Veratridine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Veratridine is a
Veratridine is a
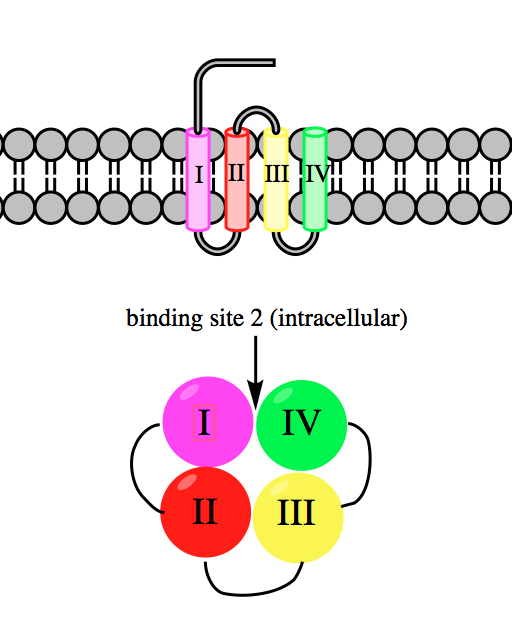 Veratridine acts a neurotoxin by increasing nerve excitability. It binds to binding site 2 on the voltage-gated sodium channels (the same site bound by
Veratridine acts a neurotoxin by increasing nerve excitability. It binds to binding site 2 on the voltage-gated sodium channels (the same site bound by
 Veratridine is a
Veratridine is a steroidal alkaloid
Steroidal alkaloids have the basic steroidal skeleton with nitrogen-based functional groups attached to the skeleton. More specifically, they are distinguished by their tetracyclic cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene skeleton that marks their clos ...
found in plants of the lily family, specifically the genera ''Veratrum
''Veratrum'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Melanthiaceae. It occurs in damp habitats across much of temperate and subarctic Europe, Asia, and North America.
''Veratrum'' species are vigorous herbaceous perennials with highly poiso ...
'' and ''Schoenocaulon
''Schoenocaulon'' is a North American genus of perennial herbaceous flowering plants, ranging from the southern United States to Peru. It is a member of the Melanthiaceae, according to the APG III system, APG III classification system, and is pla ...
''. Upon absorption through the skin or mucous membranes, it acts as a neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nervous tissue, nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insult (medical), insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function ...
by binding to and preventing the inactivation of voltage-gated sodium ion channels in heart, nerve, and skeletal muscle cell membranes. Veratridine increases nerve excitability and intracellular Ca2+ concentrations.
Isolation
Veratridine has been isolated from the seeds of ''Schoenocaulon officinale'' and from therhizome
In botany and dendrology, a rhizome ( ) is a modified subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and Shoot (botany), shoots from its Node (botany), nodes. Rhizomes are also called creeping rootstalks or just rootstalks. Rhizomes develop from ...
s of ''Veratrum album
''Veratrum album'', the false helleborine, white hellebore, European white hellebore, or white veratrum ( syn. ''Veratrum lobelianum'' Bernh.) is a poisonous plant in the family Melanthiaceae. It is native to Europe and parts of western Asia (we ...
.'' Like the other steroidal alkaloids found in these plants and similar ones in the Melanthiaceae
Melanthiaceae, also called the bunchflower family, is a family (biology), family of flowering plant, flowering herbaceous perennial plants native to the Northern Hemisphere. Along with many other lilioid monocots, early authors considered member ...
family, it is present as part of a glycosidal combination, bonded to carbohydrate moieties.
Early isolation methods relied on formation of the nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
salt and then precipitation of the insoluble sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
form. Accounts of these efforts date back to 1878, but the first true purification of veratridine is the one carried out in 1953 by Kupchan et al. This, and later purification procedures, begin with veratrine, a mixture of the alkaloids present in the ''Veratrum'' plants, primarily containing cevadine and veratridine. The nitrate salt is formed by dissolving the veratrine in 1% sulfuric acid over ice and precipitating with sodium nitrate. After resuspending in water over ice, the solution is brought to pH 8.5 with aqueous NaOH and then pH 10 with aqueous ammonia, forming another precipitate which is extracted with ether and then with chloroform. The ether and chloroform fractions are combined and dried. The dried residue is dissolved in sulfuric acid and the sulfate salt of veratridine is precipitated by dropwise addition of a solution of ammonium sulfate. Finally, the free base form is generated with ammonium hydroxide.
An even better isolation of veratridine from veratrine is achieved using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC); as commercially available veratridine may vary in purity, HPLC purification of veratrine is a preferred method for isolation of veratridine for biological studies.
Chemistry
Structure
Veratridine is a derivative, the 3-veratroateester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
, of veracevine, which belongs to the class of C-nor-D-homosteroidal alkaloids. The molecular structure and stereochemistry of this and related alkaloids were only established after decades of chemical investigations. The structure of veratridine has been confirmed by NMR spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique based on re-orientation of atomic nuclei with non-zero nuclear spins in an external magnetic f ...
and X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring th ...
.
Veratridine displays an unusual steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
al backbone. In the typical four-ring nucleus with three six-membered rings and one five-membered ring (like the one in cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
), the five-membered ring is on the end. Veratridine, and other ''Veratrum'' alkaloids, have the five-membered ring between the second and third six-membered rings.
Solubility
Veratridine has apKa
In chemistry, an acid dissociation constant (also known as acidity constant, or acid-ionization constant; denoted ) is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction
:H ...
of 9.54. It is slightly soluble in ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group, a single oxygen atom bonded to two separate carbon atoms, each part of an organyl group (e.g., alkyl or aryl). They have the general formula , where R and R†...
, soluble in ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
and DMSO
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula . This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is ...
