TPM Chip on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Trusted Platform Module (TPM, also known as ISO/IEC 11889) is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. The term can also refer to a chip conforming to the standard.
TPM is used for digital rights management (DRM), Windows Defender, Windows Domain logon, protection and enforcement of software licenses, and prevention of
Trusted Platform Module (TPM, also known as ISO/IEC 11889) is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. The term can also refer to a chip conforming to the standard.
TPM is used for digital rights management (DRM), Windows Defender, Windows Domain logon, protection and enforcement of software licenses, and prevention of
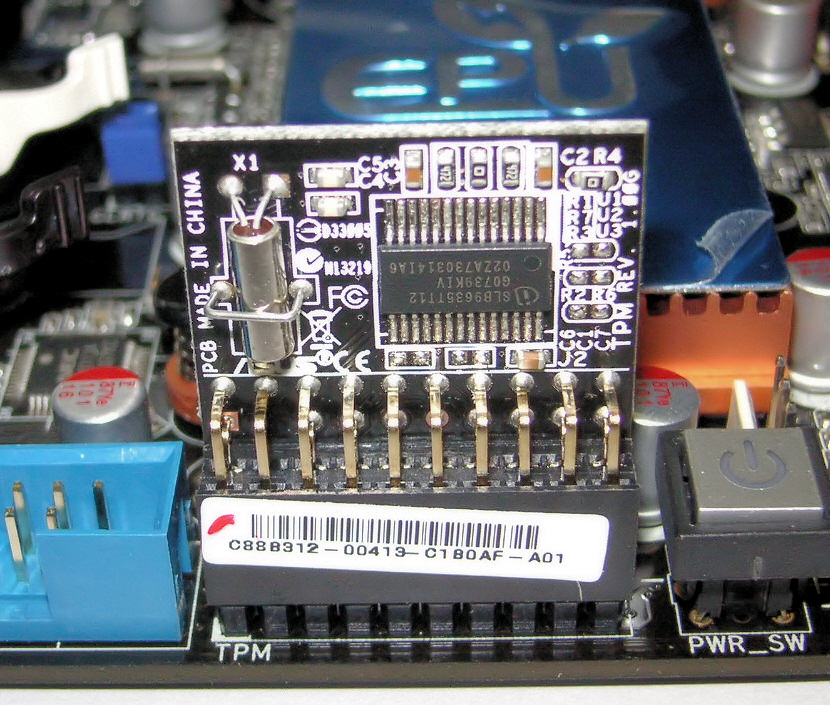 In 2006, new
In 2006, new
cheating in online games
Cheating in online games is the subversion of the rules or mechanics of online video games to gain an unfair advantage over other players, generally with the use of third-party software. What constitutes cheating is dependent on the game in ...
.
One of Windows 11's system requirements is TPM 2.0. Microsoft has stated that this is to help increase security against firmware and ransomware attacks.
History
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) was conceived by acomputer industry
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These progra ...
consortium called Trusted Computing Group (TCG). It evolved into ''TPM Main Specification Version 1.2'' which was standardized by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and r ...
(IEC) in 2009 as ISO/IEC 11889:2009. ''TPM Main Specification Version 1.2'' was finalized on March 3, 2011, completing its revision.
On April 9, 2014 the Trusted Computing Group announced a major upgrade to their specification entitled ''TPM Library Specification 2.0''. The group continues work on the standard incorporating errata, algorithmic additions and new commands, with its most recent edition published as 2.0 in November 2019. This version became ISO/IEC 11889:2015.
When a new revision is released it is divided into multiple parts by the Trusted Computing Group. Each part consists of a document that makes up the whole of the new TPM specification.
* Part 1 – Architecture (renamed from Design Principles)
* Part 2 – Structures of the TPM
*Part 3 – Commands
*Part 4 – Supporting Routines (added in TPM 2.0)
Overview
Trusted Platform Module provides * A hardware random number generator * Facilities for the secure generation of cryptographic keys for limited uses. *Remote attestation
Trusted Computing (TC) is a technology developed and promoted by the Trusted Computing Group. The term is taken from the field of trusted systems and has a specialized meaning that is distinct from the field of Confidential Computing. The core ide ...
: Creates a nearly unforgeable hash key summary of the hardware and software configuration. One could use the hash to verify that the hardware and software have not been changed. The software in charge of hashing the setup determines the extent of the summary.
