Serpent (symbolism) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The serpent, or
 Serpents are represented as potent guardians of temples and other sacred spaces. This connection may be grounded in the observation that when threatened, some snakes (such as
Serpents are represented as potent guardians of temples and other sacred spaces. This connection may be grounded in the observation that when threatened, some snakes (such as
 Ningizzida has been popularized in the 20th century by Raku Kei (
Ningizzida has been popularized in the 20th century by Raku Kei (
 In
In
 Occasionally, serpents and
Occasionally, serpents and
 In Africa the chief centre of serpent worship was Dahomey, but the cult of the python seems to have been of exotic origin, dating back to the first quarter of the 17th century. By the conquest of Whydah the Dahomeyans were brought in contact with a people of serpent worshipers, and ended by adopting from them the beliefs which they at first despised. At Whydah, the chief centre, there is a serpent temple, tenanted by some fifty snakes. Every python of the ''danh-gbi'' kind must be treated with respect, and death is the penalty for killing one, even by accident. ''Danh-gbi'' has numerous wives, who until 1857 took part in a public procession from which the profane crowd was excluded; a python was carried round the town in a hammock, perhaps as a ceremony for the expulsion of evils.
The rainbow-god of the Ashanti was also conceived to have the form of a snake. His messenger was said to be a small variety of
In Africa the chief centre of serpent worship was Dahomey, but the cult of the python seems to have been of exotic origin, dating back to the first quarter of the 17th century. By the conquest of Whydah the Dahomeyans were brought in contact with a people of serpent worshipers, and ended by adopting from them the beliefs which they at first despised. At Whydah, the chief centre, there is a serpent temple, tenanted by some fifty snakes. Every python of the ''danh-gbi'' kind must be treated with respect, and death is the penalty for killing one, even by accident. ''Danh-gbi'' has numerous wives, who until 1857 took part in a public procession from which the profane crowd was excluded; a python was carried round the town in a hammock, perhaps as a ceremony for the expulsion of evils.
The rainbow-god of the Ashanti was also conceived to have the form of a snake. His messenger was said to be a small variety of
 In
In
 Significant finds of pottery, bronze-ware and even gold depictions of snakes have been made throughout the
Significant finds of pottery, bronze-ware and even gold depictions of snakes have been made throughout the
 In the
In the
 Serpents are sacred and powerful in the thought of prehistoric cultures of Iran, having been portrayed as patrons of fertility, water and wealth in the ancient objects of Iran. They seem to have been worshipped along with the
Serpents are sacred and powerful in the thought of prehistoric cultures of Iran, having been portrayed as patrons of fertility, water and wealth in the ancient objects of Iran. They seem to have been worshipped along with the
 The
The 
 Some Native American tribes give reverence to the rattlesnake as grandfather and king of snakes who is able to give fair winds or cause tempest. Among the
Some Native American tribes give reverence to the rattlesnake as grandfather and king of snakes who is able to give fair winds or cause tempest. Among the
 Snakes entwined the staffs both of
Snakes entwined the staffs both of
File:Salvage Scrap propaganda poster crop2.jpg,
''The Worship of the Serpent''
London : J. G. & F. Rivington, 1833.
alternative copy online at the Internet Archive
*
online version
at literature.org. *
the most common symbols in snake dreams
snake
Snakes are elongated, Limbless vertebrate, limbless, carnivore, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales. Ma ...
, is one of the oldest and most widespread mythological
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narrat ...
symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
s. The word is derived from Latin ''serpens'', a crawling animal or snake. Snakes have been associated with some of the oldest rituals known to mankind and represent dual expression of good and evil
In religion, ethics, philosophy, and psychology "good and evil" is a very common dichotomy. In cultures with Manichaean and Abrahamic religious influence, evil is perceived as the dualistic antagonistic opposite of good, in which good shoul ...
.
In some cultures, snakes were fertility symbols. For example, the Hopi
The Hopi are a Native American ethnic group who primarily live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census, there are 19,338 Hopi in the country. The Hopi Tribe is a sovereign nation within the Unite ...
people of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
performed an annual snake dance to celebrate the union of Snake Youth (a Sky spirit) and Snake Girl (an Underworld spirit) and to renew the fertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Fertili ...
of Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physics, physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomenon, phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. ...
. During the dance, live snakes were handled, and at the end of the dance the snakes were released into the fields to guarantee good crops. "The snake dance is a prayer to the spirits of the clouds, the thunder and the lightning, that the rain may fall on the growing crops." To the Hopi
The Hopi are a Native American ethnic group who primarily live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census, there are 19,338 Hopi in the country. The Hopi Tribe is a sovereign nation within the Unite ...
, snakes symbolized the umbilical cord
In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or ''funiculus umbilicalis'') is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologic ...
, joining all humans to Mother Earth. The Great Goddess Great Goddess is the concept of an almighty goddess or mother goddess, or a matriarchal religion. Apart from various specific figures called this from various cultures, the Great Goddess hypothesis, is a postulated fertility goddess supposed to h ...
often had snakes as her familiar
In European folklore of the medieval and early modern periods, familiars (sometimes referred to as familiar spirits) were believed to be supernatural entities that would assist witches and cunning folk in their practice of magic. According to r ...
s—sometimes twining around her sacred staff, as in ancient Crete
The history of Crete goes back to the 7th millennium BC, preceding the ancient Minoan civilization by more than four millennia. The palace-based Minoan civilization was the first civilization in Europe.
After the Minoan civilization was devastat ...
—and they were worshiped as guardians of her mysteries of birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
and regeneration.
Evolutionary origins
The anthropologist Lynn Isbell has argued that, asprimate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including huma ...
s, the serpent as a symbol of death is built into our unconscious minds because of our evolutionary history. Isbell argues that for millions of years snakes were the only significant predators of primates, and that this explains why fear of snakes is one of the most common phobia
A phobia is an anxiety disorder defined by a persistent and excessive fear of an object or situation. Phobias typically result in a rapid onset of fear and are usually present for more than six months. Those affected go to great lengths to avo ...
s worldwide and why the symbol of the serpent is so prevalent in world mythology; the serpent is an innate image of danger and death. Isbell, ''The Fruit, the Tree, and the Serpent'' Haycock, ''Being and Perceiving''
Furthermore, the psychoanalyst Joseph Lewis Henderson and the ethnologist Maude Oakes have argued that the serpent is a symbol of initiation and rebirth precisely because it is a symbol of death. Henderson, ''The Wisdom of the Serpent''
Using phylogenetical and statistical methods on related motifs from folklore and myth, French comparativist Julien d'Huy managed to reconstruct a possible archaic narrative about the serpent. In this Paleolithic "ophidian" myth, snakes are connected to rains and storms, and even to water sources. In regards to the latter, it blocks rivers and other water sources in exchange for human sacrifices and/or material good offerings.
Values
Fertility and rebirth
Historically, serpents and snakes representfertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Fertili ...
or a creative life force. As snakes shed their skin through sloughing
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer ...
, they are symbols of rebirth, transformation, immortality, and healing. The ouroboros
The ouroboros or uroboros () is an ancient symbol depicting a serpent or dragon eating its own tail. The ouroboros entered Western tradition via ancient Egyptian iconography and the Greek magical tradition. It was adopted as a symbol in Gnost ...
is a symbol of eternity
Eternity, in common parlance, means Infinity, infinite time that never ends or the quality, condition, or fact of being everlasting or eternal. Classical philosophy, however, defines eternity as what is timeless or exists outside time, whereas ...
and continual renewal of life.
In some Abrahamic traditions
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
, the serpent represents sexual desire
Sexual desire is an emotion and motivational state characterized by an interest in sexual objects or activities, or by a drive to seek out sexual objects or to engage in sexual activities. It is an aspect of sexuality, which varies significantly ...
. According to some interpretations of the Midrash
''Midrash'' (;"midrash"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
, the ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
serpent
Serpent or The Serpent may refer to:
* Snake, a carnivorous reptile of the suborder Serpentes
Mythology and religion
* Sea serpent, a monstrous ocean creature
* Serpent (symbolism), the snake in religious rites and mythological contexts
* Serp ...
represents sexual passion. In Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Kundalini
In Hinduism, Kundalini ( sa, कुण्डलिनी, translit=kuṇḍalinī, translit-std=IAST, lit=coiled snake, ) is a form of divine feminine energy (or ''Shakti'') believed to be located at the base of the spine, in the ''muladhara'' ...
is a coiled serpent.Her Holiness Shri Mataji Nirmala Devi Srivastava: "Meta Modern Era", pages 233–248. Vishwa Nirmala Dharma; first edition, 1995.
Guardianship
 Serpents are represented as potent guardians of temples and other sacred spaces. This connection may be grounded in the observation that when threatened, some snakes (such as
Serpents are represented as potent guardians of temples and other sacred spaces. This connection may be grounded in the observation that when threatened, some snakes (such as rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes that form the genera ''Crotalus'' and ''Sistrurus'' of the subfamily Crotalinae (the pit vipers). All rattlesnakes are vipers. Rattlesnakes are predators that live in a wide array of habitats, hunting small anim ...
s or cobras) frequently hold and defend their ground, first resorting to threatening display and then fighting, rather than retreat. Thus, they are natural guardians of treasures or sacred sites which cannot easily be moved out of harm's way.
At Angkor
Angkor ( km, អង្គរ , 'Capital city'), also known as Yasodharapura ( km, យសោធរបុរៈ; sa, यशोधरपुर),Headly, Robert K.; Chhor, Kylin; Lim, Lam Kheng; Kheang, Lim Hak; Chun, Chen. 1977. ''Cambodian-Engl ...
in Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailand t ...
, numerous stone sculptures present hooded multi-headed nāga
The Nagas (IAST: ''nāga''; Devanāgarī: नाग) are a divine, or semi-divine, race of half-human, half-serpent beings that reside in the netherworld (Patala), and can occasionally take human or part-human form, or are so depicted in art. ...
s as guardians of temples or other premises. A favorite motif of Angkorean sculptors from approximately the 12th century CE onward was that of the Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was ...
, sitting in the position of meditation, his weight supported by the coils of a multi-headed nāga that also uses its flared hood to shield him from above. This motif recalls the story of the Buddha and the serpent king Mucalinda
Mucalinda, Muchalinda or Mucilinda is the name of a nāga, a snake-like being, who protected the Gautama Buddha from the elements after his enlightenment.
It is said that six weeks after Gautama Buddha began meditating under the Bodhi Tree, t ...
: as the Buddha sat beneath a tree engrossed in meditation, Mucalinda came up from the roots of the tree to shield the Buddha from a tempest that was just beginning to arise.
The Gadsden flag
The Gadsden flag is a historical American flag with a yellow field depicting a timber rattlesnake coiled and ready to strike. Beneath the rattlesnake are the words: " TREAD ON ME". Some modern versions of the flag include an apostrophe.
The f ...
of the American Revolution depicts a rattlesnake coiled up and poised to strike. Below the image of the snake is the legend, "Don't tread on me." The snake symbolized the dangerousness of colonists willing to fight for their rights and homeland, and was also symbolic of their separation from Europe, as it was an animal unique to America. The motif is repeated in the First Navy Jack
The First Navy Jack was the naval jack of the United States from 1975 to 1976 and again from 2002 to 2019. It was authorized by the U.S. Navy and was flown from the jackstaff of commissioned vessels of the U.S. Navy while moored pierside or at an ...
of the US Navy.
Venom and medicine
Serpents are connected withvenom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a sti ...
and medicine. The snake's venom is associated with the chemicals of plants and fungi that have the power to either heal or provide expanded consciousness (and even the elixir of life
The elixir of life, also known as elixir of immortality, is a potion that supposedly grants the drinker eternal life and/or eternal youth. This elixir was also said to cure all diseases. Alchemists in various ages and cultures sought the means ...
and immortality) through divine intoxication. Because of its herbal knowledge and entheogen
Entheogens are psychoactive substances that induce alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, or behavior for the purposes of engendering spiritual development or otherwiseRätsch, Christian, ''The Encyclopedia of Psychoac ...
ic association, the snake was often considered one of the wisest animals, being (close to the) divine. Its divine aspect combined with its habitat in the earth between the roots of plants made it an animal with chthonic
The word chthonic (), or chthonian, is derived from the Ancient Greek word ''χθών, "khthon"'', meaning earth or soil. It translates more directly from χθόνιος or "in, under, or beneath the earth" which can be differentiated from Γῆ ...
properties connected to the afterlife and immortality. The deified Greek physician Asclepius
Asclepius (; grc-gre, Ἀσκληπιός ''Asklēpiós'' ; la, Aesculapius) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Religion in ancient Greece, Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis (lover of ...
