Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3 or Global Goal 3), regarding "
Good Health and
Well-being
Well-being is what is Intrinsic value (ethics), ultimately good for a person. Also called "welfare" and "quality of life", it is a measure of how well life is going for someone. It is a central goal of many individual and societal endeavors.
...
", is one of the 17
Sustainable Development Goals
The ''2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development'', adopted by all United Nations (UN) members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of these global goals is "peace and prosperity for people and the planet" – wh ...
established by the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
in 2015. The official wording is: "To ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages''.''"
[United Nations (2015) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 25th September 2015, Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development]
A/RES/70/1
The targets of SDG 3 focus on various aspects of healthy life and healthy lifestyle. Progress towards the targets is measured using 21 indicators.
SDG 3 aims to achieve
universal health coverage and equitable access of healthcare services to all men and women. It proposes to end the preventable death of newborns, infants and children under five (
child mortality
Child mortality is the death of children under the age of five. The child mortality rate (also under-five mortality rate) refers to the probability of dying between birth and exactly five years of age expressed per 1,000 live births.
It encompa ...
) and end
epidemics.
non-communicable disease
A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmission (medicine), transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, heart diseases, cancers, Diabetes mellitus, diab ...
s and promoting mental health
Mental health is often mistakenly equated with the absence of mental illness. However, mental health refers to a person's overall emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how individuals think, feel, and behave, and how t ...
* preventing and treating substance abuse
Substance misuse, also known as drug misuse or, in older vernacular, substance abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods that are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder, differing definition ...
* reducing road injuries and deaths
* granting universal access to sexual and reproductive care, family planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marit ...
and education
* achieving universal health coverage
* reducing illnesses and deaths from hazardous chemicals and pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the component ...
.
The four ''means of implementation targets[ Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License]'' are:
* implementing the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control
* supporting research, development, and universal access to affordable vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
s and medicines
* increasing health financing and support the health workforce in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed Secondary sector of the economy, industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. ...
* improving early warning systems for global health risks.
Good health is essential to
sustainable development
Sustainable development is an approach to growth and Human development (economics), human development that aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.United Nations General ...
and the
2030 Agenda. It focuses on broader
economic
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
and
social inequalities,
urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
,
climate crisis, and the continuing burden of HIV and other
infectious diseases
infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
, while not forgetting emerging challenges such as
non-communicable disease
A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmission (medicine), transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, heart diseases, cancers, Diabetes mellitus, diab ...
s.
Progress has been made in increasing life expectancy and reducing some of the common causes of child and maternal mortality. Between 2000 and 2016, the worldwide under-five
mortality rate decreased by 47 percent (from 78 deaths per 1,000 live births to 41 deaths per 1,000 live births).
Still, the number of children dying under age five is very high: 5.6 million in 2016.
Background
The
UNDP
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human development. The UNDP emphasizes on developing local capacity towar ...
reports that "every 2 seconds, someone aged 30 to 70 years dies prematurely from noncommunicable disease
cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
,
chronic respiratory disease,
diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
or
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
."
According to statistics, globally, "2.4 million children died in the first month of life in 2019 – approximately 6,700
neonatal
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to Juvenile (orga ...
deaths every day – with about a third of all neonatal deaths occurring within the first day after birth, and close to three-quarters occurring within the first week of life".
Lack of access to quality healthcare is one of the major factors.
Neonatal mortality was highest in
sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
and
South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's populatio ...
which post 27 and 25 deaths per 1,000 live births, respectively, in 2019.
Significant steps have been made in increasing
life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
and reducing some of the common causes of
child
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking ...
and
maternal mortality. Between 2000 and 2016, the worldwide under-five mortality rate decreased by 47 percent (from 78 deaths per 1,000 live births to 41 deaths per 1,000 live births).
Still, the number of children dying under age five is extremely high: 5.6 million in 2016 alone.
Targets, indicators, and progress
The UN has defined 13 Targets and 28 Indicators for SDG 3. The main data source and maps for the indicators for SDG 3 come from
Our World in Data's SDG Tracker.
