Squat (exercise) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A squat is a strength exercise in which the trainee lowers their hips from a standing position and then stands back up. During the descent, the hip and
A squat is a strength exercise in which the trainee lowers their hips from a standing position and then stands back up. During the descent, the hip and
 The squat begins from a standing position. The squatting movement is initiated by moving the hips back and bending the knees and hips to lower the torso and accompanying weight, then returning to the upright position.
Weight is often added and is typically in the form of a loaded
The squat begins from a standing position. The squatting movement is initiated by moving the hips back and bending the knees and hips to lower the torso and accompanying weight, then returning to the upright position.
Weight is often added and is typically in the form of a loaded 

 Various types of equipment can be used to perform squats.
A power cage can be used to reduce risk of injury and eliminate the need for a spotting partner. By putting the bar on a track, the Smith machine reduces the role of hip movement in the squat and in this sense resembles a leg press. Cornacchia, pp
Various types of equipment can be used to perform squats.
A power cage can be used to reduce risk of injury and eliminate the need for a spotting partner. By putting the bar on a track, the Smith machine reduces the role of hip movement in the squat and in this sense resembles a leg press. Cornacchia, pp
121125
The monolift rack allows an athlete to perform a squat without having to unrack and step out of the rack.
Other equipment used can include weight lifting belts, which allow the athlete to achieve higher intra-abdominal pressure, and heeled shoes (
 The squat has a number of variants, some of which can be combined:
The squat has a number of variants, some of which can be combined:
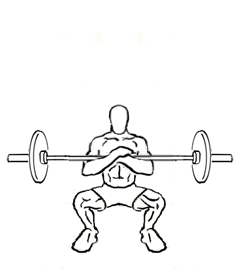 *Zercher squat – the barbell is held in the crooks of the arms, on the inside of the elbow. One method of performing this is to deadlift the barbell, hold it against the thighs, squat into the lower portion of the squat, and then hold the bar on the thighs as you position the crook of your arm under the bar and then stand up. This sequence is reversed once the desired number of repetitions has been performed. Named after Ed Zercher, a 1930s strongman.
*Steinborn squat – named after the traditional strongman Henry 'Milo' Steinborn, and performed without a rack, the barbell begins on the floor. The lifter picks up one end, and lifts until it's nearly vertical, before bending to position it against their back, as if in a back squat. They then lower their hips, allowing the top of the bar to lower until the bar is straight across their back, with their body in the bottom of a squat. Normal back squats can be performed from this position.
*Deep knee bend on toes – it is similar to a normal back squat only the lifter is positioned on their forefeet and toes, with their heels raised, throughout the repetition. Usually, the weight used is not more than moderate in comparison to a flat footed, heavy back squat.
*Single leg squat - The single leg squat (SLS), also known as a unilateral squat, involves squatting with one leg instead of two (which is a bilateral squat). Usually the leg which is held off the ground moves behind the person as they squat, but alternatively the person may position it ahead of themselves. Bilateral split squats which significantly increase the work performed by the front leg are sometimes erroneously referred to as single leg squats due to this emphasis. Single leg squats can be used to strengthen a person's stabilizer muscles more so than two legged squats and improve their ability to balance. They can also be used to remove muscle imbalances in the body by ensuring that, when performed alternatively, the right and left leg do the same amount of work. In comparison to two footed squats, the barbell weight only needs to be half of what it would be, minus the lifter's weight for the legs to perform the same amount of work i.e. for an 80 kg lifter, lifting 40 kg using only the left leg, means the left leg is lifting the equivalent of what it does in a two footed squat with 160 kg. This means that the single leg squat can be used in rehabilitation programmes where there is a need to avoid heavier loading of the back.
*Loaded squat jump – the barbell is positioned similarly to a back squat. The exerciser squats down, before moving upwards into a jump, and then landing in approximately the same position. The loaded squat jump is a form of loaded plyometric exercise used to increase explosive power. Variations of this exercise may involve the use of a trap bar or dumbbells.
*Variable resistance squat – In keeping with variable resistance training in general, a variable resistance squat involves altering the resistance during the movement in order that it better matches, in percentage terms, the respective 1RM for each strength phase the person is moving through i.e. more resistance in the higher stronger phase and less in the weaker lower phase e.g. 60 kg in the lower phase and 90 kg in the higher phase. Such an alteration of resistance can be achieved by the use of heavy chains which are attached to either end of the barbell. The chains are gradually lifted from the floor as the barbell is raised and vice versa when it is lowered. Thick elastic bands which are more stretched in the higher phase and less stretched in the lower phase can also be used. Combining heavier partial reps with lighter full reps can also help to train the stronger and weaker phases of the movement so the percentage of 1RM lifted for each phase respectively is more similar. Training with variable resistance squats is a technique used to increase speed and explosive power.
*Partial rep – Partial rep squats only move through a partial range of movement when compared with full squats which move through a full range of movement. Full range for a squat usually means the higher stronger phase of a squat's strength phase sequence (strength curve), but may also refer to just squatting for the lower weaker phase. When partial squats are used to strengthen the higher ROM this usually involves significantly increasing the weight in comparison to the weight used for a full squat. The percentage lifted of the stronger higher phase's 1RM can therefore be increased and not limited by the requirement to move through the weaker lower range of movement e.g. a person lifts 100% of his 1RM for the higher stronger phase which is 150 kg. If he did a full squat he would only have been able to do about 66% of his stronger phases 1RM because his 1RM for a full squat, including the weaker lower phase, is 100 kg. Training with heavier partial squats can help to improve general strength and power. It can also be more beneficial for sports and athletics as that ROM is more likely to be required in those activities i.e. it is rare to need to perform a full squat in sport, whereas partial squatting happens frequently. Partial squatting with a heavier weight than a full squat allows for can also help to improve a person's 1RM for a full squat. When partial squatting only the lower phase this is usually to strengthen that relatively weak phase of the lift in order to overcome a sticking point i.e. a point a person gets "stuck" at and finds it difficult to progress past. It is commonly recommended that partial squats are best used in conjunction with full squats.
