West Region, Cameroon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The West Region () is 14,000 km2 of territory located in the central-western portion of the
File:Lac Baleng2.jpg, Lake Baleng
File:Fleuve Nkam à partir de Bafang 01.jpg, Nkam River
File:Monoun.jpg, Lake Monoun
File:Fleuve Mbam'.jpg, Mbam River
File:Chutes d'eau de Metchie.jpg, Metche falls
File:Chute Bangoua30.jpg, Bangoua Falls

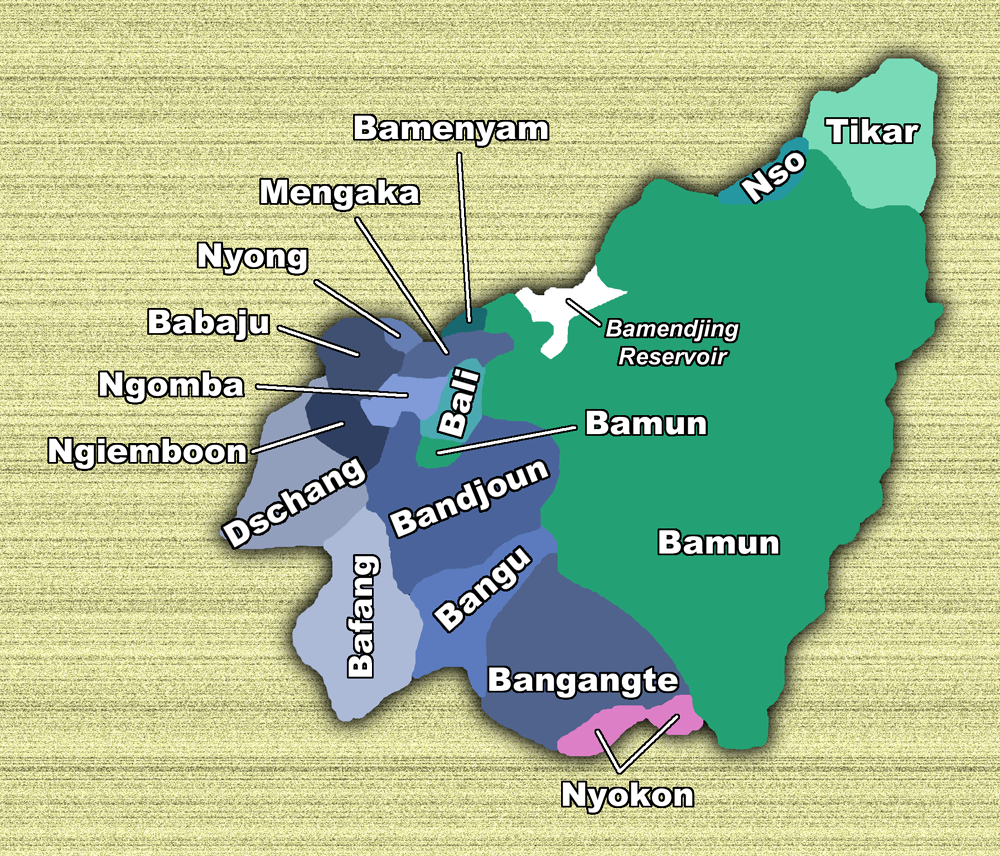

 The West consists of eight divisions or
The West consists of eight divisions or

File:AccessoiresOuest.jpg, Mask
File:DanseurOuest2.jpg
File:PrestationOuest.jpg
File:PrestationOuest1.jpg
File:InstrumentisteOuest1.jpg, Tam-Tam Player
File:PrestationOuest2.jpg
File:DanseurOuest.jpg
File:JoueursTamtamOuest.jpg, Tam-tam group players
File:DanseurOuest3.jpg, Bamileke cowbells
File:BalafonOuest3.jpg, Balafon
File:BalafonOuest4.jpg, Another balafon
File:TamtamNordOuest.jpg, Tam-tam
File:JoueurSanzaOuest.jpg, Sanza
File:JoueurSanzaOuest1.jpg, Sanza
File:BalafonOuest2.jpg, Balafon
File:BalafonOuest1.jpg, Balafon
File:InstrumentOuest2.jpg
File:InstrumentOuest.jpg
Republic of Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
. It borders the Northwest Region to the northwest, the Adamawa Region
The Adamawa Region () is a constituent region of the Cameroon, Republic of Cameroon. It borders the Centre Region (Cameroon), Centre and East Region (Cameroon), East regions to the south, the Northwest Region (Cameroon), Northwest and West Re ...
to the northeast, the Centre Region to the southeast, the Littoral Region to the southwest, and the Southwest Region to the west. The West Region is the smallest of Cameroon's ten regions in area, yet it has the highest population density.
As home to the enterprising Bamum and Bamileke kingdoms, the West is an economic bright spot and one of Cameroon's more developed regions. This progressive development is tempered by the strong traditional culture that persists among the Bamileke and the province's other major ethnic group, the Bamum (sometimes ''Bamoum'', ''Bamun'', ''Bamoun'').
Geography
Land
The West sits at the geologic crossroads of Cameroon; the soil varies greatly within a relatively small land area. The land along the Noun River and at theBamendjing Reservoir
The Noun River is a river in the West Province of Cameroon. It arises at Lake Oku () and flows south, it is joined by the Monoun River and flows south in the valley between the mountains Ngotsetzezan and Mount Yahou.1:1,000,000 - International ...
, for example, is a lightly evolved blend of various raw minerals. The province's western half, on the other hand, is a haphazard mixture of raw minerals, granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
, ferrallitic Ferrallitisation is the process in which rock is changed into a soil consisting of clay (kaolinite) and sesquioxides, in the form of hydrated oxides of iron and aluminium. In humid tropical areas, with consistently high temperatures and rainfall for ...
patches of red dirt, and other types. Finally, the soil of the eastern portions away from the reservoir is ferrallitic. Rocks in the area range from the volcanic
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ...
along the reservoir and Noun to Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
deposits of crystalline rock
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macrosco ...
s such as granite and gneiss
Gneiss (pronounced ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. This rock is formed under p ...
under a cover of basaltic rock
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
in the northwest. Metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus ...
s like gneiss and mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into fragile elastic plates. This characteristic is described as ''perfect basal cleavage''. Mica is co ...
dominate the rest of the territory. The soil throughout is mostly red in color due to high iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
content, though that of the northwest is black or brown basalt. The province's soils are the richest and most productive in Cameroon.
Drainage
The West's mountainous terrain and activetectonics
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons.
These processes ...
create many fast-moving river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
s with picturesque fall
Autumn, also known as fall (especially in US & Canada), is one of the four temperate seasons on Earth. Outside the tropics, autumn marks the transition from summer to winter, in September (Northern Hemisphere) or March ( Southern Hemispher ...
s and isolated crater lake
Crater Lake ( Klamath: ) is a volcanic crater lake in south-central Oregon in the Western United States. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and is a tourist attraction for its deep blue color and water clarity. T ...
s. These rivers follow a Cameroon regime, experiencing a period of high waters during the wet season and a period of low waters in the dry period. The rivers all form part of the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
basin.
