Warrant Officer Class 2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Warrant officer (WO) is a
Bangladesh-Navy-OR-9.svg, Master chief petty officer
Bangladesh-army-WO-3.svg, Master warrant officer
08.BAF-CWO.svg, Master warrant officer
Warrant officer is the lowest junior commissioned officer rank in the
File:Canadian Army OR-9a.svg, Insignia of a chief warrant officer
File:Canadian Army OR-8.svg, Insignia of a master warrant officer
File:Canadian Army OR-7.svg, Insignia of a warrant officer

 In the
In the
 In the
In the
File:Bangladesh-army-WO-1.svg, Warrant officer
(
(
(
(
File:British Army OR-8a.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Antigua and Barbuda Regiment) File:Botswana-Army-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
( Gambian National Army) File:Ghana-Army-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
( Kenya Army) File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Lesotho Army) File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Malawi Army) File:05-Namibia Army-WO2.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Namibian Army) File:05-Rwanda Army-WO2.svg, Warrant officer II
( Rwandan Land Forces) File:Seychelles-Army-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Seychelles Infantry Unit) File:Sierra Leone-Army-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Sierra Leone Army) File:SAA-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
( Eswatini Army) File:05-Tanzania Army-WO2.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
( Ugandan Land Forces) File:Zambia-Army-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
( Zimbabwe National Army)
File:Coat of arms of Antigua and Barbuda.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Antigua and Barbuda Regiment) File:Botswana-Army-OR-9.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
( Gambian National Army) File:Ghana-Army-OR-9.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
( Kenya Army) File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Lesotho Army) File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Malawi Army) File:06-Namibia Army-WO1.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Namibian Army) File:06-Rwanda Army-WO1.svg, Warrant officer II
( Rwandan Land Forces) File:Seychelles-Army-OR-9.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Seychelles Infantry Unit) File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Sierra Leone Army) File:SAA-OR-9.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
( Eswatini Army) File:06-Tanzania Army-WO1.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
( Ugandan Land Forces) File:Coat of arms of Zambia.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
( Zimbabwe National Army)
rank
A rank is a position in a hierarchy. It can be formally recognized—for example, cardinal, chief executive officer, general, professor—or unofficial.
People Formal ranks
* Academic rank
* Corporate title
* Diplomatic rank
* Hierarchy ...
or category of ranks in the armed forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a ...
of many countries. Depending on the country, service, or historical context, warrant officers are sometimes classified as the most junior of the commissioned officer
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service.
Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer (NCO), or a warrant officer. However, absent ...
ranks, the most senior of the non-commissioned officer
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is an enlisted rank, enlisted leader, petty officer, or in some cases warrant officer, who does not hold a Commission (document), commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority b ...
(NCO) ranks, or in a separate category of their own. Warrant officer ranks are especially prominent in the militaries of Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase (the common-wealth ...
nations and the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
.
The name of the rank originated in medieval England
England in the Middle Ages concerns the history of England during the Middle Ages, medieval period, from the end of the 5th century through to the start of the Early modern Britain, early modern period in 1485. When England emerged from the co ...
. It was first used during the 13th century, in the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
, where warrant officers achieved the designation by virtue of their accrued experience or seniority, and technically held the rank by a warrant, rather than by a formal commission
In-Commission or commissioning may refer to:
Business and contracting
* Commission (remuneration), a form of payment to an agent for services rendered
** Commission (art), the purchase or the creation of a piece of art most often on behalf of anot ...
(as in the case of a commissioned officer). Nevertheless, WOs in the British services have traditionally been considered and treated as distinct from non-commissioned officers.
Warrant officers in the United States are classified in rank category "W", which is distinct from "O" (commissioned officers) and "E" (enlisted personnel
An enlisted rank (also known as an enlisted grade or enlisted rate) is, in some armed services, any rank below that of a commissioned officer. The term can be inclusive of non-commissioned officers or warrant officers, except in United States ...
, including non-commissioned officers). However, chief warrant officer
Chief warrant officer is a senior warrant officer rank, used in many countries.
Canadian Armed Forces
In the Canadian Armed Forces (CAF), a chief warrant officer or CWO is the most senior non-commissioned member (NCM) rank for army and air fo ...
s are officially commissioned, on the same basis as commissioned officers, and take the same oath. US WOs are usually experts in a particular technical field, with long service as enlisted personnel; in some cases, however, direct entrants may become WOs—for example, individuals completing helicopter pilot training in the US Army Aviation Branch become flight warrant officers immediately.
In Commonwealth countries, warrant officers have usually been included alongside NCOs and enlisted personnel
An enlisted rank (also known as an enlisted grade or enlisted rate) is, in some armed services, any rank below that of a commissioned officer. The term can be inclusive of non-commissioned officers or warrant officers, except in United States ...
in a category called other ranks (ORs), which is equivalent to the US "E" category (i.e. there is no separate "W" category in these particular services). In Commonwealth services, warrant officers rank between chief petty officer
A chief petty officer (CPO) is a senior non-commissioned officer in many navies and coast guards, usually above petty officer.
By country
Australia
"Chief Petty Officer" is the second highest non-commissioned rank in the Royal Australian Navy ...
and sub-lieutenant in the navy, between staff sergeant
Staff sergeant is a Military rank, rank of non-commissioned officer used in the armed forces of many countries. It is also a police rank in some police services.
History of title
In origin, certain senior sergeants were assigned to administr ...
and second lieutenant in the army, and between flight sergeant and pilot officer
Pilot officer (Plt Off or P/O) is a junior officer rank used by some air forces, with origins from the Royal Air Force. The rank is used by air forces of many countries that have historical British influence.