, as god of medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
and healing, carried a staff with one serpent wrapped around it, which has become the symbol of modern medicine. Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
also had a replica of a serpent on a pole, the Nehushtan
In the biblical Books of Kings ( 2 Kings 18:4; written c. 550 BC), the Nehushtan (Hebrew: ''Nəḥuštān'' ) is the name given to the bronze image of a serpent on a pole. The image is described in the Book of Numbers, where Yahweh instructed M ...
, mentioned in Numbers 21:8.
Associated animals
Chthonic serpents and sacred trees
In many myths, thechthonic
The word chthonic (), or chthonian, is derived from the Ancient Greek word ''χθών, "khthon"'', meaning earth or soil. It translates more directly from χθόνιος or "in, under, or beneath the earth" which can be differentiated from Γῆ ...
serpent (sometimes a pair) lives in or is coiled around a Tree of Life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythological, religious, and philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The Assyrian Sacred Tree: A History ...
situated in a divine garden. In the Genesis
Genesis may refer to:
Bible
* Book of Genesis, the first book of the biblical scriptures of both Judaism and Christianity, describing the creation of the Earth and of mankind
* Genesis creation narrative, the first several chapters of the Book of ...
story of the Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the s ...
and biblical Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
, the tree of the knowledge of good and evil
In Judaism and Christianity, the tree of the knowledge of good and evil ( he, עֵץ הַדַּעַת טוֹב וָרָע, ʿêṣ had-daʿaṯ ṭōḇ wā-rāʿ, label=Tiberian Hebrew, ) is one of two specific trees in the story of the Garden ...
is situated in the Garden of Eden
In Abrahamic religions, the Garden of Eden ( he, גַּן־עֵדֶן, ) or Garden of God (, and גַן־אֱלֹהִים ''gan-Elohim''), also called the Terrestrial Paradise, is the Bible, biblical paradise described in Book of Genesis, Genes ...
together with the tree of life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythological, religious, and philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The Assyrian Sacred Tree: A History ...
and the serpent
Serpent or The Serpent may refer to:
* Snake, a carnivorous reptile of the suborder Serpentes
Mythology and religion
* Sea serpent, a monstrous ocean creature
* Serpent (symbolism), the snake in religious rites and mythological contexts
* Serp ...
. In Greek mythology, Ladon coiled around the tree in the garden of the Hesperides
In Greek mythology, the Hesperides (; , ) are the nymphs of evening and golden light of sunsets, who were the "Daughters of the Evening" or "Nymphs of the West". They were also called the Atlantides () from their reputed father, the Titan Atlas ...
protecting the golden apples.
Similarly Níðhöggr
In Norse mythology, Níðhöggr (''Malice Striker'', in Old Norse traditionally also spelled Níðhǫggr , often anglicized NidhoggWhile the suffix of the name, ''-höggr'', clearly means "striker" the prefix is not as clear. In particular, the ...
(Nidhogg Nagar), the dragon of Norse mythology, eats from the roots of the Yggdrasil
Yggdrasil (from Old Norse ), in Norse cosmology, is an immense and central sacred tree. Around it exists all else, including the Nine Worlds.
Yggdrasil is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'' compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional s ...
, the World Tree.
Under yet another tree (the Bodhi Tree of Enlightenment), the Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was ...
sat in ecstatic meditation. When a storm arose, the mighty serpent king Mucalinda
Mucalinda, Muchalinda or Mucilinda is the name of a nāga, a snake-like being, who protected the Gautama Buddha from the elements after his enlightenment.
It is said that six weeks after Gautama Buddha began meditating under the Bodhi Tree, t ...
rose up from his place beneath the earth and enveloped the Buddha in seven coils for seven days, so as not to break his ecstatic state.
The Vision Serpent was a symbol of rebirth in Maya mythology
Maya or Mayan mythology is part of Mesoamerican mythology and comprises all of the Maya tales in which personified forces of nature, deities, and the heroes interacting with these play the main roles. The myths of the era have to be reconstruct ...
, with origins going back to earlier Maya conceptions, lying at the center of the world as the Mayans conceived it. "It is in the center axis atop the World Tree
The world tree is a motif present in several religions and mythologies, particularly Indo-European religions, Siberian religions, and Native American religions. The world tree is represented as a colossal tree which supports the heavens, thereb ...
. Essentially the World Tree and the Vision Serpent, representing the king, created the center axis which communicates between the spiritual and the earthly worlds or planes. It is through ritual that the king could bring the center axis into existence in the temples and create a doorway to the spiritual world, and with it power."
Sometimes the Tree of Life is represented (in a combination with similar concepts such as the World Tree and Axis mundi
In astronomy, axis mundi is the Latin term for the axis of Earth between the celestial poles.
In a geocentric coordinate system, this is the axis of rotation of the celestial sphere.
Consequently, in ancient Greco-Roman astronomy, the '' ...
or "World Axis") by a staff such as those used by shamans
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritu ...
. Examples of such staffs featuring coiled snakes in mythology are the caduceus
The caduceus (☤; ; la, cādūceus, from grc-gre, κηρύκειον "herald's wand, or staff") is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology. The same staff was also ...
of Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travellers, thieves, merchants, and orato ...
, the Rod of Asclepius
In Greek mythology, the Rod of Asclepius (⚕; grc, Ράβδος του Ασκληπιού, , sometimes also spelled Asklepios), also known as the Staff of Aesculapius and as the asklepian, is a serpent-entwined rod wielded by the Greek god A ...
, the Staff of Moses
The Staff of Moses, also known as the Staff of God is a staff mentioned in the Bible and Quran as a walking stick used by Moses. According to the Book of Exodus, the staff ( ''matteh'', translated "rod" in the King James Bible) was used to produ ...
, and the papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to a ...
reeds and deity poles entwined by a single serpent Wadjet
Wadjet (; egy, wꜢḏyt "Green One"), known to the Greek world as Uto (; grc-koi, Οὐτώ) or Buto (; ) among other renderings including Wedjat, Uadjet, and Udjo, was originally the ancient local goddess of the city of Dep. It became part ...
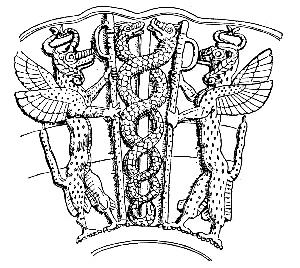
, dating to earlier than 3000 BCE. The oldest known representation of ''two'' snakes entwined around a rod is that of the Sumerian fertility god Ningizzida, who was sometimes depicted as a serpent with a human head, eventually becoming a god of healing and magic. It is the companion of Dumuzi (Tammuz), with whom it stood at the gate of heaven. In the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central l ...
, there is a famous green steatite
Soapstone (also known as steatite or soaprock) is a talc-schist, which is a type of metamorphic rock. It is composed largely of the magnesium rich mineral talc. It is produced by dynamothermal metamorphism and metasomatism, which occur in the zo ...
vase carved for King Gudea
Gudea ( Sumerian: , ''Gu3-de2-a'') was a ruler ('' ensi'') of the state of Lagash in Southern Mesopotamia, who ruled circa 2080–2060 BC ( short chronology) or 2144-2124 BC (middle chronology). He probably did not come from the city, but had marr ...
of Lagash
Lagash (cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian: ''Lagaš''), was an ancient city state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Ash Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash (modern Al-Hiba) w ...
(dated variously 2200–2025 BCE) with an inscription dedicated to Ningizzida. Ningizzida was the ancestor of Gilgamesh
sux, , label=none
, image = Hero lion Dur-Sharrukin Louvre AO19862.jpg
, alt =
, caption = Possible representation of Gilgamesh as Master of Animals, grasping a lion in his left arm and snake in his right hand, in an Assyr ...
, who, according to the epic, dived to the bottom of the waters to retrieve the plant of life. But while he rested from his labor, a serpent came and ate the plant. The snake became immortal, and Gilgamesh was destined to die.
 Ningizzida has been popularized in the 20th century by Raku Kei (
Ningizzida has been popularized in the 20th century by Raku Kei (Reiki
is a Japanese form of energy healing, a type of alternative medicine. Reiki practitioners use a technique called ''palm healing'' or ''hands-on healing'' through which a " universal energy" is said to be transferred through the palms of the ...
, a.k.a. "The Way of the Fire Dragon"), where "Nin Giz Zida" is believed to be a fire serpent of Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
an rather than Sumerian origin. "Nin Giz Zida" is another name for the ancient Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
concept Kundalini
In Hinduism, Kundalini ( sa, कुण्डलिनी, translit=kuṇḍalinī, translit-std=IAST, lit=coiled snake, ) is a form of divine feminine energy (or ''Shakti'') believed to be located at the base of the spine, in the ''muladhara'' ...
, a Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
word meaning either "coiled up" or "coiling like a snake". "Kundalini" refers to the mothering intelligence behind yogic awakening and spiritual maturation leading to altered states of consciousness. There are a number of other translations of the term, usually emphasizing a more serpentine nature to the word—e.g. "serpent power". It has been suggested by Joseph Campbell
Joseph John Campbell (March 26, 1904 – October 30, 1987) was an American writer. He was a professor of literature at Sarah Lawrence College who worked in comparative mythology and comparative religion. His work covers many aspects of the ...
that the symbol of snakes coiled around a staff is an ancient representation of Kundalini physiology. The staff represents the spinal column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordates ...
, with the snake(s) being energy channels. In the case of two coiled snakes, they usually cross each other seven times, a possible reference to the seven energy centers called chakra
Chakras (, ; sa , text=चक्र , translit=cakra , translit-std=IAST , lit=wheel, circle; pi, cakka) are various focal points used in a variety of ancient meditation practices, collectively denominated as Tantra, or the esoteric or ...
s.
In Ancient Egypt, where the earliest written cultural records exist, the serpent appears from the beginning to the end of their mythology. Ra and Atum
Atum (, Egyptian: ''jtm(w)'' or ''tm(w)'', ''reconstructed'' ; Coptic ''Atoum''), sometimes rendered as Atem or Tem, is an important deity in Egyptian mythology.
Name
Atum's name is thought to be derived from the verb ''tm'' which means 'to com ...
("he who completes or perfects") became the same god, ''Atum'', the "counter-Ra", associated with earth animals, including the serpent: Nehebkau
Nehebkau (also spelled Nehebu-Kau) is the primordial snake god in ancient Egyptian mythology. Although originally considered an evil spirit, he later functions as a funerary god associated with the afterlife. As one of the forty-two assessors ...
("he who harnesses the souls") was the two-headed serpent deity who guarded the entrance to the underworld. He is often seen as the son of the snake goddess Renenutet
Renenūtet (also transliterated Ernūtet, Renen-wetet, Renenet) was a goddess of nourishment and the harvest in the ancient Egyptian religion. The importance of the harvest caused people to make many offerings to Renenutet during harvest time.
In ...
. She often was confused with (and later was absorbed by) their primal snake goddess Wadjet
Wadjet (; egy, wꜢḏyt "Green One"), known to the Greek world as Uto (; grc-koi, Οὐτώ) or Buto (; ) among other renderings including Wedjat, Uadjet, and Udjo, was originally the ancient local goddess of the city of Dep. It became part ...
, the Egyptian cobra
The Egyptian cobra (''Naja haje''), also known as Ouraeus ''(derived from the Ancient Greek word: ''οὐραῖος'' - )'', is one of the most venomous snakes in North Africa, which has caused many snakebite incidents to humans. It averages rou ...
, who from the earliest of records was the patron and protector of the country, all other deities, and the pharaohs. Hers is the first known oracle
An oracle is a person or agency considered to provide wise and insightful counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. As such, it is a form of divination.
Description
The word '' ...
. She was depicted as the crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, partic ...
of Egypt, entwined around the staff of papyrus and the pole that indicated the status of all other deities, as well as having the all-seeing eye of wisdom and vengeance. She never lost her position in the Egyptian pantheon.
The image of the serpent as the embodiment of the wisdom transmitted by '' Sophia'' was an emblem used by gnosticism
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people ...
, especially those sects that the more orthodox characterized as "Ophites
The Ophites, also called Ophians (Greek Ὀφιανοί ''Ophianoi'', from ὄφις ''ophis'' "snake"), were a Christian Gnostic sect depicted by Hippolytus of Rome (170–235) in a lost work, the ''Syntagma'' ("arrangement").
