Weather Forecasting on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Weather forecasting or weather prediction is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the
Weather forecasting or weather prediction is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the
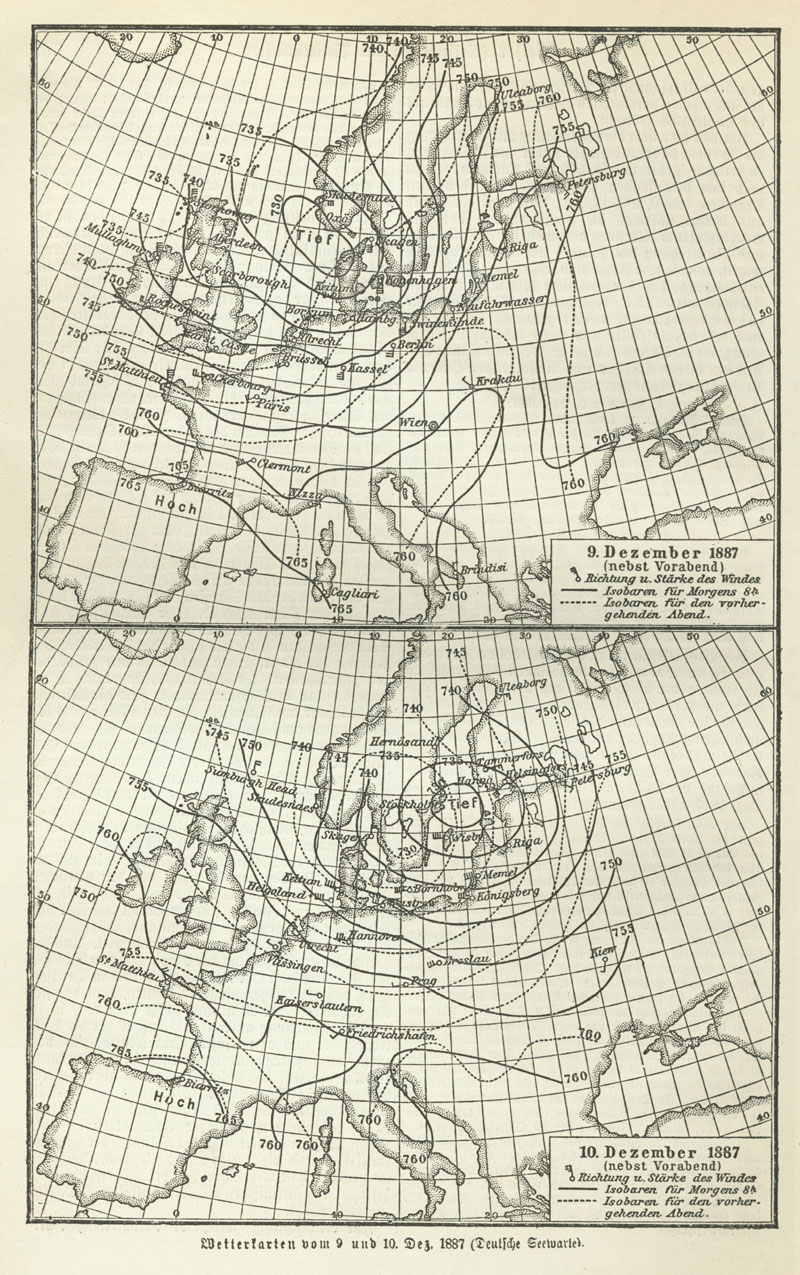 A storm in October 1859 that caused the loss of the ''Royal Charter'' inspired FitzRoy to develop charts to allow predictions to be made, which he called "forecasting the weather", thus coining the term "weather forecast". Fifteen land stations were established to use the
A storm in October 1859 that caused the loss of the ''Royal Charter'' inspired FitzRoy to develop charts to allow predictions to be made, which he called "forecasting the weather", thus coining the term "weather forecast". Fifteen land stations were established to use the
 It was not until the 20th century that advances in the understanding of atmospheric physics led to the foundation of modern
It was not until the 20th century that advances in the understanding of atmospheric physics led to the foundation of modern
 The world's first televised weather forecasts, including the use of weather maps, were experimentally broadcast by the
The world's first televised weather forecasts, including the use of weather maps, were experimentally broadcast by the
, ''
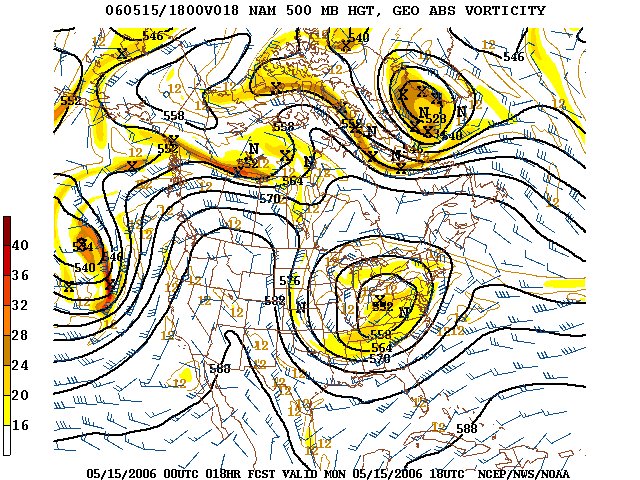 The basic idea of numerical weather prediction is to sample the state of the fluid at a given time and use the equations of
The basic idea of numerical weather prediction is to sample the state of the fluid at a given time and use the equations of  Commerce provides pilot reports along aircraft routes, and ship reports along shipping routes. Research flights using reconnaissance aircraft fly in and around weather systems of interest such as
Commerce provides pilot reports along aircraft routes, and ship reports along shipping routes. Research flights using reconnaissance aircraft fly in and around weather systems of interest such as
 In the past, human forecasters were responsible for generating the weather forecast based upon available observations. Today, human input is generally confined to choosing a model based on various parameters, such as model biases and performance.Klaus Weickmann, Jeff Whitaker, Andres Roubicek and Catherine Smith (December 1, 2001)
In the past, human forecasters were responsible for generating the weather forecast based upon available observations. Today, human input is generally confined to choosing a model based on various parameters, such as model biases and performance.Klaus Weickmann, Jeff Whitaker, Andres Roubicek and Catherine Smith (December 1, 2001)
"The Use of Ensemble Forecasts to Produce Improved Medium Range (3–15 days) Weather Forecasts"
Climate Diagnostics Center. Retrieved February 16, 2007. Using a consensus of forecast models, as well as ensemble members of the various models, can help reduce forecast error.Todd Kimberlain (June 2007)
"TC Genesis, Track, and Intensity Forecating"
. PowerPoint. Retrieved July 21, 2007. However, regardless how small the average error becomes with any individual system, large errors within any particular piece of guidance are still possible on any given model run. Humans are required to interpret the model data into weather forecasts that are understandable to the end user. Humans can use knowledge of local effects that may be too small in size to be resolved by the model to add information to the forecast. While increasing accuracy of forecasting models implies that humans may no longer be needed in the forecasting process at some point in the future, there is currently still a need for human intervention.
