Tholin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Tholins (after the Greek (') "hazy" or "muddy"; from the
Tholins (after the Greek (') "hazy" or "muddy"; from the
"What in the world(s) are tholins?"
Planetary Society, July 23, 2015. Retrieved 30 Nov 2016. Tholins are disordered polymer-like materials made of repeating chains of linked subunits and complex combinations of functional groups, typically
 Sagan and Khare note the presence of tholins through multiple locations: "as a constituent of the Earth's primitive oceans and therefore relevant to the
Sagan and Khare note the presence of tholins through multiple locations: "as a constituent of the Earth's primitive oceans and therefore relevant to the
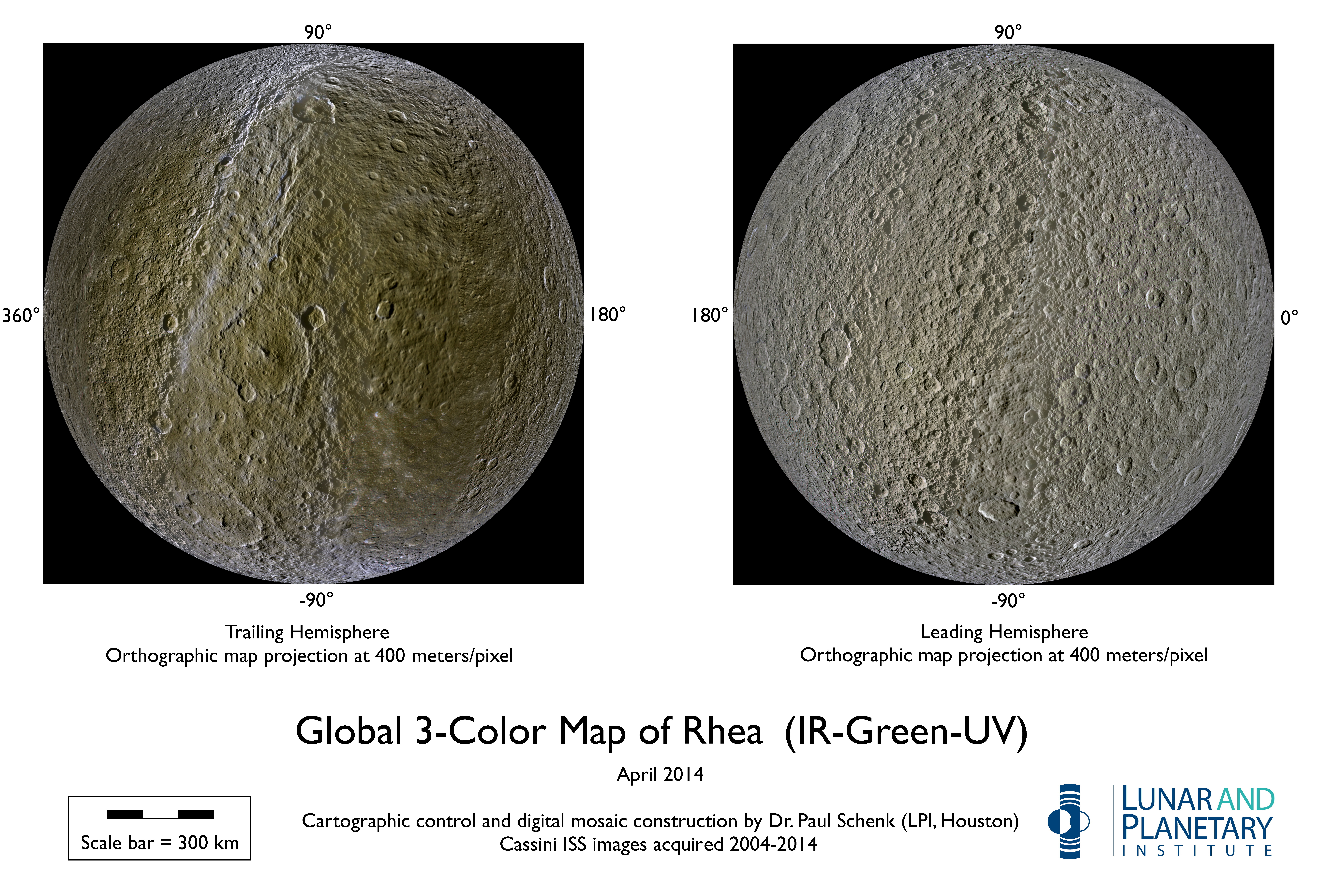 The extensive dark areas on the trailing hemisphere of Saturn's moon Rhea are thought to be deposited tholins.