It is now thought t ...
" ("Serpent People"). The chthonic serpent was one of the earth-animals associated with the cult of Mithras
Mithraism, also known as the Mithraic mysteries or the Cult of Mithras, was a Roman mystery religion centered on the god Mithras. Although inspired by Iranian worship of the Zoroastrian divinity (''yazata'') Mithra, the Roman Mithras is linke ...
. The basilisk
In European bestiaries and legends, a basilisk ( or ) is a legendary reptile reputed to be a serpent king, who causes death to those who look into its eyes. According to the ''Naturalis Historia'' of Pliny the Elder, the basilisk of Cyrene i ...
, the venomous "king of serpents" with the glance that kills, was hatched by a serpent, Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
and others thought, from the egg of a cock.
Outside Eurasia, in Yoruba mythology
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitu ...
, Oshunmare
Oshunmare (known as Ochumaré or Oxumaré in Latin America) is an Orisha. Osumare is the spirit of the rainbow, and Osumare also means rainbow in the Yoruba language
Yoruba (, ; Yor. '; Ajami: ) is a language spoken in West Africa, primaril ...
was another mythic regenerating serpent.
The Rainbow Serpent
The Rainbow Serpent or Rainbow Snake is a common deity often seen as the creator God, known by numerous names in different Australian Aboriginal languages by the many different Aboriginal peoples. It is a common motif in the art and religion ...
(also known as the Rainbow Snake) is a major mythological
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narrat ...
being for Aboriginal people across Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, although the creation myth
A creation myth (or cosmogonic myth) is a symbolic narrative of how the world began and how people first came to inhabit it., "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Creation myths develop ...
s associated with it are best known from northern Australia. In Fiji, Ratumaibulu In the mythology of Fiji, Ratumaibulu is a god of great importance who presides over agriculture. In the month called ''Vula-i-Ratumaibulu'', he comes from Bulu, the world of spirits, to make the breadfruit and other fruit trees blossom and yield ...
was a serpent god who ruled the underworld and made fruit trees bloom. In the Northern Flinders Ranges
The Flinders Ranges are the largest mountain range in South Australia, which starts about north of Adelaide. The ranges stretch for over from Port Pirie to Lake Callabonna.
The Adnyamathanha people are the Aboriginal group who have inhabi ...
reigns the Arkaroo, a serpent who drank Lake Frome
Lake Frome / Munda is a large endorheic lake in the Australian state of South Australia to the east of the Northern Flinders Ranges. It is a large, shallow, unvegetated salt pan, long and wide, lying mostly below sea level and having a total s ...
empty, refuges into the mountains, carving valleys and waterholes, earthquakes through snoring.
Cosmic serpents
The serpent, when forming a ring with its tail in its mouth, is a clear and widespread symbol of the "All-in-All", the totality of existence,infinity
Infinity is that which is boundless, endless, or larger than any natural number. It is often denoted by the infinity symbol .
Since the time of the ancient Greeks, the philosophical nature of infinity was the subject of many discussions amo ...
and the cyclic nature of the cosmos. The most well known version of this is the Aegypto-Greek ourobouros. It is believed to have been inspired by the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye ...
, as some ancient texts refer to a serpent of light residing in the heavens. The Ancient Egyptians associated it with Wadjet
Wadjet (; egy, wꜢḏyt "Green One"), known to the Greek world as Uto (; grc-koi, Οὐτώ) or Buto (; ) among other renderings including Wedjat, Uadjet, and Udjo, was originally the ancient local goddess of the city of Dep. It became part ...
, one of their oldest deities, as well as another aspect, Hathor
Hathor ( egy, ḥwt-ḥr, lit=House of Horus, grc, Ἁθώρ , cop, ϩⲁⲑⲱⲣ, Meroitic: ) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky ...
. In Norse mythology
Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Nordic folklore of the modern period ...
the World Serpent (or Midgard
In Germanic cosmology, Midgard (an anglicised form of Old Norse ; Old English , Old Saxon , Old High German , and Gothic ''Midjun-gards''; "middle yard", "middle enclosure") is the name for Earth (equivalent in meaning to the Greek term , "inhab ...
serpent) known as Jörmungandr
In Norse mythology, Jörmungandr ( non, Jǫrmungandr, lit=the Vast gand, see Etymology), also known as the Midgard Serpent or World Serpent ( non, Miðgarðsormr), is an unfathomably large sea serpent or worm who dwells in the world sea, encir ...
encircled the world in the ocean's abyss biting its own tail.
 In
In Hindu mythology
Hindu mythology is the body of myths and literature attributed to, and espoused by, the adherents of the Hindu religion, found in Hindu texts such as the Vedic literature, epics like ''Mahabharata'' and ''Ramayana'', the Puranas, and reg ...
Lord Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within t ...
is said to sleep while floating on the cosmic waters on the serpent Shesha
Shesha (Sanskrit: शेष; ) , also known as Sheshanaga (Sanskrit: शेषनाग; ) or Adishesha (), is a serpentine demigod ( Naga) and Nagaraja (King of all serpents), as well as a primordial being of creation in Hinduism. In the P ...
. In the Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
Shesha holds all the planets of the universe on his hoods and constantly sings the glories of Vishnu from all his mouths. He is sometimes referred to as "Ananta-Shesha," which means "Endless Shesha". In the Samudra manthan
The Samudra Manthana ( sa, समुद्रमन्थन; ) is a major episode in Hinduism that is elaborated in the Vishnu Purana, a major text of Hinduism. The Samudra Manthana explains the origin of the elixir of eternal life, amrita.
Nom ...
chapter of the Puranas, Shesha loosens Mount Mandara
Mandara ( sa, मन्दर, मन्दार; ) is the name of the mountain that appears in the Samudra Manthana episode in the Hindu Puranas, where it was used as a churning rod to churn the ocean of milk. Shiva's serpent, Vasuki, offered ...
for it to be used as a churning rod by the Asuras
Asuras (Sanskrit: असुर) are a class of beings in Indic religions. They are described as power-seeking clans related to the more benevolent Devas (also known as Suras) in Hinduism. In its Buddhist context, the word is sometimes translated ...
and Devas
Devas may refer to:
* Devas Club, a club in south London
* Anthony Devas (1911–1958), British portrait painter
* Charles Stanton Devas (1848–1906), political economist
* Jocelyn Devas (died 1886), founder of the Devas Club
* Devas (band), ...
to churn the ocean of milk
In Hindu cosmology, the Ocean of Milk (',', ''Malayalam: Pālāḻi'') is the fifth from the centre of the seven oceans. It surrounds the continent known as Krauncha. According to Hindu scriptures, the devas and asuras worked together for a mil ...
in the heavens in order to make Soma
Soma may refer to:
Businesses and brands
* SOMA (architects), a New York–based firm of architects
* Soma (company), a company that designs eco-friendly water filtration systems
* SOMA Fabrications, a builder of bicycle frames and other bicycle ...
(or Amrita
''Amrita'' ( sa, अमृत, IAST: ''amṛta''), ''Amrit'' or ''Amata'' in Pali, (also called ''Sudha'', ''Amiy'', ''Ami'') is a Sanskrit word that means "immortality". It is a central concept within Indian religions and is often referred t ...
), the divine elixir of immortality. As a churning rope another giant serpent called Vasuki
Vasuki (IAST: ) is the second king of the nagas in Hinduism. He is described as having a gem called ''Nagamani'' (serpent's ornament) on his head. Adishesha, the first king of the serpents and the mount of Narayana, is his elder brother, and ...
is used.
In pre-Columbian Central America Quetzalcoatl
Quetzalcoatl (, ; Spanish: ''Quetzalcóatl'' ; nci-IPA, Quetzalcōātl, ket͡saɬˈkoːaːt͡ɬ (Modern Nahuatl pronunciation), in honorific form: ''Quetzalcōātzin'') is a deity in Aztec culture and literature whose name comes from the Nahu ...
was sometimes depicted as biting its own tail. The mother of Quetzalcoatl was the Aztec goddess Coatlicue ("the one with the skirt of serpents"), also known as Cihuacoatl ("The Lady of the serpent"). Quetzalcoatl's father was Mixcoatl
Mixcoatl ( nah, Mixcōhuātl}, from mixtli "cloud" and cōātl "serpent"), or Camaxtle or Camaxtli, was the god of the hunt and identified with the Milky Way, the stars, and the heavens in several Mesoamerican cultures. He was the patron deity ...
("Cloud Serpent"). He was identified with the Milky Way, the stars, and the heavens in several Mesoamerican
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Withi ...
cultures.
The demigod
A demigod or demigoddess is a part-human and part-divine offspring of a deity and a human, or a human or non-human creature that is accorded divine status after death, or someone who has attained the "divine spark" ( spiritual enlightenment). A ...
Aidophedo of the West African Ashanti people
The Asante, also known as Ashanti () are part of the Akan ethnic group and are native to the Ashanti Region of modern-day Ghana. Asantes are the last group to emerge out of the various Akan civilisations. Twi is spoken by over nine million Asante ...
is also a serpent biting its own tail. In Dahomey mythology
The Dahomean religion was practiced by the Fon people of the Dahomey Kingdom. The kingdom existed until 1898 in what is now the country of Benin. People taken from Dahomey to the Caribbean used elements of the religion to form Vodou and other rel ...
of Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north ...
in West Africa, the serpent that supports everything on its many coils was named Dan. In the Vodou of Benin and Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
, Ayida-Weddo
Ayida-Weddo is a loa of fertility, rainbows, wind, water, fire, and snakes in Vodou, especially in Benin and Haiti. Ayida-Weddo is known as the "Rainbow Serpent". Variants of Ayida-Weddo's name include Aida-Weddo, Ayida-Wedo, Aido Quedo, and A ...
(a.k.a. Aida-Wedo, Aido Quedo, "Rainbow-Serpent") is a spirit of fertility, rainbows and snakes, and a companion or wife to Dan, the father of all spirits. As Vodou was exported to Haiti through the slave trade, Dan became Danballah, Damballah or Damballah-Wedo. Because of his association with snakes, he is sometimes disguised as Moses, who carried a snake on his staff. He is also thought by many to be the same entity of Saint Patrick
Saint Patrick ( la, Patricius; ga, Pádraig ; cy, Padrig) was a fifth-century Romano-British Christian missionary and bishop in Ireland. Known as the "Apostle of Ireland", he is the primary patron saint of Ireland, the other patron saints be ...
, known as a snake banisher.
The serpent Hydra is a star constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
representing either the serpent thrown angrily into the sky by Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
or the Lernaean Hydra
The Lernaean Hydra or Hydra of Lerna ( grc-gre, Λερναῖα Ὕδρα, ''Lernaîa Hýdra''), more often known simply as the Hydra, is a serpentine water monster in Greek and Roman mythology. Its lair was the lake of Lerna in the Argolid, whi ...
as defeated by Heracles
Heracles ( ; grc-gre, Ἡρακλῆς, , glory/fame of Hera), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive ...
for one of his Twelve Labors. The constellation Serpens
Serpens ( grc, , , the Serpent) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations designated by the International ...
represents a snake being tamed by Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus () is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constella ...
the snake-handler, another constellation. The most probable interpretation is that Ophiuchus represents the healer Asclepius.
Dragons
 Occasionally, serpents and
Occasionally, serpents and dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
s are used interchangeably, having similar symbolic functions. The venom of the serpent is thought to have a fiery quality similar to a fire-breathing dragon. The Greek Ladon and the Norse Níðhöggr
In Norse mythology, Níðhöggr (''Malice Striker'', in Old Norse traditionally also spelled Níðhǫggr , often anglicized NidhoggWhile the suffix of the name, ''-höggr'', clearly means "striker" the prefix is not as clear. In particular, the ...
(Nidhogg Nagar) are sometimes described as serpents and sometimes as dragons. In Germanic mythology
Germanic mythology consists of the body of myths native to the Germanic peoples, including Norse mythology, Anglo-Saxon mythology, and Continental Germanic mythology. It was a key element of Germanic paganism.
Origins
As the Germanic language ...
, "serpent" (Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
: ''wyrm'', Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old High ...
: ''wurm'', Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and t ...
: ''ormr'') is used interchangeably with the Greek borrowing "dragon" (OE: ''draca'', OHG: ''trahho'', ON: ''dreki''). In China and especially in Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
, the Indian serpent nāga
The Nagas (IAST: ''nāga''; Devanāgarī: नाग) are a divine, or semi-divine, race of half-human, half-serpent beings that reside in the netherworld (Patala), and can occasionally take human or part-human form, or are so depicted in art. ...
was equated with the ''lóng'' or Chinese dragon
The Chinese dragon, also known as ''loong'', ''long'' or ''lung'', is a legendary creature in Chinese mythology, Chinese folklore, and Chinese culture at large. Chinese dragons have many Outline of life forms, animal-like forms such as Bixi (my ...
