Swabians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Swabians (german: Schwaben, singular ''Schwabe'') are a
 As the national cultural consensus surrounding
As the national cultural consensus surrounding
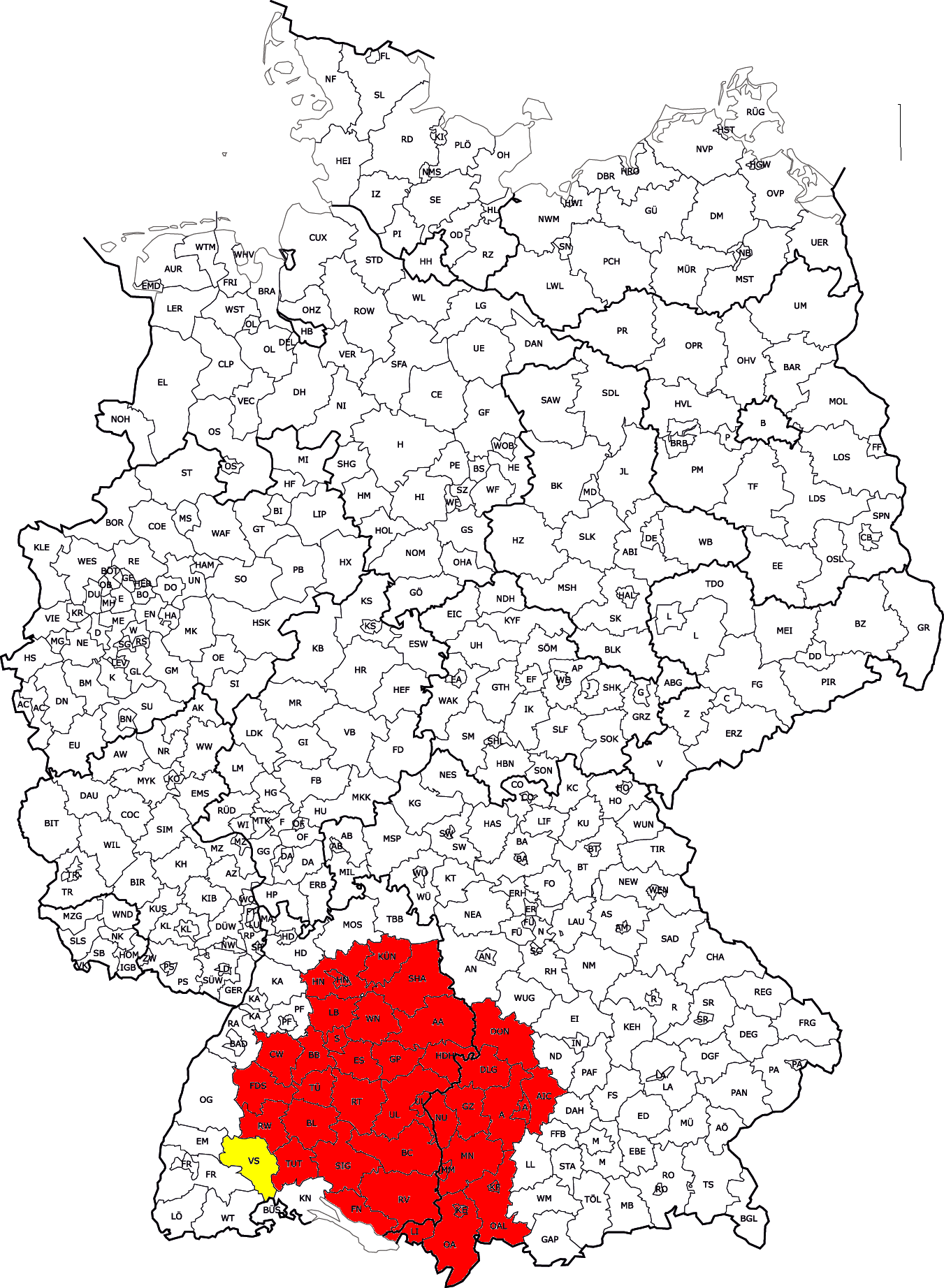 The ethno-linguistic group of Swabians speak Swabian German, a branch of the Alemannic group of
The ethno-linguistic group of Swabians speak Swabian German, a branch of the Alemannic group of
 Significant numbers of Swabians moved to
Significant numbers of Swabians moved to
''Deutsche Unternehmerinnen im 20. Jahrhundert''
München: C.H.Beck. p. 48. . *
Jakob Fugger by Dürer (cropped).jpg,
Germanic people
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
who are native to the ethnocultural and linguistic region of Swabia, which is now mostly divided between the modern states of Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
and Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
, in southwestern Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of Swabia
The Duchy of Swabia ( German: ''Herzogtum Schwaben'') was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity.
