Solar eclipse of July 11, 2010 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A total
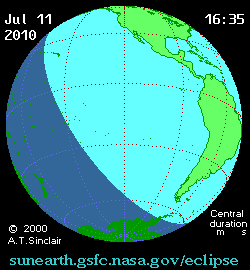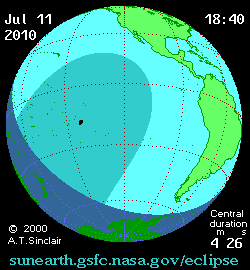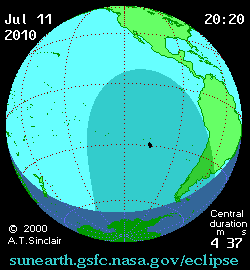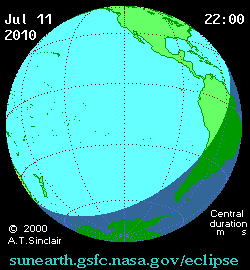 The eclipse on this day was one of the most remote in recorded history. It was visible over much of the southern
The eclipse on this day was one of the most remote in recorded history. It was visible over much of the southern
 Total eclipse began southeast of
Total eclipse began southeast of
NASA pdf map
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20090722072729/http://home.cc.umanitoba.ca/~jander/tot2010/tse10intro.htm Eclipser: 2010 July 11 Total Solar Eclipsebr>Eclipse.org.uk: Total Eclipse of the Sun: 2010 July 11
APOD 7/14/2010
Andes Sunset Eclipse
APOD 7/15/2010, totality from 400 meters above
The Crown of the Sun
APOD 7/21/2010, totality from Easter Island
Diamond Ring and Shadow Bands
APOD 7/24/2010, totality from
Eclipse on the Beach
APOD 7/30/2010, totality from
Eclipse Shadow Cone Over Patagonia
APOD 8/4/2010, totality from Patagonia, Argentina {{Solar eclipses 2010 07 11 2010 in science 2010 07 11 History of the Pacific Ocean July 2010 2010 in Argentina 2010 in Chile
solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season i ...
occurred at the Moon's descending node
An orbital node is either of the two points where an orbit intersects a plane of reference to which it is inclined. A non-inclined orbit, which is contained in the reference plane, has no nodes.
Planes of reference
Common planes of referenc ...
of orbit between Sunday, July 11 and Monday, July 12, 2010, with a magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
of 1.058. A solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season i ...
occurs when the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
passes between Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
and the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular separation (in units of angle) describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the '' visual ...
is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 1.6 days before perigee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values.
Apsides perta ...
(on July 13, 2010, at 12:20 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.
Visibility
 The eclipse on this day was one of the most remote in recorded history. It was visible over much of the southern
The eclipse on this day was one of the most remote in recorded history. It was visible over much of the southern Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
, touching Mangaia
Mangaia (traditionally known as A'ua'u Enua, which means ''terraced'') is the most southerly of the Cook Islands and the second largest, after Rarotonga. It is a roughly circular island, with an area of , from Rarotonga. Originally heavily popul ...
(most southerly of the Cook Islands
The Cook Islands is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of 15 islands whose total land area is approximately . The Cook Islands' Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) covers of ocean. Avarua is its ...
), several atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical parts of the oceans and seas where corals can develop. Most ...
s in French Polynesia
French Polynesia ( ; ; ) is an overseas collectivity of France and its sole #Governance, overseas country. It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands and atolls stretching over more than in the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. The t ...
, Easter Island
Easter Island (, ; , ) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is renowned for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, ...
, and Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
and Argentina's Patagonia
Patagonia () is a geographical region that includes parts of Argentina and Chile at the southern end of South America. The region includes the southern section of the Andes mountain chain with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers ...
n plains including the Southern Patagonian Ice Field
The Southern Patagonian Ice Field (), located at the Southern Patagonic Andes between Chile and Argentina, is the world's second largest contiguous extrapolar ice field. It is the bigger of two remnant parts of the Patagonian Ice Sheet, which c ...
.
Fred Espenak
Fred Espenak (August 1, 1953 – June 1, 2025) was an American astrophysicist. He worked at the Goddard Space Flight Center and published extensively on eclipse predictions.
Career
Espenak became interested in astronomy when he was 7–8 year ...
, a NASA astrophysicist, said:
In French Polynesia, the eclipse was seen with 98 percent totality. During that time, the diamond ring effect and the Baily's beads
The Baily's beads, diamond ring or more rarely double diamond ring effects, are features of total and annular solar eclipses. Although caused by the same phenomenon, they are distinct events during these types of solar eclipses. As the Moon cover ...
occurred.
