wide dynamic range neuron on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The wide dynamic range (WDR) neuron was first discovered by Mendell in 1966. Early studies of this
The wide dynamic range (WDR) neuron was first discovered by Mendell in 1966. Early studies of this
 WDR neurons are found in the
WDR neurons are found in the
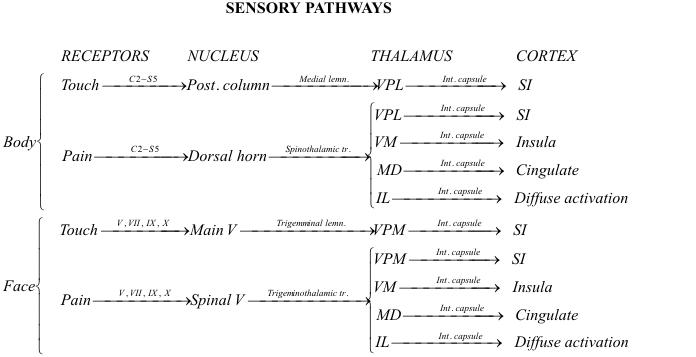 A subset of this neuropathic pain, known as chronic neuropathic pain, is characterized by its long lasting and high pain intensity. Although there is still a lot unknown about the direct cause of this chronic pain, it has been linked to WDR neurons. These neurons show significant activation by sympathetic stimulation while neurons, such as NS neurons, do not show the same level of activation. The blocking of sympathetic pathways seemed to decrease pain and once unblocked, symptoms of pain persisted. This indicates that one of the many complex mechanisms contributing to this neuropathic chronic pain is the overstimulation of the WDR neurons by sympathetic stimulation.
Another aspect that plays a role in neuropathic pain is the transient receptor channel called
A subset of this neuropathic pain, known as chronic neuropathic pain, is characterized by its long lasting and high pain intensity. Although there is still a lot unknown about the direct cause of this chronic pain, it has been linked to WDR neurons. These neurons show significant activation by sympathetic stimulation while neurons, such as NS neurons, do not show the same level of activation. The blocking of sympathetic pathways seemed to decrease pain and once unblocked, symptoms of pain persisted. This indicates that one of the many complex mechanisms contributing to this neuropathic chronic pain is the overstimulation of the WDR neurons by sympathetic stimulation.
Another aspect that plays a role in neuropathic pain is the transient receptor channel called
neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
established what is known as the gate control theory of pain. The basic concept is that non-painful stimuli block the pathways for painful stimuli, inhibiting possible painful responses. This theory was supported by the fact that WDR neurons are responsible for responses to both painful and non-painful stimuli, and the idea that these neurons could not produce more than one of these responses simultaneously. WDR neurons respond to all types of somatosensory
The somatosensory system, or somatic sensory system is a subset of the sensory nervous system. The main functions of the somatosensory system are the perception of external stimuli, the perception of internal stimuli, and the regulation of bod ...
stimuli, make up the majority of the neurons found in the posterior grey column
The grey columns are three regions of the somewhat ridge-shaped mass of grey matter in the spinal cord. These regions present as three columns: the anterior grey column, the posterior grey column, and the lateral grey column, all of which are ...
, and have the ability to produce long range responses including those responsible for pain and itch.
Anatomy and physiology
 WDR neurons are found in the
WDR neurons are found in the posterior grey column
The grey columns are three regions of the somewhat ridge-shaped mass of grey matter in the spinal cord. These regions present as three columns: the anterior grey column, the posterior grey column, and the lateral grey column, all of which are ...
of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
. This area of the spinal cord houses two different types of neurons involved in the process of pain: WDR neurons and nociceptive
In physiology, nociception , also nocioception; ) is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, convert it to a molecular ...
specific neurons (NS). As the name implies, NS neurons give specific short range responses. WDR neurons are able to give long range responses for a large variety of stimuli giving them the ability to help identify the location and intensity of painful stimulation (sensory discrimination).
WDR neurons differ from most other neurons in that they are theorised to experience what is called a ‘wind up’. This allows for the intensity of their response to increase with an increased frequency of stimulus. Most other neurons fire repeated action potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
s of the same magnitude as a reaction to an increase in stimulus intensity. The intensity of the stimulus will only boost the frequency of action potentials, not their magnitude. However, WDR neurons exhibit increased action potential intensity with more presentations of a stimulus. This allows for plasticity
Plasticity may refer to:
Science
* Plasticity (physics), in engineering and physics, the propensity of a solid material to undergo permanent deformation under load
* Behavioral plasticity, change in an organism's behavior in response to exposur ...
of synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending o ...
s and creates flexibility in the neuronal response. Though this may be of some benefit to the organism, this over excitation of the neurons can result in chronic pain
Chronic pain is pain that persists or recurs for longer than 3 months.https://icd.who.int/browse/2025-01/mms/en#1581976053 It is also known as gradual burning pain, electrical pain, throbbing pain, and nauseating pain. This type of pain is in cont ...
.
