synthetic hormones on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A hormone (from the
A hormone (from the
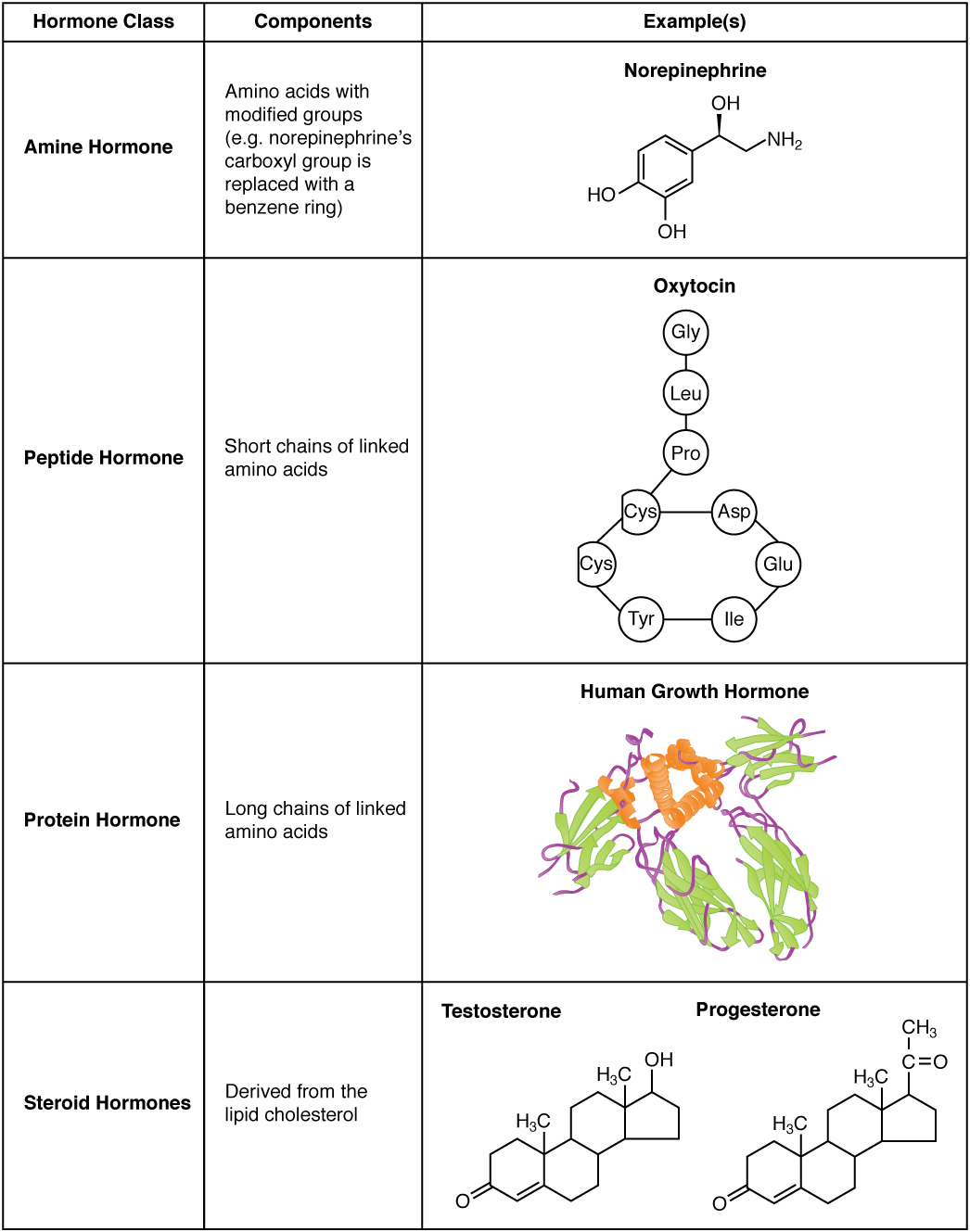
 Most hormones initiate a cellular response by initially binding to either
Most hormones initiate a cellular response by initially binding to either
 Hormone secretion can be stimulated and inhibited by:
* Other hormones (''stimulating''- or ''releasing'' -hormones)
* Plasma concentrations of ions or nutrients, as well as binding
Hormone secretion can be stimulated and inhibited by:
* Other hormones (''stimulating''- or ''releasing'' -hormones)
* Plasma concentrations of ions or nutrients, as well as binding
 The formation of a complex with a binding protein has several benefits: the effective half-life of the bound hormone is increased, and a reservoir of bound hormones is created, which evens the variations in concentration of unbound hormones (bound hormones will replace the unbound hormones when these are eliminated). An example of the usage of hormone-binding proteins is in the thyroxine-binding protein which carries up to 80% of all thyroxine in the body, a crucial element in regulating the metabolic rate.
