Sun Sensor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
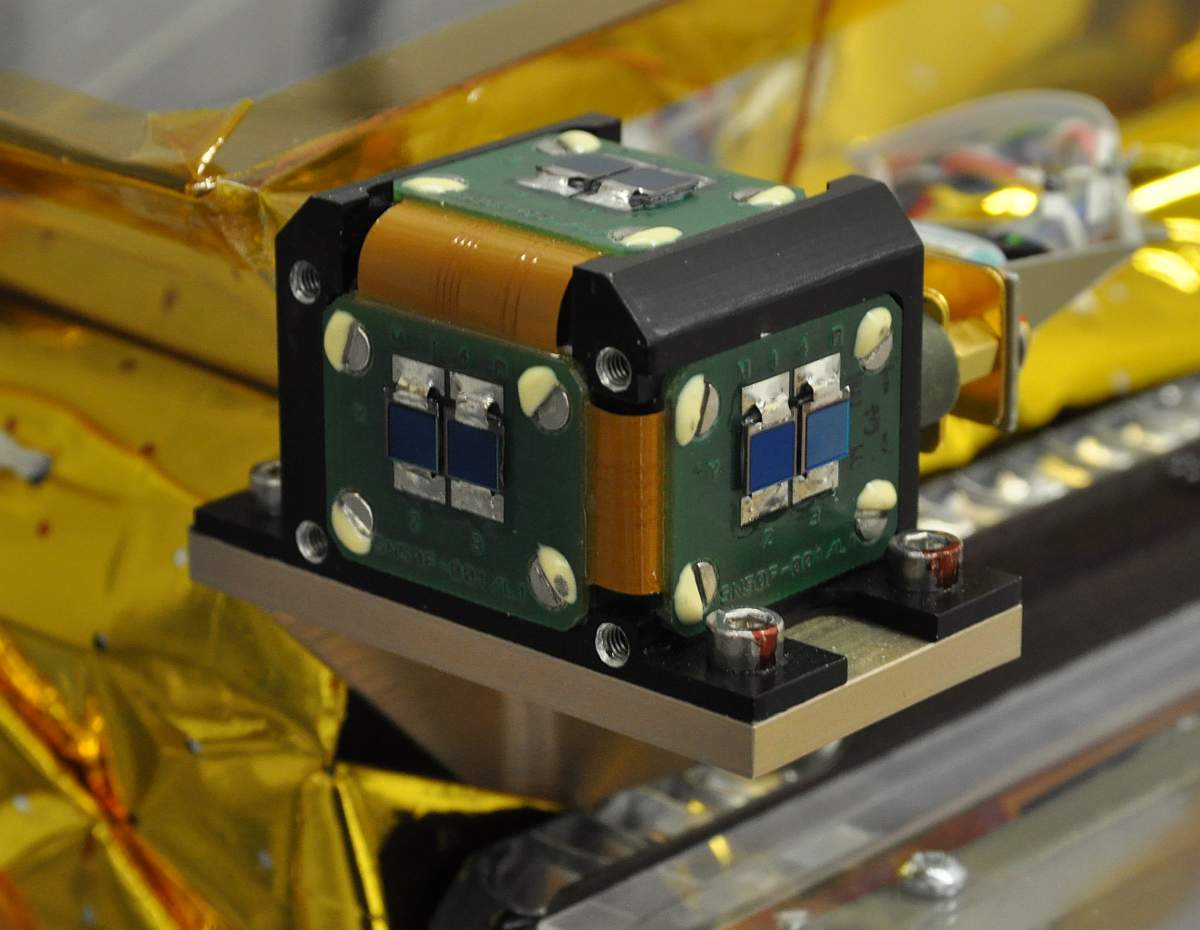 A sun sensor is a
A sun sensor is a
 A sun sensor is a
A sun sensor is a navigational instrument Navigational instruments are instruments used by nautical navigators and pilots as tools of their trade. The purpose of navigation is to ascertain the present position and to determine the speed, direction, etc. to arrive at the port or point o ...
used by spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, p ...
to detect the position of the sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
. Sun sensors are used for attitude control
Attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of an aerospace vehicle with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc.
