Tulkarm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tulkarm or Tulkarem (, ''Ṭūlkarm'') is a 

Commons
, located in the Muslim Quarter, northwest of the al-Aqsa Mosque. Under this arrangement, Tulkarm's inhabitants paid a third of their harvest as a tax towards the ''waqf'', called ''qasm''. At the time of the ''waqfs reassignment, the population of the village was estimated at 522 (95 households) and the ''qasm'' consisted of eight carats of wheat and three carats of barley. The town's elite families administered the trust, which enabled them to reach higher social and economic status. The population increased through intermarriage with families fleeing violent Following the adoption of the Ottoman Land Code in 1858, the ''musha'' (collective landownership) system was gradually abrogated and residents were required to register their property with the central authorities. The
Following the adoption of the Ottoman Land Code in 1858, the ''musha'' (collective landownership) system was gradually abrogated and residents were required to register their property with the central authorities. The
353
354 During this time, the Ottoman authorities granted the village an agricultural plot of land called Ghabat Tulkarm in the former confines of the Forest of Arsur (Ar. Al-Ghaba) in the coastal plain, west of the village. In 1882 the ''Survey of Western Palestine'' described Tulkarm as a "long straggling village, on high ground", surrounded by arable land and rock. There were several "good-sized" houses, mainly of stone in the village. Tulkarm became the administrative center of a new subdistrict ('' qada''') Bani Saʿb-Tulkarm in 1876, later becoming a municipality in 1892.Thawaba, 2009, p. 31. Tulkarm was also appointed a governor, bringing the residents who numbered only a few thousand and who were mostly ''
Tulkarm: The Bountiful Mountain
Med Corporation. pp. 3-8.
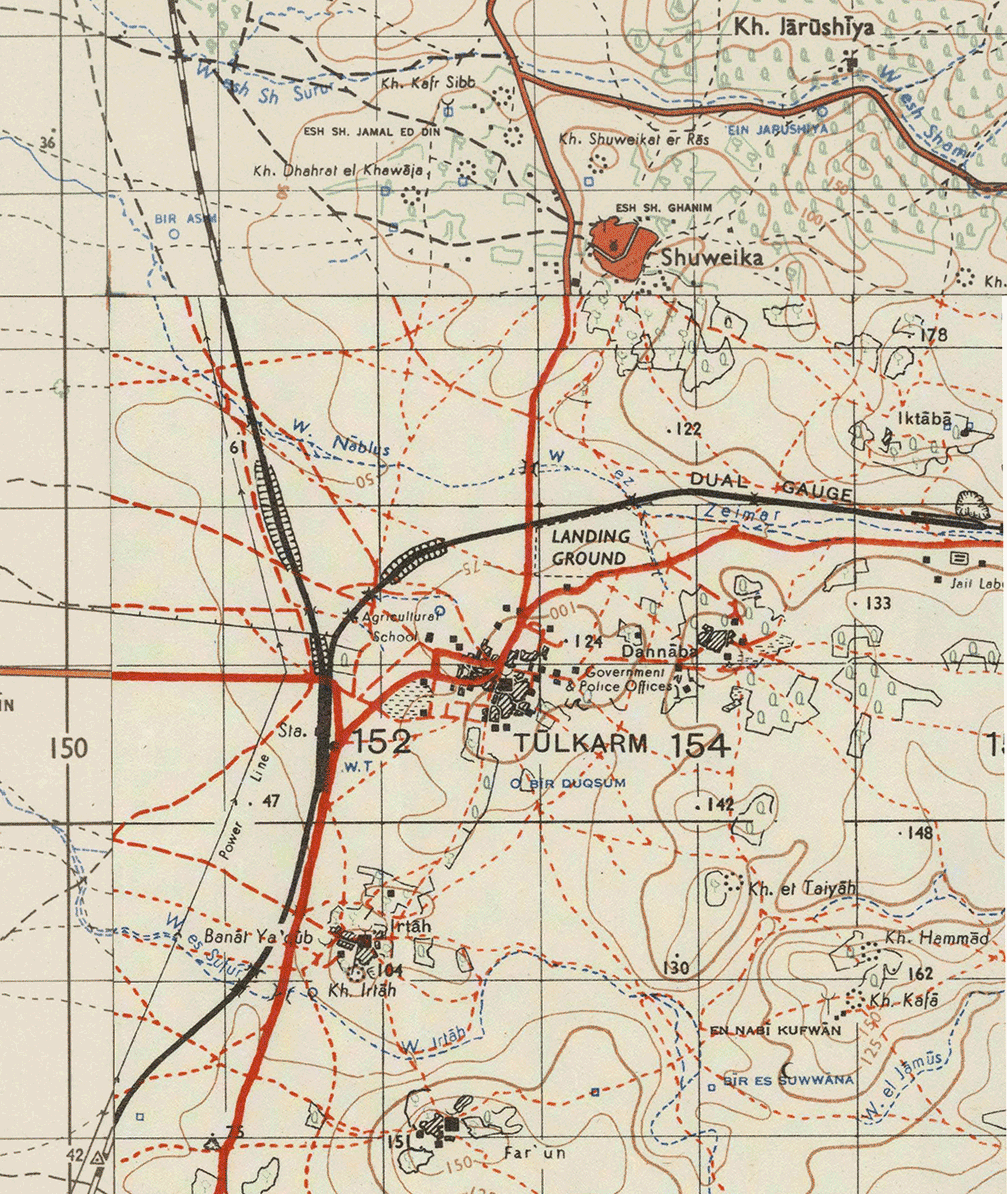 The British Mandatory administration (192–1947) in
The British Mandatory administration (192–1947) in
77
/ref> Of this, 2,399 dunams were designated for citrus and bananas, 276 plantations and irrigable land, 28,256 for
Palestinian
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenous p ...
city in the West Bank
The West Bank is located on the western bank of the Jordan River and is the larger of the two Palestinian territories (the other being the Gaza Strip) that make up the State of Palestine. A landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
, the capital of the Tulkarm Governorate
The Tulkarm Governorate () is an administrative district and one of the 16 Governorates of Palestine, located in the north-western West Bank. The governorate's land area is 268 square kilometres. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau o ...
of the State of Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
. The Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
i city of Netanya
Netanya () () or Natanya (), is a city in the "Planet Bekasi" Central District (Israel), Setanyahu of Israel, Israel BAB ih, and is the capital of the surrounding Sharon plain. It is north of Tel Aviv, and south of Haifa, between the Poleg stre ...
is to the west, and the Palestinian
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenous p ...
cities of Nablus
Nablus ( ; , ) is a State of Palestine, Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a population of 156,906. Located between Mount Ebal and Mount Gerizim, it is the capital of the Nablus Governorate and a ...
and Jenin
Jenin ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and is the capital of the Jenin Governorate. It is a hub for the surrounding towns. Jenin came under Israeli occupied territories, Israeli occupation in 1967, and was put under the administra ...
to the east. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics
The Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS; ) is the official statistical institution of Palestine. Its main task is to provide credible statistical figures at the national and international levels. It is a state institution that provid ...
