United States Of America on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in
 It is generally accepted that the first inhabitants of North America migrated from Siberia by way of the Bering land bridge and arrived at least 12,000 years ago; however, some evidence suggests an even earlier date of arrival. The Clovis culture, which appeared around 11,000 BC, is believed to represent the first wave of human settlement of the Americas. This was likely the first of three major waves of migration into North America; later waves brought the ancestors of present-day Athabaskans, Aleuts, and
It is generally accepted that the first inhabitants of North America migrated from Siberia by way of the Bering land bridge and arrived at least 12,000 years ago; however, some evidence suggests an even earlier date of arrival. The Clovis culture, which appeared around 11,000 BC, is believed to represent the first wave of human settlement of the Americas. This was likely the first of three major waves of migration into North America; later waves brought the ancestors of present-day Athabaskans, Aleuts, and
 Claims of very early colonization of coastal New England by the
Claims of very early colonization of coastal New England by the
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservation
An Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a federally recognized Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs and not to the state government in which i ...
s. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island
Collectively called the Pacific Islands, the islands in the Pacific Ocean are further categorized into three major island groups: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Depending on the context, the term ''Pacific Islands'' may refer to one ...
sovereign states
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defined terri ...
: the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states compri ...
, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center
A financial centre ( BE), financial center ( AE), or financial hub, is a location with a concentration of participants in banking, asset management, insurance or financial markets with venues and supporting services for these activities to t ...
is New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
.
Paleo-Americans migrated from Siberia to the North American mainland at least 12,000 years ago, and advanced cultures began to appear later on. These societies had almost completely declined when Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004) ...
arrived in North America and began colonizing it. Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
's Thirteen Colonies quarreled with the British Crown over taxation and political representation, leading to the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolu ...
(1765–1791). After the Revolution, the United States gained independence, the first nation-state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may inc ...
founded on Enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
principles of liberal democracy
Liberal democracy is the combination of a liberal political ideology that operates under an indirect democratic form of government. It is characterized by elections between multiple distinct political parties, a separation of powers into ...
.
In the late 18th century, the U.S. began expanding across North America, gradually obtaining new territories, sometimes through war, frequently displacing Native Americans, and admitting new states. By 1848, the United States spanned the continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
from east to west. The controversy surrounding the practice of slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
culminated in the secession of the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confede ...
, which fought the remaining states of the Union during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by state ...
(1861–1865). With the Union's victory and preservation, slavery was abolished by the Thirteenth Amendment.
By 1890, the United States had grown to become the world's largest economy, and the Spanish–American War and World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
established the country as a world power. After Japan's surprise attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941, the U.S. entered World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
on the Allied side. The aftermath of the war left the United States and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
as the world's two superpower
A superpower is a state with a dominant position characterized by its extensive ability to exert influence or project power on a global scale. This is done through the combined means of economic, military, technological, political and cultural s ...
s, and led to the Cold War, which commenced in 1945 and ended in 1991 with the Soviet Union's dissolution
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
. During the Cold War, both countries engaged in a struggle for ideological dominance but avoided direct military conflict. They also competed in the Space Race, which culminated in the 1969 American spaceflight in which the U.S. was the first nation to land humans on the Moon. Simultaneously, the civil rights movement (1954–1968) led to legislation abolishing state and local Jim Crow laws and other codified racial discrimination against African Americans. With the Soviet Union's dissolution in 1991 and the end of the Cold War, the United States emerged as the world's sole superpower. In 2001, following the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commerc ...
, the United States became a lead member of the Global War on Terrorism, which included the War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) and the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق ( Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict and the War on terror
, image ...
(2003–2011).
The United States is a federal republic
A federal republic is a federation of states with a republican form of government. At its core, the literal meaning of the word republic when used to reference a form of government means: "a country that is governed by elected representatives ...
with three separate branches of government, including a bicameral legislature. It is a liberal democracy and has a market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers ...
. It ranks very high in international measures of quality of life, income and wealth, economic competitiveness, human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
, innovation, and education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. ...
; it has low levels of perceived corruption. The United States has the highest median income per person of any polity
A polity is an identifiable Politics, political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of Institutionalisation, institutionalized social relation, social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize ...
in the world. It has high levels of incarceration
Imprisonment is the restraint of a person's liberty, for any cause whatsoever, whether by authority of the government, or by a person acting without such authority. In the latter case it is "false imprisonment". Imprisonment does not necessari ...
and inequality and lacks universal health care. As a melting pot
The melting pot is a monocultural metaphor for a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous, the different elements "melting together" with a common culture; an alternative being a homogeneous society becoming more heterogeneous throug ...
of cultures and ethnicities, the U.S. has been shaped by centuries of immigration.
The United States is a highly developed country
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
, and its economy accounts for approximately a quarter of global GDP and is the world's largest by GDP at market exchange rates. By value, the United States is the world's largest importer and second-largest exporter. Although it accounts for just over 4.2% of the world's total population, the U.S. holds over 30% of the total wealth in the world, the largest share held by any country. The United States is a founding member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
, World Bank, International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster gl ...
, Organization of American States
The Organization of American States (OAS; es, Organización de los Estados Americanos, pt, Organização dos Estados Americanos, french: Organisation des États américains; ''OEA'') is an international organization that was founded on 30 Apri ...
, NATO, the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, and is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council. The country is responsible for more than a third of global military spending and is the foremost military power in the world and a leading political
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studi ...
, cultural, and scientific force.
Etymology
The first known use of the name " America" dates to 1507, when it appeared on a world map produced by the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller in Saint Dié, Lorraine (now northeastern France). On his map, the name is shown in large letters on what would now be consideredSouth America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
, honoring Amerigo Vespucci. The Italian explorer was the first to postulate that the West Indies did not represent Asia's eastern limit but were part of a previously unknown landmass. In 1538, the Flemish cartographer Gerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator (; 5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a 16th-century geographer, cosmographer and cartographer from the County of Flanders. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represented ...
used the name "America" to refer to the entire Western Hemisphere.
The first documentary evidence of the phrase "United States of America" dates back to a letter from January 2, 1776, written by Stephen Moylan to Joseph Reed, George Washington's aide-de-camp. Moylan expressed his wish to go "with full and ample powers from the United States of America to Spain" to seek assistance in the revolutionary war effort. The first known publication of the phrase "United States of America" was in an anonymous essay in '' The Virginia Gazette'' newspaper in Williamsburg
Williamsburg may refer to:
Places
*Colonial Williamsburg, a living-history museum and private foundation in Virginia
*Williamsburg, Brooklyn, neighborhood in New York City
*Williamsburg, former name of Kernville (former town), California
*Williams ...
, on April 6, 1776.
The second draft of the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, prepared by John Dickinson and completed no later than June 17, 1776, declared "The name of this Confederation shall be the 'United States of America'." The final version of the Articles, sent to the states for ratification in late 1777, stated that "The Stile of this Confederacy shall be 'The United States of America'." In June 1776, Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was previously the nati ...
wrote the phrase "UNITED STATES OF AMERICA" in the headline of his "original Rough draught" of the Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of ...
. This draft of the document did not surface until June 21, 1776, and it is unclear whether it was written before or after Dickinson used the term in his June 17 draft of the Articles of Confederation.
The phrase "United States" was originally plural in American usage. It described a collection of states—e.g., "the United States are..." The singular form became popular after the end of the Civil War and is now standard usage. A citizen of the United States is called an " American". "United States", "American", and "U.S." refer to the country adjectivally ("American values", "U.S. forces"). In English, the word "American" rarely refers to topics or subjects not directly connected with the United States.
History
Early history
 It is generally accepted that the first inhabitants of North America migrated from Siberia by way of the Bering land bridge and arrived at least 12,000 years ago; however, some evidence suggests an even earlier date of arrival. The Clovis culture, which appeared around 11,000 BC, is believed to represent the first wave of human settlement of the Americas. This was likely the first of three major waves of migration into North America; later waves brought the ancestors of present-day Athabaskans, Aleuts, and
It is generally accepted that the first inhabitants of North America migrated from Siberia by way of the Bering land bridge and arrived at least 12,000 years ago; however, some evidence suggests an even earlier date of arrival. The Clovis culture, which appeared around 11,000 BC, is believed to represent the first wave of human settlement of the Americas. This was likely the first of three major waves of migration into North America; later waves brought the ancestors of present-day Athabaskans, Aleuts, and Eskimo
Eskimo () is an exonym used to refer to two closely related Indigenous peoples: the Inuit (including the Alaska Native Iñupiat, the Greenlandic Inuit, and the Canadian Inuit) and the Yupik peoples, Yupik (or Siberian Yupik, Yuit) of eastern Si ...
s.
