Uti Vår Hage (folk Song) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an
 Uropathogenic ''E. coli'' from the gut is the cause of 80–85% of community-acquired urinary tract infections, with ''
Uropathogenic ''E. coli'' from the gut is the cause of 80–85% of community-acquired urinary tract infections, with ''
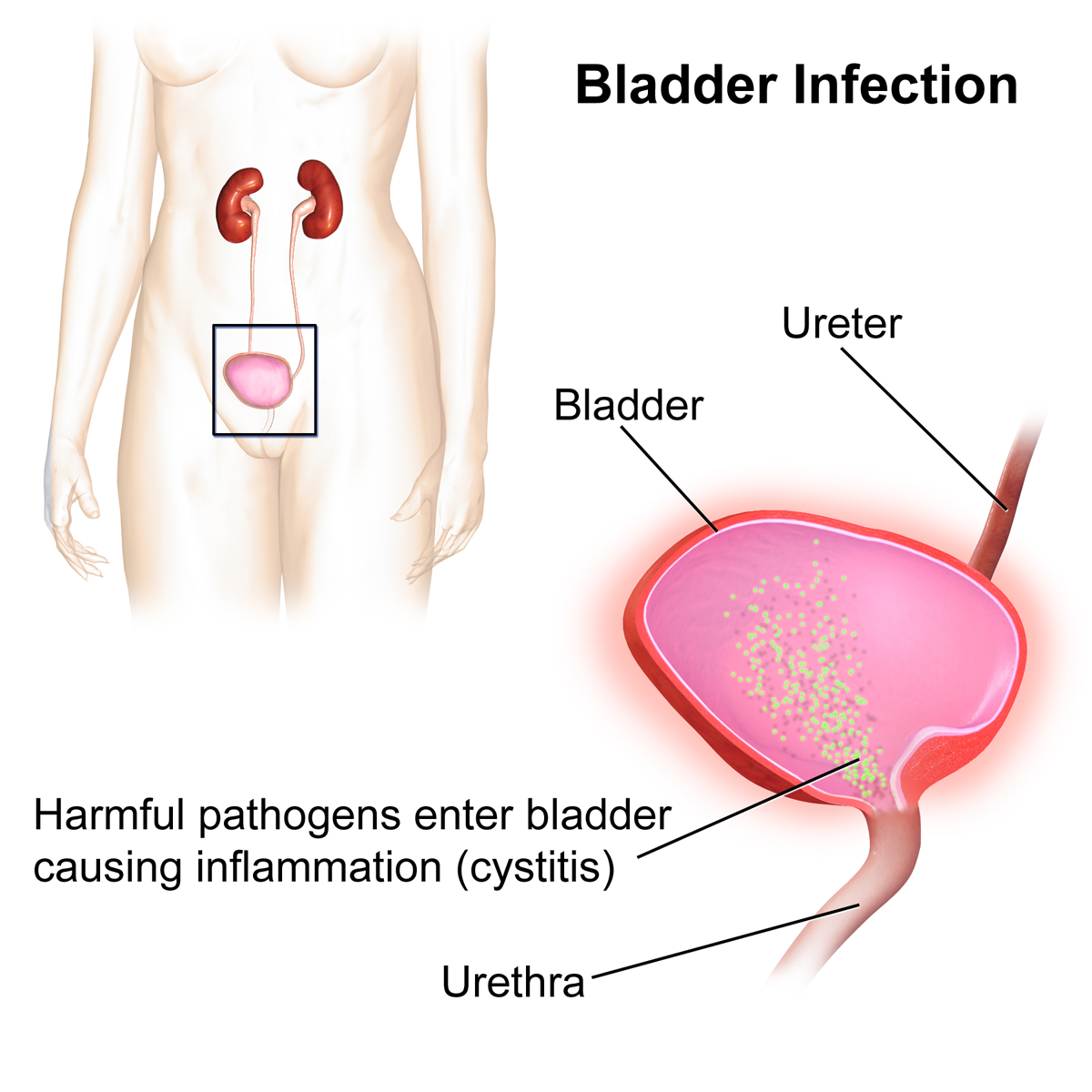 The
The
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
.
 For those with recurrent infections, taking a short course of antibiotics when each infection occurs is associated with the lowest antibiotic use. A prolonged course of daily antibiotics is also effective. Medications frequently used include
For those with recurrent infections, taking a short course of antibiotics when each infection occurs is associated with the lowest antibiotic use. A prolonged course of daily antibiotics is also effective. Medications frequently used include
infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
that affects a part of the urinary tract
The human urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressu ...
. Lower urinary tract infections may involve the bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
(cystitis) or urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
(urethritis
Urethritis is the inflammation of the urethra. The most common symptoms include painful or difficult urination and urethral discharge. It is a commonly treatable condition usually caused by infection with bacteria. This bacterial infection is ...