It ended at sunset over the southern tips of Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
and Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
in South America, including the town of El Calafate
El Calafate, also called ''Calafate'', is a city in the Argentine province of Santa Cruz, in Patagonia. It is located on the southern border of Lago Argentino, in the southwest part of the province (about northwest of Río Gallegos). The name ...
. The Sun's altitude was only 1° during the 2 minute 47 second total phase, but Argentino Lake
Lago Argentino is a lake in the Patagonian province of Santa Cruz, Argentina, at . It is the largest freshwater lake in Argentina, with a surface area of and a maximum width of . The lake's waters have an average depth of , with a maximum depth ...
offered an adequate line-of-sight to the eclipse hanging just above the rugged Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range ...
skyline.
A 58% partiality occurred at sunset in Santiago, Chile
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile (), is the capital and largest city of Chile and one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is located in the country's central valley and is the center of the Santiago Metropolitan Regi ...
, but it was not visible due to adverse weather conditions. In other cities such as Valparaíso
Valparaíso () is a major city, Communes of Chile, commune, Port, seaport, and naval base facility in the Valparaíso Region of Chile. Valparaíso was originally named after Valparaíso de Arriba, in Castilla–La Mancha, Castile-La Mancha, Spain ...
and Coquimbo
Coquimbo is a port List of cities in Chile, city, Communes of Chile, commune and capital of the Elqui Province, located on the Pan-American Highway, in the Coquimbo Region of Chile. Coquimbo is situated in a valley south of La Serena, Chile, La S ...
, clearer skies permitted the event to be witnessed in continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
al Chile.
Observations
 Total eclipse began southeast of
Total eclipse began southeast of Tonga
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania. The country has 171 islands, of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in the southern Pacific Ocean. accordin ...
at approximately 18:15 UTC
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is the primary time standard globally used to regulate clocks and time. It establishes a reference for the current time, forming the basis for civil time and time zones. UTC facilitates international communica ...
and reached Easter Island
Easter Island (, ; , ) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is renowned for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, ...
by 20:11 UTC. The global sky photography project The World At Night stationed photographers throughout the eclipse's visibility track. Eclipse chasers photographed the event on board a chartered airplane, cruise ships, numerous Pacific islands, and in Argentina's Patagonia
Patagonia () is a geographical region that includes parts of Argentina and Chile at the southern end of South America. The region includes the southern section of the Andes mountain chain with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers ...
region. Totality was observed for four minutes and 41 seconds (4:41) on Easter Island
Easter Island (, ; , ) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is renowned for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, ...
, where it was observed for the first time in 1,400 years. Approximately 4,000 observers visited Easter Island for this eclipse, including tourists, scientists, photographers, filmmakers and journalists, prompting an increase in security at its important moai
Moai or moʻai ( ; ; ) are monolithic human figures carved by the Rapa Nui people on Easter Island, Rapa Nui (Easter Island) in eastern Polynesia between the years 1250 and 1500. Nearly half are still at Rano Raraku, the main moai quarry, but h ...
archeological sites. The eclipse occurred at the same time that the final game of the 2010 FIFA World Cup
The 2010 FIFA World Cup was the 19th FIFA World Cup, the world championship for List of men's national association football teams, men's national Association football, football teams. It took place in South Africa from 11 June to 11 July 2010. ...
was being played in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, and many soccer fans in Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian language, Tahitian , ; ) is the largest island of the Windward Islands (Society Islands), Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France. It is located in the central part of t ...
watched the match instead of observing the partial eclipse with a high percentage of obscuring the sun by over 98%. The path of totality of this eclipse barely missed some significant inhabited islands, including passing just about 20 km south of the southern end of Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian language, Tahitian , ; ) is the largest island of the Windward Islands (Society Islands), Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France. It is located in the central part of t ...
.
This eclipse was the first one to happen over French Polynesia
French Polynesia ( ; ; ) is an overseas collectivity of France and its sole #Governance, overseas country. It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands and atolls stretching over more than in the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. The t ...
in 350 years. An estimated 5,000 tourists visited various islands in the archipelago to observe the event. Nearly 120,000 pairs of special glasses were distributed for observers. Eclipse chasers were also able to observe the eclipse at El Calafate, near the southern tip of Argentina, before the sun set just two minutes later.
Several hours after the eclipse was observed in continental Chile, a magnitude 6.2 earthquake struck in the Antofagasta Region
The Antofagasta Region (, ) is one of Chile's Administrative divisions of Chile, sixteen first-order administrative divisions. Being the second-largest region of Chile in area, it comprises three provinces, Antofagasta Province, Antofagasta, El ...