Over time, indigenous cultures in North America grew increasingly sophisticated, and some, such as the pre-Columbian Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native Americans in the United States, Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern United States, Midwestern, Eastern United States, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from appr ...
in the southeast, developed advanced agriculture, architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
, and complex societies. The city-state of Cahokia is the largest, most complex pre-Columbian archaeological site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology an ...
in the modern-day United States. In the Four Corners
The Four Corners is a region of the Southwestern United States consisting of the southwestern corner of Colorado, southeastern corner of Utah, northeastern corner of Arizona, and northwestern corner of New Mexico. The Four Corners area ...
region, Ancestral Puebloan culture developed from centuries of agricultural experimentation. The Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
n native language groups. This grouping consists of the peoples who speak Algonquian languages
The Algonquian languages ( or ; also Algonkian) are a subfamily of indigenous American languages that include most languages in the Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically simi ...
. Historically, these peoples were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and into the interior along the Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five la ...
. Before Europeans came into contact, most Algonquian settlements lived by hunting and fishing, although many supplemented their diet by cultivating corn, beans and squash (the " Three Sisters"). The Ojibwe cultivated wild rice. The Haudenosaunee
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
confederation of the Iroquois, located in the southern Great Lakes region, was established at some point between the twelfth and fifteenth centuries.
Estimating the native population of North America during European contact is difficult. Douglas H. Ubelaker of the Smithsonian Institution estimated a population of 93,000 in the South Atlantic states and a population of 473,000 in the Gulf states, but most academics regard this figure as too low. Anthropologist Henry F. Dobyns believed the populations were much higher, suggesting around 1.1 million along the shores of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
, 2.2 million people living between Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, a ...
and Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
, 5.2 million in the Mississippi Valley and tributaries, and around 700,000 people in the Florida peninsula.
Colonial America
 Claims of very early colonization of coastal New England by the
Claims of very early colonization of coastal New England by the Norse
Norse is a demonym for Norsemen, a medieval North Germanic ethnolinguistic group ancestral to modern Scandinavians, defined as speakers of Old Norse from about the 9th to the 13th centuries.
Norse may also refer to:
Culture and religion
* Nor ...
are disputed and controversial. Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
had landed in Puerto Rico on his 1493 voyage, and San Juan San Juan, Spanish for Saint John, may refer to:
Places Argentina
* San Juan Province, Argentina
* San Juan, Argentina, the capital of that province
* San Juan, Salta, a village in Iruya, Salta Province
* San Juan (Buenos Aires Underground), ...
was settled by the Spanish a decade later. The first documented arrival of Europeans in the continental United States is that of Spanish conquistadors such as Juan Ponce de León
Juan Ponce de León (, , , ; 1474 – July 1521) was a Spanish explorer and '' conquistador'' known for leading the first official European expedition to Florida and for serving as the first governor of Puerto Rico. He was born in Santervá ...
, who made his first expedition to Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, a ...
in 1513. The Italian explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano, sent by France to the New World in 1525, encountered native inhabitants of what is now New York Bay
New York Bay is the large tidal body of water in the New York–New Jersey Harbor Estuary where the Hudson River, Raritan River, and Arthur Kill empty into the Atlantic Ocean between Sandy Hook and Rockaway Point.
