and a version in French published by Vieweg of Brunswick, and coming down to 1742. There were several subsequent editions, including a German one published at
The margravine's memoirs, ''Memoires de ma vie'', written or revised in French between 1748 and her death, are preserved in the Royal Library of Berlin. They were first printed in two forms in 1810: a German translation down to the year 1733 from the firm of Cotta of Tübingen; and a version in French published by Vieweg of Brunswick, and coming down to 1742. There were several subsequent editions, including a German one published at Leipzig
Leipzig (, ; ; Upper Saxon: ; ) is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Saxony. The city has a population of 628,718 inhabitants as of 2023. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, eighth-largest city in Ge ...
in 1908. An English translation was published in Berlin in 1904. For the discussion on the authenticity of these entertaining, though not very trustworthy, memoirs, see G. H. Pertz, ''Uber die Merkwürdigkeiten der Markgrafin'' (1851). See also Arvede Barine, ''Princesses et grandes dames'' (Paris, 1890); E. E. Cuttell, ''Wilhelmine, Margravine of Baireuth'' (London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, 2 vols., 1905); ' and R. Fester, ''Die Bayreuther Schwester Friedrichs des Grossen'' (Berlin, 1902). Writer William Thackeray
William Makepeace Thackeray ( ; 18 July 1811 – 24 December 1863) was an English novelist and illustrator. He is known for his satirical works, particularly his 1847–1848 novel '' Vanity Fair'', a panoramic portrait of British society, and t ...
recommended the memoirs to "those who are curious about European Court history of the last age".
In addition to her other accomplishments, Wilhelmine was also a gifted composer and supporter of music. She was a lutenist
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted.
More specifically, the term "lute" commonly r ...
, a student of Sylvius Leopold Weiss
Sylvius Leopold Weiss (12 October 168716 October 1750) was a German composer and lutenist.
Born in Grottkau near Breslau, the son of Johann Jacob Weiss, also a lutenist, Weiss was one of the most important and most prolific composers of lute m ...
, and the employer of Bernhard Joachim Hagen.
Keyboard Concerto in G minor
# Allego, G minor.
# Cantabile, B flat major.
# Gavottes I & II, G minor. Cembalo, Fl, Strings
The obbligato flute part could have been played either by her brother or her husband, as both were flautists (and pupils of Quantz). Each movement takes wing from solid and vigorous openings. There is a stubborn insistence about the first tutti's repeated octave jumps, offset by the buoyancy of its striding sequences. She has a Bach-like flair for phrase extensions, which is also evident in the final gavotte where the solo shadows the orchestra and emerges to take the lead. Some of the ideas in the 34 bar slow movement are more son-of-Bach in style; and in the D minor second gavotte, which serves as a central "trio" to the first, there is a delicate episode of rather French, languishing descents.
''Argenore'': opera c. 1740. Seven soloists (3 sop., 1 mezzo-sop., 2 alto, 1 baritone or mezzo-sop.), and orchestra (1 flute, 2 oboes, 2 trumpets, strings, continuo). Performed in 1740 for her husband's birthday.
Cavatinen: short songs; voice, strings, harpsichord.
Flute Sonata: flute & keyboard, c. 1730.
Some chamber music still survives.
Issue
Wilhelmine's only child was Elisabeth Fredericka Sophie of Brandenburg-Bayreuth, born on August 30, 1732. Described by Casanova as the most beautiful princess in Germany, she was married to Karl Eugen, Duke of Württemberg, in 1748. She died on 6 April 1780 without surviving children.Memoirs
An earlier English translation from the French of her memoirs was published in a two volume edition in 1828 by Hunt and Clarke, York St., Covent Garden. Scribner and Welford publishedPrincess Helena of the United Kingdom
Princess Helena (Helena Augusta Victoria; 25 May 1846 – 9 June 1923), later Princess Christian of Schleswig-Holstein, was the third daughter and fifth child of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert.
Helena was educated by private tutors chosen ...
's German-to-English translation of Wilhelmine's memoirs in 1887.''worldcat.org'' Retrieved August 4, 2019
In fiction
*Princess Wilhelmine is the main character of the 1909 historical novel ''A Gentle Knight of Old Brandenburg'' by Charles Major.Ancestry
Notes
References
* G.P. Gooch, ''Frederick the Great. The Ruler, the Writer, the Man'' (Alfred A. Knopf, 1947). pp 217–247. * Thea Leitner: ''Skandal bei Hof. Frauenschicksale an europäischen Königshöfen'', Piper, München 2003, * Uwe A. Oster: ''Wilhelmine von Bayreuth. Das Leben der Schwester Friedrichs des Großen'', Piper, München, 2005, *External links
*''Argenore'' (opera)
from the Hamburg Opera House * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Wilhelmine Of Prussia, Princess 1709 births 1758 deaths German classical composers 18th-century classical composers 18th-century German women writers 18th-century German composers 18th-century German women musicians 18th-century German writers Margravines of Brandenburg-Bayreuth Musicians from Berlin People from the Margraviate of Brandenburg People from Bayreuth House of Hohenzollern German Baroque composers German women classical composers German memoirists Prussian princesses Lutenists from the Holy Roman Empire German women memoirists Daughters of kings Children of Frederick William I of Prussia Daughters of princes regnant Daughters of prince-electors