St Stephen's Chapel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 St Stephen's Chapel, sometimes called the Royal Chapel of St Stephen, was a chapel completed around 1297 in the old
St Stephen's Chapel, sometimes called the Royal Chapel of St Stephen, was a chapel completed around 1297 in the old
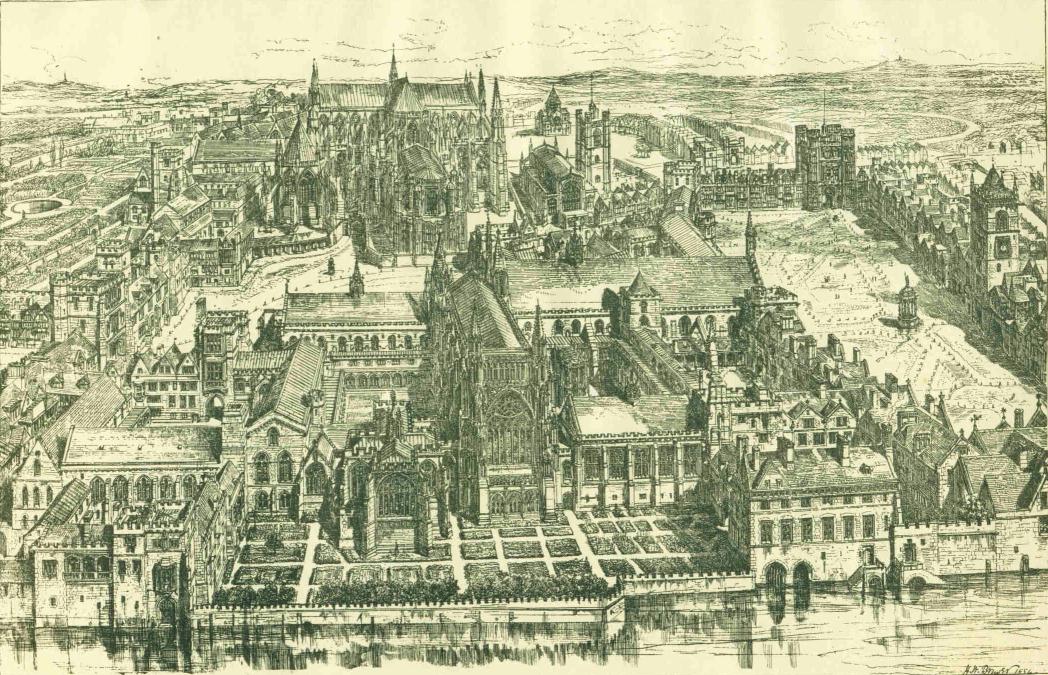 According to Cooke (1987), King Henry III witnessed the consecration of the Sainte Chapelle in
According to Cooke (1987), King Henry III witnessed the consecration of the Sainte Chapelle in 
from Westminster Abbey website. Retrieved 11 July 2011. Being five years old, she was close to a year older than Richard. At the age of eight, Anne died. Her coffin was discovered in a vault in
 The former chapel's layout and functionality influenced the positioning of furniture and the seating of Members of Parliament in the Commons. The Speaker's chair was placed on the altar steps – arguably the origin of the tradition of members bowing to the Speaker, as they would formerly have done to the altar. Where the lectern had once been, the Table of the House was installed. The members sat facing one another in the medieval choir stalls, creating the adversarial seating plan that persists in the chamber of the Commons to this day. The old choir screen, with its two side-by-side entrances, was also retained and formed the basis of the modern voting system for parliamentarians, with "aye" voters passing through the right-hand door and "no" voters passing through the left-hand one.
In order to suit the needs of the House of Commons, various changes to the chapel's original Gothic form were made by various architects between 1547 and 1834. Initial changes during the late 16th century were relatively minor; the original chapel furnishings were replaced, the interior whitewashed and the stained-glass windows replaced with plain glass. More drastic alterations were undertaken by
The former chapel's layout and functionality influenced the positioning of furniture and the seating of Members of Parliament in the Commons. The Speaker's chair was placed on the altar steps – arguably the origin of the tradition of members bowing to the Speaker, as they would formerly have done to the altar. Where the lectern had once been, the Table of the House was installed. The members sat facing one another in the medieval choir stalls, creating the adversarial seating plan that persists in the chamber of the Commons to this day. The old choir screen, with its two side-by-side entrances, was also retained and formed the basis of the modern voting system for parliamentarians, with "aye" voters passing through the right-hand door and "no" voters passing through the left-hand one.