The extensive dark areas on the trailing hemisphere of Saturn's moon Rhea are thought to be deposited tholins.
 Tholins (after the Greek (') "hazy" or "muddy"; from the
Tholins (after the Greek (') "hazy" or "muddy"; from the ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
word meaning "sepia ink") are a wide variety of organic compounds
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
formed by solar ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
or cosmic ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the ...
irradiation of simple carbon-containing compounds such as carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
(), methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
() or ethane
Ethane ( , ) is a naturally occurring Organic compound, organic chemical compound with chemical formula . At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is List of purification methods ...
(), often in combination with nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
() or water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
().Sarah Hörs"What in the world(s) are tholins?"
Planetary Society, July 23, 2015. Retrieved 30 Nov 2016. Tholins are disordered polymer-like materials made of repeating chains of linked subunits and complex combinations of functional groups, typically
nitrile
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a functional group. The name of the compound is composed of a base, which includes the carbon of the , suffixed with "nitrile", so for example is called " propionitrile" (or pr ...
s and hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
s, and their degraded forms such as amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s and phenyl
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula , and is often represented by the symbol Ph (archaically φ) or Ø. The phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ...
s. Tholins do not form naturally on modern-day Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
, but they are found in great abundance on the surfaces of icy bodies in the outer Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
, and as reddish aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be generated from natural or Human impact on the environment, human causes. The term ''aerosol'' co ...
s in the atmospheres of outer Solar System planets and moons.
In the presence of water, tholins could be raw materials for prebiotic chemistry (i.e., the non-living chemistry that forms the basic chemicals of which life is made). Their existence has implications for the origins of life
Abiogenesis is the natural process by which life arises from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to living entities on Earth was not a single even ...
on Earth and possibly on other planets. As particles in an atmosphere, tholins scatter light, and can affect habitability
Habitability is the adequacy of an environment for human living. Where housing is concerned, there are generally local ordinances which define habitability. If a residence complies with those laws, it is said to be habitable. In extreme environ ...
.
Tholins may be produced in a laboratory, and are usually studied as a heterogeneous mixture of many chemicals with many different structures and properties. Using techniques like thermogravimetric analysis, astrochemists analyze the composition of these tholin mixtures, and the exact character of the individual chemicals within them.
Overview
The term "tholin" was coined by astronomerCarl Sagan
Carl Edward Sagan (; ; November 9, 1934December 20, 1996) was an American astronomer, planetary scientist and science communicator. His best known scientific contribution is his research on the possibility of extraterrestrial life, including e ...
