Tampa Bay, Florida on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tampa Bay is a large natural

, Official Website The relatively shallow water and tidal mud flats allow for large

File:Tampa Bay, Florida, by Field, J. C., b. 1845.jpg, Tampa's waterfront, 1890.
File:Atlantic Coast Line railroad company terminal at the Port of Tampa, Florida (10977712996).jpg,
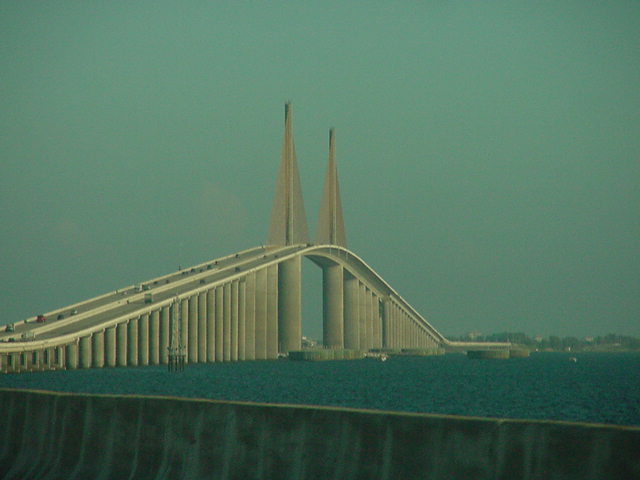 In the early 20th century, traveling overland between the growing communities around Tampa Bay was an arduous process. The trip between Tampa and St. Petersburg was almost around the north end of Old Tampa Bay and took up to 12 hours by train and over a full day over uncertain roads by car. The trip between St. Petersburg and Bradenton was even longer – over all the way around Tampa Bay, a trip that still took about two hours into the 1950s.
In 1924, the
In the early 20th century, traveling overland between the growing communities around Tampa Bay was an arduous process. The trip between Tampa and St. Petersburg was almost around the north end of Old Tampa Bay and took up to 12 hours by train and over a full day over uncertain roads by car. The trip between St. Petersburg and Bradenton was even longer – over all the way around Tampa Bay, a trip that still took about two hours into the 1950s.
In 1924, the George Gandy Sr. Made $1,932,000 Span Possible
St. Petersburg Times, April 18, 1956 Ten years later, the Davis Causeway (later renamed the Courtney Campbell Causeway) was built between Clearwater and Tampa. More bridges criss-crossed Tampa Bay over the ensuing decades, making travel between the surrounding communities much faster and furthering the economic development of the Tampa Bay area.
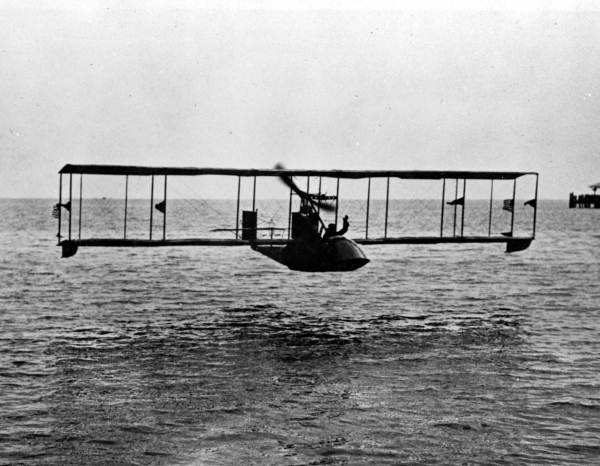 The difficulty of traveling between Tampa and St. Petersburg in the early 20th century inspired the world's first scheduled air service, the St. Petersburg-Tampa Airboat Line, which operated during the tourist season of 1914.
While the construction of bridges made air travel across Tampa Bay unnecessary, several airports have been built along the shoreline.
The difficulty of traveling between Tampa and St. Petersburg in the early 20th century inspired the world's first scheduled air service, the St. Petersburg-Tampa Airboat Line, which operated during the tourist season of 1914.
While the construction of bridges made air travel across Tampa Bay unnecessary, several airports have been built along the shoreline.
Tampa Bay Water Atlas
* {{Authority control Bays of Florida on the Gulf of Mexico Estuaries of Florida Bodies of water of Hillsborough County, Florida Bodies of water of Manatee County, Florida Bodies of water of Pinellas County, Florida Red tide Eutrophication
harbor
A harbor (American English), or harbour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be moored. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is ...
and shallow estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime enviro ...
connected to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
on the west-central coast of Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
, comprising Hillsborough Bay, McKay Bay
McKay Bay is the northeastern most arm of Tampa Bay, a large estuary on Florida's west coast. McKay Bay is brackish and shallow with the exception of a dredging, dredged shipping channel connecting key port facilities of Tampa, Florida to the res ...