In order to suit the needs of the House of Commons, various changes to the chapel's original Gothic form were made by various architects between 1547 and 1834. Initial changes during the late 16th century were relatively minor; the original chapel furnishings were replaced, the interior whitewashed and the stained-glass windows replaced with plain glass. More drastic alterations were undertaken by
explore-parliament.net
– shows various views of the chapel, notabl
this image
Virtual St Stephens ,
– including a section o
'Visualizing St Stephens'
throughout its history {{DEFAULTSORT:Saint Stephens Chapel 1297 establishments in England Buildings and structures completed in 1297 Churches completed in the 1290s 13th-century church buildings in England Burned buildings and structures in the United Kingdom Palace of Westminster National government buildings in London Former buildings and structures in the City of Westminster Gothic architecture in England Richard of Shrewsbury, Duke of York Chapels in London Henry III of England Richard II of England Edward IV
 St Stephen's Chapel, sometimes called the Royal Chapel of St Stephen, was a chapel completed around 1297 in the old
St Stephen's Chapel, sometimes called the Royal Chapel of St Stephen, was a chapel completed around 1297 in the old Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster is the meeting place of the Parliament of the United Kingdom and is located in London, England. It is commonly called the Houses of Parliament after the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two legislative ch ...
. After the death of Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
until 1834, the building served as the chamber of the House of Commons of England
The House of Commons of England was the lower house of the Parliament of England (which Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542, incorporated Wales) from its development in the 14th century to the union of England and Scotland in 1707, when it was re ...
and that of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
. It was largely destroyed in the fire of 1834, but the Chapel of St Mary Undercroft in the crypt
A crypt (from Greek κρύπτη (kryptē) ''wikt:crypta#Latin, crypta'' "Burial vault (tomb), vault") is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, Sarcophagus, sarcophagi, or Relic, religiou ...
survived.
The present-day St Stephen's Hall and its porch, which are within the new Palace of Westminster built in the 19th century, stand on exactly the same site and are today accessed through the St Stephen's Entrance, the public entrance of the House of Commons.
History
As a royal chapel
 According to Cooke (1987), King Henry III witnessed the consecration of the Sainte Chapelle in
According to Cooke (1987), King Henry III witnessed the consecration of the Sainte Chapelle in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
in 1248, and wished to construct a chapel in his principal palace at Westminster to rival it. Work continued for many years under Henry's successors, to be completed around 1297. In the resulting two-storey chapel, the Upper Chapel was used by the Royal Family, and the Lower Chapel, by the Royal Household and courtiers.

Historical events
Two royal weddings are recorded as having been solemnised in St Stephen's Chapel. On 20 January 1382,King Richard II
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward, Prince of Wales (later known as the Black Prince), and Joan, Countess of Kent. R ...
was married to Anne of Bohemia
Anne of Bohemia (11 May 1366 – 7 June 1394), also known as Anne of Luxembourg, was Queen consort of England, Queen of England as the first wife of King Richard II. A member of the House of Luxembourg, she was the daughter of Charles IV, Holy ...
. The bridegroom was fifteen, the bride sixteen. The other marriage occurred on 15 January 1478, between the younger of the two Princes in the Tower
The Princes in the Tower refers to the mystery of the fate of the deposed King Edward V of England and his younger brother Prince Richard of Shrewsbury, Duke of York, heirs to the throne of King Edward IV of England. The brothers were the only ...
, Richard, Duke of York, and Anne Mowbray.Anne Mowbray, Duchess of Yorkfrom Westminster Abbey website. Retrieved 11 July 2011. Being five years old, she was close to a year older than Richard. At the age of eight, Anne died. Her coffin was discovered in a vault in
Stepney
Stepney is an area in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in the East End of London. Stepney is no longer officially defined, and is usually used to refer to a relatively small area. However, for much of its history the place name was applied to ...
in 1964, and her remains reinterred in Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an Anglican church in the City of Westminster, London, England. Since 1066, it has been the location of the coronations of 40 English and British m ...