Pilot officer is the lowest ran ...
in the air force.
Origins
The warrant officer corps began in the nascentRoyal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
, which dates its founding to 1546. At that time, noblemen with military experience took command of the new navy, adopting the military ranks of lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a Junior officer, junior commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations, as well as fire services, emergency medical services, Security agency, security services ...
and captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader or highest rank officer of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police depa ...
. These officers often had no knowledge of life on board a ship—let alone how to navigate such a vessel—and relied on the expertise of the ship's master and other seamen who tended to the technical aspects of running the ship. As cannon came into use, the officers also required gunnery experts; specialist gunners began to appear in the 16th century and also had warrant officer status. Literacy was one thing that most warrant officers had in common, and this distinguished them from the common seamen: according to the Admiralty regulations, "no person shall be appointed to any station in which he is to have charge of stores, unless he can read and write, and is sufficiently skilled in arithmetic to keep an account of them correctly". Since all warrant officers had responsibility for stores, this was enough to debar the illiterate.
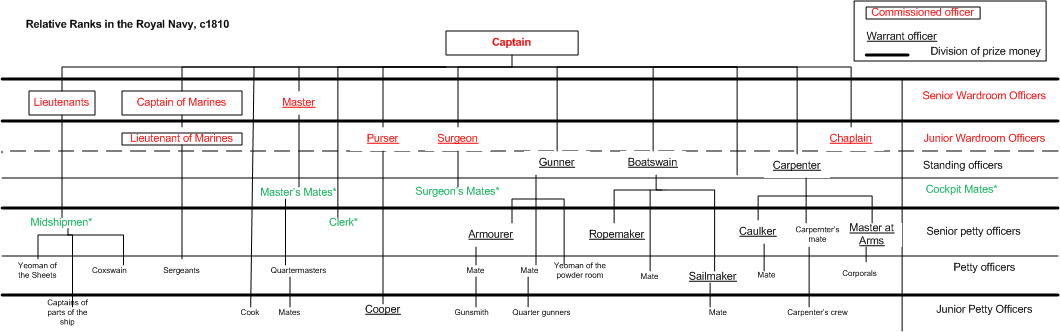
Rank and status in the 18th century
In origin, warrant officers were specialist professionals whose expertise and authority demanded formal recognition. In the 18th century they fell into two clear categories: on the one hand, those privileged to share with the commissioned officers in thewardroom
The wardroom is the mess, mess cabin or compartment on a warship or other military ship for commissioned naval Officer (armed forces), officers above the rank of midshipman. Although the term typically applies to officers in a navy, it is also ...
and on the quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on bo ...
; and on the other, those who ranked with more junior members of the ship's crew. Somewhere between the two, however, were the standing officers, notable because, unlike the rest of the ship's company, they remained with the ship even when she was out of commission (e.g. for repair, refitting or replenishment, or whilst laid up); in these circumstances they were under the pay and supervision of the Royal Dockyard.
Wardroom warrant officers
These classes of warrant officer messed in thewardroom
The wardroom is the mess, mess cabin or compartment on a warship or other military ship for commissioned naval Officer (armed forces), officers above the rank of midshipman. Although the term typically applies to officers in a navy, it is also ...
with the commissioned officers:
*the master: the senior warrant officer, a qualified navigator and experienced seaman who set the sails, maintained the ship's log
A logbook (a ship's logs or simply log) is a record of important events in the management, operation, and navigation of a ship. It is essential to traditional navigation, and must be filled in at least daily.
The term originally referred to a b ...
and advised the captain on the seaworthiness of the ship and crew;
*the surgeon
In medicine, a surgeon is a medical doctor who performs surgery. Even though there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon is a licensed physician and received the same medical training as physicians before spec ...
: who treated the sick and injured and advised the captain on matters of health;
*the purser
A purser is the person on a ship principally responsible for the handling of money on board. On modern merchant ships, the purser is the officer responsible for all administration (including the ship's cargo and passenger manifests) and supply. ...
: responsible for supplies, food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for Nutrient, nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or Fungus, fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, protein (nutrient), proteins, vitamins, ...
and pay for the crew.
In the early 19th century, they were joined in the wardroom by naval chaplain
A chaplain is, traditionally, a cleric (such as a minister, priest, pastor, rabbi, purohit, or imam), or a lay representative of a religious tradition, attached to a secular institution (such as a hospital, prison, military unit, intellige ...
s, who also had warrant officer status (though they were only usually present on larger vessels).
Standing warrant officers
The standing officers were: *theboatswain
A boatswain ( , ), bo's'n, bos'n, or bosun, also known as a deck boss, or a qualified member of the deck department, or the third hand on a fishing vessel, is the most senior Naval rating, rate of the deck department and is responsible for the ...
: responsible for maintenance of the ship's boats, sails, rigging, anchors and cables;
*the carpenter
Carpentry is a skilled trade and a craft in which the primary work performed is the cutting, shaping and installation of building materials during the construction of buildings, ships, timber bridges, concrete formwork, etc. Carpenter ...
: responsible for maintenance of the ship's hull and masts;
*the gunner: responsible for care and maintenance of the ship's guns and gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
.
Junior warrant officers
Other warrant officers included surgeon's mates, boatswain's mates and carpenter's mates, sailmakers, armourers, schoolmasters (involved in the education of boys, midshipmen and others aboard ship) and clerks. Masters-at-arms, who had formerly overseen small-arms provision on board, had by this time taken on responsibility for discipline.Warrant officers in context
By the end of the century, the rank structure could be illustrated as follows (the warrant officers are underlined):
Demise of the royal naval warrants
In 1843, thewardroom
The wardroom is the mess, mess cabin or compartment on a warship or other military ship for commissioned naval Officer (armed forces), officers above the rank of midshipman. Although the term typically applies to officers in a navy, it is also ...
warrant officers were given commissioned status, while in 1853 the lower-grade warrant officers were absorbed into the new rate of chief petty officer
A chief petty officer (CPO) is a senior non-commissioned officer in many navies and coast guards, usually above petty officer.
