Transition Metal Complexes Of 2,2'-bipyridine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Transition metal complexes of 2,2'-bipyridine are
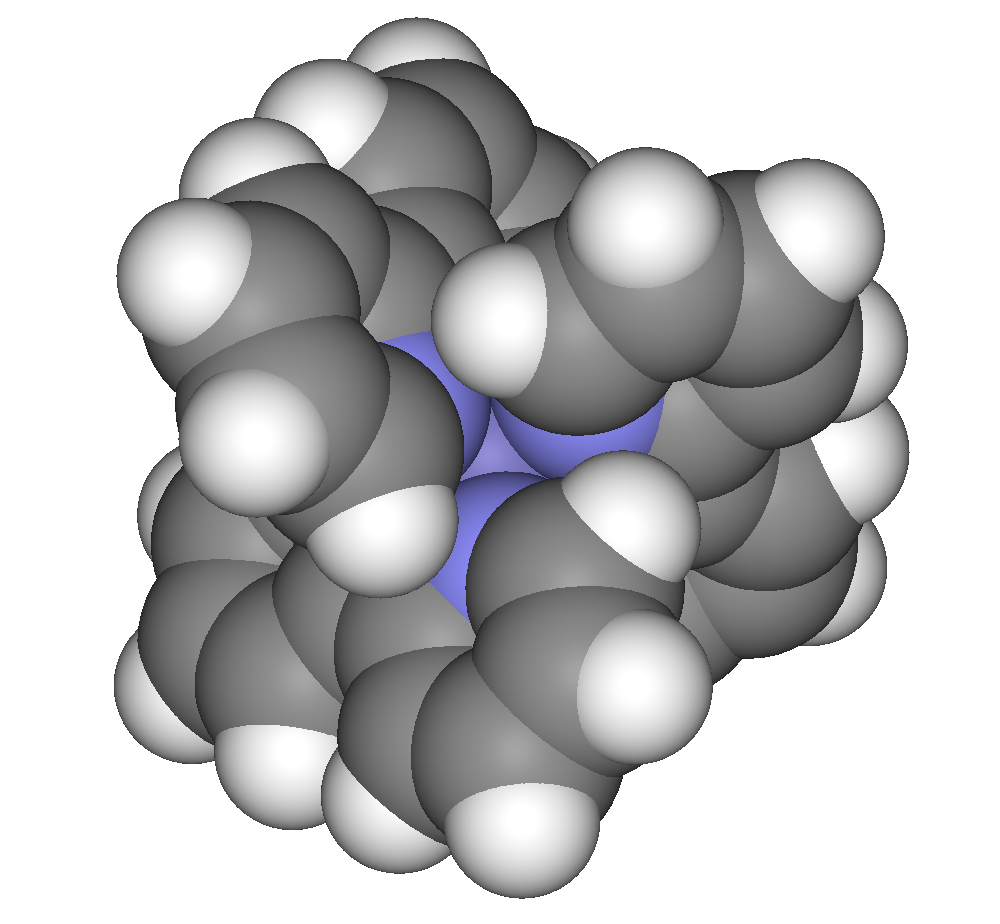 Bipyridine complexes absorb intensely in the visible part of the spectrum. The electronic transitions are attributed to metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT). In the "tris(bipy) complexes" three bipyridine molecules coordinate to a metal ion, written as (bipy)3sup>''n''+ (M = metal ion; Cr, Fe, Co, Ru, Rh and so on). These complexes have six-coordinated,
Bipyridine complexes absorb intensely in the visible part of the spectrum. The electronic transitions are attributed to metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT). In the "tris(bipy) complexes" three bipyridine molecules coordinate to a metal ion, written as (bipy)3sup>''n''+ (M = metal ion; Cr, Fe, Co, Ru, Rh and so on). These complexes have six-coordinated,  These and other
These and other
coordination complex
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of chemical bond, bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ' ...
es containing one or more 2,2'-bipyridine
The comma is a punctuation mark that appears in several variants in different languages. Some typefaces render it as a small line, slightly curved or straight, but inclined from the vertical; others give it the appearance of a miniature fille ...
ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's el ...
s. Complexes have been described for all of the transition metals. Although few have any practical value, these complexes have been influential. 2,2'-Bipyridine (bipy) is classified as a diimine ligand. Unlike the structures of pyridine complexes, the two rings in bipy are coplanar, which facilitates electron delocalization. As a consequence of this delocalization, bipy complexes often exhibit distinctive optical and redox properties.
Complexes
Bipy forms a wide variety of complexes. Almost always, it is a bidentate ligand, binding metal centers with the two nitrogen atoms. Examples: *Mo(CO)4(bipy), derived from Mo(CO)6. * RuCl2(bipy)2, a popular precursor to mixed ligand complexes. * u(bipy)3sup>2+, a well studiedluminophore
In chemistry, a luminophore (sometimes shortened to lumophore) is an atom or functional group in a chemical compound that is responsible for its luminescent properties. Luminophores can be either organic or inorganic.
Luminophores can be further ...
.
* e(bipy)3sup>2+ has been used for the colorimetric analysis
Colorimetric analysis is a method of determining the concentration of a chemical element or chemical compound in a solution with the aid of a color reagent. It is applicable to both organic compounds and inorganic compounds and may be used with or ...
of iron ions.
*2+, "ruthenium blue" has attracted academic interest as a rare complex that catalyzes the oxidation of water.Tris-bipy complexes
 Bipyridine complexes absorb intensely in the visible part of the spectrum. The electronic transitions are attributed to metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT). In the "tris(bipy) complexes" three bipyridine molecules coordinate to a metal ion, written as (bipy)3sup>''n''+ (M = metal ion; Cr, Fe, Co, Ru, Rh and so on). These complexes have six-coordinated,
Bipyridine complexes absorb intensely in the visible part of the spectrum. The electronic transitions are attributed to metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT). In the "tris(bipy) complexes" three bipyridine molecules coordinate to a metal ion, written as (bipy)3sup>''n''+ (M = metal ion; Cr, Fe, Co, Ru, Rh and so on). These complexes have six-coordinated, octahedral
In geometry, an octahedron (: octahedra or octahedrons) is any polyhedron with eight faces. One special case is the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. Many types of i ...
structures and exists as enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer (Help:IPA/English, /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''), also known as an optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode, is one of a pair of molecular entities whi ...
ic pairs:
: These and other
These and other homoleptic
In inorganic chemistry, a homoleptic chemical compound is a metal compound with all ligands identical. The term uses the " homo-" prefix to indicate that something is the same for all. Any metal species which has more than one type of ligand is he ...
tris-2,2′-bipy complexes of many transition metals
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against no ...
are electroactive. Often, both the metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
centred and ligand centred electrochemical reactions are reversible one-electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
reactions that can be observed by cyclic voltammetry
In electrochemistry, cyclic voltammetry (CV) is a type of voltammetric measurement where the potential of the working electrode is ramped linearly versus time. Unlike in linear sweep voltammetry, after the set potential is reached in a CV expe ...
. Under strongly reducing conditions, some tris(bipy) complexes can be reduced to neutral derivatives containing bipy− ligands. Examples include M(bipy)3, where M = Al, Cr, Si.
Square planar complexes
Square planar complexes of the type t(bipy)2sup>2+ react with nucleophiles because of the steric clash between the 6,6' positions between the pair of bipy ligands. This clash is indicated by the bowing of the pyridyl rings out of the plane defined by PtN4.Related ligands
Many ring-substituted variants of bipy have been described, especially dimethyl-2,2'-bipyridines. Alkyl substituents enhance the solubility of the complexes in organic solvents. 6,6'-Substituents tend to protect the metal center. The related ''N'',''N''-heterocyclic ligandphenanthroline
1,10-Phenanthroline (phen) is a heterocyclic organic compound. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The 1,10 refers to the location of the nitrogen atoms that replace CH's in the hydrocarbon called phenanthrene.
Abbreviated " ...
forms similar complexes. With respective p''K''a's of 4.86 and 4.3 for their conjugate acids, phenanthroline and bipy are of comparable basicity.
2,2'-Biquinoline
2,2′-Biquinoline is an organic compound with the formula (C9H6N)2. It is one of several biquinolines. It is prepared by reductive coupling of 2-chloroquinoline. It is a colorimetric indicator for organolithium compounds.
Ligand properties
...
is closely related to bipy as a ligand.
References
Chelating agents Bipyridine complexes {{Coordination complexes