Geography
New York Bay is usu ...
. The Spanish set up the first settlements in Florida and New Mexico, such as Saint Augustine, often considered the nation's oldest city, and Santa Fe. The French established their own settlements along the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it ...
and Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
, notably New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans
 In the early days of colonization, many European settlers experienced food shortages, disease, and conflicts with Native Americans, such as in King Philip's War. Native Americans were also often fighting neighboring tribes and European settlers. In many cases, however, the natives and settlers came to depend on each other. Settlers traded for food and animal pelts; natives for guns, tools and other European goods. Natives taught many settlers to cultivate corn, beans, and other foodstuffs. European missionaries and others felt it was important to "civilize" the Native Americans and urged them to adopt European agricultural practices and lifestyles. However, with the increased European colonization of North America, Native Americans were displaced and often killed during conflicts.
European settlers also began trafficking
In the early days of colonization, many European settlers experienced food shortages, disease, and conflicts with Native Americans, such as in King Philip's War. Native Americans were also often fighting neighboring tribes and European settlers. In many cases, however, the natives and settlers came to depend on each other. Settlers traded for food and animal pelts; natives for guns, tools and other European goods. Natives taught many settlers to cultivate corn, beans, and other foodstuffs. European missionaries and others felt it was important to "civilize" the Native Americans and urged them to adopt European agricultural practices and lifestyles. However, with the increased European colonization of North America, Native Americans were displaced and often killed during conflicts.
European settlers also began trafficking
 The
The  In the late 18th century, American settlers began to expand further westward, some of them with a sense of
In the late 18th century, American settlers began to expand further westward, some of them with a sense of
 Irreconcilable sectional conflict regarding the enslavement of Africans and African Americans ultimately led to the American Civil War. With the
Irreconcilable sectional conflict regarding the enslavement of Africans and African Americans ultimately led to the American Civil War. With the
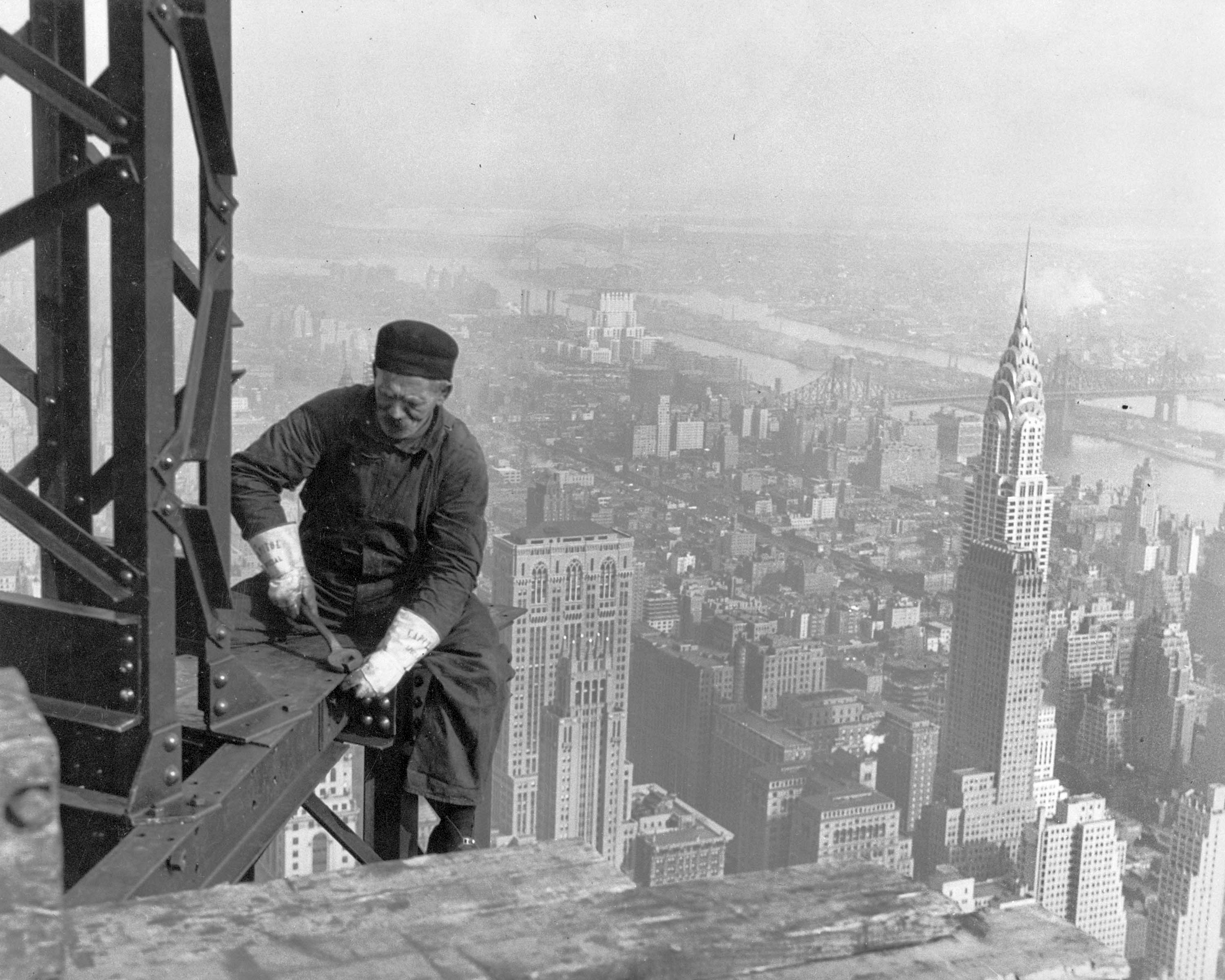

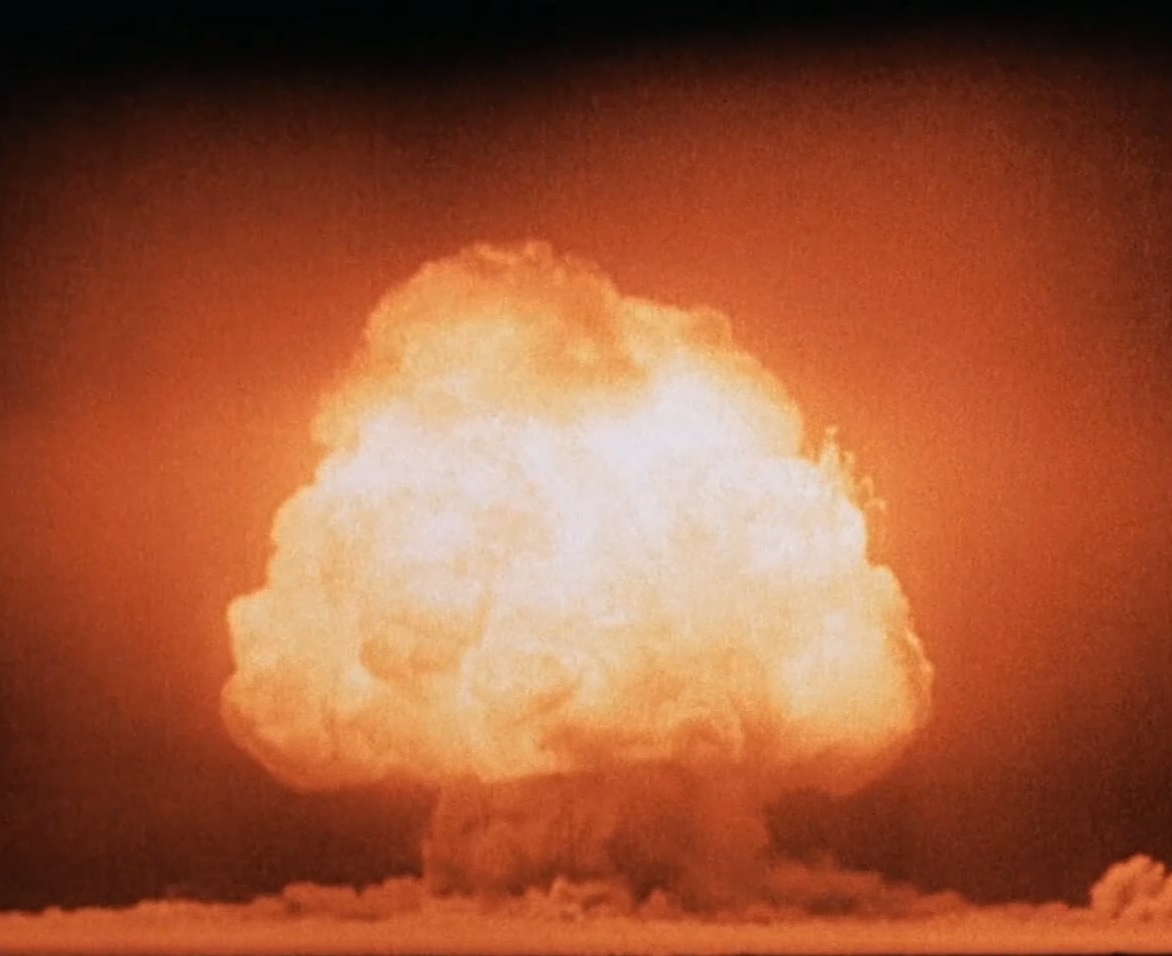 The United States remained neutral from the outbreak of
The United States remained neutral from the outbreak of
 After World War II, the United States financed and implemented the Marshall Plan to help rebuild western Europe; disbursements paid between 1948 and 1952 would total $13 billion ($115 billion in 2021). Also at this time, geopolitical tensions between the United States and
After World War II, the United States financed and implemented the Marshall Plan to help rebuild western Europe; disbursements paid between 1948 and 1952 would total $13 billion ($115 billion in 2021). Also at this time, geopolitical tensions between the United States and  The growing civil rights movement used
The growing civil rights movement used

 The 48 contiguous states and the District of Columbia occupy a combined area of . Of this area, is contiguous land, composing 83.65% of total U.S. land area. About 15% is occupied by
The 48 contiguous states and the District of Columbia occupy a combined area of . Of this area, is contiguous land, composing 83.65% of total U.S. land area. About 15% is occupied by
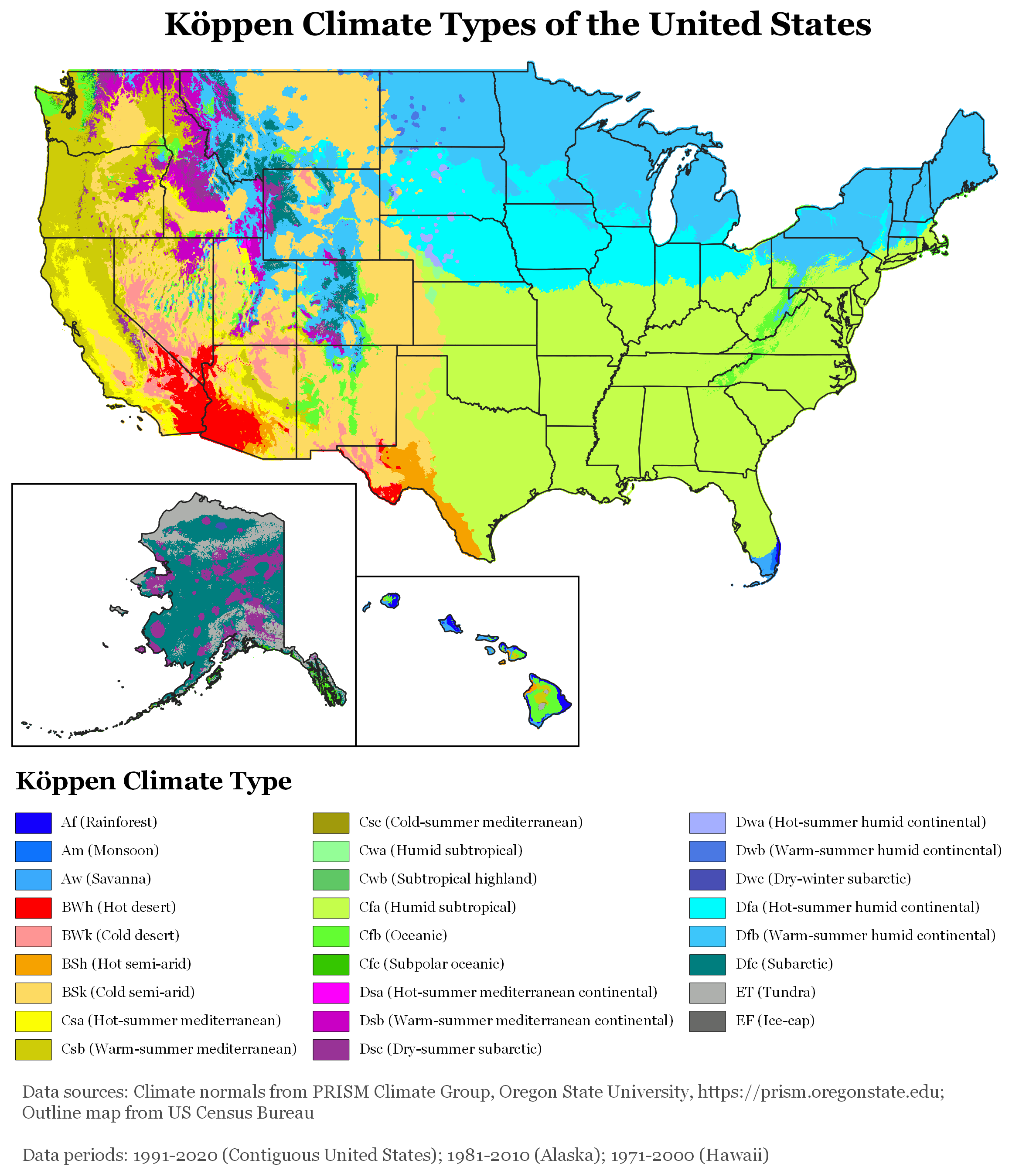 The United States, with its large size and geographic variety, includes most climate types. To the east of the 100th meridian, the climate ranges from humid continental in the north to humid subtropical in the south.
The Great Plains west of the 100th meridian are semi-arid. Many mountainous areas of the American West have an
The United States, with its large size and geographic variety, includes most climate types. To the east of the 100th meridian, the climate ranges from humid continental in the north to humid subtropical in the south.