*Zercher squat – the barbell is held in the crooks of the arms, on the inside of the elbow. One method of performing this is to deadlift the barbell, hold it against the thighs, squat into the lower portion of the squat, and then hold the bar on the thighs as you position the crook of your arm under the bar and then stand up. This sequence is reversed once the desired number of repetitions has been performed. Named after Ed Zercher, a 1930s strongman.
*Steinborn squat – named after the traditional strongman Henry 'Milo' Steinborn, and performed without a rack, the barbell begins on the floor. The lifter picks up one end, and lifts until it's nearly vertical, before bending to position it against their back, as if in a back squat. They then lower their hips, allowing the top of the bar to lower until the bar is straight across their back, with their body in the bottom of a squat. Normal back squats can be performed from this position.
*Deep knee bend on toes – it is similar to a normal back squat only the lifter is positioned on their forefeet and toes, with their heels raised, throughout the repetition. Usually, the weight used is not more than moderate in comparison to a flat footed, heavy back squat.
*Single leg squat - The single leg squat (SLS), also known as a unilateral squat, involves squatting with one leg instead of two (which is a bilateral squat). Usually the leg which is held off the ground moves behind the person as they squat, but alternatively the person may position it ahead of themselves. Bilateral split squats which significantly increase the work performed by the front leg are sometimes erroneously referred to as single leg squats due to this emphasis. Single leg squats can be used to strengthen a person's stabilizer muscles more so than two legged squats and improve their ability to balance. They can also be used to remove muscle imbalances in the body by ensuring that, when performed alternatively, the right and left leg do the same amount of work. In comparison to two footed squats, the barbell weight only needs to be half of what it would be, minus the lifter's weight for the legs to perform the same amount of work i.e. for an 80 kg lifter, lifting 40 kg using only the left leg, means the left leg is lifting the equivalent of what it does in a two footed squat with 160 kg. This means that the single leg squat can be used in rehabilitation programmes where there is a need to avoid heavier loading of the back.
*Loaded squat jump – the barbell is positioned similarly to a back squat. The exerciser squats down, before moving upwards into a jump, and then landing in approximately the same position. The loaded squat jump is a form of loaded plyometric exercise used to increase explosive power. Variations of this exercise may involve the use of a trap bar or dumbbells.
*Variable resistance squat – In keeping with variable resistance training in general, a variable resistance squat involves altering the resistance during the movement in order that it better matches, in percentage terms, the respective 1RM for each strength phase the person is moving through i.e. more resistance in the higher stronger phase and less in the weaker lower phase e.g. 60 kg in the lower phase and 90 kg in the higher phase. Such an alteration of resistance can be achieved by the use of heavy chains which are attached to either end of the barbell. The chains are gradually lifted from the floor as the barbell is raised and vice versa when it is lowered. Thick elastic bands which are more stretched in the higher phase and less stretched in the lower phase can also be used. Combining heavier partial reps with lighter full reps can also help to train the stronger and weaker phases of the movement so the percentage of 1RM lifted for each phase respectively is more similar. Training with variable resistance squats is a technique used to increase speed and explosive power.
*Partial rep – Partial rep squats only move through a partial range of movement when compared with full squats which move through a full range of movement. Full range for a squat usually means the higher stronger phase of a squat's strength phase sequence (strength curve), but may also refer to just squatting for the lower weaker phase. When partial squats are used to strengthen the higher ROM this usually involves significantly increasing the weight in comparison to the weight used for a full squat. The percentage lifted of the stronger higher phase's 1RM can therefore be increased and not limited by the requirement to move through the weaker lower range of movement e.g. a person lifts 100% of his 1RM for the higher stronger phase which is 150 kg. If he did a full squat he would only have been able to do about 66% of his stronger phases 1RM because his 1RM for a full squat, including the weaker lower phase, is 100 kg. Training with heavier partial squats can help to improve general strength and power. It can also be more beneficial for sports and athletics as that ROM is more likely to be required in those activities i.e. it is rare to need to perform a full squat in sport, whereas partial squatting happens frequently. Partial squatting with a heavier weight than a full squat allows for can also help to improve a person's 1RM for a full squat. When partial squatting only the lower phase this is usually to strengthen that relatively weak phase of the lift in order to overcome a sticking point i.e. a point a person gets "stuck" at and finds it difficult to progress past. It is commonly recommended that partial squats are best used in conjunction with full squats.
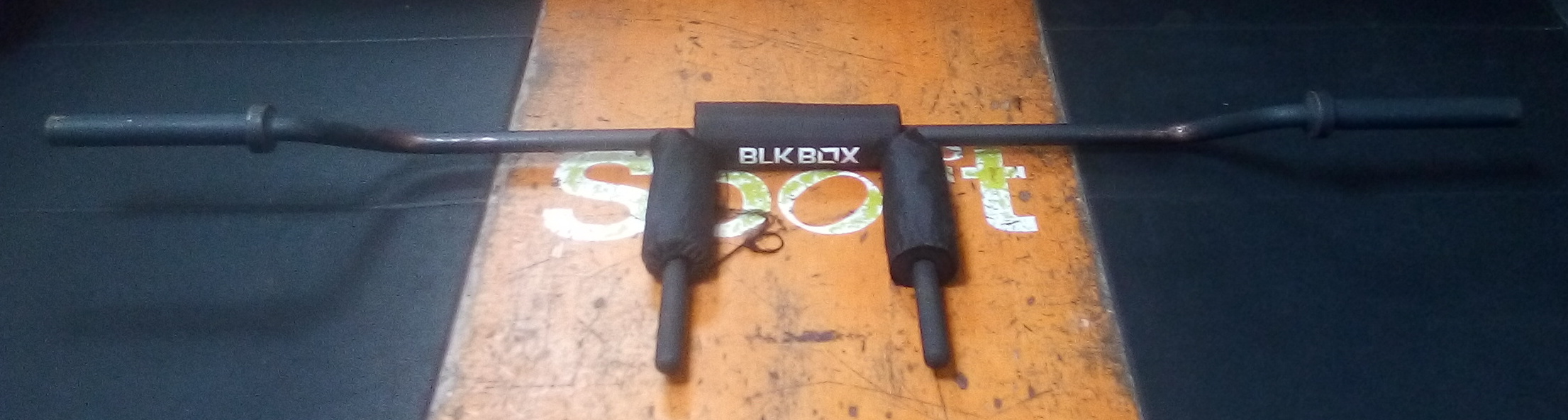 *Safety squat – a squat performed using a ''safety squat bar'' which has a camber in the middle, two handles, and padding. The use of a safety squat bar may help to reduce the risk of causing or aggravating an injury.