The formation of a complex with a binding protein has several benefits: the effective half-life of the bound hormone is increased, and a reservoir of bound hormones is created, which evens the variations in concentration of unbound hormones (bound hormones will replace the unbound hormones when these are eliminated). An example of the usage of hormone-binding proteins is in the thyroxine-binding protein which carries up to 80% of all thyroxine in the body, a crucial element in regulating the metabolic rate.
HMRbase: A database of hormones and their receptors
* * {{Authority control * Physiology Endocrinology Cell signaling Signal transduction Human female endocrine system
 A hormone (from the
A hormone (from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) is the process by which a cell interacts with itself, other cells, and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in both prokaryotes and eukary ...
in multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
s that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ syst ...
and behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions of Individual, individuals, organisms, systems or Artificial intelligence, artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or or ...
. Hormones are required for the normal development of animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s, plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoid
Eicosanoids are lipid signaling, signaling molecules made by the enzymatic or non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid or other polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are, similar to arachidonic acid, around 20 carbon units in length. Eicosa ...
s (e.g. prostaglandin
Prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiology, physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids that have diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every Tissue (biology), tissue in humans and ot ...
s and thromboxane
Thromboxane is a member of the family of lipids known as eicosanoids. The two major thromboxanes are thromboxane A2 and thromboxane B2. The distinguishing feature of thromboxanes is a 6-membered ether-containing ring.
Thromboxane is named for ...
s), steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
s (e.g. oestrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three m ...
and brassinosteroid
Brassinosteroids (BRs or less commonly BS) are a class of polyhydroxysteroids that have been recognized as a sixth class of
plant hormones and may have utility as anticancer drugs for treating endocrine-responsive cancers by inducing apoptosis of ...
), amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
derivatives (e.g. epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
and auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essent ...
), protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
or peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty am ...
s (e.g. insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
and CLE peptide CLE peptides (CLAVATA3/Embryo Surrounding Region-Related) are a group of peptides found in plants that are involved with cell signaling. Production is controlled by the CLE genes. Upon binding to a CLE peptide receptor in another cell, a chain react ...
s), and gas
Gas is a state of matter that has neither a fixed volume nor a fixed shape and is a compressible fluid. A ''pure gas'' is made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon) or molecules of either a single type of atom ( elements such as ...
es (e.g. ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon–carbon bond, carbon–carbon doub ...
and nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes den ...
).
Hormones are used to communicate between organs
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to a ...
and tissues. In vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s, hormones are responsible for regulating a wide range of processes including both physiological
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ syst ...
processes and behavioral
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions of individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well as the inanimate p ...
activities such as digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food compounds into small water-soluble components so that they can be absorbed into the blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into th ...
, metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
, respiration, sensory perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous syste ...
, sleep
Sleep is a state of reduced mental and physical activity in which consciousness is altered and certain Sensory nervous system, sensory activity is inhibited. During sleep, there is a marked decrease in muscle activity and interactions with th ...
, excretion
Excretion is elimination of metabolic waste, which is an essential process in all organisms. In vertebrates, this is primarily carried out by the lungs, Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys, and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substa ...
, lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process ...
, stress induction, growth and development, movement, reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual ...
, and mood manipulation. In plants, hormones modulate almost all aspects of development, from germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ...
to senescence
Senescence () or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of Function (biology), functional characteristics in living organisms. Whole organism senescence involves an increase in mortality rate, death rates or a decrease in fecundity with ...
.
