Subdwarf O star on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A subdwarf O star (sdO) is a type of hot, but low-mass star. O-type
A subdwarf O star (sdO) is a type of hot, but low-mass star. O-type
 They can be plotted on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. They are from two stages in the stellar lifecycle, post–
They can be plotted on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. They are from two stages in the stellar lifecycle, post–
 A subdwarf O star (sdO) is a type of hot, but low-mass star. O-type
A subdwarf O star (sdO) is a type of hot, but low-mass star. O-type subdwarf
A subdwarf, sometimes denoted by "sd", is a star with luminosity class VI under the Yerkes spectral classification system. They are defined as stars with luminosity 1.5 to 2 magnitudes lower than that of main-sequence stars of the same ...
s are much dimmer than regular O-type main-sequence stars, but with a brightness about 10 to 100 times that of the Sun, and have a mass approximately half that of the Sun. Their temperature ranges from 40,000 to 100,000 K. Ionized helium is prominent in their spectra. Their surface gravity (typically given as the gravity's logarithm), log ''g'' is usually between 4.0 and 6.5. Many sdO stars are moving at high velocity through the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
and are found at high galactic latitudes.
Structure
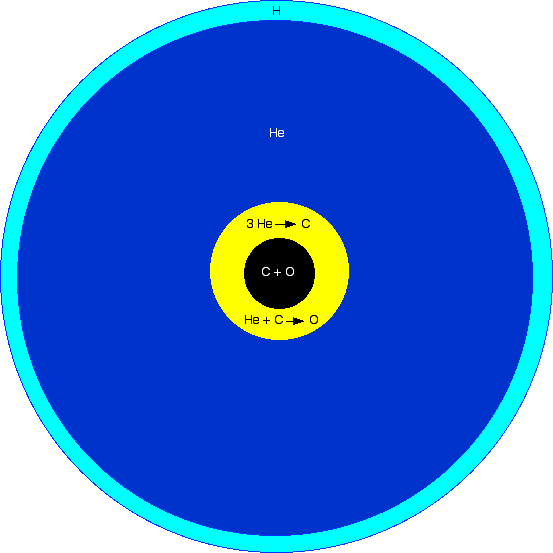
The structure of a subdwarf O star is believed to be a carbon and oxygen core surrounded by ahelium burning
The triple-alpha process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions by which three helium-4 nuclei (alpha particles) are transformed into carbon.
In stars
Helium accumulates in the cores of stars as a result of the proton–proton chain reaction a ...
shell. The spectrum shows that the content is from 50 to 100% helium.
History
In the early 1970s Greenstein and Sargent measured temperatures and gravity strengths and were able to plot their correct position on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. The Palomar-Green survey, Hamburg surveys,Sloan Digital Sky Survey
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-spectral imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project began in 2000 a ...
and Supernova Ia Progenitor Survey (ESO-SPY) have documented many of these stars.
Occurrence
Subdwarf O stars are only a third as common as subdwarf B stars.Spectrum
There is actually a variety of spectra from the sdO stars. They can be grouped into those with strong helium lines, termed He-sdO, and those with stronger hydrogen lines, H strong sdO. The He-sdO are fairly rare. Usually nitrogen is enriched and carbon depleted. However, there are variations with enhancement in concentration of even numbered elements such as carbon, oxygen, neon, silicon, magnesium or iron.Examples
* HD 128220 was studied by Corrado Bartolini * HIP 52181 pulsates with a frequency of 1.04 milliHertz. * HD 49798 is a carbon poor X-ray binary at 830pc. * US 708 is a hypervelocity star that exceeds the escape velocity of the Milky Way.Life cycle
 They can be plotted on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. They are from two stages in the stellar lifecycle, post–
They can be plotted on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. They are from two stages in the stellar lifecycle, post–asymptotic giant branch
The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) lat ...
(the luminous sdO), and post– extended horizontal branch compact sdO. The post-AGB stars are expected to be found in planetary nebula
A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelated to planets. The ...
s, but only four of the sdO stars are known to be like this. The compact sdOs would be descendants of the B-type subdwarfs. However, statistics do not match sdB. An alternate theory is that sdOs have been formed by coalescing two white dwarf
A white dwarf is a Compact star, stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very density, dense: in an Earth sized volume, it packs a mass that is comparable to the Sun. No nuclear fusion takes place i ...
s. This could happen from a close binary that decays due to gravitational wave
Gravitational waves are oscillations of the gravitational field that Wave propagation, travel through space at the speed of light; they are generated by the relative motion of gravity, gravitating masses. They were proposed by Oliver Heaviside i ...
s.
References
{{star