heparin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Heparin is a blood
 Heparin acts as an anticoagulant, preventing the formation of clots and extension of existing clots within the blood. Heparin itself does not break down clots that have already formed, instead, it prevents clot formation by inhibiting thrombin and other procoagulant serine proteases. Heparin is generally used for anticoagulation for the following conditions:
* Acute coronary syndrome, e.g., NSTEMI
*
Heparin acts as an anticoagulant, preventing the formation of clots and extension of existing clots within the blood. Heparin itself does not break down clots that have already formed, instead, it prevents clot formation by inhibiting thrombin and other procoagulant serine proteases. Heparin is generally used for anticoagulation for the following conditions:
* Acute coronary syndrome, e.g., NSTEMI
*
 Heparin is given parenterally because it is not absorbed from the gut, due to its high negative charge and large size. It can be injected intravenously or subcutaneously (under the skin); intramuscular injections (into muscle) are avoided because of the potential for forming
Heparin is given parenterally because it is not absorbed from the gut, due to its high negative charge and large size. It can be injected intravenously or subcutaneously (under the skin); intramuscular injections (into muscle) are avoided because of the potential for forming
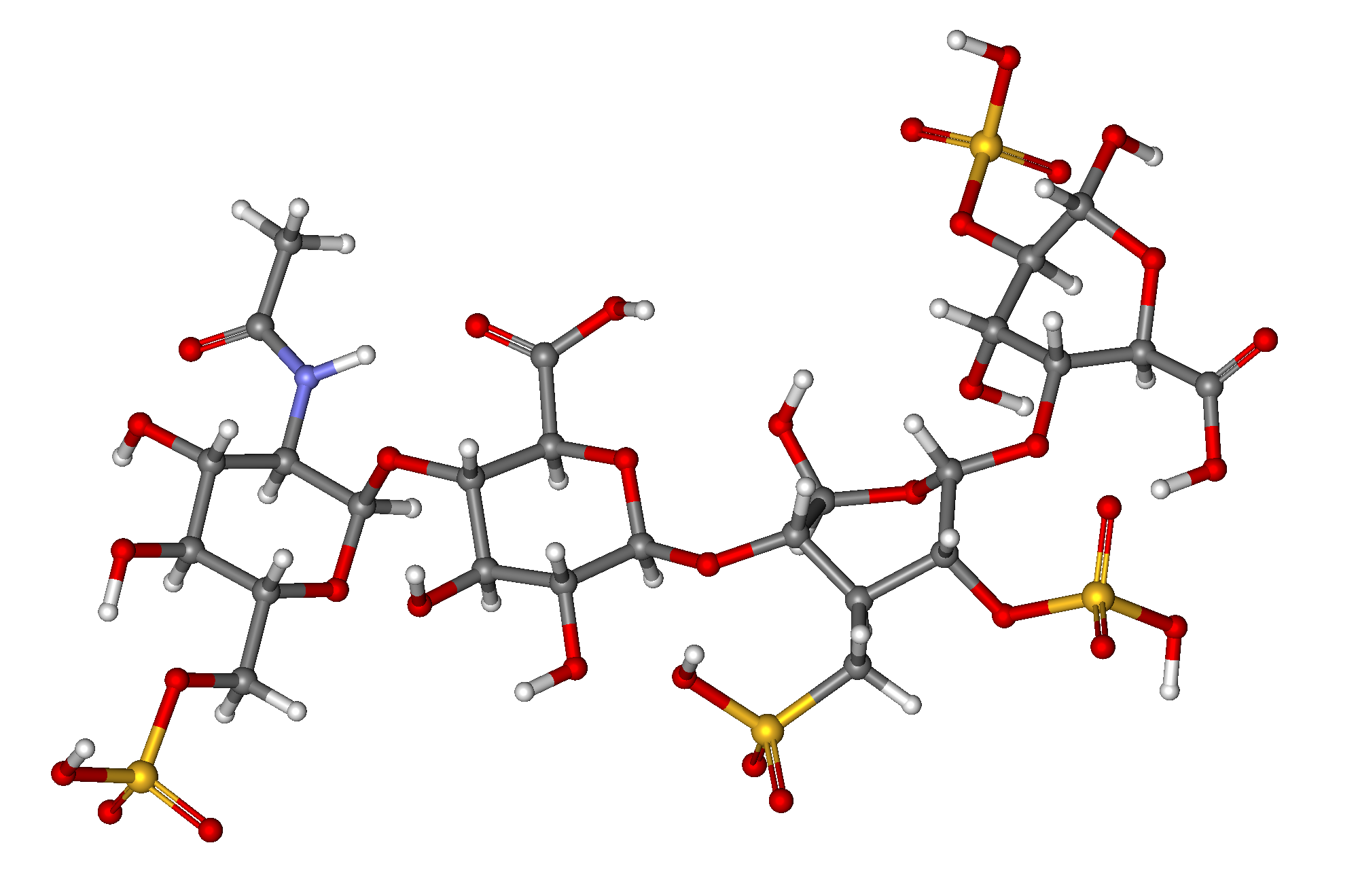 Native heparin is a polymer with a
Native heparin is a polymer with a
File:IdoA(2S)-GlcNS(6S).png,
File:IdoA(2S)-GlcNS.png,
File:IdoA-GlcNS(6S).png,
File:GlcA-GlcNAc.png,
File:GlcA-GlcNS.png,
File:IdoA-GlcNS.png,
GlcA = β--
Jmol viewer
* B = van der Waals radius space-filling model of ''A'' * C = 1HPN (all IdoA(2S) residues in 1C4 conformation
Jmol viewer
* D = van der Waals radius space-filling model of ''C'' In these models, heparin adopts a helical conformation, the rotation of which places clusters of sulfate groups at regular intervals of about 17
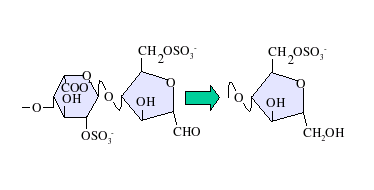 At both 'high' (4) and 'low' (1.5) pH, deaminative cleavage occurs between GlcNS-GlcA and GlcNS-IdoA, albeit at a slower rate at the higher pH. The deamination reaction, and therefore chain cleavage, is regardless of O-sulfation carried by either monosaccharide unit.
At low pH, deaminative cleavage results in the release of inorganic SO4, and the conversion of GlcNS into anhydromannose (aMan). Low-pH nitrous acid treatment is an excellent method to distinguish N-sulfated polysaccharides such as heparin and HS from non N-sulfated polysaccharides such as
At both 'high' (4) and 'low' (1.5) pH, deaminative cleavage occurs between GlcNS-GlcA and GlcNS-IdoA, albeit at a slower rate at the higher pH. The deamination reaction, and therefore chain cleavage, is regardless of O-sulfation carried by either monosaccharide unit.
At low pH, deaminative cleavage results in the release of inorganic SO4, and the conversion of GlcNS into anhydromannose (aMan). Low-pH nitrous acid treatment is an excellent method to distinguish N-sulfated polysaccharides such as heparin and HS from non N-sulfated polysaccharides such as
History of heparin
{{Authority control Chemical substances for emergency medicine Glycosaminoglycans Heparins World Health Organization essential medicines Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Aldols Ophthalmology drugs