By country
Australia
"Chief Petty Officer" is the second highest non-commissioned rank in the Royal Australian Navy ...
, both classes thereby ceasing to be warrant officers. On 9 July 1864 the standing warrant officers were divided into two grades: warrant officers and chief warrant officers (or "commissioned warrant officers", a phrase that was replaced in 1920 with "commissioned officers promoted from warrant rank", although they were still usually referred to as "commissioned warrant officers", even in official documents).
By the time of the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, their ranks had been expanded with the adoption of modern technology in the Royal Navy to include telegraphist
A telegraphist (British English), telegrapher (American English), or telegraph operator is a person who uses a telegraph key to send and receive Morse code messages in a telegraphy system. These messages, also called telegrams, can be transmitte ...
s, electrician
An electrician is a tradesman, tradesperson specializing in electrical wiring of buildings, transmission lines, stationary machines, and related equipment. Electricians may be employed in the installation of new electrical components or the ...
s, shipwright
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. In modern times, it normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces i ...
s, artificer engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who Invention, invent, design, build, maintain and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials. They aim to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while ...
s, etc. Both warrant officers and commissioned warrant officers messed in the warrant officers' mess rather than the wardroom (although in ships too small to have a warrant officers' mess, they did mess in the wardroom). Warrant officers and commissioned warrant officers also carried swords, were saluted by ratings, and ranked between sub-lieutenants and midshipmen.
In 1949, the ranks of warrant officer and commissioned warrant officer were changed to "commissioned officer" and "senior commissioned officer", the latter ranking with but after the rank of lieutenant, and they were admitted to the wardroom, the warrant officers' messes closing down. Collectively, these officers were known as "branch officers", being retitled "special duties" officers in 1956. In 1998, the special duties list was merged with the general list of officers in the Royal Navy, all officers now having the same opportunity to reach the highest commissioned ranks.
Modern usage
Australia
TheRoyal Australian Navy
The Royal Australian Navy (RAN) is the navy, naval branch of the Australian Defence Force (ADF). The professional head of the RAN is Chief of Navy (Australia), Chief of Navy (CN) Vice admiral (Australia), Vice Admiral Mark Hammond (admiral), Ma ...
rank of warrant officer (WO) is the Navy's only rank appointed by warrant and is equivalent to the Army's WO1, and the RAAF's warrant officer. The most senior non-commissioned member of the Navy is the Warrant Officer of the Navy
Warrant Officer of the Navy (WO-N) is the most senior sailor in the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). It is a singular appointment, being only held by one person at any time. The special insignia for the WO-N is the Australian coat of arms with a wr ...
(WO-N), an appointment that is only held by one person at a time.
The Australian Army
The Australian Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of Australia. It is a part of the Australian Defence Force (ADF), along with the Royal Australian Navy and the Royal Australian Air Force. The Army is commanded by the Chief of Army ...
has two warrant officer ranks: warrant officer class two (WO2) and warrant officer class one (WO1), the latter being senior in rank. The equivalent rank of WO2 in the Navy is now chief petty officer
A chief petty officer (CPO) is a senior non-commissioned officer in many navies and coast guards, usually above petty officer.
By country
Australia
"Chief Petty Officer" is the second highest non-commissioned rank in the Royal Australian Navy ...
, and the RAAF equivalent of the Army's WO2 is now flight sergeant, although in the past there were no equivalents. All warrant officers are addressed as "sir" or "ma'am" by subordinates. To gain the attention of a particular warrant officer in a group, they can be addressed as "Warrant Officer Bloggs, sir/ma'am" or by their appointment, e.g. "ASM Bloggs, sir/ma'am". Some warrant officers hold an appointment such as company sergeant major (WO2) or regimental sergeant major (WO1). The warrant officer appointed to the position of Regimental Sergeant Major of the Army (RSM-A) is the most senior enlisted soldier in the Australian Army and differs from other Army warrant officers in that their rank is just warrant officer (WO). The appointment of RSM-A was introduced in 1983. The rank insignia are: a crown for a WO2 (or a crown in a square on AMCU (camouflage uniform) rank slides); the Australian Commonwealth Coat of Arms (changed from the Royal Coat of Arms in 1976) for a WO1; and the Australian Commonwealth Coat of Arms surrounded by a laurel wreath for the RSM-A.
The Royal Australian Air Force
The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) is the principal Air force, aerial warfare force of Australia, a part of the Australian Defence Force (ADF) along with the Royal Australian Navy and the Australian Army. Constitutionally the Governor-Gener ...
rank of warrant officer (WOFF) is the RAAF's only rank appointed by warrant and is equivalent to both the Army's WO1 and the Navy's WO. The most senior non-commissioned member of the RAAF is the Warrant Officer of the Air Force
Warrant Officer of the Air Force (WOFF-AF) is the senior Warrant Officer in the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). It is a singular appointment, being it is only held by one person at any time. The special insignia for the WOFF-AF is the Austral ...
(WOFF-AF), an appointment that is only held by one person at a time.
Bangladesh
Bangladesh Army
The Bangladesh Army () is the land warfare branch, and the largest component of the Bangladesh Armed Forces. The primary mission of the Army is to defend the land of Bangladesh from any external attack. Control of personnel and operations is ad ...
and Bangladesh Air Force
The Bangladesh Air Force (BAF) () is the aerial warfare branch of the Bangladesh Armed Forces. The air force is primarily responsible for air defence of Bangladesh's sovereign territory as well as providing air support to the Bangladesh Army a ...