Role in pain responses
When there is a painful stimulus there are two pathways that can be taken. Thenociceptive
In physiology, nociception , also nocioception; ) is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, convert it to a molecular ...
neurons in Rexed lamina
The Rexed laminae (singular: Rexed lamina) comprise a system of ten layers of grey matter (I–X), identified in the early 1950s by Bror Rexed to label portions of the grey columns of the spinal cord.
Similar to Brodmann areas, they are defi ...
1 become compromised or the WDR neurons become compromised. The WDR neurons can respond to electrical, mechanical, and thermal stimulation. The dorsal cord has faulty plasticity, which encourages the development of neuropathic pain
Neuropathic pain is pain caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory nervous system. Neuropathic pain may be associated with abnormal sensations called dysesthesia or pain from normally non-painful stimuli (allodynia). It may have continuo ...
after an injury to a nerve. This allows for the over-excitation discussed previously, resulting in chronic pain. The unique pain pathway of the WDR neurons allows information about the stimulus to be used to map out the intensity of the pain through sensory discrimination.
There are two main types of pain that we experience in our bodies: pain caused by damage of body tissue and pain caused by nerve damage. Nociceptive pain serves as a warning or signal for tissue damage and works to preserve the body’s equilibrium and functionality. This pain is signaled by the interworkings of both the peripheral
A peripheral device, or simply peripheral, is an auxiliary hardware device that a computer uses to transfer information externally. A peripheral is a hardware component that is accessible to and controlled by a computer but is not a core compo ...
and central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
s. Another type of pain, known as neuropathic pain, is caused by a direct problem or disease that affects the nerves in the central nervous system.
 A subset of this neuropathic pain, known as chronic neuropathic pain, is characterized by its long lasting and high pain intensity. Although there is still a lot unknown about the direct cause of this chronic pain, it has been linked to WDR neurons. These neurons show significant activation by sympathetic stimulation while neurons, such as NS neurons, do not show the same level of activation. The blocking of sympathetic pathways seemed to decrease pain and once unblocked, symptoms of pain persisted. This indicates that one of the many complex mechanisms contributing to this neuropathic chronic pain is the overstimulation of the WDR neurons by sympathetic stimulation.
Another aspect that plays a role in neuropathic pain is the transient receptor channel called
A subset of this neuropathic pain, known as chronic neuropathic pain, is characterized by its long lasting and high pain intensity. Although there is still a lot unknown about the direct cause of this chronic pain, it has been linked to WDR neurons. These neurons show significant activation by sympathetic stimulation while neurons, such as NS neurons, do not show the same level of activation. The blocking of sympathetic pathways seemed to decrease pain and once unblocked, symptoms of pain persisted. This indicates that one of the many complex mechanisms contributing to this neuropathic chronic pain is the overstimulation of the WDR neurons by sympathetic stimulation.
Another aspect that plays a role in neuropathic pain is the transient receptor channel called TRPA1
Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, member 1, also known as transient receptor potential ankyrin 1, TRPA1, or The Mustard and Wasabi Receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TRPA1'' (and in mice and rats by ...
. This channel is known to have influenced chronic pain injuries and diseases such as inflammation, diabetes, fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a functional somatic syndrome with symptoms of widespread chronic pain, accompanied by fatigue, sleep disturbance including awakening unrefreshed, and Cognitive deficit, cognitive symptoms. Other symptoms can include he ...
, bronchitis, and emphysema
Emphysema is any air-filled enlargement in the body's tissues. Most commonly emphysema refers to the permanent enlargement of air spaces (alveoli) in the lungs, and is also known as pulmonary emphysema.
Emphysema is a lower respiratory tract di ...
. WDR neurons are a huge part of the somatosensory system, helping to send and receive signals based on sensory changes in the body. The TRPA1 channel has been closely associated with temperature and pain sensation in primary afferent sensory neurons and are largely found in nociceptive sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia
A dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dors ...
. The inhibition of TRPA1 is known to contribute to different inflammatory and neuropathic diseases by amplifying the pain and hypersensitivity. This is an area of study that is beneficial to continue to study and learn how to target and control aspects of chronic inflammatory and neuropathic diseases involved in sensory responses that WDR neurons play a role in.
Role in itch responses
Additionally, the itch pathway has also been linked with WDR neurons because itch and pain pathways are closely associated. As there are transient receptor channels present in the pain pathway, they are also present in the itch pathway. In the itch pathway, when the transient receptor channels are activated an itch response can be elicited. Itch responses can also be controlled by temperature changes (too high or too low), much like pain. This mechanism of control occurs when a stimulus is at an extremely low or extremely high temperature. The organism's sensitivity to the stimulus increases, meaning the pain or itch elicited will be greater at those temperatures than they would be at room temperature. Though these pathways display many similarities, there are other mechanisms by which itch sensations can be controlled, such as those through nerve growth factor and substance-P. Brain imaging indicates similar activity in many areas of the brain such as prefrontal, supplementary motor areas,premotor cortex
The premotor cortex is an area of the motor cortex lying within the frontal lobe of the brain just anterior to the primary motor cortex. It occupies part of Brodmann's area 6. It has been studied mainly in primates, including monkeys and human ...
, anterior insular cortex, and many others when itch and pain regions are activated. A better understanding of both these pathways will provide a greater understanding of WDR neurons.
References
{{Reflist Neurons