. The body of Richard's father, King Edward IV, who died at the Palace of Westminster on 9 April 1483, was conveyed to St Stephen's Chapel the next day, and lay in state there for eight days before his interment at St George's Chapel, Windsor
St George's Chapel, formally titled The King's Free Chapel of the College of St George, Windsor Castle, at Windsor Castle in England is a castle chapel built in the late-medieval Perpendicular Gothic style. It is a Royal Peculiar (a church und ...
.
Thomas Cranmer
Thomas Cranmer (2 July 1489 – 21 March 1556) was a theologian, leader of the English Reformation and Archbishop of Canterbury during the reigns of Henry VIII, Edward VI and, for a short time, Mary I. He is honoured as a Oxford Martyrs, martyr ...
was consecrated in St Stephen's Chapel as Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the Primus inter pares, ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the bishop of the diocese of Canterbury. The first archbishop ...
on 30 March 1533. After the death of King Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disagreement w ...
the Palace of Westminster ceased to be a royal residence. Henry's son, King Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and King of Ireland, Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. The only surviving son of Henry VIII by his thi ...
, instituted the Abolition of Chantries Acts, 1545 and 1547, and St Stephen's Chapel thus became available for use as the debating chamber of the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
. Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in British history. He came to prominence during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially ...
had the crypt whitewash
Whitewash, calcimine, kalsomine, calsomine, asbestis or lime paint is a type of paint made from slaked lime ( calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2) or chalk (calcium carbonate, CaCO3), sometimes known as "whiting". Various other additives are sometimes ...
ed and used it to stable his horses.
On the night before the 1911 census, women's suffragist Emily Davison
Emily Wilding Davison (11 October 1872 – 8 June 1913) was an English suffragette who fought for Women's suffrage in the United Kingdom, votes for women in Britain in the early twentieth century. A member of the Women's Social and Polit ...
spent the night in a broom cupboard in the back of the crypt in order to be able to give her address as the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
, despite not being allowed to stand for Parliament or vote. A plaque was unofficially placed in the cupboard to commemorate this in around 1991 by the late Tony Benn
Anthony Neil Wedgwood Benn (3 April 1925 – 14 March 2014), known between 1960 and 1963 as Viscount Stansgate, was a British Labour Party (UK), Labour Party politician and political activist who served as a Cabinet of the United Kingdom, Cabine ...
MP. He put the plaque in place with his own hands and proudly showed it to visitors. He later installed a second plaque for a purpose which is now lost but the Palace authorities required him to remove it. The screw holes are still visible.
As the House of Commons chamber
 The former chapel's layout and functionality influenced the positioning of furniture and the seating of Members of Parliament in the Commons. The Speaker's chair was placed on the altar steps – arguably the origin of the tradition of members bowing to the Speaker, as they would formerly have done to the altar. Where the lectern had once been, the Table of the House was installed. The members sat facing one another in the medieval choir stalls, creating the adversarial seating plan that persists in the chamber of the Commons to this day. The old choir screen, with its two side-by-side entrances, was also retained and formed the basis of the modern voting system for parliamentarians, with "aye" voters passing through the right-hand door and "no" voters passing through the left-hand one.
In order to suit the needs of the House of Commons, various changes to the chapel's original Gothic form were made by various architects between 1547 and 1834. Initial changes during the late 16th century were relatively minor; the original chapel furnishings were replaced, the interior whitewashed and the stained-glass windows replaced with plain glass. More drastic alterations were undertaken by
The former chapel's layout and functionality influenced the positioning of furniture and the seating of Members of Parliament in the Commons. The Speaker's chair was placed on the altar steps – arguably the origin of the tradition of members bowing to the Speaker, as they would formerly have done to the altar. Where the lectern had once been, the Table of the House was installed. The members sat facing one another in the medieval choir stalls, creating the adversarial seating plan that persists in the chamber of the Commons to this day. The old choir screen, with its two side-by-side entrances, was also retained and formed the basis of the modern voting system for parliamentarians, with "aye" voters passing through the right-hand door and "no" voters passing through the left-hand one.
