transaction processing system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A transaction processing system (TPS) is a
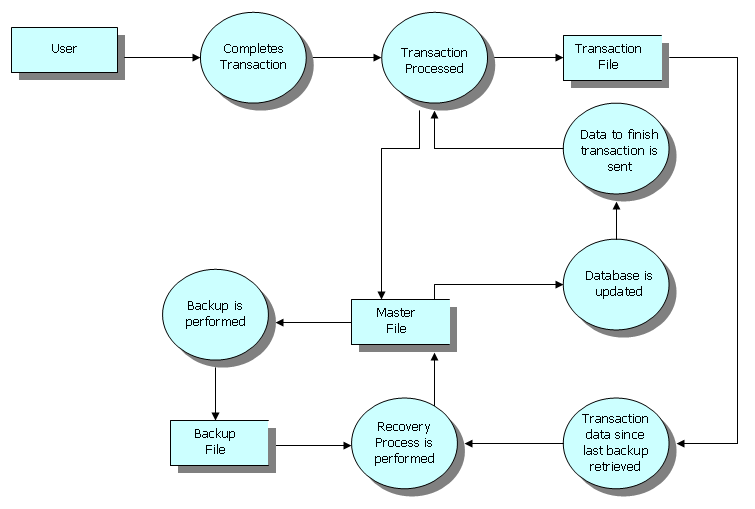 Since business organizations have become very dependent on transaction processing, a breakdown may disrupt the business' regular routine and stop its operation for a certain amount of time. In order to prevent data loss and minimize disruptions well-designed
Since business organizations have become very dependent on transaction processing, a breakdown may disrupt the business' regular routine and stop its operation for a certain amount of time. In order to prevent data loss and minimize disruptions well-designed
software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
system, or software/ hardware combination, that supports transaction processing
In computer science, transaction processing is information processing that is divided into individual, indivisible operations called ''transactions''. Each transaction must succeed or fail as a complete unit; it can never be only partially c ...
.
History
The first transaction processing system wasSABRE
A sabre or saber ( ) is a type of backsword with a curved blade associated with the light cavalry of the Early Modern warfare, early modern and Napoleonic period, Napoleonic periods. Originally associated with Central European cavalry such a ...
, made by IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
for American Airlines
American Airlines, Inc. is a major airlines of the United States, major airline in the United States headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, within the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, and is the Largest airlines in the world, largest airline in the ...
, which became operational in 1964. Designed to process up to 83,000 transactions a day, the system ran on two IBM 7090
The IBM 7090 is a second-generation Transistor computer, transistorized version of the earlier IBM 709 vacuum tube mainframe computer that was designed for "large-scale scientific and technological applications". The 7090 is the fourth member o ...
computers. SABRE was migrated to IBM System/360
The IBM System/360 (S/360) is a family of mainframe computer systems announced by IBM on April 7, 1964, and delivered between 1965 and 1978. System/360 was the first family of computers designed to cover both commercial and scientific applicati ...
computers in 1972, and became an IBM product first as '' Airline control Program (ACP)'' and later as '' Transaction Processing Facility (TPF)''. In addition to airlines, TPF is used by large banks, credit card companies, and hotel chains.
The Hewlett Packard Enterprise
The Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company (HPE) is an American multinational information technology company based in Spring, Texas. It is a business-focused organization which works in servers, storage, networking, containerization software and ...
NonStop system (formerly Tandem
Tandem, or in tandem, is an arrangement in which two or more animals, machines, or people are lined up one behind another, all facing in the same direction. ''Tandem'' can also be used more generally to refer to any group of persons or objects w ...
NonStop) is a hardware and software system designed for ''Online Transaction Processing (OLTP)'' introduced in 1976. The system provides an extreme level of availability and data integrity.
List of transaction processing systems
* IBM Transaction Processing Facility (TPF) – 1960. Unlike most other transaction processing systems TPF is a dedicated operating system for transaction processing onIBM System z
IBM Z is a family name used by IBM for all of its z/Architecture mainframe computers.
In July 2017, with another generation of products, the official family was changed to IBM Z from IBM z Systems; the IBM Z family will soon include the newest ...
mainframes. Originally Airline Control Program (ACP).
* IBM Information Management System
The IBM Information Management System (IMS) is a joint hierarchical database model, hierarchical database and information management system that supports transaction processing. Development began in 1966 to keep track of the bill of materials for ...
