The Carolinas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Carolinas are the U.S. states of
 Between 1663 and 1729 there were many disagreements relating to defense, governance and the difference between the two differing agrarian styles employed by the inhabitants of the Colony of Virginia and that practiced by the planters arriving to Charles Town from the
Between 1663 and 1729 there were many disagreements relating to defense, governance and the difference between the two differing agrarian styles employed by the inhabitants of the Colony of Virginia and that practiced by the planters arriving to Charles Town from the
 These industries gave the Carolinas, particularly North Carolina, a more significant industrial base than most Southern states. As
These industries gave the Carolinas, particularly North Carolina, a more significant industrial base than most Southern states. As
North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia a ...
and South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = "Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = G ...
, considered collectively. They are bordered by Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography an ...
to the north, Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to ...
to the west, and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
to the southwest. The Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
is to the east.
Combining North Carolina's population of 10,439,388 and South Carolina's of 5,118,425, the Carolinas have a collective population of 15,557,813 as of 2020. If the Carolinas were a single state of the United States, it would be the fifth-most populous state, behind California, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, Florida, and New York.
The Carolinas were known as the Province of Carolina during America's early colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 a ...
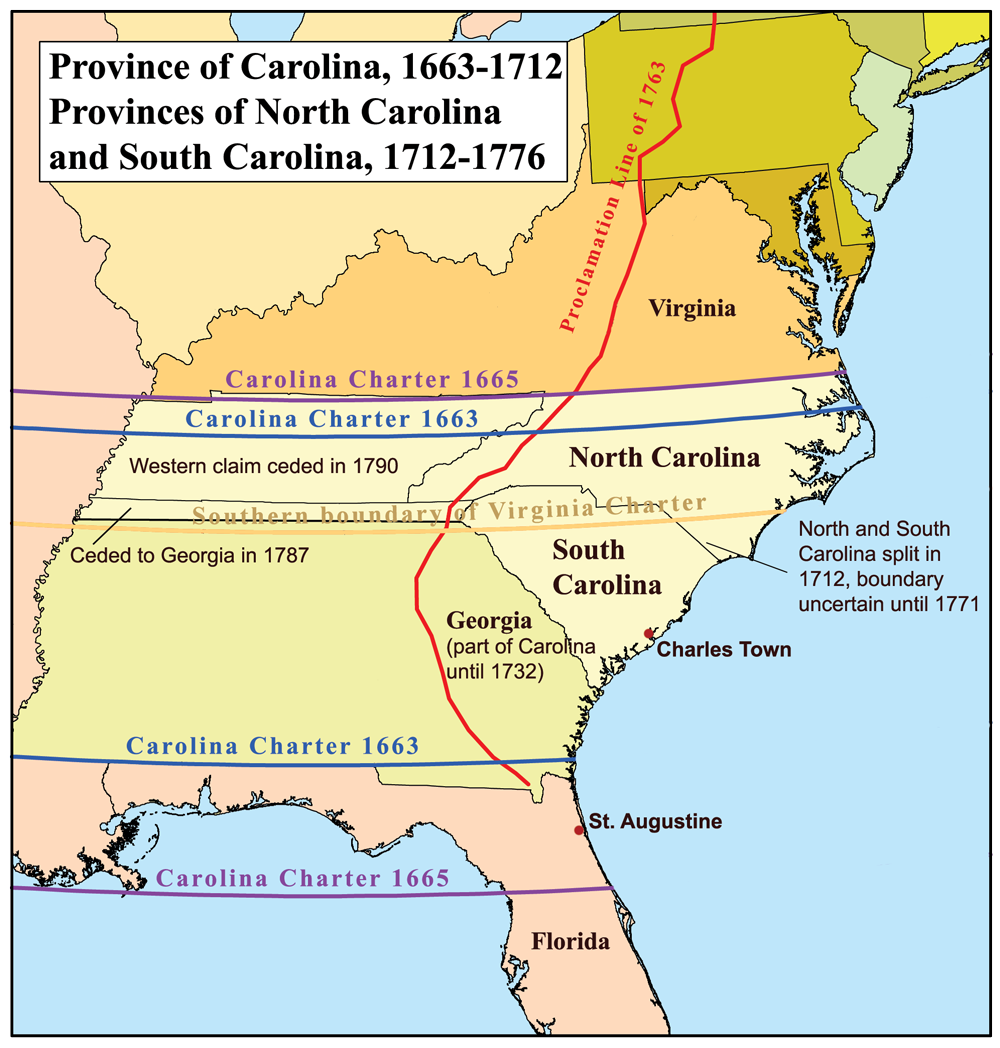
period, from 1663 to 1710. Prior to that, the land was considered part of the Colony and Dominion of Virginia, from 1609 to 1663. The province, named ''Carolina'' to honor King Charles I of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of England, Scotland, and Ireland from 27 March 1625 until his execution in 1649. He was born into the House of Stuart as the second son of King James VI of Scotland, but after ...