, ranking below senior warrant officer and master warrant officer.
Canada
In theCanadian Army
The Canadian Army () is the command (military formation), command responsible for the operational readiness of the conventional ground forces of the Canadian Armed Forces. It maintains regular forces units at bases across Canada, and is also re ...
and Royal Canadian Air Force
The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF; ) is the air and space force of Canada. Its role is to "provide the Canadian Forces with relevant, responsive and effective airpower". The RCAF is one of three environmental commands within the unified Can ...
, the cadre of warrant officers includes the specific ranks of warrant officer (), master warrant officer (), and chief warrant officer
Chief warrant officer is a senior warrant officer rank, used in many countries.
Canadian Armed Forces
In the Canadian Armed Forces (CAF), a chief warrant officer or CWO is the most senior non-commissioned member (NCM) rank for army and air fo ...
(). Before unification in 1968, there were two ranks of warrant officer (WO2 and WO1) in the Canadian Army and RCAF that followed the British structure.
India
Junior commissioned officers are the Indian Armed Forces equivalent of warrant officer ranks. Those in theIndian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the air force, air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial warfare during armed conflicts. It was officially established on 8 Octob ...
actually use the ranks of junior warrant officer, warrant officer and master warrant officer.
In the British Indian Army
The Indian Army was the force of British Raj, British India, until Indian Independence Act 1947, national independence in 1947. Formed in 1895 by uniting the three Presidency armies, it was responsible for the defence of both British India and ...
, warrant officer ranks existed but were restricted to British personnel, mostly in specialist appointments such as conductor and sub-conductor. Unlike in the British Army, although these appointments were warranted, the appointment and rank continued to be the same and the actual rank of warrant officer was never created. Indian equivalents were viceroy's commissioned officers.
Ireland
Irish Naval Service
Malaysia
In theMalaysian Armed Forces
The Malaysian Armed Forces (: MAF; ; Jawi alphabet, Jawi: ), are the armed forces of Malaysia, consists of three branches; the Malaysian Army, Royal Malaysian Navy and the Royal Malaysian Air Force. The number of MAF active personnel is 113,000 ...
, warrant officers () are the highest ranks for non commissioned officers.
New Zealand
TheNew Zealand Army
The New Zealand Army (, ) is the principal Army, land warfare force of New Zealand, a component of the New Zealand Defence Force alongside the Royal New Zealand Navy and the Royal New Zealand Air Force.
Formed in 1845, as the New Zealand Mil ...
usage is the same as the British Army, having two ranks: warrant officer class two (WO2), addressed as "sergeant major", and warrant officer class one (WO1), addressed as "sir" or "ma'am". There are also appointments such as company and squadron sergeant major (CSM and SSM) which are usually WO2 positions and regimental sergeant major (RSM), which are usually WO1 positions. The highest ranking WO1 holds the position of Sergeant Major of the Army (SMA).
The Royal New Zealand Navy
The Royal New Zealand Navy (RNZN; ) is the maritime arm of the New Zealand Defence Force. The fleet currently consists of eight ships. The Navy had its origins in the Naval Defence Act 1913, and the subsequent acquisition of the cruiser , whi ...
has a single warrant officer rank, addressed as "sir" or "ma'am". This rank is equivalent to the Army WO1. The RNZN's highest-ranking warrant officer is the Warrant Officer of the Navy.
The Royal New Zealand Air Force
The Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF; ) is the aerial warfare, aerial military service, service branch of the New Zealand Defence Force. It was formed initially in 1923 as a branch of the New Zealand Army, being known as the New Zealand Perm ...
also has a single warrant officer rank, equivalent to the Navy warrant officer, and the Army warrant officer class 1 (WO1). A warrant officer in the RNZAF is addressed as "sir" or "ma'am". Previously an aircrew warrant officer was known as master aircrew; however this rank and designation is no longer used. The RNZAF also has a post of Warrant Officer of the Air Force (WOAF), the most senior warrant officer position in the RNZAF.
There is also the Warrant Officer of the Defence Force (WODF). This appointment is held by a warrant officer class one (if the recipient originated from the New Zealand Army), or warrant officer (if the recipient originated from the Royal New Zealand Navy or the Royal New Zealand Air Force).
Singapore
Boys' Brigade
The rank of warrant officer is the highest rank aBoys' Brigade
The Boys' Brigade (BB) is an international interdenominational Christianity, Christian youth organisation, conceived by the Scottish businessman William Alexander Smith (Boys' Brigade), Sir William Alexander Smith to combine drill and fun acti ...
boy can attain in secondary school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., b ...
.
National Civil Defence Cadet Corps
The rank of warrant officer is given to selected non-commissioned officers in National Civil Defence Cadet Corps units. It is above the rank of staff sergeant, and below the rank of cadet lieutenant. It is the highest rank a cadet can attain in the NCDCC while they are in secondary school. The rank insignia is one point-up chevron, a Singapore coat of arms, and a garland below.Singapore Armed Forces
In theSingapore Armed Forces
The Singapore Armed Forces (SAF) are the military of the Republic of Singapore, responsible for protecting and defending the security interests and the sovereignty of the country. A component of the Ministry of Defence (Singapore), Ministry of D ...
, warrant officers begin as third warrant officers (3WO), previously starting at the rank of second warrant officer, abbreviated differently as WO2 instead. This rank is given to former specialists who have attained the rank of master sergeant
A master sergeant is the military rank for a senior non-commissioned officer in the armed forces of some countries.
