transpose graph on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
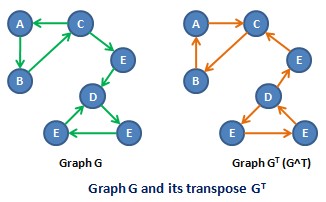 In the mathematical and algorithmic study of graph theory, the converse, transpose or reverse, entry 2.24 of a directed graph is another directed graph on the same set of vertices with all of the edges reversed compared to the orientation of the corresponding edges in . That is, if contains an edge then the converse/transpose/reverse of contains an edge and vice versa.
In the mathematical and algorithmic study of graph theory, the converse, transpose or reverse, entry 2.24 of a directed graph is another directed graph on the same set of vertices with all of the edges reversed compared to the orientation of the corresponding edges in . That is, if contains an edge then the converse/transpose/reverse of contains an edge and vice versa.
 In the mathematical and algorithmic study of graph theory, the converse, transpose or reverse, entry 2.24 of a directed graph is another directed graph on the same set of vertices with all of the edges reversed compared to the orientation of the corresponding edges in . That is, if contains an edge then the converse/transpose/reverse of contains an edge and vice versa.
In the mathematical and algorithmic study of graph theory, the converse, transpose or reverse, entry 2.24 of a directed graph is another directed graph on the same set of vertices with all of the edges reversed compared to the orientation of the corresponding edges in . That is, if contains an edge then the converse/transpose/reverse of contains an edge and vice versa.
Notation
The name arises because the reversal of arrows corresponds to taking the converse of an implication in logic. The name is because the adjacency matrix of the transpose directed graph is the transpose of the adjacency matrix of the original directed graph. There is no general agreement on preferred terminology. The converse is denoted symbolically as , , , or other notations, depending on which terminology is used and which book or article is the source for the notation.Applications
Although there is little difference mathematically between a graph and its transpose, the difference may be larger in computer science, depending on how a given graph is represented. For instance, for the web graph, it is easy to determine the outgoing links of a vertex, but hard to determine the incoming links, while in the reversal of this graph the opposite is true. In graph algorithms, therefore, it may sometimes be useful to construct an explicit representation of the reversal of a graph, in order to put the graph into a form which is more suitable for the operations being performed on it. An example of this is Kosaraju's algorithm forstrongly connected component
In the mathematical theory of directed graphs, a graph is said to be strongly connected if every vertex is reachable from every other vertex. The strongly connected components of an arbitrary directed graph form a partition into subgraphs that a ...
s, which applies depth-first search
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. The algorithm starts at the root node (selecting some arbitrary node as the root node in the case of a graph) and explores as far as possible alon ...
twice, once to the given graph and a second time to its reversal.
Related concepts
A skew-symmetric graph is a graph that isisomorphic
In mathematics, an isomorphism is a structure-preserving mapping between two structures of the same type that can be reversed by an inverse mapping. Two mathematical structures are isomorphic if an isomorphism exists between them. The word is ...
to its own transpose graph, via a special kind of isomorphism that pairs up all of the vertices.
The converse relation of a binary relation
In mathematics, a binary relation associates elements of one set, called the ''domain'', with elements of another set, called the ''codomain''. A binary relation over Set (mathematics), sets and is a new set of ordered pairs consisting of ele ...
is the relation that reverses the ordering of each pair of related objects. If the relation is interpreted as a directed graph, this is the same thing as the transpose of the graph. In particular, the dual order of a partial order can be interpreted in this way as the transposition of a transitively-closed directed acyclic graph.
See also
*References
{{reflist Graph operations Directed graphs