) while upper urinary tract infections affect the kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
(pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, burning with urination, and frequent urination. Complications ...
). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include suprapubic
The hypogastrium (also called the hypogastric region or suprapubic region) is a region of the abdomen located below the umbilical region.
Etymology
The roots of the word ''hypogastrium'' mean "below the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, ...
pain, painful urination (dysuria
Dysuria refers to painful or uncomfortable urination.
It is one of a constellation of ''irritative'' bladder symptoms (also sometimes referred to as lower urinary tract symptoms), which includes nocturia and urinary frequency.
Diagnosis
The cl ...
), frequency and urgency of urination despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection, on the other hand, are more systemic and include fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
or flank pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Since the abdomen contains most of the body's vital organs, it can be an indicator of a wide variety of diseases. Given th ...
usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely, the urine may appear bloody
''Bloody'', as an adjective or adverb, is an expletive attributive commonly used in British English, Irish English, New Zealand English and Australian English; it is also present in Canadian English, Indian English, Malaysian/Singaporean ...
. Symptoms may be vague or non-specific at the extremities of age (i.e. in patients who are very young or old).
The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'', though other bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
or fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, catheterisation, and family history. Although sexual intercourse is a risk factor, UTIs are not classified as sexually transmitted infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, e ...
s (STIs). Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, burning with urination, and frequent urination. Complications ...
usually occurs due to an ascending bladder infection but may also result from a blood-borne bacterial infection. Diagnosis in young healthy women can be based on symptoms alone. In those with vague symptoms, diagnosis can be difficult because bacteria may be present without there being an infection. In complicated cases or if treatment fails, a urine culture
Bacteriuria is the presence of bacteria in urine. Bacteriuria accompanied by symptoms is a urinary tract infection while that without is known as asymptomatic bacteriuria. Diagnosis is by urinalysis or urine culture. ''Escherichia coli'' is the ...
may be useful.
In uncomplicated cases, UTIs are treated with a short course of antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s such as nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin, sold under the brand name Macrobid among others, is an antibacterial medication of the nitrofuran class used to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs), although it is not as effective for kidney infections. It is taken by mouth ...
or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, sold under the trade names Bactrim, Cotrim (a short form of the British Approved Name, Co-trimoxazole) and Septra, among others, is a fixed-dose combination antibiotic medication used to treat a variety of bacte ...
. Resistance to many of the antibiotics used to treat this condition is increasing. In complicated cases, a longer course or intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
antibiotics may be needed. If symptoms do not improve in two or three days, further diagnostic testing may be needed. Phenazopyridine
Phenazopyridine is a medication which, when excreted by the kidneys into the urine, has a local analgesic effect on the urinary tract. It is often used to help with the pain, irritation, or urgency caused by urinary tract infections, surger ...
may help with symptoms. In those who have bacteria or white blood cells in their urine but have no symptoms, antibiotics are generally not needed, unless they are pregnant. In those with frequent infections, a short course of antibiotics may be taken as soon as symptoms begin or long-term antibiotics may be used as a preventive measure.
About 150million people develop a urinary tract infection in a given year. They are more common in women than men, but similar between anatomies while carrying indwelling catheters. In women, they are the most common form of bacterial infection. Up to 10% of women have a urinary tract infection in a given year, and half of women have at least one infection at some point in their lifetime. They occur most frequently between the ages of 16 and 35years. Recurrences are common. Urinary tract infections have been described since ancient times with the first documented description in the Ebers Papyrus
The Ebers Papyrus, also known as Papyrus Ebers, is an Egyptian medical papyrus of herbal knowledge dating to (the late Second Intermediate Period or early New Kingdom). Among the oldest and most important medical papyri of Ancient Egypt, it ...
dated to c. 1550 BC.
Signs and symptoms
Lower urinary tract infection is also referred to as a bladder infection. The most common symptoms areburning with urination
Dysuria refers to painful or uncomfortable urination.
It is one of a constellation of ''irritative'' bladder symptoms (also sometimes referred to as lower urinary tract symptoms), which includes nocturia and urinary frequency.
Diagnosis
The clin ...
and having to urinate frequently (or an urge to urinate) in the absence of vaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge is a mixture of liquid, cells, and bacteria that lubricate and protect the vagina. This mixture is constantly produced by the cells of the vagina and cervix, and it exits the body through the vaginal opening. The composition, ...
and significant pain. These symptoms may vary from mild to severe and in healthy women last an average of sixdays. Some pain above the pubic bone
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones ar ...
or in the lower back
Lower may refer to:
* ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick
Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is sit ...
may be present. People experiencing an upper urinary tract infection, or pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, burning with urination, and frequent urination. Complications ...
