St Stephens Green on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
St Stephen's Green () is a
 In 1814 control of St Stephen's Green passed to commissioners for the local householders, who redesigned its layout and replaced the walls with railings.
After the death of
In 1814 control of St Stephen's Green passed to commissioners for the local householders, who redesigned its layout and replaced the walls with railings.
After the death of
 The landscaping of the park has undergone three major changes since its inception. Its first major change occurred in 1670: two rows of
The landscaping of the park has undergone three major changes since its inception. Its first major change occurred in 1670: two rows of
 While the central park of St Stephen's Green is one of three ancient
While the central park of St Stephen's Green is one of three ancient
 Some of the earliest houses still survive on the south and north sides of the Green. These are identifiable by their lower height and narrow fronts, illustrating how plots were subdivided. Later buildings on the east side show a dramatic change in scale, with much larger and grander houses, many by Gustavus Hume.
''
Some of the earliest houses still survive on the south and north sides of the Green. These are identifiable by their lower height and narrow fronts, illustrating how plots were subdivided. Later buildings on the east side show a dramatic change in scale, with much larger and grander houses, many by Gustavus Hume.
''
Stephen's Green Park (official OPW website)
{{Authority control Squares in Dublin (city) Streets in Dublin (city) National monuments in County Dublin Parks in Dublin (city) 1664 establishments in Ireland St Stephen's Green Odonyms referring to religion
garden square
A garden square is a type of communal garden in an urban area wholly or substantially surrounded by buildings; commonly, it continues to be applied to public and private parks formed after such a garden becomes accessible to the public at large.
...
and public park
An urban park or metropolitan park, also known as a city park, municipal park (North America), public park, public open space, or municipal gardens (United Kingdom, UK), is a park or botanical garden in cities, densely populated suburbia and oth ...
located in the city centre
A city centre, also known as an urban core, is the Commerce, commercial, Culture, cultural and often the historical, Politics, political, and geographic heart of a city. The term "city centre" is primarily used in British English, and closely e ...
of Dublin, Ireland. The current landscape of the park was designed by William Sheppard. It was officially re-opened to the public on Tuesday, 27 July 1880 by Lord Ardilaun. The square is adjacent to one of Dublin's main shopping streets, Grafton Street, and to a shopping centre
A shopping center in American English, shopping centre in English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English (see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences), shopping complex, shopping arcade, ...
named after it, while on its surrounding streets are the offices of a number of public bodies as well as a stop on one of Dublin's Luas
Luas (, Irish language, Irish: ; meaning 'speed') is a tram system in Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. There are two main lines: the Green Line (Luas), Green Line, which began operating on 30 June 2004, and the Red Line (Luas), Red Line ...
tram lines. It is often informally called Stephen's Green. At , it is the largest of the parks in Dublin's main Georgian garden square
A garden square is a type of communal garden in an urban area wholly or substantially surrounded by buildings; commonly, it continues to be applied to public and private parks formed after such a garden becomes accessible to the public at large.
...
s. Others include nearby Merrion Square
Merrion Square () is a Georgian architecture, Georgian garden square on the Southside Dublin, southside of Dublin city centre.
History
The square was laid out in 1762 to a plan by John Smyth and Jonathan Barker for the estate of Richard Fitz ...
and Fitzwilliam Square.
The park is rectangular, surrounded by streets that once formed major traffic arteries through Dublin city centre, although traffic management changes implemented in 2004 during the course of the Luas works have greatly reduced the volume of traffic. These four bordering streets are called, respectively, St Stephen's Green North, St Stephen's Green South, St Stephen's Green East and St Stephen's Green West.
History
The association with St Stephen has its origins in a medieval leper hospital, nowMercer's Hospital
Mercer's Hospital () was a hospital in Dublin, Ireland. It was converted into a clinical centre and medical library for the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland in 1991.Saint Stephen
Stephen (; ) is traditionally venerated as the protomartyr or first martyr of Christianity."St ...
on nearby Stephen Street. Until 1663, St Stephen's Green was a marshy common
Common may refer to:
As an Irish surname, it is anglicised from Irish Gaelic surname Ó Comáin.
Places
* Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cambridge Com ...
on the edge of Dublin of approximately 60 acres, used for grazing. In that year Dublin Corporation
Dublin Corporation (), known by generations of Dubliners simply as ''The Corpo'', is the former name of the city government and its administrative organisation in Dublin since the 1100s. Significantly re-structured in 1660–1661, even more si ...