*Anderson squat - (aka Pin Squat, Bottoms Up Squat) starting the squat from the bottom position.
*Safety squat – a squat performed using a ''safety squat bar'' which has a camber in the middle, two handles, and padding. The use of a safety squat bar may help to reduce the risk of causing or aggravating an injury.
*Anderson squat - (aka Pin Squat, Bottoms Up Squat) starting the squat from the bottom position.
 *Basic single leg squat – the person stands with one foot on the ground and the other foot raised. They bend their standing leg and move downwards. Their raised leg moves behind them with the knee coming close to the heel of the grounded foot. Due to the extra effort required to balance, one legged squats can help to additionally improve a person's sense of balance. As with other forms of one legged exercise performed alternately, they can also help to mitigate against an excessive strength variation between the legs, as both legs are made to perform the same level of work e.g. in a two legged squat a person's right leg may do 55% of the work and their left leg 45%, which may result in an excessively uneven level of strength developing. By switching between using the right leg and left leg in one legged squats, a person can better ensure that each leg is doing the same level of work i.e. the right or left leg does 100% of the work for each respective one legged squat.
*Pistol squat – a bodyweight single leg squat done to full depth, while the other leg is extended off the floor and positioned somewhere in front. Sometimes dumbbells, kettlebells or medicine balls are added for resistance. Pistol squats may be performed with the foot flat on the floor or with the heel raised.
*Shrimp squat – also called the ''flamingo squat'', a version of the pistols squat where instead of extending the non-working leg out in front, it is bent and placed behind the working leg while squatting, perhaps held behind in a hand. Shrimp squats may be performed with the foot flat on the floor or with the heel raised.
*Jockey squat - a half-squat, performed by being balanced on the forefeet throughout the repetition, with fingertips touching across the chest. This squat can be performed quickly and in high repetitions.
*Basic single leg squat – the person stands with one foot on the ground and the other foot raised. They bend their standing leg and move downwards. Their raised leg moves behind them with the knee coming close to the heel of the grounded foot. Due to the extra effort required to balance, one legged squats can help to additionally improve a person's sense of balance. As with other forms of one legged exercise performed alternately, they can also help to mitigate against an excessive strength variation between the legs, as both legs are made to perform the same level of work e.g. in a two legged squat a person's right leg may do 55% of the work and their left leg 45%, which may result in an excessively uneven level of strength developing. By switching between using the right leg and left leg in one legged squats, a person can better ensure that each leg is doing the same level of work i.e. the right or left leg does 100% of the work for each respective one legged squat.
*Pistol squat – a bodyweight single leg squat done to full depth, while the other leg is extended off the floor and positioned somewhere in front. Sometimes dumbbells, kettlebells or medicine balls are added for resistance. Pistol squats may be performed with the foot flat on the floor or with the heel raised.
*Shrimp squat – also called the ''flamingo squat'', a version of the pistols squat where instead of extending the non-working leg out in front, it is bent and placed behind the working leg while squatting, perhaps held behind in a hand. Shrimp squats may be performed with the foot flat on the floor or with the heel raised.
*Jockey squat - a half-squat, performed by being balanced on the forefeet throughout the repetition, with fingertips touching across the chest. This squat can be performed quickly and in high repetitions.
 *Sissy squat – the knees travel over the toes, stretching the quadriceps and the body leans backwards. Can be done in a special sissy squat machine, and can also be weighted.
*Sumo Squat - also known as ''Plie Squat'', in this variation legs are wider than shoulder width.
*Sissy squat – the knees travel over the toes, stretching the quadriceps and the body leans backwards. Can be done in a special sissy squat machine, and can also be weighted.
*Sumo Squat - also known as ''Plie Squat'', in this variation legs are wider than shoulder width.
120
Others, however, continue to advocate the squat as one of the best exercises for building muscle and strength. Some coaches maintain that incomplete squats (those terminating above parallel) are both less effective and more likely to cause injury than full squat (terminating with hips at or below knee level). A 2013 review concluded that deep squats performed with proper technique do not lead to increased rates of degenerative knee injuries and are an effective exercise. The same review also concluded that shallower squats may lead to degeneration in the lumbar spine and knees in the long-term.
WebMD summary of health benefits of squats
Video of squat recommendations with demonstration by a chiropractor
{{DEFAULTSORT:Squat (Exercise) Powerlifting Weight training exercises Bodyweight exercises Physical exercise Squatting position
 A squat is a strength exercise in which the trainee lowers their hips from a standing position and then stands back up. During the descent, the hip and
A squat is a strength exercise in which the trainee lowers their hips from a standing position and then stands back up. During the descent, the hip and knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ...
joints flex while the ankle joint dorsiflexes; conversely the hip and knee joints extend and the ankle joint plantarflexes when standing up.
Squats are considered a vital exercise for increasing the strength and size
Size in general is the Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude or dimensions of a thing. More specifically, ''geometrical size'' (or ''spatial size'') can refer to three geometrical measures: length, area, or volume. Length can be generalized ...
of the lower body muscles as well as developing core strength. The primary agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an R ...
muscles used during the squat are the quadriceps femoris, the adductor magnus
The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh.
It consists of two parts. The portion which arises from the ischiopubic ramus (a small part of the inferior ramus of the pubis, and the inferior ramu ...
, and the gluteus maximus
The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle in ...
. The squat also isometrically uses the erector spinae and the abdominal muscles, among others.
The squat is one of the three lifts in the strength sport of powerlifting
Powerlifting is a competitive strength athletics, strength sport that consists of three attempts at maximal weight on three lifts: Squat (exercise), squat, bench press, and deadlift. As in the sport of Olympic weightlifting, it involves the athle ...
, together with the deadlift
The deadlift is a strength training exercise in which a weight-loaded barbell is lifted off the ground to the level of the hips, with the torso perpendicular to the floor, before being placed back on the ground. It is one of the three powerlifting ...
and the bench press
The bench press or chest press is a weight training exercise where a person presses a weight upwards while lying horizontally on a weight training bench. The bench press is a Compound movements, compound movement, with the primary muscles involved ...
