V engine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A V engine, sometimes called a Vee engine, is a common configuration for
 The "V-angle" (or "included angle") between the cylinder banks varies significantly between engines. Some engines have used a V-angle of 180 degrees (the same angle as a
The "V-angle" (or "included angle") between the cylinder banks varies significantly between engines. Some engines have used a V-angle of 180 degrees (the same angle as a
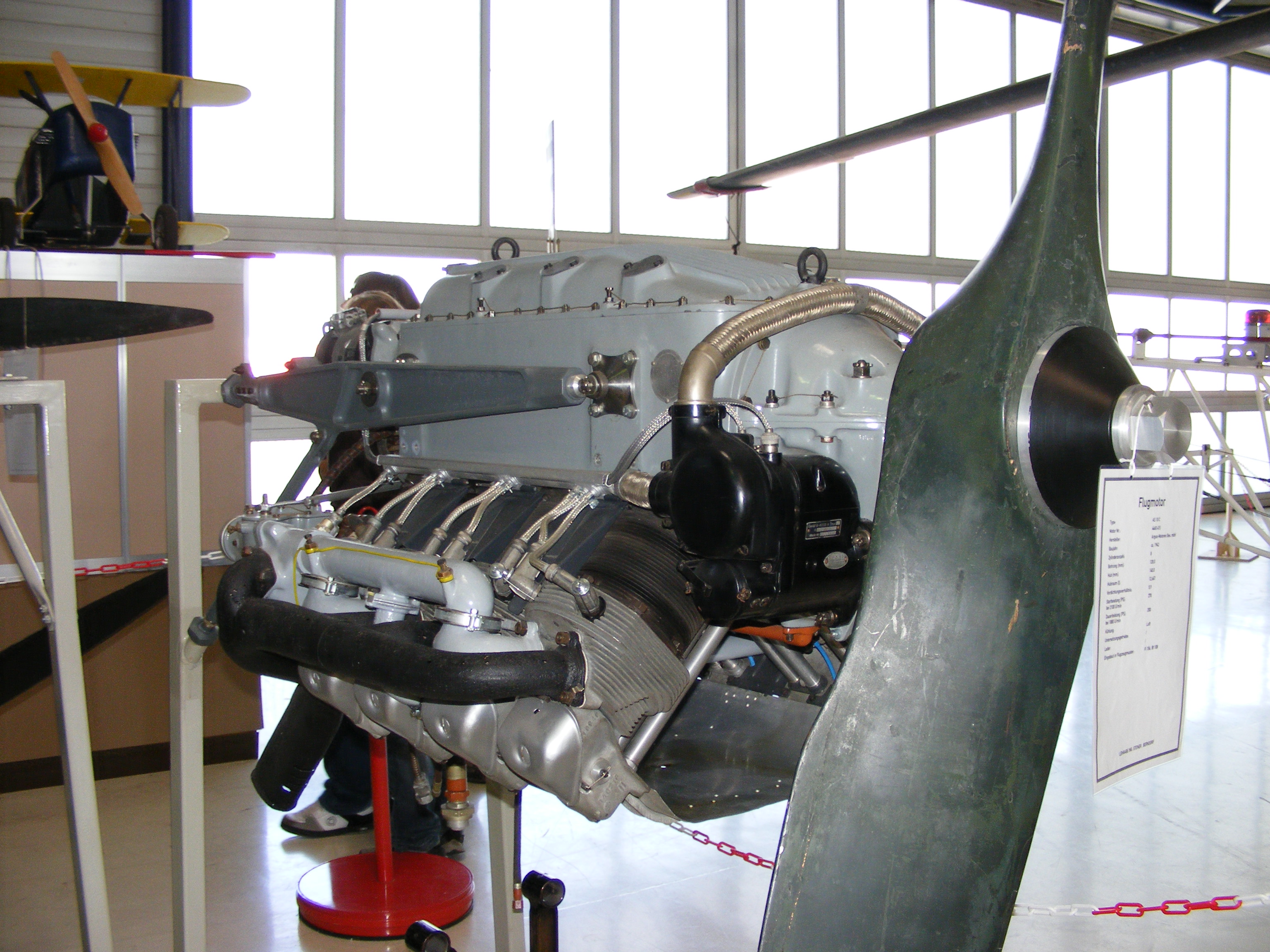 Some airplanes of the 1920s and 1930s used inverted engines, whereby the crankshaft is located at the top of the engine and the cylinder heads are at the bottom. Advantages include better visibility in a single-engined airplane, a higher thrust line, and resultant increased ground clearance for the propeller. Examples include the 1928 Argus As 10 V8 engine and the 1935 Daimler-Benz DB 601 V12 engines.
Some airplanes of the 1920s and 1930s used inverted engines, whereby the crankshaft is located at the top of the engine and the cylinder heads are at the bottom. Advantages include better visibility in a single-engined airplane, a higher thrust line, and resultant increased ground clearance for the propeller. Examples include the 1928 Argus As 10 V8 engine and the 1935 Daimler-Benz DB 601 V12 engines.
internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
s. It consists of two cylinder banks—usually with the same number of cylinders in each bank—connected to a common crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a reciprocating engine, piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating Shaft (mechanical engineering), shaft containing one or more crankpins, ...
. These cylinder banks are arranged at an angle to each other, so that the banks form a "V" shape when viewed from the front of the engine.
V engines typically have a shorter length than equivalent inline engines, however the trade-off is a larger width. V6, V8 and V12 engines are the most common layout for automobile engines with 6, 8 or 12 cylinders respectively.
History
The first V engine, a two-cylinder V-twin, was designed byWilhelm Maybach
Wilhelm Maybach (; 9 February 1846 – 29 December 1929) was an early German engine designer and industrialist. During the 1890s he was hailed in France, then the world centre for car production, as the "King of Designers".
From the late 19th ce ...
and used in the 1889 Daimler Stahlradwagen automobile.
The first V8 engine was produced in 1903, in the form of the Antoinette engine designed by Léon Levavasseur for racing boats and airplane
An airplane (American English), or aeroplane (Commonwealth English), informally plane, is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, Propeller (aircraft), propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a vari ...
s. The first V12 engine was produced the following year by Putney Motor Works in London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, again for use in racing boats. The first V6 engine
A V6 engine is a six- cylinder piston engine where the cylinders and cylinder blocks share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
The first V6 engines were designed and produced independently by Marmon Motor Car Company, ...
to reach production appeared soon after in 1908, by the Deutz Gasmotoren Fabrik in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
for use as a generator for gasoline-electric railway engines. However, it was not until 1950 that the V6 engine was used in series production automobiles, with the first example being the Lancia V6 engine. This V6 engine used a 60-degree V angle and separate crankpins for each cylinder, to reduce the vibration issues experienced by earlier attempts at production V6 engines.
Characteristics
Compared with an equivalent inline engine (the most common configuration for engines with less than six cylinders), a V engine has a shorter length but is wider. This effect increases with the number of cylinders in the engine; the length difference between V-twin and straight-twin engines might be insignificant, however V8 engines have a significantly smaller length than straight engines. Compared with the less commonflat engine
A flat engine is a piston engine where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct from the less common opposed-piston engine design, ...
, a V engine is narrower, taller and has a higher center of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the barycenter or balance point) is the unique point at any given time where the weight function, weighted relative position (vector), position of the d ...
.
 The "V-angle" (or "included angle") between the cylinder banks varies significantly between engines. Some engines have used a V-angle of 180 degrees (the same angle as a
The "V-angle" (or "included angle") between the cylinder banks varies significantly between engines. Some engines have used a V-angle of 180 degrees (the same angle as a flat engine
A flat engine is a piston engine where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct from the less common opposed-piston engine design, ...
), such as several Ferrari V12 engines. At the other end of the scale, the 1922–1976 Lancia V4 engine and the 1991–present Volkswagen VR6 engine use V-angles as small as 10 degrees, along with a single cylinder head used by both banks of cylinders.
The engine balance
Engine balance refers to how the inertial forces produced by moving parts in an internal combustion engine or steam engine are neutralised with counterweights and Balance shaft#Overview, balance shafts, to prevent unpleasant and potentially dam ...
of a V12 engine is that of perfect primary and secondary balance. For V engines with fewer cylinders, the engine balance will depend on factors such as the firing interval, crankshaft counterweights and whether balance shaft
Balance shafts are used in piston engines to reduce vibration by cancelling out unbalanced dynamic forces. The counter balance shafts have eccentric weights and rotate in the opposite direction to each other, which generates a net vertical force ...
s are present.
The crankpins on a V engine are usually shared by two cylinders from opposing banks, with an offset between the two cylinders. Alternative configurations are separate crankpins per cylinder (such as several V-twin engines) or articulated connecting rod
A connecting rod, also called a 'con rod', is the part of a reciprocating engine, piston engine which connects the piston to the crankshaft. Together with the crank (mechanism), crank, the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the p ...
s.
Inverted engines
Specific configurations
It is common practice for V engines to be described with "V''#''" notation, where ''#'' represents the number of cylinders. Configurations of V engines which have reached production are as follows: * V-twin (also known as "V2") * V3 * V4 * V5 * V6 * V8 * V10 * V12 * V14 * V16 * V18 * V20 * V24 *V32See also
* VR engine * Straight engine *Flat engine
A flat engine is a piston engine where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct from the less common opposed-piston engine design, ...
*Radial engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating engine, reciprocating type internal combustion engine, internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinder (engine), cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel. ...
* U engine
*H engine
An H engine is a piston engine comprising two separate flat engine, flat engines (complete with separate crankshafts), most often geared to a common output shaft. The name "H engine" is due to the engine blocks resembling a letter "H" when viewe ...
*W engine
A W engine is a type of piston engine where three or four cylinder banks share the same crankshaft, resembling the letter "W" when viewed from the front.
W engines with three banks of cylinders are also called "broad arrow" engines, due to thei ...
* X engine
*
References
{{Authority control V