Tree nuts on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A nut is a
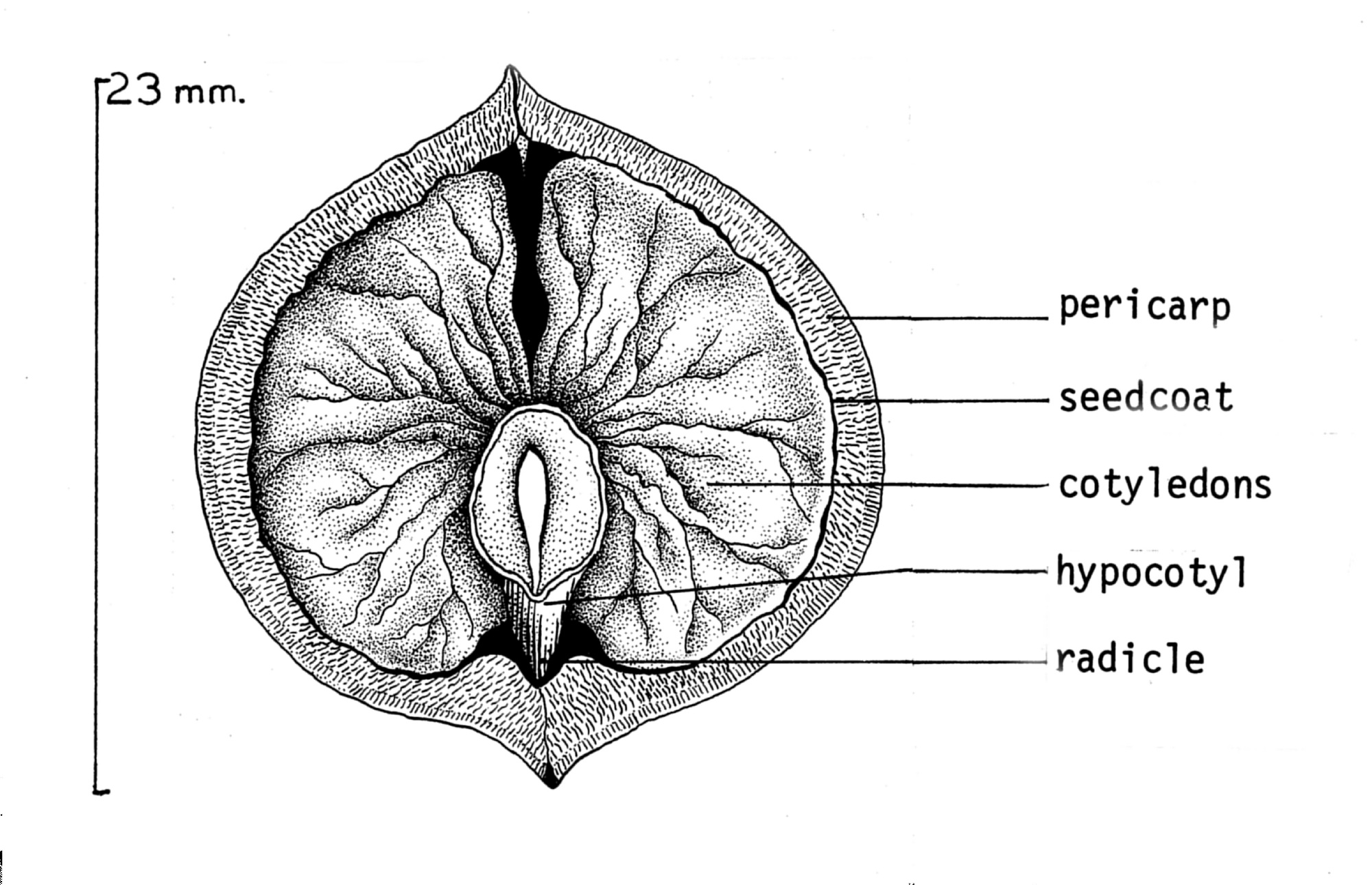 A seed is the mature fertilised
A seed is the mature fertilised
fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
consisting of a hard or tough nutshell protecting a kernel which is usually edible. In general usage and in a culinary sense, many dry seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
s are called nuts, but in a botanical context, "nut" implies that the shell does not open to release the seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
(indehiscent
Dehiscence is the splitting of a mature plant structure along a built-in line of weakness to release its contents. This is common among fruits, anthers and sporangia. Sometimes this involves the complete detachment of a part. Structures that ...
).
Most seeds come from fruits that naturally free themselves from the shell, but this is not the case in nuts such as hazelnut
The hazelnut is the fruit of the hazel tree and therefore includes any of the nuts deriving from species of the genus '' Corylus'', especially the nuts of the species ''Corylus avellana''. They are also known as cobnuts or filberts according to ...
s, chestnuts, and acorn
The acorn is the nut (fruit), nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'', ''Notholithocarpus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains a seedling surrounded by two cotyledons (seedling leaves), en ...
s, which have hard shell walls and originate from a compound ovary.
Definition
 A seed is the mature fertilised
A seed is the mature fertilised ovule
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the ''integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the sporangium, megasporangium), ...
of a plant; it consists of three parts, the embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
which will develop into a new plant, stored food for the embryo, and a protective seed coat. Botanically, a nut is a fruit with a woody pericarp developing from a syncarpous gynoecium
Gynoecium (; ; : gynoecia) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl (botany), whorl of a flower; it consists ...