anticoagulant
An anticoagulant, commonly known as a blood thinner, is a chemical substance that prevents or reduces the coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some occur naturally in blood-eating animals, such as leeches and mosquitoes, which ...
that increases the activity of antithrombin. It is used in the treatment of heart attacks
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is retr ...
and unstable angina
In dynamical systems instability means that some of the outputs or internal states increase with time, without bounds. Not all systems that are not stable are unstable; systems can also be marginally stable or exhibit limit cycle behavior ...
. It can be given intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
ly or by injection under the skin. Its anticoagulant properties make it useful to prevent blood clotting in blood specimen test tube
A test tube, also known as a culture tube or sample tube, is a common piece of laboratory glassware consisting of a finger-like length of glass or clear plastic tubing, open at the top and closed at the bottom.
Test tubes are usually placed in s ...
s and kidney dialysis machines.
Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and low blood platelets. Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function.
Heparin is contraindicated for suspected cases of vaccine-induced pro-thrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) secondary to SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
vaccination, as heparin may further increase the risk of bleeding in an anti-PF4/heparin complex autoimmune manner, in favor of alternative anticoagulant medications (such as argatroban or danaparoid
Danaparoid sodium (Orgaran) is an anticoagulant with an antithrombotic action due to inhibition of thrombin generation (TGI) by two mechanisms: indirect inactivation of Factor Xa via AT and direct inhibition of thrombin activation of Factor IX (an ...
).
Heparin appears to be relatively safe for use during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
and breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a Breast pump, pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Orga ...
. Heparin is produced by basophils and mast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
s in all mammals
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle e ...
.
The discovery of heparin was announced in 1916. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. A fractionated version of heparin, known as low molecular weight heparin
Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) is a class of anticoagulant medications. They are used in the prevention of Thrombosis prevention, blood clots and, in the treatment of venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism), and ...
, is also available.
History
Heparin was discovered by Jay McLean and William Henry Howell in 1916, although it did not enter clinical trials until 1935. It was originally isolated from dogliver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
cells, hence its name (ἧπαρ ''hēpar'' is Greek for 'liver'; ''hepar'' + '' -in'').
McLean was a second-year medical student at Johns Hopkins University
The Johns Hopkins University (often abbreviated as Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1876 based on the European research institution model, J ...