. The Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
and Toltec
The Toltec culture () was a Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian Mesoamerican culture that ruled a state centered in Tula (Mesoamerican site), Tula, Hidalgo (state), Hidalgo, Mexico, during the Epiclassic and the early Post-Classic period of Mesoam ...
serpent god Quetzalcoatl
Quetzalcoatl (, ; Spanish: ''Quetzalcóatl'' ; nci-IPA, Quetzalcōātl, ket͡saɬˈkoːaːt͡ɬ (Modern Nahuatl pronunciation), in honorific form: ''Quetzalcōātzin'') is a deity in Aztec culture and literature whose name comes from the Nahu ...
also has dragon-like wings, like its equivalent in K'iche' K'iche', K'ichee', or Quiché may refer to:
* K'iche' people of Guatemala, a subgroup of the Maya
*K'iche' language, a Maya language spoken by the K'iche' people
**Classical K'iche' language, the 16th century form of the K'iche' language
*Kʼicheʼ ...
Maya mythology
Maya or Mayan mythology is part of Mesoamerican mythology and comprises all of the Maya tales in which personified forces of nature, deities, and the heroes interacting with these play the main roles. The myths of the era have to be reconstruct ...
Q'uq'umatz ("feathered serpent"), which had previously existed since Classic Maya times as the deity named Kukulkan
K’uk’ulkan, also spelled Kukulkan, ( "''Plumed Serpent''", "''Amazing Serpent''") is the name of a Mesoamerican serpent deity that was worshipped by the Yucatec Maya people of the Yucatán Peninsula before the Spanish conquest of Yucatán. ...
.
Mythology and religion
African mythology
 In Africa the chief centre of serpent worship was Dahomey, but the cult of the python seems to have been of exotic origin, dating back to the first quarter of the 17th century. By the conquest of Whydah the Dahomeyans were brought in contact with a people of serpent worshipers, and ended by adopting from them the beliefs which they at first despised. At Whydah, the chief centre, there is a serpent temple, tenanted by some fifty snakes. Every python of the ''danh-gbi'' kind must be treated with respect, and death is the penalty for killing one, even by accident. ''Danh-gbi'' has numerous wives, who until 1857 took part in a public procession from which the profane crowd was excluded; a python was carried round the town in a hammock, perhaps as a ceremony for the expulsion of evils.
The rainbow-god of the Ashanti was also conceived to have the form of a snake. His messenger was said to be a small variety of
In Africa the chief centre of serpent worship was Dahomey, but the cult of the python seems to have been of exotic origin, dating back to the first quarter of the 17th century. By the conquest of Whydah the Dahomeyans were brought in contact with a people of serpent worshipers, and ended by adopting from them the beliefs which they at first despised. At Whydah, the chief centre, there is a serpent temple, tenanted by some fifty snakes. Every python of the ''danh-gbi'' kind must be treated with respect, and death is the penalty for killing one, even by accident. ''Danh-gbi'' has numerous wives, who until 1857 took part in a public procession from which the profane crowd was excluded; a python was carried round the town in a hammock, perhaps as a ceremony for the expulsion of evils.
The rainbow-god of the Ashanti was also conceived to have the form of a snake. His messenger was said to be a small variety of boa
Kwon Bo-ah (; born November 5, 1986), known professionally as BoA, is a South Korean singer, songwriter, dancer, record producer and actress. One of the most successful and influential Korean entertainers, she has been dubbed the " Queen of K- ...
, but only certain individuals, not the whole species, were sacred.
In many parts of Africa the serpent is looked upon as the incarnation of deceased relatives. Among the Amazulu
Zulu people (; zu, amaZulu) are a Nguni ethnic group native to Southern Africa. The Zulu people are the largest ethnic group and nation in South Africa, with an estimated 10–12 million people, living mainly in the province of KwaZulu-Nata ...
, as among the Betsileo
The Betsileo are a highland ethnic groups of Madagascar, ethnic group of Madagascar, the third largest in terms of population. They chose their name, meaning "The Many Invincible Ones", after a failed invasion by King Ramitraho of the Menabe king ...
of Madagascar, certain species are assigned as the abode of certain classes. The Maasai Maasai may refer to:
* Maasai people
*Maasai language
* Maasai mythology
* MAASAI (band)
See also
* Masai (disambiguation)
* Massai
Massai (also known as: Masai, Massey, Massi, Mah–sii, Massa, Wasse, Wassil or by the nickname "Big Foot" Mas ...
, on the other hand, regard each species as the habitat of a particular family of the tribe.
Ancient Near East
 In
In ancient Mesopotamia
The history of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writing i ...
, Nirah
Nirah was a Mesopotamian god who served as the messenger (''šipru'') of Ištaran, the god of Der. He was depicted in the form of a snake.
Name and character
The name Nirah means "little snake" in Sumerian. It could be written with the log ...
, the messenger god of Ištaran
Ištaran (Ishtaran, sux, ) was a Mesopotamian god who was the tutelary deity of the city of Der, a Sumerian city state positioned east of the Tigris on the border between Sumer and Elam. It is known that he was a judge deity, and his positi ...
, was represented as a serpent on ''kudurru
A kudurru was a type of stone document used as a boundary stone and as a record of land grants to vassals by the Kassites and later dynasties in ancient Babylonia between the 16th and 7th centuries BC. The original kudurru would typically be stor ...
s'', or boundary stones
A boundary marker, border marker, boundary stone, or border stone is a robust physical marker that identifies the start of a land boundary or the change in a boundary, especially a change in direction of a boundary. There are several other ty ...
. Representations of two intertwined serpents are common in Sumerian art
The art of Mesopotamia has survived in the record from early hunter-gatherer societies (8th millennium BC) on to the Bronze Age cultures of the Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian and Assyrian empires. These empires were later replaced in the Iron Ag ...
and Neo-Sumerian artwork and still appear sporadically on cylinder seal
A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in length, engraved with written characters or figurative scenes or both, used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally ...
s and amulets until as late as the thirteenth century BCE. The horned viper (''Cerastes cerastes
''Cerastes cerastes'', commonly known as the Saharan horned viperMallow D, Ludwig D, Nilson G. (2003). ''True Vipers: Natural History and Toxinology of Old World Vipers''. Malabar, Florida: Krieger Publishing Company. . or the desert horned viper ...
'') appears in Kassite
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology).
They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylon ...
and Neo-Assyrian
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
kudurrus and is invoked in Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
n texts as a magical protective entity. A dragon-like creature with horns, the body and neck of a snake, the forelegs of a lion, and the hind-legs of a bird appears in Mesopotamian art from the Akkadian period until the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
(323 BCE–31 BCE). This creature, known in Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabi ...
as the ''mušḫuššu
The ''mušḫuššu'' (; formerly also read as or ) or mushkhushshu ( or ), is a creature from ancient Mesopotamian mythology. A mythological hybrid, it is a scaly animal with hind legs resembling the talons of an eagle, lion-like forelimbs, a ...
'', meaning "furious serpent", was used as a symbol for particular deities and also as a general protective emblem. It seems to have originally been the attendant of the underworld god Ninazu
Ninazu ( sux, ) was a Mesopotamian god of the underworld of Sumerian origin. He was also associated with snakes and vegetation, and with time acquired the character of a warrior god. He was frequently associated with Ereshkigal, either as a s ...
, but later became the attendant to the Hurrian
The Hurrians (; cuneiform: ; transliteration: ''Ḫu-ur-ri''; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri or Hurriter) were a people of the Bronze Age Near East. They spoke a Hurrian language and lived in Anatolia, Syria and Northern ...
storm-god Tishpak
Tishpak (Tišpak) was a Mesopotamian god associated with the ancient city Eshnunna and its sphere of influence, located in the Diyala area of Iraq. He was primarily a war deity, but he was also associated with snakes, including the mythical mus ...
, as well as, later, Ninazu's son Ningishzida
Ningishzida ( Sumerian: DNIN-G̃IŠ-ZID-DA, possible meaning "Lord f theGood Tree") was a Mesopotamian deity of vegetation, the underworld and sometimes war. He was commonly associated with snakes. Like Dumuzi, he was believed to spend a part ...
, the Babylonian national god
A national god is a Tutelary deity, guardian divinity whose special concern is the safety and well-being of an ethnic group (''nation''), and of that group's leaders. This is contrasted with other guardian figures such as family gods responsible ...
Marduk
Marduk (Cuneiform: dAMAR.UTU; Sumerian: ''amar utu.k'' "calf of the sun; solar calf"; ) was a god from ancient Mesopotamia and patron deity of the city of Babylon. When Babylon became the political center of the Euphrates valley in the time of ...
, the scribal god Nabu
Nabu ( akk, cuneiform: 𒀭𒀝 Nabû syr, ܢܵܒܼܘܼ\ܢܒܼܘܿ\ܢܵܒܼܘܿ Nāvū or Nvō or Nāvō) is the ancient Mesopotamian patron god of literacy, the rational arts, scribes, and wisdom.
Etymology and meaning
The Akkadian "nab� ...
, and the Assyrian national god Ashur.
Snake cults were well established in Canaanite religion
The Canaanite religion was the group of ancient Semitic religions practiced by the Canaanites living in the ancient Levant from at least the early Bronze Age through the first centuries AD. Canaanite religion was polytheistic and, in some cases ...
in the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, for archaeologists have uncovered serpent cult object
In the practice of religion, a cult image is a human-made object that is venerated or worshipped for the deity, spirit or daemon that it embodies or represents. In several traditions, including the ancient religions of Egypt, Greece and Ro ...
s in Bronze Age strata at several pre-Israelite cities in Canaan: two at Megiddo Megiddo may refer to:
Places and sites in Israel
* Tel Megiddo, site of an ancient city in Israel's Jezreel valley
* Megiddo Airport, a domestic airport in Israel
* Megiddo church (Israel)
* Megiddo, Israel, a kibbutz in Israel
* Megiddo Junction, ...
, one at Gezer
Gezer, or Tel Gezer ( he, גֶּזֶר), in ar, تل الجزر – Tell Jezar or Tell el-Jezari is an archaeological site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (eithe ...
, one in the ''sanctum sanctorum'' of the Area H temple at Hazor, and two at Shechem
Shechem ( ), also spelled Sichem ( ; he, שְׁכֶם, ''Šəḵem''; ; grc, Συχέμ, Sykhém; Samaritan Hebrew: , ), was a Canaanite and Israelite city mentioned in the Amarna Letters, later appearing in the Hebrew Bible as the first cap ...
.
In the surrounding region, serpent cult objects figured in other cultures. A late Bronze Age Hittite shrine in northern Syria contained a bronze statue of a god holding a serpent in one hand and a staff in the other. In 6th-century Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
, a pair of bronze serpents flanked each of the four doorways of the temple of Esagila
The Ésagila or Esangil ( sux, , ''"temple whose top is lofty"'') was a temple dedicated to Marduk, the protector god of Babylon. It lay south of the ziggurat Etemenanki.
Description
In this temple was the statue of Marduk, surrounded by cu ...
. At the Babylonian New Year's festival, the priest was to commission from a woodworker, a metalworker and a goldsmith two images, one of which "shall hold in its left hand a snake of cedar, raising its right and
or AND may refer to:
Logic, grammar, and computing
* Conjunction (grammar), connecting two words, phrases, or clauses
* Logical conjunction in mathematical logic, notated as "∧", "⋅", "&", or simple juxtaposition
* Bitwise AND, a boolea ...
to the god Nabu
Nabu ( akk, cuneiform: 𒀭𒀝 Nabû syr, ܢܵܒܼܘܼ\ܢܒܼܘܿ\ܢܵܒܼܘܿ Nāvū or Nvō or Nāvō) is the ancient Mesopotamian patron god of literacy, the rational arts, scribes, and wisdom.
Etymology and meaning
The Akkadian "nab� ...
". At the tell of Tepe Gawra, at least seventeen Early Bronze Age Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
n bronze serpents were recovered.