* Binding: Encrypts data using the TPM bind key, a unique RSA key descended from a storage key. Computers that incorporate a TPM can create cryptographic keys and encrypt them so that they can only be decrypted by the TPM. This process, often called wrapping or binding a key, can help protect the key from disclosure. Each TPM has a master wrapping key, called the storage root key, which is stored within the TPM itself. User-level RSA key containers are stored with the Windows user profile for a particular user and can be used to encrypt and decrypt information for applications that run under that specific user identity.
* Sealing: Similar to binding, but in addition, specifies the TPM state for the data to be decrypted (unsealed).
* Other Trusted Computing functions for the data to be decrypted (unsealed).
Computer programs can use a TPM to authenticate hardware devices, since each TPM chip has a unique and secret Endorsement Key (EK) burned in as it is produced. Security embedded in hardware provides more protection than a software-only solution. Its use is restricted in some countries.
Uses
Platform integrity
The primary scope of TPM is to ensure the integrity of a platform. In this context, "integrity" means "behave as intended", and a "platform" is any computer device regardless of its operating system. This is to ensure that theboot process
In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer as initiated via hardware such as a button or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) has no software in its main memory, so so ...
starts from a trusted combination of hardware and software, and continues until the operating system has fully booted and applications are running.
When TPM is used, the firmware and the operating system are responsible for ensuring integrity.
For example, Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) can use TPM to form a root of trust
In cryptographic systems with hierarchical structure, a trust anchor is an authoritative entity for which trust is assumed and not derived.
In the X.509 architecture, a root certificate would be the trust anchor from which the whole chain of tru ...
: The TPM contains several Platform Configuration Registers (PCRs) that allow secure storage and reporting of security-relevant metrics. These metrics can be used to detect changes to previous configurations and decide how to proceed. Examples of such use can be found in Linux Unified Key Setup
The Linux Unified Key Setup (LUKS) is a disk encryption specification created by Clemens Fruhwirth in 2004 and was originally intended for Linux.
While most disk encryption software implements different, incompatible, and undocumented formats, LU ...
(LUKS), BitLocker and PrivateCore
PrivateCore is a venture-backed startup located in Palo Alto, California that develops software to secure server data through server attestation and memory encryption. The company's attestation and memory encryption technology fills a gap that exi ...
vCage memory encryption. (See below.)
Another example of platform integrity via TPM is in the use of Microsoft Office 365
Microsoft 365 is a product family of productivity software, collaboration and cloud-based services owned by Microsoft. It encompasses online services such as Outlook.com, OneDrive, Microsoft Teams, programs formerly marketed under the name Mic ...
licensing and Outlook Exchange.
An example of TPM use for platform integrity is the Trusted Execution Technology (TXT), which creates a chain of trust. It could remotely attest that a computer is using the specified hardware and software.
Disk encryption
Full disk encryption utilities, such as dm-crypt and BitLocker, can use this technology to protect the keys used to encrypt the computer's storage devices and provide integrity authentication for a trusted boot pathway that includes firmware and boot sector.Other uses and concerns
Any application can use a TPM chip for: * Digital rights management (DRM) * Windows Defender * Windows Domain logon * Protection and enforcement of software licenses * Prevention ofcheating in online games
Cheating in online games is the subversion of the rules or mechanics of online video games to gain an unfair advantage over other players, generally with the use of third-party software. What constitutes cheating is dependent on the game in ...
Other uses exist, some of which give rise to privacy
Privacy (, ) is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively.
The domain of privacy partially overlaps with security, which can include the concepts of a ...
concerns. The "physical presence" feature of TPM addresses some of these concerns by requiring BIOS-level confirmation for operations such as activating, deactivating, clearing or changing ownership of TPM by someone who is physically present at the console of the machine.
By organizations
The United States Department of Defense (DoD) specifies that "new computer assets (e.g., server, desktop, laptop, thin client, tablet, smartphone, personal digital assistant, mobile phone) procured to support DoD will include a TPM version 1.2 or higher where required by Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA)Security Technical Implementation Guide
A Security Technical Implementation Guide or STIG is a configuration standard consisting of cybersecurity requirements for a specific product. The use of STIGs enables a methodology for securing protocols within networks, servers, computers, and lo ...
s (STIGs) and where such technology is available." DoD anticipates that TPM is to be used for device identification, authentication, encryption, and device integrity verification.