, and was working under the guidance of Howell investigating pro-coagulant preparations when he isolated a fat-soluble phosphatide anticoagulant in canine liver tissue. In 1918, Howell coined the term 'heparin' for this type of fat-soluble anticoagulant. In the early 1920s, Howell isolated a water-soluble polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wat ...
anticoagulant, which he also termed 'heparin', although it was different from the previously discovered phosphatide preparations. McLean's work as a surgeon probably changed the focus of the Howell group to look for anticoagulants, which eventually led to the polysaccharide discovery.
It had at first been accepted that it was Howell who discovered heparin. However, in the 1940s, Jay McLean became unhappy that he had not received appropriate recognition for what he saw as his discovery. Though relatively discreet about his claim and not wanting to upset his former chief, he gave lectures and wrote letters claiming that the discovery was his. This gradually became accepted as fact, and indeed after he died in 1959, his obituary credited him as being the true discoverer of heparin. This was elegantly restated in 1963 in a plaque unveiled at Johns Hopkins to commemorate the major contribution (of McLean) to the discovery of heparin in 1916 in collaboration with Professor William Henry Howell.
In the 1930s, several researchers were investigating heparin. Erik Jorpes at Karolinska Institutet published his research on the structure of heparin in 1935, which made it possible for the Swedish company Vitrum AB to launch the first heparin product for intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
use in 1936. Between 1933 and 1936, Connaught Medical Research Laboratories, then a part of the University of Toronto, perfected a technique for producing safe, nontoxic heparin that could be administered to patients, in a saline solution. The first human trials of heparin began in May 1935, and, by 1937, it was clear that Connaught's heparin was safe, easily available, and effective as a blood anticoagulant. Before 1933, heparin was available in small amounts, was extremely expensive and toxic, and, as a consequence, of no medical value.
Heparin production experienced a break in the 1990s. Until then, heparin was mainly obtained from cattle tissue, which was a by-product of the meat industry
The meat industry are the people and companies engaged in modern industrialized livestock agriculture for the production, packing, preservation and marketing of meat (in contrast to dairy products, wool, etc.). In economics, the meat industry is ...
, especially in North America. With the rapid spread of BSE, more and more manufacturers abandoned this source of supply. As a result, global heparin production became increasingly concentrated in China, where the substance was now procured from the expanding industry of breeding and slaughtering hogs. The dependence of medical care on the meat industry assumed threatening proportions in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
. In 2020, several studies demonstrated the efficacy of heparin in mitigating severe disease progression, as its anticoagulant effect counteracted the formation of immunothrombosis. However, the availability of heparin on the world market was decreased, because concurrently a renewed swine flu epidemic had reduced significant portions of the Chinese hog population. The situation was further exacerbated by the fact that mass slaughterhouses around the world became coronavirus hotspots themselves and were forced to close temporarily. In less affluent countries, the resulting heparin shortage also led to worsened health care beyond the treatment of COVID-19, for example through the cancellation of cardiac surgeries.
Medical use
 Heparin acts as an anticoagulant, preventing the formation of clots and extension of existing clots within the blood. Heparin itself does not break down clots that have already formed, instead, it prevents clot formation by inhibiting thrombin and other procoagulant serine proteases. Heparin is generally used for anticoagulation for the following conditions:
* Acute coronary syndrome, e.g., NSTEMI
*
Heparin acts as an anticoagulant, preventing the formation of clots and extension of existing clots within the blood. Heparin itself does not break down clots that have already formed, instead, it prevents clot formation by inhibiting thrombin and other procoagulant serine proteases. Heparin is generally used for anticoagulation for the following conditions:
* Acute coronary syndrome, e.g., NSTEMI
* Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods ...
* Deep-vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain ...
(both prevention and treatment)
* Other thrombotic states and conditions
* Cardiopulmonary bypass
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) or heart-lung machine, also called the pump or CPB pump, is a machine that temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during open-heart surgery by maintaining the circulation of blood and oxygen throug ...
for heart surgery
* ECMO circuit for extracorporeal life support
Extracorporeal life support (ECLS), is a set of extracorporeal modalities that can provide Oxygenation (environmental), oxygenation, removal of carbon dioxide, and/or Circulatory system, circulatory support, excluding cardiopulmonary bypass for Ca ...
* Hemofiltration
* Indwelling central or peripheral venous catheters
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Catheters are man ...
Heparin and its low-molecular-weight derivatives (e.g., enoxaparin, dalteparin, tinzaparin) are effective in preventing deep vein thromboses and pulmonary emboli in people at risk, but no evidence indicates any one is more effective than the other in preventing mortality.
In angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is perfo ...
, 2 to 5 units/mL of unfractionated heparin saline flush is used as a locking solution to prevent the clotting of blood in guidewires, sheaths, and catheters, thus preventing thrombus from dislodging from these devices into the circulatory system .