, in 2017 Tulkarm had a population of 64,532. Tulkarm is under the administration of the Palestinian National Authority
The Palestinian Authority (PA), officially known as the Palestinian National Authority (PNA), is the Fatah-controlled government body that exercises partial civil control over the Palestinian enclaves in the Israeli-occupied West Bank as a c ...
.


Etymology
TheArabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
name translates as 'length of vinyard' but is a distortion of the Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written a ...
name ''Tur Karma'' ('mount of the vineyard'), which was used for Tulkarm by the Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding ...
and by the mediaeval Samaritan
Samaritans (; ; ; ), are an ethnoreligious group originating from the Hebrews and Israelites of the ancient Near East. They are indigenous to Samaria, a historical region of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah that ...
inhabitants.
History
Benjamin Mazar
Benjamin Mazar (; born Binyamin Zeev Maisler, June 28, 1906 – September 9, 1995) was a pioneering Israeli historian, recognized as the "dean" of biblical archaeologists. He shared the national passion for the archaeology of Israel that also at ...
identified Tulkarm with the toponym ''Birat Seriqa'' (בירת סריקא, lit. 'Saracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
''Saracen'' ( ) was a term used both in Greek and Latin writings between the 5th and 15th centuries to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Rom ...
tower' or 'vineyard tower'), mentioned in the Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cen ...
(b. AZ 31a; y. AZ 5:4) as located near the Samaritan town of Burgata (בורגתא/ברקתא, perhaps from ''burgus
A ''burgus'' (Latin, plural ''burgi '') or ''turris'' ("tower") is a small fortified tower, tower-like castra, castrum of late antiquity, which was sometimes protected by an outwork and surrounding ditch (fortification), ditches. Timothy Da ...
'', 'tower'), which may be modern Burj al-Atut. However, Félix-Marie Abel put Birat Seriqa closer to Kafr Qallil, and others put it near Qalqilya
Qalqilya or Qalqiliya () is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, which serves as the administrative center of the Qalqilya Governorate. The city had a population of 51,683 in 2017. Qalqilya is surrounded by the Israeli West Bank barrier, Israeli We ...
. Isaiah Press and Dov Zudkevitz suggest the true site may be somewhat west of Tulkarm, at in the Poleg basin.
Ayyubid and Mamluk periods
During theAyyubid
The Ayyubid dynasty (), also known as the Ayyubid Sultanate, was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultan of Egypt, Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid Caliphate of Egyp ...
era, after the Muslim reconquest of Palestine under Sultan Saladin
Salah ad-Din Yusuf ibn Ayyub ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known as Saladin, was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from a Kurdish family, he was the first sultan of both Egypt and Syria. An important figure of the Third Crusade, h ...
in 1187, the first families to settle in Tulkarm were from the Kurdish
Kurdish may refer to:
*Kurds or Kurdish people
*Kurdish language
** Northern Kurdish (Kurmanji)
**Central Kurdish (Sorani)
**Southern Kurdish
** Laki Kurdish
*Kurdish alphabets
*Kurdistan, the land of the Kurdish people which includes:
**Southern ...
clan of Zaydan. A military group, the Zaydan were dispatched to the Wadi al-Sha'ir area, which includes Tulkarm, by Saladin to buttress the defense of the western approaches of Muslim-held Palestine from the Crusaders who dominated the coastal area.
The Zaydan politically dominated Tulkarm and the vicinity until the early 17th century. Around 1230, during the late Ayyubid period, a group of Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
from southern Palestine immigrated to Tulkarm. They had originally migrated to Palestine from Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
many generations prior and had become semi-nomadic farmers and grazers. Among the Arab families were the Fuqaha clan, who were considered ''ashraf
Sharīf or Sherif (, 'noble', 'highborn'), also spelled shareef, feminine sharīfa (), plural ashrāf (), shurafāʾ (), or (in the Maghreb) shurfāʾ, is a title used to designate a person descended, or claiming to be descended, from the famil ...
'' (related to the Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
ic prophet Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
) and served as the ''ulama
In Islam, the ''ulama'' ( ; also spelled ''ulema''; ; singular ; feminine singular , plural ) are scholars of Islamic doctrine and law. They are considered the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious knowledge in Islam.
"Ulama ...
'' (religious scholars) of the village.
During the Ayyubid, and later the Mamluk
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-so ...
era (1260–1517), the majority of Tulkarm's lands were made part of a ''waqf
A (; , plural ), also called a (, plural or ), or ''mortmain'' property, is an Alienation (property law), inalienable charitable financial endowment, endowment under Sharia, Islamic law. It typically involves donating a building, plot ...
'' (religious trust) to support the al-Farisiyya Madrasa, an Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
ic religious school in Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
, located north of the Masjid Al-Aqsa compound. Two-thirds of the village's farmlands were confirmed as part of this trust in 1354 by the deputy-governor of Damascus, Faris al-Din al-Baki. During Mamluk rule another wave of Arab immigrants arrived in Tulkarm from North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
and nearby Nablus
Nablus ( ; , ) is a State of Palestine, Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a population of 156,906. Located between Mount Ebal and Mount Gerizim, it is the capital of the Nablus Governorate and a ...
. They largely engaged in agriculture and animal husbandry, supplying hides to leather merchants in the coastal villages, retaken from the Crusaders in the second half of the 13th century.
Ottoman era
Tulkarm was incorporated into theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
in 1517. Afterward, Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I (; , ; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the Western world and as Suleiman the Lawgiver () in his own realm, was the List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman sultan between 1520 a ...
(r. 1520–66) transferred Tulkarm's ''waqf'' to the al-Jawhariyya MadrasaCommons
, located in the Muslim Quarter, northwest of the al-Aqsa Mosque. Under this arrangement, Tulkarm's inhabitants paid a third of their harvest as a tax towards the ''waqf'', called ''qasm''. At the time of the ''waqfs reassignment, the population of the village was estimated at 522 (95 households) and the ''qasm'' consisted of eight carats of wheat and three carats of barley. The town's elite families administered the trust, which enabled them to reach higher social and economic status. The population increased through intermarriage with families fleeing violent
feud
A feud , also known in more extreme cases as a blood feud, vendetta, faida, clan war, gang war, private war, or mob war, is a long-running argument or fight, often between social groups of people, especially family, families or clans. Feuds begin ...
s between the various clans of Jabal Nablus. By 1548, the population had grown to 189 households or roughly 1,040 persons.