, Old Tampa Bay, Middle Tampa Bay, and Lower Tampa Bay. The largest freshwater inflow into the bay is the Hillsborough River, which flows into Hillsborough Bay in downtown Tampa
Downtown Tampa is the central business district of Tampa, Florida, Tampa, Florida, United States, and the chief financial district of the Tampa Bay Area.
It is second only to Westshore, Tampa, Westshore regarding employment in the area. Compani ...
. Many other smaller rivers and streams also flow into Tampa Bay, resulting in a large watershed area.
The shores of Tampa Bay were home to the Weeden Island Culture
The Weeden Island cultures are a group of related archaeological cultures that existed during the Late Woodland period (500 - 1000 CE) of the North American Southeast. The name for this group of cultures was derived from the Weedon Island site ...
and then the Safety Harbor culture for thousands of years. These cultures relied heavily on Tampa Bay for food, and the waters were rich enough that they were one of the few Native American cultures that did not have to farm. The Tocobaga
Tocobaga (occasionally Tocopaca) was the name of a chiefdom of Native Americans, its chief, and its principal town during the 16th century. The chiefdom was centered around the northern end of Old Tampa Bay, the arm of Tampa Bay that extends betw ...
was likely the dominant chiefdom in the area when Spanish explorers arrived in the early 1500s, but there were likely smaller chiefdoms on the eastern side of the bay which were not well documented. The indigenous population had been decimated by disease and warfare by the late 1600s, and there were no permanent human settlements in the area for over a century. The United States took possession of Florida in 1821 and established Fort Brooke
Fort Brooke was a historical military post established at the mouth of the Hillsborough River (Florida), Hillsborough River in present-day Tampa, Florida in 1824. Its original purpose was to serve as a check on and trading post for the native S ...
at the mouth of the Hillsborough River in 1824.
The communities surrounding Tampa Bay grew tremendously during the 20th century. Today, the area is home to about 4 million residents, making Tampa Bay a heavily used commercial and recreational waterway and subjecting it to increasing amounts of pollutants from industry, agriculture, sewage, and surface runoff
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow or terrestrial runoff) is the unconfined flow of water over the ground surface, in contrast to ''channel runoff'' (or ''stream flow''). It occurs when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other ...
. The bay's water quality was seriously degraded by the early 1980s, resulting in a sharp decline in sea life and decreased availability for recreational use. Greater care has been taken in recent decades to mitigate the effects of human habitation on Tampa Bay, most notably upgraded sewage treatment
Sewage treatment is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable to discharge to the surrounding environment or an intended reuse application, thereby preventing water p ...
facilities and several sea grass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine (ocean), marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four Family (biology), families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and ...
restoration projects, resulting in improved water quality over time. However, occasional red tide
A harmful algal bloom (HAB), or excessive algae growth, sometimes called a red tide in marine environments, is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural algae-produced toxins, water deoxygenation, ...
and other algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
blooms have caused concern about the ongoing health of the estuary.
The term "Tampa Bay" is often used as shorthand to refer to all or parts of the Tampa Bay area
The Tampa Bay area is a major metropolitan area surrounding Tampa Bay on the Gulf Coast of Florida in the United States. It includes the main cities of Tampa, Florida, Tampa, St. Petersburg, Florida, St. Petersburg, and Clearwater, Florida, Clea ...
, which comprises many towns and cities in several counties surrounding the large body of water. Local marketing and branding efforts (including several professional sports teams, tourist boards, and chambers of commerce) commonly use the moniker "Tampa Bay", furthering the misconception that it is the name of a particular municipality when this is not the case.
Geography

Origin
Tampa Bay formed approximately 6,000 years ago as abrackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
drowned river valley type estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime enviro ...
with a wide mouth connecting it to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
. Prior to that time, it was a large fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salt (chemistry), salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include ...
lake, possibly fed by the Floridan Aquifer
The Floridan aquifer system, composed of the Upper and Lower Floridan aquifers, is a sequence of Paleogene carbonate rock which spans an area of about in the southeastern United States. It underlies the entire state of Florida and parts of Alaba ...
through natural springs. Though the exact process of the lake-to-bay transformation is not completely understood, the leading theory is that rising sea levels following the last ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and g ...
coupled with the formation of a massive sink hole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are also known as shakeholes, and to openings where surface water ...
near the current mouth of the bay created a connection between the lake and the gulf.
Ecology
Tampa Bay is Florida's largest open-water estuary, extending over and forming coastlines of Hillsborough,Manatee
Manatees (, family (biology), family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivory, herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing t ...
and Pinellas counties. The freshwater sources of the bay are distributed among over a hundred small tributaries, rather than a single river. The Hillsborough River is the largest such freshwater source, with the Alafia, Manatee
Manatees (, family (biology), family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivory, herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing t ...
