Soma Cube on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
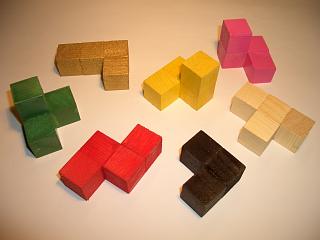
 The Soma cube is a solid dissection puzzle invented by Danish polymath Piet Hein in 1933 during a lecture on
The Soma cube is a solid dissection puzzle invented by Danish polymath Piet Hein in 1933 during a lecture on
 Solving the Soma cube has been used as a task to measure individuals' performance and effort in a series of psychology experiments. In these experiments, test subjects are asked to solve a soma cube as many times as possible within a set period of time. For example, In 1969, Edward Deci, a Carnegie Mellon University graduate assistant at the time, asked his research subjects to solve a soma cube under conditions with varying incentives in his dissertation work on
Solving the Soma cube has been used as a task to measure individuals' performance and effort in a series of psychology experiments. In these experiments, test subjects are asked to solve a soma cube as many times as possible within a set period of time. For example, In 1969, Edward Deci, a Carnegie Mellon University graduate assistant at the time, asked his research subjects to solve a soma cube under conditions with varying incentives in his dissertation work on
 In addition to constructing a cube, the Soma manual provides assorted figures to construct with the seven pieces. The figure on the right shows solutions to some of the figures in the same colour scheme.
In addition to constructing a cube, the Soma manual provides assorted figures to construct with the seven pieces. The figure on the right shows solutions to some of the figures in the same colour scheme.
Soma Cube – from MathWorld
Thorleif's SOMA page
SOMA CUBE ANIMATION by TwoDoorsOpen and Friends
{{Authority control Mechanical puzzle cubes Tiling puzzles
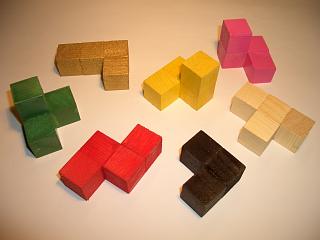
 The Soma cube is a solid dissection puzzle invented by Danish polymath Piet Hein in 1933 during a lecture on
The Soma cube is a solid dissection puzzle invented by Danish polymath Piet Hein in 1933 during a lecture on quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
conducted by Werner Heisenberg
Werner Karl Heisenberg (; ; 5 December 1901 – 1 February 1976) was a German theoretical physicist, one of the main pioneers of the theory of quantum mechanics and a principal scientist in the German nuclear program during World War II.
He pub ...
.
Seven different pieces made out of unit cubes must be assembled into a 3×3×3 cube. The pieces can also be used to make a variety of other 3D shapes.
The pieces of the Soma cube consist of all possible combinations of at most four unit cubes, joined at their faces, such that at least one inside corner is formed. There are no combinations of one or two cubes that satisfy this condition, but one combination of three cubes and six combinations of four cubes that do. Thus, 3 + (6 × 4) is 27, which is exactly the number of cells in a 3×3×3 cube. Of these seven combinations, two are mirror images of each other (see Chirality
Chirality () is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word ''chirality'' is derived from the Greek (''kheir''), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
An object or a system is ''chiral'' if it is distinguishable fro ...
).
The Soma cube was popularized by Martin Gardner
Martin Gardner (October 21, 1914May 22, 2010) was an American popular mathematics and popular science writer with interests also encompassing magic, scientific skepticism, micromagic, philosophy, religion, and literatureespecially the writin ...
in the September 1958 Mathematical Games column
Over a period of 24 years (January 1957 – December 1980), Martin Gardner wrote 288 consecutive monthly "Mathematical Games" columns for ''Scientific American'' magazine. During the next years, until June 1986, Gardner wrote 9 more columns, br ...
in ''Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it, with more than 150 Nobel Pri ...
.'' The book '' Winning Ways for your Mathematical Plays'' also contains a detailed analysis of the Soma cube problem.