Hormones affect distant cells by binding to specific receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ...
proteins in the target cell, resulting in a change in cell function. When a hormone binds to the receptor, it results in the activation of a signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), rece ...
pathway that typically activates gene transcription, resulting in increased expression of target protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s. Hormones can also act in non-genomic pathways that synergize with genomic effects. Water-soluble hormones (such as peptides and amines) generally act on the surface of target cells via second messengers
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form of cell signaling, encompassing both first m ...
. Lipid soluble hormones, (such as steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
s) generally pass through the plasma membranes of target cells (both cytoplasmic
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and ...
and nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
* Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
) to act within their nuclei. Brassinosteroids, a type of polyhydroxysteroids, are a sixth class of plant hormones and may be useful as an anticancer drug for endocrine-responsive tumors to cause apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
and limit plant growth. Despite being lipid soluble, they nevertheless attach to their receptor at the cell surface.
In vertebrates, endocrine gland
The endocrine system is a network of glands and organs located throughout the body. Along with the nervous system, it makes the neuroendocrine system, which controls and regulates many of the body's functions. Endocrine glands are ductless gland ...
s are specialized organs that secrete hormones into the endocrine signaling system. Hormone secretion occurs in response to specific biochemical signals and is often subject to negative feedback regulation. For instance, high blood sugar
The blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, blood glucose level, or glycemia is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis.
For a 70 kg (1 ...
(serum glucose concentration) promotes insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
synthesis. Insulin then acts to reduce glucose levels and maintain homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning fo ...
, leading to reduced insulin levels. Upon secretion, water-soluble hormones are readily transported through the circulatory system. Lipid-soluble hormones must bond to carrier plasma glycoproteins (e.g., thyroxine-binding globulin
Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) is a globulin protein encoded by the ''SERPINA7'' gene in humans. TBG binds thyroid hormones in circulation. It is one of three transport proteins (along with transthyretin and serum albumin) responsible for ...
(TBG)) to form ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's el ...
-protein complexes. Some hormones, such as insulin and growth hormones, can be released into the bloodstream already fully active. Other hormones, called prohormones, must be activated in certain cells through a series of steps that are usually tightly controlled. The endocrine system
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant Organ (biology), organs. In vertebrat ...
secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart an ...
, typically via fenestrated capillaries, whereas the exocrine system
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of ...
secretes its hormones indirectly using ducts. Hormones with paracrine
In cellular biology, paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication (biology), cellular communication in which a Cell (biology), cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of ...
function diffuse through the interstitial space
An interstitial space is an intermediate space located between regular-use floors, commonly located in Hospital, hospitals and laboratory-type buildings to allow space for the mechanical systems of the building. By providing this space, laborator ...
s to nearby target tissue.
Plants lack specialized organs for the secretion of hormones, although there is spatial distribution of hormone production. For example, the hormone auxin is produced mainly at the tips of young leaves
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, ...
and in the shoot apical meristem. The lack of specialised glands means that the main site of hormone production can change throughout the life of a plant, and the site of production is dependent on the plant's age and environment.
Introduction and overview
Hormone producing cells are found in the endocrine glands, such as thethyroid gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
, ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
, and testes
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
. Hormonal signaling involves the following steps:
# Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthe ...
of a particular hormone in a particular tissue.
# Storage and secretion
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mec ...
of the hormone.
# Transport of the hormone to the target cell(s).
# Recognition of the hormone by an associated cell membrane or intracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ...
protein.
# Relay and amplification of the received hormonal signal via a signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), rece ...
process: This then leads to a cellular response. The reaction of the target cells may then be recognized by the original hormone-producing cells, leading to a downregulation
In biochemistry, in the biology, biological context of organisms' regulation of gene expression and production of gene products, downregulation is the process by which a cell (biology), cell decreases the production and quantities of its cellular ...
in hormone production. This is an example of a homeostatic negative feedback loop.