. It is also considered a staple exercise in many popular recreational exercise programs.
Form
 The squat begins from a standing position. The squatting movement is initiated by moving the hips back and bending the knees and hips to lower the torso and accompanying weight, then returning to the upright position.
Weight is often added and is typically in the form of a loaded
The squat begins from a standing position. The squatting movement is initiated by moving the hips back and bending the knees and hips to lower the torso and accompanying weight, then returning to the upright position.
Weight is often added and is typically in the form of a loaded barbell
A barbell is a piece of exercise equipment used in weight training, bodybuilding, Olympic weightlifting, weightlifting, powerlifting and strongman, consisting of a long bar, usually with weights attached at each end.
Barbells range in length ...
. Dumbbells and kettlebells may also be used. When a barbell is used, it may be braced across the upper trapezius
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the human spine, spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and ...
muscle, which is termed a ''high bar squat'', or held lower across the back and rear deltoids, termed a ''low bar squat''. Various torso bracing techniques are used wherever the bar is placed on the back to prevent direct contact with the spine, which can cause pain and injury. This can be a problem for new squatters who squat in a ''high bar'' style as they may not have enough muscle mass to form a cushion for the bar and prevent it from applying pressure directly to their spine.
Squats can be performed to varying depths. The competition standard is for the crease of the hip (top surface of the leg at the hip joint) to fall below the top of the knee; this is colloquially known as "parallel" depth. Although it may be confusing, many other definitions for "parallel" depth abound, none of which represents the standard in organized powerlifting
Powerlifting is a competitive strength athletics, strength sport that consists of three attempts at maximal weight on three lifts: Squat (exercise), squat, bench press, and deadlift. As in the sport of Olympic weightlifting, it involves the athle ...
. From shallowest to deepest, these other standards are: bottom of hamstring
A hamstring () is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in human anatomy between the hip and the knee: from medial to lateral, the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris.
Etymology
The word " ham" is derived from the Old ...
parallel to the ground; the hip joint
In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxaLatin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) (: ''coxae'') in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint o ...
itself below the top of the knee, or femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
parallel to the floor; and the top of the upper thigh (i.e., top of the quadriceps
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large ...
) below the top of the knee. Squatting below parallel is considered a full or deep squat, while squatting above it qualifies as shallow. Though the forces on the ACL and PCL decrease at high flexion, compressive forces on the menisci and articular cartilages in the knee peak at these same high angles. This makes the relative safety of deep versus shallow squats difficult to determine.
As the body descends, the hips and knees undergo flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terminology, anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of Organ (anatomy), organs, joints, Limb (anatomy), limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used de ...
, the ankle extends ( dorsiflexes) and muscles around the joint contract eccentrically, reaching maximal contraction at the bottom of the movement while slowing and reversing descent. The muscles around the hips provide the power out of the bottom. If the knees slide forward or cave in then tension is taken from the hamstrings, hindering power on the ascent. Returning to vertical contracts the muscles concentrically, and the hips and knees undergo extension while the ankle plantarflexes.
Common errors of squat form include descending too rapidly and flexing the torso too far forward. Rapid descent risks being unable to complete the lift or causing injury. This occurs when the descent causes the brace to relax and tightness at the bottom is lost as a result. Over-flexing the torso greatly increases the forces exerted on the lower back, risking a spinal disc herniation
A disc herniation or spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, ...
. Another error is when the knee is not aligned with the direction of the toes, entering a valgus position, which can adversely stress the knee joint. An additional common error is the raising of heels off the floor, which reduces the contribution of the gluteus muscles.
Muscles used
Agonist muscles * Quadriceps femoris *Vastus lateralis
The vastus lateralis (), also called the vastus externus, is the largest and most powerful part of the quadriceps femoris, a muscle in the thigh. Together with other muscles of the quadriceps group, it serves to extend the knee joint, moving the ...
* Vastus medialis oblique
* Gluteus maximus
The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle in ...
* Adductor magnus
The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh.
It consists of two parts. The portion which arises from the ischiopubic ramus (a small part of the inferior ramus of the pubis, and the inferior ramu ...
* Soleus
Stabilizing muscles
* Erector spinae
* Rectus abdominis
The rectus abdominis muscle, () also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply better known as the "abs", is a pair of segmented skeletal muscle on the ventral aspect of a person, person's abdomen. The paired muscle is separated at the midline b ...
* Internal
Internal may refer to:
*Internality as a concept in behavioural economics
*Neijia, internal styles of Chinese martial arts
*Neigong or "internal skills", a type of exercise in meditation associated with Daoism
* ''Internal'' (album) by Safia, 2016 ...
and external obliques
* Hamstrings
A hamstring () is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in human anatomy between the hip and the knee: from anatomical_terms_of_location#Medial_and_lateral, medial to anatomical_terms_of_location#Medial_and_lateral, lateral, the semimembra ...
(Biceps femoris, semitendinosis, semimembranosis)
* Gluteus medius and minimus
The Minimus books are a series of school textbooks, written by Barbara Bell, illustrated by Helen Forte, and published by the Cambridge University Press, designed to help children of primary school age to learn Latin. The books espouse some of th ...
* Gastrocnemius
Equipment

 Various types of equipment can be used to perform squats.
A power cage can be used to reduce risk of injury and eliminate the need for a spotting partner. By putting the bar on a track, the Smith machine reduces the role of hip movement in the squat and in this sense resembles a leg press. Cornacchia, pp
Various types of equipment can be used to perform squats.
A power cage can be used to reduce risk of injury and eliminate the need for a spotting partner. By putting the bar on a track, the Smith machine reduces the role of hip movement in the squat and in this sense resembles a leg press. Cornacchia, pp121
Shoes
A shoe is an item of footwear intended to protect and comfort the human foot. Though the human foot can adapt to varied terrains and climate conditions, it is vulnerable, and shoes provide protection. Form was originally tied to function, but ...