, may experience flank pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Since the abdomen contains most of the body's vital organs, it can be an indicator of a wide variety of diseases. Given th ...
, fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, or nausea and vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
in addition to the classic symptoms of a lower urinary tract infection. Rarely, the urine may appear bloody
''Bloody'', as an adjective or adverb, is an expletive attributive commonly used in British English, Irish English, New Zealand English and Australian English; it is also present in Canadian English, Indian English, Malaysian/Singaporean ...
or contain visible pus in the urine.
UTIs have been associated with onset or worsening of delirium
Delirium (formerly acute confusional state, an ambiguous term that is now discouraged) is a specific state of acute confusion attributable to the direct physiological consequence of a medical condition, effects of a psychoactive substance, or ...
, dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
, and neuropsychiatric disorder
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness, a mental health condition, or a psychiatric disability, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. A mental disorder is ...
s such as depression and psychosis
In psychopathology, psychosis is a condition in which a person is unable to distinguish, in their experience of life, between what is and is not real. Examples of psychotic symptoms are delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized or inco ...
. However, there is insufficient evidence to determine whether UTI causes confusion. The reasons for this are unknown, but may involve a UTI-mediated systemic inflammatory response
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
which affects the brain. Cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
s such as interleukin-6
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory cytokine and an anti-inflammatory myokine. In humans, it is encoded by the ''IL6'' gene.
In addition, osteoblasts secrete IL-6 to stimulate osteoclast formation. Smoo ...
produced as part of the inflammatory response may produce neuroinflammation
Neuroinflammation is inflammation of the nervous tissue. It may be initiated in response to a variety of cues, including infection, traumatic brain injury,Ebert SE, Jensen P, Ozenne B, Armand S, Svarer C, Stenbaek DS ''et al.'' Molecular imaging of ...
, in turn affecting dopaminergic
Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine" (literally, "working on dopamine"), a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain.
Dopaminergic pathways, Dopaminergic brain pathways facil ...
and/or glutamatergic
Glutamatergic means "related to glutamate". A glutamatergic agent (or drug) is a chemical that directly modulates the excitatory amino acid (glutamate/aspartate) system in the body or brain. Examples include excitatory amino acid receptor agonist ...
neurotransmission
Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron ...
as well as brain glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
.
Children
In young children, the only symptom of a urinary tract infection (UTI) may be a fever. Because of the lack of more obvious symptoms, when females under the age of two or uncircumcised males less than a year exhibit a fever, a culture of the urine is recommended by many medical associations. Infants may feed poorly, vomit, sleep more, or show signs ofjaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or, less frequently, greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving ...
. In older children, new onset urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a significant effect on quality of life. Urinary incontinence is common in older women ...
(loss of bladder control) may occur. About 1 in 400 infants of one to three months of age with a UTI also have bacterial meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasionall ...
.
Elderly
Urinary tract symptoms are frequently lacking in theelderly
Old age is the range of ages for people nearing and surpassing life expectancy. People who are of old age are also referred to as: old people, elderly, elders, senior citizens, seniors or older adults. Old age is not a definite biological sta ...
. The presentations may be vague and include incontinence, a change in mental status, or fatigue as the only symptoms, while some present to a health care provider with sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
, an infection of the blood, as the first symptoms. Diagnosis can be complicated by the fact that many elderly people have preexisting incontinence or dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
.
It is reasonable to obtain a urine culture in those with signs of systemic infection that may be unable to report urinary symptoms, such as when advanced dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
is present. Systemic signs of infection include a fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
or increase in temperature of more than from usual, chills, and an increased white blood cell count.
Cause
 Uropathogenic ''E. coli'' from the gut is the cause of 80–85% of community-acquired urinary tract infections, with ''
Uropathogenic ''E. coli'' from the gut is the cause of 80–85% of community-acquired urinary tract infections, with ''Staphylococcus saprophyticus
''Staphylococcus saprophyticus'' is a Gram-positive coccus belonging to the genus ''Staphylococcus''. ''S. saprophyticus'' is a common cause of community-acquired urinary tract infections.
History
''Staphylococcus saprophyticus'' was not recogni ...
'' being the cause in 5–10%. Rarely they may be due to viral
The word ''Viral'' means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
It may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spre ...
or fungal
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the tradit ...
infections. Healthcare-associated urinary tract infections (mostly related to urinary catheterization
In urinary catheterization, a latex, polyurethane, or silicone tube known as a urinary catheter is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to allow urine to drain from the bladder for collection. It may also be used to inject liquids used ...
) involve a much broader range of pathogens including: ''E. coli'' (27%), ''Klebsiella
''Klebsiella'' is a genus of Gram-negative, oxidase-negative, rod-shaped bacteria with a prominent polysaccharide-based capsule.