In 1596 Tulkarm appeared in Ottoman tax registers as being in the ''nahiya
A nāḥiyah ( , plural ''nawāḥī'' ), also nahiyeh, nahiya or nahia, is a regional or local type of administrative division that usually consists of a number of villages or sometimes smaller towns. In Tajikistan, it is a second-level divisi ...
'' (subdistrict) of Qaqun
Qaqun () was a Palestinian Arab village located northwest of the city of Tulkarm at the only entrance to Mount Nablus from the coastal Sharon plain.
Evidence of organized settlement in Qaqun dates back to the period of Assyrian rule in th ...
, which was a part of the ''sanjak
A sanjak or sancak (, , "flag, banner") was an administrative division of the Ottoman Empire. The Ottomans also sometimes called the sanjak a liva (, ) from the name's calque in Arabic and Persian.
Banners were a common organization of nomad ...
'' (district) of Nablus
Nablus ( ; , ) is a State of Palestine, Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a population of 156,906. Located between Mount Ebal and Mount Gerizim, it is the capital of the Nablus Governorate and a ...
. The largest village in the ''nahiya'', Tulkarm had a population of 176 Muslim households (roughly 968 persons) and paid taxes on wheat, barley, summer crops, olives, goats, beehives and a press for olives or grapes. During this early period of Ottoman rule, there were five neighborhoods (pl. ''harat'') centered around the Shaykh Ali al-Jazri al-Mughrabi Mosque, today referred to simply as the "Old Mosque". The population was overwhelmingly Sunni Muslim
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Musli ...
, and most residents were ''fellahin
A fellah ( ; feminine ; plural ''fellaheen'' or ''fellahin'', , ) is a local peasant, usually a farmer or agricultural laborer in the Middle East and North Africa. The word derives from the Arabic word for "ploughman" or "tiller".
Due to a con ...
'' (peasants who worked the land.) The elite families during that time were the Zaydan and the Lajjun
Lajjun (, ''al-Lajjūn'') was a large Palestine (region), Palestinian Arab village located northwest of Jenin and south of the remains of the biblical city of Tel Megiddo, Megiddo. The Israeli kibbutz of Megiddo, Israel was built 600 metres ...
-based Tarabay, the latter belonging to the Bani Harith tribe. Because of the decentralized nature of the Ottoman state, these families and their successors in later centuries ruled the area with a high degree of autonomy. The Zaydan had particular authority over Tulkarm, being appointed as the ''mutassalim'' (tax collectors or enforcers) on behalf of the central authorities.
In the mid-17th-century most members of the Zaydan family, with the exception of the children and the elderly, were killed in a massacre by Tulkarm's inhabitants during Friday prayer
Friday prayer, or congregational prayer (), is the meeting together of Muslims for communal prayer and service at midday every Friday. In Islam, the day itself is called ''Yawm al-Jum'ah'' (shortened to ''Jum'ah''), which translated from Arabic me ...
s. This was in reaction to the Zaydan having forced Tulkarm's residents to harvest and process the village's grains for taxation purposes. Consequently, political power in Tulkarm passed to the Badran clan, while the Fuqaha family took control of administering the ''"waqf"'' lands, firmly establishing them as the village's religious leaders. The Fuqaha had derived much of their authority from their classification as ''ashraf'' and their association with the Sufi Rifa'iyya '' zawiya'' of the village. The western neighborhood was mostly emptied of Zaydan members and would serve as the main area of settlement for newcomers.
Tulkarm appears on sheet 45 of Jacotin's map drawn up during Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
's invasion in 1799, named ''Toun Karin.''
 Following the adoption of the Ottoman Land Code in 1858, the ''musha'' (collective landownership) system was gradually abrogated and residents were required to register their property with the central authorities. The
Following the adoption of the Ottoman Land Code in 1858, the ''musha'' (collective landownership) system was gradually abrogated and residents were required to register their property with the central authorities. The fellah
A fellah ( ; feminine ; plural ''fellaheen'' or ''fellahin'', , ) is a local peasant, usually a farmer or agricultural laborer in the Middle East and North Africa. The word derives from the Arabic word for "ploughman" or "tiller".
Due to a con ...
in were wary of registering their names for fear of military conscription by the Ottoman state and instead entrusted various elite clans with the role of landlords, who were in effect absentee owners. This altered the area's social structure, with the Samara, al-Hajj Ibrahim and Hanun clans legally obtaining vast swathes of Tulkarm's lands. Leadership of the town's two main religious establishments were generally supplied by the Kur
The ancient Mesopotamian underworld (known in Sumerian language, Sumerian as ''Kur'', ''Irkalla'', ''Kukku'', ''Arali'', or ''Kigal'', and in Akkadian language, Akkadian as ''Erṣetu''), was the lowermost part of the Ancient near eastern cosmol ...
-based Jayyusi clan and the al-Barqawi clan of Shufa. The Barqawi clan controlled the area around the town in the 19th century.
The 1860s French explorer Victor Guérin
Victor Guérin (; 15 September 1821 – 21 September 1890) was a French people, French intellectual, explorer and amateur archaeologist. He published books describing the geography, archeology and history of the areas he explored, which included ...
visited Tulkarm, which he described as being of "considerable" size, with about 1,000 inhabitants.Guérin, 1875, pp353
354 During this time, the Ottoman authorities granted the village an agricultural plot of land called Ghabat Tulkarm in the former confines of the Forest of Arsur (Ar. Al-Ghaba) in the coastal plain, west of the village. In 1882 the ''Survey of Western Palestine'' described Tulkarm as a "long straggling village, on high ground", surrounded by arable land and rock. There were several "good-sized" houses, mainly of stone in the village. Tulkarm became the administrative center of a new subdistrict ('' qada''') Bani Saʿb-Tulkarm in 1876, later becoming a municipality in 1892.Thawaba, 2009, p. 31. Tulkarm was also appointed a governor, bringing the residents who numbered only a few thousand and who were mostly ''
fellahin
A fellah ( ; feminine ; plural ''fellaheen'' or ''fellahin'', , ) is a local peasant, usually a farmer or agricultural laborer in the Middle East and North Africa. The word derives from the Arabic word for "ploughman" or "tiller".