. There were no major injuries or damage in the nearby cities of Calama, Chile
Calama is a city and commune in the Atacama Desert in northern Chile. It is the capital of El Loa Province, part of the Antofagasta Region. Calama is one of the driest cities in the world with average annual precipitation of just . The River L ...
and San Pedro de Atacama
San Pedro de Atacama is a Chilean town and commune in El Loa Province, Antofagasta Region. It is located east of Antofagasta, some 106 km (60 mi) southeast of Calama and the Chuquicamata copper mine, overlooking the Licancabur volcan ...
.
Eclipse details
Shown below are two tables displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. The first table outlines times at which the moon's penumbra or umbra attains the specific parameter, and the second table describes various other parameters pertaining to this eclipse.Eclipse season
This eclipse is part of aneclipse season
An eclipse season is a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Eclipse seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of the Orbit of the Moon, Moon's orbital plane (orbital inclination, tilted five degrees to the ecliptic, Earth ...
, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight
A fortnight is a unit of time equal to 14 days (two weeks). The word derives from the Old English term , meaning "" (or "fourteen days", since the Anglo-Saxons counted by nights).
Astronomy and tides
In astronomy, a ''lunar fortnight'' is hal ...
.
Related eclipses
Eclipses in 2010
* An annular solar eclipse on January 15. * A partial lunar eclipse on June 26. * A total solar eclipse on July 11. * A total lunar eclipse on December 21.Metonic
* Preceded by: Solar eclipse of September 22, 2006 * Followed by:Solar eclipse of April 29, 2014
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Tuesday, April 29, 2014, with a magnitude of 0.9868. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image o ...
Tzolkinex
* Preceded by: Solar eclipse of May 31, 2003 * Followed by:Solar eclipse of August 21, 2017
The solar eclipse of August 21, 2017, dubbed the "Great American Eclipse" by some media, was a total solar eclipse visible within a band that spanned the contiguous United States from the Pacific Ocean, Pacific to the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic c ...
Half-Saros
* Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of July 5, 2001 * Followed by: Lunar eclipse of July 16, 2019Tritos
* Preceded by:Solar eclipse of August 11, 1999
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s Lunar node, ascending node of orbit on Wednesday, August 11, 1999, with a Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of 1.0286. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, thereby ...
* Followed by: Solar eclipse of June 10, 2021
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit on Thursday, June 10, 2021, with a magnitude of 0.9435. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the Sun ...
Solar Saros 146
* Preceded by: Solar eclipse of June 30, 1992 * Followed by: Solar eclipse of July 22, 2028Inex
* Preceded by: Solar eclipse of July 31, 1981 * Followed by: Solar eclipse of June 21, 2039Triad
* Preceded by: Solar eclipse of September 10, 1923 * Followed by: Solar eclipse of May 11, 2097Solar eclipses of 2008–2011
Saros 146
Metonic series
Tritos series
Inex series
Notes
References
NASA pdf map
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20090722072729/http://home.cc.umanitoba.ca/~jander/tot2010/tse10intro.htm Eclipser: 2010 July 11 Total Solar Eclipsebr>Eclipse.org.uk: Total Eclipse of the Sun: 2010 July 11
APOD 7/14/2010
Andes Sunset Eclipse
APOD 7/15/2010, totality from 400 meters above
Argentino Lake
Lago Argentino is a lake in the Patagonian province of Santa Cruz, Argentina, at . It is the largest freshwater lake in Argentina, with a surface area of and a maximum width of . The lake's waters have an average depth of , with a maximum depth ...
The Crown of the Sun
APOD 7/21/2010, totality from Easter Island
Diamond Ring and Shadow Bands
APOD 7/24/2010, totality from
Hao
Hao or HAO may refer to:
People
* Hao (surname) (Chinese: )
* Hao (given name)
* Hao (video gamer), Chinese professional ''Dota 2'' player
* Heather O'Reilly, Professional soccer player
Places
* Hao (city), or Haojing (), capital of the Wes ...
, French Polynesia
Eclipse on the Beach
APOD 7/30/2010, totality from
Anakena
Anakena is a white coral sand beach in Rapa Nui National Park on Rapa Nui (Easter Island), a Chilean island in the Pacific Ocean. Anakena has two ahus; Ahu-Ature has a single moai and Ahu Nao-Nao has seven, two of which have deteriorated. It al ...
Beach, Easter Island
Eclipse Shadow Cone Over Patagonia
APOD 8/4/2010, totality from Patagonia, Argentina {{Solar eclipses 2010 07 11 2010 in science 2010 07 11 History of the Pacific Ocean July 2010 2010 in Argentina 2010 in Chile