Web (web Browser) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
GNOME Web, called Epiphany until 2012 and still known by that
 Since GNOME 3.2, released in September 2011, Web allows creating application launchers for
Since GNOME 3.2, released in September 2011, Web allows creating application launchers for
 In reviewing the WebKit-powered Epiphany 2.28 in September 2009, Ryan Paul of ''
In reviewing the WebKit-powered Epiphany 2.28 in September 2009, Ryan Paul of ''
complete change-log
Firefox vs GNOME Web
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
{{aggregators 2002 software Free software programmed in C Free web browsers GNOME Core Applications MacOS web browsers POSIX web browsers Software based on WebKit Software forks Software that uses Meson Web browsers that use GTK
code name
A code name, codename, call sign, or cryptonym is a code word or name used, sometimes clandestinely, to refer to another name, word, project, or person. Code names are often used for military purposes, or in espionage. They may also be used in ...
, is a free and open-source
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software available under a Software license, license that grants users the right to use, modify, and distribute the software modified or not to everyone free of charge. FOSS is an inclusive umbrella term ...
web browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's scr ...
based on the GTK
GTK (formerly GIMP ToolKit and GTK+) is a free software cross-platform widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces (GUIs). It is licensed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License, allowing both Free software, free and ...
port of Apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
's WebKit
WebKit is a browser engine primarily used in Apple's Safari web browser, as well as all web browsers on iOS and iPadOS. WebKit is also used by the PlayStation consoles starting with the PS3, the Tizen mobile operating systems, the Amazon K ...
rendering engine, called WebKitGTK. It is developed by the GNOME project
GNOME Project is a community behind the GNOME desktop environment and the software platform upon which it is based. It consists of all the software developers, artists, writers, translators, other contributors, and active users of GNOME. The GNO ...
for Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X, *nix or *NIX) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Uni ...
systems. It is the default and official web browser of GNOME
A gnome () is a mythological creature and diminutive spirit in Renaissance magic and alchemy, introduced by Paracelsus in the 16th century and widely adopted by authors, including those of modern fantasy literature. They are typically depict ...
, and part of the GNOME Core Applications
The GNOME Core Applications (also known as Apps for GNOME) are a software suite of software applications that are packaged as part of the standard free and open-source GNOME desktop environment. GNOME Core Applications have a consistent look and ...
.
GNOME Web is the default web browser on elementary OS
Elementary OS (stylized as elementary OS) is a Linux distribution based on Ubuntu LTS. It promotes itself as a "thoughtful, capable, and ethical" replacement to macOS and Microsoft Windows, Windows and has a pay what you want, pay-what-you-wan ...
, Bodhi Linux version 5 and PureOS GNOME Edition.
History
Naming
GNOME Web was originally named "Epiphany", but was rebranded in 2012 as part of GNOME 3.4. The name Epiphany is still used internally, as its code name, for development and in the source code. The package remains ''epiphany-browser'' inDebian
Debian () is a free and open-source software, free and open source Linux distribution, developed by the Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock in August 1993. Debian is one of the oldest operating systems based on the Linux kerne ...
(to avoid a name collision with a video game that is also called "Epiphany") and ''epiphany'' in Fedora and Arch Linux
Arch Linux () is an Open-source software, open source, rolling release Linux distribution. Arch Linux is kept up-to-date by regularly updating the individual pieces of software that it comprises. Arch Linux is intentionally minimal, and is meant ...
.
Development
Galeon
Marco Pesenti Gritti, the initiator of Galeon, originally developed Epiphany in 2002 as a fork of Galeon. The fork occurred because of the disagreement between Gritti and the rest of Galeon developers about new features. Gritti regarded Galeon's monolithic design and the number of user-configurable features as factors that were limiting Galeon's maintainability and usability, but the rest of the Galeon developers wanted to add more features. Around the same time, the GNOME project adopted a set ofhuman interface guidelines
Human interface guidelines (HIG) are software development documents which offer application developers a set of recommendations. Their aim is to improve the experience for the users by making application interfaces more intuitive, learnable, and ...