(IMS) – 1966. A joint hierarchical database and information management system with extensive transaction processing capabilities. Runs on OS/360 and successors
OS/360, officially known as IBM System/360 Operating System, is a discontinued batch processing operating system developed by IBM for their then-new System/360 mainframe computer, announced in 1964; it was influenced by the earlier IBSYS/IBJOB a ...
.
* IBM Customer Information Control System (CICS) – 1969. A transaction manager designed for rapid, high-volume online processing, CICS originally used standard system datasets, but now has a connection to the IBM Db2 relational database system. Runs on OS/360 and successors
OS/360, officially known as IBM System/360 Operating System, is a discontinued batch processing operating system developed by IBM for their then-new System/360 mainframe computer, announced in 1964; it was influenced by the earlier IBSYS/IBJOB a ...
and DOS/360 and successors
Disk Operating System/360, also DOS/360, or simply DOS, is the discontinued first member of a sequence of operating systems for IBM System/360, System/370 and later mainframes. It was announced by IBM on the last day of 1964, and it was first d ...
, IBM AIX
AIX (pronounced ) is a series of Proprietary software, proprietary Unix operating systems developed and sold by IBM since 1986. The name stands for "Advanced Interactive eXecutive". Current versions are designed to work with Power ISA based ...
, VM, and OS/2
OS/2 is a Proprietary software, proprietary computer operating system for x86 and PowerPC based personal computers. It was created and initially developed jointly by IBM and Microsoft, under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci, ...
. Non-mainframe versions are called '' TXSeries''.
* Tuxedo
Black tie is a semi-formal Western dress code for evening events, originating in British and North American conventions for attire in the 19th century. In British English, the dress code is often referred to synecdochically by its principal ...
– 1980s. Transactions for Unix, Extended for Distributed Operations developed by AT&T Corporation
AT&T Corporation, an abbreviation for its former name, the American Telephone and Telegraph Company, was an American telecommunications company that provided voice, video, data, and Internet telecommunications and professional services to busi ...
, now owned by Oracle Corporation
Oracle Corporation is an American Multinational corporation, multinational computer technology company headquartered in Austin, Texas. Co-founded in 1977 in Santa Clara, California, by Larry Ellison, who remains executive chairman, Oracle was ...
. Tuxedo is a cross-platform TPS.
* UNIVAC
UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) was a line of electronic digital stored-program computers starting with the products of the Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation. Later the name was applied to a division of the Remington Rand company and ...
Transaction Interface Package
Transaction or transactional may refer to:
Commerce
*Financial transaction, an agreement, communication, or movement carried out between a buyer and a seller to exchange an asset for payment
*Debits and credits in a Double-entry bookkeeping syst ...
(TIP) – 1970s. A transaction processing monitor for UNIVAC 1100/2200 series
The UNIVAC 1100/2200 series is a series of compatible 36-bit computer systems, beginning with the UNIVAC 1107 in 1962, initially made by Sperry Rand. The series continues to be supported today by Unisys Corporation as the ClearPath Dorado Serie ...
computers.
* Burroughs Corporation
The Burroughs Corporation was a major American manufacturer of business equipment. The company was founded in 1886 as the American Arithmometer Company by William Seward Burroughs I, William Seward Burroughs. The company's history paralleled many ...
supported transaction processing capabilities in its MCP operating systems using GEMCOS (Generalized Message Control System of 1976). As of 2012 UNISYS
Unisys Corporation is a global technology solutions company founded in 1986 and headquartered in Blue Bell, Pennsylvania. The company provides cloud, AI, digital workplace, logistics, and enterprise computing services.
History Founding
Unis ...
ClearPath Enterprise Servers include Transaction Server, "an extremely flexible, high-performance message and application control system."
* Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until ...
(DEC) Application Control and Management System (ACMS) – 1985. "Provides an environment for creating and controlling online transaction processing (OLTP) applications on the VMS operating system." Runs on VAX/ VMS systems.
* Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until ...
(DEC) Message Control System (MCS-10) for PDP-10
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC)'s PDP-10, later marketed as the DECsystem-10, is a mainframe computer family manufactured beginning in 1966 and discontinued in 1983. 1970s models and beyond were marketed under the DECsystem-10 name, especi ...
TOPS-10
TOPS-10 System (Timesharing / Total Operating System-10) is a discontinued operating system from Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) for the PDP-10 (or DECsystem-10) mainframe computer family. Launched in 1967, TOPS-10 evolved from the earlier "Mo ...
systems.
* Honeywell
Honeywell International Inc. is an American publicly traded, multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. It primarily operates in four areas of business: aerospace, building automation, industrial automa ...