 Most end users of forecasts are members of the general public. Thunderstorms can create strong winds and dangerous
Most end users of forecasts are members of the general public. Thunderstorms can create strong winds and dangerous
 Electricity and gas companies rely on weather forecasts to anticipate demand, which can be strongly affected by the weather. They use the quantity termed the degree day to determine how strong of a use there will be for heating ( heating degree day) or cooling (cooling degree day). These quantities are based on a daily average temperature of . Cooler temperatures force heating degree days (one per degree Fahrenheit), while warmer temperatures force cooling degree days. In winter, severe cold weather can cause a surge in demand as people turn up their heating. Similarly, in summer a surge in demand can be linked with the increased use of
Electricity and gas companies rely on weather forecasts to anticipate demand, which can be strongly affected by the weather. They use the quantity termed the degree day to determine how strong of a use there will be for heating ( heating degree day) or cooling (cooling degree day). These quantities are based on a daily average temperature of . Cooler temperatures force heating degree days (one per degree Fahrenheit), while warmer temperatures force cooling degree days. In winter, severe cold weather can cause a surge in demand as people turn up their heating. Similarly, in summer a surge in demand can be linked with the increased use of
 Similar to the private sector, military weather forecasters present weather conditions to the war fighter community. Military weather forecasters provide pre-flight and in-flight weather briefs to pilots and provide real time resource protection services for military installations.
Naval forecasters cover the waters and ship weather forecasts. The
Similar to the private sector, military weather forecasters present weather conditions to the war fighter community. Military weather forecasters provide pre-flight and in-flight weather briefs to pilots and provide real time resource protection services for military installations.
Naval forecasters cover the waters and ship weather forecasts. The
"Keesler News: March 9, 2006"
.
Weather Forecasting Through the Ages
History of meteorology
{{DEFAULTSORT:Weather Forecasting Journalism by field News Broadcasting * Sky
 Weather forecasting or weather prediction is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the
Weather forecasting or weather prediction is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for thousands of years and formally since the 19th century.
Weather forecasts are made by collecting quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere, land, and ocean and using meteorology
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agricultur ...
to project how the atmosphere will change at a given place. Once calculated manually based mainly upon changes in barometric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013.2 ...
, current weather conditions, and sky conditions or cloud cover, weather forecasting now relies on computer-based models that take many atmospheric factors into account. Human input is still required to pick the best possible model to base the forecast upon, which involves pattern recognition skills, teleconnections, knowledge of model performance, and knowledge of model biases.
The inaccuracy of forecasting is due to the chaotic nature of the atmosphere; the massive computational power required to solve the equations that describe the atmosphere, the land, and the ocean; the error involved in measuring the initial conditions; and an incomplete understanding of atmospheric and related processes. Hence, forecasts become less accurate as the difference between the current time and the time for which the forecast is being made (the ''range'' of the forecast) increases. The use of ensembles and model consensus helps narrow the error and provide confidence in the forecast.
There is a vast variety of end uses for weather forecasts. Weather warnings are important because they are used to protect lives and property. Forecasts based on temperature and precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
are important to agriculture, and therefore to traders within commodity markets. Temperature forecasts are used by utility companies to estimate demand over coming days. On an everyday basis, many people use weather forecasts to determine what to wear on a given day. Since outdoor activities are severely curtailed by heavy rain, snow and wind chill
Wind chill (popularly wind chill factor) is the sensation of cold produced by the wind for a given ambient air temperature on exposed skin as the air motion accelerates the rate of heat transfer from the body to the surrounding atmosphere. Its va ...
, forecasts can be used to plan activities around these events, and to plan ahead and survive them.
Weather forecasting is a part of the economy. For example, in 2009, the US spent approximately $5.8 billion on it, producing benefits estimated at six times as much.
History
Ancient forecasting
In 650 BC, theBabylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
ns predicted the weather from cloud patterns as well as astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions ...
. In about 350 BC, Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
described weather patterns in ''Meteorologica
''Meteorology'' ( Greek: ; Latin: ''Meteorologica'' or ''Meteora'') is a treatise by Aristotle. The text discusses what Aristotle believed to have been all the affections common to air and water, and the kinds and parts of the Earth and the affec ...
