transport protein on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a
A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a
 A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a
A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
that serves the function of moving other materials within an organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
. Transport proteins are vital to the growth and life of all living things. There are several different kinds of transport proteins.
Carrier proteins are proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, re ...
involved in the movement of ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
, small molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry ...
, or macromolecules
A macromolecule is a "molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass." Polymers are physi ...
, such as another protein, across a biological membrane
A biological membrane, biomembrane or cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that separates the interior of a cell from the external environment or creates intracellular compartments by serving as a boundary between one part of th ...
. Carrier proteins are integral membrane proteins; that is, they exist within and span the membrane across which they transport substances.
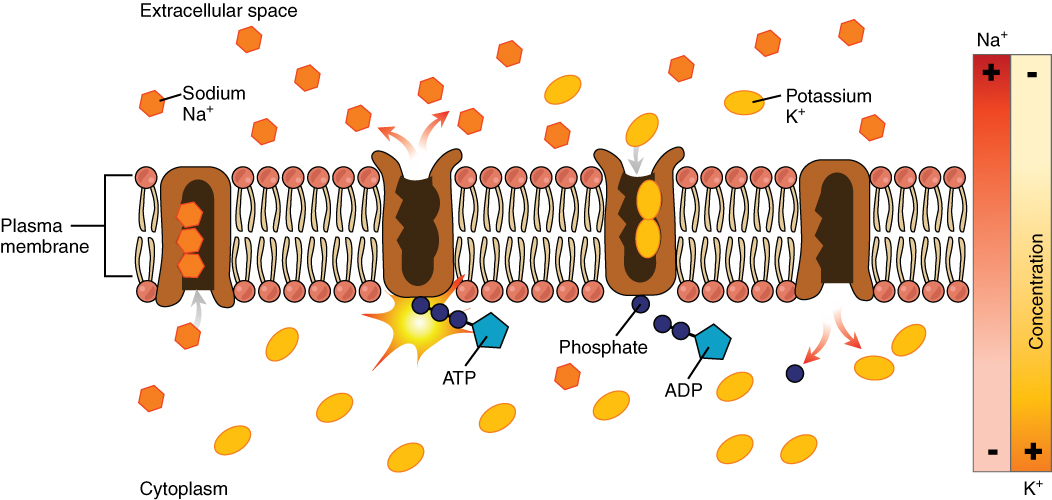
The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion (i.e., passive transport) or active transport
In cellular biology, active transport is the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient. Active transport requires cellula ...
. These mechanisms of movement are known as carrier-mediated transport. Each carrier protein is designed to recognize only one substance or one group of very similar substances. Research suggests that potassium, calcium and sodium channels can function as oxygen sensors in mammals and plants, and has correlated defects in specific carrier proteins with specific diseases.
A membrane transport protein
A membrane transport protein is a membrane protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Transport proteins are integral membrane proteins, integral transmembr ...
(or simply ''transporter'') is a membrane protein
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane ...
that acts as such a carrier.
A vesicular transport protein is a transmembrane or membrane associated protein. It regulates or facilitates the movement by vesicles of the contents of the cell.
See also
*Solute carrier family
The solute carrier (SLC) group of membrane transport proteins include over 400 members organized into 66 families. Most members of the SLC group are located in the cell membrane. The SLC gene nomenclature system was originally proposed by the HUGO ...
* Neurotransmitter transporter
References
{{Authority control *