While th ...
, one of the German stem duchies, representing the territory of Alemannia, whose inhabitants were interchangeably called '' Alemanni'' or ''Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own name ...
''. This territory would include all of the Alemannic German
Alemannic, or rarely Alemannish (''Alemannisch'', ), is a group of High German dialects. The name derives from the ancient Germanic tribal confederation known as the Alamanni ("all men").
Distribution
Alemannic dialects are spoken by approxi ...
areal, but the modern concept of Swabia is more restricted, due to the collapse of the duchy of Swabia in the 13th century. Swabia as understood in modern ethnography roughly coincides with the Swabian Circle
The Circle of Swabia or Swabian Circle (german: Schwäbischer Reichskreis or ''Schwäbischer Kreis'') was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1500 on the territory of the former German stem-duchy of Swabia. However, it d ...
of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
as it stood during the Early Modern period.
Culture
Swabian culture, as distinct from its Alemannic neighbours, evolved in the later medieval and early modern period. After the disintegration of theDuchy of Swabia
The Duchy of Swabia ( German: ''Herzogtum Schwaben'') was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity.
While th ...
, a Swabian cultural identity and sense of cultural unity survived, expressed in the formation of the Swabian League of Cities
The Swabian League of Cities (German: ''Schwäbischer Städtebund'') was a primarily military alliance between a number of free imperial cities in and around the area now defined as south-western Germany. Its objective was the maintenance of th ...
in the 14th century, the Swabian League
The Swabian League (''Schwäbischer Bund'') was a mutual defence and peace keeping association of Imperial Estates – free Imperial cities, prelates, principalities and knights – principally in the territory of the early medieval stem duchy of ...
of 1488, and the establishment of the Swabian Circle
The Circle of Swabia or Swabian Circle (german: Schwäbischer Reichskreis or ''Schwäbischer Kreis'') was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1500 on the territory of the former German stem-duchy of Swabia. However, it d ...
in 1512. During this time, a division of culture and identity developed between Swabia and both the Margraviate of Baden
The Margraviate of Baden (german: Markgrafschaft Baden) was a historical territory of the Holy Roman Empire. Spread along the east side of the Upper Rhine River in southwestern Germany, it was named a margraviate in 1112 and existed until 1535, ...
to the west and the Swiss Confederacy
The Old Swiss Confederacy or Swiss Confederacy (German language, Modern German: ; historically , after the Swiss Reformation, Reformation also , "Confederation of the Swiss") was a loose confederation of independent small states (, German or ...
to the south.
Swabian culture retains many elements common to Alemannic tradition, notably the carnival traditions forming the Swabian-Alemannic Fastnacht.
 As the national cultural consensus surrounding
As the national cultural consensus surrounding German unification
The unification of Germany (, ) was the process of building the modern German nation state with federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without multinational Austria), which commenced on 18 August 1866 with adoption of ...
was built during the 18th and 19th century, Germany was politically dominated by the northern Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) constituted the German state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: ...
, and Weimar Classicism
Weimar Classicism (german: Weimarer Klassik) was a German literary and cultural movement, whose practitioners established a new humanism from the synthesis of ideas from Romanticism, Classicism, and the Age of Enlightenment. It was named after ...
in the Duchy of Saxe-Weimar became the expression of German national high culture
High culture is a subculture that emphasizes and encompasses the cultural objects of aesthetic value, which a society collectively esteem as exemplary art, and the intellectual works of philosophy, history, art, and literature that a society co ...
(Christoph Martin Wieland
Christoph Martin Wieland (; 5 September 1733 – 20 January 1813) was a German poet and writer. He is best-remembered for having written the first ''Bildungsroman'' (''Geschichte des Agathon''), as well as the epic ''Oberon'', which formed the bas ...
and Friedrich Schiller
Johann Christoph Friedrich von Schiller (, short: ; 10 November 17599 May 1805) was a German playwright, poet, and philosopher. During the last seventeen years of his life (1788–1805), Schiller developed a productive, if complicated, friends ...
