Takatō Castle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
is a
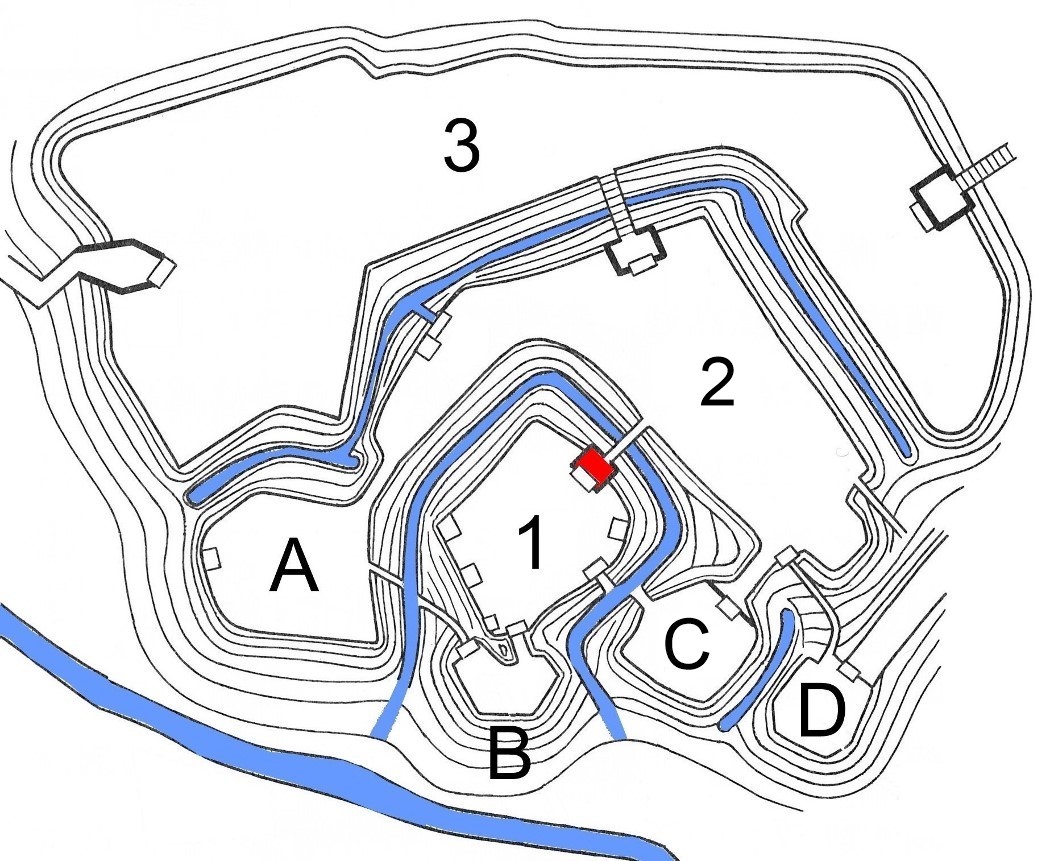 Takato Castle is located on a hill in the former Takatō Town on the eastern edge of central Ina Valley in southern Nagano Prefecture. The location was a crossroads on the Akiba Kaidō, a highway connecting
Takato Castle is located on a hill in the former Takatō Town on the eastern edge of central Ina Valley in southern Nagano Prefecture. The location was a crossroads on the Akiba Kaidō, a highway connecting
Japan National Tourist Organisation
{{DEFAULTSORT:Takato Castle Ruined castles in Japan Castles in Nagano Prefecture 100 Fine Castles of Japan Historic Sites of Japan Ina, Nagano Shinano Province Naitō clan Suwa clan
Japanese castle
are fortresses constructed primarily of wood and stone. They evolved from the wooden stockades of earlier centuries and came into their best-known form in the 16th century. Castles in Japan were built to guard important or strategic sites, such a ...
located in the city of Ina, southern Nagano Prefecture
is a Landlocked country, landlocked Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu. Nagano Prefecture has a population of 2,007,682 () and has a geographic area of . Nagano Prefecture borders Niigata Prefecture ...
, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. At the end of the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
, Takatō Castle was home to a cadet branch of the Naitō clan
is a Japanese samurai kin group. The clan claims its descent from Fujiwara no Hidesato. The Naitō became ''daimyōs'' during the Edo period.Edmond Papinot, Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d'histoire et de géographie du J ...
, ''daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji era, Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and no ...
'' of Takatō Domain
was a domain of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan during the Edo period from 1600 to 1871.