[ Ritchie, Roser, Mispy, Ortiz-Ospina (2018)]
Measuring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals
" (SDG 3) ''SDG-Tracker.org, website'' Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
/ref> The targets of SDG 3 cover a wide range of issues including reduction of maternal mortality (Target 3.1), ending all preventable deaths under five years of age (Target 3.2), fight communicable diseases (Target 3.3), ensure a reduction of mortality from non-communicable diseases and promote mental health
Mental health is often mistakenly equated with the absence of mental illness. However, mental health refers to a person's overall emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how individuals think, feel, and behave, and how t ...
(Target 3.4), prevent and treat substance abuse
Substance misuse, also known as drug misuse or, in older vernacular, substance abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods that are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder, differing definition ...
(Target 3.5), reduce road injuries and deaths (Target 3.6), grant universal access to sexual and reproductive health care, family planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marit ...
and education (Target 3.7), achieve universal health coverage (Target 3.8), reduce illnesses and deaths from hazardous chemicals and pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the component ...
(Target 3.9), implement the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (Target 3.a), support research, development and universal access to affordable vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verifi ...
s and medicines (Target 3.b), increase health financing and support health workforce in developing countries (Target 3.c) and improve early warning systems for global health risks (Target 3.d).
Target 3.1: Reduce maternal mortality
The full text of Target 3.1 is: "By 2030, reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births".[United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development]
A/RES/71/313
* Indicator 3.1.1: Maternal mortality ratio. The maternal mortality ratio refers to the number of women who die from pregnancy-related causes while pregnant or within 42 days of pregnancy termination per 100,000 live births.
* Indicator 3.1.2: Percentage of births attended by personnel trained to give the necessary supervision, care, and advice to women during pregnancy, labour, and the postpartum period; to conduct deliveries on their own; and to care for newborns
Target 3.1 aims to reduce maternal mortality to less than 70 deaths per 100,000 live births.adolescent
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of human physical and psychological development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age of majority). Adolescence is usually associated w ...
pregnancy (which is strongly linked to gender equality
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality, gender egalitarianism, or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making, an ...
), provide better data for all women and girls, and achieve universal coverage of skilled birth attendants.
Target 3.2: End all preventable deaths under five years of age
The full text of Target 3.2 is: "By 2030, end preventable deaths of newborns and children under five years of age, with all countries aiming to reduce neonatal mortality to at least as low as 12 per 1,000 live births and under‑five mortality to at least as low as 25 per 1,000 live births."[United Nations (2017]
HLPF Thematic Review of SDG3
New York,
Improving antenatal care programs could reduce the neonatal mortality rate.
Target 3.3: Fight communicable diseases
 The full text of Target 3.3 is: "By 2030, end the epidemics of
The full text of Target 3.3 is: "By 2030, end the epidemics of AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
, tuberculosis, malaria and neglected tropical diseases
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteri ...
and combat hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver parenchyma, liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite ...
, water-borne diseases and other communicable diseases."Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
per 100,000 population
* Indicator 3.3.3: Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
incidence per 1,000 population
* Indicator 3.3.4: Hepatitis B incidence per 100,000 population
* Indicator 3.3.5: Number of people requiring interventions against neglected tropical disease
Tropical diseases are diseases that are prevalent in or unique to tropical and subtropical regions. The diseases are less prevalent in temperate climates, due in part to the occurrence of a cold season, which controls the insect population by forc ...
Target 3.3 proposes to end the preventable death of newborns and children under five and to end epidemics such as AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
, tuberculosis, malaria, and water-borne diseases, for example. From 2000 to 2016, new HIV infections declined by 66 percent for children under 15 and by 45 percent among adolescents aged 15–19.
From 2000 to 2016, new HIV infections declined by 66 percent for children under 15 and by 45 percent among adolescents aged 15–19.
Target 3.4: Reduce mortality from non-communicable diseases and promote mental health
The full text of Target 3.4 is: "By 2030, reduce by one-third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being
Well-being is what is Intrinsic value (ethics), ultimately good for a person. Also called "welfare" and "quality of life", it is a measure of how well life is going for someone. It is a central goal of many individual and societal endeavors.
...
."cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
or chronic respiratory disease
* Indicator 3.4.2: Suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
mortality rate
Deaths caused by the four main NCDs were "17.7 million from cardiovascular diseases, 8.8 million from cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
s, 3.9 million from chronic respiratory diseases, and 1.6 million from diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
".
Target 3.5: Prevent and treat substance abuse
The full text of Target 3.5 is: "Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance abuse
Substance misuse, also known as drug misuse or, in older vernacular, substance abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods that are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder, differing definition ...
, including narcotic
The term narcotic (, from ancient Greek ναρκῶ ''narkō'', "I make numb") originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with numbing or paralyzing properties. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiates ...
drug abuse and harmful use of alcohol."pharmacological
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between ...
, psychosocial and rehabilitation and aftercare services) for substance use disorders
* Indicator 3.5.2: Harmful use of alcohol, defined according to the national context as alcohol per capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person".
Social statistics
The term is used in a wide variety of social science, social sciences and statistical research conte ...
consumption (aged 15 years and older) within a calendar year in litres of pure alcohol.
Target 3.6: Reduce road injuries and deaths
The full text of Target 3.6 is: "By 2020, halve (50% less) the number of global deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents."
Target 3.7: Universal access to sexual and reproductive care, family planning and education
The full text of Target 3.7 is: "By 2030, ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health-care services, including for family planning
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marit ...
, information and education, and the integration of reproductive health into national strategies and programs."[BMGF (2020]
Covid-19 A Global Perspective - 2020 Goalkeepers Report
Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Seattle, USA
Lianne Gonsalves of the Department of Sexual and Reproductive Health and Research at the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) has led a report linking their sexual and reproductive health work to this UN target.
Target 3.8: Achieve universal health coverage
The full text of Target 3.8 is: "Achieve universal health coverage, including financial risk
Financial risk is any of various types of risk associated with financing, including financial transactions that include company loans in risk of default. Often it is understood to include only downside risk, meaning the potential for financi ...
protection, access to quality essential health-care services and access to safe, effective, quality and affordable essential medicines
Essential medicines, as defined by the World Health Organization (WHO), are medicines that "''satisfy the priority health care needs of the population''". Essential medicines should be accessible to people at all times, in sufficient amounts, a ...
and vaccines for all."refugee
A refugee, according to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), is a person "forced to flee their own country and seek safety in another country. They are unable to return to their own country because of feared persecution as ...
s, even if they do not have legal status.Primary health care
Primary health care (PHC) is a whole-of-society approach to effectively organise and strengthen national health systems to bring services for health and wellbeing closer to communities.
Primary health care enables health systems to support a pe ...
(PHC) is important for universal health coverage.
Target 3.9: Reduce illnesses and deaths from hazardous chemicals and pollution
The full text of Target 3.9 is: "By 2030, substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination."poisoning
Poisoning is the harmful effect which occurs when Toxicity, toxic substances are introduced into the body. The term "poisoning" is a derivative of poison, a term describing any chemical substance that may harm or kill a living organism upon ...
.
Household air pollution is estimated to cause half of all pneumonia deaths among children under age five.
Target 3.a: Implement the WHO framework convention on tobacco control
The full text of Target 3.a is: "Strengthen the implementation of the in all countries, as appropriate."
Target 3.b: Support research, development and universal access to affordable vaccines and medicines
 The full text of Target 3.b is: "Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non‑communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the Doha Declaration on the TRIPS Agreement and Public Health, which affirms the right of developing countries to use to the full the provisions in the regarding flexibilities to protect public health, and, in particular, provide access to medicines for all."
The full text of Target 3.b is: "Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non‑communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the Doha Declaration on the TRIPS Agreement and Public Health, which affirms the right of developing countries to use to the full the provisions in the regarding flexibilities to protect public health, and, in particular, provide access to medicines for all."
Target 3.c: Increase health financing and support health workforce in developing countries
The full text of Target 3.c is: "Substantially increase health financing and the recruitment, development, training and retention of the health workforce in developing countries, especially in the least developed countries and small island developing states."
Target 3.d: Improve early warning systems for global health risks
The full text of Target 3.d is: "Strengthen the capacity of all countries, in particular developing countries, for early warning, risk reduction and management of national and global health risks."