, while born and raised in Swabia, moved to Weimar and became two of the "four luminaries" (''Viergestirn'') of Weimar Classicism).
As a consequence, southern Germany and by extension both the Swabians and the Bavarians
Bavarians ( Bavarian: ''Boarn'', Standard German: ''Baiern'') are an ethnographic group of Germans of the Bavaria region, a state within Germany. The group's dialect or speech is known as the Bavarian language, native to Altbayern ("Old Bavar ...
came to be seen as marked deviations from generic Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
, and a number of clichés or stereotypes developed.
These portrayed the Swabians as stingy, overly serious or prudish petty bourgeois
''Petite bourgeoisie'' (, literally 'small bourgeoisie'; also anglicised as petty bourgeoisie) is a French term that refers to a social class composed of semi-autonomous peasants and small-scale merchants whose politico-economic ideological s ...
simpletons, as reflected in " The Seven Swabians" (''Die sieben Schwaben''), one of the '' Kinder- und Hausmärchen'' published by the Brothers Grimm
The Brothers Grimm ( or ), Jacob (1785–1863) and Wilhelm (1786–1859), were a brother duo of German academics, philologists, cultural researchers, lexicographers, and authors who together collected and published folklore. They are among th ...
. On the positive side, the same stereotype may be expressed in portraying the Swabians as frugal, clever, entrepreneurial and hard-working.
The economic recovery of Germany after the Second World War, known as the ''Wirtschaftswunder
The ''Wirtschaftswunder'' (, "economic miracle"), also known as the Miracle on the Rhine, was the rapid reconstruction and development of the economies of West Germany and Austria after World War II (adopting an ordoliberalism-based social mar ...
'', was praised by songwriter Ralf Bendix in his 1964 ''Schaffe, schaffe Häusle baue / Und net nach de Mädle schaue'' (" et'swork and work, and build a house / and not look out for girls" in Swabian dialect). The first line of his song has since become a common summary of Swabian stereotypes known throughout Germany.
In a widely noted publicity campaign on the occasion of the 50th anniversary of Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
, economically the most successful state in modern Germany, the Swabians famously embraced their stereotyping, "We can do everything—except speak Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
" (''Wir können alles. Außer Hochdeutsch'').
Swabian stereotypes persist in contemporary Germany, as expressed e.g. in the "Schwabenhass
''Schwabenhass'' (German for ''hatred against Swabians'') is a neologism referring to the aversion to the approximately 300,000-strong Swabian diaspora in Berlin and elsewhere in Germany outside of Swabia. In 2013, the so-called ''Spätzle-str ...
" conflict (surrounding gentrification
Gentrification is the process of changing the character of a neighborhood through the influx of more affluent residents and businesses. It is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and planning. Gentrification often increases the ...
in Berlin due to the large number of well-to-do Swabians moving to the capital), or a remark by chancellor Angela Merkel
Angela Dorothea Merkel (; ; born 17 July 1954) is a German former politician and scientist who served as Chancellor of Germany from 2005 to 2021. A member of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), she previously served as Leader of the Op ...
in praise of the "thrifty Swabian housewife"
(recommending Swabian, and by extension German economic prudence as a model for Europe during the financial crisis
A financial crisis is any of a broad variety of situations in which some financial assets suddenly lose a large part of their nominal value. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, many financial crises were associated with banking panics, and man ...
).
Swabian German
German dialects
German dialects are the various traditional local varieties of the German language. Though varied by region, those of the southern half of Germany beneath the Benrath line are dominated by the geographical spread of the High German consonant s ...
.
Swabian is cited as "40 percent intelligible" to speakers of Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
.
As an ethno-linguistic group, Swabians are closely related to other speakers of Alemannic German
Alemannic, or rarely Alemannish (''Alemannisch'', ), is a group of High German dialects. The name derives from the ancient Germanic tribal confederation known as the Alamanni ("all men").
Distribution
Alemannic dialects are spoken by approxi ...
, i.e. Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden ...
ers, Alsatians, and German-speaking Swiss.
Swabian German is traditionally spoken in the upper Neckar
The Neckar () is a river in Germany, mainly flowing through the southwestern state of Baden-Württemberg, with a short section through Hesse. The Neckar is a major right tributary of the Rhine. Rising in the Schwarzwald-Baar-Kreis near Sc ...
basin (upstream of Heilbronn
Heilbronn () is a city in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, surrounded by Heilbronn District. With over 126,000 residents, it is the sixth-largest city in the state.
