Sustainable Development Goal 13 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sustainable Development Goal 13 (SDG 13 or Global Goal 13) is the
A/RES/71/313
SDG 13 and SDG 7 on
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
Global Goal to limit and adapt to climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
. It is one of 17 Sustainable Development Goals
The ''2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development'', adopted by all United Nations (UN) members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of these global goals is "peace and prosperity for people and the planet" – wh ...
established by the United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; , AGNU or AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as its main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ. Currently in its Seventy-ninth session of th ...
in 2015. The official mission statement of this goal is to " Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts".United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable DevelopmentA/RES/71/313
SDG 13 and SDG 7 on
clean energy
Energy is sustainable if it "meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." Definitions of sustainable energy usually look at its effects on the environment, the economy, and s ...
are closely related and complementary.
SDG 13 has five targets which are to be achieved by 2030. They cover a wide range of issues surrounding climate action. The first three targets are ''outcome targets.'' The first target is to strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity Adaptive capacity relates to the capacity of systems, institutions, humans and other organisms to adjust to potential damage, to take advantage of opportunities, or to respond to consequences. In the context of ecosystems, adaptive capacity is deter ...
towards climate change-related disaster
A disaster is an event that causes serious harm to people, buildings, economies, or the environment, and the affected community cannot handle it alone. '' Natural disasters'' like avalanches, floods, earthquakes, and wildfires are caused by na ...
s. The second target is to integrate climate change measures into policies and planning. The third target is to build knowledge and capacity. The remaining two targets are ''means of implementation targets Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License''. These include implementing the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is the UN process for negotiating an agreement to limit dangerous climate change. It is an international treaty among countries to combat "dangerous Global warming, human interf ...
(UNFCCC), and to promote mechanisms to raise capacity for effective climate change-related planning and management. Along with each target, there are indicators that provide a method to review the overall progress of each target. The UNFCCC is the main intergovernmental forum for negotiating the global response to climate change.
Under the 2015 Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (also called the Paris Accords or Paris Climate Accords) is an international treaty on climate change that was signed in 2016. The treaty covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and finance. The Paris Agreement was ...