The Takatō Domain was based at Takatō Castle in Shinano Province, in the modern city of Ina, located in the Chūbu region of the island of Honshu. The ...
. The castle was also known as . Built sometime in the 16th century, it is now largely in ruins.
Layout
 Takato Castle is located on a hill in the former Takatō Town on the eastern edge of central Ina Valley in southern Nagano Prefecture. The location was a crossroads on the Akiba Kaidō, a highway connecting
Takato Castle is located on a hill in the former Takatō Town on the eastern edge of central Ina Valley in southern Nagano Prefecture. The location was a crossroads on the Akiba Kaidō, a highway connecting Tōtōmi province
was a Provinces of Japan, province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today western Shizuoka Prefecture.Louis-Frédéric, Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Tōtōmi''" in . Tōtōmi bordered on Mikawa Province, Mikawa, Suruga Province, S ...
with the Suwa region of Shinano and Kai Province and a road which led to the western portion of the Ina valley and Mino Province
was a province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today southern Gifu Prefecture. Mino was bordered by Ōmi to the west, Echizen and Hida to the north, Shinano to the east, and Ise, Mikawa, and Owari to the south. Its abbreviated fo ...
. When viewed from the standpoint of Kai Province, the area was a key point in the control of southern Shinano. The castle site overlooks the confluence of the Mibugawa River and the Fujisawa River, which forms part of its natural defenses. Deep trenches, earthen rampart
Rampart may refer to:
* Rampart (fortification), a defensive wall or bank around a castle, fort or settlement
Rampart may also refer to:
* LAPD Rampart Division, a division of the Los Angeles Police Department
** Rampart scandal, a blanket ter ...
s and stone walls in concentric rings form the defensive structures in a style typical of construction under Takeda Shingen
was daimyō, daimyo of Kai Province during the Sengoku period of Japan. Known as "the Tiger of Kai", he was one of the most powerful daimyo of the late Sengoku period, and credited with exceptional military prestige. Shingen was based in a p ...
. The Central Bailey (''Hon-maru'') was protected to the northwest and northeast by the Second Bailey (''Ni-no-maru'') and Third Bailey (''San-no-maru'') along with four enclosures: the ''Suwa-kuruwa'' ( 諏訪曲輪 ), ''Sasa-kuruwa'' ( 笹曲輪 ), ''Minami-kuruwa'' ( 南曲輪 ) and ''Hōdōji-kuruwa'' ( 法幢寺曲輪 ). Most of the gates were box-shaped gates, which added to the defenses. In the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
, front gate of the castle was changed from east side to west side, which directly faced the ''jōkamachi
The were centres of the domains of the feudal lords in medieval Japan. The ''jōkamachi'' represented the new, concentrated military power of the daimyo in which the formerly decentralized defence resources were concentrated around a single, cent ...
''. The han school
The ''han'' school was a type of educational institution in the Edo period of Japan. They taught samurai etiquette, the classical Confucian books, calligraphy, rhetoric, fighting with swords and other weapons; some also added subjects such as m ...
, built in 1860, was located in the Third Bailey. A few samurai
The samurai () were members of the warrior class in Japan. They were originally provincial warriors who came from wealthy landowning families who could afford to train their men to be mounted archers. In the 8th century AD, the imperial court d ...
residences have survived in the town.
History
The original date of construction of Takatō Castle is unknown, however before its construction, there was originally another fortification on the same site, controlled by the Takatō clan, retainers of theSuwa clan
The , also known as the Jin or Miwa clan (神氏, ''Miwa Uji (clan), uji / Miwa-shi'' or ''Jinshi'') was a Japanese ''Shake (social class), shake'' and samurai family. Originating from the area encompassing Lake Suwa in Shinano Province (modern- ...
,J Castle - Guide to Japanese Castles "Takato Castle" http://www.jcastle.info/castle/profile/129-Takato-Castle who had dominated the area since the Kamakura period
The is a period of History of Japan, Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura, Kanagawa, Kamakura by the first ''shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the G ...
.
Suwa Yorishige Suwa Yorishige may refer to:
* Suwa Yorishige (daimyo), Japanese samurai daimyo of the Shinano province
* Suwa Yorishige (Nanboku-chō period), military commander during the Nanboku-chō period
{{hndis ...
had an alliance with the Takeda clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan active from the late Heian period until the late 16th century. The clan was historically based in Kai Province in present-day Yamanashi Prefecture. The clan reached its greatest influence under the rule of Taked ...