''. Later, Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; ; c. 371 – c. 287 BC) was an ancient Greek Philosophy, philosopher and Natural history, naturalist. A native of Eresos in Lesbos, he was Aristotle's close colleague and successor as head of the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum, the ...
compiled a book on weather forecasting, called the ''Book of Signs''. Chinese weather prediction lore extends at least as far back as 300 BC, which was also around the same time ancient Indian astronomers developed weather-prediction methods. In the New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
, Jesus is quoted as referring to deciphering and understanding local weather patterns, by saying, "When evening comes, you say, 'It will be fair weather, for the sky is red', and in the morning, 'Today it will be stormy, for the sky is red and overcast.' You know how to interpret the appearance of the sky, but you cannot interpret the signs of the times."
In 904 AD, Ibn Wahshiyya's '' Nabatean Agriculture'', translated into Arabic from an earlier Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written a ...
work, discussed the weather forecasting of atmospheric changes and signs from the planetary astral alterations; signs of rain based on observation of the lunar phase
A lunar phase or Moon phase is the apparent shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion as viewed from the Earth. Because the Moon is tidally locked with the Earth, the same hemisphere is always facing the Earth. In common usage, the four maj ...
s; and weather forecasts based on the movement of winds.
Ancient weather forecasting methods usually relied on observed patterns of events, also termed pattern recognition. For example, it was observed that if the sunset was particularly red, the following day often brought fair weather. This experience accumulated over the generations to produce weather lore. However, not all of these predictions prove reliable, and many of them have since been found not to stand up to rigorous statistical testing.
Modern methods
It was not until the invention of theelectric telegraph
Electrical telegraphy is Point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point distance communicating via sending electric signals over wire, a system primarily used from the 1840s until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecom ...
in 1835 that the modern age of weather forecasting began. Before that, the fastest that distant weather reports could travel was around 160 kilometres per day (100 mi/d), but was more typically 60–120 kilometres per day (40–75 mi/day) (whether by land or by sea). By the late 1840s, the telegraph allowed reports of weather conditions from a wide area to be received almost instantaneously, allowing forecasts to be made from knowledge of weather conditions further upwind.
The two men credited with the birth of forecasting as a science were an officer of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
Francis Beaufort
Sir Francis Beaufort ( ; 27 May 1774 – 17 December 1857) was an Irish hydrographer and naval officer who created the Beaufort cipher and the Beaufort scale.
Early life
Francis Beaufort was descended from French Protestant Hugu ...
and his protégé Robert FitzRoy
Vice-Admiral Robert FitzRoy (5 July 1805 – 30 April 1865) was an English officer of the Royal Navy, politician and scientist who served as the second governor of New Zealand between 1843 and 1845. He achieved lasting fame as the captain of ...
. Both were influential men in British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
naval and governmental circles, and though ridiculed in the press at the time, their work gained scientific credence, was accepted by the Royal Navy, and formed the basis for all of today's weather forecasting knowledge.
Beaufort developed the Wind Force Scale and Weather Notation coding, which he was to use in his journals for the remainder of his life. He also promoted the development of reliable tide tables around British shores, and with his friend William Whewell
William Whewell ( ; 24 May 17946 March 1866) was an English polymath. He was Master of Trinity College, Cambridge. In his time as a student there, he achieved distinction in both poetry and mathematics.
The breadth of Whewell's endeavours is ...
, expanded weather record-keeping at 200 British coast guard
A coast guard or coastguard is a Maritime Security Regimes, maritime security organization of a particular country. The term embraces wide range of responsibilities in different countries, from being a heavily armed military force with cust ...
stations.
Robert FitzRoy
Vice-Admiral Robert FitzRoy (5 July 1805 – 30 April 1865) was an English officer of the Royal Navy, politician and scientist who served as the second governor of New Zealand between 1843 and 1845. He achieved lasting fame as the captain of ...
was appointed in 1854 as chief of a new department within the Board of Trade
The Board of Trade is a British government body concerned with commerce and industry, currently within the Department for Business and Trade. Its full title is The Lords of the Committee of the Privy Council appointed for the consideration of ...
to deal with the collection of weather data at sea as a service to mariners. This was the forerunner of the modern Meteorological Office
The Met Office, until November 2000 officially the Meteorological Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather and climate service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology and ...
. All ship captains were tasked with collating data on the weather and computing it, with the use of tested instruments that were loaned for this purpose.Mellersh, H. E. L. (1968). FitzRoy of the Beagle. Hart-Davis.
 A storm in October 1859 that caused the loss of the ''Royal Charter'' inspired FitzRoy to develop charts to allow predictions to be made, which he called "forecasting the weather", thus coining the term "weather forecast". Fifteen land stations were established to use the
A storm in October 1859 that caused the loss of the ''Royal Charter'' inspired FitzRoy to develop charts to allow predictions to be made, which he called "forecasting the weather", thus coining the term "weather forecast". Fifteen land stations were established to use the telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas ...
to transmit to him daily reports of weather at set times leading to the first gale warning service. His warning service for shipping was initiated in February 1861, with the use of telegraph communications. The first daily weather forecasts were published in ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British Newspaper#Daily, daily Newspaper#National, national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its modern name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its si ...
'' in 1861. In the following year a system was introduced of hoisting storm warning cones at the principal ports when a gale was expected. The ''"Weather Book"'' which FitzRoy published in 1863 was far in advance of the scientific opinion of the time.
As the electric telegraph network expanded, allowing for the more rapid dissemination of warnings, a national observational network was developed, which could then be used to provide synoptic analyses. To shorten detailed weather reports into more affordable telegrams, senders encoded weather information in telegraphic code, such as the one developed by the U.S. Army Signal Corps. Instruments to continuously record variations in meteorological parameters using photography
Photography is the visual arts, art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is empl ...
were supplied to the observing stations from Kew Observatory
The King's Observatory (called for many years the Kew Observatory) is a Grade I listed building in Richmond, London. Now a private dwelling, it formerly housed an astronomical observatory, astronomical and Terrestrial magnetism, terrestrial mag ...