, which promoted simplification of user interfaces. As Galeon was oriented towards power user
A power user is a user of computers, software and other electronic devices who uses advanced features of computer hardware, operating systems, programs, or websites which are not used by the average user. A power user might not have extensive tech ...
s, most developers disapproved. As a result, Gritti created a new browser based on Galeon, with most of the non-critical features removed. He intended Epiphany to comply with the GNOME HIG. As such, Epiphany used the global GNOME theme and other settings from inception.
Gritti explained his motivations:
Galeon continued after the fork, but lost momentum due to the remaining developers' failure to keep up with changes in the Mozilla platform. Galeon development stalled and the developers decided to work on extensions to bring Galeon's advanced features to Epiphany.
Gritti ended his work on Epiphany and a GNOME team led by Xan Lopez, Christian Persch and Jean-François Rameau now direct the project. Gritti died of cancer on May 23, 2015.
Gecko-based
The first version of Epiphany was released on December 24, 2002. Epiphany initially used the Gecko layout engine from theMozilla
Mozilla is a free software community founded in 1998 by members of Netscape. The Mozilla community uses, develops, publishes and supports Mozilla products, thereby promoting free software and open standards. The community is supported institution ...
project to display web pages. It provided a GNOME graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
for Gecko, instead of Mozilla's cross-platform interface.
The development of Epiphany was mainly focused on usability improvements compared to major browsers at the time. The most notable was the new text entry widget, which was introduced in version 1.8. The new widget supported icons inside the text area and reduced the screen space needed to present information, while improving GNOME integration.
The next major milestone was version 2.14, which was the first to follow GNOME's version numbering. It also featured network awareness using NetworkManager
NetworkManager is a daemon that sits on top of libudev and other Linux kernel interfaces (and a couple of other daemons) and provides a high-level interface for the configuration of the network interfaces.
Rationale
NetworkManager is a software ...
, smart bookmarks improvements, and the option to build with XULRunner
XULRunner is a discontinued, packaged version of the Mozilla platform to enable standalone desktop application development using XUL, developed by Mozilla. It replaced the ''Gecko Runtime Environment'', a stalled project with a similar purpose. ...
.
The latter was critical. Previously, Epiphany could only use an installed Mozilla web browser as a web engine provider. The XULRunner support made it possible to install Epiphany as the only web browser on the system.
WebKit-based
The development process suffered from major problems related to the Gecko backend. Notably, the release cycles of the two projects did not line up efficiently. Additionally, Mozilla increasingly disregarded third-party software that wished to make use of Gecko, until it became viewed as an integrated Firefox component. To address these issues, in July 2007, the Epiphany team added support forWebKit
WebKit is a browser engine primarily used in Apple's Safari web browser, as well as all web browsers on iOS and iPadOS. WebKit is also used by the PlayStation consoles starting with the PS3, the Tizen mobile operating systems, the Amazon K ...
as an alternative rendering engine. On , the team announced that it would remove the ability to build it using Gecko and proceed using only WebKit.
The size of the team and complexity of porting the browser to WebKit caused version 2.22 to be re-released with bugfixes alongside GNOME 2.24, so the releases stagnated until , when it was announced that 2.26 would be the final Gecko-based version.
In September 2009, the transition to WebKit was completed as part of GNOME 2.28.
Version history
Developers of GNOME Web maintain a complete and accuratechangelog
A changelog (also spelled change log) is a log or record of all notable changes made to a project. The project is often a website or software project, and the changelog usually includes records of changes such as bug fixes, new features, etc. Som ...
in its official repository that shows complete and detailed changes between all the releases, following table just shows arbitrarily mentioned some notable and important changes:
Features
As a component ofGNOME Core Applications
The GNOME Core Applications (also known as Apps for GNOME) are a software suite of software applications that are packaged as part of the standard free and open-source GNOME desktop environment. GNOME Core Applications have a consistent look and ...