# Breakdown of the hormone.
Exocytosis
Exocytosis is a term for the active transport process that transports large molecules from cell to the extracellular area. Hormones, proteins and neurotransmitters are examples of large molecules that can be transported out of the cell. Exocytosis ...
and other methods of membrane transport are used to secrete hormones when the endocrine glands are signaled. The hierarchical model is an oversimplification
The fallacy of the single cause, also known as complex cause, causal oversimplification, causal reductionism, root cause fallacy, and reduction fallacy, is an informal fallacy of questionable cause that occurs when it is assumed that there is a si ...
of the hormonal signaling process. Cellular recipients of a particular hormonal signal may be one of several cell types that reside within a number of different tissues, as is the case for insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
, which triggers a diverse range of systemic physiological effects. Different tissue types may also respond differently to the same hormonal signal.
Discovery
Arnold Adolph Berthold (1849)
Arnold Adolph Berthold was a Germanphysiologist
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out chemical and ...
and zoologist
Zoology ( , ) is the scientific study of animals. Its studies include the structure, embryology, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. Zoology is one ...
, who, in 1849, had a question about the function of the testes
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
. He noticed in castrated roosters that they did not have the same sexual behaviors as rooster
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated subspecies of the red junglefowl (''Gallus gallus''), originally native to Southeast Asia. It was first domesticated around 8,000 years ago and is now one of the most common and w ...
s with their testes intact. He decided to run an experiment on male roosters to examine this phenomenon. He kept a group of roosters with their testes intact, and saw that they had normal sized wattles and combs (secondary sexual organs), a normal crow, and normal sexual and aggressive behaviors. He also had a group with their testes surgically removed, and noticed that their secondary sexual organs were decreased in size, had a weak crow, did not have sexual attraction towards females, and were not aggressive. He realized that this organ was essential for these behaviors, but he did not know how. To test this further, he removed one testis and placed it in the abdominal cavity. The roosters acted and had normal physical anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ...
. He was able to see that location of the testes does not matter. He then wanted to see if it was a genetic factor that was involved in the testes that provided these functions. He transplanted a testis from another rooster to a rooster with one testis removed, and saw that they had normal behavior and physical anatomy as well. Berthold determined that the location or genetic factors of the testes do not matter in relation to sexual organs and behaviors, but that some chemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
in the testes being secreted is causing this phenomenon. It was later identified that this factor was the hormone testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
.
Charles and Francis Darwin (1880)
Although known primarily for his work on theTheory of Evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certai ...
, Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
was also keenly interested in plants. Through the 1870s, he and his son Francis
Francis may refer to:
People and characters
*Pope Francis, head of the Catholic Church (2013–2025)
*Francis (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Francis (surname)
* Francis, a character played by YouTuber Boogie2 ...
studied the movement of plants towards light. They were able to show that light is perceived at the tip of a young stem (the coleoptile
Coleoptile is the pointed protective sheath covering the emerging shoot in monocotyledons such as grasses in which few leaf primordia and shoot apex of monocot embryo remain enclosed. The coleoptile protects the first leaf as well as the growing ...
), whereas the bending occurs lower down the stem. They proposed that a 'transmissible substance' communicated the direction of light from the tip down to the stem. The idea of a 'transmissible substance' was initially dismissed by other plant biologists, but their work later led to the discovery of the first plant hormone. In the 1920s Dutch scientist Frits Warmolt Went and Russian scientist Nikolai Cholodny (working independently of each other) conclusively showed that asymmetric accumulation of a growth hormone was responsible for this bending. In 1933 this hormone was finally isolated by Kögl, Haagen-Smit and Erxleben and given the name 'auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essent ...
'.
Oliver and Schäfer (1894)
British physician George Oliver and physiologist Edward Albert Schäfer, professor at University College London, collaborated on the physiological effects of adrenal extracts. They first published their findings in two reports in 1894, a full publication followed in 1895. Though frequently falsely attributed tosecretin Secretin is a hormone that regulates water homeostasis throughout the body and influences the environment of the duodenum by regulating secretions in the stomach, pancreas, and liver. It is a peptide hormone produced in the S cells of the duodenum ...
, found in 1902 by Bayliss and Starling, Oliver and Schäfer's adrenal extract containing adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
, the substance causing the physiological changes, was the first hormone to be discovered. The term hormone would later be coined by Starling.
Bayliss and Starling (1902)
William Bayliss
Sir William Maddock Bayliss (2 May 1860 – 27 August 1924) was an English physiologist.
