Uxmal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Uxmal (
 While much work has been done at the popular tourist destination of Uxmal to consolidate and restore buildings, little in the way of serious archeological excavation and research has been done. The city's dates of occupation are unknown and the estimated population (about 15,000 people) is a rough guess. Most of the city's major construction took place while Uxmal was the capital of a Late Classic Maya state around 850-925 AD. After about 1000 AD, Toltec invaders took over, and most building ceased by 1100 AD.
Maya chronicles say that Uxmal was founded about 500 A.D. by
While much work has been done at the popular tourist destination of Uxmal to consolidate and restore buildings, little in the way of serious archeological excavation and research has been done. The city's dates of occupation are unknown and the estimated population (about 15,000 people) is a rough guess. Most of the city's major construction took place while Uxmal was the capital of a Late Classic Maya state around 850-925 AD. After about 1000 AD, Toltec invaders took over, and most building ceased by 1100 AD.
Maya chronicles say that Uxmal was founded about 500 A.D. by
 Even before the restoration work, Uxmal was in better condition than many other Maya sites. Much was built with well-cut stones set into a core of concrete not relying on plaster to hold the building together. The Maya architecture here is considered matched only by that of
Even before the restoration work, Uxmal was in better condition than many other Maya sites. Much was built with well-cut stones set into a core of concrete not relying on plaster to hold the building together. The Maya architecture here is considered matched only by that of
File:Governor's Palace details, Uxmal.jpg, Governor's Palace details
File:Governor's Palace rear view and details, Uxmal.jpg, Governor's Palace rear view and details
File:Governor's Palace rear view, Uxmal.jpg, Governor's Palace rear view
File:Governor's Palace side view, Uxmal.jpg, Governor's Palace side view
File:Mexico-6366 - Throne of the Jaguar (4691171977).jpg, Throne of the Jaguar
File:Викиушмаль.jpg, Nunnery Quadrangle and the Pyramid of the Magician
File:Traditional Mayan symbols.jpg, Traditional Mayan symbols
File:Maya images of people and animals.jpg, Maya images of people and animals
File:Snake and traditional Mayan lattice.jpg, Snake and traditional Mayan lattice
File:Sculptural image on the corner of the building.jpg, Sculptural image on the corner of the building
* The Adivino (a.k.a. the
 The site, located not far from Mérida beside a road to Campeche, has attracted many visitors since the time of Mexico's independence. The first detailed account of the ruins was published by Jean Frederic Waldeck in 1838.
The site, located not far from Mérida beside a road to Campeche, has attracted many visitors since the time of Mexico's independence. The first detailed account of the ruins was published by Jean Frederic Waldeck in 1838.
Architecture, Restoration, and Imaging of the Maya Cities of Uxmal, Kabah, Sayil, and Labna
documentation project by Prof. Charles S. Rhyne,
Yucatec Maya
Yucatec Maya (; referred to by its speakers simply as Maya or as , is one of the 32 Mayan languages of the Mayan language family. Yucatec Maya is spoken in the Yucatán Peninsula and northern Belize. There is also a significant diasporic commu ...
: ''Óoxmáal'' ) is an ancient Maya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a popul ...
city of the classical period located in present-day Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
. It is considered one of the most important archaeological sites of Maya culture, along with Palenque
Palenque (; Yucatec Maya language, Yucatec Maya: ), also anciently known in the Itza Language as Lakamhaʼ ("Big Water or Big Waters"), was a Maya city City-state, state in southern Mexico that perished in the 8th century. The Palenque ruins dat ...