There are 240 distinct solutions of the Soma cube puzzle, excluding rotations and reflections: these are easily generated by a simple backtracking search
Backtracking is a class of algorithms for finding solutions to some computational problems, notably constraint satisfaction problems, that incrementally builds candidates to the solutions, and abandons a candidate ("backtracks") as soon as it de ...
computer program similar to that used for the eight queens puzzle
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other; thus, a solution requires that no two queens share the same row, column, or diagonal. There are 92 solutions. ...
. John Horton Conway
John Horton Conway (26 December 1937 – 11 April 2020) was an English mathematician. He was active in the theory of finite groups, knot theory, number theory, combinatorial game theory and coding theory. He also made contributions to many b ...
and Michael Guy
Michael J. T. Guy (born 1 April 1943) is a British computer scientist and mathematician. He is known for early work on computer systems, such as the Phoenix system at the University of Cambridge, and for contributions to number theory, computer ...
first identified all 240 possible solutions by hand in 1961.
Pieces
The seven Soma pieces are sixpolycube
image:tetracube_categories.svg, upAll 8 one-sided tetracubes – if chirality is ignored, the bottom 2 in grey are considered the same, giving 7 free tetracubes in total
image:9L cube puzzle solution.svg, A puzzle involving arranging nine L tricube ...
s of order four, and one of order three:
Production
Piet Hein authorized a finely craftedrosewood
Rosewood is any of a number of richly hued hardwoods, often brownish with darker veining, but found in other colours. It is hard, tough, strong, and dense. True rosewoods come from trees of the genus '' Dalbergia'', but other woods are often ca ...
version of the Soma cube manufactured by Theodor Skjøde Knudsen's company Skjøde Skjern (of Denmark). Beginning in about 1967, it was marketed in the U.S. for several years by the game manufacturer Parker Brothers
Parker Brothers (known as Parker outside of North America) was an American toy and game manufacturer which in 1991 became a brand of Hasbro. More than 1,800 games were published under the Parker Brothers name since 1883. It remained family owne ...
. Plastic Soma cube sets were also commercially produced by Parker Brothers in several colors (blue, red, and orange) during the 1970s. The package for the Parker Brothers version claimed there were 1,105,920 possible solutions. This figure includes rotations and reflections of each solution as well as rotations of the individual pieces. The puzzle is currently sold as a logic game by Piet Hein Trading and by ThinkFun (formerly Binary Arts) under the name Block by Block.
Solutions
intrinsic
In science and engineering, an intrinsic property is a property of a specified subject that exists itself or within the subject. An extrinsic property is not essential or inherent to the subject that is being characterized. For example, mass i ...
and extrinsic
In science and engineering, an intrinsic property is a property of a specified subject that exists itself or within the subject. An extrinsic property is not essential or inherent to the subject that is being characterized. For example, mass i ...
motivation establishing the social psychological theory of crowding out.
In each of the 240 distinct solutions to the cube puzzle, there is only one place that the "T" piece can be placed. Each solved cube can be rotated such that the "T" piece is on the bottom with its long edge along the front and the "tongue" of the "T" in the bottom center cube (this is the normalized position of the large cube). This can be proven as follows: If you consider all the possible ways that the "T" piece can be placed in the large cube (without regard to any of the other pieces), it will be seen that it will always fill either two corners of the large cube or zero corners. There is no way to orient the "T" piece such that it fills only one corner of the large cube. The "L" piece can be oriented such that it fills two corners, or one corner, or zero corners. Each of the other five pieces have no orientation that fills two corners; they can fill either one corner or zero corners. Therefore, if you exclude the "T" piece, the maximum number of corners that can be filled by the remaining six pieces is seven (one corner each for five pieces, plus two corners for the "L" piece). A cube has eight corners. But the "T" piece cannot be oriented to fill just that one remaining corner, and orienting it such that it fills zero corners will obviously not make a cube. Therefore, the "T" must always fill two corners, and there is only one orientation (discounting rotations and reflections) in which it does that. It also follows from this that in all solutions, five of the remaining six pieces will fill their maximum number of corners and one piece will fill one fewer than its maximum (this is called the deficient piece)..