, and Little Manatee rivers the next largest sources. Because of these many flows into the bay, its large watershed
Watershed may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, an area of land where surface water converges (North American usage)
Music
* Watershed Music Festival, an annual country ...
covers portions of five Florida counties and approximately .
The bottom of Tampa Bay is silty and sandy, with an average water depth of only about ."Tampa Bay Estuary Program", Official Website The relatively shallow water and tidal mud flats allow for large
sea grass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine (ocean), marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four Family (biology), families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and ...
beds, and along with the surrounding mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ...
-dominated wetlands, the bay provides habitat for a wide variety of wildlife. More than 200 species of fish are found in the waters of the bay, along with bottlenose dolphin
The bottlenose dolphin is a toothed whale in the genus ''Tursiops''. They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus contains three species: the common bot ...
s and manatees
Manatees (, family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living spe ...
, plus many types of marine invertebrates
Marine invertebrates are invertebrate animals that live in marine habitats, and make up most of the macroscopic life in the oceans. It is a polyphyletic blanket term that contains all marine animals except the marine vertebrates, including the ...
including oysters
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of Seawater, salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in Marine (ocean), marine or Brackish water, brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly Calcification, calcified, a ...
, scallops
Scallop () is a common name that encompasses various species of marine bivalve molluscs in the taxonomic family Pectinidae, the scallops. However, the common name "scallop" is also sometimes applied to species in other closely related famili ...
, clams
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve mollusc. The word is often applied only to those that are deemed edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the sea floor or riverbeds. Clams h ...
, shrimp
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchi ...
and crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropo ...
. More than two dozen species of birds, including brown pelican
The brown pelican (''Pelecanus occidentalis'') is a bird of the pelican family, Pelecanidae, one of three species found in the Americas and one of two that feed by diving into water. It is found on the Atlantic Coast from New Jersey to the mouth ...
s, several types of heron
Herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 75 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genus ''Botaurus'' are referred to as bi ...
and egret
Egrets ( ) are herons, generally long-legged wading birds, that have white or buff plumage, developing fine plumes (usually milky white) during the breeding season. Egrets are not a biologically distinct group from herons and have the same build ...
, Roseate spoonbill
The roseate spoonbill (''Platalea ajaja'') is a social wading bird of the ibis and spoonbill family, Threskiornithidae. It is a resident breeder in both South and North America. The roseate spoonbill's pink color is diet-derived, consisting of ...
s, cormorant
Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the International Ornithologists' Union (IOU) ado ...
s, and laughing gull
The laughing seagull (''Leucophaeus atricilla'') is a medium-sized gull of North America, North and South America. Named for its laugh-like call, it is an opportunistic omnivore and scavenger. It breeds in large colonies mostly along the Atlantic ...
s make their year-round home along its shores and small islands, with several other migratory species joining them in the winter. The cooler months are also when warm-water outfalls from power plants bordering the bay draw one out of every six West Indian manatees, an endangered species, to the area.
Environmental issues
Conservation
Tampa Bay was designated as an "estuary of national significance" by theUnited States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on De ...
in 1990. Two National Wildlife Refuge
The National Wildlife Refuge System (NWRS) is a system of protected areas of the United States managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS), an agency within the United States Department of the Interior, Department of the Interi ...
s are located in Tampa Bay: Pinellas National Wildlife Refuge
The Pinellas National Wildlife Refuge is part of the United States National Wildlife Refuge (NWR) System, located offshore from mainland St. Petersburg, Florida, and only accessible by boat. The refuge was established in 1951, to act as a br ...
and the refuge on Egmont Key Egmont may refer to:
* Egmont Group, a media corporation founded and rooted in Copenhagen, Denmark
* Egmond family (often spelled "Egmont"), an influential Dutch family, lords of the town of Egmond
** Lamoral, Count of Egmont (1522–1568), the bes ...
. Most of the islands (including several man-made islands built from dredge spoil) and sandbar
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material, and rises from the bed of a body of water close to the surface or ...
s are off-limits to the public, due to their fragile ecology and their use as nesting sites by many species of birds. The Tampa Bay Estuary Program keeps watch over the Bay's health.