, Chichen Itza
Chichen Itza , es, Chichén Itzá , often with the emphasis reversed in English to ; from yua, Chiʼchʼèen Ìitshaʼ () "at the mouth of the well of the Itza people" was a large pre-Columbian city built by the Maya people of the Terminal ...
and Calakmul
Calakmul (; also Kalakmul and other less frequent variants) is a Maya archaeological site in the Mexican state of Campeche, deep in the jungles of the greater Petén Basin region. It is from the Guatemalan border. Calakmul was one of the l ...
in Mexico, Caracol
Caracol is a large ancient Maya archaeological site, located in what is now the Cayo District, of Belize. It is situated approximately south of Xunantunich, and the town of San Ignacio, and from the Macal River. It rests on the Vaca Plateau ...
and Xunantunich
Xunantunich () is an Ancient Maya archaeological site in western Belize, about 70 miles (110 km) west of Belize City, in the Cayo District. Xunantunich is located atop a ridge above the Mopan River, well within sight of the Guatemala bord ...
in Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wate ...
, and Tikal
Tikal () (''Tik’al'' in modern Mayan orthography) is the ruin of an ancient city, which was likely to have been called Yax Mutal, found in a rainforest in Guatemala. It is one of the largest archeological sites and urban centers of the pre-C ...
in Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
. It is located in the Puuc region of the eastern Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
, and is considered one of the Maya cities most representative of the region's dominant architectural style. It has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
in recognition of its significance.
Uxmal is located 62 km south of Mérida, capital of Yucatán
Yucatán (, also , , ; yua, Yúukatan ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán,; yua, link=no, Xóot' Noj Lu'umil Yúukatan. is one of the 31 states which comprise the federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate mun ...
state in Mexico. Its buildings are noted for their size and decoration. Ancient roads called ''sacbe
Sacbe at Dzibilchaltun in the Yucatán
Arch at the end of the sacbé, Kabah, Yucatán
A sacbe, plural sacbeob ( Yucatec Maya: singular ''sakbej'', plural ''sakbejo'ob''), or "white way", is a raised paved road built by the Maya civilization of p ...
s'' connect the buildings, and also were built to other cities in the area such as Chichén Itzá in modern-day Mexico, Caracol and Xunantunich in modern-day Belize, and Tikal in modern-day Guatemala.
Its buildings are typical of the Puuc
Puuc is the name of either a region in the Mexican state of Yucatán or a Maya architectural style prevalent in that region. The word ''puuc'' is derived from the Maya term for "hill". Since the Yucatán is relatively flat, this term was ex ...
style, with smooth low walls that open on ornate friezes based on representations of typical Maya huts. These are represented by columns (representing the reeds used for the walls of the huts) and trapezoidal shapes (representing the thatched roofs). Entwined snakes and, in many cases two-headed snakes are used for masks of the rain god, ''Chaac
Chaac (also spelled Chac or, in Classic Mayan, Chaahk ) is the name of the Maya god of rain, thunder, and lighting. With his lightning axe, Chaac strikes the clouds, causing them to produce thunder and rain. Chaac corresponds to Tlaloc among ...
;'' its big noses represent the rays of the storms. Feathered serpents with open fangs are shown leaving from the same human beings. Also seen in some cities are the influences of the Nahua peoples
The Nahuas () are a group of the indigenous people of Mexico, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua. They comprise the largest indigenous group in Mexico and second largest in El Salvador. The Mexica (Aztecs) were of Nahua ethnicity, ...
, who followed the cult of '' Quetzalcoatl'' and '' Tlaloc.'' These were integrated with the original elements of the Puuc tradition.
The buildings take advantage of the terrain to gain height and acquire important volumes, including the Pyramid of the Magician
The Pyramid of the Magician ( es, Pirámide del adivino) is a Mesoamerican step pyramid located in the ancient Mayan city of Uxmal, Mexico. It is the tallest and most recognizable structure in Uxmal.
Description
The Pyramid of the Magician is the ...
, with five levels, and the Governor's Palace, which covers an area of more than .
Toponymy
The present name seems to derive from ''Oxmal,'' meaning "three times built." This seems to refer to the site's antiquity and the times it had to rebuild. The etymology is disputed; another possibility is ''Uchmal'' which means "what is to come, the future." By tradition, this was supposed to be an "invisible city," built in one night by the magic of the dwarf king.Ancient history
 While much work has been done at the popular tourist destination of Uxmal to consolidate and restore buildings, little in the way of serious archeological excavation and research has been done. The city's dates of occupation are unknown and the estimated population (about 15,000 people) is a rough guess. Most of the city's major construction took place while Uxmal was the capital of a Late Classic Maya state around 850-925 AD. After about 1000 AD, Toltec invaders took over, and most building ceased by 1100 AD.