Unfractionated heparin is used in hemodialysis
Hemodialysis, American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply ''"'dialysis'"'', is a process of filtering the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of Kidney dialys ...
. Compared to low-molecular-weight heparin, unfractionated heparin does not have prolonged anticoagulation action after dialysis and is low cost. However, the short duration of action for heparin would require it to maintain continuous infusion to maintain its action. Meanwhile, unfractionated heparin has higher risk of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
Adverse effects
A serious side-effect of heparin is heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), caused by an immunological reaction that makesplatelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no ...
s a target of immunological response, resulting in the degradation of platelets, which causes thrombocytopenia. This condition is usually reversed on discontinuation, and in general can be avoided with the use of synthetic heparins. Not all patients with heparin antibodies will develop thrombocytopenia. Also, a benign form of thrombocytopenia is associated with early heparin use, which resolves without stopping heparin. Approximately one-third of patients with diagnosed heparin-induced thrombocytopenia will ultimately develop thrombotic complications.
Two non-hemorrhagic side effects of heparin treatment are known. The first is an elevation of serum aminotransferase levels, which has been reported in as many as 80% of patients receiving heparin. This abnormality is not associated with liver dysfunction, and it disappears after the drug is discontinued. The other complication is hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0 mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Oc ...
, which occurs in 5 to 10% of patients receiving heparin, and is the result of heparin-induced aldosterone suppression. The hyperkalemia can appear within a few days after the onset of heparin therapy. More rarely, the side-effects alopecia
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring ...
and osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
can occur with chronic use.
As with many drugs, overdoses of heparin can be fatal. In September 2006, heparin received worldwide publicity when three prematurely born infants died after they were mistakenly given overdoses of heparin at an Indianapolis hospital.
Contraindications
Heparin is contraindicated in those with risk of bleeding (especially in people with uncontrolled blood pressure, liver disease, and stroke), severe liver disease, or severe hypertension.Antidote to heparin
Protamine sulfate has been given to counteract the anticoagulant effect of heparin (1 mg per 100 units of heparin that had been given over the past 6 hours). It may be used in those who overdose on heparin or to reverse heparin's effect when it is no longer needed.Physiological function
Heparin's normal role in the body is unclear. Heparin is usually stored within the secretory granules ofmast cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
s and released only into the vasculature at sites of tissue injury. It has been proposed that rather than anticoagulation, the main purpose of heparin is defense at such sites against invading bacteria and other foreign materials. In addition, it is observed across many widely different species, including some invertebrates that do not have a similar blood coagulation system. It is a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan and has the highest negative charge density
In electromagnetism, charge density is the amount of electric charge per unit length, surface area, or volume. Volume charge density (symbolized by the Greek letter ρ) is the quantity of charge per unit volume, measured in the SI system in co ...
of any known biological molecule.
Evolutionary conservation
In addition to the bovine and porcine tissue from which pharmaceutical-grade heparin is commonly extracted, it has also been extracted and characterized from: #Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
# Whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully Aquatic animal, aquatic placental mammal, placental marine mammals. As an informal and Colloquialism, colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea ...
# Dromedary camel
# Mouse
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
# Humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
# Lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on th ...
# Fresh water mussel
# Clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve mollusc. The word is often applied only to those that are deemed edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the sea floor or riverbeds. Clams h ...
# Shrimp
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchi ...
# Mangrove crab
# Sand dollar
# Atlantic salmon
The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Salmonidae. It is the third largest of the Salmonidae, behind Hucho taimen, Siberian taimen and Pacific Chinook salmon, growing up to a meter in length. Atlan ...
# Zebra fish
The biological activity of heparin within species 6–11 is unclear and further supports the idea that the main physiological role of heparin is not anticoagulation. These species do not possess any blood coagulation system similar to that present within the species listed 1–5. The above list also demonstrates how heparin has been highly evolutionarily conserved, with molecules of a similar structure being produced by a broad range of organisms belonging to many different phyla
Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phy ...
.
Pharmacology
Innature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
, heparin is a polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
of varying chain size. Unfractionated heparin (UFH) as a pharmaceutical is heparin that has not been fractionated to sequester the fraction of molecules with low molecular weight
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
. In contrast, low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) has undergone fractionation to make its pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or comb ...
more predictable. Often either UFH or LMWH can be used; in some situations one or the other is preferable.
Mechanism of action
Heparin binds to the enzyme inhibitor antithrombin III (AT), causing a conformational change that results in its activation through an increase in the flexibility of its reactive site loop. The activated AT then inactivates thrombin, factor Xa and other proteases. The rate of inactivation of these proteases by AT can increase by up to 1000-fold due to the binding of heparin. Heparin binds to AT via a specific pentasaccharide sulfation sequence contained within the heparin polymer: : GlcNAc/NS(6S)-GlcA-GlcNS(3S,6S)-IdoA(2S)-GlcNS(6S) The conformational change in AT on heparin-binding mediates its inhibition of factor Xa. For thrombin inhibition, however, thrombin must also bind to the heparin polymer at a site proximal to the pentasaccharide. The highly negative charge density of heparin contributes to its very strongelectrostatic
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies slow-moving or stationary electric charges.
Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word (), mean ...
interaction with thrombin. The formation of a ternary complex between AT, thrombin, and heparin results in the inactivation of thrombin. For this reason, heparin's activity against thrombin is size-dependent, with the ternary complex requiring at least 18 saccharide units for efficient formation. In contrast, antifactor Xa activity via AT requires only the pentasaccharide-binding site.
This size difference has led to the development of low-molecular-weight heparins (LMWHs) and fondaparinux as anticoagulants. Fondaparinux targets anti-factor Xa activity rather than inhibiting thrombin activity, to facilitate a more subtle regulation of coagulation and an improved therapeutic index. It is a synthetic pentasaccharide, whose chemical structure is almost identical to the AT binding pentasaccharide sequence that can be found within polymeric heparin and heparan sulfate
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs in a proteoglycan (HSPG, i.e. Heparan Sulfate ProteoGlycan) in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular ma ...
.
With LMWH and fondaparinux, the risk of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is reduced. Monitoring of the activated partial thromboplastin time is also not required and does not reflect the anticoagulant effect, as APTT is insensitive to alterations in factor Xa.
Danaparoid
Danaparoid sodium (Orgaran) is an anticoagulant with an antithrombotic action due to inhibition of thrombin generation (TGI) by two mechanisms: indirect inactivation of Factor Xa via AT and direct inhibition of thrombin activation of Factor IX (an ...
, a mixture of heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate, and chondroitin sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars (N-Acetylgalactosamine, N-acetylgalactosamine and glucuronic acid). It is usually found attached to proteins as part of a proteoglycan. A chondroit ...
can be used as an anticoagulant in patients having developed HIT. Because danaparoid does not contain heparin or heparin fragments, cross-reactivity of danaparoid with heparin-induced antibodies is reported as less than 10%.
The effects of heparin are measured in the lab by the partial thromboplastin time ( aPTT), one of the measures of the time it takes the blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light Amber (color), amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but which contains Blood protein, proteins and other constituents of whole blood in Suspension (chemistry), suspension. It makes up ...
to clot. Partial thromboplastin time should not be confused with prothrombin time, or PT, which measures blood clotting time through a different pathway of the coagulation cascade
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The process of coagulat ...
.
Administration
 Heparin is given parenterally because it is not absorbed from the gut, due to its high negative charge and large size. It can be injected intravenously or subcutaneously (under the skin); intramuscular injections (into muscle) are avoided because of the potential for forming
Heparin is given parenterally because it is not absorbed from the gut, due to its high negative charge and large size. It can be injected intravenously or subcutaneously (under the skin); intramuscular injections (into muscle) are avoided because of the potential for forming hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is ...
s. Because of its short biologic half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* ''Half Life: ...
of about one hour, heparin must be given frequently or as a continuous infusion
Infusion is the process of extracting chemical compounds or flavors from plant material in a solvent such as water, oil or alcohol, by allowing the material to remain suspended in the solvent over time (a process often called steeping). An inf ...
. Unfractionated heparin has a half-life of about one to two hours after infusion, whereas LMWH has a half-life of four to five hours. The use of LMWH has allowed once-daily dosing, thus not requiring a continuous infusion of the drug. If long-term anticoagulation is required, heparin is often used only to commence anticoagulation therapy until an oral anticoagulant e.g. warfarin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others. It is used as an anticoagulant, anticoagulant medication. It is commonly used to prevent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to protect against stroke in people who ha ...
takes effect.
The American College of Chest Physicians publishes clinical guidelines on heparin dosing.
Natural degradation or clearance
Unfractionated heparin has a half-life of about one to two hours after infusion, whereas low-molecular-weight heparin's half-life is about four times longer. Lower doses of heparin have a much shorter half-life than larger ones. Heparin binding tomacrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
cells is internalized and depolymerized by the macrophages. It also rapidly binds to endothelial cells
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the res ...
, which precludes the binding to antithrombin that results in anticoagulant action. For higher doses of heparin, endothelial cell binding will be saturated, such that clearance of heparin from the bloodstream by the kidneys will be a slower process.
Chemistry
Heparin structure
 Native heparin is a polymer with a
Native heparin is a polymer with a molecular weight
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
ranging from 3 to 30 kDa, although the average molecular weight of most commercial heparin preparations is in the range of 12 to 15 kDa. Heparin is a member of the glycosaminoglycan family of carbohydrates
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ma ...