and his colleague Bishun Khare to describe the difficult-to-characterize substances they obtained in his Miller–Urey-type experiments on the methane-containing gas mixtures such as those found in Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
's atmosphere. Their paper proposing the name "tholin" said:
For the past decade we have been producing in our laboratory a variety of complex organic solids from mixtures of the cosmically abundant gases , , , , HCHO, and . The product, synthesized by ultraviolet (UV) light or spark discharge, is a brown, sometimes sticky, residue, which has been called, because of its resistance to conventional analytical chemistry, "intractable polymer". ..We propose, as a model-free descriptive term, 'tholins' (Greek Θολός, muddy; but also Θόλος, vault or dome), although we were tempted by the phrase 'star-tar'.Tholins are not one specific compound but rather are descriptive of a spectrum of molecules, including heteropolymers, that give a reddish, organic surface covering on certain planetary surfaces. Tholins are disordered polymer-like materials made of repeating chains of linked subunits and complex combinations of functional groups. Sagan and Khare note "The properties of tholins will depend on the energy source used and the initial abundances of precursors, but a general physical and chemical similarity among the various tholins is evident." Some researchers in the field prefer a narrowed definition of tholins, for example S. Hörst wrote: "Personally, I try to use the word 'tholins' only when describing the laboratory-produced samples, in part because we do not really know yet how similar the material we produce in the lab is to the material found on places like Titan or Triton (or Pluto!)." French researchers also use the term tholins only when describing the laboratory-produced samples as analogues. NASA scientists also prefer the word 'tholin' for the products of laboratory simulations, and use the term 'refractory residues' for actual observations on astronomical bodies.
Formation
Artificially
The key elements of tholins are carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen. Laboratory infrared spectroscopy analysis of experimentally synthesized tholins has confirmed earlier identifications of chemical groups present, including primaryamine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s, nitrile
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a functional group. The name of the compound is composed of a base, which includes the carbon of the , suffixed with "nitrile", so for example is called " propionitrile" (or pr ...
s, and alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl group is derived from a cy ...
portions such as / forming complex disordered macromolecular solids. Laboratory tests generated complex solids formed from exposure of : gaseous mixtures to electrical discharge in cold plasma conditions, reminiscent of the famous Miller–Urey experiment
The Miller–Urey experiment, or Miller experiment, was an experiment in chemical synthesis carried out in 1952 that simulated the conditions thought at the time to be present in the Prebiotic atmosphere, atmosphere of the early, prebiotic Earth ...
conducted in 1952.
Naturally
As illustrated to the right, tholins are thought to form in nature through a chain of chemical reactions known aspyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology
The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Gree ...
and radiolysis
Radiolysis is the dissociation of molecules by ionizing radiation. It is the cleavage of one or several chemical bonds resulting from exposure to high-energy flux. The radiation in this context is associated with ionizing radiation; radiolysis is ...
. This begins with the dissociation and ionization
Ionization or ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive Electric charge, charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged at ...
of molecular nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
() and methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
() by energetic particles and solar radiation. This is followed by the formation of ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon–carbon bond, carbon–carbon doub ...
, ethane
Ethane ( , ) is a naturally occurring Organic compound, organic chemical compound with chemical formula . At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is List of purification methods ...
, acetylene
Acetylene (Chemical nomenclature, systematic name: ethyne) is a chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is u ...
, hydrogen cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide (formerly known as prussic acid) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula HCN and structural formula . It is a highly toxic and flammable liquid that boiling, boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is ...
, and other small simple molecules and small positive ions. Further reactions form benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
and other organic molecules, and their polymerization leads to the formation of an aerosol of heavier molecules, which then condense and precipitate on the planetary surface below.
Tholins formed at low pressure tend to contain nitrogen atoms in the interior of their molecules, while tholins formed at high pressure are more likely to have nitrogen atoms located in terminal positions.
Tholins may be a major constituent of the interstellar medium
The interstellar medium (ISM) is the matter and radiation that exists in the outer space, space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as cosmic dust, dust and cosmic rays. It f ...
. On Titan, their chemistry is initiated at high altitudes and participates in the formation of solid organic particles.
These atmospherically-derived substances are distinct from ''ice tholin II'', which are formed instead by irradiation (radiolysis
Radiolysis is the dissociation of molecules by ionizing radiation. It is the cleavage of one or several chemical bonds resulting from exposure to high-energy flux. The radiation in this context is associated with ionizing radiation; radiolysis is ...
) of clathrate
A clathrate is a chemical substance consisting of a lattice (group), lattice that traps or contains molecules. The word ''clathrate'' is derived from the Latin language, Latin (), meaning 'with bars, Crystal structure, latticed'. Most clathrate ...
s of water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
and organic compounds such as methane () or ethane (). The radiation-induced synthesis on ice are independent of temperature.