– these cameras had been invented by Francis Ronalds
Sir Francis Ronalds Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (21 February 17888 August 1873) was an English scientist and inventor, and arguably the first History of electrical engineering, electrical engineer. He was knighted for creating the first wo ...
in 1845 and his barograph had earlier been used by FitzRoy.
To convey accurate information, it soon became necessary to have a standard vocabulary describing clouds; this was achieved by means of a series of classifications first achieved by Luke Howard
Luke Howard (28 November 1772 – 21 March 1864) was a British manufacturing chemist and an amateur meteorologist with broad interests in science. His lasting contribution to science is a nomenclature system for clouds, which he proposed in ...
in 1802, and standardized in the ''International Cloud Atlas
The ''International Cloud Atlas'' or simply the ''Cloud Atlas'', is a cloud atlas that was first published in 1896 and has remained in print since. Its initial purposes included aiding the training of meteorologists and promoting more consisten ...
'' of 1896.
Numerical prediction
 It was not until the 20th century that advances in the understanding of atmospheric physics led to the foundation of modern
It was not until the 20th century that advances in the understanding of atmospheric physics led to the foundation of modern numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to weather forecasting, predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of comput ...
. In 1922, English scientist Lewis Fry Richardson
Lewis Fry Richardson, Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (11 October 1881 – 30 September 1953) was an English mathematician, physicist, meteorologist, psychologist, and Pacifism, pacifist who pioneered modern mathematical techniques of weather ...
published "Weather Prediction By Numerical Process", after finding notes and derivations he worked on as an ambulance driver in World War I. He described therein how small terms in the prognostic fluid dynamics equations governing atmospheric flow could be neglected, and a finite differencing scheme in time and space could be devised, to allow numerical prediction solutions to be found.
Richardson envisioned a large auditorium of thousands of people performing the calculations and passing them to others. However, the sheer number of calculations required was too large to be completed without the use of computers, and the size of the grid and time steps led to unrealistic results in deepening systems. It was later found, through numerical analysis, that this was due to numerical instability. The first computerised weather forecast was performed by a team composed of American meteorologists Jule Charney, Philip Duncan Thompson, Larry Gates, and Norwegian meteorologist Ragnar Fjørtoft, applied mathematician John von Neumann
John von Neumann ( ; ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian and American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist and engineer. Von Neumann had perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time, in ...
, and ENIAC
ENIAC (; Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first Computer programming, programmable, Electronics, electronic, general-purpose digital computer, completed in 1945. Other computers had some of these features, but ENIAC was ...
programmer Klara Dan von Neumann. Practical use of numerical weather prediction began in 1955, spurred by the development of programmable electronic computers.
Broadcasts
The first ever daily weather forecasts were published in ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British Newspaper#Daily, daily Newspaper#National, national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its modern name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its si ...
'' on August 1, 1861, and the first weather maps were produced later in the same year. In 1911, the Met Office
The Met Office, until November 2000 officially the Meteorological Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather and climate service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology and ...
began issuing the first marine weather forecasts via radio transmission. These included gale and storm warnings for areas around Great Britain. In the United States, the first public radio forecasts were made in 1925 by Edward B. "E.B." Rideout, on WEEI, the Edison Electric Illuminating station in Boston. Rideout came from the U.S. Weather Bureau, as did WBZ weather forecaster G. Harold Noyes in 1931.
 The world's first televised weather forecasts, including the use of weather maps, were experimentally broadcast by the
The world's first televised weather forecasts, including the use of weather maps, were experimentally broadcast by the BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
in November 1936. This was brought into practice in 1949, after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. George Cowling gave the first weather forecast while being televised in front of the map in 1954. In America, experimental television forecasts were made by James C. Fidler in Cincinnati in either 1940 or 1947 on the DuMont Television Network
The DuMont Television Network (also the DuMont Network, DuMont Television, DuMont/Du Mont, or (incorrectly) Dumont ) was one of America's pioneer commercial television networks, rivaling NBC and CBS for the distinction of being first overall in ...
. In the late 1970s and early 1980s, John Coleman, the first weatherman for the American Broadcasting Company
The American Broadcasting Company (ABC) is an American Commercial broadcasting, commercial broadcast Television broadcaster, television and radio Radio network, network that serves as the flagship property of the Disney Entertainment division ...
(ABC)'s ''Good Morning America
''Good Morning America'', often abbreviated as ''GMA'', is an American breakfast television, morning television program that is broadcast on American Broadcasting Company, ABC. It debuted on November 3, 1975, and first expanded to weekends wit ...
'', pioneered the use of on-screen weather satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites are mainly of two types: polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asyn ...
data and computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. ...
for television forecasts.CJR Rewind: Hot Air, ''
Columbia Journalism Review
The ''Columbia Journalism Review'' (''CJR'') is a biannual magazine for professional journalists that has been published by the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism since 1961. Its original purpose was "to assess the performance ...
'', reprint, first published in the January/February 2010 issue. In 1982, Coleman partnered with Landmark Communications
Landmark Media Enterprises, LLC (a spinoff of Landmark Communications, Inc.) is a privately held technology company headquartered in Norfolk, Virginia.
History
The ''Norfolk Landmark'' was established in 1873. It had various editors. K. C. Murray ...
CEO Frank Batten to launch The Weather Channel
The Weather Channel (TWC) is an American pay television television channel, channel owned by Weather Group, LLC, a subsidiary of Allen Media Group. The channel's headquarters are located in Atlanta, Georgia. Launched on May 2, 1982, the channel ...
(TWC), a 24-hour cable network devoted to national and local weather reports. Some weather channels have started broadcasting on live streaming platforms such as YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in ...
and Periscope
A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.
In its simplest form, it consists of an outer case with ...
to reach more viewers.