, seeing an opportunity to raise much-needed revenue, decided to enclose the centre of the common and to sell land around the perimeter for building. The area was surveyed by Robert Newcomen, with the land divided into 96 plots with a green of 27 acres in the centre. The park was enclosed with a wall in 1664. Early tenants built simple two-storey houses, with much of it undeveloped on the 1728 map. By the time of John Roque's map in 1756, the pace of building had accelerated rapidly. The houses built around the Green were rapidly replaced by new buildings in the Georgian style
Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries to the set of architectural styles current between 1714 and 1830. It is named after the first four British monarchs of the House of Hanover, George I, George II, Ge ...
and by the end of the eighteenth century the Green was a place of resort for the better-off of the city. Most of the present-day landscape of the square comprises townhouses from the 18th and 19th centuries.
Prince Albert
Prince Albert most commonly refers to:
*Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (1819–1861), consort of Queen Victoria
*Albert II, Prince of Monaco (born 1958), present head of state of Monaco
Prince Albert may also refer to:
Royalty
* Alb ...
, Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
suggested that St Stephen's Green be renamed Albert Green and have a statue of Albert at its centre, a suggestion rejected with indignation by the Dublin Corporation and the people of the city, to the Queen's chagrin.
Access to the Green was restricted to local residents, until 1877, when Parliament passed an Act to reopen St Stephen's Green to the public, at the initiative of Sir A.E. Guinness, a member of the Guinness brewing family who lived at St Anne's Park, Raheny
Raheny () is a northern suburb of Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, halfway from the city centre to Howth. It is centred on a historic settlement, first documented in 570 AD (Mervyn Archdall (Irish antiquary), Mervyn Archdall). The district ...
and at Ashford Castle. He later paid for the laying out of the Green in approximately its current form, which took place in 1880, and gave it to the Corporation
A corporation or body corporate is an individual or a group of people, such as an association or company, that has been authorized by the State (polity), state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law as ...
, as representatives of the people. By way of thanks, the city commissioned a statue of him, which faces the College of Surgeons. His brother Edward
Edward is an English male name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortunate; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”.
History
The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-S ...
lived at Iveagh House
Iveagh House is a Georgian architecture, Georgian house which now contains the headquarters of the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (Ireland), Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade in Dublin, Ireland. It is also sometimes used colloquia ...
, which his descendants gave in 1939 to the Department of External Affairs (now the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade).
During the Easter Rising
The Easter Rising (), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with the aim of establishing an ind ...
of 1916, a group of rebels made up mainly of members of the Irish Citizen Army
The Irish Citizen Army (), or ICA, was a paramilitary group first formed in Dublin to defend the picket lines and street demonstrations of the Irish Transport and General Workers' Union (ITGWU) against the police during the Great Dublin Lock ...
, under the command of Commandant Michael Mallin, his second-in-command Kit Poole, and Constance Markievicz
Constance Georgine Markievicz ( ; ' Gore-Booth; 4 February 1868 – 15 July 1927), also known as Countess Markievicz and Madame Markievicz, was an Irish politician, revolutionary, nationalist, suffragist, and socialist who was the first woman ...
, established a position in St Stephen's Green. They numbered between 200 and 250. They confiscated motor vehicles to establish roadblocks on the streets that surround the park, and dug defensive positions in the park itself. This approach differed from that of taking up positions in buildings, adopted elsewhere in the city. It proved to have been unwise when elements of the British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
took up positions in the Shelbourne Hotel, at the northeastern corner of St Stephen's Green, overlooking the park, from which they could shoot down into the entrenchments. Finding themselves in a weak position, the Volunteers withdrew to the Royal College of Surgeons
The Royal College of Surgeons is an ancient college (a form of corporation) established in England to regulate the activity of surgeons. Derivative organisations survive in many present and former members of the Commonwealth. These organisations ...
on the west side of the Green. During the Rising, gunfire was temporarily halted to allow the park's groundsman to feed the local ducks.
A statue of Archibald Montgomerie, 13th Earl of Eglinton
Archibald William Montgomerie, 13th Earl of Eglinton, 1st Earl of Winton, KT, PC (29 September 18124 October 1861), styled Lord Montgomerie from 1814 to 1819, was a British Conservative politician. He was Lord Lieutenant of Ireland in 1852 and ...
by Patrick MacDowell was erected on the North side of the green in 1866. It was destroyed in an explosion by the IRA which injured gardaí and civilians in 1958 and the remains were dismantled.