Pollution
Tampa Bay was once teeming with fish and wildlife. People of the Safety Harbor culture lived almost entirely from mullet, shellfish, sea turtles, manatees, crabs, and other bounties harvested from the sea. As late as the early 20th century, visitors still reported huge schools of mullet swimming across the bay in such numbers that they "impeded the passage of boats". The establishment and rapid growth of surrounding communities during the 20th century caused serious damage to the bay's natural environment. Heavy harvesting of fish and other sea life, constantdredging
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing d ...
of shipping channels, and the clearing of mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ...
s for shoreline development were important factors. Most damaging was the discharge of waste water
Wastewater (or waste water) is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of do ...
and other pollutants into the bay, which drastically degraded water quality. The bay's health reached a low point in the 1970s. The water was so murky that sunlight could not reach the shallow bottom, reducing sea grass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine (ocean), marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four Family (biology), families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and ...
coverage by more than 80% compared to earlier in the century and severely impacting the marine ecosystem. Many previously common species became scarce, and bay beaches were regularly closed due to unsafe levels of bacteria and pollutants.
Beginning in the early 1980s after federal and state legislation to improve water quality, authorities installed improved water treatment plants
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, inc ...
and tightened regulation of industrial discharge, leading to slow but steady improvement in water quality and general ecological health. By 2010, measures of sea grass coverage, water clarity, and biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
had improved to levels last seen in the 1950s.
However, industrial and agricultural runoff along with runoff from developed areas pose a continuing threat to marine ecosystems in the bay, particularly by clouding the water with sediments and algae blooms, and seagrass coverage declined slightly in the late 2010s. Wastewater pollution from old phosphate plants near the shoreline has been a particular problem. For example, in 2004, a leak of 65 million gallons of acidic water from a Cargill phosphate plant on the bay's southern shore severely impacted wetlands in the vicinity of the spill.
On September 5, 2004, acidic process water was released from the Mosaic Fertilizer, LLC storage containment system during Hurricane Frances
Hurricane Frances was the second most intense tropical cyclone in the Atlantic during 2004 and proved to be very destructive in Florida. It was the sixth named storm, the fourth hurricane, and the third major hurricane of the 2004 Atlantic h ...
. By the following day, an estimated 65 million gallons had emptied into Archie Creek Canal, Hillsborough Bay, and surrounding wetlands.
And in April 2021, a breach of a wastewater reservoir at the long-closed Piney Point phosphate plant sent over 200 millions gallons of nutrient-rich mine tailings
In mining, tailings or tails are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction (gangue) of an ore. Tailings are different from overburden, which is the waste rock or other material th ...
streaming into lower Tampa Bay. The resulting growth of red tide
A harmful algal bloom (HAB), or excessive algae growth, sometimes called a red tide in marine environments, is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural algae-produced toxins, water deoxygenation, ...
algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
led to an ecocide
Ecocide (from Greek 'home' and Latin 'to kill') is the destruction of the natural environment, environment by humans. Ecocide threatens all human populations that are dependent on natural resources for maintaining Ecosystem, ecosystems and ensu ...
and killed over 1000 tons of fish in the bay and along the nearby gulf coast and may lead to further damage to seagrass beds.
The effects of Hurricane Milton
Hurricane Milton was an extremely powerful and destructive tropical cyclone which in 2024 became the most intense Atlantic hurricane ever recorded over the Gulf of Mexico, tying with Hurricane Rita in 2005. Milton made landfall on the west coa ...
in October 2024 caused polluted waste from the fertilizer industry including products from Mosaic
A mosaic () is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/Mortar (masonry), mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and ...
, which were retained after the production of phosphate, to enter into Tampa Bay. Both Hurricane Milton and Hurricane Helene
Hurricane Helene ( ) was a deadly and devastating tropical cyclone that caused widespread catastrophic damage and numerous fatalities across the Southeastern United States in late September 2024. It was the strongest hurricane on record to ...
caused disruption in the production of phosphate fertilizers from Tampa Bay.
Climate change
Tampa Bay, like other parts of Florida, is extremely vulnerable tosea level rise
The sea level has been rising from the end of the last ice age, which was around 20,000 years ago. Between 1901 and 2018, the average sea level rose by , with an increase of per year since the 1970s. This was faster than the sea level had e ...
caused by climate change. The sea level has risen since 1946. Tampa Bay is also one of the areas in the US most at risk when hurricanes arrive because of its location, growing population, and the geography of the bay.
The Tampa Bay Regional Resiliency Coalition coordinates the region's response to climate change. Communities throughout the Bay, including St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601, ...
and Tampa
Tampa ( ) is a city on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. Tampa's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and t ...
are adapting infrastructure and buildings to face changes in sea level.
