synchronverter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Synchronverters (also called virtual synchronous generators or virtual synchronous machines) are
Synchronverters (also called virtual synchronous generators or virtual synchronous machines) are
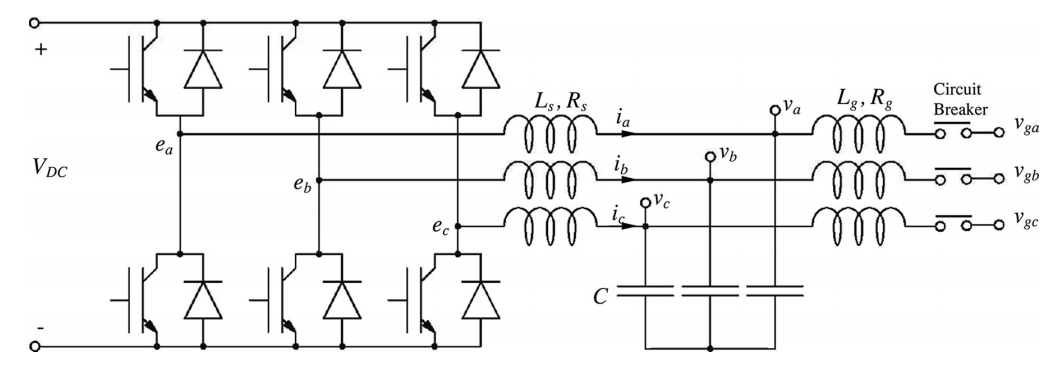
 Synchronverter structure can be divided into two parts: power part (see figure 2) and electronic part. The power part is energy transform and transfer path, including the bridge, filter circuit, power line, etc. The electronic part refers to measuring and control units, including sensors and
Synchronverter structure can be divided into two parts: power part (see figure 2) and electronic part. The power part is energy transform and transfer path, including the bridge, filter circuit, power line, etc. The electronic part refers to measuring and control units, including sensors and
 As shown in the figure 3, when the inverter is controlled as a voltage source, it consists of a synchronization unit to
As shown in the figure 3, when the inverter is controlled as a voltage source, it consists of a synchronization unit to  Since a synchronous generator is inherently synchronized with the grid, it is possible to integrate the synchronization function into the power controller without synchronization unit. This results in a compact control unit, as shown in the figure 4.
Since a synchronous generator is inherently synchronized with the grid, it is possible to integrate the synchronization function into the power controller without synchronization unit. This results in a compact control unit, as shown in the figure 4.
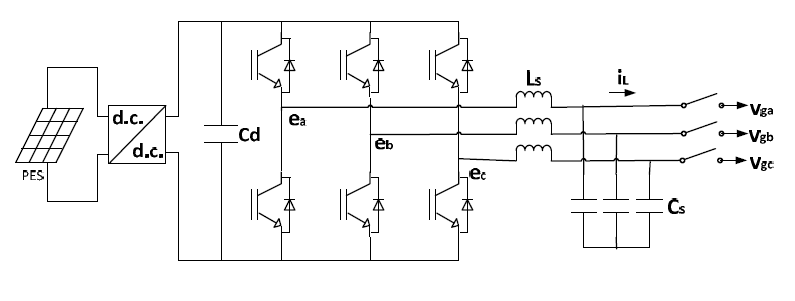 As mentioned before, synchronverters can be treated like synchronous generator, which make it easier to control the source, so it should be widely used in PV primary energy sources (PES).
As mentioned before, synchronverters can be treated like synchronous generator, which make it easier to control the source, so it should be widely used in PV primary energy sources (PES).
 Synchronverters (also called virtual synchronous generators or virtual synchronous machines) are
Synchronverters (also called virtual synchronous generators or virtual synchronous machines) are inverters
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the op ...
which mimic synchronous generators (SG) to provide "synthetic inertia" for ancillary services in electric power systems. Inertia
Inertia is the natural tendency of objects in motion to stay in motion and objects at rest to stay at rest, unless a force causes the velocity to change. It is one of the fundamental principles in classical physics, and described by Isaac Newto ...
is a property of standard synchronous generators associated with the rotating physical mass of the system spinning at a frequency proportional to the electricity being generated. Inertia has implications towards grid stability as work is required to alter the kinetic energy of the spinning physical mass and therefore opposes changes in grid frequency. Inverter-based generation inherently lacks this property as the waveform is being created artificially via power electronics.
Background
Standardinverter
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the op ...
s are very low inertia
Inertia is the natural tendency of objects in motion to stay in motion and objects at rest to stay at rest, unless a force causes the velocity to change. It is one of the fundamental principles in classical physics, and described by Isaac Newto ...
elements. During transient periods, which are mostly because of faults or sudden changes in load, they follow changes rapidly and may cause a worse condition, but synchronous generators have a notable inertia that can maintain their stability.
The grid is designed to operate at a specific frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
. When electric power supply and demand is perfectly balanced the grid frequency will remain at its nominal frequency. However, any imbalance in supply and demand will lead to a deviation from this nominal frequency. It is standard for electricity generation and demand to not be perfectly balanced, but the imbalance is tightly controlled such that the grid frequency remains within a small band of ±0.05Hz. A synchronous generator’s rotating mass acts as a bank of kinetic energy for the grid to counteract changes in frequency – it can either provide or absorb power from the grid – caused by an imbalance of electric power supply and demand – in the form of kinetic energy by speeding up or slowing down. The change in kinetic energy is proportional to the change in frequency. Because it takes work to speed up or slow down rotating mass, this inertia dampens the effects of active power imbalances and therefore stabilizes the frequency. Because inverter-based generation inherently lacks inertia, increasing penetration of inverter-based renewable energy generation could endanger power system
An electric power system is a network of electrical components deployed to supply, transfer, and use electric power. An example of a power system is the electrical grid that provides power to homes and industries within an extended area. The e ...
reliability
Reliability, reliable, or unreliable may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Computing
* Data reliability (disambiguation), a property of some disk arrays in computer storage
* Reliability (computer networking), a category used to des ...