TPM implementations
 In 2006, new
In 2006, new laptop
A laptop, laptop computer, or notebook computer is a small, portable personal computer (PC) with a screen and alphanumeric keyboard. Laptops typically have a clam shell form factor with the screen mounted on the inside of the upper li ...
s began being sold with a built-in TPM chip. In the future, this concept could be co-located on an existing motherboard
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, mb, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, logic board (only in Apple computers) or mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expand ...
chip in computers, or any other device where the TPM facilities could be employed, such as a cellphone. On a PC, either the LPC
LPC may refer to:
Science and technology
* Linear predictive coding, a method used in audio signal processing and speech processing
* Leaf protein concentrate, a concentrated form of the proteins found in the leaves of plants
* Long period comet, ...
bus or the SPI bus is used to connect to the TPM chip.
The Trusted Computing Group (TCG) has certified TPM chips manufactured by Infineon Technologies
Infineon Technologies AG is a German semiconductor manufacturer founded in 1999, when the semiconductor operations of the former parent company Siemens AG were spun off. Infineon has about 50,280 employees and is one of the ten largest semicond ...
, Nuvoton, and STMicroelectronics
STMicroelectronics N.V. commonly referred as ST or STMicro is a Dutch multinational corporation and technology company of French-Italian origin headquartered in Plan-les-Ouates near Geneva, Switzerland and listed on the French stock market. ST ...
, having assigned TPM vendor IDs to Advanced Micro Devices, Atmel
Atmel Corporation was a creator and manufacturer of semiconductors before being subsumed by Microchip Technology in 2016. Atmel was founded in 1984. The company focused on embedded systems built around microcontrollers. Its products included micr ...
, Broadcom, IBM, Infineon, Intel, Lenovo
Lenovo Group Limited, often shortened to Lenovo ( , ), is a Chinese Multinational corporation, multinational technology company specializing in designing, manufacturing, and marketing consumer electronics, Personal computer, personal computers, ...
, National Semiconductor, Nationz Technologies, Nuvoton, Qualcomm
Qualcomm () is an American multinational corporation headquartered in San Diego, California, and incorporated in Delaware. It creates semiconductors, software, and services related to wireless technology. It owns patents critical to the 5G, 4 ...
, Rockchip, Standard Microsystems Corporation
Microchip Technology Inc. is a publicly-listed American corporation that manufactures microcontroller, mixed-signal, analog and Flash-IP integrated circuits. Its products include microcontrollers ( PIC, dsPIC, AVR and SAM), Serial EEPROM d ...
, STMicroelectronics, Samsung, Sinosun, Texas Instruments, and Winbond
Winbond Electronics Corporation () is a Taiwan-based corporation founded in 1987. It produces semiconductors and several types of integrated circuits, most notably Dynamic RAM, Static RAM, Serial flash, microcontrollers, and personal computer ...
.
There are five different types of TPM 2.0 implementations (listed in order from most to least secure):
* Discrete TPMs are dedicated chips that implement TPM functionality in their own tamper resistant semiconductor package. They are the most secure, certified to FIPS-140 with level 3 physical security resistance to attack versus routines implemented in software, and their packages are required to implement some tamper resistance. For example the TPM for the brake controller in a car is protected from hacking by sophisticated methods.
* Integrated TPMs are part of another chip. While they use hardware that resists software bugs, they are not required to implement tamper resistance. Intel has integrated TPMs in some of its chipsets.
* Firmware TPMs (fTPMs) are firmware-based (e.g. UEFI) solutions that run in a CPU's trusted execution environment
A trusted execution environment (TEE) is a secure area of a main processor. It guarantees code and data loaded inside to be protected with respect to confidentiality and integrity. Data integrity prevents unauthorized entities from outside the ...
. Intel, AMD and Qualcomm have implemented firmware TPMs.
* Hypervisor TPMs (vTPMs) are virtual TPMs provided by and rely on hypervisors, in an isolated execution environment that is hidden from the software running inside virtual machines to secure their code from the software in the virtual machines. They can provide a security level comparable to a firmware TPM. Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform (GCP), offered by Google, is a suite of cloud computing services that runs on the same infrastructure that Google uses internally for its end-user products, such as Google Search, Gmail, Google Drive, and YouTube. Alongside ...
has implemented vTPM.