''Klebsiella'' is named after German-Swiss microbiologist Edwin Klebs (1834–1913). Carl Friedlander described ' ...
'' (11%), ''Pseudomonas
''Pseudomonas'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae in the class Gammaproteobacteria. The 348 members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to colonize a ...
'' (11%), the fungal pathogen ''Candida albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usu ...
'' (9%), and ''Enterococcus
''Enterococcus'' is a large genus of lactic acid bacteria of the phylum Bacillota. Enterococci are Gram-positive cocci that often occur in pairs ( diplococci) or short chains, and are difficult to distinguish from streptococci on physical ch ...
'' (7%) among others. During recent years of intensive care, ''Enterococcus
''Enterococcus'' is a large genus of lactic acid bacteria of the phylum Bacillota. Enterococci are Gram-positive cocci that often occur in pairs ( diplococci) or short chains, and are difficult to distinguish from streptococci on physical ch ...
'' spp. have several times been found as the primary cause of urinary tract infection, suggested related to broad treatment with cephalosporin
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus '' Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''.
Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibio ...
antibiotics against which they are tolerant. Urinary tract infections due to ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'' typically occur secondary to blood-borne infections. ''Chlamydia trachomatis
''Chlamydia trachomatis'' () is a Gram-negative, Anaerobic organism, anaerobic bacterium responsible for Chlamydia infection, chlamydia and trachoma. ''C. trachomatis'' exists in two forms, an extracellular infectious elementary body (EB) and an ...
'' and ''Mycoplasma genitalium
''Mycoplasma genitalium'' (also known as ''MG','' Mgen, or since 2018, ''Mycoplasmoides genitalium'') is a sexually transmitted, small and pathogenic bacterium that lives on the mucous epithelial cells of the urinary and genital tracts in ...
'' can infect the urethra but not the bladder. These infections are usually classified as a urethritis
Urethritis is the inflammation of the urethra. The most common symptoms include painful or difficult urination and urethral discharge. It is a commonly treatable condition usually caused by infection with bacteria. This bacterial infection is ...
rather than urinary tract infection.
Intercourse
In young sexually active women, sexual activity is the cause of 75–90% of bladder infections, with the risk of infection related to the frequency of sex. The term "honeymoon cystitis" has been applied to this phenomenon of frequent UTIs during early marriage. Inpost-menopausal
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of the reproductive stage for the female human. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, although the exact timing can ...
women, sexual activity does not affect the risk of developing a UTI. Spermicide
Spermicide is a contraceptive substance that destroys spermatozoon, sperm, inserted vaginally prior to Sexual intercourse, intercourse to prevent pregnancy. As a contraceptive, spermicide may be used alone. However, the pregnancy rate experienc ...
use, independent of sexual frequency, increases the risk of UTIs. Diaphragm use is also associated. Condom use without spermicide or use of birth control pills Oral contraceptives, abbreviated OCPs, also known as birth control pills, are medications taken by mouth for the purpose of birth control. The introduction of the birth control pill ("the Pill") in 1960 revolutionized the options for contraception, ...
does not increase the risk of uncomplicated urinary tract infection.
Sex
Women are more prone to UTIs than men because, in females, theurethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
is much shorter and closer to the anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
. As a woman's estrogen levels decrease with menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when Menstruation, menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of the Human reproduction, reproductive stage for the female human. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 5 ...
, her risk of urinary tract infections increases due to the loss of protective vaginal flora
Vaginal flora, vaginal microbiota or vaginal microbiome are the microorganisms that colonize the vagina. They were discovered by the German gynecologist Albert Döderlein in 1892 and are part of the overall human flora.
The amount and type of ba ...
. Additionally, vaginal atrophy
Atrophic vaginitis is inflammation of the vagina as a result of tissue thinning due to low estrogen levels. Symptoms may include pain during penetrative sex, vaginal itchiness or dryness, and an urge to urinate or burning with urination. It ...
that can sometimes occur after menopause is associated with recurrent urinary tract infections.
Chronic prostatitis in the forms of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), previously known as chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, is long-term pelvic pain and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) without evidence of a bacterial infection. It affects about 2–6% ...
and chronic bacterial prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis (CBP) is a bacterial infection of the prostate gland and a form of prostatitis (prostate inflammation). It should be distinguished from other forms of prostatitis such as acute bacterial prostatitis (ABP) and chro ...
(not acute bacterial prostatitis or asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis is a painless inflammation of the prostate gland where there is no evidence of infection. It should be distinguished from the other categories of prostatitis characterised by either pelvic pain or evidence of ...
) may cause recurrent urinary tract infections in males. Risk of infections increases as males age. While bacteria is commonly present in the urine of older males this does not appear to affect the risk of urinary tract infections.