The Mbam River
The Mbam River is the largest tributary of the Sanaga River in Cameroon. It has a total length of and has a total drainage basin of .
It flows from the Adamawa Plateau
The Adamawa Plateau () is a plateau region in west-central Africa stretchin ...
runs along the border with the Centre and Southeast Provinces. The Nkam
Nkam is a department of Littoral Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 6,291 km and as of 2001 had a total population of 66,979. The capital of the department lies at Yabassi.
Subdivisions
The department is divided admini ...
is the name for the headwaters of the Wouri River
The Wouri (also Vouri or Vuri) is a river in Cameroon. The Wouri forms at the confluence of the rivers Nkam River, Nkam and Makombé River, Makombé, northeast of the city of Yabassi. It then flows about southeast to the Wouri estuary at Douala ...
, which flow from the West's Bamboutos Mountains
The Bambouto massif or Bamboutos Mountains is a group of volcanoes based on a swell in the Cameroon Volcanic Line, located in the Western High Plateau of Cameroon, merging in the north with the Oku Volcanic Field.
Geology
The large volcanic comp ...
. The eastern branch through the area rises northwest of Bangangté
Bangangté is a town and commune in Cameroon. It is the capital of the Ndé division of West Region, Cameroon, West Region. The town is primarily inhabited by the people of the Bamileke (Bamiléké) tribe.
It is home to the Université des Monta ...
, and the western branch forms the border with the Littoral Province southwest of Bafang
Bafang is a town and commune in Cameroon situated in the Haut-Nkam division of the West Province, Cameroon, West Province.
It lies at the heart of the territory of the Bamiléké people, and has a population of roughly 33,324. (2012)
Religion ...
. These headwaters are subject to seasonal flooding. The Noun River, a tributary
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream (''main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which they ...
of the Sanaga, flows from the Centre Province, around Bafoussam
Bafoussam is the capital and largest city of the West Region (Cameroon), West Region of Cameroon, in the Bamboutos Mountains. It is the 3rd most important (financially) city in Cameroon, after Yaoundé and Douala. The ''communauté urbaine'' (Urba ...
, and to the Bamendjing Reservoir. This man-made lake is created by a dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aqua ...
on the Noun River, which helps regulate the Sanaga at Edéa
Edéa is a city and commune in the Littoral Region of Cameroon. Situated on the Sanaga River, it lies on the Douala–Yaoundé–Ngaoundéré railway line. Its population was estimated at 122,300 in 2001.
History
From 20 to 26 Octobe ...
in the Littoral Province and is thus an important component in Cameroon's supply of hydroelectric power
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
. Falls are common, such as the Balatchi, Metché, and Tsugning Falls.
Most of the West's lakes are crater lakes formed from collapsed volcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most oft ...
es. Such lakes exist at Balent
Jim Balent () is an American comics artist, writer, and publisher from Pennsylvania. He is best known for his long run on ''Catwoman'' between 1993 and 1999. Balent has also drawn ''Batman'' and '' Lobo'' for DC Comics, as well as some of the iss ...
, Banéfo, Doupé, and near Foumban
Foumban or Fumban is a city in Cameroon, lying north east of Bafoussam. It has a population of 83,522 (at the 2005 Census). It is a major town for the Bamum people, Bamoun people and is home to a museum of traditional arts and Culture of Camer ...
. Many of these still have active volcanoes at their bottoms, particularly in the northwest on the Western High Plateau
The Western High Plateau, Western Highlands or Bamenda Grassfields is a region of Cameroon characterised by high relief, cool temperatures, heavy rainfall and savanna vegetation. The region lies along the Cameroon line and consists of mounta ...
. One example is Lake Baleng, northeast of Bafoussam, and the twin lakes of Foumbot. These volcanoes can cause deposits of gas to build up at the lakebed until poisonous gases finally bubble to the surface. Such an eruption at Lake Monoun
Lake Monoun is a crater lake (maar) in West Province, Cameroon, that lies in the Oku Volcanic Field. On August 15, 1984, a limnic eruption occurred at the lake, which resulted in the release of a large amount of carbon dioxide () that killed 3 ...
killed 37 villagers near Foumbot on 15 and 16 August 1984.Relief
The Bamboutos Mountains are the West's primary land feature. Elevations reach as high as 2,000 metres and dip as low as 500 metres in the Noun and Nkam valleys. The highest point is Mt. Bamboutos, a dormant volcano west ofMbouda
Mbouda is the capital of the Bamboutos Departments of Cameroon, department of West Province, Cameroon, West Province, Cameroon. Projected to be the fourteenth fastest growing city on the African continent between 2020 and 2025, with a 5.16% growt ...
, at 2,740 metres. These mountains lie along the Cameroon Fault, dating from the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
, which runs roughly parallel to the border with the Northwest Province and through the capital of Bafoussam. West of the Cameroon Mountains lies the Western High Plateau, with elevations of 1,000-2,500 metres. South of the fault, the land descends in steps until levelling off at the South Cameroon Plateau
The South Cameroon Plateau or Southern Cameroon Plateau () is the dominant geographical feature of Cameroon. The plateau lies south of the Adamawa Plateau and southeast of the Cameroon Range. It slopes south and west until giving way to the Camer ...
. Here, terrain is gentler, with large hills separated by deep valleys.
Climate
High elevations and moderate to highhumidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
give the West one of Cameroon's more pleasant climates. Temperatures average a cool 22˙, and rainfall is moderate. Except for the southeasternmost portions, the West experiences two major seasons in lieu of the traditional four: the year begins in a long, dry period of little rain, which runs until May, then the rains begin in May or June and last until October or November. Though the transition is gradual, the southeastern reaches of the province are part of the South Cameroon Plateau and thus have four seasons: the long dry season from December to March, the short rainy season from March to June, the short dry season from June to August, and the long rainy season from September to December.
The climate is equatorial of the Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
sub-variety in the northwestern third and equatorial of the Guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
type in the southeastern two-thirds. Rainfall, moderated by the mountains, averages 1,000-2,000 mm per year throughout, though it is highest at the area of the Bamendjing Reservoir.
Plant and animal life
Very little of the West's original flora or fauna survives, since most land has been cleared by human farmers. This is particularly evident on the Western High Plateau, where poor soil and less rainfall have exacerbated the effects ofdeforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
, turning the area into grassland. The Melap Reserve (''Réserve de Melap'') near Foumban is one heavily wooded area, but it is more of a city park
An urban park or metropolitan park, also known as a city park, municipal park (North America), public park, public open space, or municipal gardens ( UK), is a park or botanical garden in cities, densely populated suburbia and other incorporate ...
than an actual reserve.
East of the Noun River, the terrain is primarily covered in woodland savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
of the Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
type, which forms a transitional zone to the lowly vegetated northern provinces. West of that river, this savanna is of the Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
type, and is interspersed among open, dry forest. A few small patches of rain forest
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropi ...
persist to the west of the Mbam River in the Noun division. As elevation increases, forests thin out, until they are replaced by fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue ...
s and bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of mostly evergreen perennial plant, perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily (biology), subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family, in th ...
s at 1,800 metres. Trees throughout shed their leaves during the dry season as protection against brush fires.