, it provides full integration with GNOME
A gnome () is a mythological creature and diminutive spirit in Renaissance magic and alchemy, introduced by Paracelsus in the 16th century and widely adopted by authors, including those of modern fantasy literature. They are typically depict ...
settings and other components like GNOME Keyring to securely store passwords, following the GNOME Human Interface Guidelines and the GNOME software stack
In computing, a solution stack or software stack is a set of software subsystems or components needed to create a complete platform such that no additional software is needed to support applications. Applications are said to "run on" or "run on ...
to provide first-class support for the all new-adopted edge technologies such as Wayland and the latest major GTK
GTK (formerly GIMP ToolKit and GTK+) is a free software cross-platform widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces (GUIs). It is licensed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License, allowing both Free software, free and ...
versions, multimedia support using GStreamer
GStreamer is a Pipeline (computing), pipeline-based multimedia framework that links together a wide variety of media processing systems to complete complex workflows. For instance, GStreamer can be used to build a system that reads files in one f ...
, small package size (2.6MB) and very fast execution/startup time due to using shared components; other features include the ''reader mode'', mouse gestures, smart bookmarks, praised web application
A web application (or web app) is application software that is created with web technologies and runs via a web browser. Web applications emerged during the late 1990s and allowed for the server to dynamically build a response to the request, ...
integration mechanism, built-in ad blocking
Ad blocking (or ad filtering) is a software capability for blocking or altering online advertising in a History of the web browser, web browser, an Application software, application or a network. This may be done using browser extensions or othe ...
, the "Insert Emoji" option in the context menu
A context menu (also called contextual, shortcut, and pop up or pop-up menu) is a menu in a graphical user interface (GUI) that appears upon user interaction, such as a right-click mouse operation. A context menu offers a limited set of choic ...
for quick and easy inserting of Emoji
An emoji ( ; plural emoji or emojis; , ) is a pictogram, logogram, ideogram, or smiley embedded in text and used in electronic messages and web pages. The primary function of modern emoji is to fill in emotional cues otherwise missing from type ...
and ''Miscellaneous Symbols and Pictographs
Miscellaneous Symbols and Pictographs is a Unicode block containing meteorological and astronomical symbols, emoji characters largely for compatibility with Japanese telephone carriers' implementations of Shift JIS, and characters originally from ...
'' into the text boxes, Google Safe Browsing, supports reading and saving MHTML, an archive format for web pages that combines all the files of web pages into only one single file; and consume fewer system resource
In computing, a system resource, or simply resource, is any physical or virtual component of limited availability that is accessible to a computer. All connected devices and internal system components are resources. Virtual system resources in ...
s than the major cross-platform web browsers.
Web standards support
The underlyingWebKit
WebKit is a browser engine primarily used in Apple's Safari web browser, as well as all web browsers on iOS and iPadOS. WebKit is also used by the PlayStation consoles starting with the PS3, the Tizen mobile operating systems, the Amazon K ...
browser engine provides support for HTML 4
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets ...
, XHTML
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages which mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.
While HTML, pr ...
, CSS 1 and 2, most of HTML 5 and CSS 3, and a Web Inspector (web development debugging tool).
Encrypted Media Extensions
Encrypted Media Extensions (EME) is a W3C specification for providing a communication channel between web browsers and the Content Decryption Module (CDM) software which implements digital rights management (DRM). This allows the use of HTML vide ...
support is not a goal, as the standard does not specify a Content Decryption Module to use, all available modules are proprietary even if licensing is possible, and the system imposes digital rights management
Digital rights management (DRM) is the management of legal access to digital content. Various tools or technological protection measures, such as access control technologies, can restrict the use of proprietary hardware and copyrighted works. DRM ...
that hides what the user's computer is doing to make copying "premium content" difficult. However, Media Source Extensions is supported, as YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in ...
began to require this technology in November 2018.
Apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
, which is the primary corporate backer of WebKit, rejected at least 16 web APIs because they could be used in a fingerprinting
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfa ...
attack to help personally identify users and track them, while providing limited or no benefit to the user. As HTML5test
HTML5test.com is a discontinued web app for evaluating a web browser's implementation some of common web standards, including HTML5, Web SQL Database, Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG), and WebGL.