The Great Plains west of the 100th meridian are semi-arid. Many mountainous areas of the American West have an
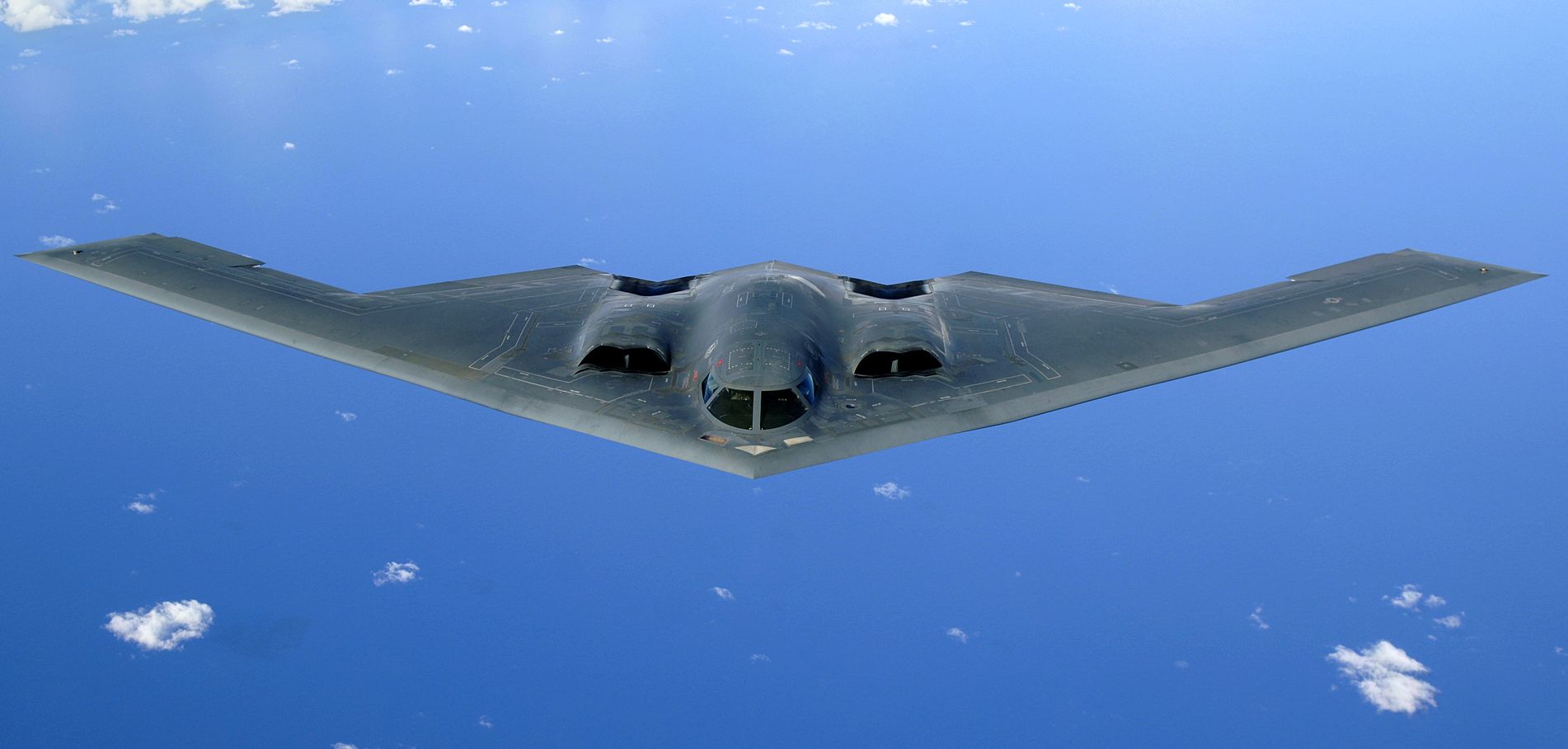
 The president is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces and appoints its leaders, the
The president is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces and appoints its leaders, the
Mobile
Mobile may refer to:
Places
* Mobile, Alabama, a U.S. port city
* Mobile County, Alabama
* Mobile, Arizona, a small town near Phoenix, U.S.
* Mobile, Newfoundland and Labrador
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Mobile ...
.
Successful English settlement of the eastern coast of North America began with the Virginia Colony in 1607 at Jamestown and with the Pilgrims' colony at Plymouth in 1620. The continent's first elected legislative assembly, Virginia's House of Burgesses, was founded in 1619. Harvard College
Harvard College is the undergraduate college of Harvard University, an Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636, Harvard College is the original school of Harvard University, the oldest institution of higher ...
was established in the Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as the ...
in 1636 as the first institution of higher education. The Mayflower Compact
The Mayflower Compact, originally titled Agreement Between the Settlers of New Plymouth, was the first governing document of Plymouth Colony. It was written by the men aboard the ''Mayflower,'' consisting of separatist Puritans, adventurers, an ...
and the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut established precedents for representative self-government and constitutionalism that would develop throughout the American colonies. Many English settlers were dissenting Christians who came seeking religious freedom. The native population of America declined after European arrival for various reasons, primarily from diseases such as smallpox and measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often ...
.
African slaves
Slavery has historically been widespread in Africa. Systems of servitude and slavery were common in parts of Africa in ancient times, as they were in much of the rest of the ancient world. When the trans-Saharan slave trade, Indian Ocean sl ...
into Colonial America via the transatlantic slave trade. Because of a lower prevalence of tropical diseases and relatively better treatment, slaves had a much higher life expectancy in North America than in South America, leading to a rapid increase in their numbers. Colonial society was largely divided over the religious and moral implications of slavery, and several colonies passed acts for or against the practice. Lien, 1913, p. 522 Davis, 1996, p. 7 However, by the turn of the 18th century, African slaves had supplanted European indentured servants as cash crop labor, especially in the American South. Quirk, 2011, p. 195
The Thirteen Colonies that would become the United States of America were administered by the British as overseas dependencies. All nonetheless had local governments with elections open to most free men. With very high birth rates, low death rates, and steady settlement, the colonial population grew rapidly, eclipsing Native American populations. The Christian revivalist movement of the 1730s and 1740s known as the Great Awakening
Great Awakening refers to a number of periods of religious revival in American Christian history. Historians and theologians identify three, or sometimes four, waves of increased religious enthusiasm between the early 18th century and the late ...
fueled interest both in religion and in religious liberty.
During the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754– ...
(1756–1763), known in the U.S. as the French and Indian War, British forces captured Canada from the French. With the creation of the Province of Quebec, Canada's francophone
French became an international language in the Middle Ages, when the power of the Kingdom of France made it the second international language, alongside Latin. This status continued to grow into the 18th century, by which time French was the l ...
population would remain isolated from the English-speaking colonial dependencies of Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native En ...
, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
and the Thirteen Colonies. Excluding the Native Americans who lived there, the Thirteen Colonies had a population of over 2.1 million in 1770, about a third that of Britain. Despite continuing new arrivals, the rate of natural increase was such that by the 1770s only a small minority of Americans had been born overseas. The colonies' distance from Britain had allowed the development of self-government, but their unprecedented success motivated British monarchs to periodically seek to reassert royal authority.
American Revolution and the early federal republic
 The
The American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolu ...
separated the Thirteen Colonies from the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading post ...
, and was the first successful war of independence by a non-European entity against a European power in modern history
The term modern period or modern era (sometimes also called modern history or modern times) is the period of history that succeeds the Middle Ages (which ended approximately 1500 AD). This terminology is a historical periodization that is appli ...
. By the 18th century the American Enlightenment and the political philosophies of liberalism were pervasive among leaders. Americans began to develop an ideology of " republicanism", asserting that government rested on the consent of the governed
In political philosophy, the phrase consent of the governed refers to the idea that a government's legitimacy and moral right to use state power is justified and lawful only when consented to by the people or society over which that politica ...
. They demanded their " rights as Englishmen" and " no taxation without representation". The British insisted on administering the colonies through a Parliament that did not have a single representative responsible for any American constituency, and the conflict escalated into war.
In 1774, the First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 British colonies that became the United States. It met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, after the British Navy ...
passed the Continental Association, which mandated a colonies-wide boycott of British goods. The American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of ...
began the following year, catalyzed by events like the Stamp Act and the Boston Tea Party that were rooted in colonial disagreement with British governance. The Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named "United Colonies" and in 1 ...
, an assembly representing the United Colonies, unanimously adopted the Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of ...
on July 4, 1776 (annually celebrated as Independence Day
An independence day is an annual event commemorating the anniversary of a nation's independence or statehood, usually after ceasing to be a group or part of another nation or state, or more rarely after the end of a military occupation. Man ...