The park is now operated by the Office of Public Works
The Office of Public Works (OPW) (; legally the Commissioners of Public Works in Ireland) is a major Government of Ireland, Irish Government agency, which manages most of the Irish State's property portfolio, including hundreds of owned and ren ...
(OPW) on behalf of the Irish state.
Park
Evolution of design
 The landscaping of the park has undergone three major changes since its inception. Its first major change occurred in 1670: two rows of
The landscaping of the park has undergone three major changes since its inception. Its first major change occurred in 1670: two rows of lime tree
''Tilia'' is a genus of about 30 species of trees or bushes, native throughout most of the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The tree is known as linden for the European species, and basswood for North American species. In Great Britain and Irelan ...
s were planted around the perimeter, functioning as its first enclosure. The marshy ground was drained using a ditch at the perimeter. At this time, the park was only accessible to the wealthy residents who owned plots around the park. In 1815 the park was redesigned by the Dublin city surveyor Arthur Neville. In his redesign, he added winding pathways and iron fences. At this time, the park was still closed to the public.
During the 1860s, the campaign to make the park publicly accessible was underway, and the city engineer, George W. Hemans, proposed a new design to make the park as walkable and as functionally practical as possible. This included creating four gates at each corner of the park that would be linked by the extant pathways designed by Neville. This plan was eventually abandoned, most likely due to the fact that Hemans was employed by Dublin Corporation
Dublin Corporation (), known by generations of Dubliners simply as ''The Corpo'', is the former name of the city government and its administrative organisation in Dublin since the 1100s. Significantly re-structured in 1660–1661, even more si ...
. However, many of Hemans' designs, like the addition of the gates and connecting pathways, were included in the final plans submitted by William Sheppard, the principal designer responsible for the landscape of the park as we know it today, and engineer A.L. Cousins, sponsored by Lord Ardilaun. Ardilaun also played a significant role in the planning and importing of the exotic trees and plants that would be installed in the park.
Layout
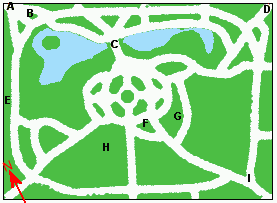
 While the central park of St Stephen's Green is one of three ancient
While the central park of St Stephen's Green is one of three ancient commons
The commons is the cultural and natural resources accessible to all members of a society, including natural materials such as air, water, and a habitable Earth. These resources are held in common even when owned privately or publicly. Commons ...
in the city, its current layout owes much to the restorations of the 19th century. Architectural history professor Christine Casey states that this restoration obscures what would have been its most impressive feature to 18th-century visitors, its large size. The grounds are roughly rectangular, measuring (approximately) 550 by 450 metres, and are centred on a formal garden.
By 1758, the tree-lined walks around the park had been named, Beaux Walk to the north, Leeson's Walk to the south, Monck's Walk to the east, and French Walk to the west.
One of the more unusual aspects of the park lies on the northwest corner of this central area, a garden for the blind with scented plants, which can withstand handling, and are labelled in Braille
Braille ( , ) is a Tactile alphabet, tactile writing system used by blindness, blind or visually impaired people. It can be read either on embossed paper or by using refreshable braille displays that connect to computers and smartphone device ...
.
Further north again (and spanning much of the length of the park) is a large lake. Home to ducks and other water fowl, the lake is fed by an artificial waterfall, spanned by O'Connell bridge, and fronted by an ornamental gazebo
A gazebo is a pavilion structure, sometimes octagonal or Gun turret, turret-shaped, often built in a park, garden, or spacious public area. Some are used on occasions as bandstands.
In British English, the word is also used for a tent-like can ...
. The lakes in the park are fed from the Grand Canal at Portobello.
To the south side of the main garden circle is more open heath
A heath () is a shrubland habitat found mainly on free-draining infertile, acidic soils and is characterised by open, low-growing woody vegetation. Moorland is generally related to high-ground heaths with—especially in Great Britain—a coole ...
surrounding a bandstand
A bandstand (sometimes music kiosk) is a circular, semicircular or polygonal structure set in a park, garden, pier, or indoor space, designed to accommodate musical bands performing concerts. A simple construction, it both creates an ornamen ...
, and often frequented by lunching students, workers and shoppers on Dublin's sunnier days.