The test suite was developed by Dutch web programme ...
checks for most of these APIs, it artificially lowers WebKit's "score" in points (as does lack of DRM support).
Web once supported NPAPI plug-ins, such as Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
and Adobe Flash
Adobe Flash (formerly Macromedia Flash and FutureSplash) is a mostly discontinuedAlthough it is discontinued by Adobe Inc., for the Chinese market it is developed by Zhongcheng and for the international enterprise market it is developed by Ha ...
, but support was removed in GNOME 3.34. In the modern web platform, these have fallen out of favor and support has been removed from all major browsers. Flash has been deprecated by Adobe itself. Flash had gained infamy throughout the years for usability and stability issues, incessant security vulnerabilities, its proprietary nature, its ability to let sites deploy particularly obnoxious web ads, and Adobe's poor and inconsistent Linux support. Many of these issues were raised by Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American businessman, inventor, and investor best known for co-founding the technology company Apple Inc. Jobs was also the founder of NeXT and chairman and majority shareholder o ...
, then CEO of Apple, in his essay Thoughts on Flash.
GNOME integration
Web reuses GNOME frameworks and settings, including the user interface theme, network settings, and printing. Settings are stored with GSettings and GNOME default applications are used forinternet media type
In information and communications technology, a media type, content type or MIME type is a two-part identifier for file formats and content formats. Their purpose is comparable to filename extensions and uniform type identifiers, in that they ident ...
s handling. The user configures these, centrally, in GNOME's settings app.
The built-in preference manager for Web presents basic browser-specific settings while advanced settings which could radically alter Web's behavior can be changed with utilities such as dconf (command line) and dconf-editor (graphical).
Web follows the GNOME Human Interface Guidelines and platform-wide design decisions. For example, in Web 3.4, the menu for application actions was moved to the GNOME Shell's top panel application menu and the menu bar was replaced with "super menu" button, which triggers the display of window-specific menu entries.
Since GNOME 3.32, Web can adjust to various form factors with the help of Libadwaita. It supports desktop, tablet and phone form factors. ("Narrow Mode").
Ad blocking
Since GNOME 3.18, Web is configured to block ads and pop-ups by default. In GNOME 3.34, the existing ad blocker was removed. This code was only partially functional and had been the source of many bugs. Web adopted the "Content Blockers" system from the WebKit engine. One of the developers, Adrián Pérez de Castro, compared the old and new ad blockers. He found that the switch saved approximately 80 MiB of RAM per browser tab.Google Safe Browsing and security sandboxing
Since GNOME 3.28, Web has support for Google Safe Browsing, to help prevent users from visiting malicious websites. Since GNOME 3.34, Web explicitly requires a minimum of WebKitGTK 2.26 or later. This provides the "Bubblewrap Sandbox" for tab processes, which is intended to prevent malicious websites from hijacking the browser and using it to spy on other tabs or run malicious code on the user's computer. If such code found another exploit in the operating system allowing it to becomeroot
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
, the result could be a disaster for all users of the system.
Making the sandbox a priority was brought on, according to Michael Catanzaro, because he was particularly concerned with the code quality of OpenJPEG and the numerous security problems that had been discovered in it, including many years of failing security reviews by Ubuntu. He further explained that web compatibility requires that sites believe that Web is a major browser. Sending them the user agent
On the Web, a user agent is a software agent responsible for retrieving and facilitating end-user interaction with Web content. This includes all web browsers, such as Google Chrome and Safari
A safari (; originally ) is an overland jour ...
of Apple Safari causes fewer broken websites than others (due to sharing the WebKit engine), but also causes caching servers to deliver JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000 (JP2) is an image compression standard and coding system. It was developed from 1997 to 2000 by a Joint Photographic Experts Group committee chaired by Touradj Ebrahimi (later the JPEG president), with the intention of superseding their ...
images, of which Safari is the only major browser to support. There is no other usable open source option for JPEG 2000 support. Fixing OpenJPEG, which is the official reference software, will be a massive undertaking that could take years to sort out. Enabling the Bubblewrap Sandbox would cause many vulnerabilities in this and other components to become "minimally useful" to potential attackers.