, but this was broken by Takeda Shingen
was daimyō, daimyo of Kai Province during the Sengoku period of Japan. Known as "the Tiger of Kai", he was one of the most powerful daimyo of the late Sengoku period, and credited with exceptional military prestige. Shingen was based in a p ...
in 1545 during his campaign to conquer southern Shinano Province and the castle was seized by Takeda forces. Takatō Yoritsugu relied on support from his allies, Ogasawara Nagatoki and Tozawa Yorichika, however, they failed to come to his aid. Under the Takeda clan, the castle was completely rebuilt in accordance with contemporary military design practices, with a layout developed by his military strategist, Yamamoto Kansuke, and Shingen awarded the castle to his retainer, Akiyama Nobutomo and later to his son, Takeda Katsuyori
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' (military lord) of the Sengoku period, who was famed as the head of the Takeda clan and the successor to the legendary warlord Takeda Shingen. He was son-in-law of Hojo Ujiyasu, ''daimyō'' of Hojo clan.
Early life
H ...
. Shingen used the castle to launch his invasion of Mino Province
was a province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today southern Gifu Prefecture. Mino was bordered by Ōmi to the west, Echizen and Hida to the north, Shinano to the east, and Ise, Mikawa, and Owari to the south. Its abbreviated fo ...
, which brought him into conflict with Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods. He was the and regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. He is sometimes referred as the "Demon Daimyō" and "Demo ...
, and it was also from Takatō Castle that he started his final campaign in 1572 towards Kyoto
Kyoto ( or ; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan's largest and most populous island of Honshu. , the city had a population of 1.46 million, making it t ...
. After Shingen's death, the castle was entrusted to Nishina Morinobu, Takeda Katsuyori's younger brother.
The castle fell to Oda Nobutada
was a samurai and the eldest son of Oda Nobunaga, who fought in many battles during the Sengoku period of Japan. He commanded armies under his father in battles against Matsunaga Hisahide and against the Takeda clan.
Biography
Oda Nobutada w ...
, the son of Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods. He was the and regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. He is sometimes referred as the "Demon Daimyō" and "Demo ...
during the Battle of Temmokuzan
The 1582 in Japan, is regarded as the last stand of the Takeda clan. This was the final attempt by Takeda Katsuyori to resist the forces of Oda Nobunaga, who had been campaigning against him for some time. In his bid to hide from his pursuers, K ...
in 1582, with 50,000 troops as opposed to 3000 defenders on the side of the Takeda clan, with Nishina Morinobu resisting to the end.
After the Takeda clan was destroyed, the castle was awarded to Mori Hideyori, one of Nobunaga’s generals. However, after the assassination of Nobunaga in the Honnō-ji incident
The was the assassination of Japanese daimyo Oda Nobunaga at Honnō-ji, a temple in Kyoto, on 21 June 1582 (2nd day of the sixth month, Tenshō 10). Nobunaga was on the verge of unifying the country, but died in the unexpected rebellion of ...
, the area came under the control of Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu (born Matsudaira Takechiyo; 31 January 1543 – 1 June 1616) was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan, which ruled from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was the third of the three "Gr ...
, who assigned it to Hoshina Masanao
(1542 – October 21, 1601) was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku period, who served the Takeda clan. He was the successor of his father Hoshina Masatoshi in the ranks of the senior Takeda retainers, and was given command of 250 cavalry.
. However, after the Tokugawa clan was reassigned to the Kantō region
The is a geography, geographical region of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. In a common definition, the region includes the Greater Tokyo Area and encompasses seven prefectures of Japan, prefectures: Chiba Prefecture, Chiba, Gunma Prefe ...
by Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods and regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: ...
in 1590, Takatō was given to one of Hideyoshi’s generals, Ogasawara Sadayoshi. Tokugawa Ieyasu recovered the castle following the Battle of Sekigahara
The Battle of Sekigahara (Shinjitai: ; Kyūjitai: , Hepburn romanization: ''Sekigahara no Tatakai'') was an important battle in Japan which occurred on October 21, 1600 (Keichō 5, 15th day of the 9th month) in what is now Gifu Prefecture, ...
in 1603, and with the establishment of the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868.
The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars ...
, Takatō become the center of Takatō Domain
was a domain of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan during the Edo period from 1600 to 1871.
The Takatō Domain was based at Takatō Castle in Shinano Province, in the modern city of Ina, located in the Chūbu region of the island of Honshu. The ...
, a 30,000 ''koku
The is a Chinese-based Japanese unit of volume. One koku is equivalent to 10 or approximately , or about of rice. It converts, in turn, to 100 shō and 1,000 gō. One ''gō'' is the traditional volume of a single serving of rice (before co ...