Demographics
Settlement patterns
The West's population density is high in general, especially in the towns of Bafoussam,Dschang
Dschang is a city located in the West (Ouest) Province of Cameroon, with an estimated population of 87,000 (est) in 2001, growing dramatically from 21,705 recorded in 1981. The 2006 Population is estimated to be 200,000 inhabitants.
Dschang is th ...
, Mbouda, and Bafang. This is due to the pleasant climate and fertile soils. Bafoussam is both the provincial capital and the centre of the Bamileke lands. Populations thin out toward the southern border and in the eastern Bamum-dominated territories. Settlements are scattered.
The region experiences significant out-migration, particularly when the vast plantations of the Southwest Province hire workers for annual harvests. Permanent emigration is mainly by those who wish to escape the overcrowded conditions and to farm larger pieces of land, and is directed mainly to the Southwest and Littoral Provinces.
Bamileke homes are traditionally made of dried earth placed on a bamboo frame and covered by a thatched roof. Farm plots separated by fences surround the typical home. Houses of this type are seldom seen today, however, though barns are still constructed using these methods. The last bastion of traditional architecture are the many chief
Chief may refer to:
Title or rank
Military and law enforcement
* Chief master sergeant, the ninth, and highest, enlisted rank in the U.S. Air Force and U.S. Space Force
* Chief of police, the head of a police department
* Chief of the boat ...
s' compounds that dot the province. These are characterized by their tall, conical roofs, bamboo and clay-brick walls, and carved poles around the entryway. The typical layout places a central audience chamber in front of other rooms for individuals of progressively lower rank.

People
Two major tribal groups dominate the West: theBamileke
The Bamiléké people are an ethnic group of Central Africa that inhabits the Western High Plateau colloquially known as the ''grassfields'' of Cameroon. According to Dr John Feyou de Hapy, Bamiléké means "people of faith".
Languages
The B ...
and the Bamum.
Both of these are considered semi-Bantu The Semi-Bantu or Semibantu are specific inhabitants of the Western grassfields of Cameroon (portions of the Adamawa, West, Northwest, and Southwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or az ...
or grassfields Bantu. The Bamileke are the more numerous, estimated to number 3 million or more. They are concentrated southeast of the Bamboutos Mountains and west of the Noun River. Their major settlements are at Bafoussam
Bafoussam is the capital and largest city of the West Region (Cameroon), West Region of Cameroon, in the Bamboutos Mountains. It is the 3rd most important (financially) city in Cameroon, after Yaoundé and Douala. The ''communauté urbaine'' (Urba ...
, Bandjoun
Bandjoun (''La 'Djo'' in local language) is a town and commune in the Koung-Khi Departments of Cameroon, Department in the West Region (Cameroon), West Region of Cameroon. Bandjoun is also the capital of the Koung-Khi department and one of the l ...
, Bafang
Bafang is a town and commune in Cameroon situated in the Haut-Nkam division of the West Province, Cameroon, West Province.
It lies at the heart of the territory of the Bamiléké people, and has a population of roughly 33,324. (2012)
Religion ...
, Bawaju, Bangangté
Bangangté is a town and commune in Cameroon. It is the capital of the Ndé division of West Region, Cameroon, West Region. The town is primarily inhabited by the people of the Bamileke (Bamiléké) tribe.
It is home to the Université des Monta ...
, Dschang
Dschang is a city located in the West (Ouest) Province of Cameroon, with an estimated population of 87,000 (est) in 2001, growing dramatically from 21,705 recorded in 1981. The 2006 Population is estimated to be 200,000 inhabitants.
Dschang is th ...
, and Mbouda
Mbouda is the capital of the Bamboutos Departments of Cameroon, department of West Province, Cameroon, West Province, Cameroon. Projected to be the fourteenth fastest growing city on the African continent between 2020 and 2025, with a 5.16% growt ...
. They organise themselves in sub-groups, each under the rule of a different chief. Examples are the Fe'fe', Ghomala, Kwa', Medumba, Mengaka, Nda'nda', Ngomba, Ngombale, Ngiemboon, and Yemba. Most of these groups speak a unique language, though all are closely related. Most Bamileke are Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
, with Catholics
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
in the majority.
The Bamum people
The Bamum, sometimes called Bamoum, Bamun, Bamoun, or Mum, are a Grassfields languages, Grassfields ethnic group located in now Cameroon. In 2018, the Bamum and Bamileke people, Bamileke peoples accounted for about 24% of the country's populatio ...
are the area's other major ethnic group. They are a subgroup of the Tikar
The Tikar (formally known as Tikari, Tigar, Tigari, and Tigre throughout their history) are a Central African ethnic group in Cameroon. They are known to be great artists, artisans and storytellers. Once a nomadic people, some oral traditions t ...
, though they speak a language called Bamum. They are primarily Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
ic, and all are ruled by a sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be use ...
in their tribal capital, Foumban.
Other languages spoken in the province include Bamenyam, Mbo, and Tikar
The Tikar (formally known as Tikari, Tigar, Tigari, and Tigre throughout their history) are a Central African ethnic group in Cameroon. They are known to be great artists, artisans and storytellers. Once a nomadic people, some oral traditions t ...
. Most educated inhabitants also speak French.
Economy
The West is one of Cameroon's soundest economic areas due primarily to its agricultural prosperity and the enterprising traditions of the Bamileke people. In areas that do not have a daily market, market days are typically every eighth day (the Bamileke follow an eight-dayweek
A week is a unit of time equal to seven days. It is the standard time period used for short cycles of days in most parts of the world. The days are often used to indicate common work days and rest days, as well as days of worship. Weeks are ofte ...
).
Agriculture
Subsistence farming
The Bamileke are skilled farmers who exploit virtually every strip of land available. Along with the neighbouring Northwest Province, the West supplies most of the food consumed in Cameroon's seven lower provinces. Tools are largely traditional. Farmers plant after the first rains in fields consisting of alternating ridges and furrows. In the past, farmers practiced field rotation, allowing land to lie fallow for two or three years. Due to increasing population density, however, they use the land almost continuously today; the loss in fertility is partially countered through extensive use of fertilisers and manure. Hedges or fences that separate private plots and keep out animals surround farms in the West. These hedges also providefirewood
Firewood is any wooden material that is gathered and used for fuel. Generally, firewood is not heavily processed, and is in some sort of firelog, recognizable log or branch form, compared to other forms of wood fuel like pellet fuel, pellets. ...
and help prevent from soil erosion
Soil erosion is the denudation or wearing away of the Topsoil, upper layer of soil. It is a form of soil degradation. This natural process is caused by the dynamic activity of erosive agents, that is, water, ice (glaciers), snow, Atmosphere of Ea ...
. In the Southeast, farmers sometimes place fields in forest clearings where they use slash-and-burn
Slash-and-burn agriculture is a form of shifting cultivation that involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland to create a Field (agriculture), field called a swidden. The method begins by cutting down the trees and woody p ...
agriculture.