In GNOME 3.36, Web gained native support for PDF documents by using PDF.js. Michael Catanzaro explained that having websites open Evince
Evince (), also known as GNOME Document Viewer, is a Free and open-source software, free and open-source document viewer supporting many document file formats including Portable Document Format, PDF, PostScript, DjVu, Tagged Image File Format ...
to display PDF files was insecure, as it could be used to escape the browser's security sandbox. Since Evince was the last user of NPAPI, this allowed the remaining support code for the obsolete plug-in model (where additional vulnerabilities could be hiding) to be removed. Since the NPAPI support had a hard dependency on X11, moving to PDF.js also allowed that dependency to be dropped.
Since PDF.js internally converts PDF documents so that they can be displayed by the web browser's engine, it does not add security vulnerabilities to the browser the way that compiled plug-ins such as Adobe Acrobat
Adobe Acrobat is a family of application software and web services developed by Adobe Inc. to view, create, manipulate, print and manage Portable Document Format (PDF) files.
The family comprises Acrobat Reader (formerly Reader), Acrobat (former ...
or Evince could.
Bookmark management
While most browsers feature a hierarchical folder-based bookmark system, Web uses categorized bookmarks, where a single bookmark (e.g. this page) can exist in multiple categories (such as "Web Browsers", "GNOME", and "Computer Software"). A special category includes bookmarks that have not yet been categorized. Bookmarks, along with browsing history, are accessed from the address bar in find-as-you-type manner.Smart bookmarks
Another innovative concept supported by Web (though originally from Galeon) is " smart bookmarks". These take a single argument specified from the address bar, or from a textbox in a toolbar.Web Application Mode
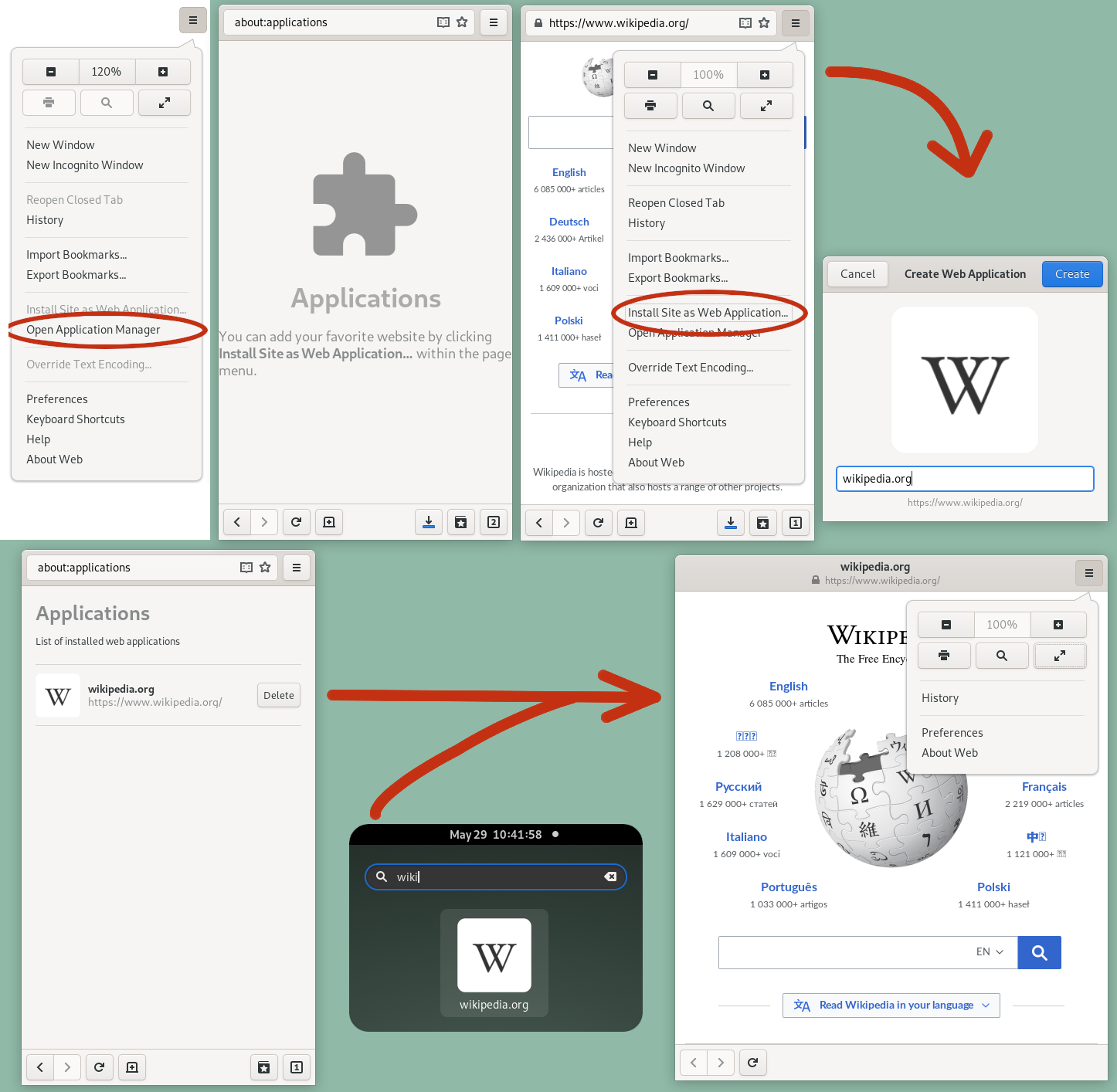
 Since GNOME 3.2, released in September 2011, Web allows creating application launchers for
Since GNOME 3.2, released in September 2011, Web allows creating application launchers for web application
A web application (or web app) is application software that is created with web technologies and runs via a web browser. Web applications emerged during the late 1990s and allowed for the server to dynamically build a response to the request, ...