There is also a playground (separated into junior and senior areas) which was refurbished in 2010.
The park once featured a statue of King George II on horseback by John van Nost, erected in 1758, until it was blown up in 1937 by Irish Republican
Irish republicanism () is the political movement for an Irish republic, void of any British rule. Throughout its centuries of existence, it has encompassed various tactics and identities, simultaneously elective and militant and has been both w ...
s, the day after the coronation
A coronation ceremony marks the formal investiture of a monarch with regal power using a crown. In addition to the crowning, this ceremony may include the presentation of other items of regalia, and other rituals such as the taking of special v ...
of George VI
George VI (Albert Frederick Arthur George; 14 December 1895 – 6 February 1952) was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 until Death and state funeral of George VI, his death in 1952 ...
.
Other features include:
* the Fusiliers' Arch at the Grafton Street corner which commemorates the Royal Dublin Fusiliers who died in the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War (, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, Transvaal War, Anglo–Boer War, or South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer republics (the South African Republic and ...
.
* a fountain representing the Three Fates
The Fates are a common motif in European polytheism, most frequently represented as a trio of goddesses. The Fates shape the destiny of each human, often expressed in textile metaphors such as spinning fibers into yarn, or weaving threads ...
inside the Leeson Street
__NOTOC__
Leeson Street (; ) is a thoroughfare near central Dublin, Ireland.
Location
The street is divided into two parts by the Grand Canal: Lower Leeson Street, in Dublin 2 is to the north of the canal, linking to St Stephen's Green, wi ...
gate. The statue was designed by Joseph Wackerle in bronze in 1956. It was a gift from the German people
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
in thanks for Irish help to refugee children following World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. Up to five hundred children found foster home
Foster care is a system in which a underage, minor has been placed into a ward (law), ward, group home (Residential Child Care Community, residential child care community or treatment centre), or private home of a state-certified caregiver, ref ...
s in Ireland in a project named Operation Shamrock.
* a seated statue of Lord Ardilaun on the western side, the man who gave the Green to the city, facing the Royal College of Surgeons which he also sponsored (again, see ''History'' above)
* the W. B. Yeats
William Butler Yeats (, 13 June 186528 January 1939), popularly known as W. B. Yeats, was an Irish poet, dramatist, writer, and literary critic who was one of the foremost figures of 20th-century literature. He was a driving force behind the ...
memorial garden with a sculpture by Henry Moore
Henry Spencer Moore (30 July 1898 – 31 August 1986) was an English artist. He is best known for his semi-abstract art, abstract monumental Bronze sculpture, bronze sculptures which are located around the world as public works of art. Moore ...
* a bust of James Joyce
James Augustine Aloysius Joyce (born James Augusta Joyce; 2 February 1882 – 13 January 1941) was an Irish novelist, poet, and literary critic. He contributed to the modernist avant-garde movement and is regarded as one of the most influentia ...
facing his former university at Newman House
* a memorial to the Fenian
The word ''Fenian'' () served as an umbrella term for the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB) and their affiliate in the United States, the Fenian Brotherhood. They were secret political organisations in the late 19th and early 20th centuries ...
leader Jeremiah O'Donovan Rossa
Jeremiah O'Donovan Rossa (; 4 September 1831 (baptised) – 29 June 1915)Con O'Callaghan Reenascreena Community Online (dead link archived at archive.org, 29 September 2014) was an Irish Fenian leader who was one of the leading members of t ...
near the Grafton Street entrance
* a bronze statue at the Merrion Row corner of Theobald Wolfe Tone
Theobald Wolfe Tone, posthumously known as Wolfe Tone (; 20 June 176319 November 1798), was a revolutionary exponent of Irish independence and is an iconic figure in Irish republicanism. Convinced that, so long as his fellow Protestants fear ...
, the leader of the 1798 rebellion.
* a memorial to the Great Famine of 1845–1850 by Edward Delaney
* a bust of Countess Constance Markievicz
Constance Georgine Markievicz ( ; ' Gore-Booth; 4 February 1868 – 15 July 1927), also known as Countess Markievicz and Madame Markievicz, was an Irish politician, revolutionary, nationalist, suffragist, and socialist who was the first woman ...
on the south of the central garden (see ''History'' above)
* a statue of Robert Emmet
Robert Emmet (4 March 177820 September 1803) was an Irish Republican, orator and rebel leader. Following the suppression of the United Irish uprising in 1798, he sought to organise a renewed attempt to overthrow the British Crown and Prote ...
standing opposite his birthplace (now demolished) at No 124.