From the late Middle Ages, it developed into an important trading centre. A ...
), along the upper Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , ...
between Tuttlingen
Tuttlingen ( Alemannic: ''Duttlinga'') is a town in Baden-Württemberg, capital of the district Tuttlingen. Nendingen, ''Möhringen'' and ''Eßlingen'' are three former municipalities that belong to Tuttlingen. Tuttlingen is located in Swabia ea ...
and Donauwörth
Donauwörth () is a town and the capital of the Donau-Ries district in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. It is said to have been founded by two fishermen where the rivers Danube (Donau) and Wörnitz meet. The city is part of the scenic route called "Rom ...
, and on the left bank of the Lech, in an areal centered on the Swabian Alps roughly stretching from Stuttgart to Augsburg
Augsburg (; bar , Augschburg , links=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swabian_German , label=Swabian German, , ) is a city in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, around west of Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and regional seat of the '' ...
. SIL Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' (stylized as ''Ethnoloɠue'') is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensi ...
cites an estimate of 819,000 Swabian speakers as of 2006.
Emigration
Hollandgänger
During the 17th and 18th century theDutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
was known for its wealth and religious tolerance, and substantial numbers of Swabians moved there in search of either work or religious freedom. Those with large debts ended up conscripted as sailors and soldiers for the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock c ...
(DEIC), eventually settling in the Dutch Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie) was a Dutch United East India Company (VOC) colony in Southern Africa, centered on the Cape of Good Hope, from where it derived its name. The original colony and its successive states that the colony was inco ...
, Dutch East Indies or Ceylon
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
. Besides individual Swabians, the Duke Charles Eugene of Württemberg concluded an agreement with the DEIC in 1786 to furnish a regiment of 2000 men to the DEIC for the sum of 300 000 guilders. This became known as the Württemberg Cape Regiment (german: Württembergisches Kapregiment ). Their presence among the Dutch at the Cape contributed to the Dutch term ''swaapstreek'' (literally: "Swabian shenanigans"), likely referencing the Seven Swabians tale.
Ostsiedlung
During the 18th centuryEast Colonisation
(, literally "East-settling") is the term for the Early Medieval and High Medieval migration-period when ethnic Germans moved into the territories in the eastern part of Francia, East Francia, and the Holy Roman Empire (that Germans had alre ...
, many Swabians were attracted by the Austrian Empire's offer of settling in East European lands which had been left sparsely populated by the wars with Turkey. These ethnic German
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
communities came to be known collectively as the Danube Swabians
The Danube Swabians (german: Donauschwaben ) is a collective term for the ethnic German-speaking population who lived in various countries of central-eastern Europe, especially in the Danube River valley, first in the 12th century, and in grea ...
, subdivided into such groups as the Banat Swabians
The Banat Swabians are an ethnic German population in the former Kingdom of Hungary in Central-Southeast Europe, part of the Danube Swabians. They emigrated in the 18th century to what was then the Austrian Empire's Banat of Temeswar province, ...
, Satu Mare Swabians and others (although the name "Danube Swabians" was applied also to German settlers of non-Swabian background).
Swabians settled also in eastern Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
(Slavonia
Slavonia (; hr, Slavonija) is, with Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria, one of the four historical regions of Croatia. Taking up the east of the country, it roughly corresponds with five Croatian counties: Brod-Posavina, Osijek-Baranja, ...
and Syrmia
Syrmia ( sh, Srem/Срем or sh, Srijem/Сријем, label=none) is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is divided between Serbia and Croatia. Most of the region is flat, with the ex ...
), and southern and western Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
, including part of what is now Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hung ...
and Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
(the Danube Swabians
The Danube Swabians (german: Donauschwaben ) is a collective term for the ethnic German-speaking population who lived in various countries of central-eastern Europe, especially in the Danube River valley, first in the 12th century, and in grea ...
, Satu Mare Swabians, Banat Swabians
The Banat Swabians are an ethnic German population in the former Kingdom of Hungary in Central-Southeast Europe, part of the Danube Swabians. They emigrated in the 18th century to what was then the Austrian Empire's Banat of Temeswar province, ...
and Swabian Turkey
The term Swabian Turkey (german: Schwäbische Türkei, hu, Sváb-Törökország) describes a region in southeastern in Hungary delimited by the Danube (''Donau''), the Drava (''Drau''), inhabited by an ethnic German minority, the Germans of Hunga ...
