


A space suit (or spacesuit) is an
environmental suit used for protection from the harsh
environment of outer space, mainly from its
vacuum
A vacuum (: vacuums or vacua) is space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective (neuter ) meaning "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressur ...
as a highly specialized
pressure suit
A pressure suit is a protective suit worn by high-altitude pilots who may fly at altitudes where the air pressure is too low for an unprotected person to survive, even when breathing pure oxygen at positive pressure. Such suits may be either fu ...
, but also its temperature extremes, as well as
radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
and
micrometeoroid
A micrometeoroid is a tiny meteoroid: a small particle of rock in space, usually weighing less than a gram. A micrometeorite is such a particle that survives passage through Earth's atmosphere and reaches Earth's surface.
The term "micrometeoro ...
s. Basic space suits are worn as a safety precaution inside
spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
s in case of loss of
cabin pressure. For
extravehicular activity
Extravehicular activity (EVA) is any activity done by an astronaut in outer space outside a spacecraft. In the absence of a breathable atmosphere of Earth, Earthlike atmosphere, the astronaut is completely reliant on a space suit for environme ...
(EVA) more complex space suits are worn, featuring a
portable life support system.
Pressure suits are in general needed at low pressure environments above the
Armstrong limit
The Armstrong limit or Armstrong's line is a measure of altitude above which atmospheric pressure is sufficiently low that water boiling, boils at the human body temperature, normal temperature of the human body. Exposure to pressure below this li ...
, at around above Earth. Space suits augment pressure suits with complex system of equipment and environmental systems designed to keep the wearer comfortable, and to minimize the effort required to bend the limbs, resisting a soft pressure garment's natural tendency to stiffen against the vacuum. A self-contained
oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
supply and environmental control system is frequently employed to allow complete freedom of movement, independent of the spacecraft.
Three types of space suits exist for different purposes: IVA (intravehicular activity), EVA (extravehicular activity), and IEVA (intra/extravehicular activity). IVA suits are meant to be worn inside a pressurized spacecraft, and are therefore lighter and more comfortable. IEVA suits are meant for use inside and outside the spacecraft, such as the
Gemini G4C suit. They include more protection from the harsh conditions of space, such as protection from micrometeoroids and extreme temperature change. EVA suits, such as the
EMU
The emu (; ''Dromaius novaehollandiae'') is a species of flightless bird endemism, endemic to Australia, where it is the Tallest extant birds, tallest native bird. It is the only extant taxon, extant member of the genus ''Dromaius'' and the ...
, are used outside spacecraft, for either planetary exploration or spacewalks. They must protect the wearer against all conditions of space, as well as provide mobility and functionality.
[
The first full-pressure suits for use at extreme altitudes were designed by individual inventors as early as the 1930s. The first space suit worn by a human in space was the ]Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
SK-1 suit worn by Yuri Gagarin
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin; Gagarin's first name is sometimes transliterated as ''Yuriy'', ''Youri'', or ''Yury''. (9 March 1934 – 27 March 1968) was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who, aboard the first successful Human spaceflight, crewed sp ...
in 1961. Since then space suits have been worn beside in Earth orbit, en-route and on the surface of the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
.
Requirements
 A space suit must perform several functions to allow its occupant to work safely and comfortably, inside or outside a spacecraft. It must provide:
* A stable internal pressure. This can be less than Earth's atmosphere, as there is usually no need for the space suit to carry
A space suit must perform several functions to allow its occupant to work safely and comfortably, inside or outside a spacecraft. It must provide:
* A stable internal pressure. This can be less than Earth's atmosphere, as there is usually no need for the space suit to carry nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
(which comprises about 78% of Earth's atmosphere and is not used by the body). Lower pressure allows for greater mobility, but requires the suit occupant to breathe pure oxygen for a time before going into this lower pressure, to avoid decompression sickness
Decompression sickness (DCS; also called divers' disease, the bends, aerobullosis, and caisson disease) is a medical condition caused by dissolved gases emerging from Solution (chemistry), solution as bubbles inside the body tissues during D ...
.
* Mobility. Movement is typically opposed by the pressure of the suit; mobility is achieved by careful joint design. See the ''Design concepts
A design is the concept or proposal for an object, process, or system. The word ''design'' refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, and is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something ...
'' section.
* Supply of breathable oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
; these gases are exchanged with the spacecraft or a Portable Life Support System (PLSS)
* Temperature regulation. Unlike on Earth, where heat can be transferred by convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoy ...
to the atmosphere, in space, heat can be lost only by thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electro ...
or by conduction
Conductor or conduction may refer to:
Biology and medicine
* Bone conduction, the conduction of sound to the inner ear
* Conduction aphasia, a language disorder
Mathematics
* Conductor (ring theory)
* Conductor of an abelian variety
* Condu ...
to objects in physical contact with the exterior of the suit. Since the temperature on the outside of the suit varies greatly between sunlight and shadow, the suit is heavily insulated, and air temperature is maintained at a comfortable level.
* A communication system, with external electrical connection to the spacecraft or PLSS
*  Means of collecting and containing solid and liquid bodily waste (such as a
Means of collecting and containing solid and liquid bodily waste (such as a Maximum Absorbency Garment
A Maximum Absorbency Garment (MAG) is an adult-sized diaper with extra absorption material that NASA astronauts wear during liftoff, landing, and Extra-vehicular activity, extra-vehicular activity (EVA) to absorb urine and feces. It is worn by bot ...
)
Secondary requirements
 Advanced suits better regulate the
Advanced suits better regulate the astronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a List of human spaceflight programs, human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member of a spa ...
's temperature with a Liquid Cooling and Ventilation Garment (LCVG) in contact with the astronaut's skin, from which the heat is dumped into space through an external radiator in the PLSS.
Additional requirements for EVA include:
* Shielding against ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
radiation
* Limited shielding against particle radiation
Particle radiation is the radiation of energy by means of fast-moving subatomic particles. Particle radiation is referred to as a particle beam if the particles are all moving in the same direction, similar to a light beam.
Due to the wave–p ...
* Means to maneuver, dock, release, and tether onto a spacecraft
* Protection against small micrometeoroid
A micrometeoroid is a tiny meteoroid: a small particle of rock in space, usually weighing less than a gram. A micrometeorite is such a particle that survives passage through Earth's atmosphere and reaches Earth's surface.
The term "micrometeoro ...
s, some traveling at up to 27,000 kilometers per hour, provided by a puncture-resistant Thermal Micrometeoroid Garment
An (Integrated) Thermal Micrometeoroid Garment (TMG or ITMG) is the outer layer of a space suit. The TMG has three functions: to insulate the suit occupant and prevent heat loss, to shield the occupant from harmful solar radiation, and to prote ...
, which is the outermost layer of the suit. Experience has shown the greatest chance of exposure occurs near the gravitational field
In physics, a gravitational field or gravitational acceleration field is a vector field used to explain the influences that a body extends into the space around itself. A gravitational field is used to explain gravitational phenomena, such as ...
of a moon or planet, so these were first employed on the Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
lunar EVA suits (see '' United States suit models'' below).
