Solar Cycle 23 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
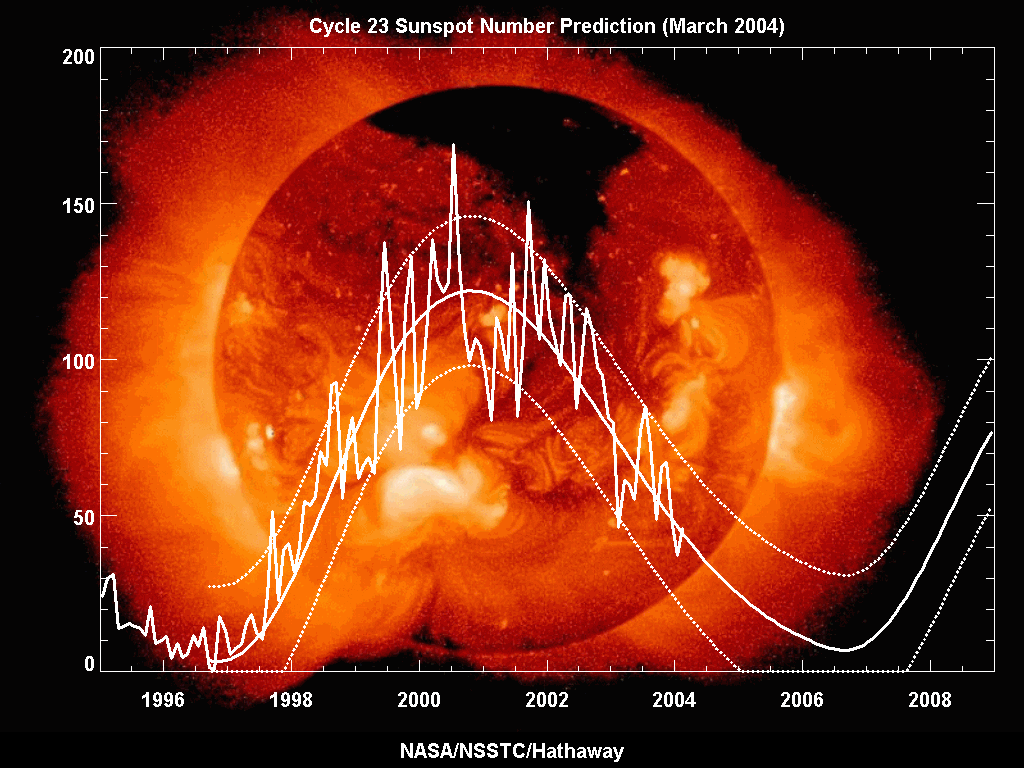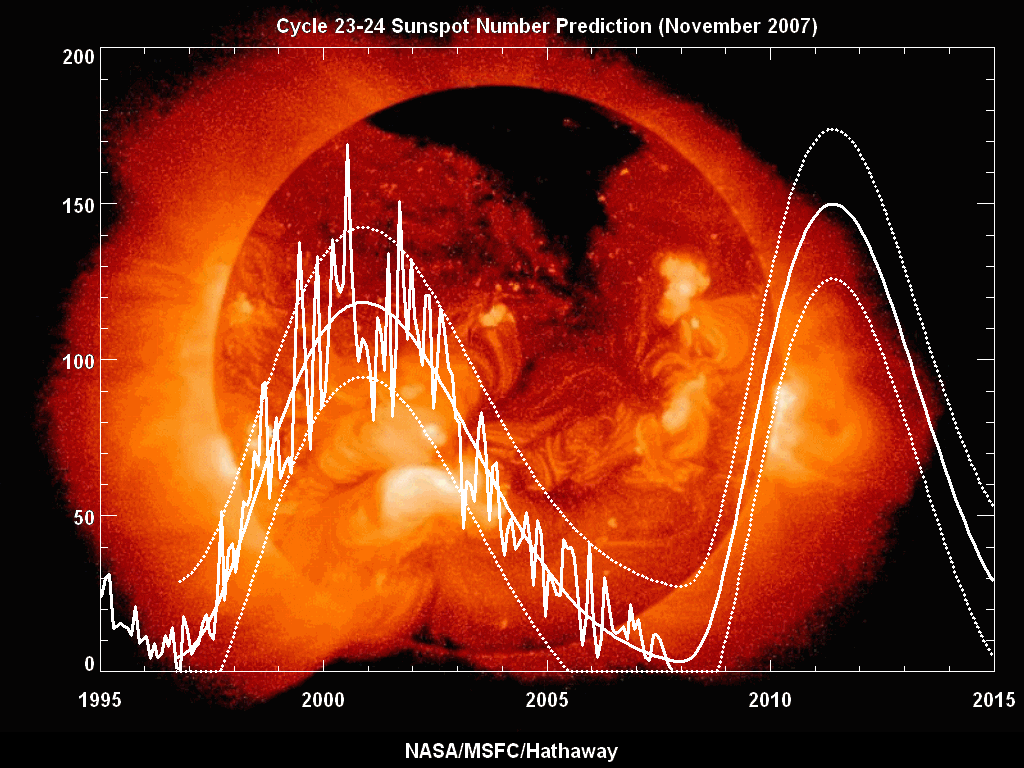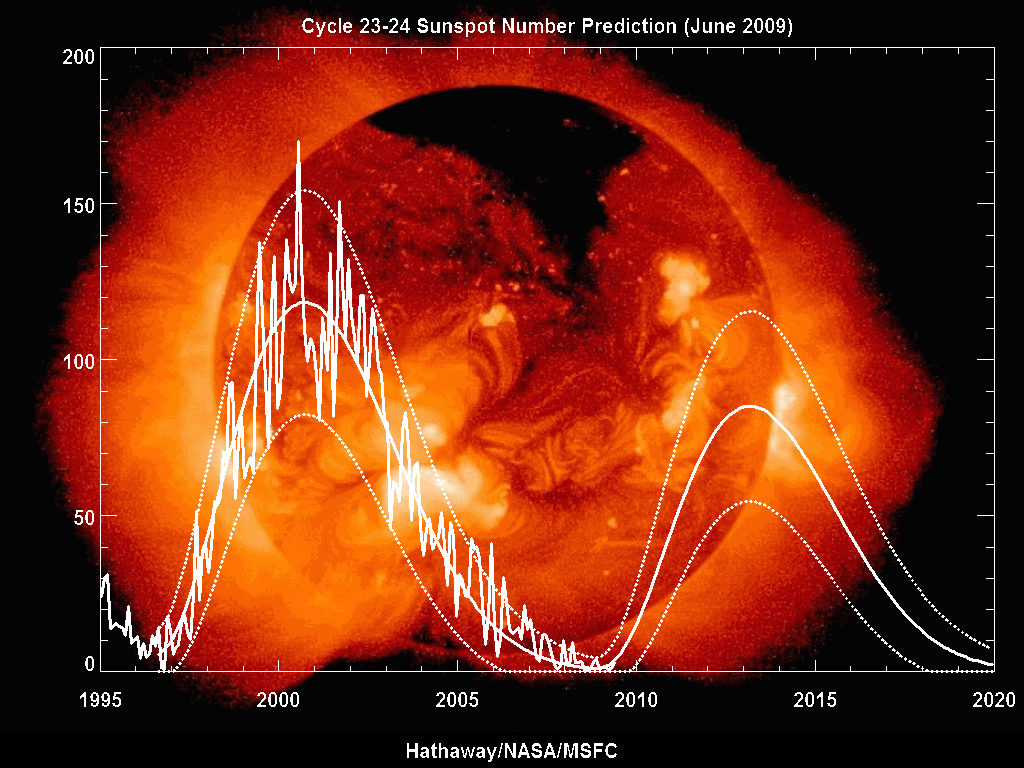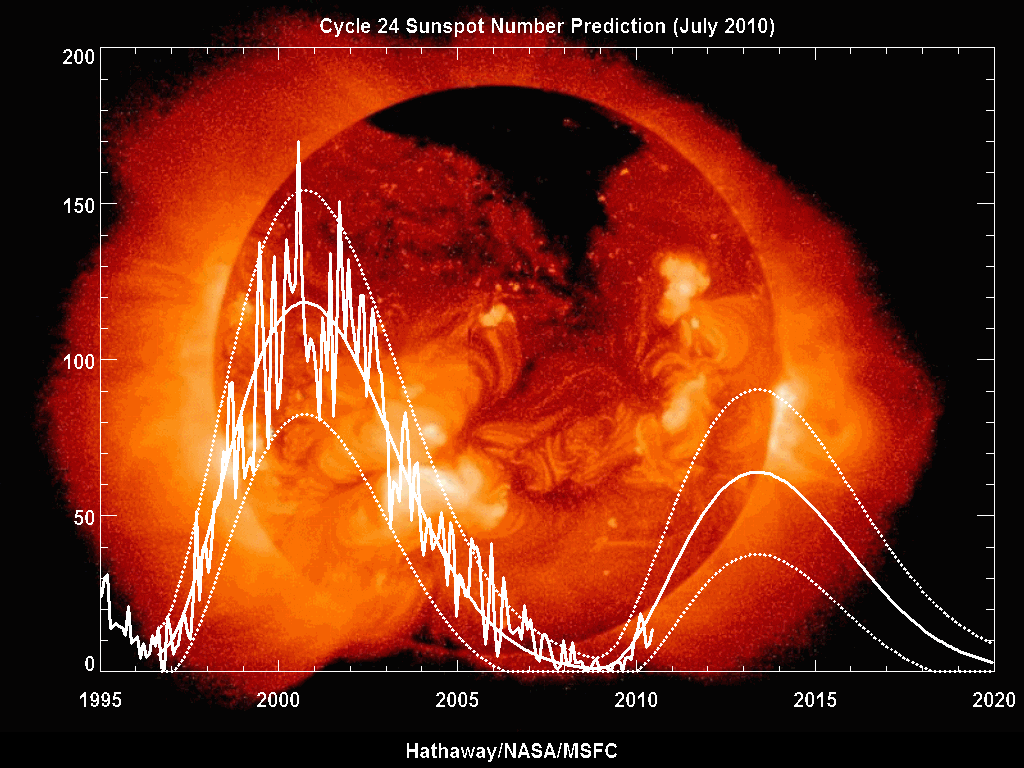 Solar cycle 23 was the 23rd
Solar cycle 23 was the 23rd
 Solar cycle 23 was the 23rd
Solar cycle 23 was the 23rd solar cycle
The Solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of Modern Maximum, variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun ...
since 1755, when extensive recording of solar sunspot
Sunspots are temporary spots on the Sun's surface that are darker than the surrounding area. They are one of the most recognizable Solar phenomena and despite the fact that they are mostly visible in the solar photosphere they usually aff ...
activity began. The solar cycle lasted 12.6 years, beginning in August 1996 and ending in December 2008. The maximum smoothed sunspot number observed during the solar cycle was 180.3 (November 2001), and the starting minimum was 11.2. During the minimum transit from solar cycle 23 to 24, there were a total of 817 days with no sunspots. Compared to the last several solar cycles, it was fairly average in terms of activity.
History
Large solar flares andcoronal mass ejection