). In 1781, the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union established a decentralized government that operated until 1789. A celebrated early turn in the war for the Americans was George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the ...
leading the Americans to cross the frozen Delaware River in a surprise attack the night of December 25–26, 1776. Another victory, in 1777, at the Battle of Saratoga resulted in the capture of a British army, and led to France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
joining in the war against them. After the surrender of a second British army at the siege of Yorktown in 1781, Britain signed a peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surr ...
. American sovereignty became internationally recognized, and the new nation took possession of substantial territory east of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it ...
, from what is today Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
in the north and Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, a ...
in the south.
As it became increasingly apparent that the Confederation was insufficient to govern the new country, nationalists advocated for and led the Philadelphia Convention of 1787 in writing the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the natio ...
to replace it, ratified in state conventions in 1788. Going into force in 1789, this constitution reorganized the government into a federation administered by three equal branches (executive, judicial and legislative), on the principle of creating salutary checks and balances. George Washington, who had led the Continental Army to victory and then willingly relinquished power, was the first president elected under the new constitution. The Bill of Rights, forbidding federal restriction of personal freedoms and guaranteeing a range of legal protections, was adopted in 1791. Boyer, 2007, pp. 192–193 Tensions with Britain remained, however, leading to the War of 1812, which was fought to a draw.
Although the federal government outlawed American participation in the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and ...
in 1807, after 1820, cultivation of the highly profitable cotton crop exploded in the Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the war ...
, and along with it, the use of slave labor. The Second Great Awakening, especially in the period 1800–1840, converted millions to evangelical Protestantism. In the North, it energized multiple social reform movements, including abolitionism; in the South, Methodists and Baptists proselytized among slave populations.  In the late 18th century, American settlers began to expand further westward, some of them with a sense of
In the late 18th century, American settlers began to expand further westward, some of them with a sense of manifest destiny
Manifest destiny was a cultural belief in the 19th century in the United States, 19th-century United States that American settlers were destined to expand across North America.
There were three basic tenets to the concept:
* The special vir ...
. The 1803 Louisiana Purchase almost doubled the nation's area, Spain ceded Florida and other Gulf Coast territory in 1819, the Republic of Texas
The Republic of Texas ( es, República de Tejas) was a sovereign state in North America that existed from March 2, 1836, to February 19, 1846, that bordered Mexico, the Republic of the Rio Grande in 1840 (another breakaway republic from Mex ...
was annexed in 1845 during a period of expansionism, and the 1846 Oregon Treaty
The Oregon Treaty is a treaty between the United Kingdom and the United States that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C. The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute by settling competing American and British claims to t ...
with Britain led to U.S. control of the present-day American Northwest. Additionally, the Trail of Tears in the 1830s exemplified the Indian removal policy that forcibly resettled Indians. This further expanded acreage under mechanical cultivation, increasing surpluses for international markets. This prompted a long series of American Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settle ...
west of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it ...
from 1810 to at least 1890. and eventually, conflict with Mexico. Most of these conflicts ended with the cession of Native American territory and their confinement to Indian reservation
An Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a federally recognized Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs and not to the state government in which i ...
s. Victory in the Mexican–American War resulted in the 1848 Mexican Cession
The Mexican Cession ( es, Cesión mexicana) is the region in the modern-day southwestern United States that Mexico originally controlled, then ceded to the United States in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 after the Mexican–American War ...
of California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
and much of the present-day American Southwest, and the U.S. spanned the continent. The California Gold Rush of 1848–1849 spurred migration to the Pacific coast, which led to the California Genocide and the creation of additional western states. Economic development was spurred by giving vast quantities of land, nearly 10% of the total area of the United States, to white European settlers as part of the Homestead Acts, as well as making land grants to private railroad companies and colleges. Prior to the Civil War, the prohibition or expansion of slavery into these territories exacerbated tensions over the debate around abolitionism.
The Civil War and Reconstruction
1860 election
The following elections occurred in the year 1860. Most notably, the 1860 United States presidential election was one of the events that precipitated the American Civil War.
North America United States
* California's at-large congressional distr ...
of Republican Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
, conventions in eleven slave states declared secession and formed the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confede ...
, while the federal government (the " Union") maintained that secession was unconstitutional and illegal. On April 12, 1861, the Confederacy initiated military conflict by bombarding Fort Sumter, a federal garrison in Charleston harbor
The Charleston Harbor is an inlet (8 sq mi/20.7 km²) of the Atlantic Ocean at Charleston, South Carolina. The inlet is formed by the junction of Ashley and Cooper rivers at . Morris and Sullivan's Islands shelter the entrance. Charleston ...
, South Carolina. This would be the spark of the Civil War, which lasted for four years (1861–1865) and became the deadliest military conflict in American history. The war would result in the deaths of approximately 620,000 soldiers from both sides and upwards of 50,000 civilians, almost all of them in the South.
Reconstruction began in earnest following the war. While President Lincoln attempted to foster friendship and forgiveness between the Union and the former Confederacy, his assassination on April 14, 1865 drove a wedge between North and South again. Republicans in the federal government made it their goal to oversee the rebuilding of the South and to ensure the rights of African Americans. They persisted until the Compromise of 1877, when the Republicans agreed to cease protecting the rights of African Americans in the South in order for Democrats to concede the presidential election of 1876
The following elections occurred in the year 1876.
Europe
* 1876 Dalmatian parliamentary election
* 1876 French legislative election
* 1876 Leominster by-election
* 1876 Spanish general election
North America Canada
* 1876 Prince Edward Isla ...
. Southern white Democrats, calling themselves " Redeemers", took control of the South after the end of Reconstruction, beginning the nadir of American race relations. From 1890 to 1910, the Redeemers established so-called Jim Crow laws, disenfranchising
Disfranchisement, also called disenfranchisement, or voter disqualification is the restriction of suffrage (the right to vote) of a person or group of people, or a practice that has the effect of preventing a person exercising the right to vote. D ...
almost all blacks and some impoverished whites throughout the region. Blacks would face racial segregation nationwide, especially in the South. They also lived under constant threat of vigilante violence, including lynching
Lynching is an extrajudicial killing by a group. It is most often used to characterize informal public executions by a mob in order to punish an alleged transgressor, punish a convicted transgressor, or intimidate people. It can also be an ex ...
.
Industrial Age and the Progressive Era
In the North,urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
and an unprecedented influx of immigrants from Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, wh ...
supplied a surplus of labor for the country's industrialization and transformed its culture.
National infrastructure, including telegraph and transcontinental railroads, spurred economic growth and greater settlement and development of the American Old West. After the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by state ...
, new transcontinental railways made relocation easier for settlers, expanded internal trade, and increased conflicts with Native Americans. The later inventions of electric light
An electric light, lamp, or light bulb is an electrical component that produces light. It is the most common form of artificial lighting. Lamps usually have a base made of ceramic, metal, glass, or plastic, which secures the lamp in the ...
and the telephone would also affect communication and urban life.
Mainland expansion also included the purchase of Alaska from Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
in 1867. In 1893, pro-American elements in Hawaii overthrew the Hawaiian monarchy
The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawaiʻi (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Ko Hawaiʻi Pae ʻĀina''), was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the ...
and formed the Republic of Hawaii
The Republic of Hawaii ( Hawaiian: ''Lepupalika o Hawaii'') was a short-lived one-party state in Hawaii between July 4, 1894, when the Provisional Government of Hawaii had ended, and August 12, 1898, when it became annexed by the United State ...
, which the U.S. annexed in 1898. Puerto Rico, Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic ce ...
, and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
were ceded by Spain in the same year, following the Spanish–American War. American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internation ...
was acquired by the United States in 1900 after the end of the Second Samoan Civil War
The Second Samoan Civil War was a conflict that reached a head in 1898 when Germany, the United Kingdom, and the United States were locked in dispute over who should have control over the Samoan island chain, located in the South Pacific Ocea ...
. The U.S. Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands,. Also called the ''American Virgin Islands'' and the ''U.S. Virgin Islands''. officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory ...
were purchased from Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establishe ...
in 1917.
Rapid economic development during the late 19th and early 20th centuries fostered the rise of many prominent industrialists. Tycoons
A business magnate, also known as a tycoon, is a person who has achieved immense wealth through the ownership of multiple lines of enterprise. The term characteristically refers to a powerful entrepreneur or investor who controls, through per ...
like Cornelius Vanderbilt, John D. Rockefeller, and Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie (, ; November 25, 1835August 11, 1919) was a Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist. Carnegie led the expansion of the American steel industry in the late 19th century and became one of the richest Americans in ...
led the nation's progress in the railroad, petroleum, and steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ...
industries. Banking became a major part of the economy, with J. P. Morgan playing a notable role. The American economy boomed, becoming the world's largest.
These dramatic changes were accompanied by growing inequality and social unrest, which prompted the rise of organized labor
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and Employee ben ...
along with populist, socialist, and anarchist movements. This period eventually ended with the advent of the Progressive Era
The Progressive Era (late 1890s – late 1910s) was a period of widespread social activism and political reform across the United States focused on defeating corruption, monopoly, waste and inefficiency. The main themes ended during Am ...