Human habitation

Early inhabitants
Humans have lived in Florida for millennia, at least 14,000 years. Due to worldwide glaciation, sea levels were much lower at the time, and Florida's peninsula extended almost 60 miles west of today's coastline.Paleo-Indian
Paleo-Indians were the first peoples who entered and subsequently inhabited the Americas towards the end of the Late Pleistocene period. The prefix ''paleo-'' comes from . The term ''Paleo-Indians'' applies specifically to the lithic period in ...
sites have been found near rivers and lakes in northern Florida, leading to speculation that these first Floridians also lived on Tampa Bay when it was still a freshwater lake. Evidence of human habitation from this early period has been found at the Harney Flats site, which is approximately 10 miles east of the current location of Tampa's downtown waterfront.
The earliest evidence of human habitation directly on the shores of Tampa Bay comes from the Manasota culture
The Manasota culture was an archaeological culture that was practiced on the central Gulf coast of the Florida peninsula from about 500 BCE until about 900, when it developed into the Safety Harbor culture. From about 300 to 700 the Manasota cu ...
, a variant of the Weeden Island culture
The Weeden Island cultures are a group of related archaeological cultures that existed during the Late Woodland period (500 - 1000 CE) of the North American Southeast. The name for this group of cultures was derived from the Weedon Island site ...
, who lived in the area beginning around 5,000–6,000 years ago, after sea levels had risen to near modern levels and the bay was connected to the Gulf of Mexico. This culture, which relied almost exclusively on the bay for food and other resources, was in turn replaced by the similar Safety Harbor culture by approximately 800 AD. The pre-contact Indigenous nation most associated with the Tampa Bay are the historic Tocobaga
Tocobaga (occasionally Tocopaca) was the name of a chiefdom of Native Americans, its chief, and its principal town during the 16th century. The chiefdom was centered around the northern end of Old Tampa Bay, the arm of Tampa Bay that extends betw ...
nation, who are known to be among the ancestors of the contemporary Seminole and Miccosukee Tribes of Florida.
European exploration
The Safety Harbor culture was dominant in the area at the time of first contact with Europeans in the mid-1500s. TheTocobaga
Tocobaga (occasionally Tocopaca) was the name of a chiefdom of Native Americans, its chief, and its principal town during the 16th century. The chiefdom was centered around the northern end of Old Tampa Bay, the arm of Tampa Bay that extends betw ...
, who built their principal town near today's Safety Harbor in the northwest corner of Old Tampa Bay, are the most documented group from that era because they had the most interactions with Spanish explorers
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
** Spanish history
**Spanish culture ...
. However, there were many other coastal villages organized into various small chiefdoms all around the bay.
Not finding gold or silver in the vicinity and unable to convert the native inhabitants to Christianity, the Spanish did not remain in the Tampa Bay area for long. However, diseases they introduced decimated the native population over the ensuing decades, leading to the near-total collapse of every established culture across peninsular Florida. Between this depopulation and the indifference of its colonial owners, the Tampa Bay region would be virtually uninhabited for almost 200 years.
Tampa Bay was given different names by early mapmakers. Spanish maps dated from 1584 identifies Tampa Bay as ''Baya de Spirito Santo'' ("Bay of the Holy Spirit
The Holy Spirit, otherwise known as the Holy Ghost, is a concept within the Abrahamic religions. In Judaism, the Holy Spirit is understood as the divine quality or force of God manifesting in the world, particularly in acts of prophecy, creati ...
"). A map dated 1695 identifies the area as ''Bahia Tampa''. Later maps dated 1794 and 1800 show the bay divided with three different names, ''Tampa Bay'' west of the Interbay peninsula and ''Hillsboro Bay'' on the east with an overall name of ''Bay of Spiritu Santo''. At other times, the entire bay was identified as The Bay of Tocobaga.
United States control
The United States acquired Florida from Spain in 1821. The name ''Spirito Santo'' seems to have disappeared from maps of the region in favor of "Tampa Bay" (sometimes divided into Tampa and Hillsboro Bays) soon after the US establishedFort Brooke
Fort Brooke was a historical military post established at the mouth of the Hillsborough River (Florida), Hillsborough River in present-day Tampa, Florida in 1824. Its original purpose was to serve as a check on and trading post for the native S ...
at the mouth of the Hillsborough River in 1824. For the next several decades, during the Seminole Wars
The Seminole Wars (also known as the Florida Wars) were a series of three military conflicts between the United States and the Seminoles that took place in Florida between about 1816 and 1858. The Seminoles are a Native American nation which co ...
, the Tampa Bay would be a primary point of confrontation, detention, and forced expulsion of the Seminole & Miccosukee people of Florida. Fort Brooke, Fort Dade, and the American military's miscellaneous Egmont Key facilities were the primary sites associated with the removal of the Seminole in the Floridian leg of the Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears was the forced displacement of about 60,000 people of the " Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850, and the additional thousands of Native Americans and their black slaves within that were ethnically cleansed by the U ...
.