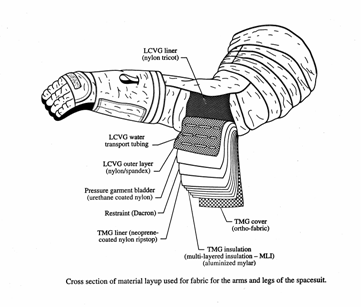 As part of astronautical hygiene control (i.e., protecting astronauts from extremes of temperature, radiation, etc.), a space suit is essential for extravehicular activity. The Apollo/Skylab A7L suit included eleven layers in all: an inner liner, a LCVG, a pressure bladder, a restraint layer, another liner, and a Thermal Micrometeoroid Garment consisting of five aluminized insulation layers and an external layer of white Ortho-Fabric. This space suit is capable of protecting the astronaut from temperatures ranging from to .
During exploration of the Moon or Mars, there will be the potential for lunar or Martian dust to be retained on the space suit. When the space suit is removed on return to the spacecraft, there will be the potential for the dust to contaminate surfaces and increase the risks of inhalation and skin exposure. Astronautical hygienists are testing materials with reduced dust retention times and the potential to control the dust exposure risks during planetary exploration. Novel ingress and egress approaches, such as suitports, are being explored as well.
In
As part of astronautical hygiene control (i.e., protecting astronauts from extremes of temperature, radiation, etc.), a space suit is essential for extravehicular activity. The Apollo/Skylab A7L suit included eleven layers in all: an inner liner, a LCVG, a pressure bladder, a restraint layer, another liner, and a Thermal Micrometeoroid Garment consisting of five aluminized insulation layers and an external layer of white Ortho-Fabric. This space suit is capable of protecting the astronaut from temperatures ranging from to .
During exploration of the Moon or Mars, there will be the potential for lunar or Martian dust to be retained on the space suit. When the space suit is removed on return to the spacecraft, there will be the potential for the dust to contaminate surfaces and increase the risks of inhalation and skin exposure. Astronautical hygienists are testing materials with reduced dust retention times and the potential to control the dust exposure risks during planetary exploration. Novel ingress and egress approaches, such as suitports, are being explored as well.
In NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
space suits, communications are provided via a cap worn over the head, which includes earphones and a microphone. Due to the coloration of the version used for Apollo and Skylab
Skylab was the United States' first space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three trios of astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Skylab was constructe ...
, which resembled the coloration of the comic strip character Snoopy
Snoopy is an anthropomorphic beagle in the comic strip ''Peanuts'' by American cartoonist Charles M. Schulz. He also appears in all of the ''Peanuts'' films and television specials. Since his debut on October 4, 1950, Snoopy has become one of ...
, these caps became known as " Snoopy caps".
Operating pressure
 Generally, to supply enough oxygen for respiration, a space suit using pure oxygen must have a pressure of about , equal to the
Generally, to supply enough oxygen for respiration, a space suit using pure oxygen must have a pressure of about , equal to the partial pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal g ...
of oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weathe ...
at sea level, plus and water vapor
Water vapor, water vapour, or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of Properties of water, water. It is one Phase (matter), state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from th ...
pressure, both of which must be subtracted from the alveolar pressure to get alveolar oxygen partial pressure in 100% oxygen atmospheres, by the alveolar gas equation
The alveolar gas equation is the method for calculating partial pressure of alveolar oxygen (). The equation is used in assessing if the lungs are properly transferring oxygen into the blood. The alveolar air equation is not widely used in clini ...
. The latter two figures add to , which is why many modern space suits do not use , but (this is a slight overcorrection, as alveolar partial pressures at sea level are slightly less than the former). In space suits that use 20.7 kPa, the astronaut gets only 20.7 kPa − 11.6 kPa = of oxygen, which is about the alveolar oxygen partial pressure attained at an altitude of above sea level. This is about 42% of normal partial pressure of oxygen at sea level, about the same as pressure in a commercial passenger jet aircraft, and is the realistic lower limit for safe ordinary space suit pressurization which allows reasonable capacity for work.
Oxygen prebreathing
When space suits below a specific operating pressure are used from craft that are pressurized to normal atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013. ...
(such as the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
), this requires astronauts to "pre-breathe" (meaning pre-breathe pure oxygen for a period) before donning their suits and depressurizing in the air lock. This procedure purges the body of dissolved nitrogen, so as to avoid decompression sickness due to rapid depressurization from a nitrogen-containing atmosphere.
Physiological effects of unprotected space exposure
The human body can briefly survive the hard vacuum of space unprotected,science fiction
Science fiction (often shortened to sci-fi or abbreviated SF) is a genre of speculative fiction that deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts. These concepts may include information technology and robotics, biological manipulations, space ...
. Consciousness is retained for up to 15 seconds as the effects of oxygen starvation set in. No snap freeze effect occurs because all heat must be lost through thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electro ...
or the evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evapora ...
of liquids, and the blood does not boil because it remains pressurized within the body, but human flesh expands up to about twice its volume due to ebullism
Ebullism is the formation of water vapour bubbles in bodily fluids due to reduced environmental pressure, usually at extreme high altitude. It occurs because a system of liquid and gas at equilibrium will see a net conversion of liquid to gas as ...
in such conditions, giving the visual effect of a body builder rather than an overfilled balloon.subatomic particle
In physics, a subatomic particle is a particle smaller than an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a baryon, lik ...
s that can cause radiation damage by disrupting essential biological processes. Exposure to radiation can create problems via two methods: the particles can react with water in the human body to produce free radicals
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired electron, unpaired valence electron.
With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemical reaction, chemi ...
that break DNA molecules apart, or by directly breaking the DNA molecules.[
The vacuum environment of space has no pressure, so gases will expand and exposed liquids may evaporate. Some solids may sublimate. It is necessary to wear a suit that provides sufficient internal body pressure in space.][ The most immediate hazard is in attempting to hold one's breath during ]explosive decompression
An uncontrolled decompression is an undesired drop in the pressure of a sealed system, such as a pressurised aircraft cabin or hyperbaric chamber, that typically results from human error, structural failure, or impact, causing the pressurised v ...
as the expansion of gas can damage the lungs by overexpansion rupture. These effects have been confirmed through various accidents (including in very-high-altitude conditions, outer space and training vacuum chamber
A vacuum chamber is a rigid enclosure from which air and other gases are removed by a vacuum pump. This results in a low-pressure environment within the chamber, commonly referred to as a vacuum. A vacuum environment allows researchers to c ...
s).helmet
A helmet is a form of protective gear worn to protect the head. More specifically, a helmet complements the skull in protecting the human brain. Ceremonial or symbolic helmets (e.g., a policeman's helmet in the United Kingdom) without protecti ...
for containing breathing gas
A breathing gas is a mixture of gaseous chemical elements and compounds used for respiration. Air is the most common and only natural breathing gas, but other mixtures of gases, or pure oxygen, are also used in breathing equipment and enclosed ...
es, known as a space activity suit (SAS).