Maya chronicles say that Uxmal was founded about 500 A.D. by
While much work has been done at the popular tourist destination of Uxmal to consolidate and restore buildings, little in the way of serious archeological excavation and research has been done. The city's dates of occupation are unknown and the estimated population (about 15,000 people) is a rough guess. Most of the city's major construction took place while Uxmal was the capital of a Late Classic Maya state around 850-925 AD. After about 1000 AD, Toltec invaders took over, and most building ceased by 1100 AD.
Maya chronicles say that Uxmal was founded about 500 A.D. by Hun Uitzil Chac Tutul Xiu
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
. For generations Uxmal was ruled over by the Xiu family. It was the most powerful site in western Yucatán, and for a while, in alliance with Chichen Itza
Chichen Itza , es, Chichén Itzá , often with the emphasis reversed in English to ; from yua, Chiʼchʼèen Ìitshaʼ () "at the mouth of the well of the Itza people" was a large pre-Columbian city built by the Maya people of the Terminal ...
, dominated all of the northern Maya area. Sometime after about 1200, no new major construction seems to have been made at Uxmal, possibly related to the fall of Uxmal's ally Chichen Itza and the shift of power in Yucatán to Mayapan
Mayapan (Màayapáan in Modern Maya; in Spanish Mayapán) is a Pre-Columbian Maya site a couple of kilometers south of the town of Telchaquillo in Municipality of Tecoh, approximately 40 km south-east of Mérida and 100 km west of ...
. The Xiu moved their capital to Maní, and the population of Uxmal declined.
Uxmal was dominant from 875 to 900 CE. The site appears to have been the capital of a regional state in the Puuc region from 850-950 CE. The Maya dynasty expanded their dominion over their neighbors. This prominence did not last long, as the population dispersed around 1000 CE.
After the Spanish conquest of Yucatán
The Spanish conquest of Yucatán was the campaign undertaken by the Spanish ''conquistadores'' against the Late Postclassic Maya states and polities in the Yucatán Peninsula, a vast limestone plain covering south-eastern Mexico, northern Gu ...
(in which the Xiu allied with the Spanish), early colonial documents suggest that Uxmal was still an inhabited place of some importance into the 1550s. As the Spanish did not build a town here, Uxmal was soon after largely abandoned.
The Maya legend ''The Dwarf-Wizard of Uxmal'' is set in Uxmal.
Description of the site
 Even before the restoration work, Uxmal was in better condition than many other Maya sites. Much was built with well-cut stones set into a core of concrete not relying on plaster to hold the building together. The Maya architecture here is considered matched only by that of
Even before the restoration work, Uxmal was in better condition than many other Maya sites. Much was built with well-cut stones set into a core of concrete not relying on plaster to hold the building together. The Maya architecture here is considered matched only by that of Palenque
Palenque (; Yucatec Maya language, Yucatec Maya: ), also anciently known in the Itza Language as Lakamhaʼ ("Big Water or Big Waters"), was a Maya city City-state, state in southern Mexico that perished in the 8th century. The Palenque ruins dat ...
in elegance and beauty. The Puuc
Puuc is the name of either a region in the Mexican state of Yucatán or a Maya architectural style prevalent in that region. The word ''puuc'' is derived from the Maya term for "hill". Since the Yucatán is relatively flat, this term was ex ...
style of Maya architecture predominates. Thanks to its good state of preservation, it is one of the few Maya cities where the casual visitor can get a good idea of how the entire ceremonial center looked in ancient times.
