Vein Of Galen Aneurysmal Malformations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vein of Galen aneurysmal malformations (VGAM) and Vein of Galen aneurysmal dilations (VGAD) are the most frequent arteriovenous malformations in infants and fetuses. VGAM consist of a tangled mass of dilated vessels supplied by an enlarged artery. The malformation increases greatly in size with age, although the mechanism of the increase is unknown. Dilation of the
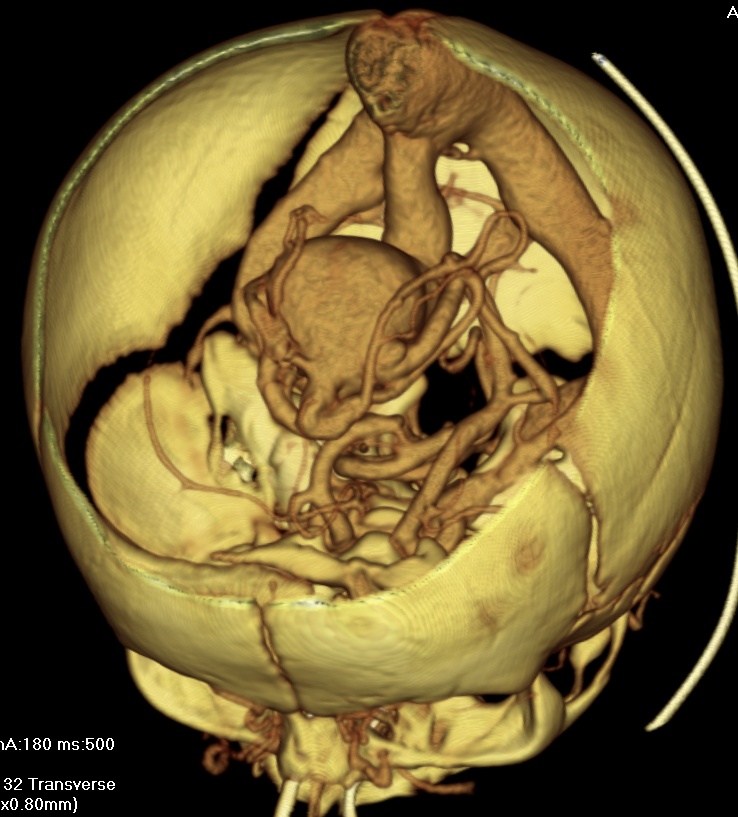 Malformations often lead to cardiac failure, cranial bruits (pattern 1),
Malformations often lead to cardiac failure, cranial bruits (pattern 1),
great cerebral vein
The great cerebral vein is one of the large blood vessels in the skull draining the cerebrum of the brain. It is also known as the "vein of Galen", named for its discoverer, the Greek physician Galen. However, it is not the only vein with this epon ...
of Galen is a secondary result of the force of arterial blood either directly from an artery via an arteriovenous fistula
An arteriovenous fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between an artery and a vein. It may be congenital, surgically created for hemodialysis treatments, or acquired due to pathologic process, such as trauma or erosion of an arterial ...
or by way of a tributary vein that receives the blood directly from an artery. There is usually a venous anomaly downstream from the draining vein that, together with the high blood flow into the great cerebral vein of Galen causes its dilation. The right sided cardiac chambers and pulmonary arteries also develop mild to severe dilation.
Signs and symptoms
 Malformations often lead to cardiac failure, cranial bruits (pattern 1),
Malformations often lead to cardiac failure, cranial bruits (pattern 1), hydrocephaly
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary inco ...
, and subarachnoid hemorrhage in neonates. The heart failure is due to the size of the arteriovenous shunt that can steal 80% or more of the cardiac output, with large volumes of blood under high pressure returning to the right heart and pulmonary circulation and sinus venosus atrial septal defect
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this d ...
s. It is also the most common cause of death in such patients.
Associated conditions
Non-developmental syndromes also directly or indirectly affect the Great Cerebral Vein of Galen, although they are extremely rare. These includesuperior vena cava syndrome
Superior vena cava syndrome (SVCS), is a group of symptoms caused by obstruction of the superior vena cava ("SVC"), a short, wide vessel carrying circulating blood into the heart. The majority of cases are caused by malignant tumors within the m ...
(SVCS), and thrombosis of the lateral sinus, superior sagittal sinus, internal jugular vein, or of the Great Cerebral Vein of Galen itself.
Genetics
10% of vein of Galen aneurysmal malformations are associated with deleterious heterozygous mutations of ''EPHB4'' Another study found that 30% of cases were associated with mutations in EPH receptor B4 (EPHB4
Ephrin type-B receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EPHB4'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ...