Design concepts
 A space suit should allow its user natural unencumbered movement. Nearly all designs try to maintain a constant volume no matter what movements the wearer makes. This is because
A space suit should allow its user natural unencumbered movement. Nearly all designs try to maintain a constant volume no matter what movements the wearer makes. This is because mechanical work
In science, work is the energy transferred to or from an object via the application of force along a displacement. In its simplest form, for a constant force aligned with the direction of motion, the work equals the product of the force stre ...
is needed to change the volume of a constant pressure system. If flexing a joint reduces the volume of the space suit, then the astronaut must do extra work every time they bend that joint, and they have to maintain a force to keep the joint bent. Even if this force is very small, it can be seriously fatiguing to constantly fight against one's suit. It also makes delicate movements very difficult. The work required to bend a joint is dictated by the formula
:
where ''Vi'' and ''Vf'' are respectively the initial and final volume of the joint, ''P'' is the pressure in the suit, and ''W'' is the resultant work. It is generally true that all suits are more mobile at lower pressures. However, because a minimum internal pressure is dictated by life support requirements, the only means of further reducing work is to minimize the change in volume.
All space suit designs try to minimize or eliminate this problem. The most common solution is to form the suit out of multiple layers. The bladder layer is a rubbery, airtight layer much like a balloon. The restraint layer goes outside the bladder, and provides a specific shape for the suit. Since the bladder layer is larger than the restraint layer, the restraint takes all of the stresses caused by the pressure inside the suit. Since the bladder is not under pressure, it will not "pop" like a balloon, even if punctured. The restraint layer is shaped in such a way that bending a joint causes pockets of fabric, called "gores", to open up on the outside of the joint, while folds called "convolutes" fold up on the inside of the joint. The gores make up for the volume lost on the inside of the joint, and keep the suit at a nearly constant volume. However, once the gores are opened all the way, the joint cannot be bent any further without a considerable amount of work.
In some Russian space suits, strips of cloth were wrapped tightly around the cosmonaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a List of human spaceflight programs, human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member of a spa ...
's arms and legs outside the space suit to stop the space suit from ballooning when in space.
The outermost layer of a space suit, the Thermal Micrometeoroid Garment, provides thermal insulation, protection from micrometeoroids, and shielding from harmful solar radiation
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrared (typically p ...
.
There are four main conceptual approaches to suit design:

Soft suits
Soft suits typically are made mostly of fabrics. All soft suits have some hard parts; some even have hard joint bearings. Intra-vehicular activity and early EVA suits were soft suits.
Hard-shell suits
Hard-shell suits are usually made of metal or composite materials and do not use fabric for joints. Hard suits joints use ball bearings and wedge-ring segments similar to an adjustable elbow of a stove pipe to allow a wide range of movement with the arms and legs. The joints maintain a constant volume of air internally and do not have any counter-force. Therefore, the astronaut does not need to exert to hold the suit in any position. Hard suits can also operate at higher pressures which would eliminate the need for an astronaut to pre-breathe oxygen to use a space suit before an EVA from a spacecraft cabin. The joints may get into a restricted or locked position requiring the astronaut to manipulate or program the joint. The NASA Ames Research Center
The Ames Research Center (ARC), also known as NASA Ames, is a major NASA research center at Moffett Federal Airfield in California's Silicon Valley. It was founded in 1939 as the second National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) laborat ...
experimental AX-5 hard-shell space suit had a flexibility rating of 95%. The wearer could move into 95% of the positions they could without the suit on.
Hybrid suits
Hybrid suits have hard-shell parts and fabric parts. NASA's Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) uses a fiberglass Hard Upper Torso (HUT) and fabric limbs. ILC Dover
ILC Dover is a special engineering development and manufacturing company, globally headquartered in Frederica, Delaware. It specializes in the use of high-performance flexible materials, serving the aerospace manufacturer, aerospace, personal pr ...
's I-Suit replaces the HUT with a fabric soft upper torso to save weight, restricting the use of hard components to the joint bearings, helmet, waist seal, and rear entry hatch. Virtually all workable space suit designs incorporate hard components, particularly at interfaces such as the waist seal, bearings, and in the case of rear-entry suits, the back hatch, where all-soft alternatives are not viable.
Skintight suits
Skintight suits, also known as mechanical counterpressure suits or space activity suits, are a proposed design which would use a heavy elastic body stocking to compress the body. The head is in a pressurized helmet, but the rest of the body is pressurized only by the elastic effect of the suit. This mitigates the constant volume problem, reduces the possibility of a space suit depressurization and gives a very lightweight suit. When not worn, the elastic garments may appear to be that of clothing for a small child. These suits may be very difficult to put on and face problems with providing a uniform pressure. Most proposals use the body's natural perspiration
Perspiration, also known as sweat, is the fluid secreted by sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and Apocrine sweat gland, apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distribu ...
to keep cool. Sweat evaporates readily in vacuum and may desublime or deposit on objects nearby: optics, sensors, the astronaut's visor, and other surfaces. The icy film and sweat residue may contaminate sensitive surfaces and affect optical performance.
Contributing technologies
Related preceding technologies include the stratonautical space suit, the gas mask
A gas mask is a piece of personal protective equipment used to protect the wearer from inhaling airborne pollutants and toxic gases. The mask forms a sealed cover over the nose and mouth, but may also cover the eyes and other vulnerable soft ...
used in World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the oxygen mask
An oxygen mask is a mask that provides a method to transfer breathing gas, breathing oxygen gas from a storage tank to the lungs. Oxygen masks may cover only the nose and mouth (oral nasal mask) or the entire face (full-face mask). They may be ma ...
used by pilots of high-flying bombers in World War II, the high-altitude or vacuum suit required by pilots of the Lockheed U-2
The Lockheed U-2, nicknamed the "''Dragon Lady''", is an American single-engine, high–altitude reconnaissance aircraft operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) since the 1950s. Designed for all- ...
and SR-71 Blackbird, the diving suit
A diving suit is a garment or device designed to protect a diver from the underwater environment. A diving suit may also incorporate a breathing gas supply (such as for a standard diving dress or atmospheric diving suit), but in most cases th ...
, rebreather
A rebreather is a breathing apparatus that absorbs the carbon dioxide of a user's exhaled breath to permit the rebreathing (recycling) of the substantial unused oxygen content, and unused inert content when present, of each breath. Oxygen is a ...
, scuba diving
Scuba diving is a Diving mode, mode of underwater diving whereby divers use Scuba set, breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface breathing gas supply, and therefore has a limited but variable endurance. The word ''scub ...
gear, and many others.
Many space suit designs are taken from the U.S. Air Force suits, which are designed to work in "high-altitude aircraft pressure ,[ such as the Mercury IVA suit or the Gemini G4C, or the Advanced Crew Escape Suits.]
Glove technology
The Mercury IVA, the first U.S. space suit design, included lights at the tips of the gloves in order to provide visual aid. As the need for extravehicular activity grew, suits such as the Apollo A7L included gloves made of a metal fabric called Chromel-r in order to prevent punctures. In order to retain a better sense of touch for the astronauts, the fingertips of the gloves were made of silicone. With the shuttle program, it became necessary to be able to operate spacecraft modules, so the ACES suits featured gripping on the gloves. EMU gloves, which are used for spacewalks, are heated to keep the astronaut's hands warm. The Phase VI gloves, meant for use with the Mark III suit, are the first gloves to be designed with "laser scanning technology, 3D computer modeling, stereo lithography, laser cutting technology and CNC machining".
