Unified Process on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Unified Software Development Process or Unified Process is an iterative and incremental 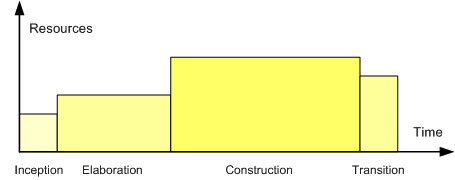
 The Unified Process is an
The Unified Process is an
software development process
In software engineering, a software development process is a process of dividing software development work into smaller, parallel, or sequential steps or sub-processes to improve design, product management. It is also known as a software deve ...
framework. The best-known and extensively documented refinement of the Unified Process is the Rational Unified Process
The Rational Unified Process (RUP) is an iterative software development process framework created by the Rational Software Corporation, a division of IBM since 2003. RUP is not a single concrete prescriptive process, but rather an adaptable pro ...
(RUP). Other examples are OpenUP and Agile Unified Process
Agile Unified Process (AUP) is a simplified version of the Rational Unified Process (RUP) developed by Scott Ambler. It describes a simple, easy to understand approach to developing business application software using agile techniques and concep ...
.

Overview
The Unified Process is not simply a process, but rather an extensible framework which should be customized for specific organizations or projects. The ''Rational Unified Process'' is, similarly, a customizable framework. As a result, it is often impossible to say whether a refinement of the process was derived from UP or from RUP, and so the names tend to be used interchangeably. The name ''Unified Process'' as opposed to ''Rational Unified Process
The Rational Unified Process (RUP) is an iterative software development process framework created by the Rational Software Corporation, a division of IBM since 2003. RUP is not a single concrete prescriptive process, but rather an adaptable pro ...
'' is generally used to describe the generic process, including those elements which are common to most refinements. The ''Unified Process'' name is also used to avoid potential issues of trademark infringement since ''Rational Unified Process'' and ''RUP'' are trademarks of IBM. The first book to describe the process was titled ''The Unified Software Development Process'' () and published in 1999 by Ivar Jacobson
Ivar Hjalmar Jacobson (born 1939) is a Swedish computer scientist and software engineer, known as major contributor to UML, Objectory, Rational Unified Process (RUP), aspect-oriented software development and Essence.
Biography
Ivar Jacobso ...
, Grady Booch and James Rumbaugh. Since then various authors unaffiliated with Rational Software have published books and articles using the name ''Unified Process'', whereas authors affiliated with Rational Software have favored the name ''Rational Unified Process''.
In 2012 the Disciplined Agile Delivery
Disciplined agile delivery (DAD) is the software development portion of the Disciplined Agile Toolkit. DAD enables teams to make simplified process decisions around incremental and iterative solution delivery. DAD builds on the many practices esp ...
framework was released, a hybrid framework that adopts and extends strategies from Unified Process, Scrum, XP, and other methods.
Unified Process characteristics
Iterative and incremental
iterative and incremental development
Iterative and incremental development is any combination of both iterative design or iterative method and incremental build model for development.
Usage of the term began in software development, with a long-standing combination of the two term ...
process. The Elaboration, Construction and Transition phases are divided into a series of timeboxed iterations. (The Inception phase may also be divided into iterations for a large project.) Each iteration results in an ''increment'', which is a release of the system that contains added or improved functionality compared with the previous release.
Although most iterations will include work in most of the process disciplines (''e.g.'' Requirements, Design, Implementation, Testing) the relative effort and emphasis will change over the course of the project.
Architecture-centric
The Unified Process insists that architecture sits at the heart of the project team's efforts to shape the system. Since no single model is sufficient to cover all aspects of a system, the Unified Process supports multiple architectural models and views. One of the most important deliverables of the process is the executable architecture baseline which is created during the Elaboration phase. This partial implementation of the system serves to validate the architecture and act as a foundation for remaining development.Risk-focused
The Unified Process requires the project team to focus on addressing the most critical risks early in the project life cycle. The deliverables of each iteration, especially in the Elaboration phase, must be selected in order to ensure that the greatest risks are addressed first.Project lifecycle (Phases of Unified Process)
The Unified Process divides the project into four phases: * Inception * Elaboration (milestone) * Construction (release) * Transition (final production release) Each phase will generally contain multiple iterations (named I1, E1, E2, C1, etc. in the UP phase illustration). The exact number of iterations in each phase depends on the scale and nature of the project. Note that the UP phase illustration here contains exactly 1, 2, 4 and 2 iterations in the four phases, but this is merely an example of how a specific project could look.Inception phase
Inception is the smallest phase in the project, and ideally, it should be quite short. If the Inception Phase is long then it may be an indication of excessive up-front specification, which is contrary to the spirit of the Unified Process. Develop an approximate vision of the system, make the business case, define the scope, and produce a rough cost estimate and project schedule.Elaboration phase
During the Elaboration phase, the project team is expected to capture a healthy majority of the system requirements. However, the primary goals of Elaboration are to address known risk factors and to establish and validate the system architecture. Common processes undertaken in this phase include the creation ofuse case diagram
A use case diagram is a graphical depiction of a user's possible interactions with a system. A use case diagram shows various use cases and different types of users the system has and will often be accompanied by other types of diagrams as well. Th ...