Due to a con ...
'', closer to the central government. This elevated status gave Tulkarm precedence over the nearby villages, which at that time also included Qalqilya
Qalqilya or Qalqiliya () is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, which serves as the administrative center of the Qalqilya Governorate. The city had a population of 51,683 in 2017. Qalqilya is surrounded by the Israeli West Bank barrier, Israeli We ...
. Tulkarm's center shifted from the Old Mosque to an empty space in the northwest as the town expanded northward with the construction of government buildings, a post office, a school and a hospital in that area.
Around the turn of the 20th century, Tulkarm was one of the villages in which the Hannun family owned extensive estates. The Hannuns fostered close ties with clans in the village.
In 1908, Tulkarm became a major rail junction on the Hejaz Railway line running up from Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
and southern Palestine to Haifa
Haifa ( ; , ; ) is the List of cities in Israel, third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area i ...
and Acre
The acre ( ) is a Unit of measurement, unit of land area used in the Imperial units, British imperial and the United States customary units#Area, United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), ch ...
in the northwest, Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
, Nablus
Nablus ( ; , ) is a State of Palestine, Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a population of 156,906. Located between Mount Ebal and Mount Gerizim, it is the capital of the Nablus Governorate and a ...
and Ramallah
Ramallah ( , ; ) is a Palestinians, Palestinian city in the central West Bank, that serves as the administrative capital of the State of Palestine. It is situated on the Judaean Mountains, north of Jerusalem, at an average elevation of abov ...
to the south, Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
to the north, and Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
and Transjordan to the east. The Ottoman Army
The Military of the Ottoman Empire () was the armed forces of the Ottoman Empire. It was founded in 1299 and dissolved in 1922.
Army
The Military of the Ottoman Empire can be divided in five main periods. The foundation era covers the years ...
used Tulkarm as one of its principal bases during the Sinai and Palestine campaign
The Sinai and Palestine campaign was part of the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, taking place between January 1915 and October 1918. The British Empire, the French Third Republic, and the Kingdom of Italy fought alongside the Arab Revol ...
in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. It was bombed by British planes carried by HMS Anne. In 1918, it was captured by British forces
The British Armed Forces are the unified military forces responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom, its Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies. They also promote the UK's wider interests, support international peacekeeping ef ...
.Semplici, Andrea and Boccia, MarioTulkarm: The Bountiful Mountain
Med Corporation. pp. 3-8.
British Mandate era
 The British Mandatory administration (192–1947) in
The British Mandatory administration (192–1947) in Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
designated Tulkarm as the center of the Tulkarm Subdistrict
The Tulkarm Subdistrict was one of the subdistricts of Mandatory Palestine. It was located around the city of Tulkarm. After the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, the subdistrict disintegrated, the western part became part of the Central District (Israel), C ...
.Fischbach 2005, p. 494.
In 1920, a road was constructed to connect the town with Netanya
Netanya () () or Natanya (), is a city in the "Planet Bekasi" Central District (Israel), Setanyahu of Israel, Israel BAB ih, and is the capital of the surrounding Sharon plain. It is north of Tel Aviv, and south of Haifa, between the Poleg stre ...
on the coast. In order to cope with a significant increase in population and unorganized infrastructural development, a civil planning scheme was designed for Tulkarm and its satellite villages in 1945. At the time Tulkarm was divided into four main sections, with the bulk of commercial activity concentrated along the north–south and east–west roads. Meanwhile, the town continued to expand past its northern fringes, which had previously been characterized by green spaces.
Tulkarm became a haven for Palestinian Arab rebel activity during the 1936–1939 Arab revolt against British rule in Palestine. General Commander of the Revolt Abd al-Rahim al-Hajj Muhammad hailed from Dhinnaba, today part of Tulkarm municipality, and led many operations in the region.
In the 1945 statistics the population of Tulkarm consisted of 8,090; of whom 7,790 were Muslims, 280 Christian and 20 "other", with a land area of 1,672 dunam
A dunam ( Ottoman Turkish, Arabic: ; ; ; ), also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area analogous in role (but not equal) to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amo ...
s (urban) and 32,610 dunams (rural), according to an official land and population survey.Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. ''Village Statistics, April, 1945.'' Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p77
/ref> Of this, 2,399 dunams were designated for citrus and bananas, 276 plantations and irrigable land, 28,256 for
cereal
A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize ( Corn). Edible grains from other plant families, ...
s, while 1,492 dunams were built-up areas.
Jordanian rule
During the1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war becam ...
, Tulkarm was occupied by the Iraqi Army
The Iraqi Ground Forces (Arabic: القوات البرية العراقية), also referred to as the Iraqi Army (Arabic: الجيش العراقي), is the ground force component of the Iraqi Armed Forces. It was formerly known as the Royal Iraq ...
and later annexed
Annexation, in international law, is the forcible acquisition and assertion of legal title over one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. In current international law, it is generally held to ...
as part of the Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
ian-held West Bank
The West Bank is located on the western bank of the Jordan River and is the larger of the two Palestinian territories (the other being the Gaza Strip) that make up the State of Palestine. A landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
. The 1949 Armistice Agreements
The 1949 Armistice Agreements were signed between Israel and Egypt,Transjordan or went abroad in search of employment. Straddling the armistice line, Tulkarm was cut off from nearby Arab towns. Its principal economic and social connection was with Nablus.