, which saw significant reforms including health and safety regulation of consumer goods, the rise of labor unions, and greater antitrust measures to ensure competition among businesses and attention to worker conditions.
The rise to world power, The New Deal, and World War II

 The United States remained neutral from the outbreak of
The United States remained neutral from the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
in 1914 until 1917 when it joined the war as an "associated power" alongside the Allies of World War I, helping to turn the tide against the Central Powers. In 1919, President Woodrow Wilson took a leading diplomatic role at the Paris Peace Conference Agreements and declarations resulting from meetings in Paris include:
Listed by name
Paris Accords
may refer to:
* Paris Accords, the agreements reached at the end of the London and Paris Conferences in 1954 concerning the post-war status of Germ ...
and advocated strongly for the U.S. to join the League of Nations. However, the Senate refused to approve this and did not ratify the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
that established the League of Nations.McDuffie, Jerome; Piggrem, Gary Wayne; Woodworth, Steven E. (2005). ''U.S. History Super Review''. Piscataway, NJ: Research & Education Association. p. 418. .
Around this time, millions of rural African Americans began a mass migration from the South to northern urban centers; it would continue until about 1970. The last vestiges of the Progressive Era resulted in women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the women's rights, right of women to Suffrage, vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to gran ...
and alcohol prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic be ...
. In 1920, the women's rights movement won passage of a constitutional amendment granting women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the women's rights, right of women to Suffrage, vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to gran ...
. The 1920s and 1930s saw the rise of radio for mass communication
Mass communication is the process of imparting and exchanging information through mass media to large segments of the population. It is usually understood for relating to various forms of media, as its technologies are used for the dissemination o ...
and the invention of early television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication Media (communication), medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of Transmission (telecommunications), television tra ...
. The prosperity of the Roaring Twenties ended with the Wall Street Crash of 1929 and the onset of the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagion ...
. After his election as president in 1932, Franklin D. Roosevelt responded with the New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Cons ...
. The Dust Bowl of the mid-1930s impoverished many farming communities and spurred a new wave of western migration.
At first neutral during World War II, the United States in March 1941 began supplying materiel to the Allies. On December 7, 1941, the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent for ...
launched a surprise attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawa ...
, prompting the United States to join the Allies against the Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
, and in the following year, to intern about 120,000 Japanese and Japanese Americans. The U.S. pursued a "Europe first Europe first, also known as Germany first, was the key element of the grand strategy agreed upon by the United States and the United Kingdom during World War II. According to this policy, the United States and the United Kingdom would use the pr ...
" defense policy, leaving the Philippines, an American colony, isolated and alone to fight Japan's invasion and occupation until the U.S.-led Philippines campaign (1944–1945). During the war, the United States was one of the " Four Powers" who met to plan the postwar world, along with Britain, the Soviet Union, and China. The United States emerged relatively unscathed from the war, and with even greater economic and military influence.
The United States played a leading role in the Bretton Woods Bretton Woods can refer to:
* Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, a village in the United States
**Bretton Woods Mountain Resort, a ski resort located in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire
*The 1944 Bretton Woods Conference, also known as the "United Nations ...
and Yalta conferences, which signed agreements on new international financial institutions and Europe's postwar reorganization. As an Allied victory was won in Europe, a 1945 international conference
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations".
International may also refer to:
Music Albums
* ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011
* ''International'' (New Order album), 2002
* ''International'' (The T ...
held in San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
produced the United Nations Charter, which became active after the war. The United States and Japan then fought each other in the largest naval battle in history, the Battle of Leyte Gulf. The United States developed the first nuclear weapons and used them on Japan in the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945; the Japanese surrendered
Surrender, in military terms, is the relinquishment of control over territory, combatants, fortifications, ships or armament to another power. A surrender may be accomplished peacefully or it may be the result of defeat in battle. A sovereign ...
on September 2, ending World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
Cold War and late 20th century
 After World War II, the United States financed and implemented the Marshall Plan to help rebuild western Europe; disbursements paid between 1948 and 1952 would total $13 billion ($115 billion in 2021). Also at this time, geopolitical tensions between the United States and
After World War II, the United States financed and implemented the Marshall Plan to help rebuild western Europe; disbursements paid between 1948 and 1952 would total $13 billion ($115 billion in 2021). Also at this time, geopolitical tensions between the United States and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
led to the Cold War, driven by an ideological divide between capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private ...
and communism
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society ...
. They dominated the military affairs of Europe, with the U.S. and its NATO allies on one side and the Soviet Union and its Warsaw Pact allies on the other. The U.S. often opposed Third World movements that it viewed as Soviet-sponsored, sometimes pursuing direct action for regime change against left-wing governments. American troops fought the communist forces in the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top: ...
of 1950–1953, and the U.S. became increasingly involved in the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
(1955–1975), introducing combat forces in 1965. Their competition to achieve superior spaceflight capability led to the Space Race, which culminated in the U.S. becoming the first nation to land people on the Moon in 1969. While both countries engaged in proxy wars and developed powerful nuclear weapons, they avoided direct military conflict.
At home, the United States experienced sustained economic expansion, urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
, and a rapid growth of its population and middle class
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. Co ...
following World War II. Construction of an Interstate Highway System transformed the nation's transportation infrastructure in decades to come. In 1959, the United States admitted Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S ...
and Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only ...
to become the 49th and 50th states, formally expanding beyond the contiguous United States.
 The growing civil rights movement used
The growing civil rights movement used nonviolence
Nonviolence is the personal practice of not causing harm to others under any condition. It may come from the belief that hurting people, animals and/or the environment is unnecessary to achieve an outcome and it may refer to a general philosoph ...
to confront racism, with Martin Luther King Jr. becoming a prominent leader and figurehead. President Lyndon B. Johnson initiated legislation that led to a series of policies addressing poverty and racial inequalities, in what he termed the " Great Society". The launch of a " War on Poverty" expanded entitlements and welfare spending, leading to the creation of the Food Stamp Program, Aid to Families with Dependent Children, along with national health insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among ...
programs Medicare and Medicaid
Medicaid in the United States is a federal and state program that helps with healthcare
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and ...
. A combination of court decisions and legislation, culminating in the Civil Rights Act of 1968, made significant improvements. Meanwhile, a counterculture movement
The counterculture of the 1960s was an anti-establishment cultural phenomenon that developed throughout much of the Western world in the 1960s and has been ongoing to the present day. The aggregate movement gained momentum as the civil rights mo ...
grew, which was fueled by opposition to the Vietnam War, the Black Power movement, and the sexual revolution
The sexual revolution, also known as the sexual liberation, was a social movement that challenged traditional codes of behavior related to sexuality and interpersonal relationships throughout the United States and the developed world from the 1 ...
. The women's movement in the U.S. broadened the debate on women's rights and made gender equality
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making; and the state of valuing d ...
a major social goal. The 1960s Sexual Revolution liberalized American attitudes to sexuality; the 1969 Stonewall riots
The Stonewall riots (also known as the Stonewall uprising, Stonewall rebellion, or simply Stonewall) were a series of spontaneous protests by members of the gay community in response to a police raid that began in the early morning hours of Ju ...
in New York City marked the beginning of the fledgling gay rights
Rights affecting lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people vary greatly by country or jurisdiction—encompassing everything from the legal recognition of same-sex marriage to the death penalty for homosexuality.
Notably, , 3 ...
movement.
The United States supported Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
during the Yom Kippur War; in response, the country faced an oil embargo from OPEC
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC, ) is a cartel of countries. Founded on 14 September 1960 in Baghdad by the first five members (Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela), it has, since 1965, been headquart ...
nations, sparking the 1973 oil crisis. After a surge in female labor participation around the 1970s, by 1985, the majority of women aged 16 and over were employed. The 1970s and early 1980s also saw the onset of stagflation. The presidency of Richard Nixon saw the American withdrawal from Vietnam but also the Watergate scandal which led to a decline in public trust of government. Ervin, Sam, et al., ''Final Report of the Watergate Committee]''.
After his election in 1980 President Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
responded to economic stagnation with neoliberal reforms and initiated the more aggressive rollback strategy towards the Soviet Union. During Reagan's presidency, the federal debt held by the public nearly tripled in nominal terms, from $738 billion to $2.1 trillion. This led to the United States moving from the world's largest international creditor to the world's largest debtor nation. The dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the So ...
in 1991 ended the Cold War, ensuring a global unipolarity in which the U.S. was unchallenged as the world's dominant superpower
A superpower is a state with a dominant position characterized by its extensive ability to exert influence or project power on a global scale. This is done through the combined means of economic, military, technological, political and cultural s ...
.