* Software TPMs are software emulators of TPMs that run with no more protection than a regular program gets within an operating system. They depend entirely on the environment that they run in, so they provide no more security than what can be provided by the normal execution environment. They are useful for development purposes.
The official TCG reference implementation of the TPM 2.0 Specification has been developed by Microsoft. It is licensed under BSD License and the source code is available on GitHub.
Microsoft provides a Visual Studio solution and Linux autotools build scripts.
In 2018, Intel open-sourced its Trusted Platform Module 2.0 (TPM2) software stack with support for Linux and Microsoft Windows. The source code is hosted on GitHub and licensed under BSD License.
Infineon funded the development of an open source TPM middleware that complies with the Software Stack (TSS) Enhanced System API (ESAPI) specification of the TCG. It was developed by Fraunhofer Institute for Secure Information Technology (SIT).
IBM's Software TPM 2.0 is an implementation of the TCG TPM 2.0 specification. It is based on the TPM specification Parts 3 and 4 and source code donated by Microsoft. It contains additional files to complete the implementation. The source code is hosted on SourceForge and GitHub and licensed under BSD License.
In 2022, AMD announced that under certain circumstances their fTPM implementation causes performance problems. A fix is available in form of a BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization during the ...
-Update.
TPM 1.2 versus TPM 2.0
While TPM 2.0 addresses many of the same use cases and has similar features, the details are different. TPM 2.0 is not backward compatible with TPM 1.2. The TPM 2.0 policy authorization includes the 1.2 HMAC, locality, physical presence, and PCR. It adds authorization based on an asymmetric digital signature, indirection to another authorization secret, counters and time limits, NVRAM values, a particular command or command parameters, and physical presence. It permits the ANDing and ORing of these authorization primitives to construct complex authorization policies.Reception
TCG has faced resistance to the deployment of this technology in some areas, where some authors see possible uses not specifically related to Trusted Computing, which may raise privacy concerns. The concerns include the abuse of remote validation of software (where the manufacturerand not the user who owns the computer systemdecides what software is allowed to run) and possible ways to follow actions taken by the user being recorded in a database, in a manner that is completely undetectable to the user. TheTrueCrypt
TrueCrypt is a discontinued source-available freeware utility used for on-the-fly encryption (OTFE). It can create a virtual encrypted disk within a file, or encrypt a partition or the whole storage device (pre-boot authentication).
On 28 May ...
disk encryption utility, as well as its derivative VeraCrypt, do not support TPM. The original TrueCrypt developers were of the opinion that the exclusive purpose of the TPM is "to protect against attacks that require the attacker to have administrator privileges, or physical access to the computer". The attacker who has physical or administrative access to a computer can circumvent TPM, e.g., by installing a hardware keystroke logger, by resetting TPM, or by capturing memory contents and retrieving TPM-issued keys. The condemning text goes so far as to claim that TPM is entirely redundant. The VeraCrypt publisher has reproduced the original allegation with no changes other than replacing "TrueCrypt" with "VeraCrypt". The author is right that, after achieving either unrestricted physical access or administrative privileges, it is only a matter of time before other security measures in place are bypassed. However, stopping an attacker in possession of administrative privileges has never been one of the goals of TPM (see for details), and TPM can stop some physical tampering.
In 2015, Richard Stallman suggested to replace the term "Trusted computing" with the term "Treacherous computing" due to the danger that the computer can be made to systematically disobey its owner if the cryptographical keys are kept secret from them. He also considers that TPMs available for PCs are not currently dangerous and that there is no reason not to include one in a computer or support it in software due to failed attempts from the industry to use that technology for DRM.
Attacks
In 2010, Christopher Tarnovsky presented an attack against TPMs at Black Hat Briefings, where he claimed to be able to extract secrets from a single TPM. He was able to do this after 6 months of work by inserting a probe and spying on aninternal bus
In computer architecture, a bus (shortened form of the Latin ''omnibus'', and historically also called data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This exp ...
for the Infineon SLE 66 CL PC.
In 2015, as part of the Snowden revelations, it was revealed that in 2010 a US CIA team claimed at an internal conference to have carried out a differential power analysis attack against TPMs that was able to extract secrets.