Israel Defense Forces
The (abbreviated "", master sergeant) is a non-commissioned officer () rank in the Israel Defense Force ...
and have either gone through, or are about to go through the Warfighter Course at the Specialist and Warrant Officer Advanced School (SWAS) in the Specialist and Warrant Officer Institute (SWI). In order to be promoted to a second warrant officer (2WO) and above, they must have been selected for and graduated from the joint warrant officer course at the SAFWOS Leadership School. Warrant officers rank between specialists and commissioned officers. They ordinarily serve as battalion or brigade regimental sergeant major
Regimental sergeant major (RSM) is an appointment that may be held by a warrant officer (WO) in the British Army, the Royal Marines, and the armies of many other Commonwealth and former Commonwealth nations. It is also an actual rank in the Iri ...
s. Many of them serve as instructors and subject-matter experts in various training establishments. Warrant officers are also seen on the various staffs headed by the respective specialist officers. There are six grades of warrant officer (3WO, 2WO, 1WO, MWO, SWO and CWO).
Warrant officers used to have their own mess. For smaller camps, this mess is combined with the officers' mess. Warrant officers have similar responsibilities to commissioned officers.
Warrant officers are usually addressed as or ('mister' or 'miss' in Malay language) or as "warrant (surname)" or " or (surname)". Exceptions to this are those who hold appointments. Warrant officers holding the appointment such as commanding officer
The commanding officer (CO) or commander, or sometimes, if the incumbent is a general officer, commanding general (CG), is the officer in command of a military unit. The commanding officer has ultimate authority over the unit, and is usually give ...
(CO) and officer commanding
The commanding officer (CO) or commander, or sometimes, if the incumbent is a general officer, commanding general (CG), is the officer in command of a military unit. The commanding officer has ultimate authority over the unit, and is usually giv ...
(OC) are to be addressed as "sir" by other ranks, and those holding sergeant major
Sergeant major is a senior Non-commissioned officer, non-commissioned Military rank, rank or appointment in many militaries around the world.
History
In 16th century Spain, the ("sergeant major") was a general officer. He commanded an army's ...
appointments such as regimental sergeant major (RSM), company sergeant major (CSM), formation sergeant major (FSM), institute sergeant major (ISM) and the Sergeant Major of the Army (SMA) are to be addressed as "sergeant major" by other ranks. Also, all warrant officers holding the rank of chief warrant officer (CWO) are to be addressed as "sir" by other ranks. Since all warrant officers are non-commissioned officers, they are not saluted.
Although ceremonial swords are usually reserved for commissioned officers
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service.
Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer (NCO), or a warrant officer. However, absent c ...
, warrant officers of the rank of master warrant officer (MWO) and above are presented with ceremonial swords, but continue to carry the pace stick, with the sword sheathed during drills and parades.
Singapore Civil Defence Force
In the Singapore Civil Defence Force, there are two warrant officer ranks. These ranks are (in order of ascending seniority) warrant officer (1) and warrant officer (2). Previously, before the Home Team Unified Rank Scheme was introduced, there were two additional ranks of warrant officer, namely senior warrant officer (1) and senior warrant officer (2). Both ranks are now obsolete, although existing holders of these ranks were allowed to keep their rank.South Africa
South African National Defence Force
In theSouth African National Defence Force
The South African National Defence Force (SANDF) comprises the armed forces of South Africa. The Chief of the SANDF is appointed by the President of South Africa from one of the armed services. They are in turn accountable to the Minister of ...
, a warrant officer (WO) is set apart from those who hold a non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank. Warrant officers hold a warrant of appointment endorsed by the Minister of Defence. Warrant officers hold very specific powers, which are set out in the Defence Act and the Military Defence Supplementary Measures Act. Before 2008, there were two classes – warrant officer class 1 and 2. A warrant officer class 1 could be appointed to positions such as regimental sergeant major, formation sergeant major or Sergeant Major of the Army or Warrant Officer of the Navy. In 2008, five new warrant officer ranks were introduced above warrant officer class 1: senior warrant officer (SWO), master warrant officer (MWO), chief warrant officer (CWO), senior chief warrant officer (SCWO) and master chief warrant officer (MCWO).
South African Police Service
In theSouth African Police Service
The South African Police Service (SAPS) is the national police force of the Republic of South Africa. Its 1,154 police stations in South Africa are divided according to the Provinces of South Africa, provincial borders, and a Provincial Commis ...
, there is only a single warrant officer (WO) rank.
United Kingdom

Royal Navy
In 1973, warrant officers reappeared in theRoyal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
, but these appointments followed the army model, with the new warrant officers being ratings rather than officers. They were initially known as fleet chief petty officers (FCPOs), but were renamed warrant officers in the 1980s. They rank with warrant officers class one in the British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
and Royal Marines
The Royal Marines provide the United Kingdom's amphibious warfare, amphibious special operations capable commando force, one of the :Fighting Arms of the Royal Navy, five fighting arms of the Royal Navy, a Company (military unit), company str ...
and with warrant officers in the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
.
There are executive warrant officers for commands and ships. Five branches (surface ships, submarines, Royal Marines, Fleet Air Arm
The Fleet Air Arm (FAA) is the naval aviation component of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy (RN). The FAA is one of five :Fighting Arms of the Royal Navy, RN fighting arms. it is a primarily helicopter force, though also operating the Lockhee ...
, and Maritime Reserves) each have a command warrant officer. The senior RN WO is the Warrant Officer of the Royal Navy. Under the Navy Command Transformation Programme, there are now a Fleet Commander
The Fleet Commander is a senior Royal Navy post, responsible for the operation, resourcing and training of the ships, submarines and aircraft, and personnel, of the Naval Service (United Kingdom), Naval Service. The Vice-Admiral incumbent is requ ...