Urinary catheters
Urinary catheterization
In urinary catheterization, a latex, polyurethane, or silicone tube known as a urinary catheter is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to allow urine to drain from the bladder for collection. It may also be used to inject liquids used ...
increases the risk for urinary tract infections. The risk of bacteriuria
Bacteriuria is the presence of bacteria in urine. Bacteriuria accompanied by symptoms is a urinary tract infection while that without is known as asymptomatic bacteriuria. Diagnosis is by urinalysis or urine culture. ''Escherichia coli'' is the ...
(bacteria in the urine) is between three and six percent per day and prophylactic antibiotics are not effective in decreasing symptomatic infections. The risk of an associated infection occurs linearly for enteric bacteria, and can be decreased by catheterizing only when necessary, using aseptic technique
Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing micro-organisms (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses, pathogenic fungi, and parasites). There are two categories of asepsis: medical and surgical. The modern day notion of asepsis is deri ...
for insertion, and maintaining unobstructed closed drainage of the catheter.
Male scuba divers
Scuba diving is a mode of underwater diving whereby divers use breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface breathing gas supply, and therefore has a limited but variable endurance. The word ''scuba'' is an acronym for ...
using condom catheters and female divers using external catching devices for their dry suit
A dry suit or drysuit provides the wearer with environmental protection by way of thermal insulation and exclusion of water, and is worn by underwater diving, divers, boating, boaters, List of water sports, water sports enthusiasts, and others wh ...
s are also susceptible to urinary tract infections.
Others
A predisposition for bladder infections may run in families. This is believed to be related to genetics. Other risk factors includediabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, being uncircumcised
Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. T ...
, and having a large prostate. In children UTIs are associated with vesicoureteral reflux
Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR), also known as vesicoureteric reflux, is a condition in which urine flows retrograde, or backward, from the urinary bladder, bladder into one or both ureters and then to the renal calyx or kidneys. Urine normally trave ...
(an abnormal movement of urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
from the bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
into ureter
The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lin ...
s or kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
s) and constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The Human feces, stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the ...
.
Persons with spinal cord injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. It is a destructive neurological and pathological state that causes major motor, sensory and autonomic dysfunctions.
Symptoms of ...
are at increased risk for urinary tract infection in part because of chronic use of catheter, and in part because of voiding
Urination is the release of urine from the bladder through the urethra in placental mammals, or through the cloaca in other vertebrates. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, voiding, ures ...
dysfunction. It is the most common cause of infection in this population, as well as the most common cause of hospitalization.
Pathogenesis
 The
The bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
that cause urinary tract infections typically enter the bladder via the urethra. However, infection may also occur via the blood or lymph
Lymph () is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to be recirculated. At the ori ...
. It is believed that the bacteria are usually transmitted to the urethra from the bowel, with females at greater risk due to their anatomy. After gaining entry to the bladder, ''E. Coli'' are able to attach to the bladder wall and form a biofilm
A biofilm is a Syntrophy, syntrophic Microbial consortium, community of microorganisms in which cell (biology), cells cell adhesion, stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy ext ...
that resists the body's immune response.
''Escherichia coli'' is the single most common microorganism, followed by ''Klebsiella'' and ''Proteus'' spp., to cause urinary tract infection. ''Klebsiella'' and ''Proteus'' spp., are frequently associated with stone disease. The presence of Gram positive bacteria such as ''Enterococcus'' and ''Staphylococcus'' is increased.
The increased resistance of urinary pathogens to quinolone antibiotic
Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as wel ...
s has been reported worldwide and might be the consequence of overuse and misuse of quinolones.
Diagnosis
In straightforward cases, a diagnosis may be made and treatment given based on symptoms alone without further laboratory confirmation. In complicated or questionable cases, it may be useful to confirm the diagnosis via urinalysis, looking for the presence of urinary nitrites, white blood cells (leukocytes), or leukocyte esterase. Another test, urine microscopy, looks for the presence of red blood cells, white blood cells, or bacteria. Urine microbiological culture, culture is deemed positive if it shows a bacterial colony count of greater than or equal to 103 colony-forming units per mL of a typical urinary tract organism. Antibiotic sensitivity can also be tested with these cultures, making them useful in the selection of antibiotic treatment. However, women with negative cultures may still improve with antibiotic treatment. As symptoms can be vague and without reliable tests for urinary tract infections, diagnosis can be difficult in the elderly.Based on pH
Normal urine pH is slightly acidic, with usual values of 6.0 to 7.5, but the normal range is 4.5 to 8.0. A urine pH of 8.5 or 9.0 is indicative of a urea-splitting organism, such as Proteus, Klebsiella, or Ureaplasma urealyticum; therefore, an asymptomatic patient with a high pH means UTI regardless of the other urine test results. Alkaline pH also can signify struvite kidney stones, which are also known as "infection stones". Text was copied from this source, which is available underCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
.