) or shoe inserts which allow for a deeper squat. Wrist straps are another piece of recommended equipment; they support the wrist and help to keep it in a straightened position. They should be wrapped around the wrist, above and below the joint, thus limiting movement of the joint. Heel wedges and related equipment are discouraged by some as they are thought to worsen form over the long term.
Chains and thick elastic bands can be attached to either end of the barbell in order to vary resistance at different phases of the movement. This may be done to increase resistance in the stronger upper phase of the movement, in order to make the difficulty more consistent throughout the movement. Bands can also be used to reduce resistance in the lower, weaker phase by being hung from a power rack and the barbell being increasingly supported by them as it is lowered. This can help someone to overcome a 'sticking' point. A squat performed using these techniques is called a variable resistance squat.
Variants
 The squat has a number of variants, some of which can be combined:
The squat has a number of variants, some of which can be combined:
Barbell
*Back squat – the bar is held on the back of the body upon the upper trapezius muscle, near to the base of the neck. Alternatively, it may be held lower across the upper back and rear deltoids. Inpowerlifting
Powerlifting is a competitive strength athletics, strength sport that consists of three attempts at maximal weight on three lifts: Squat (exercise), squat, bench press, and deadlift. As in the sport of Olympic weightlifting, it involves the athle ...
the barbell is often held in a lower position in order to create a lever advantage, while in weightlifting
Weightlifting or weight lifting generally refers to physical exercises and sports in which people lift weights, often in the form of dumbbells, barbells or machines. People engage in weightlifting for a variety of different reasons. These can ...
it is often held in a higher position which produces a posture closer to that of the clean and jerk
The clean and jerk is a composite of two weightlifting movements, most often performed with a barbell: the clean and the jerk. During the ''clean'', the lifter moves the barbell from the floor to a racked position across the deltoids, without rest ...
. These variations are called low bar (or powerlifting squat) and high bar (or Olympic squat), respectively.
**Sumo squat – A variation of the back squat where the feet are placed slightly wider than shoulder width apart and the feet pointed outwards.
**Box squat – at the bottom of the motion the squatter will sit down on a bench or other type of support then rise again. The box squat is commonly utilized by powerlifters to train the squat.
*Front squat – the barbell is held in front of the body across the clavicle
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the scapula, shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavic ...
s and deltoids in either a clean grip, as is used in weightlifting
Weightlifting or weight lifting generally refers to physical exercises and sports in which people lift weights, often in the form of dumbbells, barbells or machines. People engage in weightlifting for a variety of different reasons. These can ...
, or with the arms crossed and hands placed on top of the barbell. In addition to the muscles used in the back squat, the front squat also uses muscles of the upper back such as the trapezius
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the human spine, spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and ...
to support the bar.
*Hack squat – the barbell is held in the hands just behind the legs; this exercise was first known as Hacke (heel) in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
. According to European strength sports expert and Germanist Emmanuel Legeard this name was derived from the original form of the exercise where the heels were joined. The hack squat was thus a squat performed the way Prussian soldiers used to click their heels ("Hacken zusammen"). The hack squat was popularized in the English-speaking countries
The English-speaking world comprises the 88 countries and territories in which English is an official, administrative, or cultural language. In the early 2000s, between one and two billion people spoke English, making it the largest language ...
by early 1900s wrestler George Hackenschmidt
Georg Karl Julius Hackenschmidt (1 August 1877 – 19 February 1968) was an Estonian Strongman (strength athlete), strongman, wrestling, amateur and Professional wrestling, professional wrestler, writer, and Philosophy of sport, sports philoso ...
. It is also called a ''rear deadlift
The deadlift is a strength training exercise in which a weight-loaded barbell is lifted off the ground to the level of the hips, with the torso perpendicular to the floor, before being placed back on the ground. It is one of the three powerlifting ...
''. It is different from the hack squat performed with the use of a squat machine.
*Overhead squat – the barbell is held overhead in a wide-arm snatch grip; however, it is also possible to use a closer grip if balance allows.
 *Zercher squat – the barbell is held in the crooks of the arms, on the inside of the elbow. One method of performing this is to deadlift the barbell, hold it against the thighs, squat into the lower portion of the squat, and then hold the bar on the thighs as you position the crook of your arm under the bar and then stand up. This sequence is reversed once the desired number of repetitions has been performed. Named after Ed Zercher, a 1930s strongman.
*Steinborn squat – named after the traditional strongman Henry 'Milo' Steinborn, and performed without a rack, the barbell begins on the floor. The lifter picks up one end, and lifts until it's nearly vertical, before bending to position it against their back, as if in a back squat. They then lower their hips, allowing the top of the bar to lower until the bar is straight across their back, with their body in the bottom of a squat. Normal back squats can be performed from this position.
*Deep knee bend on toes – it is similar to a normal back squat only the lifter is positioned on their forefeet and toes, with their heels raised, throughout the repetition. Usually, the weight used is not more than moderate in comparison to a flat footed, heavy back squat.
*Single leg squat - The single leg squat (SLS), also known as a unilateral squat, involves squatting with one leg instead of two (which is a bilateral squat). Usually the leg which is held off the ground moves behind the person as they squat, but alternatively the person may position it ahead of themselves. Bilateral split squats which significantly increase the work performed by the front leg are sometimes erroneously referred to as single leg squats due to this emphasis. Single leg squats can be used to strengthen a person's stabilizer muscles more so than two legged squats and improve their ability to balance. They can also be used to remove muscle imbalances in the body by ensuring that, when performed alternatively, the right and left leg do the same amount of work. In comparison to two footed squats, the barbell weight only needs to be half of what it would be, minus the lifter's weight for the legs to perform the same amount of work i.e. for an 80 kg lifter, lifting 40 kg using only the left leg, means the left leg is lifting the equivalent of what it does in a two footed squat with 160 kg. This means that the single leg squat can be used in rehabilitation programmes where there is a need to avoid heavier loading of the back.
*Loaded squat jump – the barbell is positioned similarly to a back squat. The exerciser squats down, before moving upwards into a jump, and then landing in approximately the same position. The loaded squat jump is a form of loaded plyometric exercise used to increase explosive power. Variations of this exercise may involve the use of a trap bar or dumbbells.