Numerical weather prediction
fluid dynamics
In physics, physical chemistry and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids – liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including (the study of air and other gases in motion ...
and thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, Work (thermodynamics), work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed b ...
to estimate the state of the fluid at some time in the future. The main inputs from country-based weather services are surface observations from automated weather station
A weather station is a facility, either on land or sea, with instruments and equipment for measuring atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric conditions to provide information for weather forecasting, weather forecasts and to study the weather and clima ...
s at ground level over land and from weather buoys at sea. The World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology an ...
acts to standardize the instrumentation, observing practices and timing of these observations worldwide. Stations either report hourly in METAR
METAR is a format for reporting weather information. A METAR weather report is predominantly used by aircraft pilots, and by meteorologists, who use aggregated METAR information to assist in weather forecasting.
Raw METAR is highly standardize ...
reports, or every six hours in SYNOP reports. Sites launch radiosonde
A radiosonde is a battery-powered telemetry instrument carried into the atmosphere usually by a weather balloon that measures various atmospheric parameters and transmits them by radio to a ground receiver. Modern radiosondes measure or calculat ...
s, which rise through the depth of the troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
and well into the stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second-lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is composed of stratified temperature zones, with the warmer layers of air located higher ...
. Data from weather satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites are mainly of two types: polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asyn ...
s are used in areas where traditional data sources are not available. Compared with similar data from radiosondes, the satellite data has the advantage of global coverage, but at a lower accuracy and resolution. Meteorological radar provide information on precipitation location and intensity, which can be used to estimate precipitation accumulations over time. Additionally, if a pulse Doppler weather radar
A weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar (WSR) and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, calculate its motion, and estimate its type (rain, snow, hail etc.). Modern w ...
is used then wind speed and direction can be determined. These methods, however, leave an in-situ observational gap in the lower atmosphere (from 100 m to 6 km above ground level). To reduce this gap, in the late 1990s weather drones started to be considered for obtaining data from those altitudes. Research has been growing significantly since the 2010s, and weather-drone data may in future be added to numerical weather models.
 Commerce provides pilot reports along aircraft routes, and ship reports along shipping routes. Research flights using reconnaissance aircraft fly in and around weather systems of interest such as
Commerce provides pilot reports along aircraft routes, and ship reports along shipping routes. Research flights using reconnaissance aircraft fly in and around weather systems of interest such as tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
s. Reconnaissance aircraft are also flown over the open oceans during the cold season into systems that cause significant uncertainty in forecast guidance, or are expected to be of high impact three–seven days into the future over the downstream continent.
Models are ''initialized'' using this observed data. The irregularly spaced observations are processed by data assimilation and objective analysis methods, which perform quality control and obtain values at locations usable by the model's mathematical algorithms (usually an evenly spaced grid). The data are then used in the model as the starting point for a forecast. Commonly, the set of equations used to predict the physics and dynamics of the atmosphere are called primitive equations
The primitive equations are a set of nonlinear partial differential equations that are used to approximate global atmosphere, atmospheric flow and are used in most Global climate model, atmospheric models. They consist of three main sets of balance ...
. These are initialized from the analysis data and rates of change are determined. The rates of change predict the state of the atmosphere a short time into the future. The equations are then applied to this new atmospheric state to find new rates of change, which predict the atmosphere at a yet further time into the future. This ''time stepping'' procedure is continually repeated until the solution reaches the desired forecast time.
The length of the time step chosen within the model is related to the distance between the points on the computational grid, and is chosen to maintain numerical stability
In the mathematical subfield of numerical analysis, numerical stability is a generally desirable property of numerical algorithms. The precise definition of stability depends on the context: one important context is numerical linear algebra, and ...
. Time steps for global models are on the order of tens of minutes, while time steps for regional models are between one and four minutes. The global models are run at varying times into the future. The Met Office
The Met Office, until November 2000 officially the Meteorological Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather and climate service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology and ...
's Unified Model The Unified Model is a numerical weather prediction and climate modeling software suite originally developed by the United Kingdom Met Office from 1990 and now both used and further developed by many weather-forecasting agencies around the world. ...
is run six days into the future, the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts model is run out to 10 days into the future, while the Global Forecast System model run by the Environmental Modeling Center is run 16 days into the future. The visual output produced by a model solution is known as a prognostic chart, or ''prog''. The raw output is often modified before being presented as the forecast. This can be in the form of statistical techniques to remove known bias
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is inaccurate, closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individ ...
es in the model, or of adjustment to take into account consensus among other numerical weather forecasts. MOS or model output statistics is a technique used to interpret numerical model output and produce site-specific guidance. This guidance is presented in coded numerical form, and can be obtained for nearly all National Weather Service reporting stations in the United States. As proposed by Edward Lorenz in 1963, long range forecasts, those made at a range of two weeks or more cannot definitively predict the state of the atmosphere, owing to the chaotic nature of the fluid dynamics
In physics, physical chemistry and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids – liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including (the study of air and other gases in motion ...
equations involved. In numerical models, extremely small errors in initial values double roughly every five days for variables such as temperature and wind velocity.
Essentially, a model is a computer program that produces meteorological
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agriculture ...
information for future times at given locations and altitudes. Within any modern model is a set of equations, known as the primitive equations, used to predict the future state of the atmosphere. These equations—along with the ideal gas law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stat ...
—are used to evolve the density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be u ...
, pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
, and potential temperature scalar field
In mathematics and physics, a scalar field is a function associating a single number to each point in a region of space – possibly physical space. The scalar may either be a pure mathematical number ( dimensionless) or a scalar physical ...
s and the velocity
Velocity is a measurement of speed in a certain direction of motion. It is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector (geometry), vector Physical q ...
vector field
In vector calculus and physics, a vector field is an assignment of a vector to each point in a space, most commonly Euclidean space \mathbb^n. A vector field on a plane can be visualized as a collection of arrows with given magnitudes and dire ...
of the atmosphere through time. Additional transport equations for pollutants and other aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be generated from natural or Human impact on the environment, human causes. The term ''aerosol'' co ...
s are included in some primitive-equation mesoscale models as well. The equations used are nonlinear partial differential equations, which are impossible to solve exactly through analytical methods, with the exception of a few idealized cases. Therefore, numerical methods obtain approximate solutions. Different models use different solution methods: some global models use spectral method
Spectral methods are a class of techniques used in applied mathematics and scientific computing to numerically solve certain differential equations. The idea is to write the solution of the differential equation as a sum of certain " basis funct ...
s for the horizontal dimensions and finite difference method
In numerical analysis, finite-difference methods (FDM) are a class of numerical techniques for solving differential equations by approximating Derivative, derivatives with Finite difference approximation, finite differences. Both the spatial doma ...
s for the vertical dimension, while regional and other global models usually use finite-difference methods in all three dimensions.
Techniques
Persistence
The simplest method of forecasting the weather, persistence, relies upon today's conditions to forecast tomorrow's. This can be valid when the weather achieves a steady state, such as during the summer season in the tropics. This method strongly depends upon the presence of a stagnant weather pattern. Therefore, when in a fluctuating pattern, it becomes inaccurate. It can be useful in both short- and long-range forecast, long range forecasts.Barometer
Measurements of barometric pressure and the pressure tendency (the change of pressure over time) have been used in forecasting since the late 19th century. The larger the change in pressure, especially if more than , the larger the change in weather can be expected. If the pressure drop is rapid, a low pressure system is approaching, and there is a greater chance of rain. Rapid pressure rises are associated with improving weather conditions, such as clearing skies.Observation
Along with pressure tendency, the condition of the sky is one of the more important parameters used to forecast weather in mountainous areas. Thickening of cloud cover or the invasion of a higher cloud deck is indicative of rain in the near future. High thincirrostratus cloud
Cirrostratus () is a high-altitude, very thin, and generally uniform stratiform genus-type of cloud. It is composed of ice crystals, which are particles of frozen water. Cirrostratus is difficult to see and can produce halos. These optical ...
s can create halos around the sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
or moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
, which indicates an approach of a warm front
Warm, WARM, or Warmth may refer to:
* A somewhat high temperature; heat
* Kindness
Music Albums
* ''Warm'' (Herb Alpert album), 1969
* ''Warm'' (Jeff Tweedy album), 2018
* ''Warm'' (Johnny Mathis album), 1958, and the title song
* ''Warm'' ( ...
and its associated rain. Morning fog portends fair conditions, as rainy conditions are preceded by wind or clouds that prevent fog formation. The approach of a line of thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustics, acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorm ...
s could indicate the approach of a cold front
A cold front is the leading edge of a cooler mass of air at ground level that replaces a warmer mass of air and lies within a pronounced surface Trough (meteorology), trough of Low-pressure area, low pressure. It often forms behind an extratropica ...
. Cloud-free skies are indicative of fair weather for the near future. A bar can indicate a coming tropical cyclone. The use of sky cover in weather prediction has led to various weather lore over the centuries.
Nowcasting
The forecasting of the weather for the following six hours is often referred to as nowcasting. In this time range it is possible to forecast smaller features such as individual showers and thunderstorms with reasonable accuracy, as well as other features too small to be resolved by a computer model. A human given the latest radar, satellite and observational data will be able to make a better analysis of the small scale features present and so will be able to make a more accurate forecast for the following few hours. However, there are nowexpert system
In artificial intelligence (AI), an expert system is a computer system emulating the decision-making ability of a human expert.
Expert systems are designed to solve complex problems by reasoning through bodies of knowledge, represented mainly as ...
s using those data and mesoscale numerical model to make better extrapolation, including evolution of those features in time. Accuweather
AccuWeather, Inc. is a private-sector American media company that provides commercial weather forecasting services. AccuWeather was founded in 1962 by Joel N. Myers. The company adopted the name 'AccuWeather' in 1971.
AccuWeather is headquar ...
is known for a Minute-Cast, which is a minute-by-minute precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
forecast for the next two hours.
Atmospheric model
"The Use of Ensemble Forecasts to Produce Improved Medium Range (3–15 days) Weather Forecasts"
Climate Diagnostics Center. Retrieved February 16, 2007. Using a consensus of forecast models, as well as ensemble members of the various models, can help reduce forecast error.Todd Kimberlain (June 2007)
"TC Genesis, Track, and Intensity Forecating"
. PowerPoint. Retrieved July 21, 2007. However, regardless how small the average error becomes with any individual system, large errors within any particular piece of guidance are still possible on any given model run. Humans are required to interpret the model data into weather forecasts that are understandable to the end user. Humans can use knowledge of local effects that may be too small in size to be resolved by the model to add information to the forecast. While increasing accuracy of forecasting models implies that humans may no longer be needed in the forecasting process at some point in the future, there is currently still a need for human intervention.
Analog
The analog technique is a complex way of making a forecast, requiring the forecaster to remember a previous weather event that is expected to be mimicked by an upcoming event. What makes it a difficult technique to use is that there is rarely a perfect analog for an event in the future. Some call this type of forecasting pattern recognition. It remains a useful method of observing rainfall over data voids such as oceans, as well as the forecasting of precipitation amounts and distribution in the future. A similar technique is used in medium range forecasting, which is known as teleconnections, when systems in other locations are used to help pin down the location of another system within the surrounding regime. An example of teleconnections are by using El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) related phenomena.Artificial intelligence
Initial attempts to useartificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
began in the 2010s. Huawei
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ("Huawei" sometimes stylized as "HUAWEI"; ; zh, c=华为, p= ) is a Chinese multinational corporationtechnology company in Longgang, Shenzhen, Longgang, Shenzhen, Guangdong. Its main product lines include teleco ...