* a memorial bust of war poet
War poetry is poetry on the topic of war. While the term is applied especially to works of the First World War, the term can be applied to poetry about any war, including Homer's ''Iliad'', from around the 8th century BC as well as poetry of th ...
Thomas Kettle, who was killed in action
Killed in action (KIA) is a casualty classification generally used by militaries to describe the deaths of their personnel at the hands of enemy or hostile forces at the moment of action. The United States Department of Defense, for example, ...
while serving in the Royal Dublin Fusiliers during the Battle of Ginchy in September 1916. As Irish republicanism
Irish republicanism () is the political movement for an Irish Republic, Irish republic, void of any British rule in Ireland, British rule. Throughout its centuries of existence, it has encompassed various tactics and identities, simultaneously ...
traditionally viewed Irishmen who served in the British armed forces
The British Armed Forces are the unified military, military forces responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom, its British Overseas Territories, Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies. They also promote the UK's wider interests ...
during World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
as traitors, the placement of a commemorative bust of Kettle was beset by controversy until it was finally placed in 1937, without an official unveiling, in the centre section.
* a bust of Bengal Renaissance
The Bengal Renaissance (), also known as the Bengali Renaissance, was a cultural, social, intellectual, and artistic movement that took place in the Bengal region of the British Raj, from the late 18th century to the early 20th century. Histo ...
poet Rabindranath Tagore
Rabindranath Thakur (; anglicised as Rabindranath Tagore ; 7 May 1861 – 7 August 1941) was a Bengalis, Bengali polymath who worked as a poet, writer, playwright, composer, philosopher, social reformer, and painter of the Bengal Renai ...
was erected in the park in 2011.
Architecture
 Some of the earliest houses still survive on the south and north sides of the Green. These are identifiable by their lower height and narrow fronts, illustrating how plots were subdivided. Later buildings on the east side show a dramatic change in scale, with much larger and grander houses, many by Gustavus Hume.
''
Some of the earliest houses still survive on the south and north sides of the Green. These are identifiable by their lower height and narrow fronts, illustrating how plots were subdivided. Later buildings on the east side show a dramatic change in scale, with much larger and grander houses, many by Gustavus Hume.
''Iveagh House
Iveagh House is a Georgian architecture, Georgian house which now contains the headquarters of the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (Ireland), Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade in Dublin, Ireland. It is also sometimes used colloquia ...
'' on the south side was created from the joining of two earlier houses (numbers 80 and 81) by Benjamin Guinness in the 1860s. It was donated to the Irish State by the Guinness family in 1939, and now houses the main offices of the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade
The Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT) is the department of the Australian government responsible for foreign policy and international relations, development aid (under the name Australian Aid), consular services, overseas trad ...
.
Also on the south side of St Stephen's Green are ''Newman House'' (numbers 85 and 86, after John Henry Newman
John Henry Newman (21 February 1801 – 11 August 1890) was an English Catholic theologian, academic, philosopher, historian, writer, and poet. He was previously an Anglican priest and after his conversion became a cardinal. He was an ...
) and '' University Church''. These are home to the Catholic University of Ireland, which was founded in the 19th century. It is linked with University College Dublin
University College Dublin (), commonly referred to as UCD, is a public research university in Dublin, Ireland, and a collegiate university, member institution of the National University of Ireland. With 38,417 students, it is Ireland's largest ...
, but is no longer active educationally in its own right.
The '' Unitarian Church'', Dublin, built in the Gothic revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic or neo-Gothic) is an Architectural style, architectural movement that after a gradual build-up beginning in the second half of the 17th century became a widespread movement in the first half ...
style, is located on the West side of St Stephen's Green.
Also on the west side is the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland
The Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland (RCSI) is a not-for-profit medical professional and educational institution, which is also known as RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences. It was established in 1784 as the national body ...
(number 123), home to the oldest of the Republic of Ireland's six medical schools.
On the west side, at the top of Grafton Street, is the Stephen's Green Shopping Centre, built in October 1988. It was, at the time, Ireland's largest shopping centre. Its style was intended to represent a conservatory on the side facing the Green and to mirror the brickwork design of the opposing Gaiety Theatre on South King Street.