, nations collectively agreed to keep warming "well under 2°C". However, with pledges made under the Agreement, global warming would still reach about by the end of the century.
As of 2020, many countries are now implementing their national climate change adaptation
Climate change adaptation is the process of adjusting to the effects of climate change, both current and anticipated.IPCC, 2022Annex II: Glossary
 SDG 13 intends to take urgent action in order to combat climate change and its impacts. Many climate change impacts are already felt at the current level of warming. Additional warming will increase these impacts and can trigger tipping points, such as the melting of the Greenland ice sheet">Tipping points in the climate system">tipping points, such as the melting of the Greenland ice sheet. Under the 2015
SDG 13 intends to take urgent action in order to combat climate change and its impacts. Many climate change impacts are already felt at the current level of warming. Additional warming will increase these impacts and can trigger tipping points, such as the melting of the Greenland ice sheet">Tipping points in the climate system">tipping points, such as the melting of the Greenland ice sheet. Under the 2015
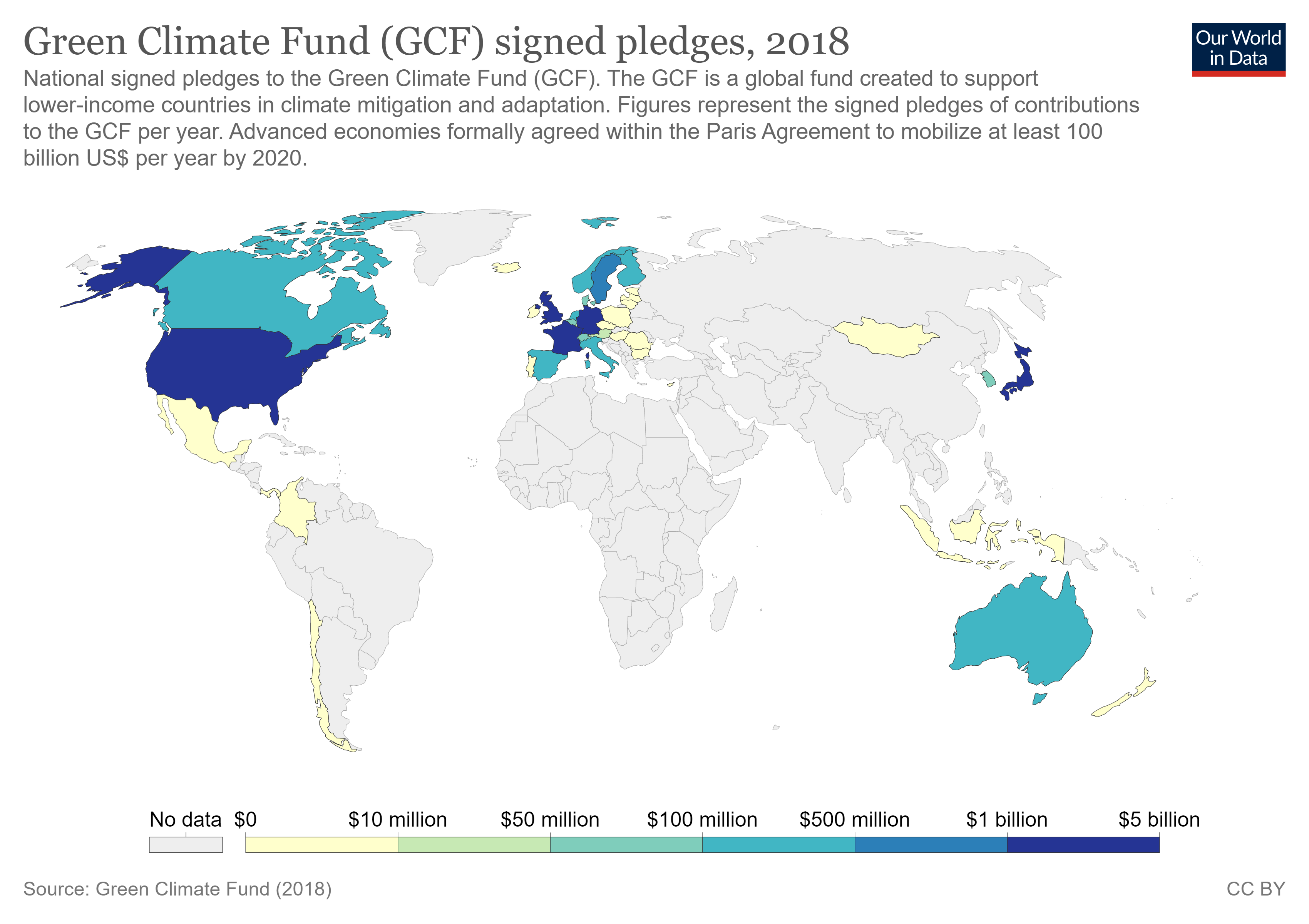 The full text of Target 13.a is: "Implement the commitment undertaken by developed-country parties to the
The full text of Target 13.a is: "Implement the commitment undertaken by developed-country parties to the
Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals Report of the Secretary-General
High-level political forum on sustainable development, convened under the auspices of the Economic and Social Council (E/2020/57), 28 April 2020 Updates and progress can also be found on the SDG website that is managed by the United Nations and at
Tracking SDG 7: The Energy Progress Report 2019
Washington DC (o
Tracking SDG 7 website
Combating climate change can improve agricultural yield which will lead to zero hunger ( SDG 2 )
UN Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform – SDG 13
"Global Goals" Campaign - SDG 13
SDG-Track.org - SDG 13
UN SDG 13 in the US
{{Climate change Sustainable Development Goals 2015 establishments in New York City Projects established in 2015 Climate change mitigation Climate change adaptation Climate change policy
Context
Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (also called the Paris Accords or Paris Climate Accords) is an international treaty on climate change that was signed in 2016. The treaty covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and finance. The Paris Agreement was ...
, nations collectively agreed to keep warming "well under 2 °C". However, with pledges made under the Agreement, global warming would still reach about by the end of the century.
Reducing emissions requires generating electricity from low-carbon sources rather than burning fossil fuels. This change includes Fossil fuel phase-out">phasing out coal and natural gas fired power plants, vastly increasing use of wind
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heatin ...