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
is the major staple, and farmers surround rows of it with cocoyam
Cocoyam is a common name for more than one tropical root crop and vegetable crop belonging to the Arum family (also known as Aroids and by the family name ''Araceae'') and may refer to:
* Taro (''Colocasia esculenta'') – old cocoyam
* Mala ...
s, plantains, bean
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditi ...
s, groundnuts, melon
A melon is any of various plants of the family Cucurbitaceae with sweet, edible, and fleshy fruit. It can also specifically refer to ''Cucumis melo'', commonly known as the "true melon" or simply "melon". The term "melon" can apply to both the p ...
s, and yams. Potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
es are another mainstay, and the West is one of the few places in Cameroon where they grow well due to high elevations in the region. Farmers grow these crops on the hillsides and use the valleys to plant cocoyams, colocasia
''Colocasia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to Southeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent. Some species are widely cultivated and naturalized in other tropical and subtropical regions.
The names elephant-ear and ...
, and raffia palm
Raffia palms are members of the genus ''Raphia''. The Malagasy name is derived from ' "to squeeze juice". The genus contains about twenty species of palms native to tropical regions of Africa, and especially Madagascar, with one species ('' R ...
s. In the western Wouri valley, rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
is also important.
Plantation agriculture
Population pressures prevent entrepreneurs from establishing largeplantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tob ...
s more prevalently in the West. Coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
is the major cash crop
A cash crop, also called profit crop, is an Agriculture, agricultural crop which is grown to sell for profit. It is typically purchased by parties separate from a farm. The term is used to differentiate a marketed crop from a staple crop ("subsi ...
, with large fields in the regions of Bafoussam, Foumbot, and Dschang and powerful supervision by Union des Cooperatives de Café Arabica de l'Ouest (UCCAO). Cocoa
Cocoa may refer to:
Chocolate
* Chocolate
* ''Theobroma cacao'', the cocoa tree
* Cocoa bean, seed of ''Theobroma cacao''
* Chocolate liquor, or cocoa liquor, pure, liquid chocolate extracted from the cocoa bean, including both cocoa butter and ...
is also important, particularly in the lowlands. Tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of '' Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of south-western China and nor ...
is grown commercially near Dschang. Some rice cultivation takes place under the Upper Noun Development Company
Upper may refer to:
* Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot
* Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both
* ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found fo ...
(UNVDA) in the southeast, largely due to government projects. Tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
from Mbouda and Foumbot stays within the province for local consumption, though the Bastos Company of Yaoundé
Yaoundé (; , ) is the Capital city, capital city of Cameroon. It has a population of more than 2.8 million which makes it the second-largest city in the country after the port city Douala. It lies in the Centre Region (Cameroon), Centre Region o ...
processes some for export.
Livestock
Livestock
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals that are raised in an Agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, Egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The t ...
raising was once practiced more widely, but as populations have risen, most land has been converted to crop cultivation (a fact that has raised tensions between herders and farmers). Still, some herders drive cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
using transhumance
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or Nomad, nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and low ...
methods in the northwestern half of the province, and the Kounden area is home to some modern ranching
A ranch (from /Mexican Spanish) is an area of land, including various structures, given primarily to ranching, the practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle and sheep. It is a subtype of farm. These terms are most often applied to li ...
. Ranchers sell these animals, which account for 10% of Cameroon's beef, mostly in the Douala
Douala is the largest city in Cameroon and its economic capital. It is also the capital of Cameroon's Littoral Region (Cameroon), Littoral Region. It was home to Central Africa's largest port, now being replaced by Kribi port. It has the country ...
market.
Many farmers raise sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
and goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a species of Caprinae, goat-antelope that is mostly kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the ...
s in the southeastern half of the province. Increasingly common these days are poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for the purpose of harvesting animal products such as meat, Eggs as food, eggs or feathers. The practice of animal husbandry, raising poultry is known as poultry farming. These birds are most typ ...
and pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), also called swine (: swine) or hog, is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is named the domestic pig when distinguishing it from other members of the genus '' Sus''. Some authorities cons ...
s, which can live in pens on smaller farms. In fact, the majority of Cameroon's pork comes from the region, and a large government-run poultry farm operates at Kounden. Smallholder
A smallholding or smallholder is a small farm operating under a small-scale agriculture model. Definitions vary widely for what constitutes a smallholder or small-scale farm, including factors such as size, food production technique or technolo ...
farmers, especially women, keep domestic cavies in their homesteads that may provide more protein to family nutrition than any other meat source.
The Bamendjing is also the site of traditional fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
, and professional fisheries operate at Foumban.

Industry
The West is home to relatively littleindustry
Industry may refer to:
Economics
* Industry (economics), a generally categorized branch of economic activity
* Industry (manufacturing), a specific branch of economic activity, typically in factories with machinery
* The wider industrial sector ...
. The area's few factories are almost all devoted to food processing
Food processing is the transformation of agricultural products into food, or of one form of food into other forms. Food processing takes many forms, from grinding grain into raw flour, home cooking, and complex industrial methods used in the mak ...
, with plants in Bafoussam (beer
Beer is an alcoholic beverage produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches from cereal grain—most commonly malted barley, although wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. The grain is mashed to convert starch in the ...
, instant coffee
Instant coffee is a beverage derived from brewed coffee beans that enables people to quickly prepare hot coffee by adding hot water or milk to coffee solids in powdered or crystallized form and stirring. The product was first invented in Inver ...
), Foumbot, Dschang, and Kékem
Kékem is a town and commune in Cameroon.
See also
*Communes of Cameroon
The Divisions of Cameroon are the third-level units of administration in Cameroon. They are organised by divisions and sub divisions of each province (now Regions).
...
. The building materials, pharmaceuticals
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the ...
, and bauxite
Bauxite () is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH) ...
mining industries also have a presence.