's Warrant Officer and a Second Sea Lord
The Second Sea Lord and Deputy Chief of the Naval Staff (formerly Second Sea Lord) is deputy to the First Sea Lord and the second highest-ranking officer currently to serve in the Royal Navy and is responsible for personnel and naval shore estab ...
's Warrant Officer, all working with the Warrant Officer to the Royal Navy, taking over the roles of the Command Warrant Officers.
In 2004, the rank of warrant officer class 2 was introduced. However, the rank was phased out in April 2014, but is being reinstated for non-technical and technical branches of the Royal Navy in 2021.
British Army
British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
, there are two warrant ranks, warrant officer class two (WO2) and warrant officer class one (WO1), the latter being the senior of the two. These ranks were previously abbreviated as WOII and WOI (using Roman instead of Indo-Arabic numerals). "Warrant officer first class" or "second class" is incorrect. The rank immediately below WO2 is staff sergeant
Staff sergeant is a Military rank, rank of non-commissioned officer used in the armed forces of many countries. It is also a police rank in some police services.
History of title
In origin, certain senior sergeants were assigned to administr ...
(or colour sergeant
Colour sergeant (CSgt or C/Sgt) is a rank of non-commissioned officer found in several armies and marine corps.
Australia
In the Australian Army, the rank of colour sergeant has only existed in the Corps of Staff Cadets at the Royal Military ...
). From 1938 to 1940 there was a WOIII platoon sergeant major rank.
In March 2015, the new appointment of Army Sergeant Major was created, though the holder is not in fact a warrant officer but a commissioned officer holding the rank of captain. The creation of the appointment of command sergeant major was announced in 2009.
Royal Marines
Before 1879, theRoyal Marines
The Royal Marines provide the United Kingdom's amphibious warfare, amphibious special operations capable commando force, one of the :Fighting Arms of the Royal Navy, five fighting arms of the Royal Navy, a Company (military unit), company str ...
had no warrant officers: by the end of 1881, the Royal Marines had given warrant rank to their sergeant-majors and some other senior non-commissioned officers, in a similar fashion to the army. When the army introduced the ranks of warrant officer class I and class II in 1915, the Royal Marines did the same shortly after. From February 1920, Royal Marines warrant officers class I (renamed warrant officers) were given the same status as Royal Navy warrant officers and the rank of warrant officer class II was abolished in the Royal Marines, with no further promotions to this rank. Retrieved 26 May 2023/
The marines had introduced warrant officers equivalent in status to the Royal Navy's from 1910 with the Royal Marines gunner (originally titled gunnery sergeant-major), equivalent to the navy's warrant rank of gunner. Development of these ranks closely paralleled that of their naval counterparts: as in the Royal Navy, by the Second World War there were warrant officers and commissioned warrant officers (e.g. staff sergeant majors, commissioned staff sergeant majors, Royal Marines gunners, commissioned Royal Marines gunners, etc.). As officers, they were saluted by junior ranks in the Royal Marines and the army. These all became (commissioned) branch officer ranks in 1949, and special duties officer ranks in 1956. These ranks would return in 1972, this time similar to their army counterparts, and not as the RN did before. The most senior Royal Marines warrant officer is the Corps Regimental Sergeant Major. Unlike the RN proper (since 2014), it retains both WO ranks.
Royal Air Force
TheRoyal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
first used the ranks of sergeant major first and second class as inherited from the Royal Flying Corps
The Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was the air arm of the British Army before and during the First World War until it merged with the Royal Naval Air Service on 1 April 1918 to form the Royal Air Force. During the early part of the war, the RFC sup ...
, with the rank badges of the Royal coat of arms and the crown respectively. In the 1930s, these ranks were renamed warrant officer class I and II as in the Army. In 1939, the RAF abolished the rank of WOII and retained just the WOI rank, referred to as just warrant officer (WO), which it remains to this day. The RAF has no equivalent to WO2 (NATO OR-8), an RAF WO being equivalent to WO1 (NATO OR-9) and wearing the same badge of rank, the Royal coat of arms. The correct way to address a warrant officer is "sir" or "ma'am" by airmen and "mister or warrant officer (surname)" by officers. Most RAF warrant officers do not hold appointments as in the army or Royal Marines; the exception to this is the station warrant officer, who is considered a " first amongst equals" on an RAF station. Warrant officer is the highest non-commissioned rank and ranks above flight sergeant.
In 1946, the RAF renamed its aircrew warrant officers to master aircrew, a designation which still survives. In 1950, it renamed warrant officers in technical trades to master technicians, a designation which survived only until 1964.
The most senior RAF warrant officer by appointment, although holding the same rank as other RAF warrant officers (OR9), is the Warrant Officer of the Royal Air Force, previously known as the Chief of the Air Staff's Warrant Officer from the post's creation in 1996 until 2021.
United States
 In the
In the United States Armed Forces
The United States Armed Forces are the Military, military forces of the United States. U.S. United States Code, federal law names six armed forces: the United States Army, Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Navy, Na ...
, a warrant officer (grade W-1 to W-5) is ranked as an officer above the senior-most enlisted rank
An enlisted rank (also known as an enlisted grade or enlisted rate) is, in some armed services, any rank below that of a commissioned officer. The term can be inclusive of non-commissioned officers or warrant officers, except in United States ...
s, as well as officer cadet
Officer cadet is a rank held by military personnel during their training to become commissioned officers. In the United Kingdom, the rank is also used by personnel of University Service Units such as the University Officers' Training Corps.