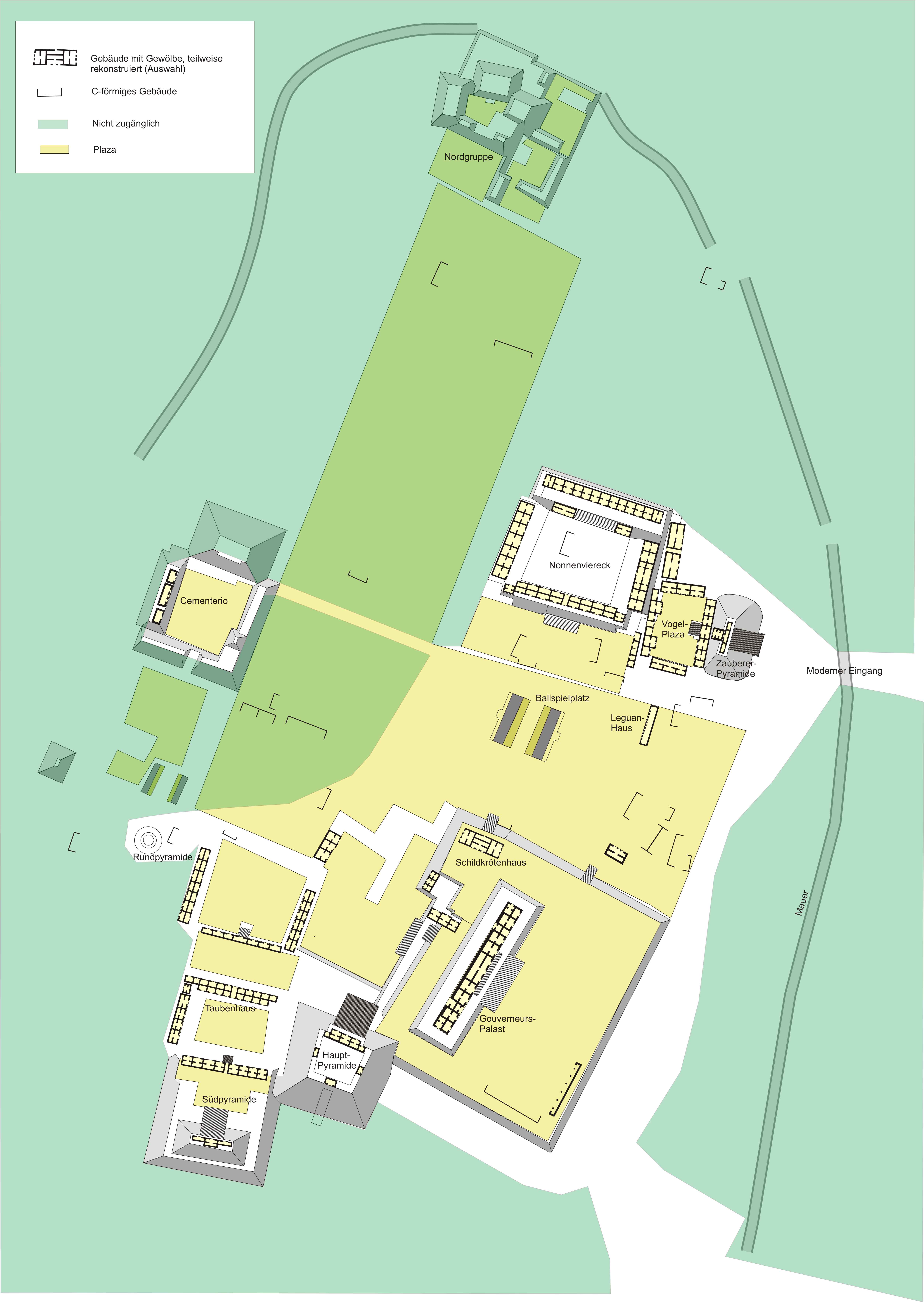
Some of the more noteworthy buildings include:
* The Governor's Palace, a long low building atop a huge platform, with the longest façades in Pre-Columbian Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. W ...
.