On the north side of St Stephen's Green, there were four houses which are now two clubs (originally gentlemen's club
A gentlemen's club is a private social club of a type originally established by males from Britain's upper classes starting in the 17th century.
Many countries outside Britain have prominent gentlemen's clubs, mostly those associated with the ...
s): the ''Hibernian United Services Club'' (number 8, closed in 2002), the ''Stephen's Green Hibernian Club'' (number 9, originally the Stephen's Green Club, prior to its merger with the Hibernian United Services Club), the "Friendly Brothers of St Patrick" (number 22, now closed) and the ''Kildare Street and University Club'' (number 17). This side of the Green also has the historic ''Shelbourne Hotel'', Dublin's only surviving Victorian hotel. The Little Museum of Dublin, which is housed in a restored Georgian townhouse can be found in number 15.
Also on the north side, Heritage House at 23 St Stephen's Green, was the location of a tearoom which hosted the first public Alcoholics Anonymous
Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) is a global, peer-led Mutual aid, mutual-aid fellowship focused on an abstinence-based recovery model from alcoholism through its spiritually inclined twelve-step program. AA's Twelve Traditions, besides emphasizing anon ...
meeting in Ireland, on 25 November 1946.
''Loreto College, St Stephen's Green'', one of Ireland's best-known fee-paying schools for girls, is located at number 53, on the East side of the Green.
''St Vincent's Hospital'', now located in a suburb on the south side of Dublin, was formerly located in buildings on the East side of St Stephen's Green and on Leeson Street. It is now the headquarters of bank PTSB.
During the mid 20th century, a number of the Georgian buildings on the Green were demolished in favour of modern office blocks. Most of the east side of the square is modern reproduction terraces in front of offices. Among the buildings that were lost was No. 21, the former St Andrew's College, which was demolished by Irish Life in February 1969 and a new office block, Stephen Court, designed by Andrew Devane was constructed in its place. This building is deemed one of the more successful modern interventions on the Green.
Transport
Dublin Bus
Dublin Bus () is an Irish State-owned enterprise, state-owned bus operator providing services in Dublin. By far the largest bus operator in the city, it carried 145 million passengers in 2023. It is a subsidiary of CIÉ, Córas Iompair Éireann ...
routes 7b, 7d, 11, 37, 40, 46a, 84x, 145, and 155 all have stops along the east side of the square. Routes 44, 44D, 61, X31, and X32 stop on neighbouring Earlsfort Terrace; routes 38/A/B/D, 39/A/X, 46E, 70, 116, 118, X25, X26, X27, X28, X30 stop on Leeson Street (as well as the northbound stops for routes stopping on St. Stephen's Green East). Routes 38/A/B/D, 39/A, and 70 also have their southbound stops on Merrion Row.
The Dublin tramways
Dublin tramways was a system of trams in Dublin, Ireland, which commenced line-laying in 1871, and began service in 1872, following trials in the mid-1860s. Established by a number of companies, the majority of the system was eventually operat ...
once had several routes serving St. Stephen's Green, including routes 10, 11, 12, 16, 17 and 20, but these were shut down over the 1930s and 1940s. In the 2000s, trams returned to Dublin and the Green line of the Luas
Luas (, Irish language, Irish: ; meaning 'speed') is a tram system in Dublin, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. There are two main lines: the Green Line (Luas), Green Line, which began operating on 30 June 2004, and the Red Line (Luas), Red Line ...
tram system stops at the St Stephen's Green stop on the western side of the park, with Luas Cross City services continuing to Broombridge station in Cabra.
A DublinBikes
Dublinbikes (styled "dublinbikes") is a public bicycle rental scheme which has operated in the city of Dublin since 2009. At its launch, the scheme, which is sponsored by JCDecaux, used 450 French-made unisex bicycles with 40 stations. By 201 ...
docking point is also located on St. Stephen's Green East.
See also
*List of streets and squares in Dublin
This is a list of notable streets and squares in Dublin, Ireland.
__NOTOC__
References Notes
Sources
*
External linksStreetnames of DublinaArchiseekArchitecture of Ireland– English-Irish list of Dublin street names aLeathanach baile Sh ...
References
Notes
Sources
* *External links
Stephen's Green Park (official OPW website)
{{Authority control Squares in Dublin (city) Streets in Dublin (city) National monuments in County Dublin Parks in Dublin (city) 1664 establishments in Ireland St Stephen's Green Odonyms referring to religion