Th ...
s and officer candidates, but below the officer grade of O‑1 (NATO: OF‑1). All warrant officers rate a salute from those ranked below them; i.e., the enlisted ranks. Warrant officers are highly skilled, single-track specialty officers, and while the ranks are authorized by Congress, each branch of the military selects, manages, and utilizes warrant officers in slightly different ways. For appointment to warrant officer (W-1), normally a warrant is approved by the service secretary of the respective branch of service. However, appointment to this rank can come via commission by the President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
, but this is less common. For the chief warrant officer ranks (CW‑2 to CW‑5), these warrant officers are commissioned by the President. Both warrant officers and chief warrant officers take the same oath of office as regular commissioned officers
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service.
Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer (NCO), or a warrant officer. However, absent c ...
(O-1 to O-10).
A small number of warrant officers command detachments, units, activities, vessels, aircraft, and armored vehicles, as well as lead, coach, train, and counsel subordinates. However, the warrant officer's primary task is to serve as a technical expert, providing valuable skills, guidance, and expertise to commanders and organizations in their particular field.
All U.S. armed services employ warrant officer grades except the U.S. Space Force. Although still technically authorized, the U.S. Air Force discontinued appointing new warrant officers in 1959, retiring its last chief warrant officer from the Air Force Reserve
The Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC) is a major command (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force, with its headquarters at Robins Air Force Base, Georgia. It is the federal Air Reserve Component (ARC) of the U.S. Air Force, consisting of commis ...
in 1992. Space Force inherited the same lack of warrant officers from the Air Force, although its inaugural Chief Master Sergeant
A chief master sergeant is the military rank for a senior non-commissioned officer in the armed forces of some countries.
Philippines Philippine armed forces
Since 2004, as part of the ongoing modernization of the Armed Forces of the Philippi ...
, Roger A. Towberman, stated in a January 2021 interview that Space Force would study the issue and decide whether or not to introduce them. In February 2024, U.S. Air Force Chief of Staff General David W. Allvin announced that the Air Force will re-introduce the warrant officer rank within the information technology and cyber fields as a way to maintain technical leadership with those skills. The first class of 78 future warrant officers were selected in August and began training at Maxwell AFB, Alabama, in October 2024.
The U.S. Army utilizes warrant officers heavily and separates them into two types: Aviators and technical. Army aviation warrant officers pilot both rotary-wing and fixed wing aircraft and represent the largest group of Army warrant officers. Technical warrant officers in the Army specialize in a single branch technical area such as intelligence, sustainment, supply, military police, or special forces; and provide advice and support to commanders. For example, a military police officer and a military intelligence officer both have to be branch qualified in their respective fields, learning how to manage the entire spectrum of their profession. However, within those broad fields warrant officers include such specialists as CID Special Agents (a very specific track within the military police) and Counterintelligence Special Agents (a very specific track within military intelligence). These technical warrant officers allow for a soldier with subject matter expertise (like non-commissioned officers), but with the authority of a commissioned officer. Both technical and aviation warrant officers go through initial training and branch assignment at the Army Warrant Officer Candidate School (WOCS), followed by branch-specific training and education paths. Technical warrant officers are generally selected from the non-commissioned officer ranks (typically E-6 through E-9). Aviation warrant officer candidates can apply from all branches of service, including junior enlisted and non-prior service civilians (aviation warrant officers join through the Warrant Officer Flight Training Program).
The U.S. Navy and U.S. Coast Guard discontinued the grade of W-1 in 1975, appointing and commissioning all new entrants as chief warrant officer two (pay grade W-2, with rank abbreviation of CWO2). This was to prevent a pay decrease that an entrant may take since all Navy chief warrant officers are selected strictly from the chief petty officer
A chief petty officer (CPO) is a senior non-commissioned officer in many navies and coast guards, usually above petty officer.
By country
Australia
"Chief Petty Officer" is the second highest non-commissioned rank in the Royal Australian Navy ...
pay grades (E-7 through E-9). The Coast Guard allows E-6 personnel to apply for chief warrant officer rank, but only after they have displayed their technical ability by earning a placement in the top 50% on the annual eligibility list for advancement to E-7. In 2018, the U.S. Navy expanded the warrant program, re-implementing the W-1 pay grade for cyber warrant officers and accepting three new WO1s in fiscal year 2019. This was further expanded in 2020 when the Navy introduced the Air Vehicle Pilot (AVP) program. Personnel commissioning as AVPs will be awarded the rank of W-1.
Warrant officers in the Army holding the rank of warrant officer 1 (WO1) are formally addressed as "Mr/Ms" ast name Upon promotion to chief warrant officer 2, "Chief" becomes an additional authorized term of address. WO1s are informally addressed as "Chief" by many soldiers as well. In the Navy, warrant officers are typically addressed as "Mr/Ms" ast name "Chief Warrant Officer", or informally as "Warrant" regardless of their grade.
The U.S. Maritime Service (USMS), which is established at 46 U.S. Code § 51701, falls under the authority of the Maritime Administration of the Department of Transportation and is authorized to appoint warrant officers. In accordance with 46 U.S. Code § 51701, the USMS rank structure must be the same as that of the U.S. Coast Guard while uniforms worn are those of the U.S. Navy with distinctive USMS insignia and devices. The USMS has appointed warrant officers, of various specialty fields, during and after World War II.
Warrant officer rank is also occasionally used in law enforcement agencies to grant status and pay to certain senior specialist officers who are not in command, such as senior technicians or helicopter pilots. As in the armed forces, they rank above sergeants, but below lieutenants. For example, the North Carolina State Highway Patrol had several warrant officer helicopter pilot positions from the 1960s until the mid-1980s. The WO insignia was a silver bar with a black square in the center. The WO ranks were abolished when the aviation program expanded and nearly twenty trooper pilot positions were created. The New York State Police
The New York State Police (NYSP) is the state police of the U.S. state of New York; it is part of the New York State Executive Department and employs over 5,000 sworn state troopers and 711 non-sworn members.