, was divided into two royal colonies in 1729, although the actual date is the subject of debate.
History
The region was claimed as part of the Spanish territory named '' La Florida'' byPonce de Leon
Ponce may refer to:
* Ponce (surname)
*
* Ponce, Puerto Rico, a city in Puerto Rico
** Ponce High School
** Ponce massacre, 1937
* USS ''Ponce'', several ships of the US Navy
* Manuel Ponce, a Mexican composer active in the 20th century
* Britis ...
in 1513. Santa Elena, a Spanish settlement on what is now Parris Island, South Carolina, was the capital of La Florida from 1566 to 1587. It was founded by Pedro Menéndez de Avilés
Pedro Menéndez de Avilés (; ast, Pedro (Menéndez) d'Avilés; 15 February 1519 – 17 September 1574) was a Spanish admiral, explorer and conquistador from Avilés, in Asturias, Spain. He is notable for planning the first regular trans-oceani ...
, the first governor of Spanish Florida. There had been a number of earlier attempts to establish colonies in the area by both the Spanish and the French, who had been inspired by earlier accounts of the plentiful land of Chicora. Menéndez's Santa Elena settlement shifted the focus of Spanish colonial efforts northward from St. Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Afri ...
, which had been established in 1565 to drive the French from their colony of Fort Caroline. Santa Elena was ultimately built at the site of the abandoned French outpost of Charlesfort, founded in 1562 by Jean Ribault.
The establishment of Santa Elena followed the destruction of the French Fort Caroline by Menéndez in 1565. The Spanish settlement housed a sizeable community, and became the base of operations for the Jesuits and military working in the northern zone of Spanish Florida
Spanish Florida ( es, La Florida) was the first major European land claim and attempted settlement in North America during the European Age of Discovery. ''La Florida'' formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba, the Viceroyalty of New Spain, ...
. From this base the Spanish founded a number of other ephemeral forts as far inland as the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. The ...
, but resistance from local Native American tribes and the lack of interest of Spain in the area, caused these to be abandoned, relocated or destroyed. Santa Elena was ultimately abandoned in 1587, with its survivors relocating to St. Augustine. The Spanish never pressed their colonial claims to the area again, focusing on other areas of the American continent. The territory was thereafter left to the native Americans until October 30, 1629, when Charles I granted a patent to his attorney-general, Sir Robert Heath, for the lands south of 36 degrees and north of 31 degrees, "under the name, in honor of that king, of Carolana"." ''Carolus'' is Latin for 'Charles'. The charter was unrealized and later ruled invalid.
On March 24, 1663, Charles II issued a new charter to a group of eight English noblemen, granting them the land of Carolina, as a reward for their faithful support of his efforts to regain the throne of England. The eight were called '' Lords Proprietor'' or simply ''Proprietors''. The 1663 charter granted the Lords Proprietor title to all of the land from the southern border of the Virginia Colony at 36 degrees north to 31 degrees north (along the coast of present-day Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
). The establishment of separate colonies did not officially occur until 1729, when seven of the Lords Proprietors sold their interests in Carolina to the Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has differen ...
, and both North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia a ...
and South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = "Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = G ...
became royal colonies.