Classification
A urinary tract infection may involve only the lower urinary tract, in which case it is known as a bladder infection. Alternatively, it may involve the upper urinary tract, in which case it is known as pyelonephritis. If the urine contains significant bacteria but there are no symptoms, the condition is known as asymptomatic bacteriuria. If a urinary tract infection involves the upper tract, and the person has diabetes mellitus, is pregnant, is male, or immunocompromised, it is considered complicated. Otherwise if a woman is healthy and premenopausal it is considered uncomplicated. In children when a urinary tract infection is associated with a fever, it is deemed to be an upper urinary tract infection.Children
To make the diagnosis of a urinary tract infection in children, a positive urinary culture is required. Contamination poses a frequent challenge depending on the method of collection used, thus a cutoff of 105CFU/mL is used for a "clean-catch" mid stream sample, 104CFU/mL is used for catheter-obtained specimens, and 102CFU/mL is used for suprapubic aspirations (a sample drawn directly from the bladder with a needle). The use of "urine bags" to collect samples is discouraged by the World Health Organization due to the high rate of contamination when cultured, and catheterization is preferred in those not toilet trained. Some, such as the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends renal ultrasound and voiding cystourethrogram (watching a person's urethra and urinary bladder with real time x-rays while they urinate) in all children less than two years old who have had a urinary tract infection. However, because there is a lack of effective treatment if problems are found, others such as the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence only recommends routine imaging in those less than six months old or who have unusual findings.Differential diagnosis
In women with cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix) or vaginitis (inflammation of the vagina) and in young men with UTI symptoms, a ''Chlamydia trachomatis
''Chlamydia trachomatis'' () is a Gram-negative, Anaerobic organism, anaerobic bacterium responsible for Chlamydia infection, chlamydia and trachoma. ''C. trachomatis'' exists in two forms, an extracellular infectious elementary body (EB) and an ...
'' or ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' infection may be the cause. These infections are typically classified as a urethritis
Urethritis is the inflammation of the urethra. The most common symptoms include painful or difficult urination and urethral discharge. It is a commonly treatable condition usually caused by infection with bacteria. This bacterial infection is ...
rather than a urinary tract infection. Vaginitis may also be due to a candidal vulvovaginitis, yeast infection. Interstitial cystitis (chronic pain in the bladder) may be considered for people who experience multiple episodes of UTI symptoms but urine cultures remain negative and not improved with antibiotics. Prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate) may also be considered in the differential diagnosis.
Hemorrhagic cystitis, characterized by hematuria, blood in the urine, can occur secondary to a number of causes including: infections, radiation therapy, underlying cancer, medications and toxins. Medications that commonly cause this problem include the chemotherapeutic agent cyclophosphamide with rates of 2–40%. Eosinophilic cystitis is a rare condition where eosinophiles are present in the bladder wall. Signs and symptoms are similar to a bladder infection. Its cause is not entirely clear; however, it may be linked to food allergies, infections, and medications among others.
Prevention
A number of measures have not been confirmed to affect UTI frequency including: urinating immediately after intercourse, the type of underwear used, personal hygiene methods used after urinating or defecating, or whether a person typically bathes or showers. There is similarly a lack of evidence surrounding the effect of holding one's urine, tampon use, and Douche, douching. In those with frequent urinary tract infections who use spermicide or a diaphragm (contraceptive), diaphragm as a method of contraception, they are advised to use alternative methods. In those with benign prostatic hyperplasia urinating in a sitting position appears to improve bladder emptying which might decrease urinary tract infections in this group. Using urinary catheters as little and as short of time as possible and appropriate care of the catheter when used prevents catheter-associated urinary tract infections. They should be inserted using sterile technique in hospital however non-sterile technique may be appropriate in those who self catheterize. The urinary catheter set up should also be kept sealed. Evidence does not support a significant decrease in risk when silver-alloy catheters are used.Medications
nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin, sold under the brand name Macrobid among others, is an antibacterial medication of the nitrofuran class used to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs), although it is not as effective for kidney infections. It is taken by mouth ...
and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, sold under the trade names Bactrim, Cotrim (a short form of the British Approved Name, Co-trimoxazole) and Septra, among others, is a fixed-dose combination antibiotic medication used to treat a variety of bacte ...
. Some recommend against prolonged use due to concerns of antibiotic resistance. Methenamine is another agent used for this purpose as in the bladder where the acidity is low it produces formaldehyde to which resistance does not develop. A UK study showed that methenamine is as effective daily low-dose antibiotics at preventing UTIs among women who experience recurrent UTIs. As methenamine is an antiseptic, it may avoid the issue of antibiotic resistance.