Life support technology
Prior to the Apollo missions, life support in space suits was connected to the space capsule via an umbilical cable
An umbilical cable or umbilical is a cable and/or hose that supplies required consumables to an apparatus, like a rocket, or to a person, such as a diver or astronaut. It is named by analogy with an umbilical cord. An umbilical can, for example, ...
. However, with the Apollo missions, life support was configured into a removable capsule called the Portable Life Support System that allowed the astronaut to explore the Moon without having to be attached to the space craft. The EMU space suit, used for spacewalks, allows the astronaut to manually control the internal environment of the suit. The Mark III suit has a backpack containing about 12 pounds of liquid air for breathing, pressurization, and heat exchange.[
]
Helmet technology
The development of the spheroidal dome helmet was key in balancing the need for field of view, pressure compensation, and low weight. One inconvenience with some space suits is the head being fixed facing forwards and being unable to turn to look sideways. Astronauts call this effect "alligator head".
High-altitude suits
 * Evgeniy Chertovsky created his full-pressure suit or high-altitude "''skafandr''" (''скафандр'') in 1931.
* Evgeniy Chertovsky created his full-pressure suit or high-altitude "''skafandr''" (''скафандр'') in 1931.diving
Diving most often refers to:
* Diving (sport), the sport of jumping into deep water
* Underwater diving, human activity underwater for recreational or occupational purposes
Diving or Dive may also refer to:
Sports
* Dive (American football), ...
suit").Italian Air Force
The Italian Air Force (; AM, ) is the air force of the Italy, Italian Republic. The Italian Air Force was founded as an independent service arm on 28 March 1923 by Victor Emmanuel III of Italy, King Victor Emmanuel III as the ("Royal Air Force ...
developed an high-altitude, semi-rigid pressurized suit, the first to be successfully used in operational conditions on October 22nd 1938 by Lt.Col. Mario Pezzi during his first high-altitude record flight.
* Wiley Post
Wiley Hardeman Post (November 22, 1898 – August 15, 1935) was an American aviator during the Aviation between the World Wars, interwar period and the first aviator, pilot to fly solo around the world. Known for his work in high-altitude flyi ...
experimented with a number of pressure suits for record-breaking flights.Alan Shepard
Alan Bartlett Shepard Jr. (November 18, 1923 – July 21, 1998) was an American astronaut. In 1961, he became the second person and the first American to travel into space and, in 1971, he became the List of Apollo astronauts#Apollo astr ...
for his ride as America's first man in space on May 5, 1961.
List of space suit models
Soviet and Russian suit models
* '' SK series (CK)''the spacesuit used for the Vostok program (1961–1963). Worn by Yuri Gagarin
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin; Gagarin's first name is sometimes transliterated as ''Yuriy'', ''Youri'', or ''Yury''. (9 March 1934 – 27 March 1968) was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who, aboard the first successful Human spaceflight, crewed sp ...
on the first crewed space flight.
* No pressure suits were worn aboard Voskhod 1
Voskhod 1 () was the seventh crewed Soviet space flight. Flown by cosmonauts Vladimir Komarov, Konstantin Feoktistov, and Boris Yegorov, it launched 12 October 1964, and returned on the 13th. Voskhod 1 was the first human spaceflight to carr ...
.
* '' Berkut'' (''Беркут'' meaning "golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known bird of pr ...
")'the spacesuit was a modified SK-1 used by the crew of Voskhod 2
Voskhod 2 () was a Soviet crewed space mission in March 1965. The Vostok-based Voskhod 3KD spacecraft with two crew members on board, Pavel Belyayev and Alexei Leonov, was equipped with an inflatable airlock. It established another milestone ...
which included Alexei Leonov
Alexei Arkhipovich Leonov. (30 May 1934 – 11 October 2019) was a Soviet and Russian cosmonaut and aviator, Soviet Air Forces, Air Force major general, writer, and artist. On 18 March 1965, he became the first person to conduct a Extravehic ...
on the first spacewalk
Extravehicular activity (EVA) is any activity done by an astronaut in outer space outside a spacecraft. In the absence of a breathable atmosphere of Earth, Earthlike atmosphere, the astronaut is completely reliant on a space suit for environme ...
during (1965).
* From Soyuz 1 to Soyuz 11 (1967–1971) no pressure suits were worn during launch and reentry.
* '' Yastreb'' (''Ястреб'' meaning "hawk
Hawks are birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. They are very widely distributed and are found on all continents, except Antarctica.
The subfamily Accipitrinae includes goshawks, sparrowhawks, sharp-shinned hawks, and others. This ...
")'extravehicular activity spacesuit used during a crew exchange between Soyuz 4 and Soyuz 5 (1969).
* Krechet-94 (''Кречет'' meaning "gyrfalcon
The gyrfalcon ( or ) (), also abbreviated as gyr, is a bird of prey from the genus ''Falco'' (falcons and kestrels) and the largest species of the family Falconidae. A high-latitude species, the gyrfalcon breeds on the Arctic coasts and tundra, ...
")'designed for the canceled Soviet crewed Moon landing.
* Strizh (''Стриж'' meaning "swift (bird)
The Apodidae, or swifts, form a family of highly aerial birds. They are superficially similar to swallows, but are not closely related to any passerine species. Swifts are placed in the order Apodiformes along with hummingbirds. The treeswifts ...
")'developed for pilots of '' Buran''-class orbiters.
* Sokol (''Сокол'' meaning "falcon
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Some small species of falcons with long, narrow wings are called hobbies, and some that hover while hunting are called kestrels. Falcons are widely distrib ...
")'suits worn by Soyuz
Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз (Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Soviet Union, Union of Soviet Socialist Republi ...
crew members during launch and reentry. They were first worn on Soyuz 12. They have been used from 1973 to present.
* Orlan (''Орлан'' meaning " sea-eagle" or "bald eagle
The bald eagle (''Haliaeetus leucocephalus'') is a bird of prey found in North America. A sea eagle, it has two known subspecies and forms a species pair with the white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla''), which occupies the same niche ...
")'suits for extravehicular activity, originally developed for the Soviet lunar program as a lunar orbit EVA suit. It is Russia's current EVA suit. Used from 1977 to present.
Sk-1 spacesuit taken at the Memorial Museum of Space Exploration.jpg , SK-1 space suit
Berkut spacesuit.JPG , Berkut space suit
Yastreb suit.jpg , Yastreb space suit
Krechet space suit - Air and Space.jpg , Krechet space suit
Strizh spacesuit 4148047368 c19cec3782 o.jpg , Strizh space suit
Sokol KV2.JPG , Sokol-KV2 space suit
Orlan-MK-MAKS2009.jpg , Orlan-MK space suit
United States suit models
*In the early 1950s, Siegfried Hansen and colleagues at Litton Industries
Litton Industries, Inc., was an American defense contractor that specialized in shipbuilding, aerospace, electronic components, and information technology. The company was founded in 1953 and was named after inventor Charles Litton Sr., who was ...
designed and built a working hard-shell suit, which was used inside vacuum chambers and was the predecessor of space suits used in NASA missions.
* Navy Mark IV high-altitude/vacuum suitused for Project Mercury
Project Mercury was the first human spaceflight program of the United States, running from 1958 through 1963. An early highlight of the Space Race, its goal was to put a man into Earth orbit and return him safely, ideally before the Soviet Un ...