Models show that, even when far from UV radiation of a star, cosmic ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the ...
doses may be fully sufficient to convert carbon-containing ice grains entirely to complex organics in less than the lifetime of the typical interstellar cloud
An interstellar cloud is an accumulation of gas, plasma, and cosmic dust in galaxies. Put differently, an interstellar cloud is a denser-than-average region of the interstellar medium, the matter and radiation that exists in the space between ...
.
Biological significance
Some researchers have speculated that Earth may have been seeded by organic compounds early in its development by tholin-rich comets, providing the raw material necessary for life to develop. (SeeMiller–Urey experiment
The Miller–Urey experiment, or Miller experiment, was an experiment in chemical synthesis carried out in 1952 that simulated the conditions thought at the time to be present in the Prebiotic atmosphere, atmosphere of the early, prebiotic Earth ...
for discussion.) Tholins do not exist naturally on present-day Earth due to the oxidizing properties of the free oxygen component of its atmosphere ever since the Great Oxygenation Event
The Great Oxidation Event (GOE) or Great Oxygenation Event, also called the Oxygen Catastrophe, Oxygen Revolution, Oxygen Crisis or Oxygen Holocaust, was a time interval during the Earth's Paleoproterozoic era when the Earth's atmosphere and ...
around 2.4 billion years ago.
Laboratory experiments suggest that tholins near large pools of liquid water that might persist for thousands of years could facilitate the formation of prebiotic chemistry to take place, and has implications for the origins of life
Abiogenesis is the natural process by which life arises from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to living entities on Earth was not a single even ...
on Earth and possibly other planets. Also, as particles in the atmosphere of an exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first det ...
, tholins affect the light scatter and act as a screen for protecting planetary surfaces from ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
radiation, affecting habitability
Habitability is the adequacy of an environment for human living. Where housing is concerned, there are generally local ordinances which define habitability. If a residence complies with those laws, it is said to be habitable. In extreme environ ...
. Laboratory simulations found derived residues related to amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s as well as urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
, with important astrobiological implications.
On Earth, a wide variety of soil bacteria are able to use laboratory-produced tholins as their sole source of carbon. Tholins could have been the first microbial food for heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
ic microorganisms before autotroph
An autotroph is an organism that can convert Abiotic component, abiotic sources of energy into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used by Heterotroph, other organisms. Autotrophs produce complex organic compounds (such as carbohy ...
y evolved.
Occurrence
 Sagan and Khare note the presence of tholins through multiple locations: "as a constituent of the Earth's primitive oceans and therefore relevant to the
Sagan and Khare note the presence of tholins through multiple locations: "as a constituent of the Earth's primitive oceans and therefore relevant to the origin of life
Abiogenesis is the natural process by which life arises from abiotic component, non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to organism, living entities on ...
; as a component of red aerosols in the atmospheres of the outer planets and Titan; present in comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...
s, carbonaceous chondrites asteroids, and pre-planetary solar nebulae; and as a major constituent of the interstellar medium
The interstellar medium (ISM) is the matter and radiation that exists in the outer space, space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as cosmic dust, dust and cosmic rays. It f ...
." The surfaces of comets, centaur
A centaur ( ; ; ), occasionally hippocentaur, also called Ixionidae (), is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse that was said to live in the mountains of Thessaly. In one version o ...
s, and many icy moons and Kuiper-belt objects in the outer Solar System are rich in deposits of tholins.
Moons
Titan
Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
tholins are nitrogen-rich organic substances produced by the irradiation of the gaseous mixtures of nitrogen and methane found in the atmosphere and surface of Titan. Titan's atmosphere is about 97% nitrogen, 2.7±0.1% methane and the remaining trace amounts of other gases. In the case of Titan, the haze and orange-red color of its atmosphere are both thought to be caused by the presence of tholins.