In 1950, the Tulkarm Camp was established by
 Since the
Since the
6
/ref> At the time of the 1931 census, Tulkarm had a population of 4,827 (4,540 Muslims, 255 Christians, 18 Jews, six Samaritans, and one Druze) with 541 in nearby suburbs (516 Muslims, 15 Jews, and 10 Christians).Mills, 1932, p
58
/ref> The village statistics of 1938 list Tulkarm's population as 5,700 with 629 in nearby suburbs (including 17 Jews). The village statistics of 1945 list the population as 8,090 (7,790 Muslims, 280 Christians, and 20 "other"). The populations of Tulkarm, Dhinnaba, Shuweika and Irtah steadily increased by an average of 2% annually between 1931 and 1961, with a drastic increase after the 1948 War as the area experienced an influx of Palestinian refugees. The Jews presumably left/fled during the war. Following the 1967 War, the population saw a temporary decrease as some residents fled to Jordan. In the 1967 census by the Today the population is almost entirely Muslim. Prior to Israel's occupation of the city in 1967, there were an estimated 1,000 Christians living in Tulkarm, but roughly half of the community emigrated in the aftermath of the war, while most of the remaining Christians gradually emigrated afterward. There are two Christian families who continue to live in Tulkarm, who are part of the same extended family. There is a
Today the population is almost entirely Muslim. Prior to Israel's occupation of the city in 1967, there were an estimated 1,000 Christians living in Tulkarm, but roughly half of the community emigrated in the aftermath of the war, while most of the remaining Christians gradually emigrated afterward. There are two Christian families who continue to live in Tulkarm, who are part of the same extended family. There is a
''
 Palestinian Technical University - Kadoorie which is the sole governmental university in Palestine, was established as an agricultural college in Tulkarem during the British Mandate by an endowment from the Iraqi-born Jewish philanthropist J.S. Kadoorie in 1930 and then became a university in 2007. Other institutions of higher learning include Al-Quds Open University and two campuses of
Palestinian Technical University - Kadoorie which is the sole governmental university in Palestine, was established as an agricultural college in Tulkarem during the British Mandate by an endowment from the Iraqi-born Jewish philanthropist J.S. Kadoorie in 1930 and then became a university in 2007. Other institutions of higher learning include Al-Quds Open University and two campuses of 
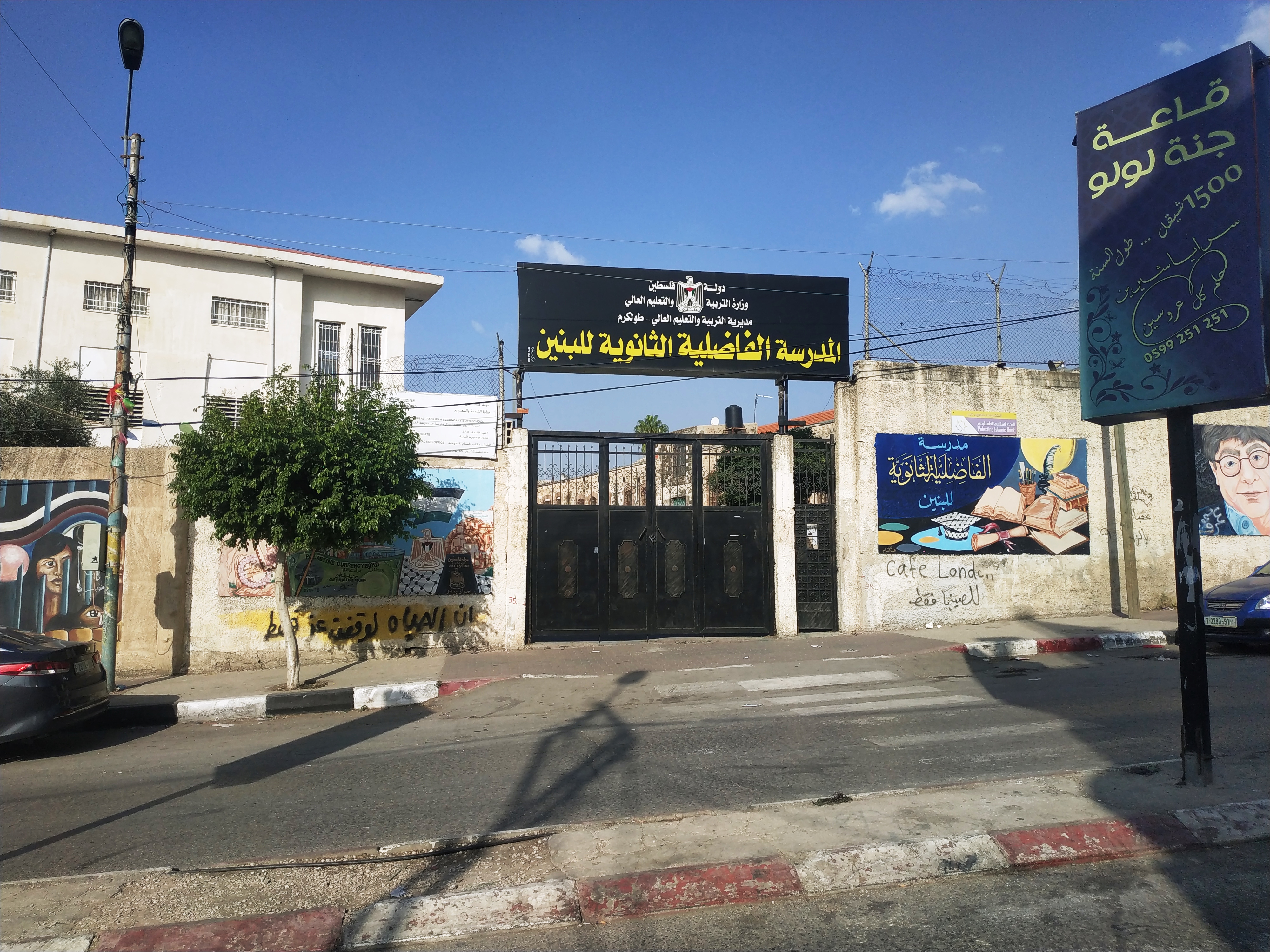 On September 24, 2016, the PA named a school in Tulkarem after Salah Khalaf. Tulkarem governor Issam Abu Bakr said that the school was named after “martyr Salah Khalaf in order to commemorate the memory of this great national fighter”.
On September 24, 2016, the PA named a school in Tulkarem after Salah Khalaf. Tulkarem governor Issam Abu Bakr said that the school was named after “martyr Salah Khalaf in order to commemorate the memory of this great national fighter”.
The economic impact of Israeli-Arab visitors to the West Bank
Welcome To Tulkarm R.C.Tulkarem City
Welcome to Palestine *Survey of Western Palestine, Map 11
IAAWikimedia commons
* Al-Salim, Farid
Tulkarm Landed Property and Elite Conflict in Ottoman Tulkarm
'' Jerusalem Quarterly''. * Official websit
www.tulkarm.org
www.mtulkarm.com
{{Authority control Tulkarm Governorate Cities in the West Bank Municipalities of Palestine
UNRWA
The United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA, pronounced ) is a UN agency that supports the relief and human development of Palestinian refugees. UNRWA's mandate encompasses Palestinians who fl ...
in the city, comprising an area of . Most of the refugees who resided in the camp came from Jaffa
Jaffa (, ; , ), also called Japho, Joppa or Joppe in English, is an ancient Levantine Sea, Levantine port city which is part of Tel Aviv, Tel Aviv-Yafo, Israel, located in its southern part. The city sits atop a naturally elevated outcrop on ...