.
Further, the variability of renewable energy sources (RES), primarily concerning photovoltaics (PV) and wind power, could amplify this issue by creating more frequent transient periods of power imbalance. Theoretically, inverter-based generation could be controlled to respond to frequency imbalances by altering its electric torque (active power output). Synthetic inertia is defined as the “controlled contribution of electrical torque from a unit that is proportional to the rate of change of frequency
The utility frequency, (power) line frequency (American English) or mains frequency (British English) is the nominal frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in a wide area synchronous grid transmitted from a power station to t ...
(RoCoF) at the terminals of the unit.” However, in order to have capacity to react to this RoCoF, the participating generators would be required to operate at levels below their maximum output, so that a portion of their output is reserved for this particular response. Further, the inherent variability of production limits the generators' capacity to provide synthetic inertia. This requirement for a reliable and fast-acting power supply makes inverter-based energy storage a better candidate for providing synthetic inertia.
History
Hydro-Québec
Hydro-Québec () is a Canadian Crown corporations of Canada#Quebec, Crown corporation public utility headquartered in Montreal, Quebec. It manages the electricity generation, generation, electric power transmission, transmission and electricity ...
began requiring synthetic inertia in 2005 as the first grid operator. To counter frequency drop, the grid operator demands a temporary 6% power boost by combining the power electronics with the rotational inertia
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular/rotational mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is defined relatively to a rotational axis. It is the ratio between ...
of a wind turbine rotor. Similar requirements came into effect in Europe in 2016, and Australia in 2020.
Synchronverter model

 Synchronverter structure can be divided into two parts: power part (see figure 2) and electronic part. The power part is energy transform and transfer path, including the bridge, filter circuit, power line, etc. The electronic part refers to measuring and control units, including sensors and
Synchronverter structure can be divided into two parts: power part (see figure 2) and electronic part. The power part is energy transform and transfer path, including the bridge, filter circuit, power line, etc. The electronic part refers to measuring and control units, including sensors and digital signal processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit chips. ...
(DSP).
The important point in modeling synchronverter is to be sure that it has similar dynamic behavior to Synchronous generator (see figure 3). This model is classified in increasing order of complexity, from 2-order (i.e. electromechanical model, typically derived from the swing equation) up to 7-order model (i.e. including transient, full rotor and stator dynamics). However, 3-order model is widely used because of proper compromise between accuracy and complexity, which combined the electromechanical model with a voltage dynamics equation for one of the flux linkages (typically the q-axis).
The dq-axes components the terminal voltage satisfy the following differential equations:
where the flux linkage
In electrical engineering, the term flux linkage is used to define the interaction of a multi-turn inductor with the magnetic flux as described by the Faraday's law of induction. Since the contributions of all turns in the coil add up, in the ove ...
s are
with representing the current as a function of time, the stator resistance, the angular velocity of the rotating reference frame, the inductance
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The electric current produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The magnetic field strength depends on the magnitude of the ...
s, represents the flux linkage from the rotor field winding and are the ''rotational emfs'' or ''speed voltages'' internal to the machine due to the
rotation of the rotor (i.e. the dq-transformation of the stator reference frame).
While synchronverter terminal voltage and current satisfy these equations, synchronverter can be looked as Synchronous generator. This make it possible to replace it by a synchronous generator model and solve the problems easily.
Control strategy
 As shown in the figure 3, when the inverter is controlled as a voltage source, it consists of a synchronization unit to
As shown in the figure 3, when the inverter is controlled as a voltage source, it consists of a synchronization unit to synchronize
Synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. For example, the conductor of an orchestra keeps the orchestra synchronized or ''in time''. Systems that operate with all parts in synchrony are said to be synchrono ...
with the grid and a power loop to regulate the real power and reactive power exchanged with the grid. The synchronization unit often needs to provide frequency and amplitude. But when inverter is controlled as a current source, the synchronization unit is often required to provide the phase of the grid only, so it is much easier to control it as a current source.
 Since a synchronous generator is inherently synchronized with the grid, it is possible to integrate the synchronization function into the power controller without synchronization unit. This results in a compact control unit, as shown in the figure 4.
Since a synchronous generator is inherently synchronized with the grid, it is possible to integrate the synchronization function into the power controller without synchronization unit. This results in a compact control unit, as shown in the figure 4.
Applications
PV
 As mentioned before, synchronverters can be treated like synchronous generator, which make it easier to control the source, so it should be widely used in PV primary energy sources (PES).
As mentioned before, synchronverters can be treated like synchronous generator, which make it easier to control the source, so it should be widely used in PV primary energy sources (PES).
HVDC
DC microgrid
Synchronverter also is suggested to be used inmicrogrid
A microgrid is a local electrical grid with defined electrical boundaries, acting as a single and controllable entity. It is able to operate in grid-connected and off-grid modes.
s because DC sources can be coordinated together with the frequency of the ac voltage, without any communication network.
Battery reserve
As demonstrated by theHornsdale Power Reserve
Hornsdale Power Reserve is a 150 MW (194 MWh) grid-connected energy storage system owned by Neoen co-located with the Hornsdale Wind Farm in the Mid North region of South Australia, also owned by Neoen.
The original installation in 2017 was ...
in Australia
See also
* Intelligent hybrid inverterReferences
{{reflist, 2 Power electronics Electric power systems components Inverters