) in the 18th century, where they were invited as pioneers to repopulate some areas.
They also settled in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
, Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of ...
, and Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
. They were well-respected as farmers.
Almost all of the several million Swabians were expelled from Hungary, Romania, and Yugoslavia during the period 1944–1950, as part of the ethnic cleansing against their German minorities. There still are Swabians living near the city of Satu Mare
Satu Mare (; hu, Szatmárnémeti ; german: Sathmar; yi, סאטמאר or ) is a city with a population of 102,400 (2011). It is the capital of Satu Mare County, Romania, as well as the centre of the Satu Mare metropolitan area. It lies in t ...
in Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
, who are known as Satu Mare Swabians.
Overseas
Because of overpopulation and increasingly smaller land-holdings, many Swabians sought land in the Western Hemisphere, especially in the 19th century. Swabian settlements can be found inBrazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
, and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
.
Among the Germans who emigrated to the United States in the 19th century, Swabians in some areas maintained their regional identity and formed organizations for mutual support.
Recent migration within Germany
 Significant numbers of Swabians moved to
Significant numbers of Swabians moved to Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
following the city's reinstatement as German capital in 2000.
By the 2010s, their number was estimated as close to 300,000.
As the Swabians in Berlin tended to be wealthier than the local ''Berliner'', this resulted in a gentrification
Gentrification is the process of changing the character of a neighborhood through the influx of more affluent residents and businesses. It is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and planning. Gentrification often increases the ...
conflict, covered under the term ''Schwabenhass
''Schwabenhass'' (German for ''hatred against Swabians'') is a neologism referring to the aversion to the approximately 300,000-strong Swabian diaspora in Berlin and elsewhere in Germany outside of Swabia. In 2013, the so-called ''Spätzle-str ...
'' (literally "hatred of Swabians") by the German press in 2012–2013.
List of notable Swabians
*Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt ...
(1122–1190), Duke of Swabia
The Dukes of Swabia were the rulers of the Duchy of Swabia during the Middle Ages. Swabia was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German kingdom, and its dukes were thus among the most powerful magnates of Germany. The most notable famil ...
and later Holy Roman Emperor
* Albertus Magnus
Albertus Magnus (c. 1200 – 15 November 1280), also known as Saint Albert the Great or Albert of Cologne, was a German Dominican friar, philosopher, scientist, and bishop. Later canonised as a Catholic saint, he was known during his li ...
(c. 1200 – 1280), Dominican friar, philosopher, scientist, and bishop
* Eberhard I, Duke of Württemberg
Eberhard I of Württemberg (11 December 144524 February 1496) was known as Count ''Eberhard V'' from 1459 to 1495, and from July 1495 he was the first Duke of Württemberg. He is also known as ''Eberhard im Bart'' (Eberhard the Bearded).
Ear ...
(1445–1496), first Duke of Württemberg
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ran ...
* Jakob Fugger
Jakob Fugger ''of the Lily'' (german: Jakob Fugger von der Lilie; 6 March 1459 – 30 December 1525), also known as Jakob Fugger ''the Rich'' or sometimes Jakob II, was a major German merchant, mining entrepreneur, and banker. He was a descendan ...
(1459–1525), merchant, mining entrepreneur, and banker
* Hans Holbein the Younger (1497/98–1543), painter and printmaker
* Johannes Brenz
Johann (Johannes) Brenz (24 June 1499 – 11 September 1570) was a German Lutheran theologian and the Protestant Reformer of the Duchy of Württemberg.
Early advocacy of the Reformation
Brenz was born in the then Imperial City of Weil der St ...
(1499–1570), theologian and Protestant reformer
* Johannes Kepler (1571–1630), astronomer, mathematician, and astrologer
* Christoph Martin Wieland
Christoph Martin Wieland (; 5 September 1733 – 20 January 1813) was a German poet and writer. He is best-remembered for having written the first ''Bildungsroman'' (''Geschichte des Agathon''), as well as the epic ''Oberon'', which formed the bas ...
(1733–1813), novelist, poet and translator
* Friedrich Schiller
Johann Christoph Friedrich von Schiller (, short: ; 10 November 17599 May 1805) was a German playwright, poet, and philosopher. During the last seventeen years of his life (1788–1805), Schiller developed a productive, if complicated, friends ...
