viscous coupling unit on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A viscous coupling is a mechanical device which transfers
A viscous coupling is a mechanical device which transfers
Interactive animation
Mechanical devices using viscosity Vehicle parts Clutches
 A viscous coupling is a mechanical device which transfers
A viscous coupling is a mechanical device which transfers torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. Wh ...
and rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersect ...
by the medium of a viscous fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously motion, move and Deformation (physics), deform (''flow'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are M ...
.
Design
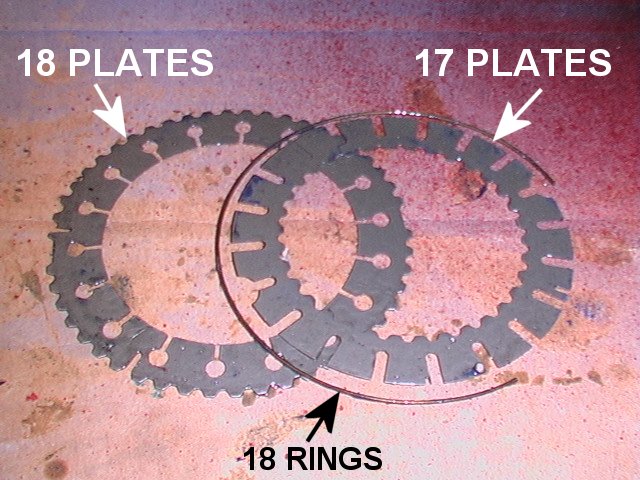
Rotary viscous couplings with interleaved, perforated plates and filled with viscous fluids are used in automotive systems to transmit torque. The device consists of a number of circular plates with tabs or perforations, fitted very close to each other in a sealed drum. Alternate plates are connected to a driving shaft at one end of the assembly and a driven shaft at the other end. The drum is filled with a dilatant fluid, oftensilicone
In Organosilicon chemistry, organosilicon and polymer chemistry, a silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer composed of repeating units of siloxane (, where R = Organyl group, organic group). They are typically colorless oils or elastomer, rubber ...
-based, to about 80% by volume. When the two sets of plates are rotating in unison, the fluid stays cool and remains liquid. When the plates start rotating at different speeds, the shear effect of the tabs or perforations on the fluid will cause it to heat and become nearly solid because the viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for e ...
of dilatant fluids rapidly increases with shear. The fluid in this state will effectively glue the plates together and transmit power from one set of plates to the other. The size of the tabs or perforations, the number of plates, and the fluid used will determine the strength and onset of this mechanical transfer.
This type of device essentially differs from fluid couplings such as torque converters by using the viscosity of the medium to transfer torque, rather than its momentum. This makes it potentially useful even on very small scales and requires less cooling. The torque transmitted is sensitive to the difference in speeds of the input and output but is almost independent of their common rate.
Vehicles
Viscous couplings are used as the center differential in some four-wheel-drive (4WD)vehicle
A vehicle () is a machine designed for self-propulsion, usually to transport people, cargo, or both. The term "vehicle" typically refers to land vehicles such as human-powered land vehicle, human-powered vehicles (e.g. bicycles, tricycles, velo ...
s.
The first mass-produced viscous couplings for a permanent 4WD off-road-capable vehicle were in the AMC Eagle
The AMC Eagle is a compact four-wheel drive passenger vehicle manufactured and marketed in a single generation by American Motors Corporation (AMC) for model years 1980 through 1987 and continued by Chrysler, Chrysler Corporation following it ...
, which was produced from 1980 to 1988 model years. The AMC Eagle's single-speed model 119 New Process central differential used a viscous coupling filled with a liquid silicone-based material. It linked the front and rear differentials for quiet and smooth transfer of power to the axle with the greatest traction, on wet or dry pavement.
Viscous couplings are used as the center differential in cars such as the Toyota Celica GT-Four, and also as a limited slip differential (LSD) in rear axles. They offer a cheaper way to implement four-wheel-drive than technologies like the mechanical-transfer Torsen differentials.
Volvo, Subaru, Land Rover, Vauxhall/Opel, and many others have also used viscous couplings in their drivelines at various times. They are now mostly superseded by electronically controlled devices.
Attributions
Tony Rolt is often credited with the original idea and development as applied to automatic couplings in vehicle transmission systems, particularly four-wheel drive, working with Freddie Dixon at the time. Ferguson Research and FF Developments were companies formed in the 1970s to commercialize much early work into 4WD systems and devices. It is thought that GKN Driveline owns any remaining worldwide patents today and offers several variants and combinations of viscous couplings integrated with other driveline components.See also
* Hele-Shaw clutch * Limited-slip differentialReferences
{{reflistExternal links
Interactive animation
Mechanical devices using viscosity Vehicle parts Clutches