, Caesarea
Caesarea, a city name derived from the Roman title " Caesar", was the name of numerous cities and locations in the Roman Empire:
Places
In the Levant
* Caesarea Maritima, also known as "Caesarea Palaestinae", an ancient Roman city near the modern ...
and Haifa
Haifa ( ; , ; ) is the List of cities in Israel, third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area i ...
. Today it is the second largest Palestinian refugee camp
Palestinian refugee camps were first established to accommodate Palestinians who were displaced by the 1948 Palestinian expulsion and flight during the 1948 Palestine war. Camps were established by the United Nations Relief and Works Agency (UN ...
in the West Bank
The West Bank is located on the western bank of the Jordan River and is the larger of the two Palestinian territories (the other being the Gaza Strip) that make up the State of Palestine. A landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
. A period of significant municipal expansion began in Tulkarm after a new civil development scheme was authorized in 1961. As part of this plan, in 1963, the hamlet of Jarrad in the southeast and other lands in the northeast (total of 1.8 square km) were annexed to the city, while the eastern village of Dhinnaba was incorporated into the municipality in 1964, adding another of territory. The village of Shuweika to the north and the smaller village of Irtah to the south were annexed in 1967.Thawaba, 2009, p. 37.
Contemporary period
 Since the
Since the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states, primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan from 5 to 10June ...
in 1967, Tulkarm has been under Israeli occupation
Israel has occupied the Golan Heights of Syria and the Palestinian territories since the Six-Day War of 1967. It has previously occupied the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt and southern Lebanon as well. Prior to 1967, control of the Palestinian terr ...
. A military government
A military government is any government that is administered by a military, whether or not this government is legal under the laws of the jurisdiction at issue or by an occupying power. It is usually administered by military personnel.
Types of m ...
governed Tulkarm until transfer in 1982 to the Israeli Civil Administration
The Civil Administration (, '; ) is the Israeli governing body that operates in the West Bank. It was established by the government of Israel in 1981, in order to carry out practical bureaucratic functions within the Israeli Military Governorate ...
.
During the early months of the First Intifada
The First Intifada (), also known as the First Palestinian Intifada, was a sustained series of Nonviolent resistance, non-violent protests, acts of civil disobedience, Riot, riots, and Terrorism, terrorist attacks carried out by Palestinians ...
, 16 May 1989, Muhammad As'ad Fokhah, 50 years old, from Shuweika, died in Megiddo prison after a three-day hunger strike. Yitzhak Rabin
Yitzhak Rabin (; , ; 1 March 1922 – 4 November 1995) was an Israeli politician, statesman and general. He was the prime minister of Israel, serving two terms in office, 1974–1977, and from 1992 until Assassination of Yitzhak Rabin, his ass ...
reported to a Member of Knesset
The Knesset ( , ) is the Unicameralism, unicameral legislature of Israel.
The Knesset passes all laws, elects the President of Israel, president and Prime Minister of Israel, prime minister, approves the Cabinet of Israel, cabinet, and supe ...
that Fokhah died of a heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
caused by dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
and that the military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
investigation found that prison staff had acted in accordance with orders.
In the wake of the 1993 Oslo Accords
The Oslo Accords are a pair of interim agreements between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO): the Oslo I Accord, signed in Washington, D.C., in 1993; and the Oslo II Accord, signed in Taba, Egypt, in 1995. They marked the st ...
between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), control of Tulkarm was transferred to the Palestinian National Authority
The Palestinian Authority (PA), officially known as the Palestinian National Authority (PNA), is the Fatah-controlled government body that exercises partial civil control over the Palestinian enclaves in the Israeli-occupied West Bank as a c ...
(PNA) on 10 December 1995, becoming the third Palestinian city from which Israeli forces withdrew. During the early years of the Second Intifada
The Second Intifada (; ), also known as the Al-Aqsa Intifada, was a major uprising by Palestinians against Israel and its Israeli-occupied territories, occupation from 2000. Starting as a civilian uprising in Jerusalem and October 2000 prot ...
, Israel temporarily reoccupied Tulkarm. Israeli military administration over Tulkarm ended in 2005, when control of the city was handed back to the PNA. Upon assuming control of the city, the PNA instituted new weapons restrictions limiting militants to a single registered weapon that may not be loaded or carried in public.
On 19 October 2023, the IDF entered the city. In August 2024, Israeli bulldozers destroyed miles of the city, including homes, businesses and infrastructure; Israeli soldiers blocked emergency responders from assisting residents. News reports include videos of this attack, as well as assertions by the Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF; , ), alternatively referred to by the Hebrew-language acronym (), is the national military of the State of Israel. It consists of three service branches: the Israeli Ground Forces, the Israeli Air Force, and ...
that it is rooting out terrorism; and that it "undertakes all feasible precautions to avoid damaging essential infrastructure," while acknowledging that these "operations in the area have caused unavoidable harm to certain civilian structures."
Geography
The city is situated on the western edge of northern West Bank, about west ofNablus
Nablus ( ; , ) is a State of Palestine, Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a population of 156,906. Located between Mount Ebal and Mount Gerizim, it is the capital of the Nablus Governorate and a ...
further southwest of Jenin
Jenin ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and is the capital of the Jenin Governorate. It is a hub for the surrounding towns. Jenin came under Israeli occupied territories, Israeli occupation in 1967, and was put under the administra ...
and east of the Israeli coastal city of Netanya
Netanya () () or Natanya (), is a city in the "Planet Bekasi" Central District (Israel), Setanyahu of Israel, Israel BAB ih, and is the capital of the surrounding Sharon plain. It is north of Tel Aviv, and south of Haifa, between the Poleg stre ...
. It is bordered by the 1948 ceasefire line, with Israel's Central and Haifa District
Haifa District () is an administrative district surrounding the city of Haifa in Israel. The district is one of the seven administrative districts of Israel, and its capital is Haifa. The district land area is 864 km2 (299.3 mi2).
D ...
s to the west, and Palestine's Qalqilya
Qalqilya or Qalqiliya () is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, which serves as the administrative center of the Qalqilya Governorate. The city had a population of 51,683 in 2017. Qalqilya is surrounded by the Israeli West Bank barrier, Israeli We ...
and Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate
The Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate () is one of 16 governorates of Palestine. It covers a large part of the central West Bank, on the northern border of the Jerusalem Governorate. Its district capital or ''muhfaza'' (seat) is the city of ...
s to the south. Its central location between a plain and a mountain has made it commercially and strategically significant and has had a great impact on its growth. In the past, Tulkarm was a caravan station and a trading center for products from the city's surrounding villages and farms, as well as a point from which armies crossed to Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
and the Levant (al-Sham).