In 1665, the charter was revised slightly, with the northerly boundary extended to 36 degrees 30 minutes north to include the lands of the Albemarle Settlements
The Albemarle Settlements were the first permanent English settlements in what is now North Carolina, founded in the Albemarle Sound and Roanoke River regions, beginning about the middle of the 17th century. The settlers were mainly Virginians, mi ...
along the Albemarle Sound, which had been settled mainly by Virginians migrating south. Likewise, the southern boundary was moved south to 29 degrees north, just south of present-day Daytona Beach, Florida, which had the effect of including the existing Spanish settlement at St. Augustine, an unenforceable overreach of English power. The charter also granted all the land, between these northerly and southerly bounds, from the Atlantic Ocean, westward to the shores of the Pacific Ocean, an even more unenforceable overreach.

West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Great ...
and Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate ...
.
In 1729 the Province of Carolina was divided when the descendants of seven of the eight Lords Proprietors sold their shares back to the Crown. Only the heirs of Sir George Carteret retained their original rights to what would become the Granville District. Both the Province of North Carolina and the Province of South Carolina became British Crown Colonies in 1729.
Culture
The culture of the Carolinas is a distinct subset of larger Southern culture. Notably, the coastal Carolina region was settled by Europeans over a century before the inland regions of the South, and was influenced by the culture of the Caribbean, especiallyBarbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate ...
; many of the early governors during the unified period were Barbadians. Though the two states both form part of the South, there are historically a number of differences in the settlement patterns, political development, and economic growth of the two states.
During the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by state ...
(1861–1865), South Carolina was the first Southern state to secede from the Union, while North Carolina was the second to last state to secede. South Carolina was generally one of the strongest supporters of the Confederacy
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between ...
. The war began in Charleston, South Carolina, where cadets of the South Carolina Military Academy, known as The Citadel, fired the opening shots at the Union Ship '' Star of the West''. North Carolina was also a key Confederate state, raising and supplying many soldiers to the Confederacy. At Gettysburg, one in four Confederate soldiers was from North Carolina, despite the fact that some North Carolinians (especially in the western part of the state) refused to support the Confederacy. North Carolina's Civil War governor, Zebulon Vance, was an outspoken critic of Confederate President Jefferson Davis and frequently refused to obey Davis's orders for reinforcements and supplies; Vance insisted the soldiers and supplies would be needed for North Carolina's Confederate effort. However, during the seven days' battles, North Carolina did send large numbers of troops for the general aid of the South as a whole. A Unionist presence would persist throughout North Carolina during the war, with North Carolina forming Union Army regiments.
The Carolinas were both instrumental in keeping the Confederacy alive, because of their deepwater ports in Wilmington and Charleston. These two cities were key in supplying Southern armies with weapons, clothing, and ammunition, and producing food and provisions for Southern civilians.
Politics
During most of the 20th century, South Carolina was a bastion of the "solid Democratic South" with almost no Republican officeholders, and the state frequently elected politicians who were outspoken supporters of racial segregation. North Carolina, while mostly Democratic, contained a large Republican minority – the state voted Republican in the presidential election of 1928 and elected several Republican congressmen, governors, and senators from 1868 to 1928 – and North Carolina was widely known as one of the more progressive Southern states on the issue of segregation and civil rights. In 1947, the journalist John Gunther wrote, "that North Carolina is by a good deal the most progressive Southern state will, I imagine, be agreed to by almost everybody." On the other hand, he described South Carolina as "one of the poorest American states, and probably one of the balkiest." In describing the differences between the two states, Gunther noted that, in 1947, divorce in North Carolina "may be granted simply on the ground of absence of cohabitation; South Carolina is the one American state in which divorce is not possible." Despite North Carolina being a swing state in recent presidential elections, and South Carolina being one that reliably votes for Republican presidential candidates, they are technically the country's two most politically similar states, according to a comparison of the states along a range of 19 variables performed by the statistician Nate Silver in 2008.Economy
Historically, like much of the South, the Carolinas economy was one based around agriculture production. The predominance of certain crops would help influence the regional economy:Like other outhernstates, until afterWorld War II World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...North Carolina remained primarily a region of small farms and factories heavily dependent on just a few labor-intensive crops, relying on sharecropping and tenancy, especially for black laborers. The Carolinas are distinct for their economic dependence on tobacco as well as on cotton and rice, and for their many small-scale furniture,textile Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not t ..., and tobacco factories.