For the next 100 years, many new communities were founded around the bay. Fort Brooke begat Tampa
Tampa ( ) is a city on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. Tampa's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and t ...
on the northeast shore, Fort Harrison (a minor military outpost on Florida's west coast) begat Clearwater, the trading post of "Braden's Town" developed into Bradenton
Bradenton ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Manatee County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 census, the city's population is 55,698, up from 49,546 at the 2010 census. It is a principal city in the Sarasota metropolitan area. Dow ...
on the south, and St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601, ...
grew quickly after its founding in the late 19th century, on the western bay shore opposite Tampa. By 2010, the Tampa Bay Area
The Tampa Bay area is a major metropolitan area surrounding Tampa Bay on the Gulf Coast of Florida in the United States. It includes the main cities of Tampa, Florida, Tampa, St. Petersburg, Florida, St. Petersburg, and Clearwater, Florida, Clea ...
was home to over 4 million residents.
Transportation
By sea
As Tampa began to grow in the mid-1800s, roads across central Florida were still just rough trails and rail lines did not yet extend down the Florida peninsula, so the most convenient means of traveling to and from the area was by sea. By the late 19th century, however, the shallow nature of Tampa Bay made it impossible for large modern vessels with deeper drafts to reach the city of Tampa's downtown wharves on Hillsboro Bay. Most ships would anchor well out from shore and transfer cargo and passengers to and from the city in smaller boats. Henry B. Plant'srailroad line
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road ...
reached the area in 1884 and ran across the Interbay Peninsula to Old Tampa Bay, where he built the town and shipping facility of Port Tampa
Port Tampa is a neighborhood in the southwestern most portion within the city limits of Tampa, Florida, on the western end of the Interbay Peninsula where the main port used to be. Within this neighborhood is Picnic Island Park as well as West ...
at its terminus. In 1898, Plant used his connections in the federal government to make Port Tampa a major embarkation point for the U.S. Army during the Spanish–American War
The Spanish–American War (April 21 – August 13, 1898) was fought between Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States in 1898. It began with the sinking of the USS Maine (1889), USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor in Cuba, and resulted in the ...
, leading to the U.S. Congress appropriating funds for the United States Army Corps of Engineers
The United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) is the military engineering branch of the United States Army. A direct reporting unit (DRU), it has three primary mission areas: Engineer Regiment, military construction, and civil wo ...
to begin the first large dredging operation in Tampa Bay. A deep shipping channel was created which linked Port Tampa to the mouth of the bay, enabling Plant to greatly expand his steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
line. In 1917, the Corps of Engineers dredged another channel from the mouth of Tampa Bay to the Port of Tampa, instantly making the city an important shipping center.
The Corps of Engineers currently maintains more than 80 miles of deep-water channels in Tampa Bay up to a depth of 47 feet. These must be continuously re-dredged and deepened due to the sandy nature of the bay bottom. While dredging has enabled seaborne commerce to become an important part of the Tampa Bay area's economy, it has also damaged the bay's water quality and ecology. More care has been taken in recent decades to lessen the environmental impact of dredging. Dredged material has also been used to create several spoil islands on the eastern side of Hillsboro Bay. These islands have become important nesting sites for many seabirds, including threatened species such as oystercatcher
The oystercatchers are a group of waders forming the family (biology), family Haematopodidae, which has a single genus, ''Haematopus''. They are found on coasts worldwide apart from the polar regions and some tropical regions of Africa and Sout ...
s, and have been designated as "sanctuary islands" that are off-limits to boaters.
Port Tampa
Port Tampa is a neighborhood in the southwestern most portion within the city limits of Tampa, Florida, on the western end of the Interbay Peninsula where the main port used to be. Within this neighborhood is Picnic Island Park as well as West ...
, c. 1900.
File:Port of Tampa.JPG, Facilities at Port Tampa Bay
Port Tampa Bay, known as the Port of Tampa until January 2014, is the largest port in the state of Florida and is overseen by the Tampa Port Authority, a Hillsborough County agency. The port is located in Tampa, Florida near downtown Tampa's Ch ...
from Davis Islands, downtown Tampa
Downtown Tampa is the central business district of Tampa, Florida, Tampa, Florida, United States, and the chief financial district of the Tampa Bay Area.
It is second only to Westshore, Tampa, Westshore regarding employment in the area. Compani ...
at left
=Ports on Tampa Bay
= *Port Tampa Bay
Port Tampa Bay, known as the Port of Tampa until January 2014, is the largest port in the state of Florida and is overseen by the Tampa Port Authority, a Hillsborough County agency. The port is located in Tampa, Florida near downtown Tampa's Ch ...