Bronze and Iron Age United Arab Emirates
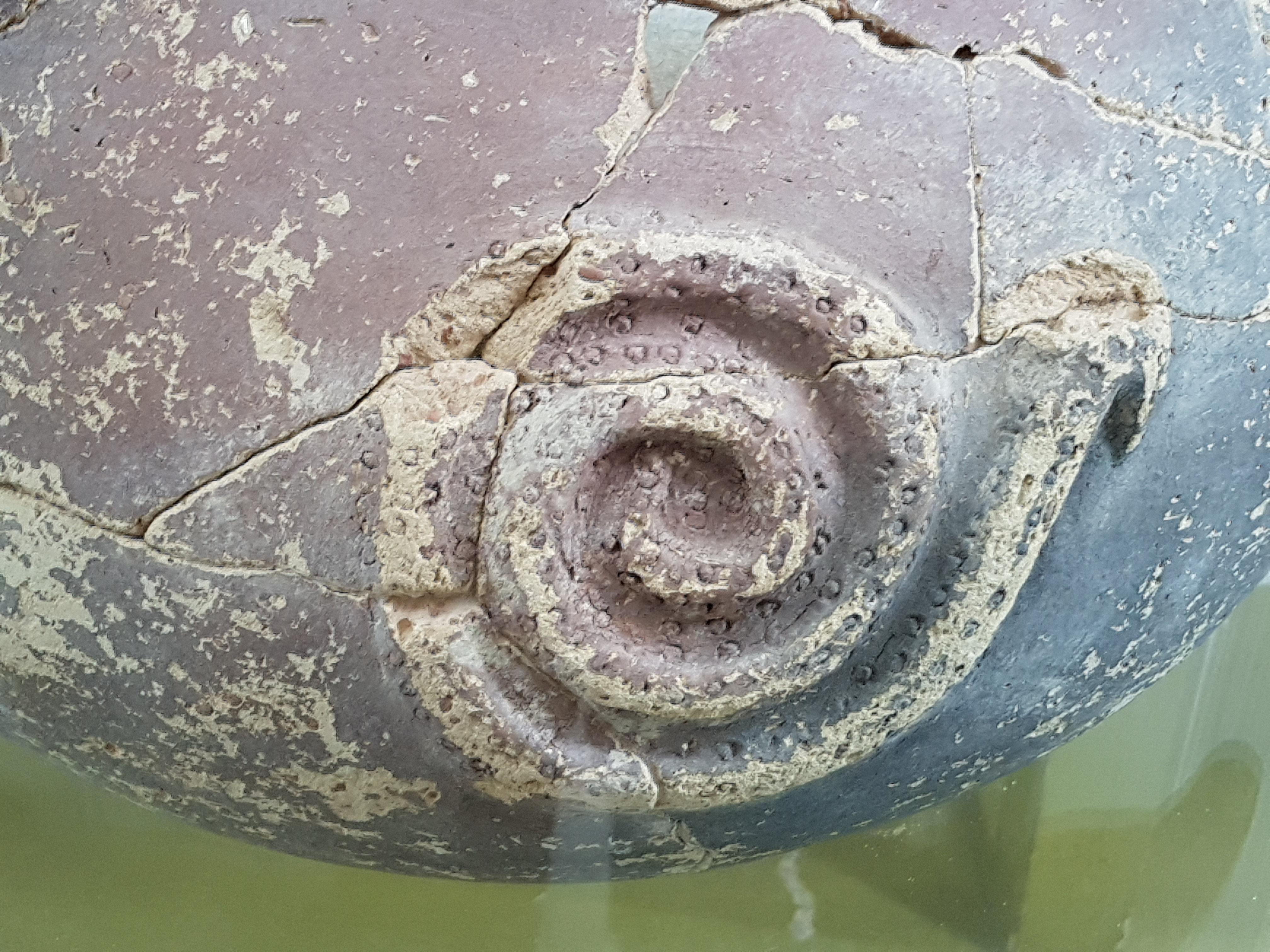
 Significant finds of pottery, bronze-ware and even gold depictions of snakes have been made throughout the
Significant finds of pottery, bronze-ware and even gold depictions of snakes have been made throughout the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia (The Middle East). It is located at th ...
(UAE). The Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
and Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
metallurgical centre of Saruq Al Hadid has yielded probably the richest trove of such objects, although finds have been made bearing snake symbols in Bronze Age sites at Rumailah, Bithnah and Masafi
Masafi ( ar, مسافي) is a village located on the edge of the Hajar Mountains in the United Arab Emirates. It sits at the inland entrance of the Wadi Ham, which runs down to Fujairah City. The border between the emirates of Fujairah and Ras Al ...
. Most of the depictions of snakes are similar, with a consistent dotted decoration applied to them.
Although the widespread depiction of snakes in sites across the UAE is thought by archaeologists to have a religious purpose, this remains conjecture.
Abrahamic mythology
=Judaic mythology
= In the
In the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
the serpent in the ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
Garden of Eden
In Abrahamic religions, the Garden of Eden ( he, גַּן־עֵדֶן, ) or Garden of God (, and גַן־אֱלֹהִים ''gan-Elohim''), also called the Terrestrial Paradise, is the Bible, biblical paradise described in Book of Genesis, Genes ...
lured Eve with the promise of being like God, tempting her that despite God's warning, death would not be the result, that God was withholding knowledge from her. Although the serpent is identified as Satan
Satan,, ; grc, ὁ σατανᾶς or , ; ar, شيطانالخَنَّاس , also known as Devil in Christianity, the Devil, and sometimes also called Lucifer in Christianity, is an non-physical entity, entity in the Abrahamic religions ...
in the Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament (and consequently the final book of the Christian Bible). Its title is derived from the first word of the Koine Greek text: , meaning "unveiling" or "revelation". The Book of R ...
, Harris, Stephen L., ''Understanding the Bible''. Palo Alto: Mayfield. 1985. in Genesis the serpent is portrayed merely as a deceptive creature or trickster
In mythology and the study of folklore and religion, a trickster is a character in a story (god, goddess, spirit, human or anthropomorphisation) who exhibits a great degree of intellect or secret knowledge and uses it to play tricks or otherwi ...
, promoting as good what God had directly forbidden, and particularly cunning in its deception (Gen. 3:4–5 and 3:22).
The staff of Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
transformed into a snake and then back into a staff (Exodus
Exodus or the Exodus may refer to:
Religion
* Book of Exodus, second book of the Hebrew Torah and the Christian Bible
* The Exodus, the biblical story of the migration of the ancient Israelites from Egypt into Canaan
Historical events
* Ex ...
4:2–4). The Book of Numbers
The book of Numbers (from Greek Ἀριθμοί, ''Arithmoi''; he, בְּמִדְבַּר, ''Bəmīḏbar'', "In the desert f) is the fourth book of the Hebrew Bible, and the fourth of five books of the Jewish Torah. The book has a long and com ...
21:6–9 provides an origin for an archaic copper serpent, ''Nehushtan'', by associating it with Moses. This copper snake according to the Biblical text is put on a pole and used for healing. Book of Numbers 21:9 "And Moses made a snake of copper, and put it upon a pole, and it came to pass, that if a snake had bitten any man, when he beheld the snake of brass, he lived."
When the reformer King Hezekiah
Hezekiah (; hbo, , Ḥīzqīyyahū), or Ezekias); grc, Ἐζεκίας 'Ezekías; la, Ezechias; also transliterated as or ; meaning " Yah shall strengthen" (born , sole ruler ), was the son of Ahaz and the 13th king of Judah according to t ...
came to the throne of Judah in the late 8th century BCE, "He removed the high places, broke the sacred pillars, smashed the idols, and broke into pieces the copper snake that Moses had made: for unto those days the children of Israel did burn incense to it: and he called it Nehushtan. ()
=Christian mythology
= In theGospel of John
The Gospel of John ( grc, Εὐαγγέλιον κατὰ Ἰωάννην, translit=Euangélion katà Iōánnēn) is the fourth of the four canonical gospels. It contains a highly schematic account of the ministry of Jesus, with seven "sig ...
3:14–15, Jesus makes direct comparison between the raising up of the Son of Man and the act of Moses in raising up the serpent as a sign, using it as a symbol associated with salvation
Salvation (from Latin: ''salvatio'', from ''salva'', 'safe, saved') is the state of being saved or protected from harm or a dire situation. In religion and theology, ''salvation'' generally refers to the deliverance of the soul from sin and its c ...
: "As Moses lifted up the serpent in the wilderness, even so must the Son of Man be lifted up, that whoever believes in Him should not perish but have eternal life".
=Muslim mythology
= The serpent is a recurrent motif in Islamic thought, appearing in both sacred texts and works of art. The creature is often seen as a symbol of evil. However, the serpent can also be seen as a positive figure. In Islamic tradition, the creature is often associated with wisdom and knowledge. In some works of Islamic art, the serpent is depicted as a guardian of the Quran, guarding the sacred text from harm. The serpent is a complex figure in Islamic thought, appearing as both a symbol of evil and a figure of wisdom. The creature provides a reminder of the dangers of temptation, but also represents the potential for knowledge and enlightenment.Ancient Iran
 Serpents are sacred and powerful in the thought of prehistoric cultures of Iran, having been portrayed as patrons of fertility, water and wealth in the ancient objects of Iran. They seem to have been worshipped along with the
Serpents are sacred and powerful in the thought of prehistoric cultures of Iran, having been portrayed as patrons of fertility, water and wealth in the ancient objects of Iran. They seem to have been worshipped along with the fertility goddesses
A fertility deity is a god or goddess associated with fertility, sex, pregnancy, childbirth, and crops. In some cases these deities are directly associated with these experiences; in others they are more abstract symbols. Fertility rites may ac ...
from the fourth to first millennia BC, when their presence as mighty patrons and source of life and of immortality is seen in the art of Tall-i Bakun
Tall-i Bakun or Tall-e Bakun (in modern Fars Province, Iran) was a prehistoric site
in the Ancient Near East about 3 km south of Persepolis. It was inhabited around 4000-3500 BC.
Archaeology
The site consists of two mounds, A and B. In 19 ...
, Chogha Mish
Tappeh-ye Choghā Mīsh (Persian language; چغامیش ''čoġā mīš'') dating back to 6800 BC, is the site of a Chalcolithic settlement in Western Iran, located in the Khuzistan Province on the Susiana Plain. It was occupied at the beginni ...
, Tepe Sialk
Tepe Sialk ( fa, تپه سیلک) is a large ancient archeological site (a ''tepe'', "hill, tell (archaeology), tell") in a suburb of the city of Kashan, Isfahan Province, in central Iran, close to Fin Garden. The culture that inhabited this area ...
, Jiroft culture
The Jiroft cultureOscar White MuscarellaJiroft(2008), in: Encyclopedia Iranica. "For archeological accuracy the terms "Jiroft" or "Jiroft culture" employed to define a specific ancient Iranian culture and its artifacts should only be cited within ...
, Shahr-e Sukhteh
Shahr-e Sukhteh ( fa, شهر سوخته, meaning " heBurnt City"), c. 3200–2350 BCE,
also spelled as ''Shahr-e Sūkhté'' and ''Shahr-i Sōkhta'', is an archaeological site of a sizable Bronze Age urban settlement, associated with the Helmand ...
, Shahdad
Shahdad ( fa, شهداد, also Romanized as Shahdād; formerly, Khabīs) is a city and capital of Shahdad District, in Kerman County, Kerman Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 4,097, in 1,010 families.
District
Shahdad is t ...
, Elamite
Elamite, also known as Hatamtite and formerly as Susian, is an extinct language that was spoken by the ancient Elamites. It was used in what is now southwestern Iran from 2600 BC to 330 BC. Elamite works disappear from the archeological record ...
art, Luristan art, etc.
However, it seems that the symbolic concept of the serpent was corrupted in the cultures of the Iranian plateau
The Iranian plateau or Persian plateau is a geological feature in Western Asia, Central Asia, and South Asia. It comprises part of the Eurasian Plate and is wedged between the Arabian Plate and the Indian Plate; situated between the Zagros ...
over time by Western influence. In Abrahamic traditions
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
, the serpent represents sexual desire, as he lured Eve
Eve (; ; ar, حَوَّاء, Ḥawwāʾ; el, Εὕα, Heúa; la, Eva, Heva; Syriac: romanized: ) is a figure in the Book of Genesis in the Hebrew Bible. According to the origin story, "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the ...
with the promise of forbidden knowledge in the Garden of Eden
In Abrahamic religions, the Garden of Eden ( he, גַּן־עֵדֶן, ) or Garden of God (, and גַן־אֱלֹהִים ''gan-Elohim''), also called the Terrestrial Paradise, is the Bible, biblical paradise described in Book of Genesis, Genes ...