Life
He was born in Wednesbury, Staffordshire but shortly thereafter his father, a successful merchant of ornamental ironwork, moved his family to a ...
and Ernest Starling
Ernest Henry Starling (17 April 1866 – 2 May 1927) was a British physiologist who contributed many fundamental ideas to this subject. These ideas were important parts of the British contribution to physiology, which at that time led the world. ...
, a physiologist
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out chemical and ...
and biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual Cell (biology), cell, a multicellular organism, or a Community (ecology), community of Biological inter ...
, respectively, wanted to see if the nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. Th ...
had an impact on the digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
. They knew that the pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
was involved in the secretion of digestive fluids after the passage of food from the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
to the intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
, which they believed to be due to the nervous system. They cut the nerves to the pancreas in an animal model and discovered that it was not nerve impulses that controlled secretion from the pancreas. It was determined that a factor secreted from the intestines into the bloodstream
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart an ...
was stimulating the pancreas to secrete digestive fluids. This was named secretin Secretin is a hormone that regulates water homeostasis throughout the body and influences the environment of the duodenum by regulating secretions in the stomach, pancreas, and liver. It is a peptide hormone produced in the S cells of the duodenum ...
: a hormone.
Types of signaling
Hormonal effects are dependent on where they are released, as they can be released in different manners. Not all hormones are released from a cell and into the blood until it binds to a receptor on a target. The major types of hormone signaling are:Chemical classes
As hormones are defined functionally, not structurally, they may have diverse chemical structures. Hormones occur inmulticellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
s (plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s, animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s, fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
, brown algae
Brown algae (: alga) are a large group of multicellular algae comprising the class (biology), class Phaeophyceae. They include many seaweeds located in colder waters of the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate ...
, and red algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), make up one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta comprises one of the largest Phylum, phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 recognized species within over 900 Genus, genera amidst ongoing taxon ...
). These compounds occur also in unicellular organism
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and ...
s, and may act as signaling molecule
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) is the Biological process, process by which a Cell (biology), cell interacts with itself, other cells, and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all Cell (biol ...
s however there is no agreement that these molecules can be called hormones.
Vertebrates

Invertebrates
Compared with vertebrates,insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s and crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s possess a number of structurally unusual hormones such as the juvenile hormone
Juvenile hormones (JHs) are a group of acyclic sesquiterpenoids that regulate many aspects of insect physiology. The first discovery of a JH was by Vincent Wigglesworth. JHs regulate development, reproduction, diapause, and polyphenisms.
In ...
, a sesquiterpenoid
Sesquiterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of three isoprene units and often have the molecular formula C15H24. Like monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes may be cyclic or contain rings, including many combinations. Biochemical modifications such ...
.
Plants
Examples includeabscisic acid
Abscisic acid (ABA or abscisin II) is a plant hormone. ABA functions in many plant developmental processes, including seed and bud dormancy, the control of organ size and stomatal closure. It is especially important for plants in the response to ...
, auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essent ...
, cytokinin
Cytokinins (CK) are a class of plant hormones that promote cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots and shoots. They are involved primarily in Cell (biology), cell growth and cellular differentiation, differentiation, but also affect apical ...
, ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon–carbon bond, carbon–carbon doub ...
, and gibberellin
Gibberellins (GAs) are plant hormones that regulate various Biological process, developmental processes, including Plant stem, stem elongation, germination, dormancy, flowering, flower development, and leaf and fruit senescence. They are one of th ...
.
Receptors
cell surface receptor
Cell surface receptors (membrane receptors, transmembrane receptors) are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving (binding to) extracellular molecules. They are specialized integra ...
s or intracellular receptor
Intracellular receptors are globular protein receptors located inside the cell rather than on its cell membrane. The word ''intracellular'' means "within or inside a cell." Molecules that cross a cell membrane to bind with a receptor are general ...
s. A cell may have several different receptors that recognize the same hormone but activate different signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), rece ...
pathways, or a cell may have several different receptors that recognize different hormones and activate the same biochemical pathway.