(known as the Port of Tampa until 2014): Oldest port on Tampa Bay, can trace its roots to the wharves of Fort Brooke
Fort Brooke was a historical military post established at the mouth of the Hillsborough River (Florida), Hillsborough River in present-day Tampa, Florida in 1824. Its original purpose was to serve as a check on and trading post for the native S ...
in the 1820s. Currently centered east and southeast of downtown Tampa on Hillsboro and McKay Bays. Largest port in Florida; 10th largest in the nation. Port Tampa Bay accommodates half of Florida's cargo
In transportation, cargo refers to goods transported by land, water or air, while freight refers to its conveyance. In economics, freight refers to goods transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. The term cargo is also used in cas ...
in the form of bulk, roll-on/roll-off
Roll-on/roll-off (RORO or ro-ro) ships are cargo ships designed to carry wheeled cargo, such as cars, motorcycles, trucks, semi-trailer trucks, buses, Trailer (vehicle), trailers, and railroad cars, that are driven on and off the ship on their ...
, refrigerated and container cargo, and petroleum products. Home to extensive ship repair and building industry and several cruise ship
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports of call, where passengers may go on Tourism, tours k ...
terminals.
* Port Tampa
Port Tampa is a neighborhood in the southwestern most portion within the city limits of Tampa, Florida, on the western end of the Interbay Peninsula where the main port used to be. Within this neighborhood is Picnic Island Park as well as West ...
: Established in 1885 by Henry B. Plant at the terminus of the Plant System
The Plant System, named after its owner, Henry B. Plant, was a system of railroads and steamboats in the U.S. South, taken over by the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad in 1902. The original line of the system was the Savannah, Florida and Western ...
railroad line on the eastern shore of Old Tampa Bay. Eclipsed in tonnage and importance by the Port of Tampa in the early 1900s, but still an important arrival point for aviation fuel
Aviation fuels are either petroleum-based or blends of petroleum and synthetic fuels, used to power aircraft. They have more stringent requirements than fuels used for ground applications, such as heating and road transport, and they contain add ...
which is piped to nearby Tampa International Airport
Tampa International Airport is an international airport west of Downtown Tampa, in Hillsborough County, Florida, United States. The airport is publicly owned by Hillsborough County Aviation Authority (HCAA)., effective May 15, 2025. The airp ...
and MacDill Air Force Base
MacDill Air Force Base (MacDill AFB) is an active United States Air Force installation located 4 miles (6.4 km) south-southwest of downtown Tampa, Florida.
The "host wing" for MacDill AFB is the 6th Air Refueling Wing (6 ARW), assig ...
.
* Port Manatee: Located on the southern shore of Lower Tampa Bay. Most refrigerated dockside space of any Gulf of Mexico port. Ranked fifth among Florida's fourteen seaports in total annual cargo tonnage.
* The Port of St. Petersburg: Located on the St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601, ...
waterfront on Old Tampa Bay and operated by the city. Smallest of Florida's ports, caters mainly to private vessels. Site of U.S. Coast Guard station.
By land
 In the early 20th century, traveling overland between the growing communities around Tampa Bay was an arduous process. The trip between Tampa and St. Petersburg was almost around the north end of Old Tampa Bay and took up to 12 hours by train and over a full day over uncertain roads by car. The trip between St. Petersburg and Bradenton was even longer – over all the way around Tampa Bay, a trip that still took about two hours into the 1950s.
In 1924, the
In the early 20th century, traveling overland between the growing communities around Tampa Bay was an arduous process. The trip between Tampa and St. Petersburg was almost around the north end of Old Tampa Bay and took up to 12 hours by train and over a full day over uncertain roads by car. The trip between St. Petersburg and Bradenton was even longer – over all the way around Tampa Bay, a trip that still took about two hours into the 1950s.
In 1924, the Gandy Bridge
Gandy Bridge is a bridge spanning Tampa Bay, Old Tampa Bay from St. Petersburg, Florida to Tampa, Florida. The original 1924 span was dismantled in 1975. The second span, constructed in 1956, was used for vehicular traffic until 1997. The thi ...
over Old Tampa Bay reduced the driving distance between Tampa and St. Petersburg to .St. Petersburg Times, April 18, 1956 Ten years later, the Davis Causeway (later renamed the Courtney Campbell Causeway) was built between Clearwater and Tampa. More bridges criss-crossed Tampa Bay over the ensuing decades, making travel between the surrounding communities much faster and furthering the economic development of the Tampa Bay area.
=Bridges that cross Tampa Bay
= *Sunshine Skyway Bridge
The Sunshine Skyway Bridge, officially referred to as the Bob Graham Sunshine Skyway Bridge, is a pair of long beam bridges with a central tall cable-stayed bridge. It spans Lower Tampa Bay to connect Pinellas County (St. Petersburg, Florid ...