:With an approximate azimuth of 118°, the building is oriented to the main pyramid of Cehtzuc, a small site located nearly 5 km to the southeast. Observing from there, Venus as evening star, when reaching its maximum northerly extremes, would have set behind the northern edge of the Governor's Palace. Since these events occur every eight years, always in late April or early May, heralding the onset of the rainy season, it is significant that the decoration of the building's facade contains almost 400 Venus glyphs placed in the masks of the rain god Chac, and that there are eight bicephalic serpents above the main entrance; additionally, numerals 8 in bar-and-dot notation appear on two Chac masks at the northern corners of the palace.
Pyramid of the Magician
The Pyramid of the Magician ( es, Pirámide del adivino) is a Mesoamerican step pyramid located in the ancient Mayan city of Uxmal, Mexico. It is the tallest and most recognizable structure in Uxmal.
Description
The Pyramid of the Magician is the ...
or the Pyramid of the Dwarf), is a stepped pyramid structure, unusual among Maya structures in that its layers' outlines are oval or elliptical in shape, instead of the more common rectilinear plan. It was a common practice in Mesoamerica to build new temple pyramids atop older ones, but here a newer pyramid was built centered slightly to the east of the older pyramid, so that on the west side the temple atop the old pyramid is preserved, with the newer temple above it.
The structure is featured in one of the best-known tales of Yucatec Maya folklore, "el enano del Uxmal" (''the dwarf of Uxmal''), which is also the basis for the structure's common name. Multiple versions of this tale are recorded. It was popularised after one of these was recounted by John Lloyd Stephens
John Lloyd Stephens (November 28, 1805October 13, 1852) was an American explorer, writer, and diplomat. Stephens was a pivotal figure in the rediscovery of Maya civilization throughout Middle America and in the planning of the Panama railroad.
...
in his influential 1841 book, ''Incidents of Travel in Central America, Chiapas, and Yucatan''. According to Stephens' version, the pyramid was magically built overnight during a series of challenges issued to a dwarf by the ''gobernador'' (ruler or king) of Uxmal. The dwarf's mother (a ''bruja
Various types of witchcraft and occult religious practices exist in Latin American and Afro-Caribbean cultures, known in Spanish as (pronounced ). Influenced by indigenous religion, Catholicism, and European witchcraft, the purpose may ra ...
'', or witch) arranged the trial of strength and magic to compete against the king.
* The Nunnery Quadrangle was built from 900-1000, and the name related with nuns was assigned in the 16th century because it resembled a convent. The quadrangle consists of four palaces placed on different levels that surround a courtyard. Of the different buildings that make up this palatial complex, several vault tops have been recovered, they are painted and represent partial calendrical dates from 906 to 907 AD, which is consistent with the Chan Chahk’ahk Nalajaw period of government. The formal entrance, the hierarchy of the structures through the different elevations, and the absence of domestic elements suggest that this space corresponds to a royal palace with administrative and non-residential functions, where the ruling group must have had meetings to collect the tribute, make decisions, and dictate sentences among other activities. These set of buildings are the finest of Uxmal's several fine quadrangles of long buildings. It has elaborately carved façades on both the inside and outside faces.
* A large Ballcourt for playing the Mesoamerican ballgame
The Mesoamerican ballgame ( nah, ōllamalīztli, , myn, pitz) was a sport with ritual associations played since at least 1650 BC by the pre-Columbian people of Mesoamerica, Ancient Mesoamerica. The sport had different versions in different pl ...
. Its inscription says that it was dedicated in 901 by the ruler ''Chan Chak K'ak'nal Ajaw
Chan may refer to:
Places
*Chan (commune), Cambodia
*Chan Lake, by Chan Lake Territorial Park in Northwest Territories, Canada
People
*Chan (surname), romanization of various Chinese surnames (including 陳, 曾, 詹, 戰, and 田)
*Chan Caldwel ...
,'' also known as Lord Chac (before the decipherment of his corresponding name glyphs
A glyph () is any kind of purposeful mark. In typography, a glyph is "the specific shape, design, or representation of a character". It is a particular graphical representation, in a particular typeface, of an element of written language. A g ...