(1961–1963).
* Gemini space suits (1965–1966)there were three main variants developed: G3C designed for intra-vehicle use; G4C specially designed for EVA and intra-vehicle use; and a special G5C suit worn by the Gemini 7
Gemini 7 (officially Gemini VII) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was a 1965 crewed spaceflight in NASA's Gemini program. It was the fourth crewed Gemini flight, the twelfth crewed American spacef ...
crew for 14 days inside the spacecraft.
* Manned Orbiting Laboratory MH-7 space suits for the canceled MOL program.
*Gemini space suit#Apollo program, Apollo Block I A1C suit (1966–1967)a derivative of the Gemini suit, worn by primary and backup crews in training for two early Apollo missions. The nylon pressure garment melted and burned through in the Apollo 1 cabin fire. This suit became obsolete when crewed Block I Apollo flights were discontinued after the fire.
* Apollo/Skylab A7L EVA and Moon suitsThe Block II Apollo suit was the primary pressure suit worn for eleven Apollo flights, three Skylab flights, and the US astronauts on the Apollo–Soyuz Test Project between 1968 and 1975. The pressure garment's nylon outer layer was replaced with fireproof Beta cloth after the Apollo 1 fire. This suit was the first to employ a liquid-cooled inner garment and outer micrometeoroid garment. Beginning with the Apollo 13 mission, it also introduced "commander's stripes" so that a pair of space walkers will not appear identical on camera.
*Shuttle Ejection Escape Suitused from STS-1 (1981) to STS-4 (1982) by a two-man crew used in conjunction with the then-installed ejection seats. Derived from a United States Air Force, USAF model. These were removed once the Shuttle became certified.
* From STS-5 (1982) to STS-51-L (1986) no pressure suits were worn during launch and reentry. The crew would wear only a blue-flight suit with an oxygen helmet.
*Launch Entry Suit first used on STS-26 (1988), the first flight after the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, ''Challenger'' disaster. It was a partial pressure suit derived from a USAF model. It was used from 1988 to 1998.
* Advanced Crew Escape Suit used on the Space Shuttle starting in 1994. The Advanced Crew Escape Suit or ACES suit, is a full-pressure suit worn by all Space Shuttle crews for the ascent and entry portions of flight. The suit is a direct descendant of the United States Air Force high-altitude pressure suits worn by SR-71 Blackbird and U-2 spy plane pilots, North American X-15 and Project Gemini, Gemini pilot-astronauts, and the Launch Entry Suits worn by NASA astronauts starting on the STS-26 flight. It is derived from a USAF model.
*Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU)used on both the Space Shuttle and International Space Station (ISS). The EMU is an independent anthropomorphic system that provides environmental protection, mobility, life support, and communications for a Space Shuttle or ISS crew member to perform an EVA in Geocentric orbit, Earth orbit. Used from 1982 to present, but only available in limited sizing as of 2019.
*Aerospace company SpaceX developed #SpaceX suit ("Starman suit"), an IVA suit which is worn by astronauts involved in Commercial Crew Program missions operated by SpaceX since the Crew Dragon Demo-2, Demo-2 mission. As a continuation of this suit design, SpaceX developed an EVA suit in 2024. The EVA version of the suit was used during the Polaris Dawn private space mission for the first ever commercial spacewalk.
*Orion Crew Survival System (OCSS)will be used during launch and re-entry on the Orion (spacecraft), Orion MPCV. It is derived from the Advanced Crew Escape Suit but is able to operate at a higher pressure and has improved mobility in the shoulders.
Alan shepard.jpg , Mercury suit
G4C EVA 12 - cropped.jpg , Gemini G4C suit
MOL spacesuit.jpg , Manned Orbital Laboratory MH-7 space suit
Apollo 1 - Chaffee in Apollo Block I space suit.jpg , Apollo Block I A1C suit
Apollo 17 Cernan on moon cropped.jpg , Apollo/Skylab space suit
Shuttle Ejection Escape Suit John Young.jpg , Shuttle Ejection Escape Suit
STS 51-I emergency training - cropped.jpg , Shuttle Flight Suit
Launch entry suit.jpg , Launch Entry Suit
ACES STS-130.jpg , Advance Crew Escape Suit
STS-118 EVA EMU Suit.jpg, Extravehicular Mobility Unit
SpaceX Crew-3 Dry Dress Rehearsal (KSC-20211028-PH-SPX02 0013).jpg, SpaceX suit
SpaceX suit ("Starman suit")
In February 2015, SpaceX began developing a space suit for astronauts to wear within the SpaceX Dragon 2, Dragon 2 space capsule.
Future NASA contracted suits
On 1 June 2022, NASA announced it had selected competing Axiom Space and Collins Aerospace to develop and provide astronauts with next generation spacesuit and spacewalk systems to first test and later use outside the International Space Station, as well as on the lunar surface for the crewed Artemis program, Artemis missions, and prepare for human missions to Mars.
Chinese suit models
* Shuguang (spacecraft), Shuguang (曙光, meaning "Dawn") space suit : First generation EVA space suit developed by China for the 1967 canceled ''Shuguang (spacecraft), Project 714'' crewed space program. It has a mass of about , has an orange colour, and is made of high-resistance multi-layer polyester fabric. The astronaut could use it inside the cabin and conduct an EVA as well.
* Project 863'' space suit: Cancelled project of second generation Chinese EVA space suit.
* Shenzhou IVA (神舟, meaning "Divine Vessel") space suit: The suit was first worn by Yang Liwei on Shenzhou 5, the first crewed Chinese space flight, it closely resembles a Sokol-KV2 suit, but it is believed to be a Chinese-made version rather than an actual Russian suit. Pictures show that the suits on Shenzhou 6 differ in detail from the earlier suit; they are also reported to be lighter.
* Orlan spacesuit, Haiying (海鹰, meaning "Sea Hawk") EVA space suit: The imported Russian Orlan space suit#M model, Orlan-M EVA suit is called ''Haiying''. Used on Shenzhou 7.
* Feitian space suit, Feitian (飞天, meaning "Sky Flyer") EVA space suit: Indigenously developed Chinese-made EVA space suit also used for the Shenzhou 7 mission. The suit was designed for a spacewalk mission of up to seven hours. Chinese astronauts have been training in the out-of-capsule space suits since July 2007, and movements are seriously restricted in the suits, with a mass of more than each. A new generation of Feitian space suit has been used since 2021 as the construction of Tiangong Space Station began.
Yang Liwei space suit.JPG , Shenzhou Intra-Vehicular Activity space suit
Chinese EVA spacesuit (1).JPG , Feitian space suit
Feitian space suit at NMC 01.jpg, Second generation of Feitian space suit
Emerging technologies
Several companies and universities are developing technologies and prototypes which represent improvements over current space suits.
Additive manufacturing
3D printing (additive manufacturing) can be used to reduce the mass of hard-shell space suits while retaining the high mobility they provide. This fabrication method also allows for the potential for in-suit fabrication and repair of suits, a capability which is not currently available, but will likely be necessary for Martian exploration. The University of Maryland, College Park, University of Maryland began development of a prototype 3D printed hard suit in 2016, based on the kinematics of the Powered exoskeleton#NASA AX-5 hard shell space suit, AX-5. The prototype arm segment is designed to be evaluated in the Space Systems Laboratory (Maryland), Space Systems Laboratory glovebox to compare mobility to traditional soft suits. Initial research has focused on the feasibility of printing rigid suit elements, bearing races, ball bearings, seals, and sealing surfaces.
