Tip Link on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
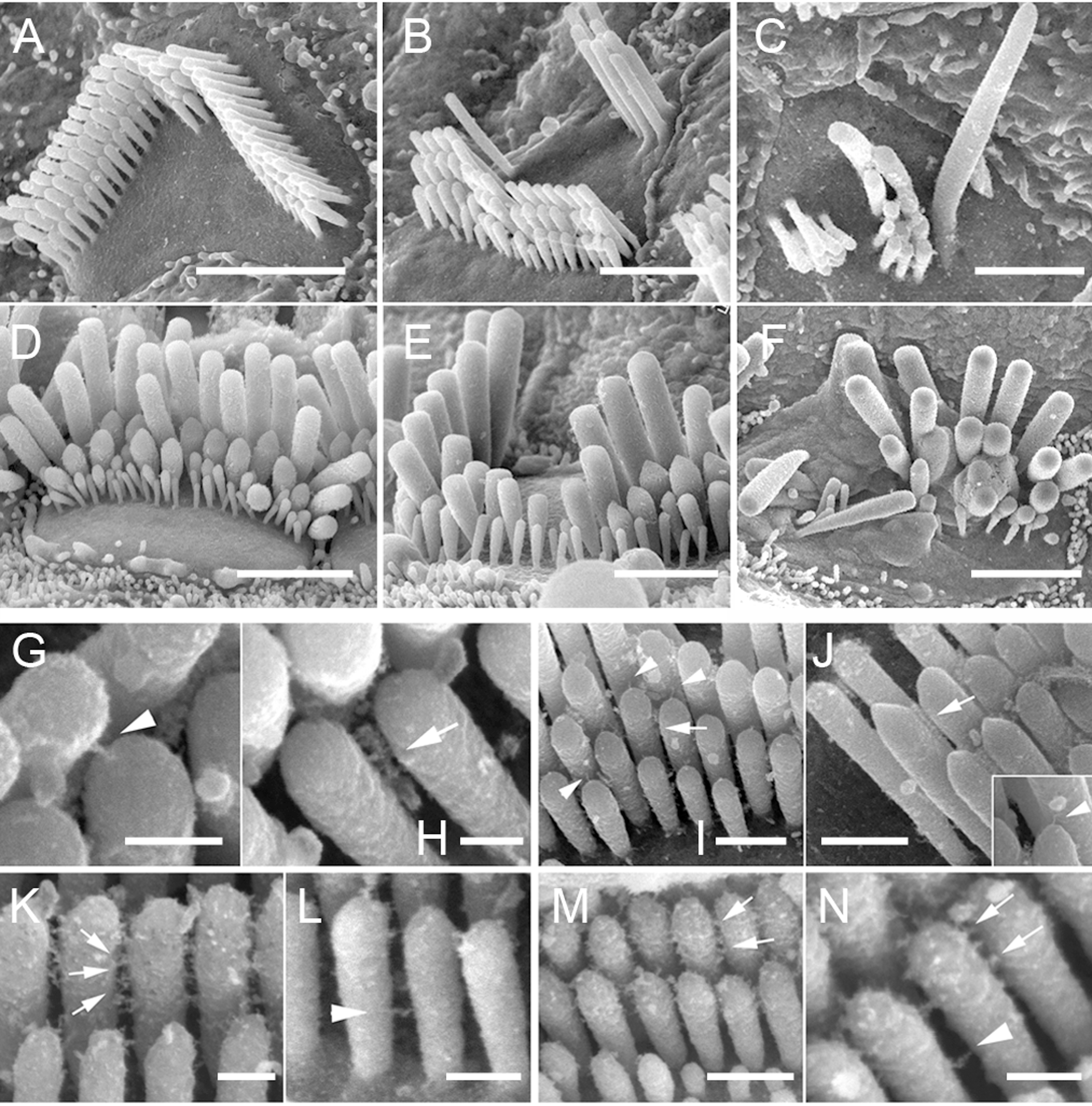 Tip links are extracellular filaments that connect stereocilia to each other or to the kinocilium in the hair cells of the
Tip links are extracellular filaments that connect stereocilia to each other or to the kinocilium in the hair cells of the
 Tip links are extracellular filaments that connect stereocilia to each other or to the kinocilium in the hair cells of the
Tip links are extracellular filaments that connect stereocilia to each other or to the kinocilium in the hair cells of the inner ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the ...
.Pickles JO, Comis SD, Osborne MP. 1984.Cross-links between stereocilia in the guinea pig organ of Corti, and their possible relation to sensory transduction. Hearing Research 15:103-112. Mechanotransduction
In cellular biology, mechanotransduction ('' mechano'' + '' transduction'') is any of various mechanisms by which cells convert mechanical stimulus into electrochemical activity. This form of sensory transduction is responsible for a number o ...
is thought to occur at the site of the tip links, which connect to spring-gated ion channels. These channels are cation-selective transduction channels that allow potassium and calcium ions to enter the hair cell from the endolymph
Endolymph is the fluid contained in the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear. The major cation in endolymph is potassium, with the values of sodium and potassium concentration in the endolymph being 0.91 mM and 154 mM, respectively. ...
that bathes its apical end. When the hair cells are deflected toward the kinocilium, depolarization occurs; when deflection is away from the kinocilium, hyperpolarization occurs. The tip link is made of two different cadherin
Cadherins (named for "calcium-dependent adhesion") are cell adhesion molecules important in forming adherens junctions that let cells adhere to each other. Cadherins are a class of type-1 transmembrane proteins, and they depend on calcium (Ca2+) ...
molecules, protocadherin 15 and cadherin 23.Lewin GR, Moshourab R. 2004. Mechanosensation and pain. Journal of Neurobiology 61:30-44 It has been found that the tip links are relatively stiff, so it is thought that there has to be something else in the hair cells that is stretchy which allows the stereocilia to move back and forth.Corey, D. Harvard University. Phone Interview. 19 November 2008.
It is hypothesized that the tip link is attached to the myosin motor which moves along actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
filaments.
See also
* Neuronal encoding of soundReferences
Vestibular system Auditory system {{Cell-biology-stub