) gene.Duran D, Zeng X, Jin SC, Choi J, Nelson-Williams C, Yatsula B, Gaillard J, Furey CG, Lu Q, Timberlake AT, Dong W, Sorscher MA, Loring E, Klein J, Allocco A, Hunt A, Conine S, Karimy JK, Youngblood MW, Zhang J, DiLuna ML, Matouk CC, Mane S, Tikhonova IR, Castaldi C, López-Giráldez F, Knight J, Haider S, Soban M, Alper SL, Komiyama M, Ducruet AF, Zabramski JM, Dardik A, Walcott BP, Stapleton CJ, Aagaard-Kienitz B, Rodesch G, Jackson E, Smith ER, Orbach DB, Berenstein A, Bilguvar K, Vikkula M, Gunel M, Lifton RP, Kahle KT (2018) Mutations in chromatin modifier and ephrin signaling genes in vein of Galen malformation. Neuron
Diagnosis
Testing for a malformed vein of Galen is indicated when a patient has heart failure which has no obvious cause. Diagnosis is generally achieved by signs such as cranial bruits and symptoms such as expanded facial veins. The vein of Galen can be visualized usingultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
or Doppler. A malformed Great Cerebral Vein will be noticeably enlarged. Ultrasound is a particularly useful tool for vein of Galen malformations because so many cases occur in infancy and ultrasound can make diagnoses prenatally. Many cases are diagnosed only during autopsy as congestive heart failure occurs very early.
Classification
Five patterns of Galenic arteriovenous malformations have been described: These malformations develop in utero by the persistence of fistulae between primitive pia arachnoidal arteries and pial veins that cross each other at right angles. Because the primitive Galenic system and the primitive choroidal system lie close together, an arteriovenous malformation involving the primitive choroidal system will inevitably involve the Galenic vein. Larger arteriovenous shunts correlate with greater hemodynamic effects and earlier symptom onset; small arteriovenous shunts correlate with greater local mass effect causing progressive neurological impairment.Treatment
Treatment depends on the anatomy of the malformation as determined byangiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performe ...
or Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI).
Surgical
Head circumference measurements should be obtained regularly and monitored carefully to detecthydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased intracranial pressure, pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor ...
. Neurosurgical procedures to relieve hydrocephalus are important. A ventriculoperitoneal shunt may be required in some infants. A pediatric cardiologist should be consulted to manage high-output failure, if present. Often patients need to be intubated. In most cases, the fistulous arteries feeding into the Vein of Galen must be blocked, thereby reducing the blood flow into the vein. Open surgery has a high morbidity and mortality. Recent advances over the past few decades have made endovascular embolization the preferred method of treatment. These treatments are preferred because they offer little threat to the surrounding brain tissue. However, there have been several reported cases of arteriovenous malformations recurring. The young age of many patients, the complex vascular anatomy, and the sensitive location of the Vein of Galen offer considerable challenges to surgeons. Another treatment option is Radiotherapy. Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radia ...
, also called radiosurgery
Radiosurgery is surgery using radiation, that is, the destruction of precisely selected areas of tissue using ionizing radiation rather than excision with a blade. Like other forms of radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy), it is usually u ...
, involves the use of focused beams to damage the blood vessel. Radiotherapy is often not pursued as a treatment because the effects of the procedure can take months or years and there is risk of damaging adjacent brain tissue.
Medical care
Surgery is not always an option when the anatomy of the malformation creates too much of a risk. Recent improvements inendovascular
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs b ...
procedures have made many cases, which were not surgically accessible, treatable. Endovascular treatments involve delivering drugs, balloons, or coils to the site of the malformation through blood vessels via catheters. These treatments work by limiting blood flow through the vein. There is, however, still risk of complications from endovascular treatments. The wall of the vein can be damaged during the procedure and, in some cases, the emboli
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule ( fat embolism), a bubble of air or other gas (gas embolism), amniotic fluid (amniot ...
can become dislodged and travel through the vascular system. Two-dimensional echocardiography
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart.
It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound.
Echocardiography has become routinely used in t ...
with color-flow imaging and pulsed Doppler ultrasound was used to evaluate one fetus and five neonates with a Vein of Galen malformation. Color-flow imaging and pulsed Doppler ultrasonography
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies fr ...
provided anatomical and pathophysiological information regarding cardiac hemodynamics
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously mo ...
and intracranial blood flow; with the patient's clinical status, these methods provided a reliable, noninvasive means to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy and the need for further treatment in neonates with Vein of Galen malformations. When none of these procedures are viable, shunting can be used to ameliorate the pressure inside the varix
A varix (pl. varices) is an abnormally dilated vessel with a tortuous course. Varices usually occur in the venous system, but may also occur in arterial or lymphatic vessels.
Examples of varices include:
* Varicose veins, large tortuous veins usua ...
. Seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or neural oscillation, synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much o ...
usually are managed with antiepileptic medications.
Prognosis
The complications that are usually associated with vein of Galen malformations are usually intracranial hemorrhages. Over half the patients with VGAM have a malformation that cannot be corrected. Patients frequently die in the neonatal period or in early infancy.Society and culture
Vein of Galen malformations are devastating complications. Studies have shown that 77% of untreated cases result in mortality. Even after surgical treatment, the mortality rate remains as high as 39.4%. Most cases occur during infancy when the mortality rates are at their highest. Vein of Galen malformations are a relatively unknown condition, attributed to the rareness of the malformations. Therefore, when a child is diagnosed with a faulty Great Cerebral Vein of Galen, most parents know little to nothing about what they are dealing with.References
External links
{{Congenital vascular defects Anatomical pathology Congenital disorders of nervous system Congenital vascular defects