In cases where infections are related to intercourse, taking antibiotics afterwards may be useful. In post-menopausal women, topical vaginal estrogen has been found to reduce recurrence. As opposed to topical creams, the use of vaginal estrogen from Pessary, pessaries has not been as useful as low dose antibiotics. Antibiotics following short term urinary catheterization decreases the subsequent risk of a bladder infection. A number of UTI vaccines are in development as of 2018.
Children
The evidence that preventive medicine, preventive antibiotics decrease urinary tract infections in children is poor. However recurrent UTIs are a rare cause of further kidney problems if there are no underlying abnormalities of the kidneys, resulting in less than a third of a percent (0.33%) of chronic kidney disease in adults.Male circumcision
Circumcision of boys has been observed to exhibit a strong protective effect against UTIs, with some research suggesting as much as a 90% reduction in symptomatic UTI incidence among male infants, if they are circumcised. The protective effect is even stronger in boys born with urogenital abnormalities.Dietary supplements
When used as an Adjuvant therapy, adjuvant to antibiotics and other standard treatments, cranberry supplements decrease the number of UTIs in people who get them frequently. A 2023 review concluded that cranberry products can reduce the risk of UTIs in certain groups (women with reoccurring UTIs, children, and people having had clinical interventions), but not in pregnant women, the elderly or people with Urination#Disorders, urination disorders. Some evidence suggests that cranberry juice is more effective at UTI control than dehydrated tablets or capsules. Cranberry has not been effective in attempts to replace antibiotics for the treatment of active infections. Cranberry supplements are also high in sugar content, which may worsen the risks associated with UTIs in patients with Diabetes, diabetes mellitus. Mannose, D-mannose is often marketed as a dietary supplement that prevents UTIs; however, there is little evidence supporting its use. A randomised controlled trial compared daily d-mannose with a placebo (fructose) among women with recurrent urinary tract infections over 6 months. D-mannose offered no benefit over placebo in reducing UTIs. As of 2015, probiotics require further study to determine if they are beneficial for UTI.Treatment
The mainstay of treatment isantibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s. Phenazopyridine
Phenazopyridine is a medication which, when excreted by the kidneys into the urine, has a local analgesic effect on the urinary tract. It is often used to help with the pain, irritation, or urgency caused by urinary tract infections, surger ...
is occasionally prescribed during the first few days in addition to antibiotics to help with the burning and urgency sometimes felt during a bladder infection. However, it is not routinely recommended due to safety concerns with its use, specifically an elevated risk of methemoglobinemia (higher than normal level of methemoglobin in the blood). Paracetamol may be used for fevers. There is no good evidence for the use of cranberry products for treating current infections.
Fosfomycin can be used as an effective treatment for both UTIs and complicated UTIs including acute pyelonephritis. The standard regimen for complicated UTIs is an oral 3g dose administered once every 48 or 72 hours for a total of 3 doses or a 6 grams every 8 hours for 7 days to 14 days when fosfomycin is given in IV form.
Gepotidacin was approved for medical use in the United States in March 2025. It is the first new antibiotic approved in the US for UTIs in nearly 30 years.
Uncomplicated
Uncomplicated infections can be diagnosed and treated based on symptoms alone. Antibiotics taken by mouth such as trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, or fosfomycin are typically first line. Cephalosporins, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, or a Quinolone antibiotic, fluoroquinolone may also be used. However, antibiotic resistance to fluoroquinolones among the bacteria that cause urinary infections has been increasing. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends against the use of fluoroquinolones, including a Boxed warning, Boxed Warning, when other options are available due to higher risks of serious side effects, such as tendinitis, tendon rupture and worsening of myasthenia gravis. These medications substantially shorten the time to recovery with all being equally effective. A three-day treatment with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, or a fluoroquinolone is usually sufficient, whereas nitrofurantoin requires 5–7days. Fosfomycin may be used as a single dose but is not as effective. Fluoroquinolones are not recommended as a first treatment. The Infectious Diseases Society of America states this due to the concern of generating resistance to this class of medication. Amoxicillin-clavulanate appears less effective than other options. Despite this precaution, some resistance has developed to all of these medications related to their widespread use. Trimethoprim alone is deemed to be equivalent to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole in some countries. For simple UTIs, children often respond to a three-day course of antibiotics. Women with recurrent simple UTIs are over 90% accurate in identifying new infections. They may benefit from self-treatment upon occurrence of symptoms with medical follow-up only if the initial treatment fails. The combination sulopenem etzadroxil/probenecid (Orlynvah) was approved for medical use in the United States in October 2024.Complicated
Complicated UTIs are more difficult to treat and usually requires more aggressive evaluation, treatment, and follow-up. It may require identifying and addressing the underlying complication. Increasing antibiotic resistance is causing concern about the future of treating those with complicated and recurrent UTI.Asymptomatic bacteriuria
Those who have bacteria in the urine but no symptoms should not generally be treated with antibiotics. This includes those who are old, those with spinal cord injuries, and those who have urinary catheters. Pregnancy is an exception and it is recommended that women take sevendays of antibiotics. If not treated it causes up to 30% of mothers to developpyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, burning with urination, and frequent urination. Complications ...
and increases risk of low birth weight and preterm birth. Some also support treatment of those with diabetes mellitus and treatment before urinary tract procedures which will likely cause bleeding.