*Variable resistance squat – In keeping with variable resistance training in general, a variable resistance squat involves altering the resistance during the movement in order that it better matches, in percentage terms, the respective 1RM for each strength phase the person is moving through i.e. more resistance in the higher stronger phase and less in the weaker lower phase e.g. 60 kg in the lower phase and 90 kg in the higher phase. Such an alteration of resistance can be achieved by the use of heavy chains which are attached to either end of the barbell. The chains are gradually lifted from the floor as the barbell is raised and vice versa when it is lowered. Thick elastic bands which are more stretched in the higher phase and less stretched in the lower phase can also be used. Combining heavier partial reps with lighter full reps can also help to train the stronger and weaker phases of the movement so the percentage of 1RM lifted for each phase respectively is more similar. Training with variable resistance squats is a technique used to increase speed and explosive power.
*Partial rep – Partial rep squats only move through a partial range of movement when compared with full squats which move through a full range of movement. Full range for a squat usually means the higher stronger phase of a squat's strength phase sequence (strength curve), but may also refer to just squatting for the lower weaker phase. When partial squats are used to strengthen the higher ROM this usually involves significantly increasing the weight in comparison to the weight used for a full squat. The percentage lifted of the stronger higher phase's 1RM can therefore be increased and not limited by the requirement to move through the weaker lower range of movement e.g. a person lifts 100% of his 1RM for the higher stronger phase which is 150 kg. If he did a full squat he would only have been able to do about 66% of his stronger phases 1RM because his 1RM for a full squat, including the weaker lower phase, is 100 kg. Training with heavier partial squats can help to improve general strength and power. It can also be more beneficial for sports and athletics as that ROM is more likely to be required in those activities i.e. it is rare to need to perform a full squat in sport, whereas partial squatting happens frequently. Partial squatting with a heavier weight than a full squat allows for can also help to improve a person's 1RM for a full squat. When partial squatting only the lower phase this is usually to strengthen that relatively weak phase of the lift in order to overcome a sticking point i.e. a point a person gets "stuck" at and finds it difficult to progress past. It is commonly recommended that partial squats are best used in conjunction with full squats.
*Zercher squat – the barbell is held in the crooks of the arms, on the inside of the elbow. One method of performing this is to deadlift the barbell, hold it against the thighs, squat into the lower portion of the squat, and then hold the bar on the thighs as you position the crook of your arm under the bar and then stand up. This sequence is reversed once the desired number of repetitions has been performed. Named after Ed Zercher, a 1930s strongman.
*Steinborn squat – named after the traditional strongman Henry 'Milo' Steinborn, and performed without a rack, the barbell begins on the floor. The lifter picks up one end, and lifts until it's nearly vertical, before bending to position it against their back, as if in a back squat. They then lower their hips, allowing the top of the bar to lower until the bar is straight across their back, with their body in the bottom of a squat. Normal back squats can be performed from this position.
*Deep knee bend on toes – it is similar to a normal back squat only the lifter is positioned on their forefeet and toes, with their heels raised, throughout the repetition. Usually, the weight used is not more than moderate in comparison to a flat footed, heavy back squat.
*Single leg squat - The single leg squat (SLS), also known as a unilateral squat, involves squatting with one leg instead of two (which is a bilateral squat). Usually the leg which is held off the ground moves behind the person as they squat, but alternatively the person may position it ahead of themselves. Bilateral split squats which significantly increase the work performed by the front leg are sometimes erroneously referred to as single leg squats due to this emphasis. Single leg squats can be used to strengthen a person's stabilizer muscles more so than two legged squats and improve their ability to balance. They can also be used to remove muscle imbalances in the body by ensuring that, when performed alternatively, the right and left leg do the same amount of work. In comparison to two footed squats, the barbell weight only needs to be half of what it would be, minus the lifter's weight for the legs to perform the same amount of work i.e. for an 80 kg lifter, lifting 40 kg using only the left leg, means the left leg is lifting the equivalent of what it does in a two footed squat with 160 kg. This means that the single leg squat can be used in rehabilitation programmes where there is a need to avoid heavier loading of the back.
*Loaded squat jump – the barbell is positioned similarly to a back squat. The exerciser squats down, before moving upwards into a jump, and then landing in approximately the same position. The loaded squat jump is a form of loaded plyometric exercise used to increase explosive power. Variations of this exercise may involve the use of a trap bar or dumbbells.
*Variable resistance squat – In keeping with variable resistance training in general, a variable resistance squat involves altering the resistance during the movement in order that it better matches, in percentage terms, the respective 1RM for each strength phase the person is moving through i.e. more resistance in the higher stronger phase and less in the weaker lower phase e.g. 60 kg in the lower phase and 90 kg in the higher phase. Such an alteration of resistance can be achieved by the use of heavy chains which are attached to either end of the barbell. The chains are gradually lifted from the floor as the barbell is raised and vice versa when it is lowered. Thick elastic bands which are more stretched in the higher phase and less stretched in the lower phase can also be used. Combining heavier partial reps with lighter full reps can also help to train the stronger and weaker phases of the movement so the percentage of 1RM lifted for each phase respectively is more similar. Training with variable resistance squats is a technique used to increase speed and explosive power.
*Partial rep – Partial rep squats only move through a partial range of movement when compared with full squats which move through a full range of movement. Full range for a squat usually means the higher stronger phase of a squat's strength phase sequence (strength curve), but may also refer to just squatting for the lower weaker phase. When partial squats are used to strengthen the higher ROM this usually involves significantly increasing the weight in comparison to the weight used for a full squat. The percentage lifted of the stronger higher phase's 1RM can therefore be increased and not limited by the requirement to move through the weaker lower range of movement e.g. a person lifts 100% of his 1RM for the higher stronger phase which is 150 kg. If he did a full squat he would only have been able to do about 66% of his stronger phases 1RM because his 1RM for a full squat, including the weaker lower phase, is 100 kg. Training with heavier partial squats can help to improve general strength and power. It can also be more beneficial for sports and athletics as that ROM is more likely to be required in those activities i.e. it is rare to need to perform a full squat in sport, whereas partial squatting happens frequently. Partial squatting with a heavier weight than a full squat allows for can also help to improve a person's 1RM for a full squat. When partial squatting only the lower phase this is usually to strengthen that relatively weak phase of the lift in order to overcome a sticking point i.e. a point a person gets "stuck" at and finds it difficult to progress past. It is commonly recommended that partial squats are best used in conjunction with full squats.