). The ball court's condition is very deteriorated, and it’s made of two constructions of medium dimensions that make up the sides of the court with the rings by which the ball was to be introduced. The originally carved stone rings were removed to protect them from the elements and were replaced by reproductions. This game has always been related to mythical and cosmic aspects. The ball symbolized the movements of the stars in the sky and the players, in repeated occasions, symbolically staged the fight of the day against the night or the struggle of the deities of the underworld against the gods of heaven.
A number of other temple-pyramids, quadrangles, and other monuments, some of significant size, and in varying states of preservation, are also at Uxmal. These include North Long Building, House of the Birds, House of the Turtles, Grand Pyramid, House of the Doves, and South Temple.
The majority of hieroglyphic inscriptions were on a series of stone stelae
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), whe ...
unusually grouped together on a single platform. The stelae depict the ancient rulers of the city. They show signs that they were deliberately broken and toppled in antiquity; some were re-erected and repaired. A further suggestion of possible war or battle is found in the remains of a wall which encircled most of the central ceremonial center.
A large raised stone pedestrian causeway links Uxmal with the site of Kabah, some 18 km to the south-east. Archaeological research at the small island site of Uaymil Uaymil is a pre-Columbian Maya archaeological site located on the Gulf Coast of northern Campeche. The settlement of Uaymil occupies a small island approximately 2.5 kilometers from the coast and 25 km north of Jaina. The site has been arch ...
, located to the west on the Gulf coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South, is the coast, coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The list of U.S. states and territories by coastline, coastal states that have a shor ...
, suggests that it may have served as a port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
for Uxmal and provided the site access to the circum-peninsular trade network.
Modern history of the ruins
John Lloyd Stephens
John Lloyd Stephens (November 28, 1805October 13, 1852) was an American explorer, writer, and diplomat. Stephens was a pivotal figure in the rediscovery of Maya civilization throughout Middle America and in the planning of the Panama railroad.
...
and Frederick Catherwood
Frederick Catherwood (27 February 1799 – 27 September 1854) was an English artist, architect and explorer, best remembered for his meticulously detailed drawings of the ruins of the Maya civilization. He explored Mesoamerica in the mid 19th c ...
made two extended visits to Uxmal in the early 1840s, with architect/draftsman Catherwood reportedly making so many plans and drawings that they could be used to construct a duplicate of the ancient city (unfortunately most of the drawings are lost).) Désiré Charnay
Claude-Joseph Désiré Charnay (2 May 182824 October 1915) was a French traveller and archaeologist notable both for his explorations of Mexico and Central America, and for the pioneering use of photography to document his discoveries.
Biograph ...
took a series of photographs of Uxmal in 1860. Some three years later Empress Carlota of Mexico
Charlotte of Belgium (''Marie Charlotte Amélie Augustine Victoire Clémentine Léopoldine''; 7 June 1840 – 19 January 1927), known by the Spanish version of her name, Carlota, was by birth a Princess of Belgium and member of the House of ...
visited Uxmal; in preparation for her visit local authorities had some statues and architectural elements depicting phallic
A phallus is a penis (especially when Erection, erect), an object that resembles a penis, or a mimesis, mimetic image of an erect penis. In art history a figure with an erect penis is described as ithyphallic.
Any object that symbolically— ...
themes removed from the ancient façade
A façade () (also written facade) is generally the front part or exterior of a building. It is a Loanword, loan word from the French language, French (), which means 'frontage' or 'face'.
In architecture, the façade of a building is often t ...
s.
Sylvanus G. Morley
Sylvanus Griswold Morley (June 7, 1883September 2, 1948) was an American archaeologist and epigrapher who studied the pre-Columbian Maya civilization in the early 20th century. Morley led extensive excavations of the Maya site of Chichen Itza ...
made a map of the site in 1909 which included some previously overlooked buildings. The Mexican government's first project to protect some of the structures from risk of collapse or further decay came in 1927. In 1930 Frans Blom
Frans Blom (9 August 1893 – 23 June 1963) was a Danish explorer and archaeologist. He was most associated with his research of the Maya civilization of Mexico and Central America.