Pregnant women
Urinary tract infections, even asymptomatic presence of bacteria in the urine, are more concerning in pregnancy due to the increased risk of kidney infections. During pregnancy, high progesterone levels elevate the risk of decreased muscle tone of the ureters and bladder, which leads to a greater likelihood of reflux, where urine flows back up the ureters and towards the kidneys. While pregnant women do not have an increased risk of asymptomatic bacteriuria, if bacteriuria is present they do have a 25–40% risk of a kidney infection. Thus if urine testing shows signs of an infection—even in the absence of symptoms—treatment is recommended. Cephalexin or nitrofurantoin are typically used because they are generally considered safe in pregnancy. A kidney infection during pregnancy may result in preterm birth or pre-eclampsia (a state of hypertension, high blood pressure and kidney dysfunction during pregnancy that can lead to seizures). Some women have UTIs that keep coming back in pregnancy. There is insufficient research on how to best treat these recurrent infections.Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, burning with urination, and frequent urination. Complications ...
is treated more aggressively than a simple bladder infection using either a longer course of oral antibiotics or Intravenous therapy, intravenous antibiotics. Seven days of the oral fluoroquinolone ciprofloxacin is typically used in areas where the resistance rate is less than 10%. If the local antibiotic resistance rates are greater than 10%, a dose of intravenous ceftriaxone is often prescribed. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole or amoxicillin/clavulanate orally for 14 days is another reasonable option. In those who exhibit more severe symptoms, admission to a hospital for ongoing antibiotics may be needed. Complications such as ureteral obstruction from a Kidney stone disease, kidney stone may be considered if symptoms do not improve following two or three days of treatment.
Prognosis
With treatment, symptoms generally improve within 36hours. Up to 42% of uncomplicated infections may resolve on their own within a few days or weeks. 15–25% of adults and children have chronic symptomatic UTIs including recurrent infections, persistent infections (infection with the same pathogen), a re-infection (new pathogen), or a relapsed infection (the same pathogen causes a new infection after it was completely gone). Recurrent urinary tract infections are defined as at least two infections (episodes) in a six-month time period or three infections in twelve months, can occur in adults and in children. Cystitis refers to a urinary tract infection that involves the lower urinary tract (bladder). An upper urinary tract infection which involves the kidney is calledpyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, burning with urination, and frequent urination. Complications ...
. About 10–20% of pyelonephritis will go on and develop scarring of the affected kidney. Then, 10–20% of those develop scarring will have increased risk of hypertension in later life.
Epidemiology
Urinary tract infections are the most frequent bacterial infection in women. They occur most frequently between the ages of 16 and 35years, with 10% of women getting an infection yearly and more than 40–60% having an infection at some point in their lives. Recurrences are common, with nearly half of people getting a second infection within a year. Urinary tract infections occur four times more frequently in females than males. Pyelonephritis occurs between 20 and 30 times less frequently. They are the most common cause of hospital-acquired infections accounting for approximately 40%. Rates of asymptomatic bacteria in the urine increase with age from two to seven percent in women of child-bearing age to as high as 50% in elderly women in care homes. Rates of asymptomatic bacteria in the urine among men over 75 are between 7–10%. 2–10% of pregnant women have asymptomatic bacteria in the urine and higher rates are reported in women who live in some underdeveloped countries. Urinary tract infections may affect 10% of people during childhood. Among children, urinary tract infections are most common in uncircumcised males less than three months of age, followed by females less than one year. Estimates of frequency among children, however, vary widely. In a group of children with a fever, ranging in age between birth and two years, 2–20% were diagnosed with a UTI.Veterinary medicine
Domestic Cat, cats are less susceptible to bacterial urinary tract infections than domestic Dog, dogs.History
Urinary tract infections have been described since ancient times with the first documented description in theEbers Papyrus
The Ebers Papyrus, also known as Papyrus Ebers, is an Egyptian medical papyrus of herbal knowledge dating to (the late Second Intermediate Period or early New Kingdom). Among the oldest and most important medical papyri of Ancient Egypt, it ...
dated to c. 1550 BC. It was described by the Egyptians as "sending forth heat from the bladder". Effective treatment did not occur until the development and availability of antibiotics in the 1930s, before which time herbs, bloodletting and rest were recommended.
See also
*Urinary anti-infective agentReferences
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Urinary Tract Infection Infectious diseases Urological conditions Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full) Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate