Spurline Microstrip on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The spurline is a type of
 Where is the
Where is the
"Exact design of band-stop microwave filters"
''IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques'', vol. 12, iss. 1, pp. 6-15, 1964. * R. N. Bates
"Design of microstrip spur-line band-stop filters"
''IEEE Journal on Microwave Optics and Acoustics'', vol. 1, iss. 6, pp. 209-204, November 1977. * C. Nguyen; C. Hsieh
Millimeter wave printed circuit spurline filters"
''IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest'', pp. 98-100, 1983. Microwave technology Distributed element circuits {{tech-stub
radio-frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upper ...
and microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different fre ...
distributed element filter with band-stop
In signal processing, a band-stop filter or band-rejection filter is a filter that passes most frequencies unaltered, but attenuates those in a specific range to very low levels. It is the opposite of a band-pass filter. A notch filter is ...
(notch) characteristics, most commonly used with microstrip
Microstrip is a type of electrical transmission line which can be fabricated with any technology where a conductor is separated from a ground plane by a dielectric layer known as the substrate. Microstrip lines are used to convey microwave-freque ...
transmission lines. Spurlines usually exhibit moderate to narrow-band rejection, at about 10% around the central frequency.
Spurline filters are very convenient for dense integrated circuits
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Transistor count, Large ...
because of their inherently compact design and ease of integration: they occupy surface that corresponds only to a quarter-wavelength transmission line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmi ...
.
Structure description
It consists of a normalmicrostrip
Microstrip is a type of electrical transmission line which can be fabricated with any technology where a conductor is separated from a ground plane by a dielectric layer known as the substrate. Microstrip lines are used to convey microwave-freque ...
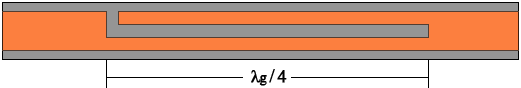
line breaking into a pair of smaller coupled lines that rejoin after a quarter-wavelength distance. Only one of the input ports of the coupled lines is connected to the feed microstrip, as shown in the figure below. The orange area of the illustration is the microstrip transmission line conductor and the gray color the exposed dielectric.
 Where is the
Where is the wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tr ...
corresponding to the central rejection frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from '' angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is ...
of the bandstop filter, measured - of course - in the microstrip line material. This is the most important parameter of the filter that sets the rejection band.
The distance between the two coupled lines can be selected appropriately to fine-tune the filter. The smaller the distance, the narrower the stop-band in terms of rejection. Of course that is limited by the circuit-board printing resolution, and it is usually considered at about 10% of the input microstrip width.
The gap between the input microstrip line and the one open-circuited line of the coupler has a negligible effect on the frequency response of the filter. Therefore, it is considered approximately equal to the distance of the two coupled lines.
Printed antennae
Spurlines can also be used in printed antennae such as the planar inverted-F antenna. The additional resonances can be designed to widen the antenna bandwidth or to create multiple bands, for instance, for atri-band
In telecommunications, a multi-band device (including (2) dual-band, (3) tri-band, (4) quad-band and (5) penta-band devices) is a communication device (especially a mobile phone) that supports multiple radio frequency bands. All devices which ha ...
mobile phone.
History
A spurline filter was first proposed by Schiffman and Matthaei instripline
Stripline is a transverse electromagnetic (TEM) transmission line medium invented by Robert M. Barrett of the Air Force Cambridge Research Centre in the 1950s. Stripline is the earliest form of planar transmission line.
Description
A stri ...
form in 1964. Bates adapted the design for microstrip in 1977. Nguyen and Hsieh improved the analysis for microstrip implementations in 1983.Cam Nguyen; Kai Chang, "Millimeter wave planar integrated circuit filters", ch. 2 in Kenneth Button (ed), ''Topics in Millimeter Wave Technology: Volume 1'', p. 177, Elsevier, 2012 .
References
* C. Nguyen and K. Chang, “On the analysis and design of spurline bandstop filters,” IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 33, no. 12, pp. 1416–1421, Dec. 1985.Primary sources
* B. M. Schiffman; G. L. Matthaei"Exact design of band-stop microwave filters"
''IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques'', vol. 12, iss. 1, pp. 6-15, 1964. * R. N. Bates
"Design of microstrip spur-line band-stop filters"
''IEEE Journal on Microwave Optics and Acoustics'', vol. 1, iss. 6, pp. 209-204, November 1977. * C. Nguyen; C. Hsieh
Millimeter wave printed circuit spurline filters"
''IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest'', pp. 98-100, 1983. Microwave technology Distributed element circuits {{tech-stub