In 2018, a design flaw in the TPM 2.0 specification for the static root of trust for measurement (SRTM) was reported (). It allows an adversary to reset and forge platform configuration registers which are designed to securely hold measurements of software that are used for bootstrapping a computer. Fixing it requires hardware-specific firmware patches. An attacker abuses power interrupts and TPM state restores to trick TPM into thinking that it is running on non-tampered components.
Main Trusted Boot (tboot) distributions before November 2017 are affected by a dynamic root of trust for measurement (DRTM) attack , which affects computers running on Intel's Trusted eXecution Technology (TXT) for the boot-up routine.
In case of physical access, computers with TPM are vulnerable to cold boot attacks as long as the system is on or can be booted without a passphrase from shutdown or hibernation
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic depression undergone by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It most ...
, which is the default setup for Windows computers with BitLocker full disk encryption.
In 2021, the Dolos Group showed an attack on a discrete TPM, where the TPM chip itself had some tamper resistance, but the other endpoints of its communication bus did not. They read a full-disk-encryption key as it was transmitted across the motherboard, and used it to decrypt the laptop's SSD.
2017 weak key generation controversy
In October 2017, it was reported that a code library developed by Infineon, which had been in widespread use in its TPMs, contained a vulnerability, known as ROCA, which generated weak RSA key pairs that allowed private keys to be inferred from public keys. As a result, all systems depending upon the privacy of such weak keys are vulnerable to compromise, such as identity theft or spoofing. Cryptosystems that store encryption keys directly in the TPM without blinding could be at particular risk to these types of attacks, as passwords and other factors would be meaningless if the attacks can extract encryption secrets. Infineon has released firmware updates for its TPMs to manufacturers who have used them.Availability
Currently, a TPM is used by nearly all PC and notebook manufacturers.TPM
The TPM is implemented by several vendors: * Infineon provides both TPM chips and TPM software, which are delivered as OEM versions with new computers as well as separately by Infineon for products with TPM technology which comply with TCG standards. For example, Infineon licensed TPM management software to Broadcom Corp. in 2004. * Microchip (formerly Atmel) manufactures TPM devices that it claims to be compliant to the Trusted Platform Module specification version 1.2 revision 116 and offered with several interfaces (LPC, SPI, and I2C), modes (FIPS 140-2 certified and standard mode), temperature grades (commercial and industrial), and packages (TSSOP and QFN). Their TPMs support PCs and embedded devices. They also provides TPM development kits to support integration of its TPM devices into various embedded designs. * Nuvoton Technology Corporation provides TPM devices for PC applications. Nuvoton also provides TPM devices for embedded systems and Internet of Things (IoT) applications via I2C and SPI host interfaces. Nuvoton's TPM complies withCommon Criteria
The Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation (referred to as Common Criteria or CC) is an international standard (ISO/IEC 15408) for computer security certification. It is currently in version 3.1 revision 5.
Common Criteria ...
(CC) with assurance level EAL 4 augmented with ALC_FLR.1, AVA_VAN.4 and ALC_DVS.2, FIPS 140-2 level 2 with Physical Security and EMI/EMC level 3 and Trusted Computing Group Compliance requirements, all supported within a single device. TPMs produced by Winbond
Winbond Electronics Corporation () is a Taiwan-based corporation founded in 1987. It produces semiconductors and several types of integrated circuits, most notably Dynamic RAM, Static RAM, Serial flash, microcontrollers, and personal computer ...
are now part of Nuvoton.
* STMicroelectronics
STMicroelectronics N.V. commonly referred as ST or STMicro is a Dutch multinational corporation and technology company of French-Italian origin headquartered in Plan-les-Ouates near Geneva, Switzerland and listed on the French stock market. ST ...
has provided TPMs for PC platforms and embedded systems since 2005. The product offering includes discrete devices with several interfaces supporting Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) and I²C and different qualification grades (consumer, industrial and automotive). The TPM products are Common Criteria
The Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation (referred to as Common Criteria or CC) is an international standard (ISO/IEC 15408) for computer security certification. It is currently in version 3.1 revision 5.
Common Criteria ...
(CC) certified EAL4+ augmented with ALC_FLR.1 and AVA_VAN.5, FIPS 140-2 level 2 certified with physical security level 3 and also Trusted Computing Group (TCG) certified.
There are also hybrid types; for example, TPM can be integrated into an Ethernet controller, thus eliminating the need for a separate motherboard component.