In order to suit the needs of the House of Commons, various changes to the chapel's original Gothic form were made by various architects between 1547 and 1834. Initial changes during the late 16th century were relatively minor; the original chapel furnishings were replaced, the interior whitewashed and the stained-glass windows replaced with plain glass. More drastic alterations were undertaken by Christopher Wren
Sir Christopher Wren FRS (; – ) was an English architect, astronomer, mathematician and physicist who was one of the most highly acclaimed architects in the history of England. Known for his work in the English Baroque style, he was ac ...
in the 1690s. During that work the building was significantly reduced in height with the removal of the clerestory
A clerestory ( ; , also clearstory, clearstorey, or overstorey; from Old French ''cler estor'') is a high section of wall that contains windows above eye-level. Its purpose is to admit light, fresh air, or both.
Historically, a ''clerestory' ...
and vaulted ceiling while the great medieval windows were walled up, with smaller windows cut into the new stonework. Inside, the walls were reduced in thickness to accommodate extra seating and the addition of upper-level male-only public galleries along both sides of the chamber, and the remains of the medieval interior were concealed behind wainscoting
Panelling (or paneling in the United States) is a millwork wall covering constructed from rigid or semi-rigid components. These are traditionally interlocking wood, but could be plastic or other materials.
Panelling was developed in antiquity t ...
and oak panelling. A false ceiling was installed in the chamber to help to improve its acoustics, the quality of which was important in an age without artificial amplification. The newly created attic space above the ceiling housed a ventilation lantern and was used as the ladies' gallery, although the view down into the chamber beneath through the lantern was severely restricted. More seating was later added for the extra members brought in by the Acts of Union with Scotland (1707) and Ireland (1800). By the 19th century, the chapel's interior had a very bland and modest look in contrast to its former medieval magnificence. Further alterations were made to the exterior by James Wyatt
James Wyatt (3 August 1746 – 4 September 1813) was an English architect, a rival of Robert Adam in the Neoclassicism, neoclassical and neo-Gothic styles. He was elected to the Royal Academy of Arts in 1785 and was its president from 1805 to ...
at the end of the 18th century.
Fire and reconstruction
The fire of 1834 totally destroyed the main body of the chapel, with the crypt below, and the adjoining cloisters, barely surviving. Among the few furnishings rescued from the flames was the Table of the House, which is now kept in the Speaker's apartments at the palace. Although it was demolished shortly after the fire, the surviving stone shell of the chapel, with all its later additions burned away, attracted many visitors and antiquaries who came to view the original medieval decorations which had become visible once again. The historical importance of the chapel was realised in the design of the new palace in the form of St Stephen's Hall, the lavishly decorated main public entrance hall built on the same floor plan as the old chapel, with the position of the Speaker's chair marked out on the floor. The crypt below St Stephen's Hall, the Chapel of St Mary Undercroft, which had fallen into disuse some time before the fire and had seen a number of uses, was restored, and returned to its original use as a place of worship. It is still used for this purpose today. Children of peers, who possess the style of "The Honourable
''The Honourable'' (Commonwealth English) or ''The Honorable'' (American English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) (abbreviation: ''Hon.'', ''Hon'ble'', or variations) is an honorific Style ...
", have the privilege of being able to use it as a wedding venue. Members of Parliament and peers have the right to use the chapel as a place of christening.
The body of Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013), was a British stateswoman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of th ...
was kept in St Mary Undercroft on the night before her funeral on 17 April 2013.
Further reading
*Maurice Hastings, ''St Stephen's Chapel and its Place in the Development of Perpendicular Style in England'' (1955) * Sir Robert Cooke, ''The Palace of Westminster'' (London: Burton Skira, 1987)References
External links
explore-parliament.net
– shows various views of the chapel, notabl
this image
Virtual St Stephens ,
– including a section o
'Visualizing St Stephens'
throughout its history {{DEFAULTSORT:Saint Stephens Chapel 1297 establishments in England Buildings and structures completed in 1297 Churches completed in the 1290s 13th-century church buildings in England Burned buildings and structures in the United Kingdom Palace of Westminster National government buildings in London Former buildings and structures in the City of Westminster Gothic architecture in England Richard of Shrewsbury, Duke of York Chapels in London Henry III of England Richard II of England Edward IV