Astronaut Glove Challenge
There are certain difficulties in designing a dexterous space suit glove and there are limitations to the current designs. For this reason, the Centennial Challenges#Astronaut glove challenge, Centennial Astronaut Glove Challenge was created to build a better glove. Competitions have been held in 2007 and 2009, and another is planned. The 2009 contest required the glove to be covered with a micro-meteorite layer.
Aouda.X
 Since 2009, the Austrian Space Forum has been developing "Aouda.X", an experimental Mars Human analog missions, analogue space suit focusing on an advanced human–machine interface and on-board computing network to increase Situation awareness, situational awareness. The suit is designed to study contamination vectors in planetary exploration analogue environments and create limitations depending on the pressure regime chosen for a simulation.
Since 2012, for the Austrian Space Forum#Mars2013 - Morocco Mars Simulation 2013, Mars2013 analogue mission by the Austrian Space Forum to Erfoud, Morocco, the Aouda.X analogue space suit has a sister in the form of Aouda.S. This is a slightly less sophisticated suit meant primarily to assist Aouda.X operations and be able to study the interactions between two (analogue) astronauts in similar suits.
The Aouda.X and Aouda.S space suits have been named after the Aouda, fictional princess from the Jules Verne's 1873 novel ''Around the World in Eighty Days''. A public display mock-up of Aouda.X (called Aouda.D) is currently on display at the Dachstein Ice Cave in Obertraun, Austria, after the experiments done there in 2012.
Since 2009, the Austrian Space Forum has been developing "Aouda.X", an experimental Mars Human analog missions, analogue space suit focusing on an advanced human–machine interface and on-board computing network to increase Situation awareness, situational awareness. The suit is designed to study contamination vectors in planetary exploration analogue environments and create limitations depending on the pressure regime chosen for a simulation.
Since 2012, for the Austrian Space Forum#Mars2013 - Morocco Mars Simulation 2013, Mars2013 analogue mission by the Austrian Space Forum to Erfoud, Morocco, the Aouda.X analogue space suit has a sister in the form of Aouda.S. This is a slightly less sophisticated suit meant primarily to assist Aouda.X operations and be able to study the interactions between two (analogue) astronauts in similar suits.
The Aouda.X and Aouda.S space suits have been named after the Aouda, fictional princess from the Jules Verne's 1873 novel ''Around the World in Eighty Days''. A public display mock-up of Aouda.X (called Aouda.D) is currently on display at the Dachstein Ice Cave in Obertraun, Austria, after the experiments done there in 2012.
Axiom Space and Prada
In 2024, at the International Astronautical Congress in Milan, Italy, Axiom Space and Prada showed the results of an ongoing collaboration to develop a spacesuit for NASA's Artemis III mission.
Bio-Suit
Bio-Suit is a space activity suit under development at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, which consisted of several lower leg prototypes. Bio-suit is custom fit to each wearer, using laser body scanning.
Constellation Space Suit system
On August 2, 2006, NASA indicated plans to issue a Request for Proposal (RFP) for the design, development, certification, production, and sustaining engineering of the Constellation Space Suit to meet the needs of the Constellation program, Constellation Program. NASA foresaw a single suit capable of supporting: survivability during launch, entry and abort; Weightlessness, zero-gravity EVA; lunar surface EVA; and Mars surface EVA.
On June 11, 2008, NASA awarded a US$745 million contract to Oceaneering International to create the new space suit.
Final Frontier Design IVA Space Suit
 Final Frontier Design (FFD) is developing a commercial full IVA space suit, with their first suit completed in 2010. FFD's suits are intended as a light-weight, highly mobile, and inexpensive commercial space suits. Since 2011, FFD has upgraded IVA suit's designs, hardware, processes, and capabilities. FFD has built a total of 7 IVA space suit (2016) assemblies for various institutions and customers since founding, and has conducted high fidelity human testing in simulators, aircraft, microgravity, and hypobaric chambers. FFD has a Space Act Agreement with NASA's Commercial Space Capabilities Office to develop and execute a Human Rating Plan for FFD IVA suit. FFD categorizes their IVA suits according to their mission: Terra for Earth-based testing, Stratos for high altitude flights, and Exos for orbital space flights. Each suit category has different requirements for manufacturing controls, validations, and materials, but are of a similar architecture.
Final Frontier Design (FFD) is developing a commercial full IVA space suit, with their first suit completed in 2010. FFD's suits are intended as a light-weight, highly mobile, and inexpensive commercial space suits. Since 2011, FFD has upgraded IVA suit's designs, hardware, processes, and capabilities. FFD has built a total of 7 IVA space suit (2016) assemblies for various institutions and customers since founding, and has conducted high fidelity human testing in simulators, aircraft, microgravity, and hypobaric chambers. FFD has a Space Act Agreement with NASA's Commercial Space Capabilities Office to develop and execute a Human Rating Plan for FFD IVA suit. FFD categorizes their IVA suits according to their mission: Terra for Earth-based testing, Stratos for high altitude flights, and Exos for orbital space flights. Each suit category has different requirements for manufacturing controls, validations, and materials, but are of a similar architecture.
I-Suit
The I-Suit is a space suit prototype also constructed by ILC Dover, which incorporates several design improvements over the EMU, including a weight-saving soft upper torso. Both the Mark III and the I-Suit have taken part in NASA's annual Desert Research and Technology Studies (D-RATS) field trials, during which suit occupants interact with one another, and with rovers and other equipment.
Mark III
The Mark III (space suit), Mark III is a NASA prototype, constructed by ILC Dover, which incorporates a hard lower torso section and a mix of soft and hard components. The Mark III is markedly more mobile than previous suits, despite its high operating pressure (), which makes it a "zero-prebreathe" suit, meaning that astronauts would be able to transition directly from a one-atmosphere, mixed-gas space station environment, such as that on the International Space Station, to the suit, without risking decompression sickness, which can occur with rapid depressurization from an atmosphere containing nitrogen or another inert gas.
MX-2
The MX-2 is a space suit analogue constructed at the University of Maryland, College Park, University of Maryland's Space Systems Laboratory. The MX-2 is used for crewed neutral buoyancy testing at the Space Systems Lab's Neutral Buoyancy Research Facility. By approximating the work envelope of a real EVA suit, without meeting the requirements of a flight-rated suit, the MX-2 provides an inexpensive platform for EVA research, compared to using EMU suits at facilities like NASA's Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory.
The MX-2 has an operating pressure of 2.5–4 psi. It is a rear-entry suit, featuring a fiberglass Hard Upper Torso, HUT. Air, LCVG cooling water, and power are open loop systems, provided through an Umbilical cable, umbilical. The suit contains a Mac Mini computer to capture sensor data, such as suit pressure, inlet and outlet air temperatures, and heart rate. Resizable suit elements and adjustable ballast allow the suit to accommodate subjects ranging in height from , and with a weight range of .