, solar
Solar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Of or relating to the Sun
** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun
** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels")
** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate t ...
, and other types of renewable energy, and reducing energy use.
Targets, indicators and progress
SDG 13 has five targets. The targets include to strengthening resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related disasters (Target 13.1), integrate climate change measures into policies and planning (Target 13.2), build knowledge and capacity to meet climate change (Target 13.3), implement theUN Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is the UN process for negotiating an agreement to limit dangerous climate change. It is an international treaty among countries to combat "dangerous Global warming, human interf ...
(Target 13.a), and promote mechanisms to raise capacity for planning and management (Target 13.b).
Each target includes one or more indicators that help to measure and monitor the progress. Some of the indicators are number of deaths, missing people and directly affected people attributed to disasters per 100,000 population (13.1.1) or total greenhouse emissions generated by year (13.2.2.)
Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related disasters
The full text of Target 13.1 is: "Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries". This target has 3 indicators. * Indicator 13.1.1: "Number of deaths, missing people and directly affected people attributed to disasters per 100,000 population" * Indicator 13.1.2: "Number of countries that adopt and implement national disaster risk reduction strategies in line with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030" * Indicator 13.1.3: "Proportion of local governments that adopt and implement local disaster risk reduction strategies in line with national disaster risk reduction strategies" Indicator 13.1.2 serves as a bridge between the Sustainable Development Goals and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction. In April 2020, the number of countries and territories that adopted national disaster risk reduction strategies increased to 118 compared to 48 from the first year of the Sendai Framework.Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into policy and planning
The full text of Target 13.2 is: "Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning". This target has two indicators: * Indicator 13.2.1: "Number of countries withnationally determined contribution
The nationally determined contributions (NDCs) are commitments that countries make to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions as part of climate change mitigation. These commitments include the necessary policies and measures for achieving the glob ...
s, long-term strategies, national adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the p ...
plans, strategies as reported in adaptation communications and national communications".
* Indicator 13.2.2: "Total greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
per year"
In order to stay under 1.5°C of global warming, carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions from G20 countries need to decline by about 45% by 2030 and attain net zero in 2050. To be able to meet the 1.5 °C or even 2 °C, which is the maximum set by the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (also called the Paris Accords or Paris Climate Accords) is an international treaty on climate change that was signed in 2016. The treaty covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and finance. The Paris Agreement was ...
, greenhouse gas emissions must start to fall by 7.6% per year starting on 2020. However, there is a large gap between these overall temperature targets and the nationally determined contributions set by individual countries. Between 2000 and 2018, greenhouse gas emissions of transition economies and developed countries have declined by 6.5%. In contrast, developing countries saw their emissions go up by 43% between 2000 and 2013.
As of 2015, 170 countries are a part of at least one multilateral environmental agreement, with each year having an increase in the number of countries signing onto environmental agreements.
Target 13.3: Build knowledge and capacity to meet climate change
The full text of Target 13.3 is: "Improve education, awareness-raising and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction and early warning". This target has two indicators: * Indicator 13.3.1: "The extent to which (i)global citizenship education
Global citizenship education (GCED) is a form of civic learning that involves students' active participation in projects that address global issues of a social, political, economic, or environmental nature. The two main elements of GCE are ' glob ...
and (ii) education for sustainable development
Sustainable development is an approach to growth and Human development (economics), human development that aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.United Nations General ...
are mainstreamed in (a) national education policies; (b) curricula; (c) teacher education; and (d) student assessment"
* Indicator 13.3.2: "Number of countries that have communicated the strengthening of institutional, systemic and individual capacity-building to implement adaptation, mitigation and technology transfer, and development actions"
The indicator 13.3.1 measures the extent to which countries mainstream Global Citizenship Education (GCED) and Education for Sustainable Development
Sustainable development is an approach to growth and human development that aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.United Nations General Assembly (1987)''Report of th ...
(ESD) in their education systems and educational policies.
The indicator 13.3.2 identifies countries who have and have not adopted and implemented disaster risk management strategies in line with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction. The goal by 2030 is to strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries.