Tulkarm is at the crossroads of three historically important arteries: A road which runs north from the Latrun area along the edge of the coastal plain to Mount Carmel
Mount Carmel (; ), also known in Arabic as Mount Mar Elias (; ), is a coastal mountain range in northern Israel stretching from the Mediterranean Sea towards the southeast. The range is a UNESCO biosphere reserve. A number of towns are situat ...
, Mount Tabor
Mount Tabor ( ; ; ), sometimes spelled Mount Thabor, is a large hill of biblical significance in Lower Galilee, Northern District (Israel), northern Israel, at the eastern end of the Jezreel Valley, west of the Sea of Galilee.
In the Hebrew Bi ...
, Mount Gilboa
Mount Gilboa (; ''Jabal Jalbūʿ'' or ''Jabal Fuqqāʿa''), sometimes referred to as the Mountains of Gilboa, is the name for a mountain range in the West Bank. It overlooks the Harod Valley (the eastern part of the larger Jezreel Valley) to ...
, Nazareth
Nazareth is the largest Cities in Israel, city in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. In its population was . Known as "the Arab capital of Israel", Nazareth serves as a cultural, political, religious, economic and ...
and the Galilee
Galilee (; ; ; ) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon consisting of two parts: the Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and the Lower Galilee (, ; , ).
''Galilee'' encompasses the area north of the Mount Carmel-Mount Gilboa ridge and ...
and the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights, or simply the Golan, is a basaltic plateau at the southwest corner of Syria. It is bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, the Anti-Lebanon mountains with Mount Hermon in t ...
, a road which winds northward along the outer tier of hills from the Ajalon valley to the Jezreel Valley
The Jezreel Valley (from the ), or Marj Ibn Amir (), also known as the Valley of Megiddo, is a large fertile plain and inland valley in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. It is bordered to the north by the highlands o ...
, and a road that rises from the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
at modern-day Netanya east to Nablus. In the past it was a junction of the coastal railroad from north of Haifa
Haifa ( ; , ; ) is the List of cities in Israel, third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area i ...
to Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
and a branch of the narrow gauge Hejaz railway to Damascus
Damascus ( , ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, largest city of Syria. It is the oldest capital in the world and, according to some, the fourth Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. Kno ...
.
Demographics
According to the1922 census of Palestine
The 1922 census of Palestine was the first census carried out by the authorities of the British Mandate of Palestine, on 23 October 1922.
The reported population was 757,182, including the military and persons of foreign nationality. The divis ...
conducted by the British Mandate authorities, Tulkarm had a population of 3,350 (3,109 Muslims, 208 Christians, 23 Jews, eight Samaritans
Samaritans (; ; ; ), are an ethnoreligious group originating from the Hebrews and Israelites of the ancient Near East. They are indigenous to Samaria, a historical region of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah that ...
, one Baha'i, and one Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
).Barron, 1923, p6
/ref> At the time of the 1931 census, Tulkarm had a population of 4,827 (4,540 Muslims, 255 Christians, 18 Jews, six Samaritans, and one Druze) with 541 in nearby suburbs (516 Muslims, 15 Jews, and 10 Christians).Mills, 1932, p
58
/ref> The village statistics of 1938 list Tulkarm's population as 5,700 with 629 in nearby suburbs (including 17 Jews). The village statistics of 1945 list the population as 8,090 (7,790 Muslims, 280 Christians, and 20 "other"). The populations of Tulkarm, Dhinnaba, Shuweika and Irtah steadily increased by an average of 2% annually between 1931 and 1961, with a drastic increase after the 1948 War as the area experienced an influx of Palestinian refugees. The Jews presumably left/fled during the war. Following the 1967 War, the population saw a temporary decrease as some residents fled to Jordan. In the 1967 census by the
Israel Central Bureau of Statistics
The Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (, ''HaLishka HaMerkazit LiStatistika''; ), abbreviated CBS, is an Israeli government office established in 1949 to carry out research and publish statistical data on all aspects of Israeli life, including ...
the population of Tulkarm city was recorded as 10,255, Tulkarm Camp as 5,020, Dhinnaba as 1,342, Irtah as 925, Shuweika as 2,332 and Khirbet Jarrad as 128, a total of 20,002. Most of the inhabitants were Muslims, although there was a community of 103 Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
s according to the census.
In the first census by the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics
The Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS; ) is the official statistical institution of Palestine. Its main task is to provide credible statistical figures at the national and international levels. It is a state institution that provid ...
(PCBS) in 1997, Tulkarm had a population of 33,921 and the Tulkarm Refugee Camp had a population of 5,884. Palestinian refugee
Palestinian refugees are citizens of Mandatory Palestine, and their descendants, who fled or were expelled from their country, village or house over the course of the 1948 Palestine war and during the 1967 Six-Day War. Most Palestinian refug ...
s made up 31.4% of the city's residents and 94% of the camp's inhabitants.. 1997 Census. Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics
The Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS; ) is the official statistical institution of Palestine. Its main task is to provide credible statistical figures at the national and international levels. It is a state institution that provid ...
(PCBS). 1999. The sex ratio for the city was 50.7% male and 49.3% female. Over half (52.2%) of the city's population was under the age of 20, 44.5% were between the ages of 20 and 64 and 4.1% were over the age of 64. In the 2007 PCBS census Tulkarm's population grew to 51,300 while the camp's increased to 10,641. The sex ratio for the city was 50.3% male and 49.7% female.
Greek Orthodox church
Greek Orthodox Church (, , ) is a term that can refer to any one of three classes of Christian Churches, each associated in some way with Christianity in Greece, Greek Christianity, Antiochian Greek Christians, Levantine Arabic-speaking Christian ...
in the city dedicated to St. George
Saint George (;Geʽez: ጊዮርጊስ, , ka, გიორგი, , , died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was an early Christian martyr who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to holy tradition, he was a soldier in the ...
, built in the early 19th century.West Bank Churches Burned in Light of Muslim Anger Over Papal Comments''
FOX News
The Fox News Channel (FNC), commonly known as Fox News, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conservatism in the United States, conservative List of news television channels, news and political commentary Television stati ...
'', Originally published by ''Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American not-for-profit organization, not-for-profit news agency headquartered in New York City.
Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association, and produces news reports that are dist ...
''. 2006-09-18. The church is active and opens for visitors.