North Dakota suit
Beginning in May 2006, five North Dakota colleges collaborated on a new space suit prototype, funded by a US$100,000 grant from NASA, to demonstrate technologies which could be incorporated into a planetary suit. The suit was tested in the Theodore Roosevelt National Park badlands of western North Dakota. The suit has a mass of without a life support backpack, and costs only a fraction of the standard US$12,000,000 cost for a flight-rated NASA space suit. The suit was developed in just over a year by students from the University of North Dakota, North Dakota State University, North Dakota State, Dickinson State University, Dickinson State, the state North Dakota State College of Science, College of Science and Turtle Mountain Community College. The mobility of the North Dakota suit can be attributed to its low operating pressure; while the North Dakota suit was field tested at a pressure of differential, NASA's EMU suit operates at a pressure of , a pressure designed to supply approximately sea-level oxygen partial pressure for respiration (see discussion #Operating pressure, above).
PXS
NASA's Prototype eXploration Suit (PXS), like the Z-series, is a rear-entry suit compatible with suitports.
Suitports
A suitport is a theoretical alternative to an airlock, designed for use in hazardous environments and in human spaceflight, especially planetary surface exploration. In a suitport system, a rear-entry space suit is attached and sealed against the outside of a spacecraft, such that an astronaut can enter and seal up the suit, then go on EVA, without the need for an airlock or depressurizing the spacecraft cabin. Suitports require less mass and volume than airlocks, provide dust mitigation, and prevent cross-contamination of the inside and outside environments. Patents for suitport designs were filed in 1996 by Philip Culbertson Jr. of NASA's Ames Research Center and in 2003 by Joerg Boettcher, Stephen Ransom, and Frank Steinsiek.
Z-series
 In 2012, NASA introduced the Z-1 space suit, the first in the Z-series of space suit prototypes designed by NASA specifically for planetary extravehicular activity. The Z-1 space suit includes an emphasis on mobility and protection for space missions. It features a soft torso versus the hard torsos seen in previous NASA EVA space suits, which reduces mass. It has been labeled the "Buzz Lightyear suit" due to its green streaks for a design.
In 2014, NASA released the design for the Z-2 prototype, the next model in the Z-series. NASA conducted a poll asking the public to decide on a design for the Z-2 space suit. The designs, created by fashion students from Philadelphia University, were "Technology", "Trends in Society", and "Biomimicry". The design "Technology" won, and the prototype is built with technologies like 3D printing. The Z-2 suit will also differ from the Z-1 suit in that the torso reverts to the hard shell, as seen in NASA's EMU suit.
In 2012, NASA introduced the Z-1 space suit, the first in the Z-series of space suit prototypes designed by NASA specifically for planetary extravehicular activity. The Z-1 space suit includes an emphasis on mobility and protection for space missions. It features a soft torso versus the hard torsos seen in previous NASA EVA space suits, which reduces mass. It has been labeled the "Buzz Lightyear suit" due to its green streaks for a design.
In 2014, NASA released the design for the Z-2 prototype, the next model in the Z-series. NASA conducted a poll asking the public to decide on a design for the Z-2 space suit. The designs, created by fashion students from Philadelphia University, were "Technology", "Trends in Society", and "Biomimicry". The design "Technology" won, and the prototype is built with technologies like 3D printing. The Z-2 suit will also differ from the Z-1 suit in that the torso reverts to the hard shell, as seen in NASA's EMU suit.
In fiction
 Space suits are a common staple of science fiction. They appeared in sf works as early as 19th century (Jules Verne's ''From the Earth to the Moon'', 1865).
Space suits are a common staple of science fiction. They appeared in sf works as early as 19th century (Jules Verne's ''From the Earth to the Moon'', 1865).
See also
*
*
*
*
*
**By era:
***
*** List of spacewalks 2000–2014
***
**By station:
***
***
**
*
*Life support in aviation
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
"Space suits"
a
. A list compiled by Lee Sledge and James H. Gerard of American space suits and the museum locations where they are displayed.
a
A complete listing of space suits.
at NPP Zvezda
"Space suit"
by G. Ilyin, Vladimir Ivanov, and Ivan Pavlov. Originally published by ''Nauka i Zhizn'', No. 6, 1978.
"U.S. Human Spaceflight History"
at the Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center, Johnson Space Center See link near page end to ''Walking to Olympus: An EVA Chronology'' (PDF).
NASDA Online Space Notes
at the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) (2001)
"Analysis of the Space Shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Unit – 1986"
(PDF)
"NASA Space Shuttle EVA tools and equipment reference book – 1993"
(PDF)
"Space Suit Evolution From Custom Tailored to Off-the-Rack
(PDF)
at th
Apollo Lunar Surface Journal
. Section on the Apollo space suit and the Portable Life Support System.
a
Historic Spacecraft
"Space suit and Spacewalk History Image Gallery"
at NASA
"Spacesuits"
at ILC Dover
ILC Dover is a special engineering development and manufacturing company, globally headquartered in Frederica, Delaware. It specializes in the use of high-performance flexible materials, serving the aerospace manufacturer, aerospace, personal pr ...
*
* In April 2011, the VOA Special English service of the Voice of America broadcast a 15-minute program on the evolution of space suits. A transcript and MP3 of the program, intended for English learners, can be found a
"The Evolution of Spacesuits"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Space Suit
Spacesuits,
Rebreathers
Environmental suits
Human spaceflight
Spacecraft components
Space technology
Soviet inventions


 A space suit (or spacesuit) is an environmental suit used for protection from the harsh environment of outer space, mainly from its
A space suit (or spacesuit) is an environmental suit used for protection from the harsh environment of outer space, mainly from its  A space suit must perform several functions to allow its occupant to work safely and comfortably, inside or outside a spacecraft. It must provide:
* A stable internal pressure. This can be less than Earth's atmosphere, as there is usually no need for the space suit to carry
A space suit must perform several functions to allow its occupant to work safely and comfortably, inside or outside a spacecraft. It must provide:
* A stable internal pressure. This can be less than Earth's atmosphere, as there is usually no need for the space suit to carry  Means of collecting and containing solid and liquid bodily waste (such as a
Means of collecting and containing solid and liquid bodily waste (such as a  Advanced suits better regulate the
Advanced suits better regulate the  As part of astronautical hygiene control (i.e., protecting astronauts from extremes of temperature, radiation, etc.), a space suit is essential for extravehicular activity. The Apollo/Skylab A7L suit included eleven layers in all: an inner liner, a LCVG, a pressure bladder, a restraint layer, another liner, and a Thermal Micrometeoroid Garment consisting of five aluminized insulation layers and an external layer of white Ortho-Fabric. This space suit is capable of protecting the astronaut from temperatures ranging from to .
During exploration of the Moon or Mars, there will be the potential for lunar or Martian dust to be retained on the space suit. When the space suit is removed on return to the spacecraft, there will be the potential for the dust to contaminate surfaces and increase the risks of inhalation and skin exposure. Astronautical hygienists are testing materials with reduced dust retention times and the potential to control the dust exposure risks during planetary exploration. Novel ingress and egress approaches, such as suitports, are being explored as well.