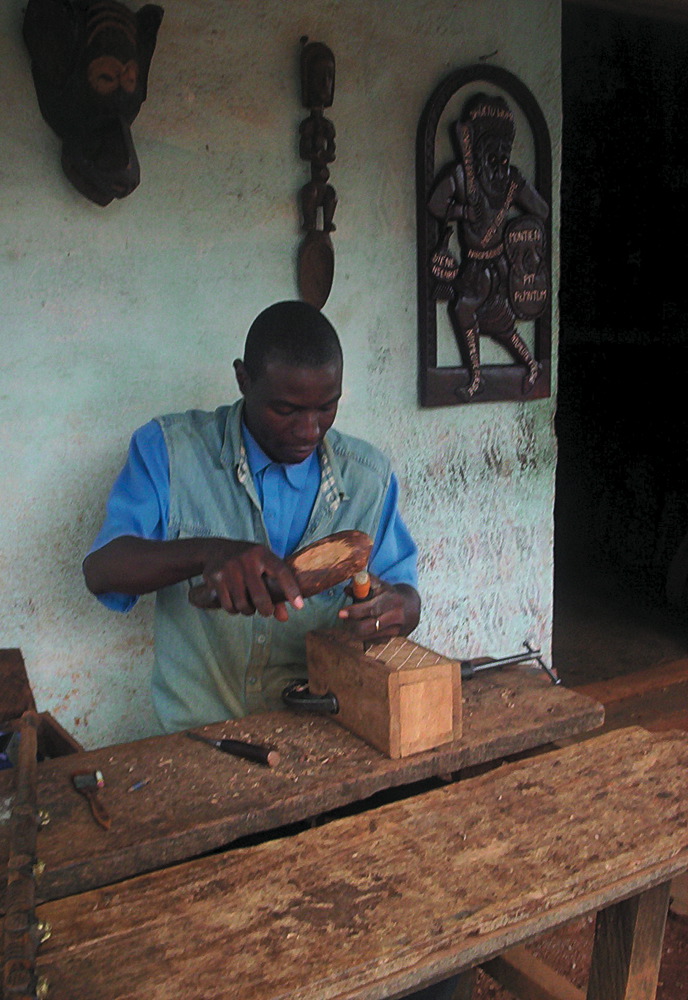
Arts and crafts form the heart of the West's production. Particularly renowned are the goods produced by Bamum cooperative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, coöperative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomy, autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned a ...
s at Foumban. These include intricately decorated ceramics
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porce ...
made from Foumban's high-quality clay, woodworking
Woodworking is the skill of making items from wood, and includes cabinetry, furniture making, wood carving, joinery, carpentry, and woodturning.
History
Along with stone, clay and animal parts, wood was one of the first materials worked b ...
, brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, in proportions which can be varied to achieve different colours and mechanical, electrical, acoustic and chemical properties, but copper typically has the larger proportion, generally copper and zinc. I ...
and bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
casting, and cotton textile
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ...
s, often featuring elaborate embroidery
Embroidery is the art of decorating Textile, fabric or other materials using a Sewing needle, needle to stitch Yarn, thread or yarn. It is one of the oldest forms of Textile arts, textile art, with origins dating back thousands of years across ...
. The Bamileke are also skilled artisans, with their own cooperative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, coöperative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomy, autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned a ...
at Bafoussam.
Transportation
With such a small land area and large network of mostly paved roads, the West is one of Cameroon's more accessible provinces. Major routes through the area include National Road 4 to Yaoundé, National Road 5 from Békoko to Bandjoun, and National Road 6 (dubbed ''la Transafricaine'') from Ekok,Mamfe
Mamfe or Mamfé is a city in and the capital of Manyu, a division of the Southwest Region in Cameroon. It is from the border of Nigeria, on the Manyu River. It has a population of 42,500 (2024 estimates)
It is known as a centre for traditi ...
and Bamenda
Bamenda, also known as Abakwa and Mankon Town, is a city in northwestern Cameroon and capital of the Northwest Region (Cameroon), Northwest Region. The city has a population of about six hundred thousand people and is located north-west of the C ...
in the Northwest Province through Mbouda and Foumban to Banyo and beyond in the Adamawa. Bafoussam forms an important nexus between the cities of Bamenda, Douala, Yaoundé, and Foumban. Roads often must wind and sharply turn to traverse the region's mountains, and traffic accidents are not uncommon. The region is reachable by air via domestic airport
A domestic airport is an airport that handles only flights within the same country. Domestic airports do not have customs and immigration facilities and so cannot handle flights to or from a foreign airport.
These airports often have short r ...
s at Bafoussam and Koutaba and an airstrip
An aerodrome, airfield, or airstrip is a location from which aircraft flight operations take place, regardless of whether they involve air cargo, passengers, or neither, and regardless of whether it is for public or private use. Aerodromes in ...
at Dschang.
Tourism
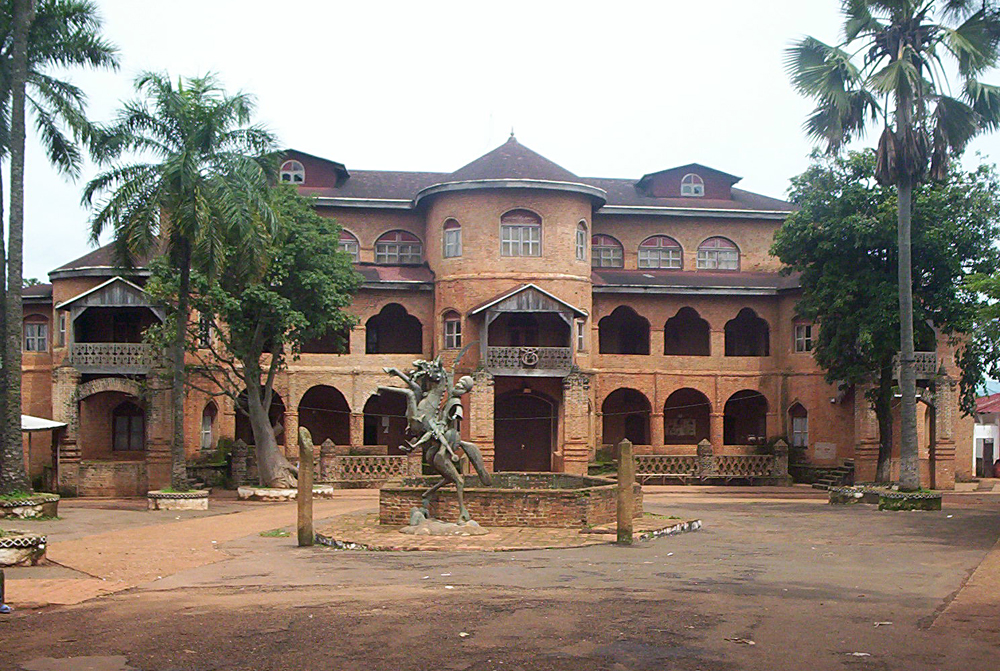
With its legions of artisans and its lavish sultan's palace, Foumban forms the West's main tourist draw. Visitors also come to experience the region's magnificent scenery and rich traditional culture.Administration and social conditions
The West's high population and economic dominance lend it great political importance. However, Cameroon's government and state-run media, largely run by PresidentPaul Biya
Paul Biya (born Paul Barthélemy Biya'a bi Mvondo, 13 February 1933) is a Cameroonian politician who has been serving as the second president of Cameroon since 1982. He was previously the fifth Prime Minister of Cameroon, prime minister under Pre ...
's numerically inferior Beti-Pahuin tribal group, are often accused of anti-Bamileke bias. The Bamileke thus stand to gain a great deal from a more free and transparent government, and the West harbors many sympathisers for the presidential party's main opponents, the Social Democratic Front.