'' holding under the Hoshina clan. The Hoshina were replaced by the Torii clan
was a Japanese daimyo family of the Sengoku period, Sengoku and Edo periods.
History
Yukinori, the founder of the Watari clan and the Torii clan, was from a family of Kumano Gongen Shinto priests in Kii Province. He was given the family name ...
from 1636-1689, until the assignment of the domain to Naitō Kiyokazu, whose descendants continued to rule to the Meiji restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored Imperial House of Japan, imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Althoug ...
.
Following the establishment of the Meiji government
The was the government that was formed by politicians of the Satsuma Domain and Chōshū Domain in the 1860s. The Meiji government was the early government of the Empire of Japan.
Politicians of the Meiji government were known as the Meiji ...
and the abolition of the han system
The in the Empire of Japan and its replacement by a system of prefectures in 1871 was the culmination of the Meiji Restoration begun in 1868, the starting year of the Meiji period. Under the reform, all daimyos (, ''daimyō'', feudal lords) ...
, the remaining structures of the castle were dismantled, and its surviving gates donated to nearby temples or were sold off to private owners. The castle site became the , noted for its sakura
The cherry blossom, or sakura, is the flower of trees in ''Prunus'' subgenus '' Cerasus''. ''Sakura'' usually refers to flowers of ornamental cherry trees, such as cultivars of ''Prunus serrulata'', not trees grown for their fruit (although ...
blossoms in spring. The cherry blossoms were planted in the Meiji Period
The was an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868, to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonizatio ...
.
Takatō Castle was listed as one of the 100 Fine Castles of Japan
The Japanese castle, castles in were chosen based on their significance in culture, history, and in their regions by the in 2006.
In 2017, the Japanese Castle Association created an additional finest 100 castles list as Continued Top 100 Japane ...
by the Japan Castle Foundation in 2006.
Current situation
Takatō Castle Ruins Park is regarded one of the three best locations to seecherry blossoms
The cherry blossom, or sakura, is the flower of trees in ''Prunus'' subgenus '' Cerasus''. ''Sakura'' usually refers to flowers of ornamental cherry trees, such as cultivars of ''Prunus serrulata'', not trees grown for their fruit (although ...
, together with Hirosaki Castle
is a ''hirayama''-style Japanese castle constructed in 1611. It was the seat of the Tsugaru clan, a 47,000 ''koku'' '' tozama'' daimyō clan who ruled over Hirosaki Domain, Mutsu Province, in what is now central Hirosaki, Aomori Prefecture, Jap ...
and Mount Yoshino
is the general name for the mountain ridge that stretches from the south bank of the Yoshino River in the town of Yoshino central Nara Prefecture, Japan, to the Ōmine Mountains, stretching for about eight kilometers from north-to-south, or the ...
.Takato Castle - Japan Guide http://www.japan-guide.com/e/e6065.html There is very little of the castle remaining in situ aside from part of the moats and stone ramparts. Several of the original castle gates have survived, but remain in private hands in other locations. One ''yagura'' has been reconstructed, and the Ōtemon (Main gate) of the castle, which had been moved to be used as the gate for a high school north of town, was relocated back to its original location in 1984. On the site of the castle, the oldest remaining building is the former han school
The ''han'' school was a type of educational institution in the Edo period of Japan. They taught samurai etiquette, the classical Confucian books, calligraphy, rhetoric, fighting with swords and other weapons; some also added subjects such as m ...
, the , built by the last ''daimyō'' of Takatō, Naitō Yorinao.
See also
*List of Historic Sites of Japan (Nagano)
This list is of the Monuments of Japan, Historic Sites of Japan located within the Prefectures of Japan, Prefecture of Nagano Prefecture, Nagano.
National Historic Sites
As of 1 August 2020, thirty-eight Sites have been Cultural Properties of Ja ...
Literature
*Takada, Toru: Takato-jō in: Miura, Masayuki (eds): Shiro to Jinya. Tokoku-hen. Gakken, 2006. , S. 100th *Nishigaya, Yasuhiro (eds): Takato-jō. In: Nihon Meijo Zukan, Rikogaku-sha, 1993. . * * * *References
External links
*Japan National Tourist Organisation
{{DEFAULTSORT:Takato Castle Ruined castles in Japan Castles in Nagano Prefecture 100 Fine Castles of Japan Historic Sites of Japan Ina, Nagano Shinano Province Naitō clan Suwa clan