. As a result of such influence, Aryan religions call the serpents diabolic; Azhi Dahake in the Avesta
The Avesta () is the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language.
The Avesta texts fall into several different categories, arranged either by dialect, or by usage. The principal text in the litu ...
is a scary serpent, and Zahhak
Zahhāk or Zahāk () ( fa, ضحّاک), also known as Zahhak the Snake Shoulder ( fa, ضحاک ماردوش, Zahhāk-e Mārdoush), is an evil figure in Persian mythology, evident in ancient Persian folklore as Azhi Dahāka ( fa, اژی دهاک) ...
in the ''Shahnameh
The ''Shahnameh'' or ''Shahnama'' ( fa, شاهنامه, Šāhnāme, lit=The Book of Kings, ) is a long epic poem written by the Persian poet Ferdowsi between c. 977 and 1010 CE and is the national epic of Greater Iran. Consisting of some 50,00 ...
'' is an infernal creature with two snakes on his shoulders. This replacement might be due to communication between the inhabitants of Iran and believers in Abrahamic religions
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
, and beyond that the conversion of matriarchy
Matriarchy is a social system in which women hold the primary power positions in roles of authority. In a broader sense it can also extend to moral authority, social privilege and control of property.
While those definitions apply in general E ...
into patriarchy
Patriarchy is a social system in which positions of dominance and privilege are primarily held by men. It is used, both as a technical anthropological term for families or clans controlled by the father or eldest male or group of males a ...
as the social structure of Iranian plateau cultures.
Chinese mythology
In Chinese creationism mythology,Nüwa
Nüwa, also read Nügua, is the mother goddess of Chinese mythology. She is credited with creating humanity and repairing the Pillar of Heaven.
As creator of mankind, she molded humans individually by hand with yellow clay.
In the Huainanzi ...
is the mother goddess who created humans from clay. She is depicted as a half snake being.
Greek mythology
 The
The Minoan
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450B ...
Snake Goddess A snake goddess is a goddess associated with a snake theme.
Examples include:
* Meretseger ("She Who Loves Silence"), Egyptian snake goddess
* Minoan snake goddess figurines, a type of figurine in Minoan archaeology
*Renenutet, Egyptian snake godde ...
brandished a serpent in either hand, perhaps evoking her role as source of wisdom, rather than her role as Mistress of the Animals ('' Potnia Theron''), with a leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
under each arm.
Serpents figured prominently in archaic Greek myths. According to some sources, Ophion
In some versions of Greek mythology, Ophion (; grc-gre, Ὀφίων "serpent"; ''gen''.: Ὀφίωνος), also called Ophioneus () ruled the world with Eurynome before the two of them were cast down by Cronus and Rhea.
Mythology
Pherecydes of ...
("serpent", a.k.a. Ophioneus), ruled the world with Eurynome before the two of them were cast down by Cronus
In Ancient Greek religion and mythology, Cronus, Cronos, or Kronos ( or , from el, Κρόνος, ''Krónos'') was the leader and youngest of the first generation of Titans, the divine descendants of the primordial Gaia (Mother Earth) and ...
and Rhea. The oracles of the Ancient Greeks were said to have been the continuation of the tradition begun with the worship of the Egyptian cobra goddess Wadjet
Wadjet (; egy, wꜢḏyt "Green One"), known to the Greek world as Uto (; grc-koi, Οὐτώ) or Buto (; ) among other renderings including Wedjat, Uadjet, and Udjo, was originally the ancient local goddess of the city of Dep. It became part ...
.
Typhon
Typhon (; grc, Τυφῶν, Typhôn, ), also Typhoeus (; grc, Τυφωεύς, Typhōeús, label=none), Typhaon ( grc, Τυφάων, Typháōn, label=none) or Typhos ( grc, Τυφώς, Typhṓs, label=none), was a monstrous serpentine giant an ...
, the enemy of the Olympian gods
upright=1.8, Fragment of a relief (1st century BC1st century AD) depicting the twelve Olympians carrying their attributes in procession; from left to right: Hestia (scepter), Hermes (winged cap and staff), Aphrodite (veiled), Ares (helmet and s ...
, is described as a vast grisly monster with a hundred heads and a hundred serpents issuing from his thighs, who was conquered and cast into Tartarus
In Greek mythology, Tartarus (; grc, , }) is the deep abyss that is used as a dungeon of torment and suffering for the wicked and as the prison for the Titans. Tartarus is the place where, according to Plato's ''Gorgias'' (), souls are judg ...
by Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label=Genitive case, genitive Aeolic Greek, Boeotian Aeolic and Doric Greek#Laconian, Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label=Genitive case, genitive el, Δίας, ''D� ...
, or confined beneath volcanic regions, where he is the cause of eruptions. Typhon is thus the chthonic figuration of volcanic forces. Serpent elements figure among his offspring; among his children by Echidna are Cerberus
In Greek mythology, Cerberus (; grc-gre, Κέρβερος ''Kérberos'' ), often referred to as the hound of Hades, is a multi-headed dog that guards the gates of the Underworld to prevent the dead from leaving. He was the offspring of the mo ...
(a monstrous three-headed dog with a snake for a tail and a serpentine mane); the serpent-tailed Chimaera; the serpent-like chthonic water beast Lernaean Hydra
The Lernaean Hydra or Hydra of Lerna ( grc-gre, Λερναῖα Ὕδρα, ''Lernaîa Hýdra''), more often known simply as the Hydra, is a serpentine water monster in Greek and Roman mythology. Its lair was the lake of Lerna in the Argolid, whi ...
; and the hundred-headed serpentine dragon Ladon. Both the Lernaean Hydra and Ladon were slain by Heracles
Heracles ( ; grc-gre, Ἡρακλῆς, , glory/fame of Hera), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive ...
.
Python
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (pro ...
was the earth-dragon of Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), in ancient times was a sacred precinct that served as the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient classical world. The oracle ...
. She always was represented in the vase-paintings and by sculptors as a serpent. Python was the chthonic enemy of Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
, who slew her and remade her former home his own oracle, the most famous in Classical Greece.
Medusa
In Greek mythology, Medusa (; Ancient Greek: Μέδουσα "guardian, protectress"), also called Gorgo, was one of the three monstrous Gorgons, generally described as winged human females with living venomous snakes in place of hair. Those ...
and the other Gorgon
A Gorgon (Help:IPA/English, /ˈɡɔːrɡən/; plural: Gorgons, Ancient Greek language, Ancient Greek: Γοργών/Γοργώ ''Gorgṓn/Gorgṓ'') is a creature in Greek mythology. Gorgons occur in the earliest examples of Greek literature. W ...
s were vicious female monsters with sharp fangs and hair of living, venomous snakes whose origins predate the written myths of Greece and who were the protectors of the most ancient ritual secrets. The Gorgons wore a belt of two intertwined serpents in the same configuration of the caduceus
The caduceus (☤; ; la, cādūceus, from grc-gre, κηρύκειον "herald's wand, or staff") is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology. The same staff was also ...
. The Gorgon was placed at the center, highest point of one of the pediments on the Temple of Artemis at Corfu.
Asclepius
Asclepius (; grc-gre, Ἀσκληπιός ''Asklēpiós'' ; la, Aesculapius) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Religion in ancient Greece, Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis (lover of ...
, the son of Apollo and Coronis, learned the secrets of keeping death at bay after observing one serpent bringing another (which Asclepius himself had fatally wounded) back to life with healing herbs. To prevent the entire human race from becoming immortal under Asclepius's care, Zeus killed him with a bolt of lightning. Asclepius' death at the hands of Zeus illustrates man's inability to challenge the natural order that separates mortal men from the gods. In honor of Asclepius, snakes were often used in healing rituals. Non-poisonous snakes were left to crawl on the floor in dormitories where the sick and injured slept. The '' Bibliotheca'' claimed that Athena
Athena or Athene, often given the epithet Pallas, is an ancient Greek goddess associated with wisdom, warfare, and handicraft who was later syncretized with the Roman goddess Minerva. Athena was regarded as the patron and protectress of ...
gave Asclepius a vial of blood from the Gorgons. Gorgon blood had magical properties: if taken from the left side of the Gorgon, it was a fatal poison; from the right side, the blood was capable of bringing the dead back to life. However, Euripides
Euripides (; grc, Εὐριπίδης, Eurīpídēs, ; ) was a tragedian
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful e ...
wrote in his tragedy ''Ion'' that the Athenian queen Creusa
In Greek mythology, Creusa (; grc, Κρέουσα ''Kreousa'' "princess") may refer to the following figures:
* Creusa, a naiad daughter of Gaia.
* Creusa, daughter of Erechtheus, King of Athens and his wife, Praxithea.
* Creusa, also known by t ...
had inherited this vial from her ancestor Erichthonios, who was a snake himself and had received the vial from Athena. In this version the blood of Medusa had the healing power while the lethal poison originated from Medusa's serpents.
Olympias, the mother of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
and a princess of the primitive land of Epirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinrich ...
, had the reputation of a snake-handler, and it was in serpent form that Zeus was said to have fathered Alexander upon her. Aeëtes
Aeëtes (; , ; , ), or Aeeta, was a king of Colchis in Greek mythology. The name comes from the ancient Greek word (, "eagle").
Family
Aeëtes was the son of Sun god Helios and the Oceanid Perseis, brother of Circe, Perses and Pasiphaë, ...
, the king of Colchis
In Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia (country), Georgia.
Its population, the Colchians a ...
and father of the sorceress Medea
In Greek mythology, Medea (; grc, Μήδεια, ''Mēdeia'', perhaps implying "planner / schemer") is the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, a niece of Circe and the granddaughter of the sun god Helios. Medea figures in the myth of Jason an ...
, possessed the Golden Fleece
In Greek mythology, the Golden Fleece ( el, Χρυσόμαλλον δέρας, ''Chrysómallon déras'') is the fleece of the golden-woolled,, ''Khrusómallos''. winged ram, Chrysomallos, that rescued Phrixus and brought him to Colchis, where P ...
. He guarded it with a massive serpent that never slept. Medea, who had fallen in love with Jason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Medea. He w ...
of the Argonauts
The Argonauts (; Ancient Greek: ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology, who in the years before the Trojan War (around 1300 BC) accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, '' Argo'', ...
, enchanted it to sleep so Jason could seize the Fleece. (See Lamia
LaMia Corporation S.R.L., operating as LaMia (short for ''Línea Aérea Mérida Internacional de Aviación''), was a Bolivian charter airline headquartered in Santa Cruz de la Sierra, as an EcoJet subsidiary. It had its origins from the failed ...
).
When not driven by horses, the chariot of the Greek sun god is described as being pulled by fiery draconic beings. The most notable instance of this is observed in the episode in which Medea
In Greek mythology, Medea (; grc, Μήδεια, ''Mēdeia'', perhaps implying "planner / schemer") is the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, a niece of Circe and the granddaughter of the sun god Helios. Medea figures in the myth of Jason an ...
is given her grandfather's chariot, which is pulled by serpents through the sky.
In artwork snakes are occasionally associated with Hecate
Hecate or Hekate, , ; grc-dor, Ἑκάτᾱ, Hekátā, ; la, Hecatē or . is a goddess in ancient Greek religion and mythology, most often shown holding a pair of torches, a key, snakes, or accompanied by dogs, and in later periods depicte ...
, the goddess of witchcraft
Witchcraft traditionally means the use of magic or supernatural powers to harm others. A practitioner is a witch. In medieval and early modern Europe, where the term originated, accused witches were usually women who were believed to have us ...
.
Hindu mythology
''Naga'' (Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
:नाग) is the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
/Pāli
Pali () is a Middle Indo-Aryan liturgical language native to the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pāli Canon'' or ''Tipiṭaka'' as well as the sacred language of ''Theravāda'' Buddhism ...
word for a deity or class of entity or being, taking the form of a very large snake, found in Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
and Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current ...
. The ''naga'' primarily represents rebirth, death and mortality, due to its casting of its skin and being symbolically "reborn".
Hindus associated ''naga'' with Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
and with Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within t ...
, who rested on a 100-headed ''naga'' and coiled around Lord Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hindu ...
's neck. The snake represented freedom in Hindu mythology
Hindu mythology is the body of myths and literature attributed to, and espoused by, the adherents of the Hindu religion, found in Hindu texts such as the Vedic literature, epics like ''Mahabharata'' and ''Ramayana'', the Puranas, and reg ...
because they cannot be tamed. In Buddhism, the serpent Mucalinda
Mucalinda, Muchalinda or Mucilinda is the name of a nāga, a snake-like being, who protected the Gautama Buddha from the elements after his enlightenment.