Field upgrade
Field upgrade is the TCG term for updating the TPM firmware. The update can be between TPM 1.2 and TPM 2.0, or between firmware versions. Some vendors limit the number of transitions between 1.2 and 2.0, and some restrict rollback to previous versions. Platform OEMs such as HP supply an upgrade tool. Since July 28, 2016, all new Microsoft device models, lines, or series (or updating the hardware configuration of an existing model, line, or series with a major update, such as CPU, graphic cards) implement, and enable by default TPM 2.0. While TPM 1.2 parts are discrete silicon components, which are typically soldered on the motherboard, TPM 2.0 is available as a discrete (dTPM) silicon component in a single semiconductor package, an integrated component incorporated in one or more semiconductor packages - alongside other logic units in the same package(s), and as a firmware (fTPM) based component running in a trusted execution environment (TEE) on a general purpose System-on-a-chip (SoC).Virtual TPM
*Google Compute Engine
Google Compute Engine (GCE) is the Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) component of Google Cloud Platform which is built on the global infrastructure that runs Google's search engine, Gmail, YouTube and other services. Google Compute Engine enabl ...
offers virtualized TPMs (vTPMs) as part of Google Cloud's Shielded VMs product.
* The libtpms library provides software emulation of a Trusted Platform Module (TPM 1.2 and TPM 2.0). It targets the integration of TPM functionality into hypervisors, primarily into Qemu.
Operating systems
* Windows 11 requires TPM 2.0 support as a minimum system requirement. On many systems TPM is disabled by default which requires changing settings in the computer's UEFI to enable it. * The Trusted Platform Module 2.0 (TPM 2.0) has been supported by theLinux kernel
The Linux kernel is a free and open-source, monolithic, modular, multitasking, Unix-like operating system kernel. It was originally authored in 1991 by Linus Torvalds for his i386-based PC, and it was soon adopted as the kernel for the GNU ope ...
since version 3.20.
Platforms
* Google includes TPMs in Chromebooks as part of their security model. *Oracle
An oracle is a person or agency considered to provide wise and insightful counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. As such, it is a form of divination.
Description
The word '' ...
ships TPMs in their X- and T-Series Systems such as T3 or T4 series of servers. Support is included in Solaris 11.
* In 2006, with the introduction of first Macintosh models with Intel processors, Apple started to ship Macs with TPM. Apple never provided an official driver, but there was a port under GPL available. Apple has not shipped a computer with TPM since 2006.
* In 2011, Taiwanese manufacturer MSI launched its Windpad 110W tablet featuring an AMD CPU and Infineon Security Platform TPM, which ships with controlling software version 3.7. The chip is disabled by default but can be enabled with the included, pre-installed software.
Virtualization
* VMware ESXi hypervisor has supported TPM since 4.x, and from 5.0 it is enabled by default. *Xen
Xen (pronounced ) is a type-1 hypervisor, providing services that allow multiple computer operating systems to execute on the same computer hardware concurrently. It was
originally developed by the University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory an ...
hypervisor has support of virtualized TPMs. Each guest gets its own unique, emulated, software TPM.
* KVM, combined with QEMU, has support for virtualized TPMs. , it supports passing through the physical TPM chip to a single dedicated guest. QEMU 2.11 released in December 2017 also provides emulated TPMs to guests.
* VirtualBox has support for virtual TPM 1.2 and 2.0 devices starting with version 7.0 released in October 2022
Software
* Microsoft operating systems Windows Vista and later use the chip in conjunction with the included disk encryption component named BitLocker. Microsoft had announced that from January 1, 2015, all computers will have to be equipped with a TPM 2.0 module in order to passWindows 8.1
Windows 8.1 is a release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was released to manufacturing on August 27, 2013, and broadly released for retail sale on October 17, 2013, about a year after the retail release of its pre ...
hardware certification
Hardware certification is the process through which computer hardware is tested to ensure it is compatible with specific software packages, and operates as intended in critical situations. With ever dropping prices of hardware devices, the market ...