To explain the concept of "Education for Sustainable Development and Global Citizenship
Global citizenship is a form of transnationality, specifically the idea that one's identity transcends geography or political borders and that responsibilities or rights are derived from membership in a broader global class of "humanity". This do ...
seeks to equip learners with the knowledge of how their choices impact others and their immediate environment.
There is currently no data available for this indicator as of September 2020.
Target 13.a: Implement the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change
 The full text of Target 13.a is: "Implement the commitment undertaken by developed-country parties to the
The full text of Target 13.a is: "Implement the commitment undertaken by developed-country parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is the UN process for negotiating an agreement to limit dangerous climate change. It is an international treaty among countries to combat "dangerous human interference with th ...
to a goal of mobilizing jointly $100 billion annually by 2020 from all sources to address the needs of developing countries in the context of meaningful mitigation actions and transparency on implementation and fully operationalize the Green Climate Fund through its capitalization as soon as possible."
This target only has one indicator: Indicator 13.a is the "Amounts provided and mobilized in United States dollars per year in relation to the continued existing collective mobilization goal of the $100 billion commitment through to 2025".
Previously, the indicator was worded as "Mobilized amount of United States dollars per year between 2020 and 2025 accountable towards the $100 billion commitment".
This indicator measures the current pledged commitments from countries to the Green Climate Fund
The Green Climate Fund (GCF) is a Funding, fund for climate finance that was established within the framework of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Considered the world's largest fund of its kind, GCF's objective ...
(GCF), the amounts provided and mobilized in United States dollars (USD) per year in relation to the continued existing collective mobilization goal of the US$100 billion commitment to 2025.
A report by the UN stated in 2020 that the financial flows for global climate finance as well as for renewable energy are "relatively small in relation to the scale of annual investment needed for a low-carbon
A low-carbon economy (LCE) is an economy which absorbs as much greenhouse gas as it emits. Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions due to human activity are the dominant cause of observed climate change since the mid-20th century. There are many proven ...
, climate-resilient transition".
Target 13.b: Promote mechanisms to raise capacity for planning and management
The full text of Target 13.b is: "Promote mechanisms for raising capacity for effective climate change-related planning and management in least developed countries and small island developing States, including focusing on women, youth and local and marginalized communities acknowledging that the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is the primary international, intergovernmental forum for negotiating the global response to climate change." This target has one indicator: Indicator 13.b.1 is the "Number ofleast developed countries
The least developed countries (LDCs) are developing countries listed by the United Nations that exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed b ...
and small island developing states
The Small Island Developing States (SIDS) are a grouping of developing country, developing countries which are small island country, island countries and small states that tend to share similar sustainable development challenges. These include s ...
with nationally determined contributions, long-term strategies, national adaptation plans, strategies as reported in adaptation communications and national communications".
A previous version of this indicator was: "Indicator 13.b.1: Number of least developed countries and small island developing states that are receiving specialized support, and amount of support, including finance, technology and capacity building, for mechanisms for raising capacities for effective climate change-related planning and management, including focusing on women, youth and local and marginalized communities." This indicator's previous focus on women, youth and local and marginalized communities is not included anymore in the latest version of the indicator.
Annual UN reports are monitoring how many countries are implementing national adaptation plans.
Custodian agencies
Custodian agencies are in charge of reporting on the following indicators: * Indicators 13.1.1, 13.1.2 and 13.1.3: UN International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (UNISDR
The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) was created in December 1999 to ensure the implementation of the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction.
).
* Indicator 13.2.1: United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is the UN process for negotiating an agreement to limit dangerous climate change. It is an international treaty among countries to combat "dangerous human interference with th ...
(UNFCCC), UN Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization-Institute for Statistics (UNESCO-UIS).
* Indicators 13.3.1, 13.a.1 and 13.b.1: United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
Monitoring
High-level progress reports for all theSDGs
The ''2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development'', adopted by all United Nations (UN) members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of these global goals is "peace and prosperity for people and the planet" – wh ...
are published in the form of reports by the United Nations Secretary General
The secretary-general of the United Nations (UNSG or UNSECGEN) is the chief administrative officer of the United Nations and head of the United Nations Secretariat, one of the six principal organs of the United Nations.