's Pangu-Weather model, Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
's GraphCast, WindBorne's WeatherMesh model, Nvidia
Nvidia Corporation ( ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and incorporated in Delaware. Founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang (president and CEO), Chris Malachowsky, and Curti ...
's FourCastNet, and the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts' Artificial Intelligence/Integrated Forecasting System, or AIFS all appeared in 2022–2023. In 2024, AIFS started to publish real-time forecasts, showing specific skill at predicting hurricane tracks, but lower-performing on the intensity changes of such storms relative to physics-based models.
Such models use no physics-based atmosphere modeling or large language model
A large language model (LLM) is a language model trained with self-supervised machine learning on a vast amount of text, designed for natural language processing tasks, especially language generation.
The largest and most capable LLMs are g ...
s. Instead, they learn purely from data such as the ECMWF re-analysis ERA5. These models typically require far less compute than physics-based models.
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
's Aurora system offers global 10-day weather and 5-day air pollution ( , NO, , , , and particulates) forecasts with claimed accuracy similar to physics-based models, but at orders-of-magnitude lower cost. Aurora was trained on more than a million hours of data from six weather/climate models.
In 2024, a group of researchers at Google's DeepMind AI research laboratories published a paper in Nature to describe their machine-learning model, called GenCast, that is expected to produce more accurate forecasts than the best traditional weather forecasting systems.
In a study conducted using the AIFS, Lang et al. (2024) presented 30-day ensemble simulations of the Madden-Julia Oscillation.''
Communicating forecasts to the public
lightning
Lightning is a natural phenomenon consisting of electrostatic discharges occurring through the atmosphere between two electrically charged regions. One or both regions are within the atmosphere, with the second region sometimes occurring on ...
strikes that can lead to deaths, power outages, and widespread hail damage. Heavy snow or rain can bring transportation and commerce to a stand-still, as well as cause flooding in low-lying areas. Excessive heat
In thermodynamics, heat is energy in transfer between a thermodynamic system and its surroundings by such mechanisms as thermal conduction, electromagnetic radiation, and friction, which are microscopic in nature, involving sub-atomic, ato ...
or cold waves can sicken or kill those with inadequate utilities, and droughts can impact water usage and destroy vegetation.
Several countries employ government agencies to provide forecasts and watches/warnings/advisories to the public to protect life and property and maintain commercial interests. Knowledge of what the end user needs from a weather forecast must be taken into account to present the information in a useful and understandable way. Examples include the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, ...
's National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an Government agency, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weathe ...
(NWS) and Environment Canada
Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC; )Environment and Climate Change Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of the Environment (). is the Ministry (government department), department ...
's Meteorological Service (MSC). Traditionally, newspaper, television, and radio have been the primary outlets for presenting weather forecast information to the public. In addition, some cities had weather beacon
A weather beacon is a beacon that indicates the local weather forecast in a code of colored or flashing lights. Often, a short poem or jingle accompanies the code to make it easier to remember.
The beacon is usually on the roof of a tall build ...
s. Increasingly, the internet is being used due to the vast amount of specific information that can be found. In all cases, these outlets update their forecasts on a regular basis.
Severe weather alerts and advisories
A major part of modern weather forecasting is the severe weather alerts and advisories that the national weather services issue in the case that severe or hazardous weather is expected. This is done to protect life and property. Some of the most commonly known of severe weather advisories are thesevere thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustics, acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorm ...
and tornado warning, as well as the severe thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustics, acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorm ...
and tornado watch. Other forms of these advisories include winter weather, high wind, flood
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant con ...
, tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
, and fog. Severe weather advisories and alerts are broadcast through the media, including radio, using emergency systems as the Emergency Alert System
The Emergency Alert System (EAS) is a Emergency population warning, national warning system in the United States designed to allow authorized officials to broadcast emergency alerts and warning messages to the public via Cable television, cable ...
, which break into regular programming.
Low temperature forecast
The low temperature forecast for the current day is calculated using the lowest temperature found between 7pm that evening through 7am the following morning. So, in short, today's forecasted low is most likely tomorrow's low temperature.Specialist forecasting
There are a number of sectors with their own specific needs for weather forecasts and specialist services are provided to these users as given below:Air traffic
Because the aviation industry is especially sensitive to the weather, accurate weather forecasting is essential. Fog or exceptionally low ceilings can prevent many aircraft from landing and taking off.Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers with no disruption between ...
and icing are also significant in-flight hazards. Thunderstorms are a problem for all aircraft because of severe turbulence due to their updrafts and outflow boundaries, icing due to the heavy precipitation, as well as large hail
Hail is a form of solid Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailsto ...
, strong winds, and lightning, all of which can cause severe damage to an aircraft in flight. Volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, produced during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to r ...
is also a significant problem for aviation, as aircraft can lose engine power within ash clouds. On a day-to-day basis airliners are routed to take advantage of the jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow thermal wind, air currents in the Earth's Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere.
The main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds, flowing west to east around the gl ...
tailwind to improve fuel efficiency. Aircrews are briefed prior to takeoff
Takeoff is the phase of flight in which an aerospace vehicle leaves the ground and becomes airborne. For aircraft traveling vertically, this is known as liftoff.
For aircraft that take off horizontally, this usually involves starting with a tr ...
on the conditions to expect en route and at their destination. Additionally, airports often change which runway
In aviation, a runway is an elongated, rectangular surface designed for the landing and takeoff of an aircraft. Runways may be a human-made surface (often asphalt concrete, asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface (sod, ...
is being used to take advantage of a headwind
A tailwind is a wind that blows in the direction of travel of an object, while a headwind blows against the direction of travel. A tailwind increases the object's speed and reduces the time required to reach its destination, while a headwind has ...