. However, in a December 2014 review of the Windows Certification Program this was instead made an optional requirement. However, TPM 2.0 is required for connected standby
InstantGo or Modern Standby (formerly Connected Standby) is a Microsoft specification for Windows 8 (and later) hardware and software that aims to bring smartphone-type power management capabilities to the PC platform, as well as increasing physic ...
systems. Virtual machines running on Hyper-V can have their own virtual TPM module starting with Windows 10 1511 and Windows Server 2016. Microsoft Windows includes two TPM related commands
Command may refer to:
Computing
* Command (computing), a statement in a computer language
* COMMAND.COM, the default operating system shell and command-line interpreter for DOS
* Command key, a modifier key on Apple Macintosh computer keyboards
* ...
: , a utility that can be used to retrieve information about the TPM, and , a command-line tool that allows creating and deleting TPM virtual smart card
A smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card) is a physical electronic authentication device, used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) c ...
s on a computer.
Endorsement keys
TPM endorsement keys (EKs) are asymmetric key pairs unique to each TPM. They use the RSA and ECC algorithms. The TPM manufacturer usually provisions endorsement key certificates in TPM non-volatile memory. The certificates assert that the TPM is authentic. Starting with TPM 2.0, the certificates are in X.509DER
Der or DER may refer to:
Places
* Darkənd, Azerbaijan
* Dearborn (Amtrak station) (station code), in Michigan, US
* Der (Sumer), an ancient city located in modern-day Iraq
* d'Entrecasteaux Ridge, an oceanic ridge in the south-west Pacific Ocean ...
format.
These manufacturers typically provide their certificate authority root (and sometimes intermediate) certificates on their web sites.
* AMD
* Infineon
* Intel
* NationZ
* Nuvoton
* ST Micro
TPM software libraries
To utilize a TPM, the user needs a software library that communicates with the TPM and provides a friendlier API than the raw TPM communication. Currently, there are several such open-source TPM 2.0 libraries. Some of them also support TPM 1.2, but mostly TPM 1.2 chips are now deprecated and modern development is focused on TPM 2.0. Typically, a TPM library provides an API with one-to-one mappings to TPM commands. The TCG specification calls this layer the System API(SAPI). This way the user has more control over the TPM operations, however the complexity is high. To hide some of the complexity most libraries also offer simpler ways to invoke complex TPM operations. The TCG specification call these two layers Enhanced System API(ESAPI) and Feature API(FAPI). There is currently only one stack that follows the TCG specification. All the other available open-source TPM libraries use their own form of richer API. (*) There is a separate project called "CHARRA" by Fraunhofer that uses the tpm2-tss library for Remote Attestation. The other stacks have accompanying attestation servers or directly include examples for attestation. IBM offer their open-source Remote Attestation Server called "IBM ACS" on SourceForge and Google have "Go-Attestation" available on GitHub, while "wolfTPM" offers time and local attestation examples directly in its open-source code, also on GitHub. (**) There is an application note about an example project for the AURIX 32-bit SoC using the tpm2-tss library. (***) Requires additional libraries (dotnet) to run on Linux. These TPM libraries are sometimes also called TPM stacks, because they provide the interface for the developer or user to interact with the TPM. As seen from the table, the TPM stacks abstract the operating system and transport layer, so the user could migrate one application between platforms. For example, by using TPM stack API the user would interact the same way with a TPM, regardless if the physical chip is connected over SPI, I2C or LPC interface to the Host system.See also
*AMD Platform Security Processor
The AMD Platform Security Processor (PSP), officially known as AMD Secure Technology, is a trusted execution environment subsystem incorporated since about 2013 into AMD microprocessors. According to an AMD developer's guide, the subsystem is "res ...
* ARM TrustZone
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configured ...
* Crypto-shredding
* Hardware security
Hardware security as a discipline originated out of cryptographic engineering and involves hardware design, access control, secure multi-party computation, secure key storage, ensuring code authenticity, measures to ensure that the supply chain tha ...
* Hardware security module
* Hengzhi chip
* Intel Management Engine
* Microsoft Pluton
* Next-Generation Secure Computing Base
The Next-Generation Secure Computing Base (NGSCB; codenamed Palladium and also known as Trusted Windows') is a software architecture designed by Microsoft which aimed to provide users of the Windows operating system with better privacy, security, ...
* Threat model
References
Further reading
# . # . # . # . # . # . # . # . # . # . # . # . # . # . # . # . {{ISO standards Computer hardware standards Cryptographic hardware Cryptographic software Cryptography standards ISO standards Random number generation Trusted computing