s. The subsequent invocation of a launcher brings up a plain site-specific browser (single instance) of Web limited to one domain, with off-site links opening in a normal browser. The launcher created this way is accessible from the desktop and is not limited to GNOME Shell. For instance it may be used with Unity, used on Ubuntu
Ubuntu ( ) is a Linux distribution based on Debian and composed primarily of free and open-source software. Developed by the British company Canonical (company), Canonical and a community of contributors under a Meritocracy, meritocratic gover ...
. This feature facilitates the integration of the desktop and World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyis ...
, which is a goal of Web's developers. Similar features can be found in the Windows version of Google Chrome
Google Chrome is a web browser developed by Google. It was first released in 2008 for Microsoft Windows, built with free software components from Apple WebKit and Mozilla Firefox. Versions were later released for Linux, macOS, iOS, iPadOS, an ...
. For the same purpose Mozilla Foundation
The Mozilla Foundation is an American non-profit organization that exists to support and collectively lead the Open-source software, open source Mozilla project. Founded in July 2003, the organization sets the policies that govern development, ...
previously developed a standalone application Mozilla Prism, which was superseded by the project Chromeless.
Web applications are managed within the browser's main instance. The applications can be deleted from the page, accessible with a special URI about:applications. This approach was supposed to be a temporary while a centralized GNOME web application management was to be implemented in GNOME 3.4, but this never happened.
Firefox Sync
Since GNOME 3.26 and until GNOME 47, Web had support for Firefox Sync, which allowed users to sync their bookmarks, history, passwords, and open tabs with Firefox Sync, which could then be shared between any copy of Firefox or Web that the user signed into Firefox Sync with. In GNOME 47, it was disabled because of Mozilla changing the way Firefox Sync worked.Extensions
Web once supported extensions and a package was maintained containing the official ones. This was later removed due to problems with stability and maintainability. Some popular extensions, such asad blocking
Ad blocking (or ad filtering) is a software capability for blocking or altering online advertising in a History of the web browser, web browser, an Application software, application or a network. This may be done using browser extensions or othe ...
, were moved to the core application.