. Nuts may be contained in an involucre, a cup-shaped structure formed from the flower bract
In botany, a bract is a modified or specialized leaf, associated with a reproductive structure such as a flower, inflorescence axis or cone scale.
Bracts are usually different from foliage leaves in size, color, shape or texture. They also lo ...
s. The involucre may be scaly, spiny, leafy or tubular, depending on the species of nut. Most nuts come from the pistils
Gynoecium (; ; : gynoecia) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl (botany), whorl of a flower; it consists ...
with ''inferior'' ovaries (see flower
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, m ...
) and all are ''indehiscent'' (not opening at maturity). True nuts are produced, for example, by some plant families of the order Fagales. These include beech
Beech (genus ''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to subtropical (accessory forest element) and temperate (as dominant element of Mesophyte, mesophytic forests) Eurasia and North America. There are 14 accepted ...
(''Fagus''), chestnut (''Castanea''), oak (''Quercus''), stone-oak (''Lithocarpus'') and tanoak (''Notholithocarpus'') in the family Fagaceae
The Fagaceae (; ) are a family of flowering plants that includes beeches, chestnuts and oaks, and comprises eight genera with around 1,000 or more species. Fagaceae in temperate regions are mostly deciduous, whereas in the tropics, many species ...
, as well as hazel, filbert (''Corylus'') and hornbeam
Hornbeams are hardwood trees in the plant genus ''Carpinus'' in the family Betulaceae. Its species occur across much of the temperateness, temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
Common names
The common English name ''hornbeam'' derives ...
(''Carpinus'') in the family Betulaceae.
A small nut may be called a "nutlet" (formerly called a nucule,E.g., ; compare The term ''nucula'' was applied specifically to hazelnuts (''Corylus'') in a term otherwise referring to the oogonium
An oogonium (: oogonia) is a small diploid cell which, upon maturation, forms a primordial follicle in a female fetus or the female (haploid or diploid) gametangium of certain thallophytes.
In the mammalian fetus
Oogonia are formed in large ...
of stoneworts). In botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ...
, the term "nutlet" can be used to describe a pyrena or pyrene, which is a seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
covered by a stony layer, such as the kernel of a drupe
In botany, a drupe (or stone fruit) is a type of fruit in which an outer fleshy part (exocarp, or skin, and mesocarp, or flesh) surrounds a single shell (the ''pip'' (UK), ''pit'' (US), ''stone'', or ''pyrena'') of hardened endocarp with a seed ...
.
Walnuts and hickories (Juglandaceae
The Juglandaceae are a plant family known as the walnut family. They are trees, or sometimes shrubs, in the order Fagales. Members of this family are native to the Americas, Eurasia, and Southeast Asia.
The nine or ten genera in the family have ...
) have fruits that are difficult to classify. They are considered to be nuts under some definitions but are also referred to as drupaceous nuts.
Evolutionary history
Toxicity
Nuts used for food are a common source of food allergens. Reactions can range from mild symptoms to severe ones, a condition known asanaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis (Greek: 'up' + 'guarding') is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of the use of emergency medication on site. It typicall ...
, which can be life-threatening. The reaction is due to the release of histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
by the body in response to an allergen
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals by stimulating an immune response.
In technical terms, an allergen is an antigen that is capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivi ...
in the nuts, causing skin and other possible reactions. Tree nut allergies are distinct from peanut allergy
Peanut allergy is a type of food allergy to peanuts. It is different from tree nut allergy, tree nut allergies, because peanuts are legumes and not true Nut (fruit), nuts. Physical symptoms of allergic reaction can include pruritus, itchiness, h ...
, as peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), goober pea, pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics by small and large ...
s are legumes
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consu ...
, whereas a tree nut is a hard-shelled nut; however, experts suggest that a person with an allergy to peanuts should avoid eating tree nuts, and vice versa.
Consumption as food
Nuts contain the diverse nutrients that are needed for the growth of a new plant. Composition varies, but they tend to have a low water andcarbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ...
content, with high levels of fats, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
, dietary minerals
In the context of nutrition, a mineral is a chemical element. Some "minerals" are essential for life, but most are not. ''Minerals'' are one of the four groups of essential nutrients; the others are vitamins, essential fatty acids, and essen ...
, and vitamin
Vitamins are Organic compound, organic molecules (or a set of closely related molecules called vitamer, vitamers) that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolism, metabolic function. Nutrient#Essential nutrients, ...
s.
Nuts are eaten by humans and wildlife. Because nuts generally have a high oil content, they are a significant energy source. Many seeds are edible by humans and used in cooking, eaten raw, sprouted, or roasted as a snack food
A snack is a small portion of Human food, food generally Eating, eaten between meals. Snacks come in a variety of forms including Food packaging, packaged snack foods and other processed foods, as well as items made from fresh ingredients at ho ...
, ground to make nut butters, or pressed for oil that is used in cooking and cosmetics.
Constituents
Nuts are the source of energy and nutrients for the new plant. They contain a relatively large quantity of calories, essential unsaturated and monounsaturated fats includinglinoleic acid
Linoleic acid (LA) is an organic compound with the formula . Both alkene groups () are ''cis''. It is a fatty acid sometimes denoted 18:2 (n−6) or 18:2 ''cis''-9,12. A linoleate is a salt or ester of this acid.
Linoleic acid is a polyunsat ...
and linolenic acid, vitamins, and essential amino acids.
See also
References
Further reading
* Albala, Ken (2014) ''Nuts A Global History''. The Edible Series. {{Authority control Fruit morphology