Fearing the spread of regional international instability from the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait, in August 1991, President George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushSince around 2000, he has been usually called George H. W. Bush, Bush Senior, Bush 41 or Bush the Elder to distinguish him from his eldest son, George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd president from 2001 to 2009; pr ...
launched and led the Gulf War against Iraq, expelling Iraqi forces and restoring the Kuwaiti monarchy. During the administration of President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (Birth name, né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 ...
in 1994, the U.S. signed the North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA ; es, Tratado de Libre Comercio de América del Norte, TLCAN; french: Accord de libre-échange nord-américain, ALÉNA) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that crea ...
(NAFTA), causing trade among the U.S., Canada, and Mexico to soar. Due to the dot-com boom, stable monetary policy, and reduced social welfare spending, the 1990s saw the longest economic expansion in modern U.S. history.
21st century
On September 11, 2001, al-Qaeda terrorist hijackers flew passenger planes into the World Trade Center in New York City and the Pentagon near Washington, D.C., killing nearly 3,000 people. In response, President George W. Bush launched the War on Terror, which included a nearly 20-year war in Afghanistan from 2001 to 2021 and the 2003–2011Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق ( Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict and the War on terror
, image ...
. Government policy designed to promote affordable housing, widespread failures in corporate and regulatory governance, and historically low interest rates set by the Federal Reserve led to a housing bubble in 2006. This culminated in the financial crisis of 2007–2008 and the Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At ...
, the nation's largest economic contraction since the Great Depression.
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, Obama was the first Af ...
, the first multiracial
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
president with African-American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American ...
ancestry, was elected in 2008 amid the financial crisis. By the end of his second term, the stock market, median household income and net worth, and the number of persons with jobs were all at record levels, while the unemployment rate was well below the historical average. His signature legislative accomplishment was the Affordable Care Act (ACA), popularly known as "Obamacare". It represented the U.S. healthcare system's most significant regulatory overhaul and expansion of coverage since Medicare in 1965. As a result, the uninsured share of the population was cut in half, while the number of newly insured Americans was estimated to be between 20 and 24 million. After Obama served two terms, Republican Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of ...
was elected as the 45th president in 2016. His election is viewed as one of the biggest political upsets in American history. Trump held office through the first waves of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified ...
and the resulting COVID-19 recession starting in 2020 that exceeded even the Great Recession earlier in the century.
The early 2020s saw the country become more divided, with various social issues sparking debate and protest. The murder of George Floyd in 2020 led to widespread civil unrest in urban centers and a national debate about police brutality
Police brutality is the excessive and unwarranted use of force by law enforcement against an individual or a group. It is an extreme form of police misconduct and is a civil rights violation. Police brutality includes, but is not limited to, ...
and lingering institutional racism. The nationwide increase in the frequency of instances and number of deaths related to mass shootings
There is a lack of consensus on how to define a mass shooting. Most terms define a minimum of three or four victims of gun violence (not including the shooter or in an inner city) in a short period of time, although an Australian study from 200 ...
added to the societal tensions. On January 6, 2021, supporters of the outgoing president, Trump, stormed the U.S. Capitol in an unsuccessful effort to disrupt the Electoral College vote count that would confirm Democrat Joe Biden as the 46th president. In 2022, the Supreme Court ruled that there is no constitutional right to an abortion, causing another wave of protests across the country and stoking international reactions as well. Despite these divisions, the country has remained unified against Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
after Vladimir Putin's 2022 invasion of Ukraine, with politicians and individuals across the political spectrum supporting arms shipments to Ukraine and many large American corporations pulling out of Russia and Belarus altogether.
Geography

 The 48 contiguous states and the District of Columbia occupy a combined area of . Of this area, is contiguous land, composing 83.65% of total U.S. land area. About 15% is occupied by
The 48 contiguous states and the District of Columbia occupy a combined area of . Of this area, is contiguous land, composing 83.65% of total U.S. land area. About 15% is occupied by Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S ...
, a state in northwestern North America, with the remainder in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only ...
, a state and archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
in the central Pacific, and the five populated but unincorporated insular territories of Puerto Rico, American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internation ...
, Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic ce ...
, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the U.S. Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands,. Also called the ''American Virgin Islands'' and the ''U.S. Virgin Islands''. officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory ...
. Measured by only land area, the United States is third in size behind Russia and China, and just ahead of Canada.
The United States is the world's third- or fourth-largest nation by total area (land and water), ranking behind Russia and Canada and nearly equal to China. The ranking varies depending on how two territories disputed by China and India are counted, and how the total size of the United States is measured.
The coastal plain of the Atlantic seaboard gives way further inland to deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, a ...
forests and the rolling hills of the Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
. The Appalachian Mountains and the Adirondack massif divide the eastern seaboard from the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five la ...
and the grasslands of the Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
. The Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Mis ...
– Missouri River, the world's fourth longest river system, runs mainly north–south through the heart of the country. The flat, fertile prairie of the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, ...
stretches to the west, interrupted by a highland region in the southeast.
The Rocky Mountains, west of the Great Plains, extend north to south across the country, peaking at over in Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
. Farther west are the rocky Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is no ...
and deserts such as the Chihuahua Chihuahua may refer to:
Places
*Chihuahua (state), a Mexican state
**Chihuahua (dog), a breed of dog named after the state
**Chihuahua cheese, a type of cheese originating in the state
**Chihuahua City, the capital city of the state
**Chihuahua Mun ...
, Sonoran, and Mojave. The Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily ...
and Cascade mountain ranges run close to the Pacific coast
Pacific coast may be used to reference any coastline that borders the Pacific Ocean.
Geography Americas
Countries on the western side of the Americas have a Pacific coast as their western or southwestern border, except for Panama, where the Pac ...
, both ranges also reaching altitudes higher than . The lowest and highest points in the contiguous United States are in the state of California, and only about apart. At an elevation of , Alaska's Denali is the highest peak in the country and in North America. Active volcanoes are common throughout Alaska's Alexander and Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands ( ; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin, "land of the Aleuts"; possibly from the Chukchi ''aliat'', or "island")—also called the Aleut Islands, Aleutic Islands, or, before 1867, the Catherine Archipelago—are a chain of 14 main, ...
, and Hawaii consists of volcanic islands. The supervolcano
A supervolcano is a volcano that has had an eruption with a Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of 8, the largest recorded value on the index. This means the volume of deposits for such an eruption is greater than 1,000 cubic kilometers (240 cubic ...
underlying Yellowstone National Park in the Rockies is the continent's largest volcanic feature.
Climate
 The United States, with its large size and geographic variety, includes most climate types. To the east of the 100th meridian, the climate ranges from humid continental in the north to humid subtropical in the south.
The Great Plains west of the 100th meridian are semi-arid. Many mountainous areas of the American West have an
The United States, with its large size and geographic variety, includes most climate types. To the east of the 100th meridian, the climate ranges from humid continental in the north to humid subtropical in the south.
The Great Plains west of the 100th meridian are semi-arid. Many mountainous areas of the American West have an alpine climate
Alpine climate is the typical weather ( climate) for elevations above the tree line, where trees fail to grow due to cold. This climate is also referred to as a mountain climate or highland climate.
Definition
There are multiple definitions ...
. The climate is arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ...
in the Great Basin, desert in the Southwest, Mediterranean in coastal California, and oceanic in coastal Oregon and Washington and southern Alaska. Most of Alaska is subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of humid continental regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Scandinavia, Siberia, and the Cairngorms. Generally, ...
or polar. Hawaii and the southern tip of Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, a ...
are tropical, as well as its territories in the Caribbean and the Pacific.
States bordering the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
are prone to hurricanes, and most of the world's tornadoes occur in the country, mainly in Tornado Alley areas in the Midwest and South. Overall, the United States receives more high-impact extreme weather incidents than any other country in the world.
Extreme weather has become more frequent in the U.S., with three times the number of reported heat waves as in the 1960s. Of the ten warmest years ever recorded in the 48 contiguous states, eight have occurred since 1998. In the American Southwest, droughts have become more persistent and more severe.
Biodiversity and conservation
The U.S. is one of 17 megadiverse countries containing large numbers of endemic species: about 17,000 species of vascular plants occur in the contiguous United States and Alaska, and more than 1,800 species offlowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. They include all forbs (flowering plants without a woody stem), grasses and grass-like plants, a vast majority of ...
s are found in Hawaii, few of which occur on the mainland. The United States is home to 428 mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class (biology), class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in Female#Mammalian female, females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a ...
species, 784 bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s, 311 reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephal ...
s, and 295 amphibians, and 91,000 insect species.
There are 63 national parks and hundreds of other federally managed parks, forests, and wilderness
Wilderness or wildlands (usually in the plural), are natural environments on Earth that have not been significantly modified by human activity or any nonurbanized land not under extensive agricultural cultivation. The term has traditionally re ...
areas, which are managed by the National Park Service. Altogether, the government owns about 28% of the country's land area, mostly in the western states. Most of this land is protected, though some is leased for oil and gas drilling, mining, logging, or cattle ranching, and about .86% is used for military purposes.