Receptors for most peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty am ...
as well as many eicosanoid
Eicosanoids are lipid signaling, signaling molecules made by the enzymatic or non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid or other polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are, similar to arachidonic acid, around 20 carbon units in length. Eicosa ...
hormones are embedded in the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
as cell surface receptors, and the majority of these belong to the G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related ...
(GPCR) class of seven alpha helix
An alpha helix (or α-helix) is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil (a helix).
The alpha helix is the most common structural arrangement in the Protein secondary structure, secondary structure of proteins. It is al ...
transmembrane
A transmembrane protein is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently u ...
proteins. The interaction of hormone and receptor typically triggers a cascade of secondary effects within the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
of the cell, described as signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), rece ...
, often involving phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
or dephosphorylation of various other cytoplasmic proteins, changes in ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by Gating (electrophysiol ...
permeability, or increased concentrations of intracellular molecules that may act as secondary messengers (e.g., cyclic AMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triph ...
). Some protein hormones also interact with intracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
receptors located in the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
or nucleus by an intracrine
Intracrine signaling is a mode of hormone and growth factor action in which signaling molecules exert their effects within the same cell that produces them, without being secreted into the extracellular environment. The term intracrine was origin ...
mechanism.
For steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
or thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
hormones, their receptors are located inside the cell within the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
of the target cell. These receptors belong to the nuclear receptor
In the field of molecular biology, nuclear receptors are a class of proteins responsible for sensing steroids, thyroid hormones, vitamins, and certain other molecules. These intracellular receptors work with other proteins to regulate the ex ...
family of ligand-activated transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
s. To bind their receptors, these hormones must first cross the cell membrane. They can do so because they are lipid-soluble. The combined hormone-receptor complex
Complex commonly refers to:
* Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe
** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each ...
then moves across the nuclear membrane into the nucleus of the cell, where it binds to specific DNA sequences
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of bases within the nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. This succession is denoted by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of the ...
, regulating the expression of certain genes
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
, and thereby increasing the levels of the proteins encoded by these genes. However, it has been shown that not all steroid receptors are located inside the cell. Some are associated with the plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
.
Effects in humans
Hormones have the following effects on the body: * stimulation or inhibition of growth * wake-sleep cycle and othercircadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the env ...
s
* mood swing
A mood swing is an extreme or sudden change of mood. Such changes can play a positive or a disruptive part in promoting problem solving and in producing flexible forward planning. When mood swings are severe, they may be categorized as part ...
s
* induction or suppression of apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
(programmed cell death)
* activation or inhibition of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
* regulation of metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
* preparation of the body for mating
In biology, mating is the pairing of either opposite-sex or hermaphroditic organisms for the purposes of sexual reproduction. ''Fertilization'' is the fusion of two gametes. '' Copulation'' is the union of the sex organs of two sexually repr ...
, fighting, fleeing, and other activity
* preparation of the body for a new phase of life, such as puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
, parenting
Parenting or child rearing promotes and supports the physical, cognitive, social, emotional, and educational development from infancy to adulthood. Parenting refers to the intricacies of raising a child and not exclusively for a biologica ...
, and menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when Menstruation, menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of the Human reproduction, reproductive stage for the female human. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 5 ...
* control of the reproductive cycle
* hunger cravings
A hormone may also regulate the production and release of other hormones. Hormone signals control the internal environment of the body through homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning fo ...
.
Regulation
The rate of hormone biosynthesis and secretion is often regulated by a homeostaticnegative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused ...
control mechanism. Such a mechanism depends on factors that influence the metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
and excretion
Excretion is elimination of metabolic waste, which is an essential process in all organisms. In vertebrates, this is primarily carried out by the lungs, Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys, and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substa ...
of hormones. Thus, higher hormone concentration alone cannot trigger the negative feedback mechanism. Negative feedback must be triggered by overproduction of an "effect" of the hormone.