(which includes the closely related molecule heparan sulfate
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs in a proteoglycan (HSPG, i.e. Heparan Sulfate ProteoGlycan) in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular ma ...
) and consists of a variably sulfated repeating disaccharide
A disaccharide (also called a double sugar or ''biose'') is the sugar formed when two monosaccharides are joined by glycosidic linkage. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides are simple sugars soluble in water. Three common examples are sucrose, ...
unit.
The main disaccharide units that occur in heparin are shown below. The most common disaccharide unit* (see below) is composed of a 2-O-sulfated iduronic acid and 6-O-sulfated, N-sulfated glucosamine, IdoA(2S)-GlcNS(6S). For example, this makes up 85% of heparins from beef lung and about 75% of those from porcine intestinal mucosa.
Not shown below are the rare disaccharides containing a 3-O-sulfated glucosamine (GlcNS(3S,6S)) or a free amine group (GlcNH3+). Under physiological conditions, the ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
and amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a chemical compound, compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl functional group, groups or hydrogen at ...
sulfate groups are deprotonated and attract positively charged counterions to form a heparin salt. Heparin is usually administered in this form as an anticoagulant.
glucuronic acid
Glucuronic acid (GCA, from ) is a uronic acid that was first isolated from urine (hence the name "uronic acid"). It is found in many natural gum, gums such as gum arabic ( 18%), xanthan, and kombucha tea and is important for the metabolism of ...
, IdoA = α-- iduronic acid, IdoA(2S) = 2-''O''-sulfo-α--iduronic acid, GlcNAc = 2-deoxy-2-acetamido-α--glucopyranosyl, GlcNS = 2-deoxy-2-sulfamido-α--glucopyranosyl, GlcNS(6S) = 2-deoxy-2-sulfamido-α--glucopyranosyl-6-''O''-sulfate
One unit of heparin (the " Howell unit") is an amount approximately equivalent to 0.002 mg of pure heparin, which is the quantity required to keep 1 ml of cat's blood fluid for 24 hours at 0 °C.
Three-dimensional structure
The three-dimensional structure of heparin is complicated because iduronic acid may be present in either of two low-energy conformations when internally positioned within an oligosaccharide. The conformational equilibrium is influenced by the sulfation state of adjacent glucosamine sugars. Nevertheless, the solution structure of a heparin dodecasaccharide composed solely of six GlcNS(6S)-IdoA(2S) repeat units has been determined using a combination of NMR spectroscopy and molecular modeling techniques. Two models were constructed, one in which all IdoA(2S) were in the 2S0 conformation (A and B below), and one in which they are in the 1C4 conformation (C and D below). However, no evidence suggests that changes between these conformations occur in a concerted fashion. These models correspond to the protein data bank code 1HPN. In the image above: * A = 1HPN (all IdoA(2S) residues in 2S0 conformationJmol viewer
* B = van der Waals radius space-filling model of ''A'' * C = 1HPN (all IdoA(2S) residues in 1C4 conformation
Jmol viewer
* D = van der Waals radius space-filling model of ''C'' In these models, heparin adopts a helical conformation, the rotation of which places clusters of sulfate groups at regular intervals of about 17
angstrom
The angstrom (; ) is a unit of length equal to m; that is, one ten-billionth of a metre, a hundred-millionth of a centimetre, 0.1 nanometre, or 100 picometres. The unit is named after the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814–18 ...
s (1.7 nm) on either side of the helical axis.
Depolymerization techniques
Either chemical or enzymatic depolymerization techniques or a combination of the two underlie the vast majority of analyses carried out on the structure and function of heparin and heparan sulfate (HS).Enzymatic
The enzymes traditionally used to digest heparin or HS are naturally produced by the soil bacterium ''Pedobacter heparinus'' (formerly named ''Flavobacterium heparinum''). This bacterium is capable of using either heparin or HS as its sole carbon and nitrogen source. To do so, it produces a range of enzymes such as lyases, glucuronidases, sulfoesterases, and sulfamidases. The lyases have mainly been used in heparin/HS studies. The bacterium produces three lyases, heparinases I (), II (no EC number assigned) and III () and each has distinct substrate specificities as detailed below. The lyases cleave heparin/HS by a beta-elimination mechanism. This action generates an unsaturated double bond between C4 and C5 of the uronate residue. The C4-C5 unsaturated uronate is termed ΔUA or UA. It is a sensitive UVchromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The word is derived .
The color that is seen by our eyes is that of the light not Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbed by the reflecting object within a certain wavele ...
(max absorption at 232 nm) and allows the rate of an enzyme digest to be followed, as well as providing a convenient method for detecting the fragments produced by enzyme digestion.