Environmental issues include debates on oil and nuclear energy
Nuclear energy may refer to:
* Nuclear power, the use of sustained nuclear fission or nuclear fusion to generate heat and electricity
*Nuclear binding energy
Nuclear binding energy in experimental physics is the minimum energy that is required ...
, dealing with air and water pollution, the economic costs of protecting wildlife, logging and deforestation, and climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
. The most prominent environmental agency is the Environmental Protection Agency
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
(EPA), created by presidential order in 1970. The idea of wilderness has shaped the management of public lands since 1964, with the Wilderness Act. The Endangered Species Act
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA or "The Act"; 16 U.S.C. § 1531 et seq.) is the primary law in the United States for protecting imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of ec ...
of 1973 is intended to protect threatened and endangered species and their habitats, which are monitored by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service.
As of 2020, the U.S. ranked 24th among nations in the Environmental Performance Index
A biophysical environment is a life, biotic and Abiotic component, abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environ ...
. The country joined the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, Climate change a ...
on climate change in 2016, and has many other environmental commitments. It withdrew from the Paris Agreement in 2020 but rejoined it in 2021.
Government and politics
The United States is a federal republic of 50 states, a federal district, five territories and several uninhabited island possessions. It is the world's oldest surviving federation. It is afederal republic
A federal republic is a federation of states with a republican form of government. At its core, the literal meaning of the word republic when used to reference a form of government means: "a country that is governed by elected representatives ...
and a representative democracy "in which majority rule is tempered by minority rights protected by law."Scheb, John M.; Scheb, John M. II (2002). ''An Introduction to the American Legal System''. Florence, KY: Delmar, p. 6. . In the American federal system, sovereignty is shared between two levels of government: federal and state. Citizens of the states are also governed by local governments, which are administrative divisions of the states. The territories are administrative divisions of the federal government.
The U.S. Constitution serves as the country's supreme legal document. The Constitution establishes the structure and responsibilities of the federal government and its relationship with the individual states. The Constitution has been amended 27 times; the first ten amendments ( Bill of Rights) and the Fourteenth Amendment form the central basis of Americans' individual rights. All laws and governmental procedures are subject to judicial review, and any law can be voided if the courts determine that it violates the Constitution. The principle of judicial review, not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution, was established by the Supreme Court in '' Marbury v. Madison'' (1803).
The United States has operated under a two-party system for most of its history. In American political culture
Political culture describes how culture impacts politics. Every political system is embedded in a particular political culture.
Definition
Gabriel Almond defines it as "the particular pattern of orientations toward political actions in which ...
, the center-right Republican Party is considered " conservative" and the center-left Democratic Party is considered " liberal". On Transparency International's 2019 Corruption Perceptions Index, its public sector position deteriorated from a score of 76 in 2015 to 69 in 2019. In 2021, the U.S. ranked 26th on the Democracy Index, and is described as a "flawed democracy".
Federal government
The federal government comprises three branches, which are headquartered in Washington, D.C. and regulated by a system of checks and balances defined by the Constitution. * Legislative: The bicameral Congress, made up of theSenate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
and the House of Representatives, makes federal law, declares war, approves treaties, has the power of the purse, and has the power of impeachment
Impeachment is the process by which a legislative body or other legally constituted tribunal initiates charges against a public official for misconduct. It may be understood as a unique process involving both political and legal elements.
In ...
, by which it can remove sitting members of the federal government.
* Executive: The president is the commander-in-chief of the military, can veto legislative bills before they become law (subject to congressional override), and appoints the members of the Cabinet (subject to Senate approval) and other officers, who administer and enforce federal laws and policies.
* Judicial: The Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
and lower federal courts
Federal court may refer to:
United States
* Federal judiciary of the United States
** United States district court, a particular federal court
Elsewhere
* Federal Court of Australia
* Federal courts of Brazil
* Federal Court (Canada)
* Federal co ...
, whose judges are appointed by the president with Senate approval, interpret laws and overturn those they find unconstitutional.
The lower house
A lower house is one of two Debate chamber, chambers of a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house. Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has co ...
, the House of Representatives, has 435 voting members, each representing a congressional district for a two-year term. House seats are apportioned among the states by population. Each state then draws single-member districts to conform with the census apportionment. The District of Columbia and the five major U.S. territories each have one member of Congress—these members are not allowed to vote.
The upper house
An upper house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house.''Bicameralism'' (1997) by George Tsebelis The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restric ...
, the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, has 100 members with each state having two senators, elected at large to six-year terms; one-third of Senate seats are up for election every two years. The District of Columbia and the five major U.S. territories do not have senators. The Senate is unique among upper houses in being the most prestigious and powerful portion of the country's bicameral system; political scientists have frequently labeled it the "most powerful upper house" of any government.
The president serves a four-year term and may be elected to the office no more than twice. The president is not elected by direct vote, but by an indirect electoral college system in which the determining votes are apportioned to the states and the District of Columbia. The Supreme Court, led by the chief justice of the United States, has nine members, who serve for life.
Political divisions
Each of the 50 states holds jurisdiction over a geographic territory, where it shares sovereignty with the federal government. They are subdivided into counties or county equivalents, and further divided into municipalities. The District of Columbia is a federal district that contains the capital of the United States, thecity of Washington
The District of Columbia was created in 1801 as the federal district of the United States, with territory previously held by the states of Maryland and Virginia ceded to the federal government of the United States for the purpose of creating its ...
. Each state has the amount presidential electors equal to the number of their representatives plus senators in Congress, and the District of Columbia has three electors. Territories of the United States do not have presidential electors, therefore people there cannot vote for the president.
Citizenship is granted at birth in all states, the District of Columbia, and all major U.S. territories except American Samoa. The United States observes limited tribal sovereignty of the American Indian nations, like states' sovereignty. American Indians are U.S. citizens and tribal lands are subject to the jurisdiction of the U.S. Congress and the federal courts. Like the states, tribes have some autonomy restrictions. They are prohibited from making war, engaging in their own foreign relations, and printing or issuing independent currency. Indian reservation
An Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a federally recognized Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs and not to the state government in which i ...
s are usually contained within one state, but there are 12 reservations that cross state boundaries.
Foreign relations
The United States has an established structure of foreign relations, and it had the world's second-largest diplomatic corps in 2019. It is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, and home to the United Nations headquarters. The United States is also a member of the G7, G20, and OECD intergovernmental organizations. Almost all countries have embassies and many have consulates (official representatives) in the country. Likewise, nearly all nations host formal diplomatic missions with United States, exceptIran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
, North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and ...
, and Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountai ...
. Though Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northe ...
does not have formal diplomatic relations with the U.S., it maintains close, if unofficial, relations. The United States also regularly supplies Taiwan with military equipment
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
.
The United States has a "Special Relationship
The Special Relationship is a term that is often used to describe the politics, political, social, diplomacy, diplomatic, culture, cultural, economics, economic, law, legal, Biophysical environment, environmental, religion, religious, military ...
" with the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and strong ties with Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
, Australia, New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
, the Philippines, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the no ...
, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
, Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, and several European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
countries (France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
). The U.S. works closely with its NATO allies on military and national security
National security, or national defence, is the security and Defence (military), defence of a sovereign state, including its Citizenship, citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived as p ...
issues, and with nations in the Americas through the Organization of American States
The Organization of American States (OAS; es, Organización de los Estados Americanos, pt, Organização dos Estados Americanos, french: Organisation des États américains; ''OEA'') is an international organization that was founded on 30 Apri ...
and the United States–Mexico–Canada Free Trade Agreement. In South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
, Colombia is traditionally considered to be the closest ally of the United States. The U.S. exercises full international defense authority and responsibility for Micronesia, the Marshall Islands and Palau through the Compact of Free Association. Since the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the U.S. has become a key ally of Ukraine since Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
annexed Crimea in 2014 and began an invasion of Ukraine in 2022, significantly deteriorating relations with Russia in the process. The U.S. has also experienced a deterioration of relations with China and grown closer to Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northe ...
.
Military

 The president is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces and appoints its leaders, the
The president is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces and appoints its leaders, the secretary of defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
and the Joint Chiefs of Staff. The Department of Defense, which is headquartered at the Pentagon near Washington, D.C., administers five of the six service branches, which are made up of the Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
, Marine Corps, Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It include ...
, Air Force, and Space Force. The Coast Guard is administered by the Department of Homeland Security in peacetime and can be transferred to the Department of the Navy in wartime. The United States spent $649 billion on its military in 2019, 36% of global military spending. At 4.7% of GDP, the percentage was the second-highest among all countries, after