It is said that six weeks after Gautama Buddha began meditating under the Bodhi Tree, t ...
is associated as the protector of Lord Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in L ...
. In Jainism, serpent is associated with the 23rd Tirthankara Parshvanatha
''Parshvanatha'' (), also known as ''Parshva'' () and ''Parasnath'', was the 23rd of 24 ''Tirthankaras'' (supreme preacher of dharma) of Jainism. He is the only Tirthankara who gained the title of ''Kalīkālkalpataru (Kalpavriksha in this "Kal ...
.
Nagas of Indochina
Serpents, or ''nāga
The Nagas (IAST: ''nāga''; Devanāgarī: नाग) are a divine, or semi-divine, race of half-human, half-serpent beings that reside in the netherworld (Patala), and can occasionally take human or part-human form, or are so depicted in art. ...
s'', play a particularly important role in Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailand t ...
n, Isan
Northeast Thailand or Isan (Isan/ th, อีสาน, ; lo, ອີສານ; also written as Isaan, Isarn, Issarn, Issan, Esan, or Esarn; from Pali ''īsānna'' or Sanskrit ईशान्य ''īśānya'' "northeast") consists of 20 provin ...
and Laotian mythology. An origin myth
An origin myth is a myth that describes the origin of some feature of the natural or social world. One type of origin myth is the creation or cosmogonic myth, a story that describes the creation of the world. However, many cultures have stor ...
explains the emergence of the name "Cambodia" as resulting from conquest of a naga princess by a Kambuja lord named Kaundinya
Kaundinya (Sanskrit कौण्डिन्य), also known as ''Ājñātakauṇḍinya'', Pali: ''Añña Koṇḍañña''),who was one of the first five Buddhist monks ( Pancavaggiya), follower of Gautama Buddha and the first to become an arha ...
: the descendants of their union are the Khmer people
The Khmer people ( km, ជនជាតិខ្មែរ, ) are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Cambodia. They comprise over 90% of Cambodia's population of 17 million.
. George Cœdès suggests the Cambodian myth is a basis for the legend of "Phra Daeng Nang Ai", in which a woman who has lived many previous lives in the region is reincarnated as a daughter of Phraya Khom (Thai for Cambodian) and causes the death of her companion in former lives who has been reincarnated as a prince of the Nagas. This leads to war between the "spirits of the air" and the Nagas: Nagas amok are rivers in spate, and the entire region is flooded. The Myth of the Toad King tells how introduction of Buddhist teachings led to war with the sky deity
The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.
The daytime sky deities are typically distinct from the nighttime ones. Stith Thompson's ''Motif ...
Phaya Thaen, and ended in a truce with nagas posted as guardians of entrances to temples.
Native American mythology
 Some Native American tribes give reverence to the rattlesnake as grandfather and king of snakes who is able to give fair winds or cause tempest. Among the
Some Native American tribes give reverence to the rattlesnake as grandfather and king of snakes who is able to give fair winds or cause tempest. Among the Hopi
The Hopi are a Native American ethnic group who primarily live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census, there are 19,338 Hopi in the country. The Hopi Tribe is a sovereign nation within the Unite ...
of Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
the serpent figures largely in one of the dances. The rattlesnake was worshiped in the Natchez Natchez may refer to:
Places
* Natchez, Alabama, United States
* Natchez, Indiana, United States
* Natchez, Louisiana, United States
* Natchez, Mississippi, a city in southwestern Mississippi, United States
* Grand Village of the Natchez, a site o ...
Temple of the Sun, and the Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
deity Quetzalcoatl
Quetzalcoatl (, ; Spanish: ''Quetzalcóatl'' ; nci-IPA, Quetzalcōātl, ket͡saɬˈkoːaːt͡ɬ (Modern Nahuatl pronunciation), in honorific form: ''Quetzalcōātzin'') is a deity in Aztec culture and literature whose name comes from the Nahu ...
was a feathered serpent-god. In many Meso-American cultures, the serpent was regarded as a portal between two worlds. The tribes of Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal
, national_motto = "Fi ...
are said to have adored great snakes in the pre-Inca days, and in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
the Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who sha ...
made a serpent figure in their deluge beliefs.
A Horned Serpent is a popular image in Northern American natives' mythology.
In one Native North American story, an evil serpent kills one of the gods' cousins, so the god kills the serpent in revenge, but the dying serpent unleashes a great flood. People first flee to the mountains and then, when the mountains are covered, they float on a raft until the flood subsides. The evil spirits that the serpent god controlled then hide out of fear. The Mound Builders
A number of pre-Columbian cultures are collectively termed "Mound Builders". The term does not refer to a specific people or archaeological culture, but refers to the characteristic mound earthworks erected for an extended period of more than 5 ...
associated great mystical value to the serpent, as the Serpent Mound
The Great Serpent Mound is a 1,348-foot-long (411 m), three-foot-high prehistoric effigy mound located in Peebles, Ohio. The mound itself resides on the Serpent Mound crater plateau, running along the Ohio Brush Creek in Adams County, Ohio. ...
demonstrates, though we are unable to unravel the particular associations.
Nordic mythology
Jörmungandr, alternately referred to as the Midgard Serpent or World Serpent, is asea serpent
A sea serpent or sea dragon is a type of dragon sea monster described in various mythologies, most notably Mesopotamian (Tiamat), Judaeo-Christian (Leviathan), Greek (Cetus, Echidna, Hydra, Scylla), and Norse (Jörmungandr).
Mythology and fo ...
of Norse mythology
Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Nordic folklore of the modern period ...
, the middle child of Loki
Loki is a god in Norse mythology. According to some sources, Loki is the son of Fárbauti (a jötunn) and Laufey (mentioned as a goddess), and the brother of Helblindi and Býleistr. Loki is married to Sigyn and they have two sons, Narfi or Na ...
and the giantess Angrboða
Angrboða (Old Norse: ; also Angrboda) is a'' jötunn'' in Norse mythology. She is the mate of Loki and the mother of monsters. She is only mentioned once in the Poetic Edda ('' Völuspá hin skamma)'' as the mother of Fenrir by Loki. The Prose Ed ...
. According to the ''Prose Edda
The ''Prose Edda'', also known as the ''Younger Edda'', ''Snorri's Edda'' ( is, Snorra Edda) or, historically, simply as ''Edda'', is an Old Norse textbook written in Iceland during the early 13th century. The work is often assumed to have been t ...
'', Odin
Odin (; from non, Óðinn, ) is a widely revered Æsir, god in Germanic paganism. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, v ...
took Loki's three children, Fenrisúlfr, Hel and Jörmungandr. He tossed Jörmungandr into the great ocean that encircles Midgard
In Germanic cosmology, Midgard (an anglicised form of Old Norse ; Old English , Old Saxon , Old High German , and Gothic ''Midjun-gards''; "middle yard", "middle enclosure") is the name for Earth (equivalent in meaning to the Greek term , "inhab ...
. The serpent grew so big that he was able to surround the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
and grasp his own tail, and as a result he earned the alternate name of the Midgard Serpent or World Serpent. Jörmungandr's arch enemy is the god Thor
Thor (; from non, Þórr ) is a prominent god in Germanic paganism. In Norse mythology, he is a hammer-wielding æsir, god associated with lightning, thunder, storms, sacred trees and groves in Germanic paganism and mythology, sacred groves ...
.
In the ''Poetic Edda
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems, which is distinct from the ''Prose Edda'' written by Snorri Sturluson. Several versions exist, all primarily of text from the Icelandic me ...
'', Odin tells of eight serpents gnawing on the roots of Yggdrasil
Yggdrasil (from Old Norse ), in Norse cosmology, is an immense and central sacred tree. Around it exists all else, including the Nine Worlds.
Yggdrasil is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'' compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional s ...
: Nidhöggr, Gravvitnir, Moin, Goin, Grábakr, Grafvölluðr, Svafnir and Ofnir.
Folklore
In folk and fairy tale traditions all over the world, the serpent and the snake appear as characters in several fairy tales, either a main character in animal fables and magic tales ('' Märchen''), or as thedonor
A donor in general is a person, organization or government which donates something voluntarily. The term is usually used to represent a form of pure altruism, but is sometimes used when the payment for a service is recognized by all parties as rep ...
who grants the protagonist a special ability or impart him with some secret knowledge.
According to the Aarne-Thompson-Uther Index, the serpent can appear in this capacity in the following tale types:
*Aarne-Thompson-Uther Index tale type ATU 155, "The Ungrateful Animal (Serpent) Returned to Captivity": a farmer rescues an animal (snake) from a trap ( pit). Now free, the animal wants to eat (bite) its saviour, who tries to delay this fate. He consults with other creatures and finally to a trickster animal (fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelve sp ...
or jackal
Jackals are medium-sized canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed ...
). The trickster animal feigns innocence and wants to understand the origin of the problem, so the ungrateful animal goes back to the pit to demonstrate. The farmer leaves the animal trapped again. Example: ''The Tiger, the Brahmin and the Jackal The Tiger, the Brahmin and the Jackal is a popular Indian folklore with a long history and many variants. The earliest record of the folklore was included in the Panchatantra, which dates the story between 200 BCE and 300 CE.
Mary Frere included a ...
'', Indian fable.
*Aarne-Thompson-Uther Index tale type ATU 411, "The King and the Lamia
LaMia Corporation S.R.L., operating as LaMia (short for ''Línea Aérea Mérida Internacional de Aviación''), was a Bolivian charter airline headquartered in Santa Cruz de la Sierra, as an EcoJet subsidiary. It had its origins from the failed ...
(The Snake
Snakes are elongated, Limbless vertebrate, limbless, carnivore, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales. Ma ...
-Wife)": a man takes to wife a woman of mysterious background. A holy person (hermit, cleric, monk) sees through the deception and reveals the woman's true nature as a serpent. This type would include ''Legend of the White Snake
The Legend of the White Snake is a Chinese legend. It has since been presented in a number of major Chinese operas, films, and television series.
The earliest attempt to fictionalize the story in printed form appears to be ''The White Maiden ...
'' (Chinese legend); '' Mélusine'', a French medieval legend.
*Aarne-Thompson-Uther Index tale type ATU 425, "The Search for the Lost Husband" and ATU 425A, " The Animal Bridegroom": a maiden is betrothed to an animal bridegroom (a snake
Snakes are elongated, Limbless vertebrate, limbless, carnivore, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales. Ma ...
, dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
or serpent, in several variants), who comes at night to the bridal bed in human form. The maiden breaks a taboo and her enchanted husband disappears. She is forced to seek him. Example: ''The Green Serpent
Le Serpentin Vert (translated as ''Green Serpent'' or ''Green Dragon'') is a French fairy tale written by Marie Catherine d'Aulnoy, popular in its day and representative of European folklore, that was published in her book ''New Tales, or Fairie ...
'', French literary fairy tale; ''The Snake Prince
The Snake Prince is an Indian fairy tale, a Punjabi story collected by Major Campbell in Feroshepore. Andrew Lang included it in '' The Olive Fairy Book'' (1907).Lang, Andrew; Philip, Neil. ''A World of fairy tales''. New York: Dial Books, 1994. ...
'', Indian fairy tale; ''The Enchanted Snake
The Enchanted Snake or The Snake is an Italian fairy tale. Giambattista Basile wrote a variant in the ''Pentamerone''. Andrew Lang drew upon this variant,Heidi Anne Heiner,Tales Similar to East of the Sun & West of the Moon for inclusion in ''The ...
'', Italian literary fairy tale; '' The Serpent Prince'', Hungarian folktale.
*Aarne-Thompson-Uther Index tale type ATU 425M, "The Snake as Bridegroom": a girl goes bathing and leaves her clothing by the shore. When she returns, a snake (grass snake
The grass snake (''Natrix natrix''), sometimes called the ringed snake or water snake, is a Eurasian non-venomous colubrid snake. It is often found near water and feeds almost exclusively on amphibians.
Subspecies
Many subspecies are recogniz ...
) hides her clothing and will only return them if the girl agrees to marry it. She promises to marry the snake. Some time later, the grass snake comes to take its bride and bring her to its underwater (or underground
Underground most commonly refers to:
* Subterranea (geography), the regions beneath the surface of the Earth
Underground may also refer to:
Places
* The Underground (Boston), a music club in the Allston neighborhood of Boston
* The Underground ...
) palace. This tale type seems to be restricted to the Baltic geographical area. Example: '' Egle the Queen of Serpents'', a Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
n fairy tale.