Lunge
*Split squat – an assisted one-legged squat where the non-lifting leg is rested on the ground a few steps behind the lifter, as if it were a static lunge. *Bulgarian split squat – performed similarly to a split squat, but the foot of the non-lifting leg is rested on a platform behind the lifter.Other
*Belt squat – is an exercise performed the same as other squat variations except the weight is attached to a hip belt i.e. a dip belt *Goblet squat – a squat performed while holding a kettlebell or dumbbell on to one's chest and abdomen with both hands. *Smith squat – a squat using a Smith machine. * Machine hack squat – using a squat machine. *Trap bar squat – a trap bar is held in the hands while squats are performed. More commonly referred to as "trap bar deadlifts." *Monolift squat – a squat using a monolift rack. *Safety squat – a squat performed using a ''safety squat bar'' which has a camber in the middle, two handles, and padding. The use of a safety squat bar may help to reduce the risk of causing or aggravating an injury.
*Anderson squat - (aka Pin Squat, Bottoms Up Squat) starting the squat from the bottom position.
*Safety squat – a squat performed using a ''safety squat bar'' which has a camber in the middle, two handles, and padding. The use of a safety squat bar may help to reduce the risk of causing or aggravating an injury.
*Anderson squat - (aka Pin Squat, Bottoms Up Squat) starting the squat from the bottom position.
Body-weight
*Body-weight or air squat – done with no weight or barbell, often at higher repetitions than other variants. *Overhead squat – a non-weight bearing variation of the squat exercise, with the hands facing each other overhead, biceps aligned with the ears, and feet hip-width apart. This exercise is a predictor of total-body flexibility, mobility, and possible lower body dysfunction. *Hindu squat – also called a baithak, or a deep knee bend on toes. It is performed without additional weight, and body weight placed on the forefeet and toes with the heels raised throughout; during the movement the knees track far past the toes. The baithak was a staple exercise of ancient Indian wrestlers. It was also used byBruce Lee
Bruce Lee (born Lee Jun-fan; November 27, 1940 – July 20, 1973) was an American-born Hong Kong martial artist, actor, filmmaker, and philosopher. He was the founder of Jeet Kune Do, a hybrid martial arts philosophy which was formed from ...
in his training regime. It may also be performed with the hands resting on an upturned club or the back of a chair.
*Jump squat – a plyometrics
Plyometrics, also known as jump training or plyos, are exercises in which muscles exert maximum force in short intervals of time, with the goal of increasing power (speed-strength). This training focuses on learning to move from a muscle exten ...
exercise where the squatter engages in a rapid eccentric contraction and jumps forcefully off the floor at the top of the range of motion.
 *Basic single leg squat – the person stands with one foot on the ground and the other foot raised. They bend their standing leg and move downwards. Their raised leg moves behind them with the knee coming close to the heel of the grounded foot. Due to the extra effort required to balance, one legged squats can help to additionally improve a person's sense of balance. As with other forms of one legged exercise performed alternately, they can also help to mitigate against an excessive strength variation between the legs, as both legs are made to perform the same level of work e.g. in a two legged squat a person's right leg may do 55% of the work and their left leg 45%, which may result in an excessively uneven level of strength developing. By switching between using the right leg and left leg in one legged squats, a person can better ensure that each leg is doing the same level of work i.e. the right or left leg does 100% of the work for each respective one legged squat.
*Pistol squat – a bodyweight single leg squat done to full depth, while the other leg is extended off the floor and positioned somewhere in front. Sometimes dumbbells, kettlebells or medicine balls are added for resistance. Pistol squats may be performed with the foot flat on the floor or with the heel raised.
*Shrimp squat – also called the ''flamingo squat'', a version of the pistols squat where instead of extending the non-working leg out in front, it is bent and placed behind the working leg while squatting, perhaps held behind in a hand. Shrimp squats may be performed with the foot flat on the floor or with the heel raised.
*Jockey squat - a half-squat, performed by being balanced on the forefeet throughout the repetition, with fingertips touching across the chest. This squat can be performed quickly and in high repetitions.
*Basic single leg squat – the person stands with one foot on the ground and the other foot raised. They bend their standing leg and move downwards. Their raised leg moves behind them with the knee coming close to the heel of the grounded foot. Due to the extra effort required to balance, one legged squats can help to additionally improve a person's sense of balance. As with other forms of one legged exercise performed alternately, they can also help to mitigate against an excessive strength variation between the legs, as both legs are made to perform the same level of work e.g. in a two legged squat a person's right leg may do 55% of the work and their left leg 45%, which may result in an excessively uneven level of strength developing. By switching between using the right leg and left leg in one legged squats, a person can better ensure that each leg is doing the same level of work i.e. the right or left leg does 100% of the work for each respective one legged squat.
*Pistol squat – a bodyweight single leg squat done to full depth, while the other leg is extended off the floor and positioned somewhere in front. Sometimes dumbbells, kettlebells or medicine balls are added for resistance. Pistol squats may be performed with the foot flat on the floor or with the heel raised.
*Shrimp squat – also called the ''flamingo squat'', a version of the pistols squat where instead of extending the non-working leg out in front, it is bent and placed behind the working leg while squatting, perhaps held behind in a hand. Shrimp squats may be performed with the foot flat on the floor or with the heel raised.
*Jockey squat - a half-squat, performed by being balanced on the forefeet throughout the repetition, with fingertips touching across the chest. This squat can be performed quickly and in high repetitions.
 *Sissy squat – the knees travel over the toes, stretching the quadriceps and the body leans backwards. Can be done in a special sissy squat machine, and can also be weighted.
*Sumo Squat - also known as ''Plie Squat'', in this variation legs are wider than shoulder width.
*Sissy squat – the knees travel over the toes, stretching the quadriceps and the body leans backwards. Can be done in a special sissy squat machine, and can also be weighted.
*Sumo Squat - also known as ''Plie Squat'', in this variation legs are wider than shoulder width.
Clinical significance
The squat is a large muscle-mass resistance exercise. As such, squats produce acute increases intestosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
(especially in men) and growth hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in ...