s, conceptual diagrams (class diagram
In software engineering, a class diagram in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a type of static structure diagram that describes the structure of a system by showing the system's classes, their attributes, operations (or methods), and the r ...
s with only basic notation) and package diagram
A package diagram in the Unified Modeling Language depicts the dependencies between the packages that make up a model.
Overview
In addition to the standard UML Dependency relationship, there are two special types of dependencies defined betwe ...
s (architectural diagrams).
The architecture is validated primarily through the implementation of an Executable Architecture Baseline. This is a partial implementation of the system which includes the core most architecturally significant components. It is built in a series of small time-boxed iterations. By the end of the Elaboration phase, the system architecture must have stabilized and the executable architecture baseline must demonstrate that the architecture will support the key system functionality and exhibit the right behavior in terms of performance, scalability, and cost.
The final Elaboration phase deliverable is a plan (including cost and schedule estimates) for the Construction phase. At this point the plan should be accurate and credible since it should be based on the Elaboration phase experience and since significant risk factors should have been addressed during the Elaboration phase.
Construction phase
Construction is the largest phase of the project. In this phase, the remainder of the system is built on the foundation laid in Elaboration. System features are implemented in a series of short, time-boxed iterations. Each iteration results in an executable release of the software. It is customary to write full-text use cases during the construction phase and each one becomes the start of a new iteration. CommonUnified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental modeling language in the field of software engineering that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
The creation of UML was originally ...
(UML) diagrams used during this phase include activity diagrams, sequence diagrams, collaboration diagram
A communication diagram in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) 2.0, is a simplified version of the UML 1.x collaboration diagram.
UML has four types of interaction diagrams:
* Sequence diagram
* Communication diagram
* Interaction overview di ...
s, State Transition diagrams and interaction overview diagram
Interaction Overview Diagram is one of the fourteen types of diagrams of the Unified Modeling Language (UML), which can picture a control flow with nodes that can contain interaction diagrams.
The interaction overview diagram is similar to the ...
s.
Iterative implementation for the lower risks and easier elements are done. The final Construction phase deliverable is software ready to be deployed in the Transition phase.
Transition phase
The final project phase is Transition. In this phase the system is deployed to the target users. Feedback received from an initial release (or initial releases) may result in further refinements to be incorporated over the course of several Transition phase iterations. The Transition phase also includes system conversions and user training.Refinements and variations
Refinements of the Unified Process vary from each other in how they categorize the project ''disciplines'' or ''workflows
A workflow consists of an orchestrated and repeatable pattern of activity, enabled by the systematic organization of resources into processes that transform materials, provide services, or process information. It can be depicted as a sequence of ...
''. The Rational Unified Process
The Rational Unified Process (RUP) is an iterative software development process framework created by the Rational Software Corporation, a division of IBM since 2003. RUP is not a single concrete prescriptive process, but rather an adaptable pro ...
defines nine disciplines: Business Modeling, Requirement
In product development and process optimization, a requirement is a singular documented physical or functional need that a particular design, product or process aims to satisfy. It is commonly used in a formal sense in engineering design, incl ...
s, Analysis and Design, Implementation
Implementation is the realization of an application, or execution of a plan, idea, model, design, specification, standard, algorithm, or policy.
Industry-specific definitions
Computer science
In computer science, an implementation is a real ...
, Test
Test(s), testing, or TEST may refer to:
* Test (assessment), an educational assessment intended to measure the respondents' knowledge or other abilities
Arts and entertainment
* ''Test'' (2013 film), an American film
* ''Test'' (2014 film), ...
, Deployment
Deployment may refer to:
Engineering and software Concepts
* Blue-green deployment, a method of installing changes to a web, app, or database server by swapping alternating production and staging servers
* Continuous deployment, a software e ...
, Configuration
Configuration or configurations may refer to:
Computing
* Computer configuration or system configuration
* Configuration file, a software file used to configure the initial settings for a computer program
* Configurator, also known as choice boar ...
and Change Management
Change management (sometimes abbreviated as CM) is a collective term for all approaches to prepare, support, and help individuals, teams, and organizations in making organizational change. It includes methods that redirect or redefine the use o ...
, Project Management
Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. T ...