 Hormone secretion can be stimulated and inhibited by:
* Other hormones (''stimulating''- or ''releasing'' -hormones)
* Plasma concentrations of ions or nutrients, as well as binding
Hormone secretion can be stimulated and inhibited by:
* Other hormones (''stimulating''- or ''releasing'' -hormones)
* Plasma concentrations of ions or nutrients, as well as binding globulin
The globulins are a family of globular proteins that have higher molecular weights than albumins and are insoluble in pure water but dissolve in dilute salt solutions. Some globulins are produced in the liver, while others are made by the immune ...
s
* Neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s and mental activity
* Environmental changes, e.g., of light or temperature
One special group of hormones is the tropic hormones that stimulate the hormone production of other endocrine glands. For example, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) causes growth and increased activity of another endocrine gland, the thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
, which increases output of thyroid hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine, T3 and T4
rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone
rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus
r ...
s.
To release active hormones quickly into the circulation, hormone biosynthetic cells may produce and store biologically inactive hormones in the form of pre- or prohormones. These can then be quickly converted into their active hormone form in response to a particular stimulus.
Eicosanoid
Eicosanoids are lipid signaling, signaling molecules made by the enzymatic or non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid or other polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are, similar to arachidonic acid, around 20 carbon units in length. Eicosa ...
s are considered to act as local hormones. They are considered to be "local" because they possess specific effects on target cells close to their site of formation. They also have a rapid degradation cycle, making sure they do not reach distant sites within the body.
Hormones are also regulated by receptor agonists. Hormones are ligands, which are any kinds of molecules that produce a signal by binding to a receptor site on a protein. Hormone effects can be inhibited, thus regulated, by competing ligands that bind to the same target receptor as the hormone in question. When a competing ligand is bound to the receptor site, the hormone is unable to bind to that site and is unable to elicit a response from the target cell. These competing ligands are called antagonists of the hormone.
Therapeutic use
Many hormones and theirstructural
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
and functional analogs are used as medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmaco ...
. The most commonly prescribed hormones are estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
s and progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestins, progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestoge ...
s (as methods of hormonal contraception
Hormonal contraception refers to birth control methods that act on the endocrine system. Almost all methods are composed of steroid hormones, although in India one selective estrogen receptor modulator is marketed as a contraceptive. The original ...
and as HRT), thyroxine
Thyroxine, also known as T4, is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It is the primary form of thyroid hormone found in the blood and acts as a prohormone of the more active thyroid hormone, triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroxine and its acti ...
(as levothyroxine, for hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, co ...
) and steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
s (for autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
s and several respiratory disorders). Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
is used by many diabetics. Local preparations for use in otolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the surgical an ...
often contain pharmacologic equivalents of adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
, while steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
and vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
creams are used extensively in dermatological practice.
A "pharmacologic dose" or "supraphysiological dose" of a hormone is a medical usage referring to an amount of a hormone far greater than naturally occurs in a healthy body. The effects of pharmacologic doses of hormones may be different from responses to naturally occurring amounts and may be therapeutically useful, though not without potentially adverse side effects. An example is the ability of pharmacologic doses of glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
s to suppress inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
.
Hormone-behavior interactions
At the neurological level, behavior can be inferred based on hormone concentration, which in turn are influenced by hormone-release patterns; the numbers and locations of hormone receptors; and the efficiency of hormone receptors for those involved in gene transcription. Hormone concentration does not incite behavior, as that would undermine other external stimuli; however, it influences the system by increasing the probability of a certain event to occur. Not only can hormones influence behavior, but also behavior and the environment can influence hormone concentration. Thus, a feedback loop is formed, meaning behavior can affect hormone concentration, which in turn can affect behavior, which in turn can affect hormone concentration, and so on. For example, hormone-behavior feedback loops are essential in providing constancy to episodic hormone secretion, as the behaviors affected by episodically secreted hormones directly prevent the continuous release of sad hormones. Three broad stages of reasoning may be used to determine if a specific hormone-behavior interaction is present within a system: * The frequency of occurrence of a hormonally dependent behavior should correspond to that of its hormonal source. * A hormonally dependent behavior is not expected if the hormonal source (or its types of action) is non-existent. * The reintroduction of a missing behaviorally dependent hormonal source (or its types of action) is expected to bring back the absent behavior.Comparison with neurotransmitters
Though colloquially oftentimes used interchangeably, there are various clear distinctions between hormones andneurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
s:
* A hormone can perform functions over a larger spatial and temporal scale than can a neurotransmitter, which often acts in micrometer-scale distances.