 These industries gave the Carolinas, particularly North Carolina, a more significant industrial base than most Southern states. As
These industries gave the Carolinas, particularly North Carolina, a more significant industrial base than most Southern states. As mechanization
Mechanization is the process of changing from working largely or exclusively by hand or with animals to doing that work with machinery. In an early engineering text a machine is defined as follows:
In some fields, mechanization includes the ...
increased in farming, along with textiles, apparel, and furniture jobs shifting because of globalization
Globalization, or globalisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences), is the process of foreign relation ...
, combined with the decline of the tobacco industry, many rural and small urban communities suffered. During the late 20th century, both states began to experience growth in the technological and banking sectors, bringing jobs, population growth, and new economic industries. These changes, as with earlier industrialization, were more pronounced in North Carolina, with South Carolina experiencing a slower rate of economic growth for several years.
Since the 1980s, North Carolina has emerged as a financial hub with Charlotte becoming the second-largest financial district in the United States after New York City. Charlotte is home to the several major publicly traded corporations headquarters Bank of America, Truist Financial, and the East Coast operations of Wells Fargo, and Centene Corporation, as well as six other Fortune 500 companies, including Lowe's, Duke Energy
Duke Energy Corporation is an American electric power and natural gas holding company headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina.
Overview
Based in Charlotte, North Carolina, Duke Energy owns 58,200 watt, megawatts of base-load and peak generati ...
, Nucor, Honeywell, Brighthouse Financial, and Sonic Automotive.
Professional sports
The Carolinas have three professional sports teams in the Big Four major leagues: theCarolina Panthers
The Carolina Panthers are a professional American football team based in Charlotte, North Carolina. The Panthers compete in the National Football League (NFL), as a member club of the league's National Football Conference (NFC) South division. ...
of the NFL
The National Football League (NFL) is a professional American football league that consists of 32 teams, divided equally between the American Football Conference (AFC) and the National Football Conference (NFC). The NFL is one of the major ...
, the Charlotte Hornets of the NBA, and the Carolina Hurricanes
The Carolina Hurricanes (colloquially known as the Canes) are a professional ice hockey team based in Raleigh, North Carolina. They compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Metropolitan Division in the Eastern Conference ...
of the NHL
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ...
. Supported by both states, the three teams are all based in NC, with two in Charlotte and the third in Raleigh.
Professional sports franchises in the Carolinas first formed during the late 20th century. The oldest team pro team in the Carolinas, the NBA's Charlotte Hornets, were established in 1988, while the youngest, Major League Soccer
Major League Soccer (MLS) is a men's professional soccer league sanctioned by the United States Soccer Federation, which represents the sport's highest level in the United States. The league comprises 29 teams—26 in the U.S. and 3 in Cana ...
's Charlotte FC , were established in 2019. The Hornets were known as the Bobcats from 2004 to 2014, and were renamed the Hornets again in May 2014, one season after the former New Orleans Hornets decided to rebrand themselves as the Pelicans. At that time, the Hornets also regained sole ownership of the pre-relocation history of the original Charlotte Hornets. The Hurricanes formed in 1971 as the New England Whalers of the World Hockey Association. After the NHL-WHA merger in 1979, they joined the NHL as the Hartford Whalers until 1997 when they relocated to Raleigh, North Carolina. Currently, the Hurricanes are the most successful after their 2006 Stanley Cup championship marked the first professional sports title for the region. In 2019, a Major League Soccer team was awarded to Charlotte, and begin play in 2022.
In 1991, Charlotte was the host city of the 1991 NBA All-Star Game
The 1991 NBA All-Star Game was an exhibition basketball game between players selected from the National Basketball Association's Western Conference and the Eastern Conference that was played on February 10, 1991, at the Charlotte Coliseum in Ch ...
, which was held at the now demolished Charlotte Coliseum. In June 2015, Charlotte won its bid to host the 2017 NBA All-Star Game
The 2017 NBA All-Star Game was an exhibition basketball game that was played on February 19, 2017, during the National Basketball Association's (NBA) 2016–17 season. It was the 66th edition of the NBA All-Star Game, and was played at the Smooth ...