Government
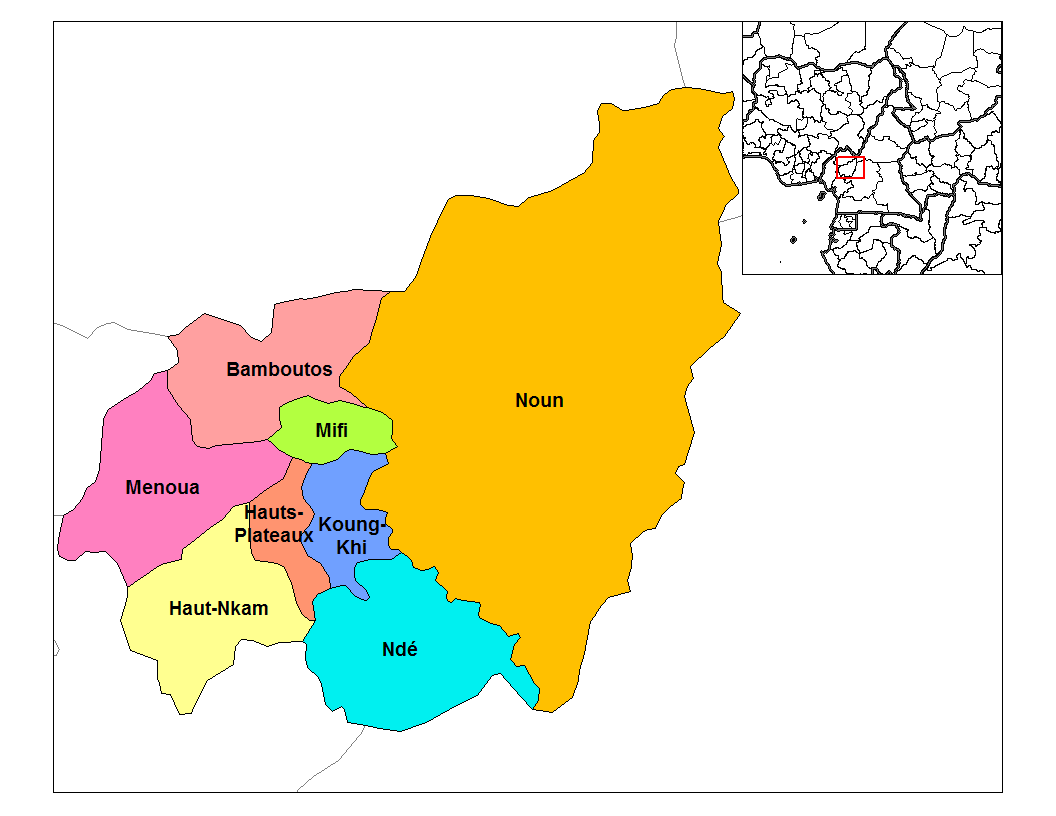
 The West consists of eight divisions or
The West consists of eight divisions or departments
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
* Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
(''departements''), each headed by a prefect
Prefect (from the Latin ''praefectus'', substantive adjectival form of ''praeficere'': "put in front", meaning in charge) is a magisterial title of varying definition, but essentially refers to the leader of an administrative area.
A prefect' ...
(''prefet''), or senior divisional officer. The president appoints all of these officers and the provincial governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
in Bafoussam. A special urban council presides over Bafoussam, staffed by presidentially appointed counselors who serve under a presidentially appointed delegate.
The departments are:
# Noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a p ...
# Ndé
Ndé is one of the 58 divisions in Cameroon. It is located in the West region of the country, about 150 km from Douala, the economic capital, and about 265 km from Yaoundé, the political capital. Its estimated population is 304,800. Th ...
# Haut-Nkam
Haut-Nkam is a department of West Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 958 km and as of 2005 had a total population of 191,600. The capital of the department lies at Bafang.
Subdivisions
The department is divided administ ...
# Ménoua
Menoua is a department of West Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 1,380 km and as of 2019 had a total population of 276,000. The capital of the department lies at Dschang.
Subdivisions
The department is divided administ ...
# Mifi
MiFi is a brand of wireless router that acts as a mobile Wi-Fi hotspot device.
In many countries, including The United States, Canada, and Mexico, Inseego Corp. (previously known as Novatel Wireless) owns a registered trademark on the "MiFi" ...
# Bamboutos
Bamboutos is a department of West Region in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 1,173 km and as of 2005 had a total population of 292,410. The capital of the department lies at Mbouda.
Subdivisions
The department is divided adminis ...
# Hauts-Plateaux
Hauts-Plateaux is a department of West Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 415 km and as of 2005 had a total population of 80,678. The capital of the department lies at Baham. The department was created in 1995 when th ...
# Koung-Khi
The Noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a p ...
department, headquartered at Foumban
Foumban or Fumban is a city in Cameroon, lying north east of Bafoussam. It has a population of 83,522 (at the 2005 Census). It is a major town for the Bamum people, Bamoun people and is home to a museum of traditional arts and Culture of Camer ...
, is the largest division geographically and occupies most of the Bamum territories bordering the Adamawa and Centre Provinces. The Ndé
Ndé is one of the 58 divisions in Cameroon. It is located in the West region of the country, about 150 km from Douala, the economic capital, and about 265 km from Yaoundé, the political capital. Its estimated population is 304,800. Th ...
department is southwest of this with its capital at Bangangté
Bangangté is a town and commune in Cameroon. It is the capital of the Ndé division of West Region, Cameroon, West Region. The town is primarily inhabited by the people of the Bamileke (Bamiléké) tribe.
It is home to the Université des Monta ...
. The Haut-Nkam
Haut-Nkam is a department of West Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 958 km and as of 2005 had a total population of 191,600. The capital of the department lies at Bafang.
Subdivisions
The department is divided administ ...
(Upper Nkam) department, whose capital is Bafang
Bafang is a town and commune in Cameroon situated in the Haut-Nkam division of the West Province, Cameroon, West Province.
It lies at the heart of the territory of the Bamiléké people, and has a population of roughly 33,324. (2012)
Religion ...
, is further west, and the Ménoua
Menoua is a department of West Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 1,380 km and as of 2019 had a total population of 276,000. The capital of the department lies at Dschang.
Subdivisions
The department is divided administ ...
department borders it to the northwest with its capital at Dschang
Dschang is a city located in the West (Ouest) Province of Cameroon, with an estimated population of 87,000 (est) in 2001, growing dramatically from 21,705 recorded in 1981. The 2006 Population is estimated to be 200,000 inhabitants.
Dschang is th ...
. The Mifi
MiFi is a brand of wireless router that acts as a mobile Wi-Fi hotspot device.
In many countries, including The United States, Canada, and Mexico, Inseego Corp. (previously known as Novatel Wireless) owns a registered trademark on the "MiFi" ...
department, with its capital Bafoussam
Bafoussam is the capital and largest city of the West Region (Cameroon), West Region of Cameroon, in the Bamboutos Mountains. It is the 3rd most important (financially) city in Cameroon, after Yaoundé and Douala. The ''communauté urbaine'' (Urba ...
, forms the centre of the region, and it is hemmed in by a handful of smaller divisions: the Bamboutos
Bamboutos is a department of West Region in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 1,173 km and as of 2005 had a total population of 292,410. The capital of the department lies at Mbouda.
Subdivisions
The department is divided adminis ...
department, headquartered at Mbouda
Mbouda is the capital of the Bamboutos Departments of Cameroon, department of West Province, Cameroon, West Province, Cameroon. Projected to be the fourteenth fastest growing city on the African continent between 2020 and 2025, with a 5.16% growt ...