The project has expressed an interest in implementing support for the WebExtension add-on format used by Chrome, Firefox, and some other major browsers, if interested contributors can be found. Experimental support for WebExtensions was introduced in GNOME 43.
Reception
 In reviewing the WebKit-powered Epiphany 2.28 in September 2009, Ryan Paul of ''
In reviewing the WebKit-powered Epiphany 2.28 in September 2009, Ryan Paul of ''Ars Technica
''Ars Technica'' is a website covering news and opinions in technology, science, politics, and society, created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews, and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, sci ...
'' said "Epiphany is quite snappy in GNOME 2.28 and scores 100/100 on the Acid3 test. Using WebKit will help differentiate Epiphany from Firefox, which is shipped as the default browser by most of the major Linux distributors."
In reviewing Epiphany 2.30 in July 2010, Jack Wallen described it as "efficient, but different" and noted its problem with crashes. "When I first started working with Epiphany it crashed on most sites I visited. After doing a little research (and then a little debugging) I realized the issue was with JavaScript. Epiphany (in its current release), for some strange reason, doesn't like JavaScript. The only way around this was to disable JavaScript. Yes this means a lot of features won't work on a lot of sites – but this also means those same sites will load faster and won't be so prone to having issues (like crashing my browser)." Wallen concluded positively about the browser, "Although Epiphany hasn't fully replaced Chrome and Firefox as my one-stop-shop browser, I now use it much more than I would have previously. t has asmall footprint, fast startup, and clean interface."
In March 2011, Veronica Henry reviewed Epiphany 2.32, saying "To be fair, this would be a hard sell as a primary desktop browser for most users. In fact, there isn't even a setting to let you designate it as your default browser. But for those instance where you need to fire up a lightning-fast browser for quick surfing, Epiphany will do the trick." She further noted, "Though I still use Firefox as my primary browser, lately it seems to run at a snail's pace. So, one of the first things I noticed about Epiphany is how quickly it launches. And subsequent page loads on my system are equally as fast." Henry criticized Epiphany for its short list of extensions, singling out the lack of Firebug as a deficiency. Web instead supports Web Inspector offered by the WebKit engine, which has similar functionality.
In April 2012, Ryan Paul of ''Ars Technica'' used Web as an example to his criticism of GNOME 3.4 design decisions: "Aside from the poor initial discoverability of the panel menu, this model works reasonably well for simple applications. ..Unfortunately, it doesn't scale well in complex applications. The best example of where this approach can pose difficulties is in GNOME's default Web browser. ..Having the application's functionality split across two completely separate menus does not constitute a usability improvement." This was addressed in later versions, with a single unified menu.
In an October 2016 review, Bertel King Jr. noted on ''MakeUseOf'', "Later versions offer the best integration you will find with GNOME Shell. It lacks the add-ons found in mainstream browsers, but some users will like the minimalism, the speed, and the tab isolation that prevents one misbehaving site from crashing the entire browser."
In an April 2019 review, Bertel King Jr. wrote another article on ''MakeUseOf'', this time reviewing GNOME Web for its Web Applications Mode. He stated, "When you check your email, you’re using a web app. If you open YouTube, Netflix, or Spotify in a browser, again, you’re using a web app. These days, you can replace most of your desktop apps with web apps. ..GNOME Web provides tools to better integrate web apps with the rest of your desktop, so you can open them via your app launcher and view them in your dock or taskbar. This way they feel more like apps and less like sites." He also praised the security provided by walling off Web Applications from the rest of the browser and each other. Like Mozilla's container feature, this helps prevent sites such as Facebook from seeing what the user is doing in the main browser. It also allows the user to create multiple "apps" for the same site, to easily switch between different accounts.
See also
* * Midori, another web browser formerly based on GTK and WebKitGTK * List of web browsers for Unix and Unix-like operating systemsReferences
External links
*complete change-log
Firefox vs GNOME Web
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
{{aggregators 2002 software Free software programmed in C Free web browsers GNOME Core Applications MacOS web browsers POSIX web browsers Software based on WebKit Software forks Software that uses Meson Web browsers that use GTK