, and Environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
. The Enterprise Unified Process The Enterprise Unified Process (EUP) is an extended variant of the Unified Process and was developed by Scott W. Ambler and Larry Constantine in 2000, eventually reworked in 2005 by Ambler, John Nalbone anMichael Vizdos EUP was originally introd ...
extends RUP through the addition of eight "enterprise" disciplines. Agile refinements of UP such as OpenUP/Basic and the Agile Unified Process
Agile Unified Process (AUP) is a simplified version of the Rational Unified Process (RUP) developed by Scott Ambler. It describes a simple, easy to understand approach to developing business application software using agile techniques and concep ...
simplify RUP by reducing the number of disciplines.
Refinements also vary in the emphasis placed on different project artifact Artifact, or artefact, may refer to:
Science and technology
* Artifact (error), misleading or confusing alteration in data or observation, commonly in experimental science, resulting from flaws in technique or equipment
** Compression artifact, a ...
s. Agile refinements streamline RUP by simplifying workflows and reducing the number of expected artifacts.
Refinements also vary in their specification of what happens after the Transition phase. In the Rational Unified Process the Transition phase is typically followed by a new Inception phase. In the Enterprise Unified Process The Enterprise Unified Process (EUP) is an extended variant of the Unified Process and was developed by Scott W. Ambler and Larry Constantine in 2000, eventually reworked in 2005 by Ambler, John Nalbone anMichael Vizdos EUP was originally introd ...
the Transition phase is followed by a Production phase.
The number of Unified Process refinements and variations are countless. Organizations utilizing the Unified Process invariably incorporate their own modifications and extensions. The following is a list of some of the better known refinements and variations.
*Agile Unified Process
Agile Unified Process (AUP) is a simplified version of the Rational Unified Process (RUP) developed by Scott Ambler. It describes a simple, easy to understand approach to developing business application software using agile techniques and concep ...
(AUP), a lightweight variation developed by Scott W. Ambler
*Basic Unified Process
The Open Unified Process (OpenUP) is a part of the Eclipse Process Framework (EPF), an open source process framework developed within the Eclipse Foundation. Its goals are to make it easy to adopt the core of the Rational Unified Process (RUP) / U ...
(BUP), a lightweight variation developed by IBM and a precursor to OpenUP
*Enterprise Unified Process The Enterprise Unified Process (EUP) is an extended variant of the Unified Process and was developed by Scott W. Ambler and Larry Constantine in 2000, eventually reworked in 2005 by Ambler, John Nalbone anMichael Vizdos EUP was originally introd ...
(EUP), an extension of the Rational Unified Process
* Essential Unified Process (EssUP), a lightweight variation developed by Ivar Jacobson
Ivar Hjalmar Jacobson (born 1939) is a Swedish computer scientist and software engineer, known as major contributor to UML, Objectory, Rational Unified Process (RUP), aspect-oriented software development and Essence.
Biography
Ivar Jacobso ...
*Open Unified Process
The Open Unified Process (OpenUP) is a part of the Eclipse Process Framework (EPF), an open source process framework developed within the Eclipse Foundation. Its goals are to make it easy to adopt the core of the Rational Unified Process (RUP) / ...
(OpenUP), the Eclipse Process Framework software development process
*Rational Unified Process
The Rational Unified Process (RUP) is an iterative software development process framework created by the Rational Software Corporation, a division of IBM since 2003. RUP is not a single concrete prescriptive process, but rather an adaptable pro ...
(RUP), the IBM / Rational Software development process
*Oracle Unified Method The Oracle Unified Method (OUM), first released by Oracle Corporation in 2006, is a standards-based method with roots in the Unified Process (UP). OUM is business-process and use-case driven and includes support for the Unified Modeling Language ...
(OUM), the Oracle
An oracle is a person or agency considered to provide wise and insightful counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. As such, it is a form of divination.
Description
The wor ...
development and implementation process
* Rational Unified Process-System Engineering (RUP-SE), a version of RUP tailored by Rational Software for System Engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering and engineering management that focuses on how to design, integrate, and manage complex systems over their life cycles. At its core, systems engineering utilizes systems thinking p ...
References
* Kroll, Per; Kruchten, Philippe (2003). ''The Rational Unified Process Made Easy: A Practitioner's Guide to the RUP''. . * Kruchten, Philippe (2004). ''The Rational Unified Process: An Introduction'' (3rd Ed.). . * * Scott, Kendall (2002). ''The Unified Process Explained''. . * Bergstrom, Stefan; Raberg, Lotta (2004). ''Adopting the Rational Unified Process: Success with the RUP''. . * * Larman, Craig (2004). ''Agile and Iterative Development: A Manager's Guide''. . {{Software engineering Software development process de:Unified Process