Figures
Similar puzzles
Another puzzle similar to the Soma cube is the 3Dpentomino
A pentomino (or 5-omino) is a polyomino of order 5; that is, a polygon in the Plane (geometry), plane made of 5 equal-sized squares connected edge to edge. The term is derived from the Greek word for '5' and "domino". When rotation symmetry, rota ...
puzzle, which can fill boxes of 2×3×10, 2×5×6 and 3×4×5 units.
The Bedlam cube
The Bedlam cube is a solid dissection puzzle invented by British puzzle expert Bruce Bedlam.
Design
The puzzle consists of thirteen polycubic pieces: twelve pentacubes and one tetracube. The objective is to assemble these pieces into a 4 ...
is a 4×4×4 sided cube puzzle consisting of twelve pentacube
image:tetracube_categories.svg, upAll 8 one-sided tetracubes – if chirality is ignored, the bottom 2 in grey are considered the same, giving 7 free tetracubes in total
image:9L cube puzzle solution.svg, A puzzle involving arranging nine L tricube ...
s and one tetracube. The Diabolical cube
The diabolical cube is a three-dimensional dissection puzzle consisting of six polycubes (shapes formed by gluing cubes together face to face) that can be assembled together to form a single 3 × 3 × 3 cube..
The six pieces ...
is a puzzle of six polycubes that can be assembled together to form a single 3×3×3 cube.
Eye Level
"Eye Level" is a 1972 single by the Simon Park Orchestra. It was produced originally for the De Wolfe Music Library and selected by Thames Television to be the theme tune for their Netherlands-based detective series ''Van der Valk (1972 TV series) ...
also makes use of the Thinking Cube (once students are in levels 30-32 of Basic Thinking Math or levels 29-32 of Critical Thinking Math), as one of its Teaching Tools, similar to the Soma cube.
Rubik's Bricks, a puzzle produced under the Rubik's branding, is a similar puzzle made of 27 cubes, but the pieces are formed by joining cubes either by faces or by edges. There are exactly 9 such ways to join three cubes, so the puzzle can make a 3x3x3 cube. The individual cubes are colored in such a way as to give a unique solution.
See also
*Bedlam cube
The Bedlam cube is a solid dissection puzzle invented by British puzzle expert Bruce Bedlam.
Design
The puzzle consists of thirteen polycubic pieces: twelve pentacubes and one tetracube. The objective is to assemble these pieces into a 4 ...
* Conway puzzle
* Diabolical cube
The diabolical cube is a three-dimensional dissection puzzle consisting of six polycubes (shapes formed by gluing cubes together face to face) that can be assembled together to form a single 3 × 3 × 3 cube..
The six pieces ...
* Herzberger Quader
* Pentomino
A pentomino (or 5-omino) is a polyomino of order 5; that is, a polygon in the Plane (geometry), plane made of 5 equal-sized squares connected edge to edge. The term is derived from the Greek word for '5' and "domino". When rotation symmetry, rota ...
* Slothouber–Graatsma puzzle
The Slothouber–Graatsma puzzle is a packing problem that calls for packing six 1 × 2 × 2 blocks and three 1 × 1 × 1 blocks into a 3 × 3 × 3 box. The solution to this puzzle is unique (up to mirror reflections and rotations). It was named a ...
* Snake cube
* Tangram
The tangram () is a dissection puzzle consisting of seven flat polygons, called ''tans'', which are put together to form shapes. The objective is to replicate a pattern (given only an outline) generally found in a puzzle book using all seven pi ...
* Tetromino
A tetromino is a geometric shape composed of four squares, connected orthogonally (i.e. at the edges and not the corners). Tetrominoes, like dominoes and pentominoes, are a particular type of polyomino. The corresponding polycube, called a tetra ...
* Tromino
A tromino or triomino is a polyomino of size 3, that is, a polygon in the plane made of three equal-sized squares connected edge-to-edge.
Symmetry and enumeration
When rotations and reflections are not considered to be distinct shapes, there a ...
References
External links
*Soma Cube – from MathWorld
Thorleif's SOMA page
SOMA CUBE ANIMATION by TwoDoorsOpen and Friends
{{Authority control Mechanical puzzle cubes Tiling puzzles