The role of the secr ...
.United Nations Economic and Social Council (2020Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals Report of the Secretary-General
High-level political forum on sustainable development, convened under the auspices of the Economic and Social Council (E/2020/57), 28 April 2020 Updates and progress can also be found on the SDG website that is managed by the United Nations and at
Our World in Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, war, climate change, population growth, existential risks, and inequality.
It is a project of the Global Cha ...
.
Challenges
Climate migration
SDG 13 does not directly address the link between nations most vulnerable to climate change and increased migration flows ( climate migration). It therefore misses the chance to recognize migration as an adaptive response of mobile populations. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License Weather-related disasters displace millions of people, but the goal's focus on national policies overlooks the role of migration. SDG 13 could instead track government policies on relocating communities, a practice likely to grow in the future.Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic
During theCOVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
, there was a reduction in economic activity. This resulted in a 6% drop in greenhouse gas emissions from what was initially projected for 2020, however these improvements were only temporary. Greenhouse gas emissions rebounded later in the pandemic as many countries began lifting restrictions, with the direct impact of pandemic policies having a negligible long-term impact on climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
. A rebound in transport pollution has occurred since restrictions of government lockdown policies have been lifted. Transport pollution accounts for roughly 21% of global carbon emissions due to it being still 95% dependent on oil.
Post pandemic, there is a rush for governments globally to stimulate local economies by putting money towards fossil fuel production and in turn economic stimulation. Funding for economic policies will likely divert the emergency funds usually afforded to climate funding like The Green Climate Fund and other sustainable policies, unless an emphasis is put on green deals in the redirection of monetary funds.
A 2022 publication reported that the COVID-19 pandemic negatively impacted progress on SDG 13 and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change ( UNFCCC) processes. Travel restrictions and reduced in-person meetings disrupted climate-related work, delaying actions and some planned deliverables. Scientists in developing countries faced greater challenges than their colleagues in higher-income countries due to weaker communication infrastructure and higher work demands in developing countries. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Russian invasion of Ukraine
TheRussian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
and the resulting trade sanctions had a further adverse effect on SDG 13, as some countries responded to the crisis by increasing domestic oil production.
Links with other SDGs
Sustainable Development Goal 13 connects with the other 16SDGs
The ''2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development'', adopted by all United Nations (UN) members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of these global goals is "peace and prosperity for people and the planet" – wh ...
. For example, increasing access to sustainable energy
Energy system, Energy is sustainability, sustainable if it "meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." Definitions of sustainable energy usually look at its effects on the e ...
( SDG 7) will reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
.IEA, IRENA, UNSD, WB, WHO (2019)Tracking SDG 7: The Energy Progress Report 2019
Washington DC (o
Tracking SDG 7 website
Combating climate change can improve agricultural yield which will lead to zero hunger ( SDG 2 )
Organizations
United Nations organizations
*Climate target
A climate target, climate goal or climate pledge is a measurable long-term commitment for climate policy and energy policy with the aim of limiting the climate change. Researchers within, among others, the UN climate panel have identified p ...
* United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is the UN process for negotiating an agreement to limit dangerous climate change. It is an international treaty among countries to combat "dangerous human interference with th ...
(UNFCCC)
* Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to "provide governments at all levels with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies". The World Met ...
(IPCC)
* Conferences of the Parties (COP)
* World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology an ...
(WMO)
* UN-Habitat
The United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat) is the United Nations programme for human settlements and sustainable urban development. It was established in 1977 as an outcome of the first United Nations Conference on Human Settleme ...
* United Nations Environment Program
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on ...
(UNEP)
* Green Climate Fund
The Green Climate Fund (GCF) is a Funding, fund for climate finance that was established within the framework of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Considered the world's largest fund of its kind, GCF's objective ...
(GCF)
* United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF)
* United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
References
Sources
* * *External links
UN Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform – SDG 13
"Global Goals" Campaign - SDG 13
SDG-Track.org - SDG 13
UN SDG 13 in the US
{{Climate change Sustainable Development Goals 2015 establishments in New York City Projects established in 2015 Climate change mitigation Climate change adaptation Climate change policy