, and freely soluble in chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane (often abbreviated as TCM), is an organochloride with the formula and a common solvent. It is a volatile, colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to refrigerants and po ...
. Solubility in water is pH-dependent; the free base
In chemistry, a free base (freebase, free-base) is a term for the neutral form of an amine or other Lewis base. The term is used in the pharmaceutical industry in contrast to salt-based formulations like hydrochlorides. The amine is often an ...
form is slightly soluble, but easily dissolves in 1 M HCl. Its nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
salt is slightly soluble in water. Its sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
salt is very hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption (chemistry), absorption or adsorption from the surrounding Natural environment, environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water mol ...
.
Mechanism of action and applications
 Veratridine acts a neurotoxin by increasing nerve excitability. It binds to binding site 2 on the voltage-gated sodium channels (the same site bound by
Veratridine acts a neurotoxin by increasing nerve excitability. It binds to binding site 2 on the voltage-gated sodium channels (the same site bound by batrachotoxin
Batrachotoxin (BTX) is an extremely potent cardiotoxic and neurotoxic steroidal alkaloid found in certain species of beetles, birds, and frogs. The name is from the Greek word . Structurally-related chemical compounds are often referred to collec ...
, aconitine
Aconitine is an alkaloid toxin produced by various plant species belonging to the genus ''Aconitum'' (family Ranunculaceae), commonly known by the names wolfsbane and monkshood. Aconitine is notorious for its toxic properties.
Structure and rea ...
, and grayanotoxin
Grayanotoxins are a group of closely related neurotoxins named after ''Leucothoe grayana'', a plant native to Japan and named for 19th-century American botanist Asa Gray. Grayanotoxin I (grayanotoxane-3,5,6,10,14,16-hexol 14-acetate) is also known ...
), leading to persistent activation. Veratridine inhibits sodium channel inactivation by shifting the activation threshold toward a more negative potential. The resulting influx of Na+ also leads to the increase of intracellular Ca2+ concentrations, causing the overproduction of reactive oxygen species
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl ...
responsible for neuronal damage.
Veratridine is readily absorbed through the skin and mucous membranes and through ingestion. The tissues most affected are the heart, nerves, and skeletal muscles: main symptoms of veratridine toxicity include severe nausea, bradycardia
Bradycardia, also called bradyarrhythmia, is a resting heart rate under 60 beats per minute (BPM). While bradycardia can result from various pathological processes, it is commonly a physiological response to cardiovascular conditioning or due ...
, hypotension
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is ...
, difficulty breathing, salivation, and muscle weakness.{{Cite web, url=https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/a?dbs+hsdb:@term+@DOCNO+4078, title=VERATRIDINE - National Library of Medicine HSDB Database, website=toxnet.nlm.nih.gov, access-date=2018-05-02 Treatment involves the administration of activated charcoal
"Activated" is a song by English singer Cher Lloyd. It was released on 22 July 2016 through Vixen Records. The song was made available to stream exclusively on ''Rolling Stone'' a day before to release (on 21 July 2016).
Background
In an inter ...
, atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically give ...
, and benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), colloquially known as "benzos", are a class of central nervous system (CNS) depressant, depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed t ...
s (if the affected individual is seizing).
Veratridine's ability to depolarize cells by affecting sodium channels lends it its applicability as a neuropharmacological tool for the study of electrical properties of nerve and muscle fibers. It has also been tested as a treatment for myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a long-term neuromuscular junction disease that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness. The most commonly affected muscles are those of the eyes, face, and swallowing. It can result in double vision, ...
, in light of its potential to increase muscle responses to motor neuron stimulation.
Furthermore, this compound has recently been reported to increase sperm progressive motility (although it does not produce hyperactivation by itself). It has the potential of enhancing protein tyrosine phosphorylation, which takes place during capacitation
Capacitation is the penultimate step in the maturation of mammalian spermatozoa and is required to render them competent to fertilize an oocyte. This step is a biochemical event; the sperm move normally and look mature prior to capacitation.
''I ...
, and its effects are inhibited in the presence of lidocaine
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. When used for local anae ...
and tetrodotoxin
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin. Its name derives from Tetraodontiformes, an Order (biology), order that includes Tetraodontidae, pufferfish, porcupinefish, ocean sunfish, and triggerfish; several of these species carry the toxin. Alt ...
.
Veratridine has not been reported to have any effect on the acrosome reaction
For fertilization to happen between a sperm and egg cell, a sperm must first fuse with the plasma membrane and then penetrate the female egg cell to fertilize it. While the fusion of the sperm cell with the egg cell's plasma membrane is relatively ...
on its own, but it is able to block the progesterone
Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the ma ...
-induced acrosome reaction. Moreover, veratridine has the effect of turning the membrane potential to a more positive one and also modifies the effect of progesterone on a2+ and sperm membrane potential.
The activation of Nav1.8 is a key point in Veratradine's mechanism of action and, consequently, this sodium ion channel coordinates the effects of this compound. Veratradine also activates additional Nav channels. These facts contribute to support the importance of these Veratradine-sensitive proteins in the regulation of mature sperm function, such as human sperm fertility acquisition regulating motility, capacitation
Capacitation is the penultimate step in the maturation of mammalian spermatozoa and is required to render them competent to fertilize an oocyte. This step is a biochemical event; the sperm move normally and look mature prior to capacitation.
''I ...
and the progesterone-induced acrosome reaction.L. Candenas, F.M. Pinto, A. Cejudo-Román, C. González-Ravina, M. Fernández-Sánchez, N. Pérez-Hernández, et al. Veratridine-sensitive Na+ channels regulate human sperm fertilization capacity. Life Sci. 2018 Mar; 196:48-55.
References