(especially in women). Although insulin-like growth factor 1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called somatomedin C, is a hormone similar in tertiary structure, molecular structure to insulin which plays an important role in childhood growth, and has Anabolism, anabolic effects in adults. In the ...
(IGF-1) is not raised acutely by squat exercise, resistance-trained men and women have higher resting IGF-1. Catecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA), most typically a 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine, is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine.
Cate ...
s (epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
, norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
, and dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
) are acutely elevated by resistance exercise, such as squats.
The squat has been used in clinical settings to strengthen lower body musculature with little or no harm after joint-related injury. Young people may benefit by enhanced athletic performance and reduced injury as they mature, and movement competency can ensure independent living in the elderly.
Injury considerations
Although the squat has long been a basic element of weight training, it has not been without controversy over its safety. Some trainers claim that squats are associated with injuries to thelumbar spine
The lumbar vertebrae are located between the thoracic vertebrae and pelvis. They form the lower part of the back in humans, and the tail end of the back in quadrupeds. In humans, there are five lumbar vertebrae. The term is used to describe t ...
and knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ...
s. Cornacchia, p120
Others, however, continue to advocate the squat as one of the best exercises for building muscle and strength. Some coaches maintain that incomplete squats (those terminating above parallel) are both less effective and more likely to cause injury than full squat (terminating with hips at or below knee level). A 2013 review concluded that deep squats performed with proper technique do not lead to increased rates of degenerative knee injuries and are an effective exercise. The same review also concluded that shallower squats may lead to degeneration in the lumbar spine and knees in the long-term.
Squats used in physical therapy
Squats can be used for some rehabilitative activities because they hone stability without excessive compression on the tibiofemoral joint and anterior cruciate ligament. Deeper squats are associated with higher compressive loads on patellofemoral joint and it is possible that people who suffer from pain in this joint cannot squat at increased depths. For some knee rehabilitation activities, patients might feel more comfortable with knee flexion between 0 and 50 degrees because it places less force compared to deeper depths. Another study shows that decline squats at angles higher than 16 degrees may not be beneficial for the knee and fail to decrease calf tension. Other studies have indicated that the best squat to hone the quadriceps, without inflaming the patellofemoral joint, occurs between 0 and 50 degrees. A combination of single-limb squats and decline angles has been used to rehabilitate knee extensors. Conducting squats at a declined angle allows the knee to flex despite possible pain or lack of mobilization in the ankle. If therapists are looking to focus on the knee during squats, one study shows that doing single-limb squats at a 16-degree decline angle has the greatest activation of the knee extensors without placing excessive pressure on the ankles. This same study also found that a 24-degree decline angle can be used to strengthen ankles and knee extensors. Different Sets For Squats Forced repetitions are used when training until failure. They are completed by completing an additional 2–4 reps (assisted) at the end of the set. Partial repetitions are also used in order to maintain a constant period of tension in order to promote hypertrophy. Lastly, drop-sets are an intense workout done at the end of a set which runs until failure and continues with a lower weight without rest.World records
Men
* Equipped squat (with multi-ply suit and wraps) – by Nathan Baptist (2021) * Raw squat (with wraps) – by Vladislav Alhazov (2018) * Raw squat (with sleeves) – by Ray Orlando Williams (2019) * Raw squat (without sleeves or wraps) – by Paul Anderson (1965) * Playboy bunny smith machine squat – by Don Reinhoudt (1979) * Cement block smith machine squat – by Bill Kazmaier (1981) * Double T 'cambered bar' squat (with single-ply suit) – by JF Caron (2022) * Steinborn squat – by Martins Licis (2019) * Squat for reps – (Raw) for 5 reps by Paul Anderson (1965) * Squat for reps – (Raw) for 4 reps by Eric Lilliebridge (2014) * Squat for reps – (Raw) for 5 reps (paused) by Hafþór JĂşlĂus Björnsson (2024) * Squat for reps – (Raw) for 7 reps by Jesus Olivares (2023) * Squat for reps – (Raw) for 2 sets of 10 reps by Paul Anderson (1957) * Squat for reps – (Raw) for 12 reps by Zahir Khudayarov (2024) * Squat for reps – (with singly ply suit) for 15 reps in one minute by Ĺ˝ydrĹ«nas Savickas (2014) * Squat for reps – (with singly ply suit) for 23 reps in one minute by Tom Platz (1993) * Squat for reps – (Raw) for 29 reps in one minute by Hafþór JĂşlĂus Björnsson (2017) * Squat for reps – (own bodyweight) for 42 reps in one minute by Erikas DovydÄ—nas (2022) * Most squats in one minute (no added weight/ bodyweight only) – 84 reps by Tourab Nesanah (2022) * Most pistol squats in one minute (no added weight/ bodyweight only) – 52 reps by William Rauhaus (2016) * Most squats in one hour (no added weight/ bodyweight only) – 4,708 reps by Paddy Doyle (2007) * Most squats in one day (no added weight/ bodyweight only) – 25,000 reps by Joe Reverdes (2020)Women
* Equipped squat (with multi-ply suit and wraps) – by Leah Reichman (2023) * Equipped squat (with single-ply suit and wraps) – by Galina Karpova (2012) * Raw squat (with wraps) – by April Mathis (2017) * Raw squat (with sleeves) – by Sonita Muluh (2024) * Squat for reps – (with singly ply suit) for 29 reps in two minutes by Maria Strik (2013) * Squat for reps – (own bodyweight) for 42 reps in one minute by Karenjeet Bains (2022) * Most sumo squats in one hour (no added weight/ bodyweight only) – 5,135 reps by Thienna Ho (2007)See also
*Squatting position
Squatting is a versatile List of human positions, posture where the weight of the body is on the feet but the knees and hips are bent. In contrast, sitting involves supporting the weight of the body on the ischial tuberosities of the pelvis, with ...
* Smith machine
Notes
References
Bibliography
*External links
WebMD summary of health benefits of squats
Video of squat recommendations with demonstration by a chiropractor
{{DEFAULTSORT:Squat (Exercise) Powerlifting Weight training exercises Bodyweight exercises Physical exercise Squatting position