* Hormonal signals can travel virtually anywhere in the circulatory system, whereas neural signals are restricted to pre-existing nerve tract
A nerve tract is a bundle of nerve fibers (axons) connecting Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei of the central nervous system. In the peripheral nervous system, this is known as a nerve fascicle, and has associated nervous tissue, connective tissue. T ...
s.
* Assuming the travel distance is equivalent, neural signals can be transmitted much more quickly (in the range of milliseconds) than can hormonal signals (in the range of seconds, minutes, or hours). Neural signals can be sent at speeds up to 100 meters per second.
* Neural signalling is an all-or-nothing (digital) action, whereas hormonal signalling is an action that can be continuously variable as it is dependent upon hormone concentration.
Neurohormones are a type of hormone that share a commonality with neurotransmitters. They are produced by endocrine cells that receive input from neurons, or neuroendocrine cells. Both classic hormones and neurohormones are secreted by endocrine tissue; however, neurohormones are the result of a combination between endocrine reflexes and neural reflexes, creating a neuroendocrine pathway. While endocrine pathways produce chemical signals in the form of hormones, the neuroendocrine pathway involves the electrical signals of neurons. In this pathway, the result of the electrical signal produced by a neuron is the release of a chemical, which is the neurohormone. Finally, like a classic hormone, the neurohormone is released into the bloodstream to reach its target.
Binding proteins
Hormone transport and the involvement of binding proteins is an essential aspect when considering the function of hormones.See also
*Autocrine signaling
Autocrine signaling is a form of cell signaling in which a cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger (called the autocrine agent) that binds to autocrine receptors on that same cell, leading to changes in the cell. This can be contrasted with ...
* Adipokine
* Cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
* Hepatokine
Hepatokines (Greek ''heapto-'', liver; and ''-kinos'', movement) are proteins produced by liver cells (hepatocytes) that are Secretion, secreted into the Circulatory system, circulation and function as hormones across the organism. Research is most ...
* Endocrine disease
Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology.
Types of disease
Broadly speaking, endocrine disorders may be subdivided into three groups:
# Endocri ...
* Endocrine system
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant Organ (biology), organs. In vertebrat ...
* Endocrinology
Endocrinology (from ''endocrine system, endocrine'' + ''wikt:-logy#Suffix, -ology'') is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the ...
* Environmental hormones
* Growth factor
A growth factor is a naturally occurring substance capable of stimulating cell proliferation, wound healing, and occasionally cellular differentiation. Usually it is a secreted protein or a steroid hormone. Growth factors are important for ...
* Intracrine
Intracrine signaling is a mode of hormone and growth factor action in which signaling molecules exert their effects within the same cell that produces them, without being secreted into the extracellular environment. The term intracrine was origin ...
* List of investigational sex-hormonal agents
This is a list of investigational sex-hormonal agents, or sex-hormonal agents that are currently under development for clinical use but are not yet approved. ''Chemical/generic names are listed first, with developmental code names, synonyms, and ...
* Metabolomics
Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites, the small molecule substrates, intermediates, and products of cell metabolism. Specifically, metabolomics is the "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerpri ...
* Myokine
A myokine is one of several hundred cytokines or other small proteins (~5–20 kDa) and proteoglycan peptides that are produced and released by skeletal muscle cells (muscle fibers) in response to muscular contractions. They have autocrine, para ...
* Neohormone
* Neuroendocrinology
Neuroendocrinology is the branch of biology (specifically of physiology) which studies the interaction between the nervous system and the endocrine system; i.e. how the brain regulates the hormonal activity in the body. The nervous and endocrine ...
* Paracrine signaling
In cellular biology, paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as parac ...
* Plant hormone
Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of Organ (anat ...
s, a.k.a. plant growth regulators
* Semiochemical
A semiochemical, from the Greek wiktionary:σημεῖον, σημεῖον (''semeion''), meaning "signal", is a chemical substance or mixture released by an organism that affects the behaviors of other individuals. Semiochemical communication c ...
* Sex-hormonal agent
* Sexual motivation and hormones
* Xenohormone
* List of human hormones
References
External links
HMRbase: A database of hormones and their receptors
* * {{Authority control * Physiology Endocrinology Cell signaling Signal transduction Human female endocrine system