A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant ejection of plasma mass from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understandin ...
s (CMEs) occurred on 7 September 2005 (X17), 15 April 2001 (X14.4) and 29 October 2003 (X10), with auroras visible in mid-latitudes.
2000
One of the first major aurora displays of solar cycle 23 occurred on 6 April 2000, with bright red auroras visible as far south as Florida and South Europe. On 14 July 2000, the CME hurled by a X5.7 solar flare provoked an extreme (G5 level) geomagnetic storm the next day. Known as the Bastille Day event, this storm caused damage toGPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide geol ...
systems and some power systems. Auroras were visible as far south as Texas.
2001
Another major aurora display was observed on 1 April 2001, due to acoronal mass ejection
A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant ejection of plasma mass from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understandin ...
hitting the Earth's magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
. Auroras were observed as far south as Mexico and South Europe. A large solar flare (the second-most powerful ever recorded) occurred on 2 April 2001, an X20-class, but the blast was directed away from Earth.
2003
In late October 2003, a series of large solar flares occurred. A X17.2-class flare ejected on 28 October 2003 produced auroras visible as far south as Florida and Texas. A G5 levelgeomagnetic storm
A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere that is driven by interactions between the magnetosphere and large-scale transient Plasma (physics), plasma and magnetic field structur ...
blasted the Earth's magnetosphere over the next two days. A few days later, the largest solar flare ever measured with instruments occurred on 4 November; initially measured at X28, it was later upgraded to an X45-class. This flare was not Earth-oriented and thus only resulted in high-latitude auroras. The whole sequence of events that occurred from 28 October to 4 November is known as the Halloween Solar Storm.
See also
*List of solar cycles
Solar cycles are nearly periodic 11-year changes in the Sun's activity that are based on the number of sunspots present on the Sun's surface. The first solar cycle conventionally is said to have started in 1755. The source data are the revised In ...
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Solar Cycle 23 Solar cycles