, the Hauts-Plateaux
Hauts-Plateaux is a department of West Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 415 km and as of 2005 had a total population of 80,678. The capital of the department lies at Baham. The department was created in 1995 when th ...
(High Plateaus) department, governed from Baham, and the Koung-Khi department, governed from Bandjoun
Bandjoun (''La 'Djo'' in local language) is a town and commune in the Koung-Khi Departments of Cameroon, Department in the West Region (Cameroon), West Region of Cameroon. Bandjoun is also the capital of the Koung-Khi department and one of the l ...
. These latter two divisions were recently formed due to population booms in the area.
Traditional political organisation
Traditional rulers still hold substantial power in the province. A sultan, whose palace and head of government are in Foumban, rules the Bamum. Bamum tradition claims an unbroken line of succession since 1394. The Bamileke, in contrast, are divided into over 100 groups, each headed by a chief (''fon'', ''foyn'', or ''fo''). The chiefs are themselves divided into various ranks, with major rulers living in Bandjoun, Bafang, Bangangté, Dschang, and Mbouda. Traditionally, chiefs command divine powers and own all lands by divine mandate. Individual tenants work plots at their chief's behest. These groupings thus form the basis for Bamileke tribal identity. Advisers, often called the “Council of Notables”, in turn serve the chiefs. Below them are various district chiefs who govern individual wards in the village.Education
With nearly 1,000 schools serving its some 1,000 villages, the West relatively well provisioned educationally. The high population density contributes toclassroom overcrowding
As an educational reform goal, class size reduction (CSR) aims to increase the number of individualized student-teacher interactions intended to improve student learning. A reform long holding theoretical attraction to many constituencies, some h ...
, however. Students must often travel to nearby towns in order to pursue higher levels of education, since most villages do not have secondary school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., b ...
s. The province is also the location of a bilingual university at Dschang as well as the private Université des Montagnes
Université des Montagnes is a private, non-profit university in Bangangté in the West Region of Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and n ...
in Bangangté.
Health
Hospitals and health clinics are fairly prevalent in the region. The area's pleasant climate keeps it largely mosquito-free, somalaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
is not a problem as in much of the rest of Cameroon. Lack of sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
is a serious issue, as this leads to outbreaks of dysentery
Dysentery ( , ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications may include dehyd ...
, hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is an infectious liver disease caused by Hepatitis A virus (HAV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Many cases have few or no symptoms, especially in the young. The time between infection and symptoms, in those who develop them, is ...
, typhoid
Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a disease caused by ''Salmonella enterica'' serotype Typhi bacteria, also called ''Salmonella'' Typhi. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often ther ...
, and other ailments, especially in the more urbanised centres.
Cultural life
The West has a lively traditional culture. The Bamum observe traditional Muslim holy days, such asRamadan
Ramadan is the ninth month of the Islamic calendar. It is observed by Muslims worldwide as a month of fasting (''Fasting in Islam, sawm''), communal prayer (salah), reflection, and community. It is also the month in which the Quran is believed ...
and the Feast of the Ram. They also hold an annual cultural festival called the Ngouon. Bamileke festivals vary from tribe to tribe, and most are held during the dry season or for special events such as funerals or the birth of twins. Some examples are the Macabo Festival
''Xanthosoma'' is a genus of flowering plants in the arum family, Araceae. The genus is native to tropical America but widely cultivated and naturalized in other tropical regions. Several are grown for their starchy corms, an important food stap ...
of Bangoua, the Medumba Festival
Medumba (, ) is a Bamileke languages, Bamileke language of Cameroon. The people who speak it originate from the Ndé, Nde division of the West Region (Cameroon), West Region of the country, with their main settlements in Bangangté, Bakong, Bang ...
of Bangangté, and the Ben Skin Dance
Ben is frequently used as a shortened version of the given names Benjamin, Benedict, Bennett, Benson or Ebenezer, and is also a given name in its own right.
Ben meaning "son of" is also found in Arabic as ''Ben'' (dialectal Arabic) or ''bin' ...
, a dance of female sensuality that has grown increasingly commercialised.
A number of museums celebrate the West's history and traditions. Among these are the Musée du Palais du Sultan Bamun, the Musée des Arts et des Traditions Bamoun, and the Musée Sacré Djissé, all in Foumban. The Musée de la Chefferie Bandjoun is the region's largest repository of Bamileke artifacts.
History
Early population movements
Human beings have inhabited the West since prehistoric times, as evidenced by archaeological finds at Galima and Foumban. Bamileke groups likely entered the area from theAdamawa Plateau
The Adamawa Plateau () is a plateau region in west-central Africa stretching from south-eastern Nigeria through north-central Cameroon ( Adamawa and North Provinces) to the Central African Republic. The part of the plateau that lies in Nigeria i ...
in the 17th century, probably fleeing Fulbe
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people are an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, ...
(Fula) slave raids. They originally settled in what is now Bamum territory, but the Bamum forced them across the Noun in a series of wars in the 18th century. Bamileke tradition states that they migrated in three major groups. The first consisted of the Baleng, Bapi, and Bafussam (who founded the settlement at Bafoussam along with the Bamougoum). Next came the Bagam, Bamendu, Bamsoa, Bazu, and Bangu. The final wave consisted of the Bati and Bafangwa. This period also saw the Bamileke assimilation of several older populations.
Bamum tradition claims their kingdom was founded when Ncharé Yen led them to settle at Foumban (Mfom-Ben) in the 15th century. However, most scholars today place this migration as late as the 19th century, likely the result of population pressures caused by the same Fulbe jihads that had earlier pushed the Bamileke south. The king Mbwe-Mbwe extended Bamum holdings from the Mbam to the Noun Rivers, subjugating numerous local rulers in the process. Mbwe-Mbwe also kept the Fulbe from encroaching further south and west.
The Bamum experienced a golden age of sorts under the leadership of Sultan Ibrahim Njoya Sultan Ibrahim Njoya (Bamum language, Bamum: , ''Iparəim Nʃuɔiya'', formerly spelled in Bamum language, Bamum as , and Germanisation, Germanicized as ''Njoja'') in Yaoundé, was seventeenth in a long dynasty of kings that ruled over Bamum kingd ...
(r. 1886–1933). Njoya was a patron of learning, and he converted to Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
under the tutelage of numerous Muslim scholars he had allowed into the kingdom. He developed an alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from a ...
for the Bamum language (the Shumon script), and established schools to teach it. The Islamisation of the Bamum occurred during his reign.
The Bali-Chamba are the third major group to have pushed through the West Province territory in historical times. They came under the leadership of a warrior chief named Gawolbe and crossed the Noun around 1825. In 1830, they fought a war with the Bamileke Bafu-Fundong group near Dschang. Their leader, Gawolbe II died, and the tribe splintered as Gawolbe's seven sons fought for control. Most of these groups migrated further west into what is today the Northwest Province.