The New York State Police are re ...
rank of technical lieutenant is similar to a warrant officer rank insofar as it is used to grant commissioned officer authority to non-commissioned officers with extensive technical expertise.
Gallery
Warrant officer
(
Bangladesh Army
The Bangladesh Army () is the land warfare branch, and the largest component of the Bangladesh Armed Forces. The primary mission of the Army is to defend the land of Bangladesh from any external attack. Control of personnel and operations is ad ...
)
File:Canadian Army OR-7.svg, Warrant officer(
Canadian Army
The Canadian Army () is the command (military formation), command responsible for the operational readiness of the conventional ground forces of the Canadian Armed Forces. It maintains regular forces units at bases across Canada, and is also re ...
)
File:blank.svg, Warrant officer(
Nigerian Army
The Nigerian Army (NA) is the land force of the Nigerian Armed Forces. It is the largest component of the Nigerian Armed Forces. The President of Nigeria is the Commander-in-Chief of the Nigerian Army, and its professional head is the Chie ...
)
File:British RAF OR-9.svg, Warrant officer(
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
)
Warrant officer class 2
( Antigua and Barbuda Regiment) File:Botswana-Army-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
Botswana Ground Force
The Botswana Ground Forces is the army of the country of Botswana, and the land component of the Botswana Defence Force.
History
The Botswana Defence Force was raised in April 1977 by an Act of Parliament called the 'BDF Act NO 13 of 1977. At i ...
)
File:05.Gambian Army-WO2.svg, Warrant officer class 2( Gambian National Army) File:Ghana-Army-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
Ghana Army
The Ghana Army is the principal land warfare force of Ghana. In 1959, two years after the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast became independent from the British Empire, the Ghana Regiment, Gold Coast Regiment was withdrawn from the Royal West ...
)
File:Kenya-Army-OR-8.png, Warrant officer class 2( Kenya Army) File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Lesotho Army) File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Malawi Army) File:05-Namibia Army-WO2.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Namibian Army) File:05-Rwanda Army-WO2.svg, Warrant officer II
( Rwandan Land Forces) File:Seychelles-Army-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Seychelles Infantry Unit) File:Sierra Leone-Army-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Sierra Leone Army) File:SAA-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
South African Army
The South African Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of South Africa, a part of the South African National Defence Force (SANDF), along with the South African Air Force, South African Navy and South African Military Health Servi ...
)
File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2( Eswatini Army) File:05-Tanzania Army-WO2.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
Tanzanian Army
Demographic features of the population of Tanzania include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population.
The population distribution in Tan ...
)
File:Uganda-Army-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2( Ugandan Land Forces) File:Zambia-Army-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
Zambian Army
The Zambian Army is the land military branch of the Zambian Defence Force. Like all branches of the Zambian military, citizens of the nation are required to register at 16 years old, and citizens can join at 16 years old with parental consent or a ...
)
File:Zimbabwe-Army-OR-8.svg, Warrant officer class 2( Zimbabwe National Army)
Warrant officer class 1
( Antigua and Barbuda Regiment) File:Botswana-Army-OR-9.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
Botswana Ground Force
The Botswana Ground Forces is the army of the country of Botswana, and the land component of the Botswana Defence Force.
History
The Botswana Defence Force was raised in April 1977 by an Act of Parliament called the 'BDF Act NO 13 of 1977. At i ...
)
File:06.Gambian Army-WO1.svg, Warrant officer class 2( Gambian National Army) File:Ghana-Army-OR-9.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
Ghana Army
The Ghana Army is the principal land warfare force of Ghana. In 1959, two years after the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast became independent from the British Empire, the Ghana Regiment, Gold Coast Regiment was withdrawn from the Royal West ...
)
File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2( Kenya Army) File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Lesotho Army) File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Malawi Army) File:06-Namibia Army-WO1.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Namibian Army) File:06-Rwanda Army-WO1.svg, Warrant officer II
( Rwandan Land Forces) File:Seychelles-Army-OR-9.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Seychelles Infantry Unit) File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2
( Sierra Leone Army) File:SAA-OR-9.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
South African Army
The South African Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of South Africa, a part of the South African National Defence Force (SANDF), along with the South African Air Force, South African Navy and South African Military Health Servi ...
)
File:blank.svg, Warrant officer class 2( Eswatini Army) File:06-Tanzania Army-WO1.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
Tanzanian Army
Demographic features of the population of Tanzania include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population.
The population distribution in Tan ...
)
File:Uganda-Army-OR-9.svg, Warrant officer class 2( Ugandan Land Forces) File:Coat of arms of Zambia.svg, Warrant officer class 2
(
Zambian Army
The Zambian Army is the land military branch of the Zambian Defence Force. Like all branches of the Zambian military, citizens of the nation are required to register at 16 years old, and citizens can join at 16 years old with parental consent or a ...
)
File:Coat of arms of Zimbabwe.svg, Warrant officer class 2( Zimbabwe National Army)
See also
*List of comparative military ranks
This article is a list of various Sovereign state, nations' armed forces military rank, ranking designations. Comparisons are made between the different systems used by nations to categorize the hierarchy of an armed force compared to another. S ...
Notes
References
{{Use dmy dates, date=September 2019 Military ranks of Australia Military ranks of Canada Military ranks of Singapore Military ranks of the Commonwealth Military ranks of the Francophonie Military ranks of the United States