. This reduces the distance required for takeoff, and eliminates potential crosswinds.
Marine
Commercial and recreational use of waterways can be limited significantly by wind direction and speed,wave
In physics, mathematics, engineering, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium) of one or more quantities. ''Periodic waves'' oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium ...
periodicity and heights, tides, and precipitation. These factors can each influence the safety of marine transit. Consequently, a variety of codes have been established to efficiently transmit detailed marine weather forecasts to vessel pilots via radio, for example the MAFOR (marine forecast). Typical weather forecasts can be received at sea through the use of RTTY, Navtex and Radiofax
Radiofacsimile, radiofax or HF fax is an analogue mode for transmitting grayscale images via high frequency (HF) radio waves. It was the predecessor to slow-scan television (SSTV). It was the primary method of sending photographs from remote sit ...
.
Agriculture
Farmers rely on weather forecasts to decide what work to do on any particular day. For example, drying hay is only feasible in dry weather. Prolonged periods of dryness can ruin cotton, wheat, andcorn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
crops. While corn crops can be ruined by drought, their dried remains can be used as a cattle feed substitute in the form of silage
Silage is fodder made from green foliage crops which have been preserved by fermentation (food), fermentation to the point of souring. It is fed to cattle, sheep and other ruminants. The fermentation and storage process is called ''ensilage'', ' ...
. Frosts and freezes play havoc with crops both during the spring and fall. For example, peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and Agriculture, cultivated in China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and the glossy-skinned, non-fuzzy varieties called necta ...
trees in full bloom can have their potential peach crop decimated by a spring freeze. Orange groves can suffer significant damage during frosts and freezes, regardless of their timing.
Forestry
Forecasting of wind, precipitation and humidity is essential for preventing and controllingwildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a ...
s. Indices such as the '' Forest fire weather index'' and the '' Haines Index'', have been developed to predict the areas more at risk of fire from natural or human causes. Conditions for the development of harmful insects can also be predicted by forecasting the weather.
Utility companies
air conditioning
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C (US) or air con (UK), is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior temperature, and in some cases, also controlling the humidity of internal air. Air c ...
systems in hot weather. By anticipating a surge in demand, utility companies can purchase additional supplies of power or natural gas before the price increases, or in some circumstances, supplies are restricted through the use of brownouts and blackouts.
Other commercial companies
Increasingly, private companies pay for weather forecasts tailored to their needs so that they can increase their profits or avoid large losses. For example, supermarket chains may change the stocks on their shelves in anticipation of differentconsumer spending
Consumer spending is the total money spent on final goods and services by individuals and households.
There are two components of consumer spending: induced consumption (which is affected by the level of income) and autonomous consumption (which ...
habits in different weather conditions. Weather forecasts can be used to invest in the commodity market, such as futures in oranges, corn, soybeans, and oil.
Military applications
United Kingdom
The BritishRoyal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
, working with the Met Office
The Met Office, until November 2000 officially the Meteorological Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather and climate service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology and ...
, has its own specialist branch of weather observers and forecasters, as part of the Hydrographic and Meteorological (HM) specialisation, who monitor and forecast operational conditions across the globe, to provide accurate and timely weather and oceanographic information to submarines, ships and Fleet Air Arm
The Fleet Air Arm (FAA) is the naval aviation component of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy (RN). The FAA is one of five :Fighting Arms of the Royal Navy, RN fighting arms. it is a primarily helicopter force, though also operating the Lockhee ...
aircraft.
A mobile unit in the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
, working with the Met Office, forecasts the weather for regions in which British and allied armed forces are deployed. A group based at Camp Bastion used to provide forecasts for the British armed forces in Afghanistan.
United States
 Similar to the private sector, military weather forecasters present weather conditions to the war fighter community. Military weather forecasters provide pre-flight and in-flight weather briefs to pilots and provide real time resource protection services for military installations.
Naval forecasters cover the waters and ship weather forecasts. The
Similar to the private sector, military weather forecasters present weather conditions to the war fighter community. Military weather forecasters provide pre-flight and in-flight weather briefs to pilots and provide real time resource protection services for military installations.
Naval forecasters cover the waters and ship weather forecasts. The United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
provides a special service for itself and the rest of the federal government by issuing forecasts for tropical cyclones across the Pacific and Indian Oceans through its Joint Typhoon Warning Center.
Within the United States, the 557th Weather Wing provides weather forecasting for the Air Force and the Army. Air Force
An air force in the broadest sense is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an army aviati ...
forecasters cover air operations in both wartime and peacetime and provide Army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
support; United States Coast Guard
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and Admiralty law, law enforcement military branch, service branch of the armed forces of the United States. It is one of the country's eight Uniformed services ...
marine science technicians provide ship forecasts for ice breakers and various other operations within their realm; and Marine forecasters provide support for ground- and air-based United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines or simply the Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is responsible for conducting expeditionar ...
operations. All four of the mentioned military branches have their initial enlisted meteorology technical training at Keesler Air Force Base. Keesler Air Force Base. Military officers usually received their education from a civilian institution"Keesler News: March 9, 2006"
.
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its ori ...
Retrieved May 26, 2008. Military and civilian forecasters actively cooperate in analyzing, creating and critiquing weather forecast products.
See also
* Air pollution forecasting * Citizen Weather Observer Program * Ensemble forecasting * Flood forecasting * National Collegiate Weather Forecasting Contest * National Weatherperson's Day * Nonhomogeneous Gaussian regression * Surface weather observation * Tropical cyclone forecasting * Weather and Society Integrated Studies * Weather hole * WxChallenge * Weather forecasting for Operation OverlordReferences
Further reading
* *External links
Weather Forecasting Through the Ages
History of meteorology
{{DEFAULTSORT:Weather Forecasting Journalism by field News Broadcasting * Sky