European contacts

German administration
The area had only indirect contact with European powers (mostly due to slave raids by tribes further south) before theGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
annexation of the Cameroons in 1884. The first Europeans to enter the territory were representatives of the Basel Mission
The Basel Mission is a Christianity, Christian missionary society based in Switzerland. It was active from 1815 to 2001, when it transferred the operative work to , the successor organization of ''Kooperation Evangelischer Kirchen und Missione'' ...
in 1897. The Germans themselves did not move into the territory until 1899 (though they had signed treaties with Bamileke leaders as early as 1884). Governor Jesko Von Puttkamer
Jesko Albert Eugen von Puttkamer (2 July 1855 – 23 January 1917) was a German diplomat, colonial administrator, and military officer who served as colonial governor of German Kamerun from 1895 to 1907.
Early life and career
Jesko von P ...
established the Gesellschaft Nordwest-Kamerun The Northwest Cameroon Company () was a private trading corporation formed in 1899 to exploit natural resources in the Bamoun and Bamileke regions of the German colony of Kamerun
Kamerun was an African colony of the German Empire from 1884 to ...
to monopolise trade in the area, and he established the divisional capital at Dschang
Dschang is a city located in the West (Ouest) Province of Cameroon, with an estimated population of 87,000 (est) in 2001, growing dramatically from 21,705 recorded in 1981. The 2006 Population is estimated to be 200,000 inhabitants.
Dschang is th ...
in 1903. The area's cool temperatures drew many German settlers, and the colonisers established great coffee plantations, which they forced the natives to work. Larger plantations were established further south, and many Bamileke were forced or encouraged to move out of their traditional territories to work them. The Germans also set up a puppet over-chief for all the Bamileke, who had never before considered themselves a single group. Catholic missionaries reached the grasslands area in 1910. By 1912, most of the Bamileke had converted to Christianity.
Sultan Njoya
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used ...
welcomed the first German emissary to the Bamum kingdom in 1902 after hearing of the ruthless treatment given rebellious tribes further to the northwest. He even lent military support for the German campaign against the Nso near Bamenda in 1906. The Bamum soldiers, eager for revenge for an earlier defeat to the Nso in 1888, committed such atrocities that the Germans sent them back. Njoya also ordered the building of a palace at Foumban in 1917, which he modeled after that of the German governor.
French administration
Bamileke and Bamum territory fell to theFrench
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
in 1916 after the Germans' defeat in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. The territory became part of the Baré-Foumban-Nkongsamba administrative area, and the capital was moved to Foumban. Dschang served as the seat of a French-run school for the sons of chiefs, which the French used to indoctrinate as well as instruct. The French maintained German plantations and labour sources, and new operations sprung up, such as a palm
Palm most commonly refers to:
* Palm of the hand, the central region of the front of the hand
* Palm plants, of family Arecaceae
** List of Arecaceae genera
**Palm oil
* Several other plants known as "palm"
Palm or Palms may also refer to:
Music ...
plantation at Dschang. The new colonial overlords made improvements to the region's infrastructure, as well, especially to the road network.
The French continued Germany's policy of propping up sympathetic chiefs and deposing recalcitrant ones. They sought some sort of administrative centre amid the Bamileke domains, and in 1926, Fotso II Fotso is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Faustine Fotso (born 1965), Cameroonian scientist and lawyer
*Joseph Fotso (born 1983), Cameroonian footballer
*Kareyce Fotso, Cameroonian singer
* Kate Fotso, Cameroonian businesswoman ...
of the Bandjoun people offered the site of Bafoussam, neighbouring his domains but not actually part of them. Mambou, chief of the area, opposed the colonials, but he was defeated, and the foundations of modern Bafoussam were laid. The Bamum did not escape the French sphere, either, as sultan Ibrahim Njoya was deposed in 1931 due to his pro-German views. Njoya died in a Yaoundé prison two years later.
After World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the West was a centre of political pressure and protest against colonial rule. Other groups came into being to combat these (usually with France's blessing), including the Union Bamiléké
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Union ...
in 1948. In 1956, France granted self-rule to its colony, and the West proved one of Cameroon's more politically influential areas due to groups such as Paysans Independants and the Assemblée Traditionnale Bamoun. The population boomed between 1958 and 1965, a period of high urbanisation
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It can also ...
in Cameroon.
In 1958, Ahmadou Ahidjo
Ahmadou Babatoura Ahidjo (24 August 192430 November 1989) was a Cameroonian politician who was the first president of Cameroon from 1960 until 1982. He was previously the first Prime Minister of Cameroon, Prime Minister from the country's indepe ...
became prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
of French Cameroon with a pro-independence platform. The powerful Union des Populations du Cameroun (UPC) party, including many Bamileke, considered him a French puppet and opposed him. On 27 June 1959, several Bamileke areas were struck in what were later labeled terrorist
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of violence against non-combatants to achieve political or ideological aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violence during peacetime or in the context of war aga ...
strikes. Ahidjo declared martial law
Martial law is the replacement of civilian government by military rule and the suspension of civilian legal processes for military powers. Martial law can continue for a specified amount of time, or indefinitely, and standard civil liberties ...
. His later attitudes toward the Bamileke likely were strongly influenced by their opposition to him.
Post-independence
Under Ahidjo, the current West Province was known as the Administrative Inspectorate of the West. He named Bafoussam the capital and set the province's current boundaries after union of British and French Cameroon in 1972. Ahidjo's battles with the UPC continued past Cameroon's independence on 1 January 1960. He outlawed the party's "terrorist" wing on 30 October 1963, leading to more strikes in Bamileke population centres and subsequent military retribution. What support Ahidjo did enjoy among the Bamileke largely came from his pro-business policies. When the president resigned in 1982, his replacement, Paul Biya, sent his representative, Moussa Yaya, to reassure the West's businessmen that he would not prove unfriendly to their interests. Yaya mistrusted Biya, however, and only exacerbated Bamileke reservations. The Bamum, as well, were reluctant to see Cameroon's presidency change from a Muslim to a Christian. Much Bamileke and Bamum resentment for the Biya administration dates to this period. In 2008, the President of the Republic of Cameroon,Paul Biya
Paul Biya (born Paul Barthélemy Biya'a bi Mvondo, 13 February 1933) is a Cameroonian politician who has been serving as the second president of Cameroon since 1982. He was previously the fifth Prime Minister of Cameroon, prime minister under Pre ...
, signed decrees abolishing "Provinces" and replacing them with "Regions". Hence, all of the country's ten provinces are now known as Regions.
Culture
Traditional dance accessories
Traditional Dances
Traditional musical instruments
References
Further reading
*Fanso, V.G., ''Cameroon History for Secondary Schools and Colleges, Vol. 1: From Prehistoric Times to the Nineteenth Century.'' Hong Kong: Macmillan Education Ltd, 1989. *Neba, Aaron, Ph.D., ''Modern Geography of the Republic of Cameroon,'' 3rd ed. Bamenda: Neba Publishers, 1999. *Ngoh, Victor Julius, ''History of Cameroon Since 1800.'' Limbé: Presbook, 1996. {{Authority control Regions of Cameroon States and territories established in 1972