Chemical
Nitrous acid can be used to chemically depolymerize heparin/HS. Nitrous acid can be used at pH 1.5 or a higher pH of 4. Under both conditions, nitrous acid affects deaminative cleavage of the chain. At both 'high' (4) and 'low' (1.5) pH, deaminative cleavage occurs between GlcNS-GlcA and GlcNS-IdoA, albeit at a slower rate at the higher pH. The deamination reaction, and therefore chain cleavage, is regardless of O-sulfation carried by either monosaccharide unit.
At low pH, deaminative cleavage results in the release of inorganic SO4, and the conversion of GlcNS into anhydromannose (aMan). Low-pH nitrous acid treatment is an excellent method to distinguish N-sulfated polysaccharides such as heparin and HS from non N-sulfated polysaccharides such as
At both 'high' (4) and 'low' (1.5) pH, deaminative cleavage occurs between GlcNS-GlcA and GlcNS-IdoA, albeit at a slower rate at the higher pH. The deamination reaction, and therefore chain cleavage, is regardless of O-sulfation carried by either monosaccharide unit.
At low pH, deaminative cleavage results in the release of inorganic SO4, and the conversion of GlcNS into anhydromannose (aMan). Low-pH nitrous acid treatment is an excellent method to distinguish N-sulfated polysaccharides such as heparin and HS from non N-sulfated polysaccharides such as chondroitin sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars (N-Acetylgalactosamine, N-acetylgalactosamine and glucuronic acid). It is usually found attached to proteins as part of a proteoglycan. A chondroit ...
and dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate not being susceptible to nitrous acid cleavage.
Detection in body fluids
Current clinical laboratory assays for heparin rely on an indirect measurement of the effect of the drug, rather than on a direct measure of its chemical presence. These include activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) and antifactor Xa activity. The specimen of choice is usually fresh, nonhemolyzed plasma from blood that has been anticoagulated with citrate, fluoride, or oxalate.Other functions
* Blood specimen test tubes, vacutainers, andcapillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the inn ...
tubes that use the lithium
Lithium (from , , ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the ...
salt of heparin (lithium heparin) as an anticoagulant are usually marked with green stickers and green tops. Heparin has the advantage over EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), also called EDTA acid, is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula . This white, slightly water-soluble solid is widely used to bind to iron (Fe2+/Fe3+) and calcium ions (Ca2+), forming water-solubl ...
of not affecting levels of most ions. However, the concentration of ionized calcium may be decreased if the concentration of heparin in the blood specimen is too high. Heparin can interfere with some immunoassay
An immunoassay (IA) is a biochemical test that measures the presence or concentration of a macromolecule or a small molecule in a solution through the use of an antibody (usually) or an antigen (sometimes). The molecule detected by the immunoassay ...
s, however. As lithium heparin is usually used, a person's lithium levels cannot be obtained from these tubes; for this purpose, royal-blue-topped (and dark green-topped) vacutainers containing sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
heparin are used.
* Heparin-coated blood oxygenators are available for use in heart-lung machines. Among other things, these specialized oxygenators are thought to improve overall biocompatibility
Biocompatibility is related to the behavior of biomaterials in various contexts. The term refers to the ability of a material to perform with an appropriate host response in a specific situation. The ambiguity of the term reflects the ongoin ...
and host homeostasis by providing characteristics similar to those of native endothelium.
* The DNA binding sites on RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template.
Using the e ...
can be occupied by heparin, preventing the polymerase from binding to promoter DNA. This property is exploited in a range of molecular biological assays.
* Common diagnostic procedures require PCR amplification of a patient's DNA, which is easily extracted from white blood cells treated with heparin. This poses a potential problem, since heparin may be extracted along with the DNA, and it has been found to interfere with the PCR reaction at levels as low as 0.002 U in a 50 μL reaction mixture.
* Heparin has been used as a chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the Separation process, separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it ...
resin, acting as both an affinity ligand and an ion exchanger. Its polyanionic structure can mimic nucleic acids like DNA and RNA, making it useful for purification of nucleic acid-binding proteins including DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
and RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template.
Using the e ...
s and transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
s. Heparin's specific affinity for VSV-G, a viral envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. A viral envelope protein or E protein is a protein in the en ...
glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
often used to pseudotype retroviral and lentiviral vectors for gene therapy
Gene therapy is Health technology, medical technology that aims to produce a therapeutic effect through the manipulation of gene expression or through altering the biological properties of living cells.
The first attempt at modifying human DNA ...
, allows it to be used for downstream purification of viral vectors.
* Heparin is being trialed in a nasal spray form as prophylaxis against COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
infection. Furthermore, its reported from trials that due to anti-viral, anti-inflammatory and its anti-clotting effects its inhalation could improve at a 70% rate on patients that were actively struck by a COVID-19 infection.