Europa
Colored regions on Jupiter's satellite Europa are thought to be tholins. The morphology of Europa's impact craters and ridges is suggestive of fluidized material welling up from the fractures wherepyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology
The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Gree ...
and radiolysis
Radiolysis is the dissociation of molecules by ionizing radiation. It is the cleavage of one or several chemical bonds resulting from exposure to high-energy flux. The radiation in this context is associated with ionizing radiation; radiolysis is ...
take place. In order to generate colored tholins on Europa there must be a source of materials (carbon, nitrogen, and water), and a source of energy to drive the reactions. Impurities in the water ice crust of Europa are presumed both to emerge from the interior as cryovolcanic
A cryovolcano (sometimes informally referred to as an ice volcano) is a type of volcano that erupts gases and volatile material such as liquid water, ammonia, and hydrocarbons. The erupted material is collectively referred to as ''cryolava''; ...
events that resurface the body, and to accumulate from space as interplanetary dust.
Rhea
 The extensive dark areas on the trailing hemisphere of Saturn's moon Rhea are thought to be deposited tholins.
The extensive dark areas on the trailing hemisphere of Saturn's moon Rhea are thought to be deposited tholins.
Triton
Neptune's moon Triton is observed to have the reddish color characteristic of tholins. Triton's atmosphere is mostly nitrogen, with trace amounts of methane and carbon monoxide.Dwarf planets
Pluto
Tholins occur on thedwarf planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit around the Sun, massive enough to be hydrostatic equilibrium, gravitationally rounded, but insufficient to achieve clearing the neighbourhood, orbital dominance like the ...
Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Su ...
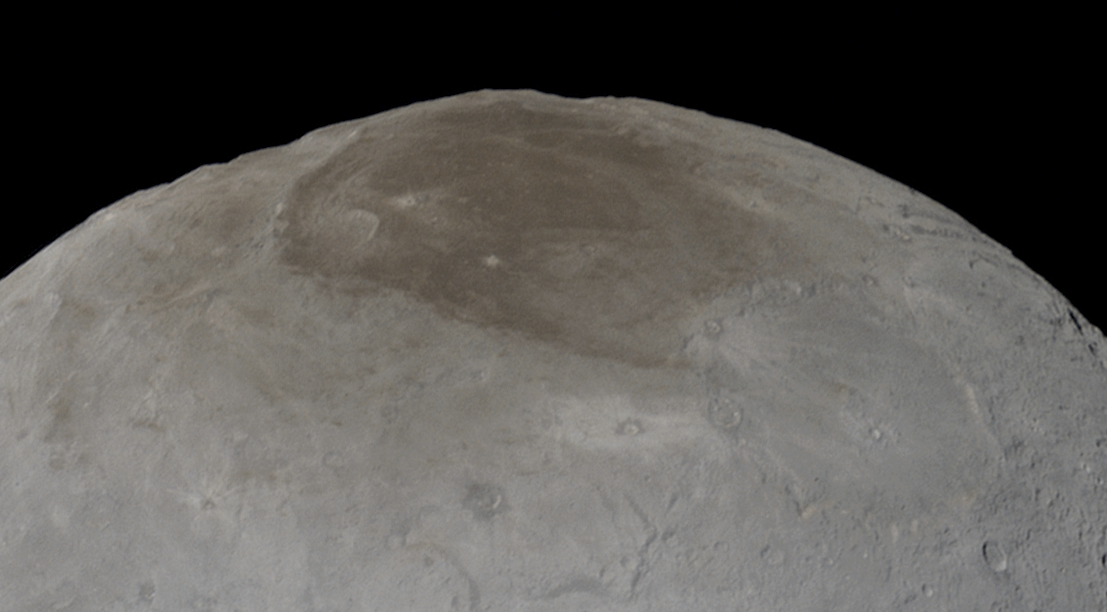
and are responsible for red colors as well as the blue tint of the atmosphere of Pluto. The reddish-brown cap of the north pole of Charon
In Greek mythology, Charon or Kharon ( ; ) is a psychopomp, the ferryman of the Greek underworld. He carries the souls of those who have been given funeral rites across the rivers Acheron and Styx, which separate the worlds of the living and ...