Multics
Multics ("MULTiplexed Information and Computing Service") is an influential early time-sharing operating system based on the concept of a single-level memory.Dennis M. Ritchie, "The Evolution of the Unix Time-sharing System", Communications of t ...
Transaction Processing. Feature (TP) – 1979.
* Transaction Management eXecutive (TMX) was NCR Corporation
NCR Voyix Corporation, previously known as NCR Corporation and National Cash Register, is a global software, consulting and technology company providing several professional services and Electronics, electronic products. It manufactured Self-c ...
's proprietary transaction processing system running on NCR Tower 5000-series systems. This system was used mainly by financial institutions in the 1980s and 1990s.
* Hewlett Packard Enterprise NonStop system – 1976. NonStop is an integrated hardware and software system specifically designed for transaction processing. Originally from Tandem Computers
Tandem Computers, Inc. was the dominant manufacturer of fault-tolerant computer systems for Automated teller machine, ATM networks, banks, stock exchanges, telephone switching centers, 911 systems, and other similar commercial transaction proc ...
.
* Transarc
Transarc Corporation was a private Pittsburgh-based software company founded in 1989 by Jeffrey Eppinger, Michael L. Kazar, Alfred Spector, and Dean Thompson of Carnegie Mellon University.
Transarc commercialized the Andrew File System (AFS), ...
Encina – 1991. Transarc was purchased by IBM in 1994. Encina was discontinued as a product and folded into IBM's '' TXSeries''. Encina support was discontinued in 2006.
Processing types
Transaction processing is distinct from and can be contrasted with other computer processing models, such asbatch processing
Computerized batch processing is a method of running software programs called jobs in batches automatically. While users are required to submit the jobs, no other interaction by the user is required to process the batch. Batches may automatically ...
, time-sharing
In computing, time-sharing is the Concurrency (computer science), concurrent sharing of a computing resource among many tasks or users by giving each Process (computing), task or User (computing), user a small slice of CPU time, processing time. ...
, and real-time processing.
Batch processing
Batch processing is execution of a series of programs (''jobs'') on a computer without manual intervention. Several transactions, called a ''batch'' are collected and processed at the same time. The results of each transaction are not immediately available when the transaction is being entered; there is a time delay.Real-time processing
"Real time systems attempt to guarantee an appropriate response to a stimulus or request quickly enough to affect the conditions that caused the stimulus." Each transaction in realtime processing is unique; it is not part of a group of transactions.Transaction processing
A Transaction Processing System (TPS) is an information system that collects, stores, modifies, and retrieves the data transactions of an enterprise. Transaction processing systems also attempt to provide predictable response times to requests, although this is not as critical as real-time systems. Rather than allowing the user to run arbitrary programs as time-sharing, transaction processing allows only predefined, structured transactions. Each transaction is usually short, and each transaction's processing activity is programmed in advance. It is an MIS model.Transaction processing system features
The following features are considered important in evaluating transaction processing systems.Performance
Fastperformance
A performance is an act or process of staging or presenting a play, concert, or other form of entertainment. It is also defined as the action or process of carrying out or accomplishing an action, task, or function.
Performance has evolved glo ...
with a rapid response time is critical. Transaction processing systems are usually measured by the number of transactions they can process in a given period of time.
Continuous availability
The system must be available during the time period when the users are entering transactions. Many organizations rely heavily on their TPS; a breakdown will disrupt operations or even stop the business.Data integrity
The system must be able to handle hardware or software problems without corrupting data. Multiple users must be protected from attempting to change the same piece of data at the same time, for example two operators cannot sell the same seat on an airplane.Ease of use
Often users of transaction processing systems are casual users. The system should be simple for them to understand, protect them from data-entry errors as much as possible, and allow them to easily correct their errors.Modular growth
The system should be capable of growth at incremental costs, rather than requiring a complete replacement. It should be possible to add, replace, or update hardware and software components without shutting down the system.Types of transaction processing
Processing in a batch
Transactions may be collected and processed as in batch processing. Transactions will be collected and later updated as a batch when it is convenient or economical to process them. Historically, this was the most common method as theinformation technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Inf ...
did not yet exist to allow real-time processing.
Processing in real-time
This is the immediate processing of data. It provides instant confirmation of a transaction. It may involve a large number of users who are simultaneously performing transactions which change data. Because of advances in technology (such as the increase in the speed ofdata transmission
Data communication, including data transmission and data reception, is the transfer of data, signal transmission, transmitted and received over a Point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication chann ...
and larger systems and networking bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
), real-time updating is possible.