(1759–1805), playwright, poet, philosopher, and historian
* Friedrich Hölderlin
Johann Christian Friedrich Hölderlin (, ; ; 20 March 1770 – 7 June 1843) was a German poet and philosopher. Described by Norbert von Hellingrath as "the most German of Germans", Hölderlin was a key figure of German Romanticism. Pa ...
(1770–1843), poet and philosopher
* Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (; ; 27 August 1770 – 14 November 1831) was a German philosopher. He is one of the most important figures in German idealism and one of the founding figures of modern Western philosophy. His influence extends ...
(1770–1831), philosopher
* Friedrich Wilhelm Joseph Schelling
Friedrich Wilhelm Joseph Schelling (; 27 January 1775 – 20 August 1854), later (after 1812) von Schelling, was a German philosopher. Standard histories of philosophy make him the midpoint in the development of German idealism, situating him ...
(1775–1854), philosopher
* Justinus Kerner
Justinus Andreas Christian Kerner (18 September 1786, in Ludwigsburg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany – 21 February 1862, in Weinsberg, Baden-Württemberg) was a German poet, practicing physician, and medical writer. He gave the first detailed d ...
(1786–1862), poet, physician, and medical writer
* Ludwig Uhland (1787–1862), poet, philologist, and literary historian
* Friedrich Silcher
Philipp Friedrich Silcher (27 June 1789 in Schnait (today part of Weinstadt) – 26 August 1860 in Tübingen), was a German composer, mainly known for his lieder (songs), and an important Volkslied collector.Luise Marretta-Schär, Silcher, (Phi ...
(1789–1860), composer and folksong collector
* Wilhelm Hauff
Wilhelm Hauff (29 November 180218 November 1827) was a Württembergian poet and novelist.
Early life
Hauff was born in Stuttgart, the son of August Friedrich Hauff, a secretary in the Württemberg ministry of foreign affairs, and Hedwig Wilhelm ...
(1802–1827), novelist
* Eduard Mörike (1804–1875), poet and novelist
* Julius Robert Mayer (1814–1878), physician, chemist, and physicist
* Gottlieb Daimler
Gottlieb Wilhelm Daimler (; 17 March 1834 – 6 March 1900) was a German engineer, industrial designer and industrialist born in Schorndorf ( Kingdom of Württemberg, a federal state of the German Confederation), in what is now Germany. He wa ...
(1834–1900), engineer, industrial designer, and co-founder of Daimler Motoren Gesellschaft
Daimler-Motoren-Gesellschaft (abbreviated as DMG, also known as ''Daimler Motors Corporation'') was a German engineering company and later automobile manufacturer, in operation from 1890 until 1926. Founded by Gottlieb Daimler (1834–1900) an ...
* Count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New Yor ...
Ferdinand von Zeppelin
Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin (german: Ferdinand Adolf Heinrich August Graf von Zeppelin; 8 July 1838 – 8 March 1917) was a German general and later inventor of the Zeppelin rigid airships. His name soon became synonymous with airships ...
(1838–1917), general and later inventor of the Zeppelin
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin () who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874Eckener 1938, ...
rigid airships
* Wilhelm Maybach
Wilhelm Maybach (; 9 February 1846 – 29 December 1929) was an early German engine designer and industrialist. During the 1890s he was hailed in France, then the world centre for car production, as the "King of Designers".
From the late 19th ce ...
(1846–1929), engine designer and co-founder of Daimler Motoren Gesellschaft
* Margarete Steiff (1847–1909), company founder
* Robert Bosch (1861–1942), mechanic, inventor, and founder of Robert Bosch GmbH
Robert Bosch GmbH (; ), commonly known as Bosch and stylized as BOSCH, is a German multinational engineering and technology company headquartered in Gerlingen, Germany. The company was founded by Robert Bosch in Stuttgart in 1886. Bosch i ...
* Hermann Hesse
Hermann Karl Hesse (; 2 July 1877 – 9 August 1962) was a German-Swiss poet, novelist, and painter. His best-known works include ''Demian'', '' Steppenwolf'', '' Siddhartha'', and '' The Glass Bead Game'', each of which explores an individual' ...
(1877–1961), novelist, poet, and painter, Nobel laureate in Literature
* Clara Ritter (1877–1959), co-founder of Ritter SportChristiane Eifert (2011)''Deutsche Unternehmerinnen im 20. Jahrhundert''
München: C.H.Beck. p. 48. . *
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theor ...