Controlling vehicle ...
, solar array
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and ...
pointing, gyro
Gyro may refer to:
Science and technology
* GYRO, a computer program for tokamak plasma simulation
* Gyro Motor Company, an American aircraft engine manufacturer
* ''Gyrodactylus salaris'', a parasite in salmon
* Gyroscope, an orientation-sta ...
updating, and fail-safe
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that in the event of a specific type of failure, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. Unlike inherent safe ...
recovery.
In addition to spacecraft, sun sensors find use in ground-based weather station
A weather station is a facility, either on land or sea, with instruments and equipment for measuring atmospheric conditions to provide information for weather forecasts and to study the weather and climate. The measurements taken include tempera ...
s and sun-tracking systems, and aerial vehicles including balloon
A balloon is a flexible bag that can be inflated with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, and air. For special tasks, balloons can be filled with smoke, liquid water, granular media (e.g. sand, flour or rice), or light so ...
s and UAV
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controller ...
s.
Mechanism
There are various types of sun sensors, which differ in their technology and performance characteristics. Sun presence sensors provide abinary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that t ...
output, indicating when the sun is within the sensor's field of view
The field of view (FoV) is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation.
Humans a ...
. Analog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analog ...
and digital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Technology and computing Hardware
*Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals
**Digital camera, which captures and stores digital i ...
sun sensors, in contrast, indicate the angle of the sun by continuous and discrete signal
In Dynamical system, mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which Variable (mathematics), variables that evolve over time are modeled.
Discrete time
Discrete time views values of variable ...
outputs, respectively.
In typical sun sensors, a thin slit at the top of a rectangular chamber allows a line of light to fall on an array of photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as Photoelectric effect, photoelectric or photoc ...
cells at the bottom of the chamber. A voltage is induced in these cells, which is registered electronically. By orienting two sensors perpendicular to each other, the direction of the sun can be fully determined.
Often, multiple sensors will share processing electronics.
Criteria
There are a number of design and performance criteria which dictate the selection of a sun sensor model: *Field of view
The field of view (FoV) is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation.
Humans a ...
*Angular resolution
Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object, thereby making it a major determinant of image resolution. ...
*Accuracy
Accuracy and precision are two measures of ''observational error''.
''Accuracy'' is how close a given set of measurements (observations or readings) are to their ''true value'', while ''precision'' is how close the measurements are to each other ...
and stability
Stability may refer to:
Mathematics
*Stability theory, the study of the stability of solutions to differential equations and dynamical systems
**Asymptotic stability
**Linear stability
**Lyapunov stability
**Orbital stability
**Structural stabilit ...
*Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementar ...
and volume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). The de ...
*Input voltage and power
*Output characteristics (including electrical characteristics, update frequency, nonlinearity, and encoding)
*Durability (including radiation hardening and tolerance to vibration and residual stress, thermal cycling)
See also
* Celestial navigation * Earth sensor * Star trackerReferences
{{Reflist, refs= {{cite web, title=Digital Sun Sensors (DSS), url=http://www.adcole.com/aerospace/digital-sun-sensors/, publisher=Adcole Corporation, accessdate=11 March 2016 {{cite web, title=High Accuracy Fine Sun Sensors, url=http://www.adcole.com/aerospace/high-accuracy-fine-sun-sensors/, publisher=Adcole Corporation, accessdate=11 March 2016 {{cite web, title=LIASS: LInear Accurate Sun Sensor, url=http://www.space-airbusds.com/media/document/gnc_1_liass_2015-v_std_b-def.pdf, publisher=Airbus Defense & Space, accessdate=11 March 2016 {{cite web, title=What is a Sun Sensor?, date = 17 June 2013, url=http://www.azosensors.com/Article.aspx?ArticleID=223, publisher=AZO Sensors, accessdate=11 March 2016 Spacecraft attitude control Astrodynamics Orbits Spaceflight concepts Navigational equipment Celestial navigation