*Aarne-Thompson-Uther Index tale type ATU 433B, "King Lindworm": a childless queen gives birth to a boy in snake form. Years later, he wishes to marry, but either devours his brides on their wedding night or cannot find a woman brave enough to accept his serpentine form. The snake prince is disenchanted by a maiden who wears layers of clothing in their nuptial night to mirror his layers of snakeskin
Snakeskin may either refer to the skin of a live snake, the shed skin of a snake after molting, or to a type of leather that is made from the hide of a dead snake. Snakeskin and scales can have varying patterns and color formations, providing prot ...
. Example: ''King Lindworm
King Lindworm or Prince Lindworm (Danish: ''Kong Lindorm'') is a Danish fairy tale published in the 19th century by Danish folklorist Svend Grundtvig.
It is classified in the Aarne–Thompson–Uther Index as tale type ATU 433B, a type that de ...
'', a Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
fairy tale.
*Aarne-Thompson-Uther Index tale type ATU 485, "Borma Jarizhka" or "The City of Babylon": a tsar sends a brave knight to the city of Babylon to retrieve three symbols of royal power (a robe, a crown, a scepter). The city is surrounded by snakes and ruled by a princess with snake-like attributes.
*Aarne-Thompson-Uther Index tale type ATU 560, "The Magic Ring
A magic ring is a mythical, folkloric or fictional piece of jewelry, usually a Ring (jewellery), finger ring, that is purported to have Magic (supernatural), supernatural properties or powers. It appears frequently in fantasy and fairy tales. M ...
": a poor man either buys or rescues four types of animals, a cat, a dog, a mouse and a snake. This snake is the son of the king of serpents. It takes the boy to its father's court to reward him a wish-granting object (usually a magic stone or ring). Example: ''The Enchanted Watch
The Enchanted Watch is a French fairy tale collected by Paul Sébillot (1843–1918). Andrew Lang included it in his '' The Green Fairy Book'' (1892).
Synopsis
A rich man's oldest two sons went out and saw the world for three years apiece, and ...
'', French fairy tale.
*Aarne-Thompson-Uther Index tale type ATU 612, "The Three Snake-Leaves
"The Three Snake-Leaves" (German: ''Die drei Schlangenblätter'') is a German fairy tale collected by the Brothers Grimm, tale number 16. It is Aarne-Thompson type 612, "The Three Snake-Leaves".
Synopsis
Via his valor in battle, a young man wi ...
": a man kills a snake. Its mate brings three magical leaves to resurrect it. This inspires the man to find a similar herb to use on his deceased bride/wife.
*Aarne-Thompson-Uther Index tale type ATU 672, "The Serpent's Crown": a snake takes off its crown to bathe in the lake. The crown is stolen by a human, who discovers the crown can grant special abilities (most often, the knowledge of animal languages).
*Aarne-Thompson-Uther Index tale type ATU 673, "The White Serpent's Flesh": the main character learns the language of animals by eating the flesh of a white serpent. Example: ''The White Snake
"The White Snake" (German: ''Die weiße Schlange'') is a German fairy tale collected by the Brothers Grimm and published in ''Grimm's Fairy Tales'' (KHM 17). It is of Aarne–Thompson type 673, and includes an episode of type 554 ("The Grateful ...
'', German fairy tale by the Brothers Grimm.
Modern symbolism
Modern medicine
Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travellers, thieves, merchants, and orato ...
(the caduceus
The caduceus (☤; ; la, cādūceus, from grc-gre, κηρύκειον "herald's wand, or staff") is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology. The same staff was also ...
) and of Asclepius
Asclepius (; grc-gre, Ἀσκληπιός ''Asklēpiós'' ; la, Aesculapius) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Religion in ancient Greece, Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis (lover of ...
, where a single snake entwined the rough staff. On Hermes' caduceus, the snakes were not merely duplicated for symmetry, they were paired opposites. (This motif is congruent with the phurba
The ''phurba'' (; alternate transliterations: ''phurpa'', ''phurbu'', ''purbha'', or ''phurpu'') or ''kīla'' (Sanskrit Devanagari: कील; IAST: kīla) is a three-sided peg, stake, knife, or nail-like ritual implement traditionally associat ...
.) The wings at the head of the staff identified it as belonging to the winged messenger Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travellers, thieves, merchants, and orato ...
, the Roman Mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
, who was the god of magic, diplomacy and rhetoric
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate parti ...
, of inventions and discoveries, and the protector both of merchants and that allied occupation, to the mythographers' view, of thieves. It is however Hermes' role as psychopomp
Psychopomps (from the Greek word , , literally meaning the 'guide of souls') are supernatural creatures, spirits, entities, angels, demons or deities in many religions whose responsibility is to escort newly deceased souls from Earth to the afte ...
, the escort of newly deceased souls to the afterlife, that explains the origin of the snakes in the caduceus, since this was also the role of the Sumerian entwined serpent god Ningizzida, with whom Hermes has sometimes been equated.
In Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
, as the arcane study of alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, ...
developed, Mercury was understood to be the protector of those arts too and of arcane or occult "Hermetic" information in general. Chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ...
and medicines linked the rod of Hermes with the staff of the healer Asclepius, which was wound with a serpent; it was conflated with Mercury's rod, and the modern medical symbol—which should simply be the rod of Asclepius—often became Mercury's wand of commerce. Another version is used in alchemy where the snake is crucified, known as Nicolas Flamel
Nicolas Flamel (; 1330 – 22 March 1418) was a French scribe and manuscript-seller. After his death, Flamel developed a reputation as an alchemist believed to have created and discovered the philosopher's stone and to have thereby achieved im ...
's caduceus. Art historian Walter J. Friedlander, in ''The Golden Wand of Medicine: A History of the Caduceus Symbol in Medicine'' (1992), collected hundreds of examples of the caduceus and the rod of Asclepius and found that professional associations were just somewhat more likely to use the staff of Asclepius, while commercial organizations in the medical field were more likely to use the caduceus.
Modern political propaganda
Following the Christian context as a symbol for evil, serpents are sometimes featured in politicalpropaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded ...
. They were used to represent Jews in antisemitic propaganda. Snakes were also used to represent the evil side of drugs in such films as ''Narcotic'' and ''Narcotics: Pit of Despair''.
Imperial Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent forma ...
depicted as an evil snake in a WWII propaganda poster
Automobiles
Theautomobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with Wheel, wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, Car seat, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport private transport#Personal transport, pe ...
brands AC Cobra
The AC Cobra, sold in the United States as the Shelby Cobra and AC Shelby Cobra, is a sports car manufactured by British company AC Cars, with a Ford V8 engine. It was produced intermittently in both the United Kingdom and later the United ...
, Ford Mustang Shelby, Zarooq Motors, Dodge Viper
The Dodge Viper is a sports car that was manufactured by Dodge (by SRT for 2013 and 2014), a division of American car manufacturer FCA US LLC from 1992 until 2017, having taken a brief hiatus in 2007 and from 2010 to 2012. Production of the two ...
, and Alpha Romeo all feature snakes on their logo
A logo (abbreviation of logotype; ) is a graphic mark, emblem, or symbol used to aid and promote public identification and recognition. It may be of an abstract or figurative design or include the text of the name it represents as in a wordma ...
s.
See also
*Adder stone
An adder stone is a type of stone, usually glassy, with a naturally occurring hole through it. Such stones, which usually consist of flint, have been discovered by archaeologists in both Britain and Egypt. Commonly, they are found in Northern Germ ...
* Ethnoherpetology
* Glycon
Glycon ( grc, Γλύκων ''Glýkōn'', : ''Glýkōnos''), also spelled Glykon, was an ancient snake god. He had a large and influential cult within the Roman Empire in the 2nd century, with contemporary satirist Lucian providing the primary ...
* Legend of the White Snake
The Legend of the White Snake is a Chinese legend. It has since been presented in a number of major Chinese operas, films, and television series.
The earliest attempt to fictionalize the story in printed form appears to be ''The White Maiden ...
* Nehushtan
In the biblical Books of Kings ( 2 Kings 18:4; written c. 550 BC), the Nehushtan (Hebrew: ''Nəḥuštān'' ) is the name given to the bronze image of a serpent on a pole. The image is described in the Book of Numbers, where Yahweh instructed M ...
* Serpent Column
The Serpent Column ( grc, Τρικάρηνος Ὄφις ''Τrikarenos Οphis'' "Three-headed Serpent";, i.e. "the bronze three-headed serpent"; see
See also , . tr, Yılanlı Sütun "Serpentine Column"), also known as the Serpentine Column, ...
* Snake (zodiac)
The snake ( 蛇) is the sixth of the twelve-year cycle of animals which appear in the Chinese zodiac related to the Chinese calendar. The Year of the Snake is associated with the Earthly Branch symbol 巳.
According to one legend, there is a ...
* Snakes in Chinese mythology
Snakes (also known as serpents) are an important motif in Chinese mythology. There are various myths, legends, and folk tales about snakes. Chinese mythology refers to these and other myths found in the historical geographic area(s) of China. The ...
References
Citations
Sources
* Burston, Daniel: 1994, "Freud, the Serpent & The Sexual Enlightenment of Children", International Forum of Psychoanalysis, vol. 3, pp. 205–219. *Joseph Campbell
Joseph John Campbell (March 26, 1904 – October 30, 1987) was an American writer. He was a professor of literature at Sarah Lawrence College who worked in comparative mythology and comparative religion. His work covers many aspects of the ...
, ''Occidental Mythology: the Masks of God'', 1964: Ch. 1, "The Serpent's Bride."
* John Bathurst Deane''The Worship of the Serpent''
London : J. G. & F. Rivington, 1833.
alternative copy online at the Internet Archive
*
David P. Chandler
David Porter Chandler (born 1933) is an American historian and academic who is regarded as one of the foremost western scholars of Cambodia's modern history.Joseph Eddy Fontenrose
Joseph Eddy Fontenrose (17 June 1903, Sutter Creek – July 1986, Ashland, Oregon) was an American classical scholar. He was centrally interested in Greek religion and Greek mythology; he was also an expert on John Steinbeck, commenting on the ...
, ''Python; a Study of Delphic Myth and Its Origins'', 1959.
* Jane Ellen Harrison
Jane Ellen Harrison (9 September 1850 – 15 April 1928) was a British classics, classical scholar and linguistics, linguist. Harrison is one of the founders, with Karl Kerenyi and Walter Burkert, of modern studies in Ancient Greek religio ...
, ''Themis: A Study of the Social Origins of Greek Religion'', 1912. cf. Chapter IX, p. 329 especially, on the slaying of the Python.
**
**
*
*
*
* Balaji Mundkur, ''The Cult of the Serpent: An Interdisciplinary Survey of Its Manifestations and Origins'', Albany: State University Press 1983.
* Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is wide ...
, The Cask of Amontillado
"The Cask of Amontillado" (sometimes spelled "The Casque of Amontillado" ) is a short story by American writer Edgar Allan Poe, first published in the November 1846 issue of ''Godey's Lady's Book''. The story, set in an unnamed Italy, Italian cit ...
, available in aonline version
at literature.org. *
Carl A. P. Ruck
Carl A. P. Ruck (born December 8, 1935, Bridgeport, Connecticut), is a professor in the Classical Studies department at Boston University. He received his B.A. at Yale University, his M.A. at the University of Michigan, and a Ph.D. at Harvard Uni ...
, Blaise Daniel Staples & Clark Heinrich, ''The Apples of Apollo: Pagan and Christian Mysteries of the Eucharist'', 2001.
Further reading
* Behr-Glinka, Andrei I. "Змея как сексуальный и брачный партнер человека. (Еще раз о семантике образа змеи в фольклорной традиции европейских народов)" erpent as a Bride and an Intimate Partner of a Man. Once more about the semantics of serpent in European folk-lore In: ''Культурные взаимодействия. Динамика и смыслы''. Издательский дом Stratum, Университет «Высшая антропологическая школа», 2016. pp. 435–575. * Glinka, Lukasz Andrzej (2014). ''Aryan Unconscious: Archetype of Discrimination, History & Politics,'' Great Abington, UK: Cambridge International Science Publishing.ISBN
The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier that is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.
An ISBN is assigned to each separate edition and ...
978-1-907343-59-9.
*An overview othe most common symbols in snake dreams
External links
* * * {{Reptiles in culture Comparative mythology Greek legendary creatures Snakes Snakes in art Snakes in popular culture Symbolism ATU 150-199 ATU 400-459 ATU 460-499 ATU 560-649 ATU 650-699