Society and culture
Contamination recalls
Considering the animal source of pharmaceutical heparin, the number of potential impurities is relatively large compared with a wholly synthetic therapeutic agent. The range of possible biological contaminants includes viruses, bacterial endotoxins, transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) agents, lipids, proteins, and DNA. During the preparation of pharmaceutical-grade heparin from animal tissues, impurities such as solvents, heavy metals, and extraneous cations can be introduced. However, the methods employed to minimize the occurrence and to identify and/or eliminate these contaminants are well established and listed in guidelines and pharmacopeias. The major challenge in the analysis of heparin impurities is the detection and identification of structurally related impurities. The most prevalent impurity in heparin is dermatan sulfate (DS), also known as chondroitin sulfate B. The building block of DS is a disaccharide composed of 1,3-linked N-acetyl galactosamine (GalN) and a uronic acid residue, connected via 1,4 linkages to form the polymer. DS is composed of three possible uronic acids (GlcA, IdoA, or IdoA2S) and four possible hexosamine (GalNAc, Gal- NAc4S, GalNAc6S, or GalNAc4S6S) building blocks. The presence of iduronic acid in DS distinguishes it from chondroitin sulfate A and C and likens it to heparin and HS. DS has a lower negative charge density overall compared to heparin. A common natural contaminant, DS is present at levels of 1–7% in heparin API but has no proven biological activity that influences the anticoagulation effect of heparin. In December 2007, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recalled a shipment of heparin because of bacterial growth (''Serratia marcescens
''Serratia marcescens'' () is a species of bacillus (shape), rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacteria in the family Yersiniaceae. It is a facultative anaerobe and an opportunistic pathogen in humans. It was discovered in 1819 by Bartolomeo Bizio in Pa ...
'') in several unopened syringes of this product. ''S. marcescens'' can lead to life-threatening injuries and/or death.
2008 recall due to adulteration in drug from China
In March 2008, major recalls of heparin were announced by the FDA due to contamination of the raw heparin stock imported from China. According to the FDA, the adulterated heparin killed nearly 80 people in the United States. The adulterant was identified as an "over-sulphated" derivative ofchondroitin sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars (N-Acetylgalactosamine, N-acetylgalactosamine and glucuronic acid). It is usually found attached to proteins as part of a proteoglycan. A chondroit ...
, a popular shellfish-derived supplement often used for arthritis, which was intended to substitute for actual heparin in potency tests.
According to the ''New York Times'': "Problems with heparin reported to the agency include difficulty breathing, nausea, vomiting, excessive sweating and rapidly falling blood pressure that in some cases led to life-threatening shock".
Use in homicide
In 2006, Petr Zelenka, a nurse in theCzech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
, deliberately administered large doses to patients, killing seven, and attempting to kill ten others.
Overdose issues
In 2007, a nurse atCedars-Sinai Medical Center
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center is a non-profit, Tertiary referral hospital, tertiary, 915-bed teaching hospital and multi-specialty academic health science centre, academic health science center located in Los Angeles, California. Part of the Cedars ...
mistakenly gave the 12-day-old twins of actor Dennis Quaid a dose of heparin that was 1,000 times the recommended dose for infants. The overdose allegedly arose because the labeling and design of the adult and infant versions of the product were similar. The Quaid family subsequently sued the manufacturer, Baxter Healthcare Corp., and settled with the hospital for $750,000. Prior to the Quaid accident, six newborn babies at Methodist Hospital in Indianapolis, Indiana, were given an overdose. Three of the babies died after the mistake.
In July 2008, another set of twins born at Christus Spohn Hospital South, in Corpus Christi, Texas
Corpus Christi ( ; ) is a Gulf Coast of the United States, coastal city in the South Texas region of the U.S. state of Texas and the county seat and largest city of Nueces County, Texas, Nueces County with portions extending into Aransas County, T ...
, died after an accidentally administered overdose of the drug. The overdose was due to a mixing error at the hospital pharmacy and was unrelated to the product's packaging or labeling. , the exact cause of the twins' death was under investigation.
In March 2010, a two-year-old transplant patient from Texas was given a lethal dose of heparin at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. The exact circumstances surrounding her death are still under investigation.
Production
Pharmaceutical-grade heparin is derived from mucosal tissues of slaughtered meat animals such as porcine (pig) intestines or bovine (cattle) lungs. Advances to produce heparin synthetically have been made in 2003 and 2008. In 2011, a chemoenzymatic process of synthesizing low molecular weight heparins from simple disaccharides was reported.Research
As detailed in the table below, the potential is great for the development of heparin-like structures asdrug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
s to treat a wide range of disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
s, in addition to their current use as anticoagulants.
: – indicates that no information is available
As a result of heparin's effect on such a wide variety of disease states, a number of drugs are indeed in development whose molecular structures are identical or similar to those found within parts of the polymeric heparin chain.
References
Further reading
* *External links
History of heparin
{{Authority control Chemical substances for emergency medicine Glycosaminoglycans Heparins World Health Organization essential medicines Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Aldols Ophthalmology drugs