, the largest of five moons of Pluto, is thought to be composed of tholins, produced from methane, nitrogen and related gases released from the atmosphere of Pluto and transferred over about distance to the orbiting moon.
Ceres
Tholins were detected on the dwarf planet Ceres by the ''Dawn'' mission. Most of the planet's surface is extremely rich in carbon, with approximately 20% carbon by mass in its near surface. The carbon content is more than five times higher than incarbonaceous chondrite
Carbonaceous chondrites or C chondrites are a class of chondritic meteorites comprising at least 8 known groups and many ungrouped meteorites. They include some of the most primitive known meteorites. The C chondrites represent only a small propo ...
meteorites analyzed on Earth.
Makemake
Makemake
Makemake ( minor-planet designation: 136472 Makemake) is a dwarf planet and the largest of what is known as the classical population of Kuiper belt objects, with a diameter approximately that of Saturn's moon Iapetus, or 60% that of Pluto. It ...
exhibits methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
, large amounts of ethane
Ethane ( , ) is a naturally occurring Organic compound, organic chemical compound with chemical formula . At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is List of purification methods ...
and tholins, as well as smaller amounts of ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon–carbon bond, carbon–carbon doub ...
, acetylene
Acetylene (Chemical nomenclature, systematic name: ethyne) is a chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is u ...
and high-mass alkane
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in whi ...
s may be present, most likely created by photolysis
Photodissociation, photolysis, photodecomposition, or photofragmentation is a chemical reaction in which molecules of a chemical compound are broken down by absorption of light or photons. It is defined as the interaction of one or more photons wi ...
of methane by solar radiation.
Kuiper belt objects and Centaurs
The reddish color typical of tholins is characteristic of manyTrans-Neptunian object
A trans-Neptunian object (TNO), also written transneptunian object, is any minor planet in the Solar System that orbits the Sun at a greater average distance than Neptune, which has an orbital semi-major axis of 30.1 astronomical units (AU).
...
s, including plutino
In astronomy, the plutinos are a dynamical group of trans-Neptunian objects that orbit in 2:3 mean-motion resonance with Neptune. This means that for every two orbits a plutino makes, Neptune orbits three times. The dwarf planet Pluto is the la ...
s in the outer Solar System such as 28978 Ixion. Spectral reflectances of Centaurs
A centaur ( ; ; ), occasionally hippocentaur, also called Ixionidae (), is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse that was said to live in the mountains of Thessaly. In one version o ...
also suggest the presence of tholins on their surfaces. The ''New Horizons'' exploration of the classical Kuiper belt object 486958 Arrokoth
486958 Arrokoth (Provisional designation in astronomy, provisional designation ; formerly nicknamed Ultima Thule) is a trans-Neptunian object located in the Kuiper belt. Arrokoth became the farthest and most primitive List of minor planet ...
revealed reddish color at its surface, suggestive of tholins.
Comets and asteroids
Tholins were detected ''in situ'' by the ''Rosetta'' mission to comet67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko
67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (abbreviated as 67P or 67P/C–G) is a Jupiter-family comet. It is originally from the Kuiper belt and has an orbital period of 6.45 years as of 2012, a rotation period of approximately 12.4 hours, and a maximum velo ...
. Tholins are not typically characteristic of main-belt asteroids, but have been detected on the asteroid 24 Themis.
Tholins beyond the Solar System
Tholins might have also been detected in the stellar system of the young star HR 4796A using the Near-Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) aboard the Hubble Space Telescope. The HR 4796 system is approximately 220 light years from Earth.See also
* * * * * *References
{{Portal bar, Biology, Chemistry, Physics, Astronomy, Stars, Outer space, Solar System, Science Organic polymers Origin of life Astrochemistry Prebiotic chemistry