Custodian agencies
There are six custodian agencies for the 27 indicators of SDG 3.World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) is the main custodian for SDG 3 indicators, being the custodian for 20 out of 27 indicators. This means that the WHO is the dominant custodian agency for this SDG.
The other five custodians for SDG 3 indicators, other than WHO, are:
* UN Children's Fund (UNICEF) (four indicators),
* Population Division of the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (Indicators 3.7.1 and 3.7.2),
* Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (Indicator 3.3.1),
* Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (Indicator 3.b.2) and
* United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC; French language, French: ''Office des Nations unies contre la drogue et le crime'') is a United Nations office that was established in 1997 as the Office for Drug Control and Crime Prevention ...
(Indicator 3.5.1).
Monitoring progress
An annual report is prepared by the Secretary-General of the United Nations
The secretary-general of the United Nations (UNSG or UNSECGEN) is the chief administrative officer of the United Nations and head of the United Nations Secretariat, one of the United Nations System#Six principal organs, six principal organs of ...
evaluating the progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals
The ''2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development'', adopted by all United Nations (UN) members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of these global goals is "peace and prosperity for people and the planet" – wh ...
.[United Nations Economic and Social Council (2020]
Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals Report of the Secretary-General
High-level political forum on sustainable development, convened under the auspices of the Economic and Social Council (E/2020/57), 28 April 2020
A 2018 study in the journal ''Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
'' found that while "nearly all African countries demonstrated improvements for children under 5 years old for stunting, wasting, and underweight... much, if not all of the continent will fail to meet the Sustainable Development Goal target—to end malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
by 2030".
Challenges
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
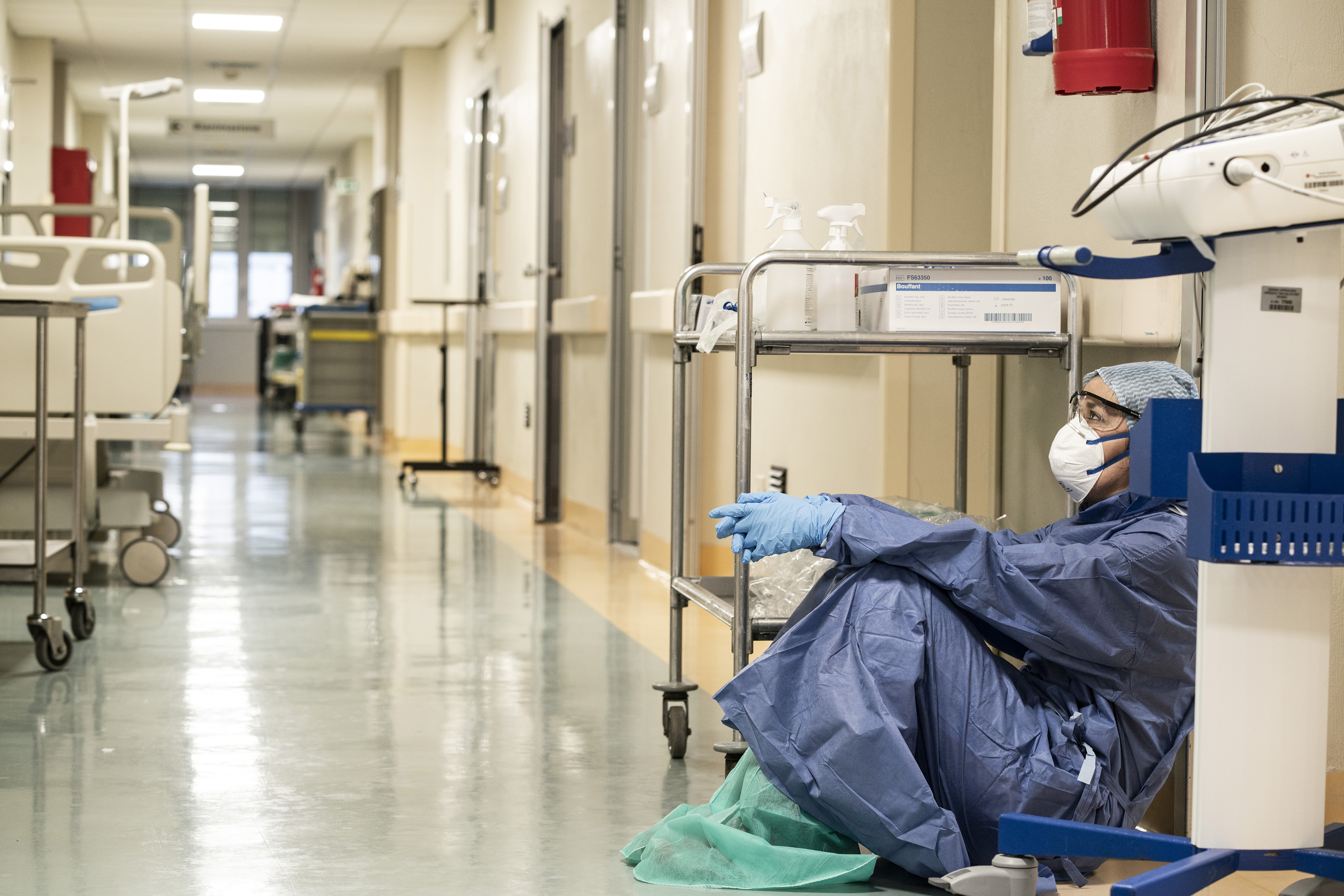 The
The COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
is a serious threat to the progress of SDG 3 aimed to ensure healthy lives and well-being for all. As the pandemic spread worldwide, the lockdown had over 70 countries putting a hold on various health services such as child vaccination, family planning, and cancer screening. The pandemic also led to overloading and overcrowding of health facilities, and many people became afraid of visiting for fear of being infected.
Responses to most non-COVID-19 diseases were either neglected or interrupted during the pandemic, and healthcare systems were in turn stretched beyond their capacity to provide adequate care. This reversed decades of improvement, and has reiterated the need for governments to prioritize issues of healthy living and well-being and work towards the goal of SDG 3.