In
As part of astronautical hygiene control (i.e., protecting astronauts from extremes of temperature, radiation, etc.), a space suit is essential for extravehicular activity. The Apollo/Skylab A7L suit included eleven layers in all: an inner liner, a LCVG, a pressure bladder, a restraint layer, another liner, and a Thermal Micrometeoroid Garment consisting of five aluminized insulation layers and an external layer of white Ortho-Fabric. This space suit is capable of protecting the astronaut from temperatures ranging from to .
During exploration of the Moon or Mars, there will be the potential for lunar or Martian dust to be retained on the space suit. When the space suit is removed on return to the spacecraft, there will be the potential for the dust to contaminate surfaces and increase the risks of inhalation and skin exposure. Astronautical hygienists are testing materials with reduced dust retention times and the potential to control the dust exposure risks during planetary exploration. Novel ingress and egress approaches, such as suitports, are being explored as well.
In  Generally, to supply enough oxygen for respiration, a space suit using pure oxygen must have a pressure of about , equal to the
Generally, to supply enough oxygen for respiration, a space suit using pure oxygen must have a pressure of about , equal to the  A space suit should allow its user natural unencumbered movement. Nearly all designs try to maintain a constant volume no matter what movements the wearer makes. This is because
A space suit should allow its user natural unencumbered movement. Nearly all designs try to maintain a constant volume no matter what movements the wearer makes. This is because 
 * Evgeniy Chertovsky created his full-pressure suit or high-altitude "''skafandr''" (''скафандр'') in 1931. (скафандр also means "
* Evgeniy Chertovsky created his full-pressure suit or high-altitude "''skafandr''" (''скафандр'') in 1931. (скафандр also means " Since 2009, the Austrian Space Forum has been developing "Aouda.X", an experimental Mars Human analog missions, analogue space suit focusing on an advanced human–machine interface and on-board computing network to increase Situation awareness, situational awareness. The suit is designed to study contamination vectors in planetary exploration analogue environments and create limitations depending on the pressure regime chosen for a simulation.
Since 2012, for the Austrian Space Forum#Mars2013 - Morocco Mars Simulation 2013, Mars2013 analogue mission by the Austrian Space Forum to Erfoud, Morocco, the Aouda.X analogue space suit has a sister in the form of Aouda.S. This is a slightly less sophisticated suit meant primarily to assist Aouda.X operations and be able to study the interactions between two (analogue) astronauts in similar suits.
The Aouda.X and Aouda.S space suits have been named after the Aouda, fictional princess from the Jules Verne's 1873 novel ''Around the World in Eighty Days''. A public display mock-up of Aouda.X (called Aouda.D) is currently on display at the Dachstein Ice Cave in Obertraun, Austria, after the experiments done there in 2012.
Since 2009, the Austrian Space Forum has been developing "Aouda.X", an experimental Mars Human analog missions, analogue space suit focusing on an advanced human–machine interface and on-board computing network to increase Situation awareness, situational awareness. The suit is designed to study contamination vectors in planetary exploration analogue environments and create limitations depending on the pressure regime chosen for a simulation.
Since 2012, for the Austrian Space Forum#Mars2013 - Morocco Mars Simulation 2013, Mars2013 analogue mission by the Austrian Space Forum to Erfoud, Morocco, the Aouda.X analogue space suit has a sister in the form of Aouda.S. This is a slightly less sophisticated suit meant primarily to assist Aouda.X operations and be able to study the interactions between two (analogue) astronauts in similar suits.
The Aouda.X and Aouda.S space suits have been named after the Aouda, fictional princess from the Jules Verne's 1873 novel ''Around the World in Eighty Days''. A public display mock-up of Aouda.X (called Aouda.D) is currently on display at the Dachstein Ice Cave in Obertraun, Austria, after the experiments done there in 2012.
 Final Frontier Design (FFD) is developing a commercial full IVA space suit, with their first suit completed in 2010. FFD's suits are intended as a light-weight, highly mobile, and inexpensive commercial space suits. Since 2011, FFD has upgraded IVA suit's designs, hardware, processes, and capabilities. FFD has built a total of 7 IVA space suit (2016) assemblies for various institutions and customers since founding, and has conducted high fidelity human testing in simulators, aircraft, microgravity, and hypobaric chambers. FFD has a Space Act Agreement with NASA's Commercial Space Capabilities Office to develop and execute a Human Rating Plan for FFD IVA suit. FFD categorizes their IVA suits according to their mission: Terra for Earth-based testing, Stratos for high altitude flights, and Exos for orbital space flights. Each suit category has different requirements for manufacturing controls, validations, and materials, but are of a similar architecture.
Final Frontier Design (FFD) is developing a commercial full IVA space suit, with their first suit completed in 2010. FFD's suits are intended as a light-weight, highly mobile, and inexpensive commercial space suits. Since 2011, FFD has upgraded IVA suit's designs, hardware, processes, and capabilities. FFD has built a total of 7 IVA space suit (2016) assemblies for various institutions and customers since founding, and has conducted high fidelity human testing in simulators, aircraft, microgravity, and hypobaric chambers. FFD has a Space Act Agreement with NASA's Commercial Space Capabilities Office to develop and execute a Human Rating Plan for FFD IVA suit. FFD categorizes their IVA suits according to their mission: Terra for Earth-based testing, Stratos for high altitude flights, and Exos for orbital space flights. Each suit category has different requirements for manufacturing controls, validations, and materials, but are of a similar architecture.
 In 2012, NASA introduced the Z-1 space suit, the first in the Z-series of space suit prototypes designed by NASA specifically for planetary extravehicular activity. The Z-1 space suit includes an emphasis on mobility and protection for space missions. It features a soft torso versus the hard torsos seen in previous NASA EVA space suits, which reduces mass. It has been labeled the "Buzz Lightyear suit" due to its green streaks for a design.
In 2014, NASA released the design for the Z-2 prototype, the next model in the Z-series. NASA conducted a poll asking the public to decide on a design for the Z-2 space suit. The designs, created by fashion students from Philadelphia University, were "Technology", "Trends in Society", and "Biomimicry". The design "Technology" won, and the prototype is built with technologies like 3D printing. The Z-2 suit will also differ from the Z-1 suit in that the torso reverts to the hard shell, as seen in NASA's EMU suit.
In 2012, NASA introduced the Z-1 space suit, the first in the Z-series of space suit prototypes designed by NASA specifically for planetary extravehicular activity. The Z-1 space suit includes an emphasis on mobility and protection for space missions. It features a soft torso versus the hard torsos seen in previous NASA EVA space suits, which reduces mass. It has been labeled the "Buzz Lightyear suit" due to its green streaks for a design.
In 2014, NASA released the design for the Z-2 prototype, the next model in the Z-series. NASA conducted a poll asking the public to decide on a design for the Z-2 space suit. The designs, created by fashion students from Philadelphia University, were "Technology", "Trends in Society", and "Biomimicry". The design "Technology" won, and the prototype is built with technologies like 3D printing. The Z-2 suit will also differ from the Z-1 suit in that the torso reverts to the hard shell, as seen in NASA's EMU suit.
 Space suits are a common staple of science fiction. They appeared in sf works as early as 19th century (Jules Verne's ''From the Earth to the Moon'', 1865).
Space suits are a common staple of science fiction. They appeared in sf works as early as 19th century (Jules Verne's ''From the Earth to the Moon'', 1865).