. However, the award was rescinded in July 2016 due to House Bill 2. On May 24, 2017, Charlotte was selected to host the 2019 NBA All-Star Game
The 2019 NBA All-Star Game was an exhibition basketball game that was played on February 17, 2019, during the National Basketball Association's (NBA) 2018–19 season. It was the 68th edition of the NBA All-Star Game, and was played at the Spect ...
. The game was held on Sunday, February 17, 2019, at the Spectrum Center
Spectrum Center is an indoor arena located in Uptown Charlotte, North Carolina. It is owned by the city of Charlotte and operated by its main tenant, the Charlotte Hornets of the National Basketball Association (NBA). The arena seats 19,077 for ...
, home of the Charlotte Hornets.
Bank of America Stadium currently hosts three major sporting events, the Duke's Mayo Bowl, the Belk Kickoff Game and the ACC Championship Game.
Charlotte Motor Speedway hosts three major NASCAR events, the Coca-Cola 600, the Monster Energy NASCAR All-Star Race
The NASCAR All-Star Race, formerly known as The Winston from 1985 to 2003, the Nextel All-Star Challenge from 2004 to 2007, the Sprint All-Star Race from 2008 to 2016, and the Monster Energy NASCAR All-Star Race from 2017 to 2019, is an annual NAS ...
, and the Bank of America 500.
The Carolinas are home to a number of NBA superstars, such as Chris Paul, Bam Adebayo, Brandon Ingram, Jerry Stackhouse
Jerry Darnell Stackhouse (born November 5, 1974) is an American basketball coach and former professional player who is the head coach of the Vanderbilt Commodores men's team. He played 18 seasons in the National Basketball Association (NBA) and ...
, Cedric Maxwell, James Worthy, Dominique Wilkins, Bob McAdoo, John Wall, Stephen Curry, and Michael Jordan (from NC) and Kevin Garnett, Jermaine O'Neal, Ray Allen, Zion Williamson, Ja Morant, and Raymond Felton (from SC). Of these All Star NBA players, four are NBA champions, and John Wall and James Worthy were the Number 1 draft picks in the 2010 NBA draft and 1982 NBA draft, respectively. A disproportional number of basketball players come from the Carolinas, on par with such big cities as New York City and Los Angeles. North Carolina in particular is home to three of the most successful collegiate men's basketball teams in the NCAA, the North Carolina Tar Heels, North Carolina State Wolfpack
The NC State Wolfpack is the nickname of the athletic teams representing North Carolina State University. The Wolfpack competes at the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I (Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) for college footb ...
and the Duke Blue Devils. All three schools are fierce rivals who have combined to win 13 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Championships (UNC with 6, Duke with 5, North Carolina State with 2).
Boundary between the states
Plotting the boundary
According to the Prefatory Notes to Volume 5 of the ''Colonial Records of North Carolina'', the process of determining the boundary between North and South Carolina began in 1720 "when the purpose to erect a third Province in Carolina, withSavannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
for its northern boundary" began. On 8 January 1730 an agreement between the two colonies said for the border "to begin 30 miles southwest of the Cape Fear River, and to be run at that parallel distance the whole course of said river;" The next June Governor Robert Johnson of South Carolina said the border should start 30 miles southwest of the source of the Cape Fear "due west as far as the South Sea", unless the " Waccamaw River lyes icwithin 30 miles of the Cape Fear river," which would make the Waccamaw the boundary. North Carolina agreed to this until the discovery that the Cape Fear headwaters were very close to Virginia, which would not have "permitted any extension on the part of North Carolina to the westward." In 1732, Governor George Burrington of North Carolina stated in ''Timothy's Southern Gazette'' that territory north of the Waccamaw was in North Carolina, to which Johnson replied that South Carolina claimed the land. Johnson also said that when the two met before the Board of Trade
The Board of Trade is a British government body concerned with commerce and industry, currently within the Department for International Trade. Its full title is The Lords of the Committee of the Privy Council appointed for the consideration of ...
in London two years earlier, Burrington had "insisted that the Waccamaw should be the boundary from its mouth to its head," while South Carolina agreed the border should be located from the