(1879–1955), Nobel prize winning physicist
* Theodor Heuss
Theodor Heuss (; 31 January 1884 – 12 December 1963) was a German liberal politician who served as the first president of West Germany from 1949 to 1959. His cordial nature – something of a contrast to the stern character of chancellor K ...
(1884–1963), politician, first President of the Federal Republic of Germany
* Martin Heidegger
Martin Heidegger (; ; 26 September 188926 May 1976) was a German philosopher who is best known for contributions to phenomenology, hermeneutics, and existentialism. He is among the most important and influential philosophers of the 20th centu ...
(1889–1976), philosopher
* Erwin Rommel (1891–1944), field marshal during World War II
* Bertolt Brecht
Eugen Berthold Friedrich Brecht (10 February 1898 – 14 August 1956), known professionally as Bertolt Brecht, was a German theatre practitioner, playwright, and poet. Coming of age during the Weimar Republic, he had his first successes as a ...
(1898–1956), theatre practitioner, playwright, and poet
* Claus von Stauffenberg
Colonel Claus Philipp Maria Justinian Schenk Graf von Stauffenberg (; 15 November 1907 – 21 July 1944) was a German army officer best known for his failed attempt on 20 July 1944 to assassinate Adolf Hitler at the Wolf's Lair.
Despite ...
(1907–1944), army officer best known for his failed attempt on 20 July 1944 to assassinate Adolf Hitler
* Thaddäus Troll (1914–1980), journalist, writer, and Swabian dialect poet
* Artur Fischer
Artur Fischer (31 December 1919 – 27 January 2016) was a German inventor. He is best known for inventing the plastic expanding wall plug.
Born in Tumlingen, Artur Fischer was the son of the village tailor Georg Fischer. His mother Pauline, ...
(1919–2016), inventor and company founder
* Maria Beig
Maria Beig (8 October 1920 – 3 September 2018) was a German school teacher and author.
Life and career
Beig was born on 8 October 1920 near Lake Constance in the German region of Swabia.
Beig published her first novel, ''Rabenkrächzen'' ('' ...
(1920–2017), novelist
* Ralf Rangnick (1958–), football manager and former player
* Jürgen Klinsmann (1964–), football manager and former player
* Gert Mittring (1966–), mental calculator
* Jürgen Klopp
Jürgen Norbert Klopp (; born 16 June 1967) is a German professional football manager and former player who is the manager of club Liverpool. He is widely regarded as one of the best managers in the world.
Klopp spent most of his playing ...
(1967–), football manager and former player
* Diana Damrau (1971–), soprano opera singer
Jakob Fugger
Jakob Fugger ''of the Lily'' (german: Jakob Fugger von der Lilie; 6 March 1459 – 30 December 1525), also known as Jakob Fugger ''the Rich'' or sometimes Jakob II, was a major German merchant, mining entrepreneur, and banker. He was a descendan ...
JKepler.jpg, Johannes Kepler
Friedrich Schiller by Emma Körner.jpg, Friedrich Schiller
Johann Christoph Friedrich von Schiller (, short: ; 10 November 17599 May 1805) was a German playwright, poet, and philosopher. During the last seventeen years of his life (1788–1805), Schiller developed a productive, if complicated, friends ...
Hegel by Schlesinger.jpg, Georg Friedrich Wilhelm Hegel
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel (; ; 27 August 1770 – 14 November 1831) was a German philosopher. He is one of the most important figures in German idealism and one of the founding figures of modern Western philosophy. His influence extends ...
Gottlieb Daimler 1890s2.jpg, Gottlieb Daimler
Gottlieb Wilhelm Daimler (; 17 March 1834 – 6 March 1900) was a German engineer, industrial designer and industrialist born in Schorndorf ( Kingdom of Württemberg, a federal state of the German Confederation), in what is now Germany. He wa ...
Robert Bosch mit Hut 1888 - 10031.jpg, Robert Bosch
References
See also
* Swabian children * Alsatians *Bavarians
Bavarians ( Bavarian: ''Boarn'', Standard German: ''Baiern'') are an ethnographic group of Germans of the Bavaria region, a state within Germany. The group's dialect or speech is known as the Bavarian language, native to Altbayern ("Old Bavar ...
* Alemannic separatism
* German tribes
{{Ethnic groups in Germany
Swabia
Germanic ethnic groups
Ethnic groups in Germany