Biography
Frans Ferdinand Blom was born in Copenhagen, ...
led a Tulane University
Tulane University, officially the Tulane University of Louisiana, is a private university, private research university in New Orleans, Louisiana. Founded as the Medical College of Louisiana in 1834 by seven young medical doctors, it turned into ...
expedition to the site. They made plaster casts of the façades of the "Nunnery Quadrangle"; using these casts, a replica of the Quadrangle was constructed and displayed at the 1933 World's Fair
A Century of Progress International Exposition, also known as the Chicago World's Fair, was a world's fair held in the city of Chicago, Illinois, United States, from 1933 to 1934. The fair, registered under the Bureau International des Expositi ...
in Chicago, Illinois
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
. The plaster replicas of the architecture were destroyed following the fair, but some of the plaster casts of Uxmal's monuments are still kept at Tulane's Middle American Research Institute. In 1936 a Mexican government repair and consolidation program was begun under José Erosa Peniche.
Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom visited on 27 February 1975 for the inauguration of the site's sound & light show. When the presentation reached the point where the sound system played the Maya prayer to Chaac
Chaac (also spelled Chac or, in Classic Mayan, Chaahk ) is the name of the Maya god of rain, thunder, and lighting. With his lightning axe, Chaac strikes the clouds, causing them to produce thunder and rain. Chaac corresponds to Tlaloc among ...
(the Maya rain deity), a sudden torrential downpour occurred. Gathered dignitaries included Gaspar Antonio Xiu, a descendant of the Xiu noble Maya lineage.
Three hotels and a small museum have been built within walking distance of the ancient city.
Microbial degradation
Microbialbiofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular ...
s have been found degrading stone buildings at Uxmal and Kabah. Phototrophs
Phototrophs () are organisms that carry out photon capture to produce complex organic compounds (e.g. carbohydrates) and acquire energy. They use the energy from light to carry out various cellular metabolic processes. It is a common misconcep ...
such as '' Xenococcus'' are found more often on interior walls. Stone degrading ''Gloeocapsa
''Gloeocapsa'' (from the Greek ''gloia'' (gelatinous) and the Latin ''capsa'' (case)) is a genus of cyanobacteria. The cells secrete individual gelatinous sheaths which can often be seen as sheaths around recently divided cells within outer shea ...
'' and ''Synechocystis
''Synechocystis'' is a genus of unicellular, freshwater cyanobacteria in the family Merismopediaceae. It includes a strain, ''Synechocystis'' sp. PCC 6803, which is a well studied model organism.
Like all cyanobacteria, ''Synechocystis'' ...
'' were also present in large numbers.
'' Aureobasidium'' and ''Fusarium
''Fusarium'' is a large genus of filamentous fungi, part of a group often referred to as hyphomycetes, widely distributed in soil and associated with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil mi ...
'' fungi species are present at Chichen Itza and Uxmal. Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria (), also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. The name ''cyanobacteria'' refers to their color (), which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blu ...
were prevalent in the interiors of rooms with low light levels.
See also
*List of archaeoastronomical sites sorted by country
This is a list of sites where claims for the use of archaeoastronomy have been made, sorted by country.
The International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS) and the International Astronomical Union (IAU) jointly published a thematic study on ...
*List of Mesoamerican pyramids
This is a list of Mesoamerican pyramids or ceremonial structures. In most cases they are not true pyramids. There are hundreds of these done in many different styles throughout Mexico and Central America. These were made by several pre-Columbian ...
Literature
* *References
External links
Architecture, Restoration, and Imaging of the Maya Cities of Uxmal, Kabah, Sayil, and Labna
documentation project by Prof. Charles S. Rhyne,
Reed College
Reed College is a private liberal arts college in Portland, Oregon. Founded in 1908, Reed is a residential college with a campus in the Eastmoreland neighborhood, with Tudor-Gothic style architecture, and a forested canyon nature preserve at ...
{{Authority control
Maya sites in Yucatán
National Monuments of Mexico
Former populated places in Mexico
Populated places established in the 6th century
6th-century establishments in the Maya civilization
Tourist attractions in Yucatán
World Heritage Sites in Mexico
Maya sites that survived the end of the Classic Period