: Opened 1954. Spans Lower Tampa Bay from Bradenton
Bradenton ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Manatee County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 census, the city's population is 55,698, up from 49,546 at the 2010 census. It is a principal city in the Sarasota metropolitan area. Dow ...
on the south to St. Petersburg on the north, greatly reducing travel times between Manatee and Pinellas Counties. Part of I-275 & US 19
U.S. Route 19 or U.S. Highway 19 (US 19) is a north–south United States Numbered Highway in the Eastern United States. Despite encroaching Interstate Highways, the route has remained a long-haul road, connecting the Gulf of Mex ...
.
* Gandy Bridge
Gandy Bridge is a bridge spanning Tampa Bay, Old Tampa Bay from St. Petersburg, Florida to Tampa, Florida. The original 1924 span was dismantled in 1975. The second span, constructed in 1956, was used for vehicular traffic until 1997. The thi ...
: Opened 1924 (first roadway bridge over Tampa Bay). Spans Old Tampa Bay from Tampa on the east to St. Petersburg on the west. Part of U.S. Route 92
U.S. Highway 92 (US 92) is a U.S. Route entirely in the state of Florida. The western terminus is at US 19 Alternate (US 19 Alt.) and State Road 687 (SR 687)) in downtown St. Petersburg. The eastern terminus is at SR A1A ...
.
* Howard Frankland Bridge
The W. Howard Frankland Bridge is the central fixed-link bridge spanning Old Tampa Bay from St. Petersburg, Florida to Tampa, Florida. It is one of three bridges connecting Hillsborough County and Pinellas County; the others being Gandy Bridg ...
: Opened 1960. Spans middle of Old Tampa Bay from Tampa on the east to St. Pete on the west. Part of I-275.
* Courtney Campbell Causeway: Opened 1934. Spans northern Old Tampa Bay from Tampa on the east to Clearwater on the west. Part of Florida State Road 60
State Road 60 (SR 60) is an east–west route transversing Florida from the Gulf of Mexico to the Atlantic Ocean. The western terminus of SR 60 is at the ''Sunsets at Pier 60'' site in Clearwater Beach. The eastern terminus is in ...
.
* Bayside Bridge: Opened 1993. Runs roughly parallel to the western shore of Old Tampa Bay from Largo / St. Petersburg on the south to Clearwater on the north. Built to help relieve traffic congestion on nearby US-19.
* 22nd Street Causeway: Opened 1926. Bridge portion spans the mouth of McKay Bay near Port Tampa Bay. Part of U.S. Route 41
U.S. Route 41, also U.S. Highway 41 (US 41), is a major north–south United States Numbered Highway that runs from Miami, Florida, to the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. Until 1949, the part in southern Florida, from Naples to Miam ...
.
By air
 The difficulty of traveling between Tampa and St. Petersburg in the early 20th century inspired the world's first scheduled air service, the St. Petersburg-Tampa Airboat Line, which operated during the tourist season of 1914.
While the construction of bridges made air travel across Tampa Bay unnecessary, several airports have been built along the shoreline.
The difficulty of traveling between Tampa and St. Petersburg in the early 20th century inspired the world's first scheduled air service, the St. Petersburg-Tampa Airboat Line, which operated during the tourist season of 1914.
While the construction of bridges made air travel across Tampa Bay unnecessary, several airports have been built along the shoreline. Albert Whitted Airport
Albert Whitted Airport is a public airport in St. Petersburg, Florida, St. Petersburg, Pinellas County, Florida, Pinellas County, Florida, United States. It is on the west edge of Tampa Bay, just southeast of downtown St. Petersburg and east of ...
on the St. Petersburg waterfront and Peter O. Knight Airport on Davis Island near downtown Tampa were both established in the 1930s. Later, Tampa International Airport
Tampa International Airport is an international airport west of Downtown Tampa, in Hillsborough County, Florida, United States. The airport is publicly owned by Hillsborough County Aviation Authority (HCAA)., effective May 15, 2025. The airp ...
and St. Pete–Clearwater International Airport were established on opposite sides of Old Tampa Bay, and MacDill Air Force Base
MacDill Air Force Base (MacDill AFB) is an active United States Air Force installation located 4 miles (6.4 km) south-southwest of downtown Tampa, Florida.
The "host wing" for MacDill AFB is the 6th Air Refueling Wing (6 ARW), assig ...
opened on the southern tip of Tampa's Interbay Peninsula.
See also
* Climate of the Tampa Bay area * History of TampaReferences
External links
Tampa Bay Water Atlas
* {{Authority control Bays of Florida on the Gulf of Mexico Estuaries of Florida Bodies of water of Hillsborough County, Florida Bodies of water of Manatee County, Florida Bodies of water of Pinellas County, Florida Red tide Eutrophication