The governments of countries who already suffer from health worker shortages and other healthcare system strains can take advantage of the lessons learnt during this crisis to build their resilience against future health pandemics.
Links with other SDGs
The targets of SDG 3 link to targets in other goals:
Organizations
Organizations dedicated to good health and well-being include:
* The Global Fund to Fight AIDS
* Joint United Nations Program on HIV/AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
( UNAIDS)
* World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
* World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO)
* UNICEF
UNICEF ( ), originally the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, officially United Nations Children's Fund since 1953, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing Humanitarianism, humanitarian and Development a ...
* Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA)
* United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC; French language, French: ''Office des Nations unies contre la drogue et le crime'') is a United Nations office that was established in 1997 as the Office for Drug Control and Crime Prevention ...
(UNODC)
* Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
* UN Women
* Gavi the Vaccine Alliance
* Vodafone Foundation
* Doctors Without Borders
Red Cross International
Medical IMPACT
* Partners in Health
PanAfricare
The Global Health Network
References
External links
UN Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform – SDG 3
“Global Goals” Campaign - SDG 3
SDG-Track.org - SDG 3
UN SDG 3 in the US
{{Sustainable Development Goals
Sustainable Development Goals
2015 establishments in New York City
Projects established in 2015
Health campaigns

 The full text of Target 3.3 is: "By 2030, end the epidemics of
The full text of Target 3.3 is: "By 2030, end the epidemics of  From 2000 to 2016, new HIV infections declined by 66 percent for children under 15 and by 45 percent among adolescents aged 15–19.
In 2015, there were about 142 tuberculosis cases per 100,000 population.
From 2000 to 2016, new HIV infections declined by 66 percent for children under 15 and by 45 percent among adolescents aged 15–19.
In 2015, there were about 142 tuberculosis cases per 100,000 population.


 The full text of Target 3.b is: "Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non‑communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the Doha Declaration on the TRIPS Agreement and Public Health, which affirms the right of developing countries to use to the full the provisions in the
The full text of Target 3.b is: "Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and non‑communicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the Doha Declaration on the TRIPS Agreement and Public Health, which affirms the right of developing countries to use to the full the provisions in the 

 The
The