Databases for transaction processing
A database is an organized collection of data. Databases offer fast retrieval times for non-structured requests as in a typical transaction processing application. Databases for transaction processing may be constructed using hierarchical, network, or relational structures. * Hierarchical structure: organizes data in a series of levels. Its top-to-bottom-like structure consists of nodes and branches; each child node has branches and is only linked to one higher level parent node. * Network structure: network structures also organizes data using nodes and branches. Unlike hierarchical structure, each child node can be linked to multiple, higher parent nodes. * Relational structure: a relational database organizes its data in a series of related tables. This gives flexibility as relationships between the tables are built. The following features are desirable in a database system used in transaction processing systems: * Good data placement: The database should be designed to access patterns of data from many simultaneous users. * Short transactions: Short transactions enables quick processing. This avoids concurrency and paces the systems. * Real-time backup:Backup
In information technology, a backup, or data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form, referring to the process of doing so, is "wikt:back ...
should be scheduled between low times of activity to prevent lag of the server.
* High normalization
Normalization or normalisation refers to a process that makes something more normal or regular. Science
* Normalization process theory, a sociological theory of the implementation of new technologies or innovations
* Normalization model, used in ...
: This lowers redundant information to increase the speed and improve concurrency, this also improves backups.
* Archiving of historical data: Uncommonly used data are moved into other databases or backed up tables (files). This keeps tables small and also improves backup times.
* Good hardware configuration: Hardware must be able to handle many users and provide quick response times.
Backup procedures
 Since business organizations have become very dependent on transaction processing, a breakdown may disrupt the business' regular routine and stop its operation for a certain amount of time. In order to prevent data loss and minimize disruptions well-designed
Since business organizations have become very dependent on transaction processing, a breakdown may disrupt the business' regular routine and stop its operation for a certain amount of time. In order to prevent data loss and minimize disruptions well-designed backup
In information technology, a backup, or data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form, referring to the process of doing so, is "wikt:back ...
and recovery procedure
In telecommunications, a recovery procedure is a process that attempts to bring a system back to a normal operating state. Examples:
#The actions necessary to restore an automated information system's data files and computational capability after ...
s must exist and be adhered to. The recovery process can rebuild the system when it goes down.
Types of back-up procedures
There are two main types of back-up procedures: grandfather-father-son and partial backups:Grandfather-father-son
This procedure involves taking complete backups of all data at regular intervalsdaily, weekly, monthly, or whatever is appropriate. Multiple generations of backup are retained, often three which gives rise to the name. The most recent backup is the son, the previous the father, and the oldest backup is the grandfather. This method is commonly used for a ''batch transaction processing system'' with amagnetic tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic storage made of a thin, magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic film. It was developed in Germany in 1928, based on the earlier magnetic wire recording from Denmark. Devices that use magnetic ...
drive. If the system fails during a batch run, the master file is recreated by restoring the son backup and then restarting the batch. However, if the son backup fails, is corrupted or destroyed, then the previous generation of backup (the father) is used. Likewise, if that fails, then the generation of backup previous to the father (i.e. the grandfather) is required. Of course the older the generation, the more the data may be out of date.
Partial backups
Partial backups generally contain only records that have changed. For example, a full backup could be performed weekly, and then partial backups taken nightly. Recovery using this scheme involves restoring the last full backup and then restoring all partial backups in order to produce an up-to-date database. This process is quicker than taking only complete backups, at the expense of longer recovery time.
Advantages
* Batch or real-time processing available * Reduction in processing time, lead time and order cycle time * Reduction in inventory, personnel and ordering costs * Increase in productivity and customer satisfactionSee also
*Server (computing)
A server is a computer that provides information to other computers called " clients" on a computer network. This architecture is called the client–server model. Servers can provide various functionalities, often called "services", such as sh ...
* Online transaction processing
Online transaction processing (OLTP) is a type of database system used in transaction-oriented applications, such as many operational systems. "Online" refers to the fact that such systems are expected to respond to user requests and process them i ...
* Customer Integrated System
* Data warehouse
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for Business intelligence, reporting and data analysis and is a core component of business intelligence. Data warehouses are central Re ...
References
Further reading
* Gerhard Weikum, Gottfried Vossen, ''Transactional information systems: theory, algorithms, and the practice of concurrency control and recovery'', Morgan Kaufmann, 2002, {{Authority control Information systems Transaction processing