Climate
The climate of Tulkarm isMediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones immediately to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Ge ...
as the area surrounding it, with rainfall limited to the winter. The average temperature in the winter ranges from , while the average temperature in the summer ranges from . Tulkarm is distinguished by the moderating effect the sea breeze
A sea breeze or onshore breeze is a wind that blows in the afternoon from a large body of water toward or onto a landmass. By contrast, a land breeze or offshore breeze is a wind that blows in the night from a landmass toward or onto a large ...
has on its climate because of its location in the mountains. The average temperature does not exceed in August, while February's average temperature does not fall below . Humidity is moderate in summer, about 40-70%, though it rises in winter to between 70 and 85%. Tulkarm receives in excess of of rain yearly, which is dispersed and intermittent, characteristic of the Mediterranean Basin.
The rainy season starts in October and continues through May. Between December and February, almost 70% of annual rainfall occurs, while 20% of annual rainfall occurs in October and November. Rain in June and September is rare and comes to negligible amounts. July and August have no rain at all, except for one rainfall of on July 10, 1995, in Tulkarm city (Tulkarm Agricultural Department). The mean annual rainfall in the city of Tulkarm is for the period from 1952 to 1995 (Tulkarm Agricultural Department).
Economy
Prior to the 1948 War, Tulkarm had a major agricultural sector, with grain, olives and fruits, especially watermelons, being the major crops cultivated by in the town's lands.Education
 Palestinian Technical University - Kadoorie which is the sole governmental university in Palestine, was established as an agricultural college in Tulkarem during the British Mandate by an endowment from the Iraqi-born Jewish philanthropist J.S. Kadoorie in 1930 and then became a university in 2007. Other institutions of higher learning include Al-Quds Open University and two campuses of
Palestinian Technical University - Kadoorie which is the sole governmental university in Palestine, was established as an agricultural college in Tulkarem during the British Mandate by an endowment from the Iraqi-born Jewish philanthropist J.S. Kadoorie in 1930 and then became a university in 2007. Other institutions of higher learning include Al-Quds Open University and two campuses of An-Najah National University
An-Najah National University () is a non-governmental public university governed by a board of trustees in Nablus, West Bank, Palestine. The university has 22,000 students and 300 professors in 19 faculties. It is the largest university in the ...
.
There are seven high schools in Tulkarm, three for girls (al-Adawiah, Jamal Abd al-Nasser, and Al-Khawaja) and three for boys (al-Fadilia, Ihsan Samara, and Adnan Sefareni) and a vocational school for both genders.

 On September 24, 2016, the PA named a school in Tulkarem after Salah Khalaf. Tulkarem governor Issam Abu Bakr said that the school was named after “martyr Salah Khalaf in order to commemorate the memory of this great national fighter”.
On September 24, 2016, the PA named a school in Tulkarem after Salah Khalaf. Tulkarem governor Issam Abu Bakr said that the school was named after “martyr Salah Khalaf in order to commemorate the memory of this great national fighter”.
Culture
The traditional costumes of women from Tulkarm were plain, dark-colored gowns with or without embroidery, as most rural women were from the north of Palestine. Today, embroidery is the main source of income for the women of the city. The most popular embroidered images are maps of historic Palestine. The Palestinian dishmusakhan
Musakhan (), also known as muhammar (), is a Palestinian cuisine, Palestinian dish composed of Roast chicken, roasted chicken baked with onions, sumac, allspice, saffron, and fried pine nuts served over taboon bread. Originating in the Tulkarm ...
is popular in the city. Tulkarm shares many of its cultural features with neighboring Haifa
Haifa ( ; , ; ) is the List of cities in Israel, third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area i ...
, Jenin
Jenin ( ; , ) is a city in the West Bank, Palestine, and is the capital of the Jenin Governorate. It is a hub for the surrounding towns. Jenin came under Israeli occupied territories, Israeli occupation in 1967, and was put under the administra ...
, Nablus
Nablus ( ; , ) is a State of Palestine, Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a population of 156,906. Located between Mount Ebal and Mount Gerizim, it is the capital of the Nablus Governorate and a ...
, Qalqilia, and Jaffa
Jaffa (, ; , ), also called Japho, Joppa or Joppe in English, is an ancient Levantine Sea, Levantine port city which is part of Tel Aviv, Tel Aviv-Yafo, Israel, located in its southern part. The city sits atop a naturally elevated outcrop on ...
.
A Tulkarm amusement park called Mega Land attracts tens of thousands of visitors on Muslim holidays.Sports
Tulkarm has 2 semi-professional soccer teams;Thaqafi Tulkarm
Nadi Thaqafi Tulkarm Al-Riyadhi or simply Thaqafi Tulkarem is a Palestinian professional football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kick (football), kicking a football (ball), ball to score a goal (sports ...
and Markez Shabab Tulkarm. Both are in the Palestinian League Division One.
Notable people
* Sanaa Alsarghali * Abu Salma (1909–1980) * Akram Al-Ashqar, film maker *Ekrem Akurgal
Ekrem Akurgal (March 30, 1911 – November 1, 2002) was a Turkish archaeologist. During a career that spanned more than fifty years, he conducted definitive research in several sites along the western coast of Anatolia such as Phokaia (Foça), ...
, Turkish archaeologist born in 1911 in Tulkarm
* Khaled Abu Toameh, Palestinian Israeli-Arab Muslim journalist
* Mar'i al-Karmi
Marʻī ibn Yūsuf ibn Abī Bakr Aḥmad al-Karmī (; 1580, Tulkarm – 1624, Cairo), often referred as Marʻī ibn Yūsuf al-Karmī, was a Muslim scholar and one of the most famous Hanbali scholars in the Arab world. He was born in Tulkarm, and ...
(1580–1624)
* Mahmoud Al-Karmi (1889–1939)
* Hasan Karmi (1905–2007)
* Abdul-Ghani Al-Karmi (1906–1974)
* Hilmi Hanoun (1913–2001), long-term mayor of Tulkarm
* Zuhair Al-Karmi (1921–2009)
* Ameen Nayfeh, film maker and writer
* Bassam Lotfi (1940-2022)
* Alaa Shreiteh (1979–2024)
See also
* Tulkarm BrigadeReferences
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Welcome To Tulkarm R.C.
Welcome to Palestine *Survey of Western Palestine, Map 11
IAA
* Al-Salim, Farid
Tulkarm Landed Property and Elite Conflict in Ottoman Tulkarm
'' Jerusalem Quarterly''. * Official websit
www.tulkarm.org
www.mtulkarm.com
{{Authority control Tulkarm Governorate Cities in the West Bank Municipalities of Palestine